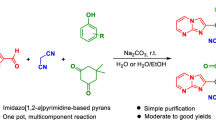
Abstract
Facile and efficient NaOH-promoted one-pot regioselective synthesis of 5,7-dimethyl-3-(arylamino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-diones and 5,7-dimethyl-3-(arylamino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-ones as pharmaceutically interesting compounds has been developed based on a three-component reaction between aryl isothiocyanates, N,N-dimethylbarbituric acid or N,N-dimethyl-2-thiobarbituric acid, and hydroxylamine hydrochloride in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) at room temperature. This new protocol has advantages such as simple operation, regioselectivity, metal-free operation, high atom economy, moderate to high yield, easy work-up procedure, and applicability on the gram scale.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Nowadays, heterocyclic chemistry is one of the major areas of organic and medicinal chemistry [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. Isoxazole and fused-isoxazole frameworks, bearing both nitrogen and oxygen atoms, are important five-membered heterocyclic compounds with a wide range of biological activities [16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42]. They are important constituents of various drugs such as paliperidone (a dopamine antagonist and 5-HT2A antagonist), risperidone, ocaperidone, and iloperidone (antipsychotics), zonisamide (anticonvulsant), leflunomide (antirheumatic), isoxicam and valdecoxib (non-steroidal anti-inflammatories), parecoxib (analgesic, antipyretic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, and selective COX-2 inhibitor), oxacillin, cloxacillin, dicloxacillin, and sulfamethoxazole (antibiotics), tivozanib (VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor), and micafungin (antifungal) (Fig. 1) [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55]. Among the fused isoxazole systems, isoxazolopyrimidines show potential biological activities including anti-inflammatory [56], antitumor [57, 58], adenosine antagonist [59], inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) [60], and anxiolytic activity [61]. Recently, some 3-(piperidine-4-yl)isoxazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine derivatives have been reported as novel PI3Kδ inhibitors [62]. Also, Kurth and co-workers reported isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidines as novel small-molecule correctors of cystic fibrosis mutant protein ∆F508-CFTR [63]. Furthermore, in 2018, Phillips and co-workers discovered inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) with antimalarial activity based on some isoxazolopyrimidine frameworks [64].
One-pot multicomponent reactions (MCRs) are an important and valuable strategy in organic synthesis [65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83]. MCRs offer pivotal advantages over classical multi-step protocols by minimizing waste production, decreasing energy consumption, being more cost-effective and time-efficient, having very simple operation, and avoiding protection and deprotection of functional groups. On the other hand, the formation of carbon–nitrogen and carbon–oxygen bonds through one-pot MCRs has received attention in organic synthesis due to their utility in the preparation of diverse bioactive molecules [84,85,86,87,88,89,90].
As part of our ongoing research in the field of synthesis of heterocyclic compounds via MCRs [91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101], we report herein a convenient and practical method for the regioselective synthesis of new 5,7-dimethyl-3-(arylamino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-diones and 5,7-dimethyl-3-(arylamino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-ones by NaOH-promoted one-pot three-component reaction between aryl isothiocyanates, N,N-dimethylbarbituric acid (DMBA) or N,N-dimethyl-2-thiobarbituric acid (DMTBA), and hydroxylamine hydrochloride (NH2OH·HCl) in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) as an organic solvent at room temperature (Scheme 1). The key advantages of this newly developed protocol are the use of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) as a very cheap base promoter, use of commercially available starting materials, regioselectivity, high atom economy, and moderate to high yield. Furthermore, this new protocol is also applicable on the gram scale. To the best of our knowledge, use of this or similar protocols for construction of isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives has not been reported in the literature.
Results and discussion
Considering the broad range of remarkable properties and applications of isoxazole skeletons in medicinal chemistry, development of novel, simple, and efficient strategies for the construction of new isoxazole derivatives is always desirable in the synthetic community. In our initial trials, phenyl isothiocyanate (1a), N,N-dimethylbarbituric acid (2a), and hydroxylamine hydrochloride (7) were reacted in the presence of potassium hydroxide (KOH) in DMF as a polar aprotic solvent at room temperature for 10 h. The desired product, 5,7-dimethyl-3-(phenylamino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3a) was successfully obtained in 81 % yield (Table 1, entry 1). No improved yield was observed upon using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), CH2Cl2, dioxane, ethanol, or water as solvent (Table 1, entries 2–6). Next, a series of bases, namely 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane (DABCO), 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU), 1,5-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-ene (DBN), NaOH, and K2CO3, were screened (Table 1, entries 7–11). Interestingly, sodium hydroxide was found to be the most suitable base for this valuable one-pot transformation (Table 1, entry 10). Notably, decreasing or increasing the molar ratio of NaOH (100 mol%), resulted in a diminished yield of the desired isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine (3a) (Table 1, entries 12–14). Furthermore, increasing the reaction temperature led to the reduction of the yield (Table 1, entry 15). Also, when the reaction was carried out in the catalyst-free condition, a trace amount of 3a was obtained (Table 1, entry 16). Note that, when the above-mentioned one-pot reaction was carried out in DMF or DMSO, water was needed to extract the desired product 3a from the reaction medium. In this regard, after reaction completion in DMF or DMSO (in the presence of all mentioned catalysts except K2CO3), 3a was obtained as yellow sediment after adding water (10–15 mL). However, when the reaction was carried out in the presence of K2CO3 as a base promoter, no sediment was observed after adding water (10–100 mL). Therefore, to obtain the desired product 3a, 2 M HCl solution (10 mL) was added to the reaction pot (Table 1, entry 11).

