Abstract
Clonorchis sinensis, Opisthorchis viverrini, and O. felineus are liver flukes of human and animal pathogens occurring across much of Europe and Asia. Nevertheless, they are often underestimated compared to other, better known neglected diseases in spite of the fact that many millions of people are infected and hundreds of millions are at risk. This is possibly because of the chronic nature of the infection and disease and that it takes several decades prior to a life-threatening pathology to develop. Several studies in the past decade have provided more information on the molecular biology of the liver flukes which clearly lead to better understanding of parasite biology, systematics, and population genetics. Clonorchiasis and opisthorchiasis are characterized by a chronic infection that induces hepatobiliary inflammation, especially periductal fibrosis, which can be detected by ultrasonography. These chronic inflammations eventually lead to cholangiocarcinoma (CCA), a usually fatal bile duct cancer that develops in some infected individuals. In Thailand alone, opisthorchiasis-associated CCA kills up to 20,000 people every year and is therefore of substantial public health importance. Its socioeconomic impacts on impoverished families and communities are considerable. To reduce hepatobiliary morbidity and CCA, the primary intervention measures focus on control and elimination of the liver fluke. Accurate diagnosis of liver fluke infections in both human and other mammalian, snail and fish intermediate hosts, are important for achieving these goals. While the short-term goal of liver fluke control can be achieved by praziquantel chemotherapy, a comprehensive health education package targeting school children is believed to be more beneficial for a long-term goal/solution. It is recommended that a transdisciplinary research or multisectoral control approach including one health and/or eco health intervention strategy should be applied to combat the liver flukes, and hence contribute to reduction of cholangiocarcinoma in endemic areas.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 History and Taxonomy
Opisthorchiid flukes most commonly occur in the bile duct, gall bladder, and liver of their mammalian and avian hosts (Scholz 2008). They are small to medium sized with 33 recognized genera in the family Opisthorchiidae. These are divided into 13 subfamilies (King and Scholz 2001; Scholz 2008). Both of the genera Clonorchis and Opisthorchis fall within the subfamily Opisthorchiinae. Clonorchis sinensis from East Asia and Opisthorchis viverrini from the Lower Mekong Basin are currently recognized as the most important human pathogens. Both are involved in the development of human cholangiocarcinoma and have been classified as group one carcinogens by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, a part of the World Health Organization (IARC 2012). The presence of C. sinensis and O. viverrini in East and continental Southeast Asia, respectively, is strongly correlated with the incidence of cholangiocarcinoma, particularly in northeast Thailand which has the highest incidence worldwide (IARC 2012). Although Opisthorchis felineus , which occurs from Europe across to eastern Siberia, has not yet been recognized as a carcinogen there is evidence suggesting that this is the case (Erhardt et al. 1962). It is, nevertheless, a pathogen of considerable significance in its own right in terms of hepatobiliary diseases originated from biliary fibrosis (Pozio et al. 2013).
Opisthorchis lobatus , a new species recently found in freshwater fish in Lao PDR, may also cause zoonosis but its role in humans is not known and it will not be dealt with here (Thaenkham et al. 2011). Nor will the avian species including O. cheelis, O. longissimus, and O. parageminus also reported from Southeast Asia (Nawa et al. 2015; Doanh and Nawa 2016; Dao et al. 2017). Dao et al. (2016) reported the sympatric distribution of duck and human genotypes of “O. viverrini”. The discovery of several species in the genus Opisthorchis in addition to the species complex of O. viverrini reflects complicated host and parasite interaction and their co-evolution.
Clonorchis sinensis was first described by JFP McConnell in the August 21st issue of the Lancet in 1875 from postmortem specimens collected from the bile duct of a Chinese seaman who died in Calcutta, India. On September 18th of the same year, TS Cobbold wrote a short letter, also published in the Lancet, indicating that from McConnell’s description of the trematodes it was undoubtedly a new species which he then named Distoma sinense . This name was later revised by Looss (1907), as Clonorchis sinensis, the type species for the genus. At the time of its discovery, McConnell noted “The morbid anatomy of the liver in this case seems unequivocally to point to the presence of the flukes in its biliary ducts as the exciting cause of the acute and extensive structural degeneration of the proper structure of that organ, and of that cholemic condition induced by the obstruction of the biliary channels which appears to have been the immediate cause of death.” clearly pointing out the pathological significance of this species.
The discovery of Opisthorchis viverrini initially follows a quite different path. Poirier (1886) was the first to discover and describe this species which had been retrieved from the biliary ducts of a fishing cat ( Prionailurus viverrinus ) which had been kept in the Zoological Gardens attached to the Paris Natural History Museum. It was only over 20 years later that Leiper (1915) described the first specimens from humans supplied by WFJ Kerr from Chiang Mai in the north of Thailand. In 1916, Kerr published a parasitologically more detailed paper listing 17% of the 230 adult male prisoners examined to be infected. Interestingly, 74% of those examined were Laotians who had lived in the Chiang Mai area for their whole lives—there were very few Thais in the sample group. In this paper, Kerr originally identified the species as Opisthorchis felineus , but in a postscript indicates that they were identified by Leiper as O. viverrini. About a decade after Kerr’s paper, Prommas (1927) reported the first case of infection (again as O. felineus) from the northeast of Thailand at Roi-et while Bedier and Chesneau (1929) reported high prevalences of 25% and 15% from Thakhek and Vientiane, respectively, in Lao PDR.
Gurlt was the first to describe and illustrate O. felineus (subfamily Opisthorchiinae) although he confused it with Distomum conus Creplin 1825 (Erhardt et al. 1962). It was only in 1885 that O. felineus which had been isolated from cats were described as a valid species by Rivolta as Distomum felineum (Rivolta 1884). It was later moved from the genus Distomum, Opisthorchis, created by Blanchard in 1895. This is the type genus for the family Opisthorchiidae Looss, 1899. Opisthorchiasis in humans caused by O. felineus was first described by Vinogradoff (1892) from Siberia.
2 Current Status and Geographical Distribution
Human populations show high levels of infection with all three liver fluke species within each of their distributional ranges. Up to 680 million people worldwide are at risk of infection (Keiser and Utzinger 2005). Recent estimates indicate that 45 million people living in Asia and Europe are infected, with approximately 35 million C. sinensis cases, ten million O. viverrini cases, and 1.2 million cases of O. felineus (WHO 1995; Sithithaworn et al. 2012a).
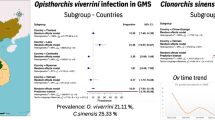
Clonorchis sinensis is the most frequent human parasite of the three with 600 million people at risk of infection (Keiser and Utzinger 2005) in East Asia from mid-Vietnam through much of China, including Taiwan, into Korea and the far east of Russia (Rim 2005; Hong and Fang 2012). Although C. sinensis was previously endemic in Japan, the last human case was in 1991 and no autochthonous case has been reported since (Lun et al. 2005). Doanh and Nawa (2016) suggest that previous identifications of C. sinensis and O. viverrini from Vietnam may have been flawed leading to overestimates in the prevalences of both species in this country. The second most common species is O. viverrini which is found along the Lower Mekong and its tributaries in the north and northeast of Thailand, Lao PDR, Cambodia, and southern Vietnam, with recent reports from Myanmar (Aung et al. 2017; Sanpool et al. 2018). Data for the last three countries are sparse and for O. viverrini most of our information comes from the north and northeast of Thailand with an increasing list of publications from Lao PDR (Sithithaworn and Haswell-Elkins 2003; Andrews et al. 2008; Petney et al. 2013). Movement of people within the Mekong area is probably, at least in part, responsible for the presence of O. viverrini infection in other parts of Thailand (Buathong et al. 2017). The information which is available suggests that as many as 67 million people may be at risk of infection (Keiser and Utzinger 2005).
Although O. felineus, the European liver fluke, is the most poorly studied of the three species it has been reported from continental European countries except Finland, Norway, and Sweden. It does not occur in the UK. Animal hosts are wild and domestic carnivores (Erhardt et al. 1962) but humans probably play a significant role in parasite transmission (Petney et al. 2013). Human cases have been reported to occur in Belarus, Germany, Greece, Italy, Poland, Romania, Russia, Spain, the Ukraine, the Baltic countries, Moldova, and Kazakhstan, but records from some of these countries are over 50 years old (Erhardt et al. 1962; Mordvinov et al. 2012; Pozio et al. 2013). O. felineus represents a significant health problem in certain areas of Siberia where evidence indicates that its prevalence in both humans and in animals increases from west to east (Mordvinov et al. 2012). In the Ob-Irtysh basin, where the prevalence of infection peaks, it is of particular medical significance (Mordvinov et al. 2012; Fedorova et al. 2017).
Although clonorchiasis is endemic to East Asia and opisthorchiasis to the Mekong area of Southeast Asia and parts of eastern Russia all can occasionally be found in non-endemic areas having been introduced by infected tourists, refuges, or workers, who have moved from endemic to non-endemic areas (Hira et al. 1987; Molina et al. 1988; WHO 1995; Saksirisampant et al. 2002; Fried and Abruzzi 2010). The flukes have, however, not currently become endemic in these areas due to the lack of suitable intermediate hosts.
A predictive future climate model for Thailand suggests that the distribution of O. viverrini will be significantly affected by anticipated changes in precipitation and temperature with the northeast becoming increasingly unsuitable (Suwannatrai et al. 2017).
3 Biology and Life Cycle
Liver flukes are hermaphroditic trematodes which are dorso-ventrally flattened. The body has an oral sucker situated anteriorly and a ventral sucker at mid-body. The differentiation of the species is based on morphology. The adult worms differ in the shape and position of their testes and the arrangement of the vitelline glands. C. sinensis can be separated from the other two species by the presence of branched testes in a tandem position and the continuously distributed vitelline glands (Fig. 6.1). Although O. viverrini is similar to O. felineus in having lobed testes and a cluster vitelline gland, it differs by having deeper lobulation of and greater extremity of the testes and also lacks transversely compressed patterns of vitelline follicles. The size of the adult flukes depends on the species involved. O. viverrini is the smallest, measuring 5.5–10 × 0.77–1.65 mm. O. felineus is somewhat larger measuring 7–12 × 2–3 mm (Kaewkes 2003; Pozio et al. 2013) while C. sinensis is the largest measuring 10–25 × 3–5 mm. Variation in the size of the adults is density dependent, with individuals being smaller the higher the infestation, and also dependent on the diameter of the bile duct they inhabit (Flavell et al. 1983).
The eggs of C. sinensis, O. felineus, and O. viverrini are morphologically similar making them difficult to distinguish from one another. The operculum of each species has a distinct shoulder while a small knob or comma shape appendage is found at the abopercular end (Kaewkes 2003). The surface of the egg shell is rough and irregular having been described as having a “musk-melon pattern” by scanning electron microscopy (Tesana et al. 1991).
The transmission cycle of all three liver fluke species goes through three phases: (1) the infection of the snail first intermediate hosts via host feces, (2) cercarial release and finding fish second intermediate hosts for development of the infective metacercariae stage, and (3) ingestion of metacercariae in raw or partially cooked fish by humans. Petney et al. (2013) argue that the three species differ in terms of the relative significance of the zoonotic and anthroponotic components of the epidemiological cycle with O. viverrini having mainly human final hosts, O. felineus in Europe mainly wild carnivore hosts and C. sinensis and O. felineus in its Asian range a mixture of the two. This has considerable epidemiological significance, particularly in control and prevention programs.
The life cycles (Fig. 6.2) of all three species are very similar with a snail first intermediate host with usually low prevalences of infection, fish second intermediate hosts with substantially higher levels of infection, and usually a carnivorous mammal as final host (Schuster 2002; Zhang et al. 2007). The low prevalences of infection in the snail first intermediate hosts is, at least in part, compensated for by the often very high prevalences in fish, the infective phase for humans.
The distribution of each species is closely related to that of their hosts. This is particularly true of the snail first intermediate hosts that tend to be more restricted in the number of species used (Hong and Fang 2012; Kiatsopit et al. 2012; Petney et al. 2012). For O. viverrini, the presence of snails of Bithynia siamensis goniomphalos in nearby freshwater sources is a prerequisite for the presence of the parasite in the human population (Petney et al. 2012; Wang et al. 2013).
The importance of fecal contamination of freshwater sources inhabited by intermediate snail hosts by wild and domestic animal hosts (i.e., the zoonotic cycle) varies greatly between the three fluke species. In its European range fecal matter containing O. felineus eggs is almost exclusively found in wild and domestic carnivores. In areas with widespread human infection, fecal contamination of freshwater by infected animals is certainly reduced and in the case of O. viverrini probably only plays a minor role in infecting snails.
Clonorchis sinensis is a species with a relatively broad range of hosts sharing anthroponotic and zoonotic components in its epidemiological cycle (Petney et al. 2013). C. sinensis is known to use 8 main snail species as intermediate hosts. These come from 5 different families (Assimineidae, Bithyniidae, Hydrobiidae, Melaniidae, Thiaridae) (Lun et al. 2005). There is some geographic differentiation in the distribution and prevalence of C. sinensis in the different snail species. Prevalences vary locally and may be as high as 27% for Alocinma longicornis in parts of Guangdong and 8% for Bithynia fuchsianus in parts of Guangxi although most values are substantially lower (Lun et al. 2005).
Once the snail has ingested the embryonated eggs, which are passed in the feces of the final host, the eggs hatch to release miracidia which then undergo development to sporocysts then rediae and finally cercariae in the snail. The tailed cercarial stage escapes from the snail host and actively swims to find a suitable fish second intermediate host which it then penetrates, losing its tail and encysting to become a metacercaria embedded either in the muscles of the fish or under the scales.
C. sinensis utilizes predominantly fish in 11 families, with 46 genera and 132 species of which 32 genera and 71 species belong to the family Cyprinidae, but also several crustacean second intermediate hosts (Lun et al. 2005). The fish include a number of species which are commonly used in aquaculture fish, including the common carp (Cyprinus carpio), the grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus), the silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix), as well as tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) (Lowe et al. 2000; Naylor et al. 2000; Lun et al. 2005; Gozlan et al. 2010). Wild fish species can also have high prevalences and intensities of infection (Bui et al. 2016).
