Abstract
The characteristics of ncRNA in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) were observed to disclose a theoretical basis for further research on molecular markers for early warning of ASD. Children with ASD and normal control children were recruited to collect peripheral blood RNA samples. The concentration of PVT1 and miR-21-5p was quantitatively analyzed by qRT-PCR. Pearson correlation coefficient method was used to evaluate the link between PVT1 level and miR-21-5p level of the children. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were applied to reckon the predictive value of PVT1, miR-21-5p, and their combination in ASD. The interconnection of PVT1 with miR-21-5p was represented by luciferase reporter assay. The targeted genes of miR-21-5p were predicted. The enrichment and protein interaction analysis of these genes was carried out to find the important core genes and analyze their value in ASD. In the disease group, the level of PVT1 was downregulated, while the content of miR-21-5p was upregulated. The expression level of serum miR-21-5p was negatively correlated with the level of PVT1. Luciferase reporter gene assay documented that PVT1 directly targeted miR-21-5p. ROC curve showed that PVT1, miR-21-5p, and their combination showed clinical value for disease diagnosis. The functional enrichment analysis showed that the targets of miR-21-5p participated in ASD by regulating related functions and pathways. Reduced expression of PVT1 and raised miR-21-5p were good diagnostic markers for ASD, which would provide a basis for effective prevention, early diagnosis, and early intervention of ASD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurological dysfunction that emerges during childhood and persists throughout the whole life (Lord et al. 2018; Richards et al. 2020). Onset typically begins in infancy, with gradual development noticeable by 18 months of age, and diagnosis attainable by 24 months (Zhang et al. 2020). Studies indicate that ASD is mainly related to genetic factors, maternal pregnancy, perinatal factors, neurobiological factors, neurobiochemical factors, infection and immune factors, and nutritional factors (Alvarez-Arellano et al. 2020). ASD is a complex condition, primarily connected to abnormal nerve development, dysfunction of nerve pathways, abnormal synaptogenesis and nerve connection, and neurotransmitter imbalance (Tran et al. 2019). The primary symptoms of children with ASD are social interaction disorder, communication disorder, and stereotyped repetitive behavior and interest (Kodak and Bergmann 2020; Liu et al. 2022a). The diagnosis of ASD is based on behavioral manifestations and developmental situations (Smith et al. 2019). There are numerous diagnostic scales commonly used in clinics; however, a conclusive diagnosis of ASD often requires the observation and evaluation of professionally trained professional evaluators, or long-term observation and evaluation (Shulman et al. 2020). Early behavior reinforcement intervention can significantly influence development, particularly in behavior, adaptability, and communication aptitude (Landa 2018). Therefore, promoting early detection, verification, and treatment is recommended to improve children’s socially acceptable behavior and reduce or eradicate negative behavior.
Among many possible pathogeneses of ASD, the regulation of long-chain non-coding RNA (lncRNA) has attracted wide attention (Ghafouri-Fard et al. 2022). The expression of MEG3 was increased in children with ASD, and MEG3 could distinguish children with ASD from the control group (Taheri et al. 2021). In ASD cases, the concentrations of DISC2, PRKAR2A-AS1, and LOC101928237 increased, which could be a possible reference for this disease (Tamizkar et al. 2021). LncRNA PVT1 leads to possible early development and differentiation of the nervous system. Studies have shown that abnormal expression of PVT1 could affect the normal development of the central nervous system (Li et al. 2021). The expression of MIAT and PVT1 in exosomes of untreated schizophrenia patients was changed (Guo et al. 2022). PVT1 of schizophrenic patients is downregulated, leading to a shred of evidence that lncRNA is involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia (Safari et al. 2019). It is widely recognized that schizophrenia and ASD are both mental illnesses. Therefore, PVT1 might potentially be linked to ASD and other neurodevelopmental disorders and could serve as a biomarker for early screening of ASD. The purpose of this observation was to explore the expression characteristics of lncRNA in children with ASD and to unveil a basis for further study on ASD screening biomarkers.