After establishing the optimized reaction conditions, we explored the substrate scope and limitations of the methodology. In this regard, we employed a wide range of aryl isothiocyanates (1a–m) with both N,N-dimethylbarbituric acid (2a) and N,N-dimethyl-2-thiobarbituric acid (2b). In general, aryl isothiocyanates bearing electron-withdrawing or electron-donating functional groups at different positions reacted smoothly to generate the corresponding products (3a–z) in moderate to high yield.
The structural elucidation and attribution of all the newly obtained isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives (3a–z) were unambiguously determined by their Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR), 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopic data, CHN analysis, and melting point; For example, in the 1H NMR spectrum of compound 3a, the presence of a singlet peak in the downfield region at δ = 13.92 ppm is ascribed to the NH proton. Furthermore, the 1H NMR spectrum of 3a showed multiplet peaks between δ = 7.44–7.34 ppm for the aromatic protons and also two peaks at δ = 3.48 ppm and δ = 3.42 ppm belonging to the two N–CH3 groups. On the other hand, the observation of 11 distinct signals in the 13C NMR spectrum of compound 3a is in agreement with the proposed structure. It is noteworthy that Matsumoto and Takashi [102] reported synthesis of a 5,7-dimethyl-3-(phenylamino)isoxazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione derivative (12a) by a classical step-by-step synthetic operation. Differences in melting point and 1H NMR spectroscopic data (especially NH proton) confirm our structural assignment (Scheme 2). The 1H NMR spectra of 12a showed a singlet peak at δ = 8.19 ppm for NH proton, whereas 3a showed a corresponding singlet peak at δ = 13.92 ppm.
A plausible reaction mechanism for the synthesis of the new isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine derivatives is outlined in Scheme 3. First, in the presence of NaOH as an inorganic base promoter, 2a, b converts to the anionic form (intermediate 5a–b). Subsequently, attack of 5a–b on the aromatic isothiocyanate (1a–m) affords β-oxo thioamide (intermediate 6a–z). Next, 6a–z readily undergoes regioselective nucleophilic attack by the NH2 group of hydroxylamine hydrochloride (7) preferentially at the soft electrophilic center of the intermediate β-oxo thioamide (8a–z), in agreement with the hard and soft Lewis acid and base (HSAB) principle [54, 103,104,105,106,107], which subsequently gives the final product (3a–z) through cyclization with the oxo functionality and elimination of water. Note that, in NH2OH·HCl as a hetero-binucleophile molecule, nitrogen center is softer as well as more nucleophilic in nature than the oxygen center (Table 2).
To demonstrate the practical utility of the present one-pot three-component protocol, a gram-scale reaction was performed successfully with 1a (1.08 g, 8 mmol), 2a (1.25 g, 8 mmol), and hydroxylamine hydrochloride (0.56 g, 8 mmol) using 100 mol% (0.32 g) of NaOH at room temperature in DMF, achieving synthesis of 3a in 70 % yield (Scheme 4).
Experimental
Melting points were determined on an Electrothermal 9200 apparatus. Infrared spectra were recorded on a Perkin Elmer Spectrum Two FT-infrared spectrophotometer, measured as KBr disks. 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance 300 MHz spectrometer at 300 and 75 MHz, respectively. Chemical shifts were measured in DMSO-d6 as solvent relative to tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the internal standard. Elemental analyses were performed by using a Leco Analyzer 932.
General procedure for the one-pot synthesis of isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidines (3a–z)
In a round-bottomed flask (25 mL) equipped with a magnetic stirrer, in the presence of sodium hydroxide (100 mol%), a mixture of aryl isothiocyanate (1 mmol), N,N-dimethylbarbituric acid or N,N-dimethyl-2-thiobarbituric acid (1 mmol), and hydroxylamine hydrochloride (1 mmol) in DMF (5 mL) was stirred at 25 °C (room temperature). After reaction completion, water (10–15 mL) was added to the reaction mixture. Then, the precipitate was filtered and washed with hot methanol (3 × 5 mL) to afford the pure products.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-(phenylamino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3a)
Yellow powder; 85 %; m.p. 156 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.92 (s, 1H, NH), 7.44–7.34 (m, 5H, Ar), 3.48 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.42 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 185.6, 168.0, 163.9, 137.3, 130.1, 128.1, 126.8, 126.5, 124.7, 28.2, 27.4; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3400, 2922, 2865, 1716, 1597, 1545, 1452, 1384, 1295, 1237, 1102, 1002, 815, 759, 688, 619, 503 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H12N4O3: C, 57.35; H, 4.44; N, 20.58. Found: C, 57.48; H, 4.49; N, 20.38.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((4-bromophenyl)amino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3b)
Yellow powder; 89 %; m.p. 147 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.91 (s, 1H, NH), 7.55 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 2H, Ar), 7.34 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, Ar), 3.47 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.40 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 186.3, 168.1, 163.8, 136.4, 133.3, 133.2, 131.2, 128.4, 126.2, 28.3, 26.4; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3392, 3084, 2925, 1710, 1635, 1578, 1535, 1488, 1447, 1396, 1378, 1073, 1013, 869, 830, 791, 752, 619, 505 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H11BrN4O3: C, 44.46; H, 3.16; N, 15.96. Found: C, 44.56; H, 3.10; N, 16.26.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((4-fluorophenyl)amino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3c)