The mammalian final hosts are infected when they eat raw or partially cooked fish containing the metacercariae of C. sinensis. This fluke has an unusually broad final host spectrum that includes human associated species such as cats and dogs, stock animals such as pigs and the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus), all of which are effective reservoir hosts, as well as a wide variety of wild fish-eating carnivores and occasionally birds (Mas-Coma and Bargues 1997; Lun et al. 2005). Nevertheless, humans are considered to be the most important final host (Lun et al. 2005).
After being eaten, the metacercariae excyst in the host’s duodenum and then move through the hepatopancreatic ampulla into the biliary ducts and towards the liver. Here they attach to the mucosal lining and develop into hermaphrodite adults. These begin reproduction after about 3–4 weeks and may remain viable for years (Rim 2005). Attwood and Chou (1978) reported that parasites survive up to 26 years in an infected human. In the case of humans, infection occurs through the deliberate ingestion of raw, partially cooked or fermented fish containing the infective metacercariae as part of tradition a food culture (Grundy-Warr et al. 2012; Onsurathum et al. 2016a, b).
Although there are varying estimates of the number of humans infected with C. sinensis, it appears that this number is increasing (WHO 1995). This is particularly the case in China where prevalence was estimated to be 4.7 million in the early 1990s to almost 13 million today (WHO 1995; Fang et al. 2008). In the Republic of Korea, the picture is variable with estimates of 4.6% in 1971, 1.4% in 1997, and 2.4% in 2004 (Kim et al. 2009b). Unfortunately, little long-term records are available from Vietnam.
In addition to its direct influence on human health, Clonorchis infection in the second intermediate host can also reach substantial prevalences in aquaculture fish potentially limiting profitability in the aquaculture industry (Keiser and Utzinger 2005). Chen et al. (2010) found that freshwater fish in aquaculture had a 37.09% prevalence of infection with a mean number of 10.7 cercariae/fish, while 3.07% of shrimps from freshwater ponds carried on average a single metacercaria.
Molecular methods will probably extend our knowledge of the distribution of opisthorchid parasites. Traub et al. (2009) , using PCR-based technology, detected C. sinensis eggs in 23% (5/22) of human feces which tested positive by microscopy as well as PCR for “Opisthorchis” like eggs. The samples came from a rural community in Eastern Thailand (Chachoengsao Province) extending the known range of C. sinensis substantially to the south and east of its recognized distribution in an area where it is sympatric with O. viverrini. Whether C. sinensis overlaps elsewhere with O. viverrini or O. felineus is currently unknown. C. sinensis is known to infect a variety of mammalian hosts including domestic dogs, cats, and pigs (Rim 2005; Lai et al. 2016). Dogs and cats can have high prevalences of infection (0.8–48.5% in dogs, 0–64.1% in cats), which, however, varies, considerably between endemic areas in China (Hong and Fang 2012). The higher prevalence in cats, as for O. viverrini, is probably due to their preference for eating fish. Pigs, which are omnivorous, had a prevalence of infection of 27% in southern China (Lin et al. 2005).
Opisthorchis viverrini is known only from three currently recognized taxa within a single snail genus, Bithynia funiculata, B. siamensis gomiomphalos, and B. s. siamensis, from Southeast Asia (Petney et al. 2012). In Thailand, all three taxa of Bithynia are found, namely B. funiculata in the north, B. s. siamensis in the center, and B. s. goniomphalos in the northeast (Sithithaworn et al. 2007b). However, a recent study based on combined morphological and molecular identification methods found that in addition to B. funiculata, B. s. siamensis and B. s. goniomphalos were also distributed in the north of Thailand (Naruemon et al., unpublished). No regional separation of Bithynia snails has been reported in other parts of Southeast Asia, probably due to insufficient surveys (Kiatsopit et al. 2013).
The prevalence of O. viverrini infection in Bithynia snails is variable, with numerous collections being parasite free. If the parasite is present, cercarial release commonly occurs from about 0.1–2% of individuals, but some collections have infection rates of 6–9% (Table 6.1) (Kiatsopit et al. 2012; Petney et al. 2012). Snail population density is strongly seasonal, being highly abundant later in the rainy season, when reproduction occurs. At this time, the Bithynia are extensively distributed in shallow water and rice fields. They can be found at a depth of at least 3 m, albeit in a much lower density (Suwannatrai et al. 2011). During the dry season, the population density crashes and the snails which survive are often found buried in the mud for seasonal aestivation (Brockelman et al. 1986; Petney et al. 2012).
The snails are infected by ingesting the embryonated eggs of the parasite which are excreted with fecal matter. Indeed, human fecal bacterial contamination of freshwater bodies can act as an indicator for the seasonal transmission of O. viverrini eggs to snail intermediate hosts (Kaewkes et al. 2012b). Once ingested, the eggs hatch to a miracidium which in turn develops to a sporocyst (Kaewkes 2003). Peak hatching occurred at temperatures between 24 and 28 °C and could be induced with porcine leucine aminopeptidase (Khampoosa et al. 2018). By way of contrast, Prasopdee et al. (2015) found that a temperature of 34 °C gave the highest rate of infection of 44%, and that the likelihood of infection in small snails was significantly higher than for medium-sized snails. Once the sporocyst has developed within its snail host, it gives rise to numerous rediae that in turn produce numerous pleurolophocerous cercariae. The factors determining the time of cercarial release and the number released appear to vary dependent on season, location, and snail size although the pattern is not consistent (Namsanor et al. 2015; Laoprom et al. 2016). After released, they actively seek an appropriate fish second intermediate host, in the case of O. viverrini these belong to the family Cyprinidae (Sithithaworn et al. 2007b; Zhang et al. 2007; Mordvinov et al. 2012).
The process of host finding by cercariae is complex. Free swimming cercariae are very efficient at actively locating the appropriate species of fish in a large volume of water (Haas et al. 1990). The intensity of infection in fish varies by season, species, individuals, and types of water bodies. Most metacercariae are distributed throughout the body of fish with some being found in the head. For O. viverrini, metacercarial burdens peak in winter (October–February) and become low in the rainy season and summer; thus, transmission of the parasite from fish to humans is probably seasonal. Donthaisong et al. (2014) found over 80% of metacercariae in the body of the fish and that cercarial infection dosage, and age and size of fish were important determinants for a successful infection.
Many species of cyprinid fish have been reported as potential hosts for O. viverrini (WHO 1995; Petney et al. 2013, 2018). In Thailand, Lao PDR and Cambodia, at least 40 species of fish from 18 genera have been reported to serve as intermediate hosts of O. viverrini. Of these, the genera Cyclocheilichthys, Puntius, and Hampala are considered to be the most important (Pitaksakulrat et al. 2013). For O. viverrini, the prevalence of infection in the fish second intermediate host is very much higher than in the Bithynia snail first intermediate hosts (Table 6.2). This is, however, species of fish and locality dependent, and ranges from 2.1 to 100% (Waikagul 1998). For example, 30.4–97.1% prevalence was found in C. apogon (Touch et al. 2009), 43.1–100% in C. armatus (Rim et al. 2008; Manivong et al. 2009), 69.9–93.7% in P. leiacanthus (Vichasri et al. 1982), and 33.3–74.1% in H. dispar (Rim et al. 2008; Manivong et al. 2009). The average number of metacercariae infecting fish varies from one to thousands with the highest intensity (average 1989.8/fish) in C. armatus from Savannakhet, Lao PDR (Rim et al. 2008).
Humans are the dominant hosts for O. viverrini, while other domestic mammals, for instance dogs and cats, can act as reservoir hosts (Sithithaworn et al. 2007b; Aunpromma et al. 2012, 2016). A mathematical model of O. viverrini transmission by Bürli et al. (2018b) indicates that humans are necessary for the maintenance of the transmission cycle and can sustain this cycle without additional reservoir hosts. Domestic cats have been found to have a relatively high prevalence in the northeast of Thailand, making them potentially significant zoonotic sources of the disease during human-based control programs (Aunpromma et al. 2012). Dogs usually have a much lower prevalence (Aunpromma et al. 2012) although Prakobwong et al. (2017) found the reverse with dogs having 18% prevalence compared to cats with 11%. Hamsters, rabbits, and guinea pigs are experimentally highly susceptible to infection (WHO 1995). There is no current information for native mammals and other fish-eating animals which may also be infected.
For O. viverrini, when fecal contamination from humans is reduced or eliminated by mass treatment and/or improved sanitation the prevalence of infection can be substantially reduced (Saowakontha et al. 1993; Jongsuksuntigul and Imsomboon 2003). However, complete elimination of infection may not be possible if domestic cat and dog reservoir hosts maintain the source of parasite and hence play a critical role in maintaining the life cycle. Based on the pattern of age-intensity profiles, O. viverrini may survive for 10–20 years (Sithithaworn and Haswell-Elkins 2003).
In the case of C. sinensis or O. viverrini, which are both known to cause significant health problems (Sithithaworn et al. 2007b), considerable epidemiological information is available, e.g., prevalence and intensity of infection increase with age and males tend to have a higher prevalence of infection than females (Sithithaworn et al. 2007b). Thus, hepatobiliary morbidity is more frequent in older individuals and males than in younger people and females. In addition, as is usual with many parasite species, the distribution in the host population is neither random nor uniform, but overdispersed with a few individuals harboring most of the worms (Sithithaworn et al. 1991). Interestingly, some individuals appear to be predisposed to a heavy infection, with the intensity of infection returning to pretreatment levels after treatment (Upatham et al. 1988). Such epidemiological characteristics must be incorporated into the models on which control and eradication programs are based.
The infective metacercariae of all species discussed here are found only in their specific (mostly cyprinid) fish second intermediate hosts. These fish, when eaten raw, fermented or undercooked, act as the source of infection to humans and animal hosts (Grundy-Warr et al. 2012). Traditional dishes based on raw fish are the main sources of infection of C. sinensis throughout its range, for example, goi ca mai (raw fish salad) and slices of raw silver carp in Vietnam, yusheng, a raw fish salad in China and sushi, sliced raw fish, in Korea and Japan (Rim 2005). The length of time which the metacercariae remain viable depends on the method of preparing the food. In areas where less infected fish dishes are eaten, being replaced by beef or pork, infection prevalence and intensity can be reduced (Feldmeier et al. 2016).
In Southeast Asia, particularly in Thailand and Lao PDR, the raw or partially cooked fish dishes which act as the source of the liver fluke infection can be grouped into 3 categories. Fresh raw fish dishes without heating are called “koi pla.” These pose a high risk of infection. A moderate risk is presented by quickly fermented dish (1–2 days) known as “pla som.” The last dish is fermented fish known as “pla ra” which normally requires long-term fermentation but short-term and variable ingredients may provide favorable environments for metacercarial survival. Pla ra is a common ingredient for cooking in Southeast Asia, for example, in papaya salad (som tum) (Grundy-Warr et al. 2012). In Lao PDR, the fermented fish is known as “pla dak,” In other countries such as Cambodia raw fish are prepared as “pla hoc” which is similar to pla som and this may serve as a source of infection. The usual sources of O. felineus infection in Russia are dried or salted fish. Other dishes include sliced raw fish (stroganina), which is popular among native Siberians, and fish pickled in vinegar.
The number of Bithynia species present in the Eurasian area from a single species, Bithynia leachi, to four morphologically similar species, B. inflata, B. leachi, B. troscheli, and B. sibirica (Lazutkina et al. 2009) of which the first three of these can act as intermediate hosts for O. felineus (Mordvinov et al. 2012). As with O. viverrini, cyprinid fish also act as the exclusive second intermediate hosts for O. felineus (Erhardt et al. 1962). These include the ide (Leuciscus idus), roach (Rutilus rutilus), European dace (Leuciscus leuciscus), tench (Tinca tinca), verhovka (Leuciscus delineatus), and silver crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) (Mordvinov et al. 2012). After an outbreak of O. felineus infection in Italy, 83.1% of tench from Lake Bolsena were found to be infected (Armignacco et al. 2008). Apart from this outbreak, people are seldom infected in Europe probably because raw fish is not common in the human diet in this area (Pozio et al. 2013). However, prevalences can be very high in people in the Asian distributional area of this species where raw fish are more commonly consumed (Ogorodova et al. 2007).
In Europe, domestic cats and dogs can act as hosts (Erhardt et al. 1962; Hering-Hagenbeck and Schuster 1996) in addition to a wide range of wild carnivores. These include several fox species, the raccoon dog and wolves, as well as Martes and Mustela spp., badger, otter and wolverine (Erhardt et al. 1962; Shimalov and Shimalov 2003). Unlike C. sinensis and O. viverrini, O. felineus has also been reported from the Pinnipedia: the Caspian seal (Pusa caspica) from the brackish Caspian Sea, the bearded seal (Erignathus barbatus) from the Arctic and the gray seal (Halichoerus grypus) (Erhardt et al. 1962; Mordvinov et al. 2012). Non-carnivore and therefore presumably accidental hosts include chipmunks (Eutamias sibiricus) (Mordvinov et al. 2012), beaver (Castor fiber), European water vole (Arvicola terrestris), the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus), rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus), and wild and domestic pig (Sus scrofa) (Erhardt et al. 1962; Mordvinov et al. 2012).
4 Molecular Biology, Genetics, and Evolution
Advances in molecular biology have provided opportunities for increasing our understanding of the developmental and reproductive biology, as well as genetic diversity and evolution, of medically important trematodes including Opisthorchis and Clonorchis. They have also helped us to understand host–parasite interactions and the pathogenesis of the diseases caused by these flukes. This has aided in the improvement of diagnostic methods, new drug treatments, and potentially vaccine development. In addition, it is likely that new molecular data will help in the examining theories on the molecular basis of chronic clonorchiasis and opisthorchiasis-induced cholangiocarcinoma. Below we will also discuss the cytogenetics, genomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics of these species.