Materials and Methods
Research Objects
This study comprised of 60 patients with ASD treated in a local psychiatric hospital. Their average age was 7.07 ± 2.56 years old, IQ was 68.13 ± 15.86, and they were of Han nationality (Table 1). In this study, ASD was selected based on the diagnostic criteria published by the American Psychiatric Association (Wakefield 2016). According to the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), the patients were diagnosed with social communication deficits as well as restricted interests and repetitive behaviors. Patients with other neuropsychiatric diseases such as Wright’s syndrome, fragile X syndrome, epilepsy, schizophrenia, obsessive–compulsive disorder, affective disorder, congenital heart disease, trisomy 21 syndrome, and other congenital diseases were excluded from the study. The ADOS score was estimated for each patient in four categories (Table 1). The guardian of each participant was fully informed and provided a written informed consent form before joining the study. The Ethics Committee of Shenzhen Polytechnic University provided the approval for this research.
The peripheral venous blood 2 ml of the study object was collected and stored in the tube with the medical record number and name of each participant clearly marked on the label. These specimens were centrifuged for 10 min using a desktop low-speed centrifuge at 3500 rpm. The serum was then collected in an autoclaved 1.5-ml tube and frozen at − 80 °C.
Clarification of lncRNA and miRNA Expression
Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (qPCR) was carried out according to the instructions of TaqMan kit (TaqMan universal mixed kit II, ABI company). PVT1 and miR-21-5p sequences were queried from GenBank. Primer 3 software was used to design primers and quantitative primers were synthesized by Shanghai Jikang Biological Co., Ltd. (China). TRIzol (ThermoFisher, USA) was used to extract RNA. RNA of 1 μg was taken for reverse transcription, and reverse transcriptional reaction was performed as per the instructions of kit (TaqMan RNA and microRNA reverse transcription kits, ABI company, USA). The standard cDNA after reverse transcription was amplified by PCR. The primers used in this detection were as follows: PVT1 forward, 5′-TGAGAACTGTCCTTACGTGACC-3′ and reverse 5′-AGAGCACCAAGACTGGCTCT-3′; miR-21-5p RT primer, 5′-GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGG GTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTCAACATCAGT-3', forward, 5′-GGCGGTAGCTTATCAGACTGATG-3′, and reverse 5′-GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTC-3′.
Affirmation of Target of PVT1
The Bioinformatics website LncBook 2.0 (https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/lncbook/home) was utilized to anticipate the binding sites between PVT1 and miR-21-5p. The luciferase activity assay was then carried out to certify the target relationship. In this assay, we constructed recombinant plasmids pmirGLO-PVT1-wide type (WT) and pmirGLO-PVT1-mutant (MUT). PVT1-WT and its mutant derivative without miR-21-5p putative site were sub-cloned into the luciferase gene coding region located downstream of HEK 293T. The cells were cultured in 24-well plates and co-transfected 48 h after transfection, using Lipofectamine 2000 reagent. The fluorescence values in each group were gained using a luciferase system (Promega, USA).
GO Functional Enrichment and KEGG Signaling Pathway Analysis of Target Genes
The targeted genes of miR-21-5p were predicted on EVmiRNA, miRDB, TargetScan, and miRtarbase. The intersection of predictive genes was performed using a Venn diagram.
The DAVID data library (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/) was used for Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of targeted genes, including biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF). The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) signal path enrichment results were also obtained in this library. The enrichment conditions were P < 0.05 as the threshold.
Construction of Protein–protein Interaction (PPI) networks
The corresponding PPI network for targeted genes was constructed using the online database STRING (https://string-db.org/). The interaction score > 0.500 was selected and the disconnected nodes in this network were hidden.
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were reckoned with SPSS 20.0 software. The t-test analysis, one-way, and two-way analyses of variance (ANOVA) were utilized for comparing discrepancies. Pearson analysis was the method for correlation certification. The clinical values of the single lncRNA, miRNA, and combination were evidenced by the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. P > 0.05 was on behalf of statistical significance.