White powder; 83 %; m.p. 139 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.83 (s, 1H, NH), 7.45–7.35 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.13 (t, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H, Ar), 3.48 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.41 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 186.5, 168.0, 163.9, 152.6, 132.2, 128.8, 126.6, 117.3, 117.0, 114.8, 28.3, 27.2; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3420, 3076, 2962, 2863, 1703, 1625, 1604, 1448, 1397, 1213, 1198, 1092, 1000, 836, 814, 789, 754, 657, 489 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H11FN4O3: C, 53.80; H, 3.82; N, 19.30. Found: C, 53.92; H, 3.85; N, 19.59.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((4-nitrophenyl)amino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3d)
Yellow powder; 81 %; m.p. 139 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 14.38 (s, 1H, NH), 8.00 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.76 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H, Ar), 7.10 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, Ar), 3.50 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.42 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 187.3, 168.4, 163.8, 125.9, 125.6, 124.4, 124.3, 123.7, 123.4, 29.4, 28.5; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3420, 3387, 3101, 3068, 2974, 2900, 1718, 1637, 1579, 1536, 1450, 1434, 1394, 1381, 1201, 1000, 819, 790, 781, 752, 604, 504 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H11N5O5: C, 49.22; H, 3.49; N, 22.07. Found: C, 49.33; H, 3.55; N, 22.34.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3e)
Yellow powder; 83 %; m.p. 159 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.82 (s, 1H, NH), 7.34–7.21 (m, 4H, Ar), 3.41 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.34 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 2.39 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 185.3, 167.8, 163.9, 137.7, 134.7, 130.7, 128.7, 126.6, 124.5, 28.1, 27.3, 22.0; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3402, 3068, 2966, 2925, 1706, 1630, 1581, 1515, 1500, 1448, 1399, 1379, 1300, 1200, 1107, 1002, 799, 752, 636, 487 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C14H14N4O3: C, 58.74; H, 4.93; N, 19.57. Found: C, 58.90; H, 4.95; N, 19.88.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3f)
Yellow powder; 87 %; m.p. 159 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.74 (s, 1H, NH), 7.31 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H, Ar), 6.95 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ar), 3.84 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.46 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.40 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 185.4, 167.8, 163.9, 130.0, 128.1, 126.0, 126.0, 115.3, 113.3, 54.4, 27.1, 26.2; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3412, 3318, 3105, 3072, 2945, 2847, 1714, 1582, 1556, 1545, 1508, 1444, 1397, 1374, 1257, 1175, 1035, 829, 750, 505 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C14H14N4O4: C, 55.63; H, 4.67; N, 18.53. Found: C, 55.77; H, 4.61; N, 18.73.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((3-bromophenyl)amino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3g)
White powder; 72 %; m.p. 146 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.97 (s, 1H, NH), 7.65 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.48–7.25 (m, 3H, Ar), 3.48 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.40 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 186.6, 168.1, 163.8, 131.3, 129.8, 129.4, 129.2, 127.7, 125.5, 123.3, 122.4, 28.3, 26.4; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3457, 3383, 3093, 3072, 2966, 2884, 1716, 1637, 1576, 1535, 1449, 1428, 1395, 1381, 1295, 1193, 1070, 998, 815, 779, 752, 691, 615, 503 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H11BrN4O3: C, 44.46; H, 3.16; N, 15.96. Found: C, 44.57; H, 3.20; N, 16.26.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((3-chlorophenyl)amino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3h)
White powder; 71 %; m.p. 159 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.97 (s, 1H, NH), 7.51 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.39–7.28 (m, 3H, Ar), 3.48 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.41 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 186.6, 168.1, 163.8, 138.5, 131.1, 128.9, 127.0, 126.5, 126.5, 125.0, 122.8, 28.3, 27.4; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3457, 3117, 3084, 2958, 1710, 1636, 1607, 1592, 1511, 1450, 1398, 1379, 1347, 1110, 1004, 858, 785, 753, 700, 615, 505 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H11ClN4O3: C, 50.91; H, 3.62; N, 18.27. Found: C, 50.99; H, 3.57; N, 18.48.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3i)
Yellow powder; 78 %; m.p. 162 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.88 (s, 1H, NH), 7.38–7.12 (m, 4H, Ar), 3.47 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.41 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 2.40 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 185.2, 167.9, 163.9, 137.2, 129.9, 129.4, 127.8, 127.2, 125.2, 123.9, 121.6, 28.2, 27.2, 22.2; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3387, 3322, 3019, 2929, 2798, 1705, 1662, 1590, 1554, 1494, 1447, 1398, 1382, 1320, 1293, 1109, 887, 791, 772, 681, 499 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C14H14N4O3: C, 58.74; H, 4.93; N, 19.57. Found: C, 58.86; H, 5.00; N, 19.89.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((3-methoxyphenyl)amino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3j)
Yellow powder; 75 %; m.p. 153 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.92 (s, 1H, NH), 7.38–7.25 (m, 1H, Ar), 7.01 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H, Ar), 6.87 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, Ar), 3.82 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.46 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.39 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 185.3, 167.9, 163.9, 138.4, 130.8, 128.7, 116.8. 114.3, 114.3, 112.4, 110.2, 54.4, 28.2, 27.3; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3441, 3301, 3105, 3011, 2966, 2839, 1717, 1639, 1614, 1588, 1547, 1450, 1397, 1295, 1223, 1158, 1050, 855, 776, 752, 689, 505 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C14H14N4O4: C, 55.63; H, 4.67; N, 18.53. Found: C, 55.74; H, 4.73; N, 18.80.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((2-bromophenyl)amino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3k)