4.1 Cytogenetic Analysis
The cytogenetic study of the liver flukes focuses on the study of the structure and function of the chromosomes. It includes the analysis of G-banded chromosomes, other cytogenetic banding techniques, as well as molecular cytogenetics, such as fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) and comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). The karyotypes of C. sinensis are reported to be either of 2n = 14 (samples from the far east of Russia) (Zadesenets et al. 2012b) and 2n = 56 (samples from Korea and China) (Park et al. 2000a). The 2n = 56 karyotype was described according to the number and morphology of chromosomes, probably being the octaploid form of typical opisthorchiid karyotype with 2n = 14 (Zadesenets et al. 2012b). The karyotypes from Russia consisted of pairs of large meta- and submetacentric chromosomes and five pairs of small chromosomes (Zadesenets et al. 2012b). Those from Korea and China can be divided into two groups based on their sizes, with 8 pairs of large and 20 pairs of small chromosomes. They have the same number of 16 submetacentric and 8 subtelomeric pairs, but the Korean isolates have 3 metacentric and 1 meta-/submetacentric pairs, whereas the Chinese isolates have 2 and 2 pairs. In addition, the mean total length of the diploid complements of the specimens collected in China is slightly longer than that of those collected in the Korea (Park et al. 2000a). The question of the phylogenetic relationship between C. sinensis from Russia, China, and Korea therefore remains open. The liver fluke described in China and Korea could be an octaploid form of normal C. sinensis or possibly distinct species (Zadesenets et al. 2012b).
The karyotype of O. felineus collected from West Siberia was 2n = 14 and consisted of two pairs of large submetacentrics and five pairs of small chromosomes. There are 3 pairs of metacentric and 4 pairs of submetacentric chromosomes (Polyakov et al. 2010). A comparison of the relative length and centromere indices of the chromosomes of these O. felineus did not reveal significant differences (Polyakov et al. 2010).
In contrast, the karyotype of O. viverrini is 2n = 12 and includes two pairs of large submetacentrics, one pair of medium-sized submetacentrics, one pair of small-sized subtelocentrics or acrocentrics and one pair of small-sized acrocentric chromosomes (Komalamisra 1999). The medium-sized submetacentric chromosome of O. viverrini is probably the result of the fusion of two chromosomes from ancestral karyotypes (Zadesenets et al. 2012b). However, the comparative analysis of mitotic and meiotic chromosomes by heterologous FISH revealed six pairs of chromosomes in the karyotype of O. viverrini, indicating a relatively recent chromosomal fusion event which took place in the formation of the modern karyotype (Zadesenets et al. 2012b). However, none of the O. viverrini chromosomes have shown any interstitial telomere sequences (ITSs) after FISH by telomeric DNA probe or PNA telomere probe (Zadesenets et al. 2012a). More recently, the chromosome number, length, and nomenclature of each chromosome were determined by scanning electron microscopy. The six chromosomes consist of one large metacentric, one medium-sized metacentric, two small-sized metacentric, one small-sized submetacentric, and one small-sized acrocentric chromosomes (Kaewkong et al. 2012a). Moreover, the repetitive sequences show that despite the small size of opisthorchis genomes, a large amount of interspersed repetitive DNA sequence is distributed along the euchromatic regions (Zadesenets et al. 2012c).
4.2 Genome
There are some reports on the genomic features characterizing C. sinensis, but very few on O. viverrini and O. felineus. The assembled genome of C. sinensis has a total size of 516 Mb with approximately 16,000 reliable protein-coding gene models. Genes for the complete pathways for glycolysis, the Krebs cycle and fatty acid metabolism were found, but key genes involved in fatty acid biosynthesis are missing from the genome, reflecting the fact that the liver fluke receives lipids from the bile of its host. Moreover, genes encoding proteases, kinases, and phosphatase enzymes, tegument and excretory-secretory products, host-binding proteins and receptors were also discovered. In addition, 53 genes related to sex determination, sex differentiation, and sexual reproduction were identified (Wang et al. 2011). The genome of C. sinensis contained more than 100 copies of a long terminal-repeat retrotransposon (CsRn1) which belongs to the Ty3/gypsy-like long terminal-repeat transposon family. The functional domains of Gag, proteinase, reverse transcriptase, Rnase H, and subdomains of integrase are strongly conserved in CsRn1, which has been predicted to be mobile element based on structural considerations and from the presence of mRNA transcripts (Bae et al. 2001). Insertions of CsRn1 appear preferentially at repetitive and agenic chromosomal regions. Furthermore, CsRn1 was reported to induce variations in the genome that may influence the evolution of C. sinensis (Bae and Kong 2003). The finding of such genomic characters of C. sinensis reveal the evolutionary interplay between parasite and host, which may be valuable for understanding host and parasite interactions (Wang et al. 2011). In the case of O. viverrini, the estimated genomes size reported by real-time PCR was 75.95 Mb (Kaewkong et al. 2012b). However, whole genome sequencing of these liver flukes has not been reported.
The complete mitochondrial genomes of all three liver flukes have been successfully characterized. The mtDNA sequences of O. viverrini, O. felineus, and C. sinensis were variable and ranged between 13,510 and 14,277 bp and comprised 36 genes (Shekhovtsov et al. 2010; Cai et al. 2012). Of these, 12 genes encoded for proteins, i.e., cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 (CO1), CO2, CO3, NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 (ND1), ND2, ND3, ND4, ND4L, ND5, ND6, cytochrome b and ATPase subunit 6. Two genes encoded for ribosomal RNA, i.e., small subunit rRNA (rrnS) and large subunit rRNA (rrnL). The number of tRNA encoding genes varied between the different species, i.e., 20 genes for O. viverrini and 22 genes for O. felineus and C. sinensis (Shekhovtsov et al. 2010; Cai et al. 2012). The gene content and arrangement were almost identical between species. There were two non-coding regions, the long non-coding region (LNR) and the short non-coding region (SNR). For the C. sinensis, there is a lack of tandem repeat (Cai et al. 2012), whereas there was tandem repeat, interrupted in LNR region, in O. felineus. Moreover, when comparing the length of non-coding region of the mtDNA of C. sinensis from Russia and Vietnam there were significant differences between species (Shekhovtsov et al. 2010).
4.3 Transcriptome
Expressed sequence tags (ESTs) for adult C. sinensis and O. viverrini have been reported with at least 3000 and 4194 ESTs, respectively, and have been registered in public dbEST databases (Mulvenna et al. 2010; Huang et al. 2012). The most abundant genes in adult C. sinensis include cysteine proteases and mitochondrial genes, which may support biliary epithelia destruction by adult liver flukes to evade host immune attack (Kang et al. 2004; Nagano et al. 2004). The second most abundant gene transcripts were proteins constituting muscular tissues, which enable adult flukes to abrade and feed on the biliary epithelium (Kwon et al. 2005). Vitelline precursor protein was the third most abundantly expressed gene product. It is responsible for hardening the eggshell encasing the germ cell and surrounding yolk cells (Tang et al. 2005).
The ESTs of the metacercarial stage of C. sinensis could be assembled into 322 genes. Those expressed most abundantly were for proteases and metabolic, transcription and translation housekeeping proteins (Huang et al. 2012). To obtain an insight in the developmental gene expression and regulation of C. sinensis, the adult and metacercariae ESTs of C. sinensis were compared. It was found that genes encoding structural and cytoskeletal proteins, transcription and translation machinery proteins, and energy metabolism-related proteins were highly expressed in C. sinensis metacercariae, while the other genes were highly expressed in the adult stage. These data may explain, to some extent at least, that C. sinensis metacercariae in fish hosts have a quite different physiology and metabolism compared with adult C. sinensis in mammals (Huang et al. 2012).
The most abundant genes in adult O. viverrini encoded for myoglobin, vitelline precursors, egg shell proteins and glutathione S-transferase. The other abundantly expressed genes encoded proteins involved in host-parasite relationships and included proteases, saposin-like proteins and dynein light chains (Laha et al. 2007). Homologues of some of the most abundantly represented proteins in C. sinensis and O. viverrini ESTs are cysteine protease, myoglobin and vitelline B precursors, whereas others were over-expressed in each species (Laha et al. 2007). The open reading frame (ORF) region in ESTs was also used to predict the expressed proteins in proteomic analysis. Such ORFs were generated from 4194 available EST sequences of O. viverrini and subsequently analyzed for secretory signal sequence and the transmembrane domain. A total of 897 potential ORFs were identified, of which 78 were predicted to contain a secretory signal sequence and 42 to contained two or more transmembrane domains (Mulvenna et al. 2010). Proteases were highly presented in the O. viverrini transcripts encoding secreted proteins , with five different cathepsins, a legumain and an S1 type serine protease all predicted to contain a signal sequence (Mulvenna et al. 2010). In addition, more than 50% of the predicted protein sequences of C. sinensis and O. viverrini were inferred to be homologues, reflecting their relatively close biological and physiological relationships (Young et al. 2010). Comparison of the predicted proteins of liver flukes and other trematodes, S. japonicum, S. mansoni, F. hepatica found that 29–31% protein sequences were homologous (Young et al. 2010). However, this prediction of expressed proteins may not be satisfactory as some ORF encoded sequences might not express or express a low protein level. Thus, additional proteomic analysis is needed to provide more informative data on the proteins expressed in these liver flukes.
4.4 Proteome
Proteomic analyses should provide information on potential new and specific targets for treatment the infection. Moreover, the identification of parasitic-specific proteins could clearly facilitate the design of new tools for rapid and cheap diagnosis, which in turn could help breaking the transmission cycle of the parasite, as well as help in the identification of potential targets for vaccination, one of the best ways to control these parasite infections (Toledo et al. 2011).
The adult stage of all three flukes dwells in the bile duct which provides an anaerobic environment where a large amount of exogenous glucose is used as a carbon source for energy metabolism. Thus, the most important endogenous proteins examined in the liver flukes are glycolytic enzymes which play an important role in the glycolysis pathway. Phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK), a glycolytic enzyme, was found extensively, localized in the muscular tissues of the oral and ventral suckers, ovary, testes, tegument and intrauterine eggs of C. sinensis (Hong et al. 2000, 2003a). The inhibitors of several glycolytic enzymes of C. sinensis have also been reported, e.g., vanadate can inhibit phosphoglycerate mutase (PGM) (Song et al. 2007), whereas lactase dehydrogenase (LDH) was inhibited by Cu+2, Fe+2 and Zn+2 (Yang et al. 2006). The cytosolic and mitochondrial malate dehydrogenases (cMDH and mMDH) of C. sinensis share low amino acid sequence homology (22%) and these enzymes are differentially inhibited by 4.4’-bisdimethylamino diphenylcarbol. cMDH is more stable against heat and acidity than mMDH. Moreover, cMDH plays a pivotal role on the cytosolic side of the malate-aspartate shuttle. mMDH is a key enzyme in the tricarboxylic acid cycle and in the malate-aspartate shuttle. Thus these glycolytic enzymes are required for the survival and pathogenesis of these liver flukes (Zheng et al. 2005, 2006, 2008).
The mechanism of pathogenesis due to liver fluke infection mainly involves the interaction between parasite antigens and the host immune response (Sripa et al. 2007). Therefore, the excretory-secretory (ES) proteins and tegumental proteins of the liver fluke play crucial roles in host-parasite interactions, pathogenesis and disease outcomes. Myoglobin is an abundant protein in the ES products of C. sinensis. It may play an oxygen-capturing role and then slowly release this oxygen to metabolic pathways in bile duct. Recombinant myoglobin reacted with the sera of C. sinensis-infected rabbits and clonorchiasis patients. Lysophosphatidic acid phosphatase (LPAP), belonging to the acid phosphatase family, has been identified as an ES-antigen in adult C. sinensis. It shows high sensitivity and specificity in the serodiagnosis of human clonorchiasis (Kim et al. 2009a). The proteomic analyses by the 2-D proteome mapping of C. sinensis ES products identified 62 protein spots including thioredoxin peroxidase, myoglobin and a number cysteine proteases that were expressed abundantly (Ju et al. 2009). More recently, Zheng et al. (2011) reported a proteome analysis of ES products of C. sinensis using LC-MS/MS analysis and found 110 proteins including 39 known functional proteins and 71 unknown proteins. The enzyme fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (Cs-FPBase) within the ES product was a potential causative agent of hepatic fibrosis (Zheng et al. 2011).
A comparative proteomic analysis of the developmental stages from juvenile to adults of O. viverrini was made by 2-D gel electrophoresis (Boonmee et al. 2003). The total number of protein spots varied between 210 and 239 according to the age of the worm (1–4 weeks). Only small differences in the pattern of protein spots were found during parasite maturation (Boonmee et al. 2003). The secreted and surface-exposed proteomes of O. viverrini has also been reported (Mulvenna et al. 2010). The secretory proteins were analyzed using peptide OFFGEL electrophoresis (OGE) and (multiple reaction monitoring) MRM. A total of 25 proteins, 13 from MS/MS analysis of OGE and 12 from MRM identifications, were positively identified as constituents of Day 1 ES (in vitro culture of worms), whereas the remaining 18 proteins identified in Day 17 ES are a likely consequence of the culturing process (Mulvenna et al. 2010). Proteases were abundant, but proteolytic enzymes were under-represented in the ES of O. viverrini. However, the prediction of the secretory proteins from a signal sequence or based on a transmembrane domain in the ESTs found 26 known proteins and 39 unknown proteins to be secretory proteins. Of these, only five, i.e., cathepsin F-like cysteine protease, cathepsin D, venom allergen-like protein 8, cystatin and granulin were detected by proteomic identification (Mulvenna et al. 2010). Granulin, which is a homologue of human granulin, is a potent growth factor involved in cell proliferation and wound healing. A granulin of O. viverrini (Ov-GRN-1) was examined and found to be expressed in most parasite tissue, particularly the gut and tegument. Ov-GRN-1 is probably the major growth factor protein in the ES products secreted by O. viverrini that can induce the proliferation of host cells which may ultimately manifest in cholangiocarcinoma (Smout et al. 2009). The O. viverrini proteome and host-parasite interaction has been recently reviewed (Suttiprapa et al. 2018).