Results
PVT1 and miR-21-5p Expression
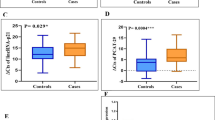
Content of non-coding RNAs was reflected by the qPCR, and the results were displayed in Fig. 1. The relative expression levels of PVT1 in the ASD group were diminished compared with controls (P < 0.001, Fig. 1A). MiR-21-5p was overexpressed in patients with ASD (P < 0.001, Fig. 1B). Collectively, ASD development might lead to the abnormal expression of PVT1 and miR-21-5p. To validate the link between miR-21-5p and PVT1, the Pearson analysis was employed to determine their correlations in patients. As depicted in Fig. 2, the elevated content of miR-21-5p was inversely proportional to the quantification of PVT1 (r = -0.708, P < 0.001).
Predictive Value of PVT1 and miR-21-5p in Patients with ASD
The predictive significance of PVT1, miR-21-5p, and their combination in patients with ASD was presented in Fig. 3. ROC curve analysis showed that the lower area under the curve (AUC) for PVT1 was 0.848 (95% CI = 0.78–0.92) with a sensitivity and specificity of 85.0% and 79.3%, respectively (Fig. 3A). The expression of miR-21-5p also showed a diagnostic ability in ASD patients (AUC = 0.921, sensitivity = 78.3%, specificity = 91.4%, Fig. 3B). When PVT1 was combined with miR-21-5p, the AUC increased to 0.954 with a 95% CI of 0.91–0.98, suggesting that miR-21-5p and PVT1 combination had high accuracy in predicting ASD patients (Fig. 3C). The results above indicated that both PVT1 and miR-21-5p alone could distinguish between ASD children and healthy individuals. Additionally, an improvement in diagnostic value was observed when the two genes were combined.
The Targeted Connection Between miR-21-5p and PVT1
The putative regions between PVT1 and miR-21-5p were depicted in Fig. 4A. The results from double luciferase reporter gene detection showed that the high expression of miR-21-5p significantly inhibited the fluorescence intensity of pmirGLO-PVT1-WT plasmid, while miR-21-5p inhibitors promoted the luciferase activity (P < 0.001, Fig. 4B). However, there was no effect on fluorescence intensity in the pmirGLO–PVT1-MUT group (P > 0.05, Fig. 4B).
GO Enrichment Analysis and KEGG Pathway Analysis of Targets
Through bioinformatics analysis, the EVmiRNA, TargetScan, miRDB, and miRtarbase identified 1667, 384, 469, and 649 target genes, respectively (Fig. 5). A total of 95 shared genes were screened by the Venn method (Fig. 5).
The results of the GO enrichment analysis characterized that the targeted genes were enriched in the asymmetric synapse, post-synaptic specialization, neuron to neuron synapse, and neurotrophin receptor binding (Fig. 6A). The KEGG analysis recognized that pathways mainly included the MAPK signaling pathway, neurotrophin signaling pathway, and FoxO signaling pathway (Fig. 6B).
The PPI of target genes was constructed by the STRING database, which consisted of 140 nodes and 62 edges (Fig. 6C). The top ten nodes of this PPI network were shown in Table 2; STAT3, PDCD4, and SMAD7 were identified as the main genes related to ASD.
Discussion
ASD is a type of neurodevelopmental disorder (Hu et al. 2020). According to the estimation of the World Health Organization, the global prevalence rate of autism spectrum disorder is 6.25‰ (Ilijoski et al. 2022). The prevalence of ASD is around four times higher in males than in females and has been increasing over time (India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative Mental Disorders Collaborators 2020). There is currently no specific medication or treatment available for the core symptoms, often leading to complications with other diseases. As a result, the prognosis for patients is generally bleak and may require lifelong care (Iles 2021). It seriously destroys the quality of patients’ lives. Accordingly, identifying the underlying cause of the disease is of utmost importance.