White powder; 90 %; m.p. 148 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.79 (s, 1H, NH), 7.70 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.55 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.39 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.25 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H, Ar), 3.48 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.42 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 187.4, 168.1, 163.8, 130.4, 130.3, 130.1, 128.9, 128.2, 128.1, 126.7, 126.6, 28.3, 27.5; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3400, 3232, 3142, 3064, 2966, 1707, 1627, 1572, 1505, 1449, 1399, 1377, 1303, 1205, 1001, 791, 770, 762, 755, 729, 660, 497 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H11BrN4O3: C, 44.46; H, 3.16; N, 15.96. Found: C, 44.58; H, 3.20; N, 16.21.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-(o-tolylamino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3l)
White powder; 78 %; m.p. 161 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.63 (s, 1H, NH), 7.36–7.24 (m, 4H, Ar), 3.48 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.42 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 2.28 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 186.1, 167.8, 164.0, 130.0, 129.4, 128.2, 127.6, 127.3, 127.2, 126.1, 125.6, 28.1, 27.4, 17.1; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3408, 3109, 2956, 1719, 1631, 1571, 1453, 1302, 1115, 1005, 808, 753, 644, 506 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C14H14N4O3: C, 58.74; H, 4.93; N, 19.57. Found: C, 58.87; H, 4.96; N, 19.83.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((2-methoxyphenyl)amino)isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (3m)
White powder; 86 %; m.p. 149 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.77 (s, 1H, NH), 7.32 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.32 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.02 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ar), 3.88 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.47 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.42 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 185.1, 167.8, 163.8, 127.9, 127.5, 126.1, 125.7, 119.2, 119.1, 110.5, 110.4, 55.8, 28.1, 27.4; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3399, 3120, 3060, 2942, 2832, 2763, 1711, 1583, 1542, 1497, 1445, 1290, 1251, 1192, 1118, 1027, 920, 854, 741, 579, 503, 456 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C14H14N4O4: C, 55.63; H, 4.67; N, 18.53. Found: C, 55.76; H, 4.60; N, 18.79.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-(phenylamino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3n)
White powder; 70 %; m.p. 178 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.96 (s, 1H, NH), 7.50–7.32 (m, 5H, Ar), 3.91 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.84 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 185.5, 166.4, 161.8, 130.3, 130.2, 128.2, 126.8, 126.8, 124.7, 37.3, 36.6; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3427, 3227, 3177, 2950, 1636, 1589, 1539, 1480, 1451, 1434, 1412, 1331, 1116, 766, 689, 651, 484 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H12N4O2S: C, 54.16; H, 4.20; N, 19.43. Found: C, 54.28; H, 4.13; N, 19.70.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((4-bromophenyl)amino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3o)
Yellow powder; 88 %; m.p. 208 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.97 (s, 1H, NH), 7.58 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H, Ar), 7.36 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ar), 3.91 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.83 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 186.2, 166.5, 161.7, 133.4, 133.3, 131.3, 126.2, 126.1, 126.1, 37.4, 36.7; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3411, 3093, 2922, 1633, 1579, 1536, 1437, 1363, 1132, 1116, 1018, 829, 788, 647, 611, 491 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H11BrN4O2S: C, 42.52; H, 3.02; N, 15.26. Found: C, 42.67; H, 3.11; N, 15.58.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((4-fluorophenyl)amino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3p)
Yellow powder; 81 %; m.p. 149 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.88 (s, 1H, NH), 7.45–7.35 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.15 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ar), 3.90 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.83 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 186.4, 166.4, 161.7, 128.8, 128.8, 126.6, 126.5, 117.4, 117.1, 117.0, 37.3, 36.3; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3407, 3137, 3062, 1639, 1605, 1547, 1508, 1412, 1364, 1332, 1238, 1157, 1117, 835, 774, 517 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H11FN4O2S: C, 50.97; H, 3.62; N, 18.29. Found: C, 51.11; H, 3.70; N, 18.59.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((4-nitrophenyl)amino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3q)
Yellow powder; 79 %; m.p. 176 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 14.41 (s, 1H, NH), 8.32 (d, J = 9 Hz, 2H, Ar), 7.78 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H, Ar), 3.93 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.84 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 187.3, 166.8, 161.7, 125.7, 125.7, 125.6, 124.5, 124.4, 123.5, 37.5, 36.8; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3111, 3085, 2980, 2872, 1647, 1608, 1588, 1517, 1437, 1405, 1339, 1260, 1113, 855, 833, 761, 647, 615, 483 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H11N5O4S: C, 46.84; H, 3.33; N, 21.01. Found: C, 46.99; H, 3.26; N, 21.35.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-(p-tolylamino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3r)
Yellow powder; 82 %; m.p. 169 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.88 (s, 1H, NH), 7.35–7.22 (m, 5H, Ar), 3.90 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.83 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 2.40 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 185.1, 166.2, 161.8, 130.8, 128.8, 128.8, 128.7, 124.4, 124.4, 38.5, 37.3, 36.6; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3460, 3101, 2917, 2864, 1662, 1509, 1468, 1393, 1255, 1112, 860, 818, 741, 517 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C14H14N4O2S: C, 55.62; H, 4.67; N, 18.53. Found: C, 55.72; H, 4.65; N, 18.76.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((4-methoxyphenyl)amino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3s)