The tegumental syncytium, which is the outermost surface of liver flukes, is considered to be very important for host response and parasite survival. Thus, it is generally seen as the most susceptible target for vaccines and drugs. Several tegumental proteins of the liver flukes have been characterized and identified. The tegumental protein of C. sinensis, CsTP31.8, has been proven to be an antigenic protein (Huang et al. 2007). CsTP20.8 is expressed in adult worms and metacercariae but not at the egg stage. However, CsTP20.8 protein is considered to have limited value for the serodiagnosis of clonorchiasis because it shows only moderate sensitivity and although it has high specificity (Zhou et al. 2007). Another tegumental protein CsTP21.1 was identified from adult C. sinensis by bioinformatics analysis. It is localized in the tegument of adult worms (Chen et al. 2011). Interestingly, CsTP21.1 is considered a trematode-nematode pan-specific antigen that could be useful for the development of a universal immunodiagnostic kit for human infection with trematodes and nematodes (Chen et al. 2011).
Membrane-spanning proteins of O. viverrini are predicted to include 28 known proteins belonging to the transporters/channels, protease/hydrolytic enzymes, structural/membrane organization proteins and other miscellaneous proteins, as well 8 unknown proteins based on transmembrane domains. However, proteomic identification found only four membrane proteins, i.e., ATP-ADP antiporter, Sm-TSP-2, succinate dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase complex, subunit C expressed in O. viverrini (Mulvenna et al. 2010).
4.5 Vaccine Development
It is clear that a vaccine against any of the major human pathogens within the Opisthorchiidae would greatly aid control measures although progress in research in this direction, which has been under way for some time has been limited (Sripa et al. 2012). The goal for the development of a vaccine against O. viverrini and/or C. sinensis is not only to limit the pathologic sequels due to acute and chronic infections, but, as is the case with other carcinogenic pathogens such as human papilloma virus, it could also protect against cancer (Frazer et al. 2011). Genomic studies on both O. viverrini and C. sinensis may well facilitate the development of vaccines with time. As indicated above, the tegument is generally viewed as the most susceptible target for vaccines and drugs in liver flukes because it is a dynamic host-interactive layer with roles in nutrition, immune evasion and modulation, pathogenesis, excretion and signal transduction (Jones et al. 2004; Van Hellemond et al. 2006). Large proteins such as multifunctional secreted proteases and tegumental proteins have been identified as potential targets for the development of drugs and vaccines (Wang et al. 2011).
DNA vaccines against C. sinensis were produced by encoding cysteine proteinase and a fatty acid-binding protein and tested in a rat model. They showed 31.5% and 40.9% protection efficacy, respectively (Kim et al. 2006). In addition, an oral vaccine using C. sinensis tegumental protein 22.3 kDa fused with the Bacillus subtilis spore coat CotC showed 44.7% protection in the rat model (Zhou et al. 2008). An O. viverrini-crude somatic antigen (CSAg) administered with complete Freund’s adjuvant or alum was used to stimulate immune responses in O. viverrini-primed hamsters. The greatest protection was 48.4% and elevated TGF-β induced by O. viverrini may play an important role in parasite survival (Jittimanee et al. 2012). The reported protection rate of the vaccine candidate molecules against these liver flukes is not satisfactory and more studies are required.
4.6 Phylogenetics, Systematics, and Genetic Diversity
A variety of molecular markers/techniques has been used to examine the genetic diversity of Clonorchis and Opisthorchis species at the inter- and intra-species levels. Although there are considerable similarities between C. sinensis, O. viverrini, and O. felineus, there is also a great deal of regional variation both within and between species. Adaptation to differences in the environment and host selection process, as well as limited gene flow between different water sheds can all play a considerable role in determining the genetic constitution of each isolated species and population (Sithithaworn et al. 2012b). Although all three species are closely related, their systematic position remains controversial (Petney et al. 2018). Some reports indicate that O. viverrini is more closely related to C. sinensis than O. felineus when examined using 12 mitochondrial protein-coding genes (Shekhovtsov et al. 2009) and the ninth intron region of the paramyosin gene (Cai et al. 2012). By contrast, it has also been suggested that C. sinensis is more closely related to O. felineus than to O. viverrini based on ITS2 and mitochondrial DNA (Katokhin et al. 2008; Saijuntha et al. 2009; Liu et al. 2012), or even that C. sinensis and O. viverrini are more closely related to one another than to O. felineus when examined by ITS and CO1 sequences (Kang et al. 2008). Thus the situation is far from clear and more powerful genetic markers together with greater sample sizes and more geographical isolates need to be studied for a comprehensive phylogenetic analysis among these liver flukes.
Considerable genetic diversity has been observed in C. sinensis, based on its geographic distribution within China, Korea and the Russian Federation, as well as among different reservoir hosts including people. More details of genetic variation exploring of this fluke has been recently reviewed (Wang et al. 2018). Isoenzyme markers can be used to differentiate C. sinensis into the two populations from two different geographical isolates from Korea and China (Park et al. 2000b; Park and Yong 2001). However, the DNA regions of ribosomal DNA and mitochondrial DNA sequences were strongly conserved and nearly identical between different isolates (Park and Yong 2001; Lee and Huh 2004; Park 2007). In another study based on ITS1 sequencing, two levels of intra-specific variation, i.e., inter- and intra-individual, were observed and these showed a “northern” and a “southern” genetic group of C. sinensis according to their distribution in China, Korea and the Russian Federation (Tatonova et al. 2012). Moreover, the eggs of C. sinensis collected from a well preserved Chinese body which had been buried in 167 BC revealed differences in the ITS1 sequence at 15 nucleotide positions compared to the present samples, suggesting sequence divergence through time (Liu et al. 2007). More recently the genetic variation and phylogeography of C. sinensis was studied from two geographical localities in southern far east Russian and compared to the other geographic localities from China, Korea, Japan and Vietnam by CO1 sequence. A total of 18 haplotypes were observed. Of these 4 were common to Russian and Chinese isolates, and the other two were common to Russian and the other isolates. The Russian isolates differed from those of the other localities in haplotype frequencies (Tatonova et al. 2013).
The role which animal reservoir hosts play in genetic variation of C. sinensis is currently being investigated. Both RAPD and MGE-PCR was used to examine the genetic variation among individual adult C. sinensis collected from cats and dogs in two geographical areas, Guangdong province in the South and Heilongjiang province in the North of China (Lai et al. 2008; Liu et al. 2012). Both revealed genetic polymorphisms among C. sinensis individuals from these hosts in each location. In a recent study from different geographical localities in Korea, as well as in China, using mitochondrial genes sequences, the genetic variation present in C. sinensis from naturally infected cats, dogs, rabbits and humans was examined. Intra-specific nucleotide variation of the Korean population ranged between 0 and 1.6% (Liu et al. 2012), whereas 0–1.7% was found in the Chinese population (Xiao et al. 2013). Recently the microsatellite marker of C. sinensis has been characterized and found that 24 of 40 loci showed potential to differentiate between C. sinensis and O. viverrini. Of these, seven loci revealed heterozygous, which could be further used for study population genetic of C. sinensis (Nguyen et al. 2015).
Genetic diversity of O. viverrini has been intensively investigated based on a variety factors, e.g., spatial, temporal and host factors. Unlike C. sinensis, there is no report of genetic variation between specimens collected from different reservoir hosts. An initial report was published on different geographical isolates by Ando et al. (2001) using rDNA and mitochondrial DNA sequences but with a restricted sample size. The next study involved the establishment of 32 enzyme (allozymes) loci using multilocus enzyme electrophoresis (MEE) to comprehensively examine the genetic variation among natural populations of O. viverrini from 11 different geographical localities in Thailand and four localities in Lao PDR (Saijuntha et al. 2006a, b, 2007). Two major evolutionary lineages of O. viverrini were found, which could be additionally subdivided into at least six distinct genetic groups which correlated with five different wetland systems (Saijuntha et al. 2007). RAPD and microsatellite analyses in O. viverrini also showed significant differences between the isolates from Thailand and Lao PDR (Sithithaworn et al. 2007a). These comprehensive molecular systematics studies (Ando et al. 2001; Saijuntha et al. 2006a, b, 2007; Sithithaworn et al. 2007a) have transformed our perception of the systematic and taxonomic status of O. viverrini that O. viverrini is not a single species but that it is indeed a species complex “O. viverrini sensu lato (sl)” that contains two evolutionary lineages with many cryptic species (morphologically similar but genetically distinct species) occurring in distinct wetland systems in Thailand and Lao PDR. Interestingly, the MEE data provided evidence of potential co-evolution between O. viverrini and its snail host, B. s. goniomphalos, as there was a high concordance of lineages and specific genetic groups (Saijuntha et al. 2007; Kiatsopit et al. 2013). An additional O. viverrini genetic isolate from Savannakhet, Lao PDR was analyzed using 20 allozyme markers and also found to be associated with a specific wetland system (Kiatsopit et al. 2011).
Microsatellite markers and MEE have been used to explore the population genetics and systematics of O. viverrini from different geographical isolates (Saijuntha et al. 2007; Laoprom et al. 2010, 2012). In addition, O. viverrini populations collected from different years (temporal), as well as from different fish host species, was carried out by MEE (Saijuntha et al. 2007, 2009). The level of genetic differentiation between the populations from Thailand and Lao PDR was very high, whereas it was low for comparisons among populations from Thailand. The same pattern was found among different fish host species and temporal populations (Saijuntha et al. 2007, 2009). Based on the MEE and microsatellite analyses, O. viverrini populations almost always deviated from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium with varying levels of heterozygote deficiencies (Saijuntha et al. 2007, 2008). In addition, microsatellite markers could be used to examine the genetic differences among O. viverrini populations over small-scale geographical distances within Khon Kaen Province, Thailand (Laoprom et al. 2012). MEE was also used to explore the genetic structure of O. viverrini populations at Vientiane Province, Lao PDR (Kiatsopit et al. 2014). The analyses based on microsatellites, together with allozyme data, revealed that the predominant mode of reproduction in O. viverrini is selfing (inbreeding) rather than cross-fertilization (outbreeding). The demonstration of significant genetic heterogeneity, as well as biological variation between the different geographical isolates of O. viverrini from Thailand and Lao PDR, provide independent evidence that O. viverrini is a species complex (Saijuntha et al. 2007; Laoprom et al. 2009). The O. viverrini-like egg recovered from the resident of from Sanamchaikate District, Chachoengsao Province, Thailand, has been genetically characterized using mitochondrial CO1 and ND1 sequences, which was more closely related to the isolates from Lao PDR (Buathong et al. 2017). Recently, a new cryptic group of O. viverrini was discovered in Songkhram River Basin, Sakon Nakhon Province, Thailand, by using six independent nuclear and mitochondrial DNA markers (Pitaksakulrat et al. 2018). The polymorphic intron region of taurocyamine kinase has been characterized to explore genetic variation of O. viverrini and the results correspond to Pitaksakulrat et al. (2018) that a new cryptic group from Sakon Nakhon province was genetically distinct from the other O. viverrini (Saijuntha et al., unpublished).
Genetic variation within O. felineus from different geographical localities was investigated using three different polymorphic genetic markers, i.e., CO1, CO3 and ITS1 sequences (Brusentsov et al. 2013). All O. felineus populations were classified into three geographically isolated groups, namely from eastern Europe (the drainage basins of the Volga, the Don and the Ural rivers), northern Asia (Siberia, the Ob-Irtysh and the Yenisei river basins) and Central Asia (Kazakh, the Nura-Sarysu Basin, part of the endorheic Aral-Caspian basin). Only low genetic differentiation between these geographically distinct European and Asian O. felineus population was observed. This homogenization of population structure could result from potentially high levels of gene flow between populations, accompanied by active migrations of definitive hosts, including humans, during the Holocene (Brusentsov et al. 2013). More recently, ISSR and allozyme analyses were used to examine genetic variation of O. felineus from six rivers of Western Siberia. In addition, ISSR was also used to explore the genetic variability of metacercariae of O. felineus collected from different fish host species (Zhigileva et al. 2013). Again, only a low degree of genetic polymorphism and differentiation among O. felineus population was observed. Southern O. felineus samples from the Tobol and Tura rivers showed higher polymorphism levels than the samples from rivers in northern part (Zhigileva et al. 2013). However, the metacercariae of O. felineus collected from different fish species showed no genetic differences (Zhigileva et al. 2013). The results so far suggest that population genetic data based on other genetic markers such as microsatellite DNA are required.
5 Diagnosis
The most common diagnostic method for fish-borne zoonotic trematodes (FZT), which involves finding eggs in fecal samples, seems still to be far from ideal. In low egg output and a low prevalence situation, sensitivity is also low using this method is a puzzle that challenges scientific efforts. Recent advances in the diagnosis and detection of O. viverrini infection in human and their intermediate hosts has been reviewed (Saijuntha et al. 2018).
5.1 Parasitological Methods
Fecal examination is the routine method used for the diagnosis of liver fluke infection. It has the advantages of the simplicity of sample collection and of being non-invasive. Once a fecal sample is available, the modified formalin-ether (or ethyl acetate) concentration technique (FECT) (Elkins et al. 1990), the modified thick Kato smear (Hong et al. 2003b), or Stoll’s dilution egg count technique can be used (Viyanant et al. 1983). Although these techniques are highly specific there are limitations because of the prepatent period of infection before eggs are produced, poor sensitivity when infection intensities are low, or intermittent egg excretion associated with bile duct obstruction. Both sensitivity and specificity vary depending on the method used but also on the experience of the examiner. The diagnostic value of these methods lies in their ability to detect relatively light infections, which occur in the majority of infected individuals, and in individuals recently treated with praziquantel. As a single examination does not necessarily provide diagnostic certainty, repeated examinations are needed to improve diagnostic sensitivity. Thus, three consecutive Kato-Katz thick smears are more sensitive than a single examination by FECT (Lovis et al. 2009). However, even using such repeated stool examination there can be a discrepancy between egg count and worm detection so that a false negative diagnosis remains a real possibility.
In an autopsy study, adult O. viverrini were recovered directly from 139 livers. Examination of postmortem fecal samples from these individuals showed that only 67% were positive for O. viverrini infection. The detection limit using normal fecal examination was estimated to be 20 worms or approximately 1000 EPG. Individuals with low infection intensities and limited egg output are likely to be underdiagnosed by as much as ∼20% (Sithithaworn et al. 1991). Although there is some evidence of density-dependent fecundity, there is in general a linear relationship between fecal egg count and worm burden.