LncRNAs could potentially act as biological markers for early detection of ASD. Several foreign experiments have been undertaken to identify biological markers linked to ASD, including complement system and synaptogenesis (Aspra et al. 2022; Mansur et al. 2021). As of yet, no definitive biological markers have been found for early clinical screening and diagnosis. Publications documented that lncRNAs were involved in ASD and other neurodevelopmental disorders. The study by Ziats et al. showed abnormal changes in LncRNAs in the brain tissues of ASD patients (Ziats and Rennert 2013). LncRNA IFNG-as1 expression declined in children with ASD, which might be a contributing indicator to chronic inflammation of this disease (Fallah et al. 2020). PVT1 played an important regulatory role in complex diseases where environmental and genetic factors interact (Lv et al. 2019; Tang et al. 2022b). PVT1 might be a target for the treatment of peripheral neuropathy induced by diabetes and crush-injured sciatic nerves, promoting that PVT1 could correlate to crush-injured sciatic nerves (Chen et al. 2018; Pan et al. 2023). In the current research, the expression of PVT1 was decreased in ASD patients, documenting that ASD appearance might lead to inhibited PVT1 expression. Schizophrenia is a chronic mental disorder. Safari et al. established that PVT1 was down-regulated in Schizophrenic patients, lending a piece of evidence that PVT1 played an inhibitory role in mental disorder diseases (Safari et al. 2019). MiR-21-5p is an attractive target in various conditions due to its critical role in many biological functions and diseases, including nerve injury, ionizing radiation, and malignancies (Liu et al. 2022b; Mahmoudi et al. 2022; Singh et al. 2021). The genome of miR-21-5p is located on chromosome 17 (17q.23.1) in the intron region of TMEM49 gene (Tang et al. 2022a). The outcome of this research indicated enhanced expression of miR-21-5p in ASD patients, declaring its association with ASD occurrence. Additionally, the negative relationship between miR-21-5p and PVT1 was observed in ASD patients, further suggesting their close interaction in ASD.
It is acknowledged that lncRNA and miRNA have the potential as biomarkers of disease diagnosis and prognosis. Cui et al. confirmed that PVT1 had potential diagnostic value in early lung cancer, and the overexpression of PVT1 in cancer tissues indicated a poor prognosis (Cui et al. 2016). In a publication on clinical engagement in sepsis, PVT1 revealed the possibility of acting as a predictive marker in sepsis patients (Chen et al. 2022a). A study has confirmed that in patients with schizophrenia, miR-21-5p was linked with the development of schizophrenia and could function as a biomarker for schizophrenia patients (Liu et al. 2017). The results of ROC curve analysis in this study showed that PVT1 and miR-21-5p displayed comparable diagnostic values in children with ASD. Additionally, the combined ROC curve of PVT1 and miR-21-5p demonstrated superior diagnostic capability. Therefore, it was conceivable that the diagnostic value of the combination of the PVT1 and miR-21-5p was more satisfactory to that of single diagnostic approach. Although the diagnostic value of PVT1 has been substantiated through experimental methods, and the combination of PVT1 and miR-21-5p has been preliminarily confirmed for ASD, the specific mechanism of PVT1 and miR-21-5p in ASD and how they regulate the disease remain elusive. Future studies should be performed to verify the results of this study.