Yellow powder; 86 %; m.p. 178 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.80 (s, 1H, NH), 7.33 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H, Ar), 6.97 (d, J = 9 Hz, 2H, Ar), 3.89 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.85 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.83 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 185.2, 166.1, 161.8, 129.9, 125.9, 115.4, 115.3, 113.5, 113.4, 56.4, 37.2, 36.6; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3401, 3202, 2999, 2962, 2832, 1609, 1590, 1542, 1511, 1480, 1332, 1246, 1116, 1030, 827, 619, 517 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C14H14N4O3S: C, 52.82; H, 4.43; N, 17.60. Found: C, 52.99; H, 4.49; N, 17.96.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((3-bromophenyl)amino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3t)
Yellow powder; 71 %; m.p. 155 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 14.00 (s, 1H, NH), 7.66 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.48 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.42 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.33 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 1H, Ar), 3.90 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.83 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 186.5, 166.6, 161.7, 138.5, 131.8, 131.4, 129.3, 127.6, 127.5, 125.4, 122.5, 37.4, 36.7; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3466, 3097, 3064, 1636, 1578, 1532, 1465, 1434, 1413, 1362, 1331, 1258, 1201, 1118, 877, 811, 780, 693, 615, 484 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H11BrN4O2S: C, 42.52; H, 3.02; N, 15.26. Found: C, 42.65; H, 3.11; N, 15.54.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((3-chlorophenyl)amino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3u)
White powder; 70 %; m.p. 164 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 14.01 (s, 1H, NH), 7.52 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.42–7.30 (m, 3H, Ar), 3.91 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.83 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 186.5, 166.6, 161.7, 131.2, 129.0, 127.0, 126.9, 126.7, 124.9, 122.9, 122.7, 37.4, 36.7; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3410, 3097, 3072, 2849, 1637, 1599, 1579, 1536, 1467, 1433, 1413, 1363, 1331, 1201, 1118, 1037, 881, 781, 696, 488 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H11ClN4O2S: C, 48.38; H, 3.44; N, 17.36. Found: C, 48.49; H, 3.35; N, 17.70.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-(m-tolylamino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3v)
White powder; 76 %; m.p. 156 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.92 (s, 1H, NH), 7.35 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.23 (s, 1H, Ar), 7.17 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H, Ar), 3.90 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.84 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 2.41 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 185.1, 166.3, 161.8, 139.4, 137.1, 129.7, 129.7, 127.9, 127.2, 123.8, 121.6, 39.3, 37.3, 36.4; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3113, 2953, 2921, 2798, 1667, 1604, 1586, 1549, 1492, 1440, 1396, 1332, 1313, 1117, 887, 787, 742, 681, 482 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C14H14N4O2S: C, 55.62; H, 4.67; N, 18.53. Found: C, 55.72; H, 4.60; N, 18.83.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((3-methoxyphenyl)amino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3w)
Yellow powder; 74 %; m.p. 161 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.97 (s, 1H, NH), 7.36 (t, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.02 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 2H, Ar), 6.90 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H, Ar), 3.90 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.84 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.83 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 185.2, 166.3, 161.8, 131.0, 128.9, 118.9, 116.8, 116.7, 114.6, 112.6, 110.1, 56.4, 37.3, 36.6; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3418, 3097, 2980, 2872, 1647, 1608, 1588, 1517, 1437, 1405, 1339, 1261, 1113, 855, 833, 761, 647, 615, 483 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C14H14N4O3S: C, 52.82; H, 4.43; N, 17.60. Found: C, 52.97; H, 4.49; N, 17.92.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((2-bromophenyl)amino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3x)
Yellow powder; 89 %; m.p. 165 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.83 (s, 1H, NH), 7.71 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.56 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.41 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.25 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H, Ar), 3.91 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.85 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 187.3, 166.5, 161.7, 132.3, 132.2, 130.5, 129.9, 129.0, 128.4, 126.8, 126.7, 37.4, 36.7; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3203, 3056, 2950, 1643, 1573, 1517, 1468, 1435, 1410, 1362, 1330, 1117, 1026, 786, 761, 720, 663, 460 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C13H11BrN4O2S: C, 42.52; H, 3.02; N, 15.26. Found: C, 42.69; H, 3.11; N, 15.54.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-(o-tolylamino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3y)
White powder; 77 %; m.p. 142 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.70 (s, 1H, NH), 7.33–7.27 (m, 4H, Ar), 3.90 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.84 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 2.95 (s, 3H, CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 186.1, 167.8, 164.0, 134.6, 130.0, 129.4, 127.6, 127.3, 127.2, 126.1, 125.6, 37.4, 36.7, 30.1; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3445, 3184, 2962, 1638, 1582, 1522, 1434, 1332, 1208, 1118, 896, 788, 648, 467 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C14H14N4O2S: C, 55.62; H, 4.67; N, 18.53. Found: C, 55.72; H, 4.62; N, 18.88.