The commercial stool concentrator kits which are designed to reduce processing time such as Parasep SF were available, however, these show a lower sensitivity than FECT although they have a higher sensitivity than the simple smear method (Sithithaworn, unpublished). Based on this preliminary study, the performance of this kit is comparable with that of the widely used Kato-Katz method.
Eggs can also be detected during treatment of bile duct obstruction either in bile from nasobiliary or percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage (PTBD) or in the duodenal fluid. Adult worms are ejected during expulsion chemotherapy (Ramsay et al. 1989; Elkins et al. 1991; Radomyos et al. 1994; Joo and Bang 2005). Similar data to those available for O. viverrini are now also available for C. sinensis. These indicate that this species lays more eggs than O. viverrini (514 EPG/worm), probably due larger size of adult worms (Kim et al. 2011). Worm burdens determined by expulsion chemotherapy ranged from 1 to about 100 worms for C. sinensis (Shen et al. 2007; Kim et al. 2011).
In some endemic areas for liver flukes, for example in Southeast Asia, intestinal flukes coexist leading to a potential diagnostic problem if conventional fecal examination is used. The eggs of O. viverrini, which are identified by their characteristic rough and thick egg shells are very similar to the eggs of several species of other food-borne trematodes belonging to the families Opisthorchiidae, Heterophyidae, and Lecithodendriidae. The latter two families are commonly referred to as minute intestinal flukes (MIF) due to their small size compared to the liver flukes (Kaewkes 2003; Chai et al. 2005; De and Le 2011). These species are, like the liver flukes, fish-borne trematodes (FBT) or fish-borne zoonotic trematode (FZT) (Lan-Anh et al. 2009; Phan et al. 2010a, b). The similarity between the eggs of these other FBT species and those of O. viverrini and C. sinensis can substantially increase the likelihood of a false positive diagnosis, depending on the prevalence of these species. They thus reduce diagnostic specificity and the identification of adult worms and PCR confirmation may be necessary for correct species identification in areas where a number of species exist.
5.2 Immunological Methods
Several serological tests for clonorchiasis and opisthorchiasis have been developed for use in a diagnostic assay with greater sensitivity and specificity than fecal examination. These include the intradermal test (IDT), immunoelectrophoresis (IEP), indirect hemagglutination assay (IHA), indirect fluorescent antibody test (IFAT), and indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (indirect ELISA) (Wongratanacheewin et al. 2003; Kim et al. 2010; Hong and Fang 2012). Indirect ELISA is commonly preferred for the detection of antibodies although, due to the complexity of the antigen, neither sensitivity nor specificity is constant. Crude somatic extracts of adult worms of both O. viverrini and C. senensis used for ELISA provide higher sensitivities than fecal examination (Poopyruchpong et al. 1990; Wongsaroj et al. 2001; Hong and Fang 2012), while ES antigens show a superior or equivalent performance to the crude antigen (Sirisinha et al. 1990; Choi et al. 2003). Interestingly, antigen extracted from the Bithynia intermediate host snails has also been used as an antibody detecting antigen for the diagnosis of human Opisthorchis infection (Waikagul et al. 2002; Watthanakulpanich et al. 2003) although the value of such tests has yet to be evaluated.
Recombinant antigen for serum antibody detection by ELISA has been produced from eggs and egg shells (Wongsaroj et al. 2001; Ruangsittichai et al. 2006). In addition, the propeptide of cathepsin L, glutathione S-transferases, adenylate kinase 3, phosphoglycerate kinases, phosphoglycerate mutase, lysophosphatidic acid phosphatase and cathepsin B, cathepsin F, cathepsin L-like, legumain, taurocyamine kinase have been characterized and show better diagnostic sensitivity and specificity over conventional fecal examination diagnostic methods (Hong et al. 2000, 2002; Ruangsittichai et al. 2006; Hu et al. 2007; Chen et al. 2011; Li et al. 2011, 2012). Nevertheless, the increased specificity and reduced cross reactivity of these proteins need to be tested under field conditions before they can be judged good enough to replace the commonly used native crude antigen (Hong and Fang 2012). The detection by ELISA of antibodies in non-fecal clinical samples such as urine and saliva, has been considered and saliva found to be of potential use for the serodiagnosis of opisthorchiasis (Sawangsoda et al. 2012).
In the case of clonorchiasis in China, a combination of serological and parasitological techniques could improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce the false negative diagnosis rate. ELISA used as an auxiliary diagnostic method was suggested for a large-scale screening test in monitoring the prevalence and assessing the risk factors of clonorchiasis (Han et al. 2012). A major drawback of antibody-based detection is the inability of this method to differentiate between past and present infections because of the persistence of antibodies in the patient even after a cure has been effected (Hong 1988; Ruangkunaporn et al. 1994; Johansen et al. 2010). One way of overcoming this problem is to use an antigen-based detection which indicates if current infection is present (Sirisinha et al. 1991, 1995; Chaicumpa et al. 1992). Monoclonal antibody (mAb)-based systems offer increased diagnostic sensitivity, as they are able to detect secretory products from only a few adult worms. This is effective in low-scale infections when eggs are not detectable in fecal samples (Sirisinha et al. 1995). This has been corroborated in an autopsy study (Sithithaworn et al. 1991). Studies in animal models for C. sinensis (Mazidur Rahman et al. 2012) and O. viverrini (Duanngai, unpublished) showed promising results. Recently it was suggested that copro-antigen detection is useful for detecting positive cases, again especially when fecal examination negative although the antigen level is also correlated with the intensity of infection (Watwiengkam et al. 2013).
In 2015, Worasith et al. (2015) reported a novel antigen detection method using urine samples for the diagnosis of opisthorchiasis. Recently, a comparison of urine and copro-antigen detection yielded similarly high diagnostic performances compared with standard fecal examination (Worasith, unpublished). Because of the ease and acceptance of urine specimen collection and handling, urine antigen detection has a high potential for the diagnosis and mass screening of opisthorchiasis in control and elimination programs. In particular, the antigen detection is useful approach for the detection of mild infections and for the evaluation of the effectiveness of pharmaceutical cure.
5.3 Molecular Biological Methods
A number of target genes from both C. sinensis and O. viverrini have been tested for their diagnostic suitability including satellite DNA, ITS1, ITS2 and mitochondrial DNA. These were used for both conventional PCR and real-time PCR diagnosis showing high specificity but variable sensitivity (Wongratanacheewin et al. 2003; Hong and Fang 2012; Qiao et al. 2012). The detection of O. viverrini egg DNA in human stools using PCR and based on primers complementary to the repeat DNA element showed a specificity of 98% and a sensitivity of 100% for moderate to heavy infections with more than 1000 EPG. In light infections with less than 200 EPG the sensitivity was reduced to only 68% (Wongratanacheewin et al. 2001, 2002). More recently, the retrotransposon of O. viverrini (OV-RTE-1) has been found to be the new alternative genetic marker of high sensitivity and specificity for the PCR diagnosis of opisthorchiasis (Phung et al. 2014). Another PCR-based study using the same target DNA showed low sensitivity (50%) at high egg counts of more than 1000 EPG in stool samples from Lao PDR (Stensvold et al. 2006). However, if the quality of the DNA was improved by using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) during its preparation to remove PCR inhibitors the sensitivity was increased to 79% (Duenngai et al. 2008). PCR-positive tests occurred in a 29% of cases which were parasite negative in this study using the conventional fecal examination method indicating its potential diagnostic value for light infections. Another O. viverrini-specific primer pair was established which was able to detect adult worms with 1–12 ng of DNA, and metacercariae when 3 or more occurred in a fish sample (Parvathi et al. 2008). Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) has been established for the detection of both O. viverrini and C. sinensis with a higher sensitivity than conventional PCR (Cai et al. 2010; Arimatsu et al. 2012; Le et al. 2012).
Species-specific PCRs are now also available to distinguish between the three species of liver fluke: O. viverrini (Ando et al. 2001; Wongrata-nacheewin et al. 2001), O. felineus (Pauly et al. 2003), C. sinensis (Le et al. 2006). In addition, several genetic markers/approaches involving conventional PCR, PCR-RFLP, multiplex PCR, real-time PCR and multiplex ligation-depended probe amplification (MLPA) pyrosequencing can be used to differentiate between species involved (Le et al. 2006; Sato et al. 2009; Sun et al. 2011; Sanpool et al. 2012).
The molecular methods discussed above will contribute significantly towards a more effective and accurate diagnosis of trematode infections although further simplification of the tests and an understanding of cost effectiveness under various socioeconomic scenarios is needed. In addition, the validation of DNA positive test results is required although evidence from animal models is accumulating and supported human studies. (Rahman et al. 2011; Duenngai et al. 2013).
Real-time PCR can also now be used to quantify the intensity of infection with C. sinensis (Kim et al. 2009a). In addition, molecular identification techniques, can be used in cases of multiparasite infections in a single host (Sato et al. 2009; Thaenkham et al. 2011). Such approaches can also be used in a food security setting to test for the presence of liver flukes in aquaculture or native fisheries products, particularly for export (Parvathi et al. 2007, 2008; Cai et al. 2010).
Due to their high specificity, such molecular diagnostic tests are likely to play an increasingly significant role in anthelminthic drug efficacy evaluations, the rigorous monitoring of reinfection patterns, and to investigate changes in the endemic range of the liver flukes (Touch et al. 2009; Traub et al. 2009).
6 Consequence of Infection
6.1 Pathogenesis, Pathology and Morbidity
Liver fluke infection causes significant pathological changes to the bile ducts which the worms inhabit. The pathology can also extend to affect both the liver and gall bladder (Rim 2005; Sithithaworn et al. 2007b). Syrian golden hamsters provide a suitable animal model to examine these changes (Bhamarapravati et al. 1978; Lee et al. 1993). During the early phase of infection with O. viverrini there is an acute inflammatory reaction in the large intrahepatic bile ducts as well as portal connective tissue. Once the infection has become chronic (at about 30 days post infection) hyperplasia and adenomatous formations of the bile duct epithelium occur (Sripa 2003). Granulomatous responses to both the adult flukes as well as to the eggs which they produce lead to periductal fibrosis and scarring. This is the most prominent feature during the chronic stage of infection (Bhamarapravati et al. 1978). The extensive fibrosis is associated with a significant increase in the synthesis and the hepatic content of collagen (Hutadilok and Ruenwongsa 1983; Chotigeat and Ruenwongsa 1986). With the onset of the chronic phase of infection the inflammatory responses become less severe suggesting that immune modulation may occur. Fibrotic tissue accumulates due to repair dysfunction and an imbalance in synthesis and degradation of the fibrotic tissue. These factors may lead to cell proliferation which, in the presence of cofactors, significantly contributes to cancer development (Kenny and Bissell 2003). In humans, periductal fibrosis is a significant cause of hepatobiliary disease and leads to an increased risk of CCA development (Mairiang et al. 1992, 2012). In O. viverrini patients with advanced periductal fibrosis there was an 8 times higher level of IL-6 responses to O. viverrini-excretory/secretory products than in patients without fibrosis, indicating the role of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of advanced periductal fibrosis in opisthorchiasis (Sripa et al. 2009).
Chronic infection by the liver flukes corroborated by a marked humoral immune response indicated by the presence of parasite-specific IgG, IgA, and IgE in the serum and bile of humans infected with O. viverrini (Itoh et al. 1994; Akai et al. 1995). Although the IgG level against crude somatic antigen correlated with hepatobiliary abnormalities diagnosed by ultrasonography, there was weak correlation with the intensity of infection (Elkins et al. 1996).
The bile ducts which harbor the adult worms show the most significant and potentially dangerous gross and microscopic pathological changes in both O. viverrini and C. sinensis infections but development is long term taking up to seven to 15 years for O. viverrini (Riganti et al. 1989). Immunomodulation during both the acute and chronic phases of infection is responsible for the pathological changes observed (Rim 2005).
Light infections may be inapparent with no significant symptoms. Pathology depends on both the duration and the intensity of infection as well as to the susceptibility of the host (Behr et al. 1998; Sithithaworn et al. 2007b; Hong and Fang 2012; Armignacco et al. 2013). For heavy infections the peripheral bile ducts may become thickened beneath the fibrotic capsule of the liver. A recent outbreak of opisthorchiasis in Italy caused by O. felineus infection presented as a febrile syndrome with eosinophilia and cholestasis (Traverso et al. 2012). This outbreak is interesting as 37 (82%) of the 45 infected individuals showed symptoms of the disease and 8 (17.7%) were admitted to hospital for treatment.
As indicated above, inapparent infections are common with only about 5% morbidity occurs among infected individuals (Upatham et al. 1984). Once the symptoms become apparent they are usually non-specific, involving general abdominal discomfort. In such cases hepatobiliary abnormalities and/or CCA can usually be detected by ultrasonography (Choi et al. 2005; Mairiang et al. 2012).
6.2 Liver Flukes and Cholangiocarcinoma
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a cancer of the epithelial cells in the bile ducts arising along either the intrahepatic or extra-hepatic biliary tree (Nakeeb et al. 1996; Blechacz and Gores 2008) although studies on molecular pathogenesis are currently confined to the intrahepatic CCA type. CCA is responsible for as much as 15% of liver cancers worldwide, most of which are associated with trematode infection (Parkin et al. 1993; Parkin 2006). Large-scale epidemiological studies of CCA indicate an increase in both the incidence and mortality rates. Currently CCA is the second most frequent primary liver cancer worldwide (Khan et al. 2007). The highest incidence of CCA worldwide occurs in northeast Thailand (Sithithaworn et al. 2014). In addition to CCA induced by either C. sinensis or O. viverrini, early observations indicate that around 400 cases of this disease currently occur every year in patients heavily infected with O. felineus (Hotez and Alibek 2011).
The induction of cancer by these liver flukes appears to be dependent on a variety of factors including host genetic background, past exposure to infection as determined by elevated O. viverrini antibody levels, liver cirrhosis, chronic infection with hepatitis C virus and heavy alcohol consumption (Tyson and El-Serag 2011).