LncRNAs usually serve as the “miRNA sponge” to inhibit the expression of miRNAs, thereby exerting a fundamental regulatory effect. In diabetic foot ulcer and hypoxia/reoxygenation injury, PVT1 sponged miR-21-5p, suggesting the targeted relationship between them (Chen et al. 2022b; Wu et al. 2021). In the sequence test of ASD brain specimens, the expression of miR-21-5p was overexpressed, and it might exert a biological function in the brain of ASD (Mor et al. 2015). Thus, miR-21-5p is selected as the target of PVT1. Gill et al. found that increasing the expression level of miR-21-5p was verified in ASD using sequencing profiles, involving the proliferation and death of neuronal cells (Gill et al. 2022). The targeted interconnection between miR-21-5p and PVT1 was identified by the luciferase reporter test, which showed miR-21-5p was a ceRNA of PVT1. In this article, we predicted the targets of miR-21-5p and found 95 shared targets. The bioinformatic analysis was used to support the function of these targets. Through the GO enrichment method, the targets were mainly enriched in asymmetric synapse, post-synaptic specialization, neuron to neuron synapse, and neurotrophin receptor binding. The synapse was composed of asymmetric synapse, post-synaptic specialization, neuron to neuron synapse, which is the foundation of information exchange and schizophrenia pathophysiology (Zhang et al. 2023). The neurotrophin receptor binding was essential in nerve growth (Conroy and Coulson 2022). Briefly, the targeted genes might participate in ASD by regulating the above-mentioned biological elements or functions. Through KEGG analysis, the targets participated in the MAPK signaling pathway and neurotrophin signaling pathway. The MAPK signaling pathway was the top enrichment pathway, which is correlated to ASD by modulating neuronal physiology (Vithayathil et al. 2018). The neurotrophin signaling pathway is a cell signaling mechanism that plays a crucial role in the development, plasticity, and repair of the nervous system (Liang et al. 2019). STAT3, PDCD4, and SMAD7 were the main genes in the PPI network. Among these genes, STAT3 takes part in ASD by regulating relative pathways, PDCD4 regulates the central nervous system, and SMAD7 may influence the glucose metabolism in neurons (Di Paolo et al. 2020; Li et al. 2022; Yuan et al. 2020).
To sum up, this study confirmed the declined expression of PVT1 in the serum of children with ASD, while the expression of miR-21-5p was enhanced, and the level of miR-21-5p was raised with the decrease of PVT1 level. ROC curve proved the clinical value of PVT1 and miR-21-5p as biomarkers in the diagnosis of diseases. In addition, PVT1/miR-21-5p axis might regulate neuropathologic function, thus relating to ASD.
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alvarez-Arellano L, Salazar-García M, Corona JC (2020) Neuroprotective effects of quercetin in pediatric neurological diseases. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25235597
Aspra Q et al (2022) Epigenome-wide analysis reveals DNA methylation alteration in ZFP57 and its target RASGFR2 in a Mexican population cohort with autism. Children (Basel, Switzerland) 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/children9040462
Chen J, Ren H, Liu B (2022a) Evaluating the potency of blood long noncoding RNA PVT1 as candidate biomarker reflecting inflammation, multiple organ dysfunction, and mortality risk in sepsis patients. J Clin Lab Anal 36:e24268. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.24268
Chen L, Gong HY, Xu L (2018) PVT1 protects diabetic peripheral neuropathy via PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:6905–6911. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201810_16160
Chen X, Peng Y, Xue H, Liu G, Wang N, Shao Z (2022b) MiR-21 regulating PVT1/PTEN/IL-17 axis towards the treatment of infectious diabetic wound healing by modified GO-derived biomaterial in mouse models. J Nanobiotechnol 20:309. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-022-01516-4
Conroy JN, Coulson EJ (2022) High-affinity TrkA and p75 neurotrophin receptor complexes: a twisted affair. J Biol Chem 298:101568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101568
Cui D, Yu CH, Liu M, Xia QQ, Zhang YF, Jiang WL (2016) Long non-coding RNA PVT1 as a novel biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biology: The Journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 37:4127–4134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4261-x
Di Paolo A et al (2020) PDCD4 regulates axonal growth by translational repression of neurite growth-related genes and is modulated during nerve injury responses. RNA (New York, NY) 26:1637–1653. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.075424.120