5,7-Dimethyl-3-((2-methoxyphenyl)amino)-6-thioxo-6,7-dihydroisoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one (3z)
White powder; 85 %; m.p. 169 °C (dec.). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 13.83 (s, 1H, NH), 7.76 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H, Ar), 7.38–7.28 (m, 1H, Ar), 7.03 (t, J = 8.4 Hz, 2H, Ar), 3.90 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.85 (s, 3H, N–CH3), 3.81 (s, 3H, N–CH3); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): 181.3, 167.8, 161.7, 134.3, 129.4, 127.9, 127.7, 126.1, 121.6, 119.4, 119.2, 58.8, 38.4, 36.4; FT-IR (KBr) v: 3453, 3118, 2949, 1649, 1604, 1540, 1466, 1435, 1406, 1367, 1333, 1312, 1260, 1112, 1025, 764, 673, 489 cm−1. Anal. calcd. for C14H14N4O3S: C, 52.82; H, 4.43; N, 17.60. Found: C, 52.94; H, 4.48; N, 17.89.
Conclusions
We report a new, simple, and efficient NaOH-promoted regioselective synthesis of a wide range of isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidines as pharmaceutically interesting compounds via the one-pot three-component reaction of aryl isothiocyanates, N,N-dimethylbarbituric acid or N,N-dimethyl-2-thiobarbituric acid, and hydroxylamine hydrochloride in DMF at room temperature. The impressive features of this new one-pot protocol are high regioselectivity, simple operation, very easy work-up, high atom economy, moderate to high yield, and the purity of the products. Also, this reaction could be performed on the gram scale, and the obtained compounds have potential pharmaceutical properties.
References
C.H. Gill, A.V. Chat, G.Y. Shinde, A.P. Sarkate, S.V. Tiwari, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 4029 (2018)
M.A. Shaikh, M. Farooqui, S. Abed, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 5483 (2018)
M.H. Sayahi, S. Bahadorikhalili, S.J. Saghanezhad, M. Mahdavi, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 5241 (2018)
M. Ghashang, S. Janghorban, S.J. Roudbaraki, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 5013 (2018)
A.V. Chate, R.M. Dongre, M.K. Khaire, G.M. Bondle, J.N. Sangshetti, M. Damale, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 6119 (2018)
S. Kasaboina, R. Bollu, P.M. Gomedhika, V. Ramineni, L. Nagarapu, N. Dumala, P. Grover, J.B. Nanubolu, Tetrahedron Lett. 59, 3015 (2018)
A. Mohammadinezhad, B. Akhlaghinia, Aust. J. Chem. 71, 32 (2018)
J.S. Savithri, P. Rajakumar, Aust. J. Chem. 71, 399 (2018)
B. Xu, J. Su, J. Wang, G.-C. Zhou, Aust. J. Chem. 69, 1646 (2016)
B. Karmakar, Aust. J. Chem. 69, 1117 (2016)
N. Devi, R. Shankar, V. Singh, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 55, 373 (2018)
S.-C. Wang, F.-X. Wan, S. Liu, S. Zhang, L. Jiang, J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 65, 445 (2018)
M. Rimaz, H. Mousavi, M. Behnam, L. Sarvari, B. Khalili, Curr. Chem. Lett. 6, 55 (2017)
M. Rimaz, H. Mousavi, M. Behnam, B. Khalili, Curr. Chem. Lett. 5, 145 (2016)
M. Yousaf, A.F. Zahoor, S. Faiz, S. Javed, M. Irfan, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 55, 2447 (2018)
S. Balalaie, M. Shamakli, A. Nikbakht, N.S. Alavijeh, F. Rominger, S. Rostamizadeh, H.R. Bijanzadeh, Org. Biomol. Chem. 15, 5737 (2017)
A.O. Chagarovskiy, E.M. Budynina, O.A. Ivanova, V.B. Rybakov, I.V. Trushkov, M.Y. Melnikov, Org. Biomol. Chem. 14, 2905 (2016)
J.-S. Poh, C. García-Ruiz, A. Zúñiga, F. Meroni, D.C. Blakemore, D.L. Browne, S.V. Ley, Org. Biomol. Chem. 14, 5983 (2016)
W. Liu, P. Zhou, C. Chen, Q. Zhang, Z. Zhu, Org. Biomol. Chem. 11, 542 (2013)
D.V. Vorobyeva, N.M. Karimova, I.L. Odinets, G.-V. Röschenthaler, S.N. Osipov, Org. Biomol. Chem. 9, 7335 (2011)
M. Kaur, A. Kaur, B. Singh, B. Singh, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 54, 80 (2017)
J. Gaddameedi, D.P. Yelda, R.R. Kuchukulla, K. Chavva, S.R. Pillalamarri, S.K. Gautham, G.K. Chityal, N. Banda, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 54, 194 (2017)
A.P. Chavan, A.B. Pinjari, P.C. Mhaske, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 52, 1911 (2015)
H. Kiyani, F. Ghorbani, Res. Chem. Intermed. 42, 6831 (2016)
R.H. Vekariya, K.D. Patel, H.D. Patel, Res. Chem. Intermed. 42, 7559 (2016)
A. Mouradzadegun, F. Abadast, S. Elahi, N. Askarikia, Res. Chem. Intermed. 42, 3147 (2016)