The association between O. viverrini and CCA was first determined in a hospital-based, case-control study conducted in Thailand in the late 1980s (Parkin et al. 1991). A total of 103 patients with CCA were compared with an equal number of age- and sex-matched controls and elevated O. viverrini antibody titers were positively correlated with an increased risk of CCA (Parkin et al. 1991). This was confirmed in a repeat study based on 129 cases the cancer. This study indicated that the population-attributable risk is as high as 88% in endemic areas (Honjo et al. 2005). Another a case-control study, this time on C. sinensis from Korea, compared 41 patients with CCA with 406 controls and found a similarly strong association between liver fluke eggs in fecal samples and CCA (Shin et al. 1996). A recent meta-analysis including 912 cases and 4909 controls confirmed this association (Shin et al. 2010). The population-attributable risk was lower than that calculated for O. viverrini but was nevertheless 27.9% for men and 16.2% for women.
In patients with a C. sinensis infection the formation of calculi in the intrahepatic biliary passages is a characteristic pathological change. This may be associated with suppurative cholangitis, cholecystitis, and biliary abscess or the so-called cholangiohepatitis. It can eventually lead to the development of primary liver cancer, especially CCA. The occurrence of calculi is probably caused by bile stagnation, which in turn causes mechanical obstruction by C. sinensis worms and eggs in the bile ducts. The calculi in the intra- and extra-hepatic bile ducts are made up of bilirubin and calcium salts. The formation of such pigment stones in clonorchiasis is thought to be due to bile stagnation leading to changes in the composition of bilirubin, cholesterol, phospholipid, bile acid and the activity of bacterial glucuronidase. The goblet cell metaplasia of the bile duct epithelium is responsible for the high content of mucous secretion in the bile. This mucin-rich bile in conjunction with the worms and eggs not only cause cholestasis but also provide a suitable environment for secondary bacterial infection. This is usually due to Escherichia coli which cause ascending cholangitis from the intestine (Rim 2005). Studies on C. sinensis indicate that this species also stimulates biliary epithelial hyperplasia (Hong et al. 1993), which is considered to play a significant role in carcinogenesis (Lee et al. 1993, 1994). Clonorchiasis-associated CCA involves substantial mucin secretion, usually accompanied by extensive fibrosis (Chou and Chan 1976; Choi et al. 1988). Although the larger bile ducts are only slightly enlarged and fibrotic, they are commonly blocked by adult worms or calcium bilirubinate stones (Kim et al. 1989). Clonorchiasis-associated CCA has develops in a discrete nodular or confluent mass in which smaller ducts with adenomatous hyperplasia undergo malignant transformation occur (Hou 1956). Chronic inflammation is of particular significance for the induction of CCA due to oxidative and nitrative DNA damage (Yongvanit et al. 2012).
Although most of these studies indicate that liver flukes cause tissue damage by mechanical and chemical irritation, some recent studies suggest that parasite-specific immune responses may also play a major role (Yongvanit et al. 2012). A genetic polymorphism in the detoxifying enzyme glutathione S-transferase (GSTM1) in association with seropositivity for opisthorchiasis was found to modify the cancer risk factor for CCA (Honjo et al. 2005). Thus, gene-environment interactions (current or past infection of O. viverrini infection) can play a significant role in individual susceptibility to CCA.
Carcinogenesis of CCA is still not clearly understood, however, it appears to be a multistage process with a variety of factors being involved of which chronic infections and persistent inflammation are predominant (Ohshima and Bartsch 1994). It is also possible that nitric oxide (NO), which can generate DNA-reactive agents and N-nitrosamines, is involved (Yongvanit et al. 2012). Excess NO production plays an important role in a number of pathological processes, including the induction of cancer (see Yongvanit et al. 2012). If a host becomes infected with a liver fluke, macrophages and other cell types (e.g., mast cells, eosinophils, and epithelial cells) are activated by parasite-specific T cells and cytokines and synthesize NO from l-arginine via the induction of iNOS with the aim of eliminating the intruder. Nitric oxide is not only cytotoxic , it is also genotoxic by reacting with superoxide to form the highly reactive peroxynitrite which leads to oxidative and nitrative DNA damage via the formation of 8-oxodG and 8-nitroguanine (Inoue and Kawanishi 1995). These can be used to indicate DNA damage in the affected tissues. The overproduction of NO caused by O. viverrini infection can also lead to the endogenous nitrosation of amine precursors to form potentially carcinogenic N-nitrosamines such as N-dimethylnitrosamine (NDMA) (Satarug et al. 1998). NDMA, which is a carcinogenic product of the nitrosation reaction, has been detected in the urine of O. viverrini-infected subjects. It seems to be associated with lymphoproliferative responses to active liver fluke antigens which ceases after praziquantel treatment and the death of the parasites (Satarug et al. 1998). During an active O. viverrini infection of either hamsters (the animal model) or humans, an isoform of cytochrome P-450 (CYP) enzymes, CYP2A6 is formed (Kirby et al. 1994; Satarug et al. 1996). NDMA requires metabolic activation, mainly by CYP2E1 and CYP2A6, before becoming carcinogenic. It is hypothesized that this increase in CYP2A6-related enzyme activity in O. viverrini-infected individuals is an important link between inflammatory processes due to chronic liver fluke infection and a high risk for CCA.
6.3 Associated Pathogens
In a study in the northeast of Thailand individuals with O. viverrini infection had a significantly higher rate of leptospirosis than those without. In addition, O. viverrini metacercariae from the fish were positive for Leptospira interrogans, suggesting a close association between these two pathogens (Van et al. 2017). In individuals with a C. sinensis infection, the abundance of Dorea (Lachnospiraceae), a potentially pro-inflammatory microbe, was higher than in healthy individuals, while Variovorax (Comamonadaceae) was only detected in infected subjects (Xu et al. 2018). The frequency, structure and pathogenic significance of multiple parasite communities has been reviewed by Petney and Andrews (1998) .
7 Epidemiology
A somewhat dated national survey carried out by the Ministry of Public Health in Thailand in 2001 showed that helminth infections are common with a country wide total prevalence of 22.5%. Of the species involved hookworms are the most common (11.4%), while O. viverrini ranked second with an average prevalence of 9.6% although the central and southern areas of the country showed a very limited presence of the parasite (Jongsuksuntigul 2002). In the northeast, there is substantial variation in the prevalence of opisthorchiasis among provinces, ranging from 4% to 33% (Jongsuksuntigul 2002). In Lao PDR, O. viverrini is common in the lowlands among people with close ethnic ties to the majority of the northeast Thai population probably due to high levels of partially enforced migration from Lao PDR into Thailand in the past (Giboda et al. 1991). The prevalence in certain areas is as high as 36–60% (Sithithaworn et al. 2012a). This is much higher than previous records indicate (Kobayashi et al. 1996, 2000). The presence of mixed infections including O. viverrini and heterophyid and lecithodendriid flukes found in communities along the Mekong River, potentially make conventional fecal diagnosis difficult (Chai et al. 2005).
Limited information on the incidence of infection in endemic communities in Thailand is available (Sornmani et al. 1984; Upatham et al. 1988; Saowakontha et al. 1993). In a study of 3 villages in Khon Kaen Province, the incidence was 1.7–25% over a 6-month period (Saowakontha et al. 1993). In a central Thai village containing a migrant population from the northeast of the country the incidence was 21.6% per year (Suwannahitatorn et al. 2013). Similarly, in the north of Thailand immigrants from the northeast were more likely to be infected with O. viverrini than local people (Pumidonming et al. 2018). The high levels of incidence in some villages correspond with the high prevalences in some areas. For example, with an incidence of 40% per year, only 6 years are required for the prevalence of an originally uninfected cohort to exceed 95% (Upatham et al. 1985). In northeast Thailand information on the rate of reinfection after treatment also show a high incidence of reinfection. After a pretreatment prevalence of 55.1%, it took one year for the prevalence to return to 54.8% (Sornmani et al. 1984). Upatham et al. (1988) reported that in an area in Chonnabot, Khon Kaen Province, where 97.4% of villagers were infected, the prevalence had reached 94% one-year post-praziquantel treatment. It is significant that individuals with a high pretreatment intensity of infection tended to have a high intensity of reinfection. This may be a predisposition to heavy infection in some individuals. This hypothesis is supported by evidence from other parasites, such as Ascaris lumbricoides (Elkins et al. 1986), Necator americanus (Schad and Anderson 1985), Trichuris trichiura (Bundy and Golden 1987) and Schistosoma mansoni (Bensted-Smith et al. 1987). Rapid reinfection after treatment shows little evidence for protective immunity although this may occur in some individuals.
Clonorchis sinensis shows considerable variation in prevalences in the Republic of Korea dependent on the river system involved (Jeong et al. 2016). In this country males (11.2%) are more commonly infected than females (6.2%) as are individuals aged between 50 and 59 years (Jeong et al. 2016).
Although the rates of O. viverrini and C. sinensis infection vary considerably between villages, communities, (Kaewpitoon et al. 2015; Jeong et al. 2016; Prakobwong et al. 2017) and provinces (Miyamoto et al. 2014; Thaewnongiew et al. 2014; Lai et al. 2016), the pattern of infection is similar. Infection is age-dependent with the youngest age groups (0–5 years) having a low prevalence and intensity of infection. These increase through the pre- and early teenage years, often reaching a plateau in late teenagers (e.g., 15–19 years). This is in contrast to data published in the 1980s that showed very high prevalences in young school children, a situation that has now improved markedly (Khuntikeo et al. 2016). In some areas, the intensity of eggs released increased with age (Upatham et al. 1984), but the worm burden declined after the age of 50–60 (Haswell-Elkins et al. 1991; Sithithaworn et al. 1991). A number of possible reasons have been suggested for this decline including the late development of an immune response, lower parasite survival in more heavily fibrosed bile ducts, death of parasite in heavily infected people, or reduced exposure to infection in older age groups. Infection in infants may be due to mothers feeding them raw fish which is often finely ground (Sadun 1955; Upatham et al. 1982, 1984). However, the reported intensities of infection under the age of 4 are invariably low and there is little evidence that young children experience frequent exposure to infection.
In general, the prevalence and average intensity of O. viverrini infection is either not sex related or is slightly higher among males compared to females (Wykoff et al. 1965; Upatham et al. 1982, 1984; Haswell-Elkins et al. 1991) although more heavy infections may be found among males than females. This is also the case for C. sinensis (Joo et al. 1997). Males could therefore be more at risk of significant pathology, including cancer, as this increases in a non-linear fashion with infection (Haswell-Elkins et al. 1994; Elkins et al. 1996).
As with other helminths, O. viverrini, and probably all of the liver flukes dealt with here, is highly overdispersed with the majority of worms being found in only a few heavily infected individuals (Ramsay et al. 1989). The maximum worm load was 565 with a mean of 85 (S.D. = 154). Haswell-Elkins et al. (1991) observed that 81% of 11,000 worms recovered after treatment of 246 village residents were expelled by just 25 individuals (10% of the sample population). The highest burdens were over 100 worms. Interestingly, a number of individuals who did not expel worms were nevertheless positive for eggs. In an autopsy study in Khon Kaen, northeast Thailand, in which the worm burden was accurately measured, Sithithaworn et al. (1991) found that 30 out of 181 cadavers contained 66% of all the worms recovered and that only 13 people (7%) had worm burdens greater than 400.
A preliminary analysis by Khuntikeo et al. (2018) shows that deaths caused by O. viverrini-induced cholangiocarcinoma cause a high socioeconomic burden on the families and potentially communities involved. Data are required before a quantitative estimate of this burden can be made. On a broader level, data for the year 2009 show that in Thailand medical care and loss of wages alone costs about $120 million annually (Kaewpitoon et al. 2015).
8 Treatment
Treatment programs vary considerably between countries. In general, infection with O. felineus is so limited in Europe where only local control is necessary if a particular community or group is infected (Pozio et al. 2013). In Thailand, a trial liver fluke control program was developed as early as 1967 in Sakon Nakhon Province (Jongsuksuntigul and Imsomboon 2003). This, as with other control programs in Thailand was based on the selective treatment of infected individuals as opposed to mass treatment. One of the limitations of this approach is that although the drug of choice, praziquantel, has a high efficacy (90–95%) and there is no evidence of drug resistance, the reinfection rate is high. This suggests that control by chemotherapy alone is unlikely to be completely successful, which is supported by the “residual” prevalence found in many areas after control measures were conducted (Jongsuksuntigul and Imsomboon 2003). With the advent of praziquantel in the mid-1970s, which is effective in about 90% of cases, the duration and toxicity problems were largely eliminated (Bunnag and Harinasuta 1981). The recommended daily dose for treatment of C. sinensis was 3 × 25 mg/kg × 1 day with cure rate of 85% and egg reduction rate of 99.7% (Rim and Yoo 1979), for O. viverrini the dose of 40 mg/kg with cure rate of 90% and egg reduction rate of >99.7 (Bunnag and Harinasuta 1981; Lovis et al. 2012), and for O. felineus the dose of 3 × 25 mg/kg × 1 day with cure rate of 90% and egg reduction rate of 100% (Wegner 1984; Zavoikin et al. 1994).
Recent data based on higher sensitivity methods such as PCR, however, suggest, that the treatment efficacy may be lower than previous estimates suggest, an area which clearly requires urgent investigation. Nevertheless, treatment with praziquantel usually leads to the elimination of symptoms. As an alternative to praziquantel, tribendimidine has been examined and it gave an efficacy comparable to praziquantel in the treatment of C. sinensis infection and resulted in fewer adverse events (Qian et al. 2013) but more study is required.