Fallah H, Sayad A, Ranjbaran F, Talebian F, Ghafouri-Fard S, Taheri M (2020) IFNG/IFNG-AS1 expression level balance: implications for autism spectrum disorder. Metab Brain Dis 35:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00510-4
Ghafouri-Fard S, Noroozi R, Brand S, Hussen BM, Eghtedarian R, Taheri M, Ebrahimzadeh K (2022) Emerging role of non-coding RNAs in autism spectrum disorder. J Mol Neurosci 72:201–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01934-3
Gill PS et al (2022) Integrated microRNA-mRNA expression profiling identifies novel targets and networks associated with autism. J Pers Med 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12060920
Guo C et al (2022) Aberrant expressions of MIAT and PVT1 in serum exosomes of schizophrenia patients. Schizophrenia Res 240:71–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2021.12.013
Hu T, Dong Y, He C, Zhao M, He Q (2020) The gut microbiota and oxidative stress in autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:8396708. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8396708
Iles A (2021) Autism spectrum disorders. Prim Care 48:461–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2021.04.003
Ilijoski B, Ackovska N, Zorcec T, Popeska Z (2022) Extending robot therapy for children with autism using mobile and web application. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22165965
India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative Mental Disorders Collaborators (2020) The burden of mental disorders across the states of India: The global burden of disease study 1990–2017. Lancet Psychiatry 7:148–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2215-0366(19)30475-4
Kodak T, Bergmann S (2020) Autism spectrum disorder: characteristics, associated behaviors, and early intervention. Pediatr Clin North Am 67:525–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcl.2020.02.007
Landa RJ (2018) Efficacy of early interventions for infants and young children with, and at risk for, autism spectrum disorders. Int Rev Psychiatry (Abingdon, England) 30:25–39. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540261.2018.1432574
Li A, Liao W, Xie J, Song L, Zhang X (2022) Plasma proteins as occupational hazard risk monitors for populations working in harsh environments: a mendelian randomization study. Front Public Health 10:852572. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.852572
Li M, Chi C, Zhou L, Chen Y, Tang X (2021) Circular PVT1 regulates cell proliferation and invasion via miR-149–5p/FOXM1 axis in ovarian cancer. J Cancer 12:611–621. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.52234
Liang S et al (2019) Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis reveals epigenetic pattern of SH2B1 in Chinese monozygotic twins discordant for autism spectrum disorder. Front Neurosci 13:712. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00712
Liu J, Hu J, Li Q, Zhao X, Liu Y, Liu S (2022a) Atypical processing pattern of gaze cues in dynamic situations in autism spectrum disorders. Sci Rep 12:4120. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-08080-9
Liu S et al (2017) Diagnostic value of blood-derived micrornas for schizophrenia: Results of a meta-analysis and validation. Sci Rep 7:15328. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15751-5
Liu YP et al (2022b) Exosome-mediated miR-21 was involved in the promotion of structural and functional recovery effect produced by electroacupuncture in sciatic nerve injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:7530102. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7530102
Lord C, Elsabbagh M, Baird G, Veenstra-Vanderweele J (2018) Autism spectrum disorder. Lancet (London, England) 392:508–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31129-2
Lv ZH, Wang ZY, Li ZY (2019) LncRNA PVT1 aggravates the progression of glioma via downregulating UPF1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:8956–8963. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201910_19294
Mahmoudi R, Saidijam M, Nikzad S, Tapak L, Alvandi M, Afshar S (2022) Human exposure to low dose ionizing radiation affects miR-21 and miR-625 expression levels. Mol Biol Rep 49:1321–1327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06960-3
Mansur F et al (2021) Complement C4 is reduced in iPSC-derived astrocytes of autism spectrum disorder subjects. Int J Mol Sci 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147579
Mor M, Nardone S, Sams DS, Elliott E (2015) Hypomethylation of miR-142 promoter and upregulation of microRNAs that target the oxytocin receptor gene in the autism prefrontal cortex. Mol Autism 6:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13229-015-0040-1