S.N. Maddila, S. Maddila, W.E. van Zyl, S.B. Jonnalagadda, Res. Chem. Intermed. 42, 2553 (2016)
H. Kiyani, F. Ghorbani, Res. Chem. Intermed. 41, 2653 (2015)
H. Kiyani, H. Kanaani, D. Ajloo, F. Ghorbani, M. Vakili, Res. Chem. Intermed. 41, 7739 (2015)
S.S. Basha, K. Divya, A. Padmaja, V. Padmavahthi, Res. Chem. Intermed. 41, 10067 (2015)
G. Roman, Res. Chem. Intermed. 40, 2039 (2014)
N. Irannejad-Gheshlaghchaei, A. Zare, S.S. Sajadikhah, A. Banaei, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 6253 (2018)
G.N. Pairas, F. Perperopoulou, P.G. Tsoungas, G. Varvounis, ChemMedChem 12, 408 (2017)
A. Oancea, E. Georgescu, F. Georgescu, A. Nicolescu, E.I. Oprita, C. Tudora, L. Vladulescu, M.-C. Vladulescu, F. Oancea, C. Deleanu, Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 13, 659 (2017)
E. Gilberg, D. Stumpfe, J. Bajorath, RSC Adv. 7, 35638 (2017)
T. Iami, H. Togo, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 29, 1377 (2018)
S. Xue, J. Liu, C. Wang, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2450 (2016)
J. Zhu, J. Mo, H.-Z. Lin, Y. Chen, H.-P. Sun, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 26, 3065 (2018)
C. Lei, L. Geng, X. Xu, X. Shao, Z. Li, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 28, 831 (2018)
S.S. Prasad, S. Baskaran, J. Org. Chem. 83, 1558 (2018)
T. Morita, S. Fukuhara, S. Fuse, H. Nakamura, Org. Lett. 20, 433 (2018)
M. Mo, J. Yang, X.-C. Jiang, Y. Cao, J. Fei, Y. Chen, X. Qi, Y. Chu, L. Zhou, D. Ye, J. Med. Chem. 61, 8241 (2018)
X. Zhou, X. Xu, Z. Shi, K. Liu, H. Gao, W. Li, Org. Biomol. Chem. 14, 5246 (2016)
B.A. Chalyk, I.Y. Kandaurova, K.V. Hrebeniuk, O.V. Manoilenko, I.B. Kulik, R.T. Iminov, V. Kubyshkin, A.V. Tverdokhlebov, O.K. Ablialimov, P.K. Mykhailiuk, RSC Adv. 6, 25713 (2016)
Y. He, Y.-Y. Xie, Y.-C. Wang, X.-M. Bin, D.-C. Hu, H.-S. Wang, Y.-M. Pan, RSC Adv. 6, 58988 (2016)
S. Mohammad, R.A. Vishwakarma, S.B. Bharate, RSC Adv. 5, 3470 (2015)
A. Mishra, B.B. Mishra, V.K. Tiwari, RSC Adv. 5, 41520 (2015)
S. Nagaraju, N. Satyanarayana, B. Paplal, A.K. Vasu, S. Kanvah, B. Sridhar, P. Sripadi, D. Kashinath, RSC Adv. 5, 94474 (2015)
M.M. Bassaco, M.P. Fortes, D.F. Back, T.S. Kaufman, C.C. Silveira, RSC Adv. 4, 60785 (2014)
C. Görgen, T.J.J. Müller, Chem. Heterocycl. Comp. 53, 422 (2017)
W. Chen, J. Zhang, B. Wang, Z. Zhao, X. Wang, Y. Hu, J. Org. Chem. 80, 2413 (2015)
C.M. Nunes, I. Reva, R. Fausto, J. Org. Chem. 78, 10657 (2013)
I. Triandafillidi, C.G. Kokotos, Org. Lett. 19, 106 (2017)
S. Samai, T. Chanda, H. Ila, M.S. Singh, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 4026 (2013)
A. Atahan, N. Gencer, C. Bilen, E. Yavuz, H. Genc, F. Sonmez, M. Zengin, M. Ceylan, M. Kucukislamoglu, ChemistrySelect 3, 529 (2018)
V.A. Adhikari, V.V. Badiger, Arch. Pharm. 320, 1124 (1987)
W.S. Hamama, M.E. Ibrahim, H.H. Zoorob, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 53, 2007 (2016)
E. Wagner, L. Becan, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 55, 1880 (2018)
I.A. Shehata, R.A. Glennon, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 24, 1291 (1987)
Z. Ji, A.A. Ahmed, D.H. Albert, J.J. Bouska, P.F. Bousquet, G.A. Cunha, K.B. Glaser, J. Guo, J. Li, P.A. Marcotte, M.D. Moskey, L.J. Pease, K.D. Stewart, M. Yates, S.K. Davidsen, M.R. Michaelides, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 16, 4326 (2006)
E. Wagner, L. Becan, E. Nowakowska, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 12, 265 (2004)
J.-J. Guo, Y.-Y. Liu, Y.-Z. Pei, Chin. Chem. Lett. 26, 1283 (2015)
G.J. Yu, B. Yang, A.S. Verkman, M.J. Kurth, Synlett 7, 1063 (2010)
S. Kokkonda, F.E. Mazouni, K.L. White, J. White, D.M. Shackleford, M.J. Lafuente-Monasterio, P. Rowland, K. Manjalanagara, J.T. Joseph, A. Garcia-Ṕerez, J. Fernandez, F.J. Gamo, D. Waterson, J.N. Burrows, M.J. Palmer, S.A. Charman, P.K. Rathod, M.A. Philips, ACS Omega 3, 9227 (2018)
V.N. Mahire, G.P. Patil, A.B. Deore, P.G. Chavan, H.D. Jirmali, P.P. Mahulikar, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 5801 (2018)
T. Zhang, J. Zhou, Y. Chen, Y. Li, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 5329 (2018)
F. Mousavizadeh, M. Talebizadeh, M. Anary-Abbasinejad, Tetrahedron Lett. 59, 2970 (2018)