9 Prevention and Control
Methods of prevention and control aim at breaking the transmission cycle to humans. The millions of people infected and at risk of infection, as well as the direct and indirect economic losses resulting from liver fluke infection indicate the great importance of implementing effective and long-lasting prevention and control measures. There have been a number of attempts to do this both via direct treatment and also education aimed at reducing or elimination the consumption of raw or partially cooked fish. For O. viverrini, when fecal contamination from humans is reduced or eliminated by mass treatment and/or improved sanitation, the prevalence of infection can be substantially reduced (Sithithaworn and Haswell-Elkins 2003). A control program initiated in 1989 in certain provinces, particularly in the north and northeast of the country, resulted in a reduction in prevalence from 35.6% in 1988 to 8.7–9.4% during 2001–2009 (Jongsuksuntigul et al. 1992; Sithithaworn et al. 2012a). However, complete elimination of infection may not be possible if domestic cat and dog reservoir hosts maintain the source of parasite therefore playing a critical role in maintaining the life cycle. The difficulty involved in detecting infected cases with only a light infection (<1000 EPG) and the problem of reinfection after treatment also present serious problems to effective, long-term control. At the social level, education has proven both difficult to implement and ineffective to reduce the consumption of raw or partially cooked fish in Thailand (Sithithaworn and Haswell-Elkins 2003).
An easy and promising method of preventing infection is to kill the infective metacercariae before fish are consumed. Unfortunately, as the consumption of raw or partially cooked fish is a deeply imbedded tradition in areas where opisthorchiasis and clonorchiasis are most common, the relevant populations have proven refractory to change (Grundy-Warr et al. 2012).
Particularly, in Thailand and Lao PDR there are 3 types of fish dishes which act as a source of infection with O. viverrini. “Koi pla” is prepared from fresh raw fish which are seasoned with lemon juice and spices and consumed without heating, posing a high risk of infection. “Pla som,” which is a dish made out of fish which have been fermented for 1–2 days, poses a moderate risk, while “Pla ra” which undergoes less than the usual long term, although less risky, may provide a favorable environment for metacercarial survival (Grundy-Warr et al. 2012). Other Mekong countries have their traditional potential sources of infection; fermented “Pla dak” in Lao PDR, raw “Pla hoc” in Cambodia which is similar to “Pla som,” “goi ca mai” (raw fish salad) and slices of raw silver carp in Vietnam, a raw fish salad in China, and sushi in Korea (Rim 2005). In Russia, O. felineus infection may come through eating dried or salted fish or sliced raw fish ("stroganina") which is popular among native Siberians, as well as fish pickled in vinegar.
Salted fish is generally considered ready in a day or two. It has been shown, however, that metacercariae remain viable under high salt concentrations for up to 2 weeks. The popular dishes in Russia and Eastern Europe of slightly salted fish are not safe at all. The same is true for dried fish where greater than 12 days of drying is required to kill 99% of metacercariae. Given that the weight of fish and the temperature of drying are not constant even at fish plants or after 12-day period, dried fish remain dangerous for consumption. Cold smoking has similar effects to those of drying and salting (Yossepowitch et al. 2004).
A recent investigation in fish farms in Lao PDR supported by Food and Agriculture Organization demonstrated that some carp species commonly cultured in fish ponds contained O. viverrini metacercariae (unpublished data). This preliminary result suggests that apart from captured fish, culture fish can provide an additional source of infection to consumers and thus urgently need attention control body to ensure food safety.
Control efforts are primarily focused on the reduction and elimination of parasite transmission by ensuring proper food preparation, promoting the development of improved diagnostic techniques, providing chemotherapy, and improving sanitation. A combination of health education, mass treatment, and governmental aid could significantly reduce liver fluke infection. Emphasis on health education should be placed on the younger generation in school as a part of the conventional education curriculum.
Interrupting the life cycle of the parasite has always been regarded as a promising way of disease control, for example, application of molluscicides (chemicals that kill snails) to control snail populations (Petney et al. 2012; Tesana et al. 2012). Low concentrations of certain molluscicides (e.g., phenasal, niclosamide) are lethal for infected snails, sublethal for uninfected ones, and, it is presumed, nontoxic for other animals (Tesana et al. 2012). The biggest case against this approach is that it involves interference of the ecosystem which can have dramatic consequences including potential toxicity to fish in rice fields (Calumpang et al. 1995; Tesana et al. 2012). Economic factors also negate its usage as the application of molluscicides is practical only for small water bodies since the costs of treating big areas are extremely high. Additionally, it has been shown that snail populations are restored in about 5 years, hence repeated treatments are necessary. Therefore, decontamination of aquatic bodies has been abandoned in Russia.
In order to achieve overall, long-term control of liver flukes, a multidisciplinary approach is necessary. This must aim at breaking the transmission cycle at the level of the first and second intermediate hosts, i.e., at the level of general hygiene as well as at the fisheries and aquaculture levels. This must also be extended to the food production and distribution industries. Of great significance, is that the population at risk must be educated as to how infection occurs and how it can thus be avoided, and to the risks of infection, particularly the development of CCA, should it occur.
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) recognizes the necessity of determining the importance of aquaculture in comparison with capture fisheries in the likelihood of human infection with food-borne trematodes. This is a primary requirement in food safety assurance from aquaculture at both the domestic and international trade levels. Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) methodologies are already available to assist control approaches at the food production stage; however, more work is required taking into account the economics of the costs accruing through implementation of these approaches.
Thailand is considered the hot spot of opisthorchiasis and CCA and the public health importance is acknowledged. In order to prioritize the health problems associated with liver fluke infection, an estimation of burden of disease (BOD) in Thailand was instigated in 1999 and data are available from 2004 (Bundhamcharoen et al. 2011). Generally, BOD are based on two measurements, namely Disability Adjusted Life Year (DALY) and, when accurate mortality data are lacking, estimated number of Years of Life Loss (YLL). DALY is a summary measure of population health for setting priorities since this measure combines both fatal and non-fatal health outcomes. BOD estimates are far from complete, especially in developing countries where resources and budget are not adequate. The BOD study in Thailand has identified a short list of the top 20 diseases based on mortality, DALY, and YLL. Of these only the top 10 diseases were selected. Liver cancer ranks 5th in males and 8th in females. A total of 27,500 people die every year of liver cancer, while YLL is estimated to be 400,000. Both of these figures show the high significance of opisthorchiasis, and CCA, as a public health problem in Thailand.
Thailand was one of the first nations to initiate a program of liver fluke control. This was based initially on funding supplied by USAID as early as 1950. This was followed up by a Thai government program supported by the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (German Society for Technical Cooperation, GTZ). These programs have been successful in reducing the prevalence of O. viverrini infection from approximately 63.6% in 1984–1987 to 9.6% in the year 2001 (Jongsuksuntigul and Imsomboon 2003). In spite of this success, a nationwide survey showed that there was still a residual prevalence of 8.7% in 2009. The northeast of Thailand currently still has the highest prevalence with 16.6% with northern Thailand at 10%. Both central (1.3%) and southern Thailand (0.1%) have low infection prevalences (Sithithaworn et al. 2012a). These data indicate that although the control programs have been successful in reducing the prevalence, they have not eliminated the infection.
The control programs to date have relied on the use of praziquantel (40 mg/kg) curing (>95% cure rate) infected individuals. Most infected individuals involved in the control programs are now estimated to have only light infections (EPG <1000). Treatment with praziquantel, although it is successful in killing adult worms, does not prevent reinfection. Indeed, evidence is accumulating to suggest that it may compromise the immune system or cause liver complications when used repeatedly for reinfections (Pinlaor et al. 2008). This leads us to the conclusion that the current control programs require urgent modification.
Both short-term and a long-term program components should be reassessed. The short-term program requires a modification in the current selective treatment strategy by including traditional methods applied with increased accuracy, as well as molecular diagnostics. Multiple stool samples taken from an individual can be analyzed using the Kato-Katz method or the more sensitive formalin-ethyl acetate method. In addition, the cure rate based on the administration of praziquantel must be regularly monitored. This is particularly relevant given the different genetic groups of parasites present in different areas (Andrews et al. 2008). Control approaches must also include zoonotic cycles in carnivore reservoir hosts as they will increase in significance as human prevalences decrease.
One of the most important aspects in the long-term strategy involves an education program based on food safely. Current programs have shown that long-term, continuous education is required as raw or partially cooked fish consumption is a deeply rooted, raw attitude in the areas where it occurs (Grundy-Warr et al. 2012). Ziegler et al. (2011) recommend school-based health education for young children in order to imprint the importance of food preparation and hygiene in relation to public health. Such educational programs can be promoted through participatory activities in schools. It is anticipated that the information will not only become part of the child’s background knowledge as they grow to adulthood, but that it will also be discussed at home during the period of schooling. Such a program should have a major impact at the family, extended family, and village levels. An approach of this intensity and magnitude will have the potential for a long-term impact that is not present with national and international selective treatment strategies.
Regarding the control options, Bürli et al. (2018b) utilized a mathematical model and suggested that education and improved sanitation would have to have a very high coverage to lead to O. viverrini elimination, whereas annual drug distribution at medium coverage is sufficient. Work by Laithavewat et al. (2018) and Khuntikeo et al. (2016) indicate that the education programs carried out to date in Thailand have had a major influence both on the knowledge of school children regarding the association between O. viverrini infection and cholangiocarcinoma and most importantly on the prevalence of infection in these children. This is not the case in Lao PDR where a recent study found 83% of children aged 5–15 years were infected and that the likelihood of infection was positively correlated with maternal infection (Araki et al. 2018). Based on their model, Bürli et al. (2018a) suggest that best solution is a combination of drug distribution at a medium level of coverage and as high as possible coverage of education and improved sanitation.
Moreover, the One Health approach recommended by the World Health Organization is a worldwide strategy for expanding interdisciplinary collaborations and communication in all aspects of health care for humans, animals, and the environment that is applicable for liver fluke control. This helps to improve our understanding of the social, economic, and ecological dimensions of liver fluke transmission including opisthorchiasis in Thailand and other Southeast Asian countries.
An integrated control program against C. sinensis infection based on education, improved sanitation, and use of praziquantel in Lou Village, Guangdong Province, China, proved to be remarkably successful with reductions in parasite prevalence and intensity of infections in human and fish hosts (Huang et al. 2017).
Long-term strategies, and indeed a good deal more research, are needed to overcome the dynamic situation caused by land-use and climatic changes either taking place or predicted for the Thailand. Such changes are often coupled with dynamic changes in parasite transmission (Patz et al. 2003, 2004). Given the public health significance of O. viverrini infection, the Thai Ministry of Public Health recently initiated the “Esan agenda: eradicate the liver fluke to reduce CCA” which is primarily aimed at screening for CCA patients. If the cancer is recognized sufficiently early, curative surgery may lead to an effective cure. Such a strategy, however, does not attack the problem at its roots as relatively very few people are involved compared with the population at risk based on infection with O. viverrini. Currently, at least 26 million people are at risk of infection in the north and northeast of Thailand. Any control program aimed at reducing the long-term burden of Opisthorchis infection must address this population group as the initiation point for the effective control of opisthorchiasis and its associated CCA.