Pan B et al (2023) Long noncoding RNA Pvt1 promotes the proliferation and migration of Schwann cells by sponging microRNA-214 and targeting c-Jun following peripheral nerve injury. Neural Regen Res 18:1147–1153. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.353497
Richards R, Greimel E, Kliemann D, Koerte IK, Schulte-Körne G, Reuter M, Wachinger C (2020) Increased hippocampal shape asymmetry and volumetric ventricular asymmetry in autism spectrum disorder. NeuroImage Clin 26:102207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102207
Safari MR, Komaki A, Arsang-Jang S, Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S (2019) Expression pattern of long non-coding rnas in schizophrenic patients. Cell Mol Neurobiol 39:211–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-018-0640-3
Shulman C, Esler A, Morrier MJ, Rice CE (2020) Diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder across the lifespan child and adolescent. Psychiatr Clin North Am 29:253–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chc.2020.01.001
Singh A et al (2021) The role of microRNA-21 in the onset and progression of cancer. Future Med Chem 13:1885–1906. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc-2021-0096
Smith AM, King JJ, West PR, Ludwig MA, Donley ELR, Burrier RE, Amaral DG (2019) Amino acid dysregulation metabotypes: potential biomarkers for diagnosis and individualized treatment for subtypes of autism spectrum disorder. Biol Psychiatry 85:345–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.08.016
Taheri M, Honarmand Tamizkar K, Omrani S, Arsang-Jang S, Ghafouri-Fard S, Omrani MD (2021) MEG3 lncRNA is over-expressed in autism spectrum disorder. Metab Brain Dis 36:2235–2242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00764-x
Tamizkar KH, Ghafouri-Fard S, Omrani MD, Pouresmaeili F, Arsang-Jang S, Taheri M (2021) Altered expression of lncRNAs in autism spectrum disorder. Metab Brain Dis 36:983–990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00681-z
Tang Q, Zhang Y, Yue L, Ren H, Pan C (2022a) Ssc-MiR-21–5p and Ssc-MiR-615 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of leydig cells by targeting SOX5. Cells 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11142253
Tang SS, Li H, Tang CK (2022b) PVT1 in cardiovascular disease: a promising therapeutic target. Int J Cardiol 366:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2022.07.006
Tran SS et al (2019) Widespread RNA editing dysregulation in brains from autistic individuals. Nat Neurosci 22:25–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0287-x
Vithayathil J, Pucilowska J, Landreth GE (2018) ERK/MAPK signaling and autism spectrum disorders. Prog Brain Res 241:63–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pbr.2018.09.008
Wakefield JC (2016) Diagnostic issues and controversies in DSM-5: return of the false positives problem. Ann Rev Clin Psychol 12:105–132. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032814-112800
Wu F et al (2021) ZFP36L2 regulates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and attenuates mitochondrial fusion and fission by LncRNA PVT1. Cell Death Dis 12:614. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03876-5
Yuan F et al (2020) Overexpression of Smad7 in hypothalamic POMC neurons disrupts glucose balance by attenuating central insulin signaling. Mol Metab 42:101084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101084
Zhang K, Liao P, Wen J, Hu Z (2023) Synaptic plasticity in schizophrenia pathophysiology. IBRO Neurosci Rep 14:244–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibneur.2023.01.008
Zhang L et al (2020) Symptom improvement in children with autism spectrum disorder following bumetanide administration is associated with decreased GABA/glutamate ratios. Transl Psychiatry 10:9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-020-0692-2
Ziats MN, Rennert OM (2013) Aberrant expression of long noncoding RNAs in autistic brain. J Mol Neurosci: MN 49:589–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-012-9880-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Mingjun Jiang and Guanwen Chen. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Mingjun Jiang, and all the authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The Ethics Committee of Shenzhen Polytechnic University provided the approval for this research.
Consent to Participate
The guardian of the study knew and signed the informed consent form before joining the study.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, M., Chen, G. Investigation of LncRNA PVT1 and MiR-21-5p Expression as Promising Novel Biomarkers for Autism Spectrum Disorder. J Mol Neurosci 73, 865–873 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-023-02161-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-023-02161-8