W. Qian, D. Wang, H. Wang, P. Yu, S. Liu, S. Chen, Tetrahedron Lett. 59, 2167 (2018)
B. Mitra, S. Mukherjee, G.C. Pariyar, P. Ghosh, Tetrahedron Lett. 59, 1385 (2018)
G. Khanna, P. Saluja, J.M. Khurana, Aust. J. Chem. 70, 1285 (2017)
V. Ajavakom, T. Yutthaseri, R. Chantanatrakul, A. Suksamran, A. Ajavakom, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 55, 13 (2018)
S. Gadekar, P.M.K. Lande, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 3267 (2018)
S.F. Hojati, A. Amiri, S. Mohamadi, N. Moeini Eghbali, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 2275 (2018)
N. Azizi, M. Edrisi, Res. Chem. Intermed. 43, 379 (2017)
C.-W. Lü, J.-J. Wang, F. Li, S.-J. Yu, Y. An, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 1035 (2018)
K.G. Patel, N.M. Misra, R.H. Vekariya, R.R. Shettigar, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 289 (2018)
M. Rimaz, H. Mousavi, P. Keshavarz, B. Khalili, Curr. Chem. Lett. 4, 159 (2015)
M. Ghandi, S. Rahimi, N. Zarezadeh, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 54, 102 (2017)
J. Safaei-Ghomi, H. Shahbazi-Alavi, S.H. Nazemzadeh, J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 64, 1213 (2017)
Z.R. Moosavi-Zare, H. Goudarziafshar, S. Dastbaz, J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 64, 727 (2017)
H. Alinezhad, V. Alinezhad, S. Mohseni Tavakkoli, J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 64, 385 (2017)
E. Tabrizian, A. Amoozadeh, J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 64, 331 (2017)
B. Zeynizadeh, R. Younesi, H. Mousavi, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 7331 (2018)
M.K. Mehra, M.P. Tantak, V. Arun, I. Kumar, D. Kumar, Org. Biomol. Chem. 15, 4959 (2017)
G. Ramachandran, N.S. Karthikeyan, P. Giridharan, K.I. Sathiyanarayanan, Org. Biomol. Chem. 10, 5343 (2012)
J.-Y. Liu, H. Zhang, B.-M. Feng, B. Jiang, S.-L. Wang, S.-J. Tu, Org. Biomol. Chem. 10, 8533 (2012)
H. Ma, C. Guo, Z. Zhan, G. Lu, Y. Zhang, X. Luo, X. Cui, G. Huang, New J. Chem. 41, 5280 (2017)
S. Ambethkar, M.M. Kalaiselvi, V. Padmini, N. Bhuvanesh, ChemistrySelect 2, 5329 (2017)
K.-H. Wang, J. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Su, D. Huang, Y. Fu, Z. Du, Y. Hu, Synthesis 50, 1907 (2018)
M. Safarzaei, M.T. Maghsoodlou, E. Mollashahi, N. Hazeri, M. Lashkari, Res. Chem. Intermed. 44, 7449 (2018)
M. Rimaz, H. Mousavi, Turk. J. Chem. 37, 252 (2013)
M. Rimaz, H. Rabiei, B. Khalili, R.H. Prager, Aust. J. Chem. 67, 283 (2014)
M. Rimaz, Aust. J. Chem. 68, 1529 (2015)
M. Rimaz, Z. Jalalian, H. Mousavi, R.H. Prager, Tetrahedron Lett. 57, 105 (2016)
M. Rimaz, J. Khalafy, H. Mousavi, Res. Chem. Intermed. 42, 8185 (2016)
M. Rimaz, F. Aali, Chin. J. Catal. 37, 517 (2016)
M. Rimaz, F. Aali, B. Khalili, R.H. Prager, Aust. J. Chem. 70, 660 (2017)
M. Rimaz, H. Mousavi, L. Nikpey, B. Khalili, Res. Chem. Intermed. 43, 3925 (2017)
M. Rimaz, J. Khalafy, H. Mousavi, S. Bohlooli, B. Khalili, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 54, 3174 (2017)
M. Rimaz, B. Khalili, G. Khatyal, H. Mousavi, F. Aali, Aust. J. Chem. 70, 1274 (2017)
M. Rimaz, H. Mousavi, B. Khalili, F. Aali, J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 65, 1389 (2018)
N. Matsumoto, M. Takahashi, Tetrahedron 58, 10073 (2002)
T.-L. Ho, Chem. Rev. 75, 1 (1975)
T.-L. Ho, J. Chem. Educ. 55, 335 (1978)
P.K. Chattaraj, H. Lee, R.G. Parr, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113, 1855 (1991)
P.K. Chattaraj, P.V.R. Schleyer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116, 1067 (1994)
R.G. Pearson, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 85, 3533 (1963)
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for financial support from the Research Council of Payame Noor University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rimaz, M., Mousavi, H., Ozzar, L. et al. Facile, capable, atom-economical one-pot multicomponent strategy for the direct regioselective synthesis of novel isoxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidines. Res Chem Intermed 45, 2673–2694 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-019-03757-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-019-03757-9