References
Adam R, Arnold H, Pipitgool V, Sithithaworn P, Hinz E, Storch V (1993) Studies on lophocercous cercariae from Bithynia siamensis goniomphalos (Prosobranchia: Bithyniidae). Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 24:697–700
Akai PS, Pungpak S, Chaicumpa W, Kitikoon V, Ruangkunaporn Y, Bunnag D, Befus AD (1995) Serum antibody responses in opisthorchiasis. Int J Parasitol 25:971–973
Ando K, Sithithaworn P, Nuchjungreed C, Tesana S, Srisawangwong T, Limviroj W, Chinzei Y (2001) Nucleotide sequence of mitochondrial CO I and ribosomal ITS II genes of Opisthorchis viverrini in northeast Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 32(Suppl 2):17–22
Andrews RH, Sithithaworn P, Petney TN (2008) Opisthorchis viverrini: an underestimated parasite in world health. Trends Parasitol 24:497–501
Araki H, Ong KIC, Lorphachan L, Soundala P, Iwagami M, Shibanuma A, Hongvanthong B, Brey PT, Kano S, Jimba M (2018) Mothers’ Opisthorchis viverrini infection status and raw fish dish consumption in Lao People’s Democratic Republic: determinants of child infection status. Trop Med Health 46:29
Arimatsu Y, Kaewkes S, Laha T, Hong SJ, Sripa B (2012) Rapid detection of Opisthorchis viverrini copro-DNA using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Parasitol Int 61:178–182
Armignacco O, Caterini L, Marucci G, Ferri F, Bernardini G, Natalini Raponi G, Ludovisi A, Bossu T, Gomez Morales MA, Pozio E (2008) Human illnesses caused by Opisthorchis felineus flukes, Italy. Emerg Infect Dis 14:1902–1905
Armignacco O, Ferri F, Gomez-Morales MA, Caterini L, Pozio E (2013) Cryptic and asymptomatic Opisthorchis felineus infections. Am J Trop Med Hyg 88:364–366
Attwood HD, Chou ST (1978) The longevity of Clonorchis sinensis. Pathology 10:153–156
Aung WPP, Htoon TT, Tina HH, Thinn KK, Sanpool O, Jongthawin J, Sadaow L, Phosuk I, Rodpai R, Intapan PM, Maleewong W (2017) First report and molecular identification of Opisthorchis viverrini infection in human communities from Lower Myanmar. PLoS One 12:e0177130
Aunpromma S, Tangkawattana P, Papirom P, Kanjampa P, Tesana S, Sripa B, Tangkawattana S (2012) High prevalence of Opisthorchis viverrini infection in reservoir hosts in four districts of Khon Kaen Province, an opisthorchiasis endemic area of Thailand. Parasitol Int 61:60–64
Aunpromma S, Kanjampa P, Papirom P, Tangkawattana S, Tangkawattana P, Tesana S, Boonmars T, Suwannatrai A, Uopsai S, Sukon P, Sripa B (2016) Prevalence and risk factors for Opisthorchis viverrini infection among cats and dogs in six districts surrounding the Ubolratana Dam, an endemic area for human opisthorchiasis in Northeastern Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 47:1153–1159
Awiruttapanich M (2004) Epidemiology of liver fluke (Opisthorchis viverrini) in pla kao na (Cyclocheilichthys armatus). Dissertation, Khon Kaen University
Bae YA, Kong Y (2003) Evolutionary course of CsRn1 long-terminal-repeat retrotransposon and its heterogeneous integrations into the genome of the liver fluke, Clonorchis sinensis. Korean J Parasitol 41:209–219
Bae YA, Moon SY, Kong Y, Cho SY, Rhyu MG (2001) CsRn1, a novel active retrotransposon in a parasitic trematode, Clonorchis sinensis, discloses a new phylogenetic clade of Ty3/gypsy-like LTR retrotransposons. Mol Biol Evol 18:1474–1483
Bedier E, Chesneau P (1929) Distomatose hepatique a Opisthorchis au Laos (a Vientiane et Thakhek). Bull Soc Pathol Exot 22:331–334
Behr MA, Gyorkos TW, Kokoskin E, Ward BJ, MacLean JD (1998) North American liver fluke (Metorchis conjunctus) in a Canadian aboriginal population: a submerging human pathogen? Can J Public Health 89:258–259
Bensted-Smith R, Anderson RM, Butterworth AE, Dalton PR, Kariuki CH, Koech D, Mugambi M, Ouma JH, Arap Siongok TK, Sturrock RF (1987) Evidence for predisposition of individual patients to reinfections with Schistosoma mansoni after treatment. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 81:651–656
Bhamarapravati N, Thammavit W, Vajrasthira S (1978) Liver changes in hamsters infected with a liver fluke of man, Opisthorchis viverrini. Am J Trop Med Hyg 27:787–794
Blechacz BR, Gores GJ (2008) Cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Liver Dis 12:131–150
Boonmee S, Imtawil K, Wongkham C, Wongkham S (2003) Comparative proteomic analysis of juvenile and adult liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini. Acta Trop 88:233–238
Brockelman WY, Upatham ES, Viyanant V, Ardsungnoen S, Chantanawat R (1986) Field studies on the transmission of the human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini, in northeast Thailand: population changes of the snail intermediate host. Int J Parasitol 16:545–552
Brusentsov II, Katokhin AV, Brusentsova IV, Shekhovtsov SV, Borovikov SN, Goncharenko GG, Lider LA, Romashov BV, Rusinek OT, Shibitov SK, Suleymanov MM, Yevtushenko AV, Mordvinov VA (2013) Low genetic diversity in wide-spread Eurasian liver fluke Opisthorchis felineus suggests special demographic history of this trematode species. PLoS One 8:e62453
Buathong S, Leelayoova S, Mungthin M, Ruang-areerate T, Naaglor T, Suwannahitatorn P, Piyaraj P, Taamasri P, Tan-ariya P (2017) Molecular discrimination of Opisthorchis-like eggs from residents in a rural community of central Thailand. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 11:e0006030
Bui TN, Pham TT, Nguyen NT, Nguyen HV, Murrell D, Phan VT (2016) The importance of wild fish in the epidemiology of Clonorchis sinensis in Vietnam. Parasitol Res 115:3401–3408
Bundhamcharoen K, Odton P, Phulkerd S, Tangcharoensathien V (2011) Burden of disease in Thailand: changes in health gap between 1999 and 2004. BMC Public Health 11:53
Bundy DA, Golden MH (1987) The impact of host nutrition on gastrointestinal helminth populations. Parasitology 95(Pt 3):623–635
Bunnag D, Harinasuta T (1981) Studies on the chemotherapy of human opisthorchiasis: III. Minimum effective dose of praziquantel. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 12:413–417
Bürli C, Harbrecht H, Odermatt P, Sayasone S, Chitnis N (2018a) Analysis of interventions against the liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini. Math Biosci 303:115–125
Bürli C, Harbrecht H, Odermatt P, Sayasone S, Chitnis N (2018b) Mathematical analysis of the transmission dynamics of the liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini. J Theor Biol 439:181–194
Cai XQ, Xu MJ, Wang YH, Qiu DY, Liu GX, Lin A, Tang JD, Zhang RL, Zhu XQ (2010) Sensitive and rapid detection of Clonorchis sinensis infection in fish by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Parasitol Res 106:1379–1383
Cai XQ, Liu GH, Song HQ, Wu CY, Zou FC, Yan HK, Yuan ZG, Lin RQ, Zhu XQ (2012) Sequences and gene organization of the mitochondrial genomes of the liver flukes Opisthorchis viverrini and Clonorchis sinensis (Trematoda). Parasitol Res 110:235–243
Calumpang SM, Medina MJ, Tejada AW, Medina JR (1995) Environmental impact of two molluscicides: niclosamide and metaldehyde in a rice paddy ecosystem. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 55:494–501
Chai JY, Park JH, Han ET, Guk SM, Shin EH, Lin A, Kim JL, Sohn WM, Yong TS, Eom KS, Min DY, Hwang EH, Phommmasack B, Insisiengmay B, Rim HJ (2005) Mixed infections with Opisthorchis viverrini and intestinal flukes in residents of Vientiane Municipality and Saravane Province in Laos. J Helminthol 79:283–289
Chaicumpa W, Ybanez L, Kitikoon V, Pungpak S, Ruangkunaporn Y, Chongsa-nguan M, Sornmani S (1992) Detection of Opisthorchis viverrini antigens in stools using specific monoclonal antibody. Int J Parasitol 22:527–531
Chen D, Chen J, Huang J, Chen X, Feng D, Liang B, Che Y, Liu X, Zhu C, Li X, Shen H (2010) Epidemiological investigation of Clonorchis sinensis infection in freshwater fishes in the Pearl River Delta. Parasitol Res 107:835–839
Chen J, Xu H, Zhang Z, Zeng S, Gan W, Yu X, Hu X (2011) Cloning and expression of 21.1-kDa tegumental protein of Clonorchis sinensis and human antibody response to it as a trematode-nematode pan-specific serodiagnosis antigen. Parasitol Res 108:161–168
Choi BI, Park JH, Kim YI, Yu ES, Kim SH, Kim WH, Kim CY, Han MC (1988) Peripheral cholangiocarcinoma and clonorchiasis: CT findings. Radiology 169:149–153
Choi MH, Ryu JS, Lee M, Li S, Chung BS, Chai JY, Sithithaworn P, Tesana S, Hong ST (2003) Specific and common antigens of Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini (Opisthorchidae, Trematoda). Korean J Parasitol 41:155–163
Choi CD, Savage J, Stephens DN, O'Donnell M (2005) An integrated semicompliant balloon ultrasound catheter for quantitative feedback and image guidance during stent deployment. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 52:1498–1503
Chotigeat W, Ruenwongsa P (1986) Types of collagen in Opisthorchis viverrini infected hamster liver. Mol Biochem Parasitol 18:377–387
Chou ST, Chan CW (1976) Mucin-producing cholangiocarcinoma: an autopsy study in Hong Kong. Pathology 8:321–328
Dao TT, Abatih EN, Nguyen TT, Tran HT, Gabriel S, Smit S, Le PN, Dorny P (2016) Prevalence of Opisthorchis viverrini-like fluke infection in ducks in Binh Dinh Province, central Vietnam. Korean J Parasitol 54:357–361
Dao TTH, Nguyen TTG, Gabriel S, Bui KL, Dorny P, Le TH (2017) Updated molecular phylogenetic data for Opisthorchis spp. (Trematoda: Opisthorchioidea) from ducks in Vietnam. Parasit Vectors 10:575
De NV, Le TH (2011) Human infections of fish-borne trematodes in Vietnam: prevalence and molecular specific identification at an endemic commune in Nam Dinh province. Exp Parasitol 129:355–361
Ditrich O, Scholz T, Giboda M (1990) Occurrence of some medically important flukes (Trematoda: Opisthorchiidae and Heterophyidae) in Nam Ngum water reservoir, Laos. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 21:482–488
Doanh PN, Nawa Y (2016) Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis spp. in Vietnam: current status and prospects. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 110:13–20
Donthaisong C, Arunsan P, Suwannatrai K, Prasopdee S, Kulsantiwong J, Wongmaneeprateep S, Suwannatrai A, Tesana S (2014) Experimental infection of Opisthorchis viverrini cercariae to the cyprinid fish, Barbonymus gonionotus. Acta Trop 136:118–122
Duenngai K, Sithithaworn P, Rudrappa UK, Iddya K, Laha T, Stensvold CR, Strandgaard H, Johansen MV (2008) Improvement of PCR for detection of Opisthorchis viverrini DNA in human stool samples. J Clin Microbiol 46:366–368
Duenngai K, Boonmars T, Sithithaworn J, Sithithaworn P (2013) Diagnosis of early infection and post chemotherapeutic treatment by copro-DNA detection in experimental opisthorchiasis. Parasitol Res 112:271–278
Dung VT, Waikagul J, Thanh BN, Vo DT, Nguyen DN, Murrell KD (2014) Endemicity of Opisthorchis viverrini liver flukes, Vietnam, 2011-2012. Emerg Infect Dis 20:152–154
Elkins DB, Haswell-Elkins M, Anderson RM (1986) The epidemiology and control of intestinal helminths in the Pulicat Lake region of Southern India. I. Study design and pre- and post-treatment observations on Ascaris lumbricoides infection. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 80:774–792
Elkins DB, Haswell-Elkins MR, Mairiang E, Mairiang P, Sithithaworn P, Kaewkes S, Bhudhisawasdi V, Uttaravichien T (1990) A high frequency of hepatobiliary disease and suspected cholangiocarcinoma associated with heavy Opisthorchis viverrini infection in a small community in north-east Thailand. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 84:715–719
Elkins DB, Sithithaworn P, Haswell-Elkins M, Kaewkes S, Awacharagan P, Wongratanacheewin S (1991) Opisthorchis viverrini: relationships between egg counts, worms recovered and antibody levels within an endemic community in northeast Thailand. Parasitology 102(Pt 2):283–288
Elkins DB, Mairiang E, Sithithaworn P, Mairiang P, Chaiyakum J, Chamadol N, Loapaiboon V, Haswell-Elkins MR (1996) Cross-sectional patterns of hepatobiliary abnormalities and possible precursor conditions of cholangiocarcinoma associated with Opisthorchis viverrini infection in humans. Am J Trop Med Hyg 55:295–301
Erhardt A, Germer WD, Hörning B (1962) Die Opisthorchiasis hervorgerufen durch den Katzenleberegel Opisthorchis felineus (Riv.). Parasitol Schriftenr 15:1–171
Fang YY, Chen YD, Li XM, Wu J, Zhang QM, Ruan CW (2008) Current prevalence of Clonorchis sinensis infection in endemic areas of China. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis 26:99–103
Fedorova OS, Kovshirina YV, Kovshirina AE, Fedotova MM, Deev IA, Petrovskiy FI, Filimonov AV, Dmitrieva AI, Kudyakov LA, Saltykova IV, Odermatt P, Ogorodova LM (2017) Opisthorchis felineus infection and cholangiocarcinoma in the Russian Federation: a review of medical statistics. Parasitol Int 66:365–371
Feldmeier H, Hazay M, Sato M, Tiengkham P, Nishimoto F, Jiang H, Sopraseuth V, Moji K (2016) Morbidity assessment of Opisthorchis viverrini infection in rural Laos: I. Parasitological, clinical, ultrasonographical and biochemical findings. Trop Med Health 44:12
Flavell DJ, Flavell SU, Field GF (1983) Opisthorchis viverrini: the relationship between egg production, worm size and intensity of infection in the hamster. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 77:538–545
Frazer IH, Leggatt GR, Mattarollo SR (2011) Prevention and treatment of papillomavirus-related cancers through immunization. Annu Rev Immunol 29:111–138
Fried B, Abruzzi A (2010) Food-borne trematode infections of humans in the United States of America. Parasitol Res 106:1263–1280
Giboda M, Ditrich O, Scholz T, Viengsay T, Bouaphanh S (1991) Current status of food-borne parasitic zoonoses in Laos. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 22(Suppl):56–61
Gozlan RE, Britton JR, Cowx I, Copp GH (2010) Current knowledge on non-native freshwater fish introductions. J Fish Biol 76:751–786
Grundy-Warr C, Andrews RH, Sithithaworn P, Petney TN, Sripa B, Laithavewat L, Ziegler AD (2012) Raw attitudes, wetland cultures, life-cycles: socio-cultural dynamics relating to Opisthorchis viverrini in the Mekong Basin. Parasitol Int 61:65–70
Haas W, Granzer M, Brockelman CR (1990) Opisthorchis viverrini: finding and recognition of the fish host by the cercariae. Exp Parasitol 71:422–431
Han S, Zhang X, Wen J, Li Y, Shu J, Ling H, Zhang F (2012) A combination of the Kato-Katz methods and ELISA to improve the diagnosis of clonorchiasis in an endemic area, China. PLoS One 7:e46977
Haswell-Elkins MR, Elkins DB, Sithithaworn P, Treesarawat P, Kaewkes S (1991) Distribution patterns of Opisthorchis viverrini within a human community. Parasitology 103(Pt 1):97–101
Haswell-Elkins MR, Mairiang E, Mairiang P, Chaiyakum J, Chamadol N, Loapaiboon V, Sithithaworn P, Elkins DB (1994) Cross-sectional study of Opisthorchis viverrini infection and cholangiocarcinoma in communities within a high-risk area in northeast Thailand. Int J Cancer 59:505–509
Hering-Hagenbeck S, Schuster R (1996) A focus of opisthorchiidosis in Germany. Appl Parasitol 37:260–265
Hira PR, Al-Enizi AA, Al-Kandari S, Behbehani K (1987) Opisthorchiasis in Kuwait: first report of infections in Thai migrant workers in the Arabian Gulf. Ann Soc Bel Med Trop 67:363–368
Hong ST (1988) Changes of anti-Clonorchis sinensis IgG antibody in serum after praziquantel treatment in human clonorchiasis. Korean J Parasitol 26:1–8
Hong ST, Fang Y (2012) Clonorchis sinensis and clonorchiasis, an update. Parasitol Int 61:17–24
Hong ST, Kho WG, Kim WH, Chai JY, Lee SH (1993) Turnover of biliary epithelial cells in Clonorchis sinensis infected rats. Korean J Parasitol 31:83–89
Hong SJ, Seong KY, Sohn WM, Song KY (2000) Molecular cloning and immunological characterization of phosphoglycerate kinase from Clonorchis sinensis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 108:207–216
Hong SJ, Yun Kim T, Gan XX, Shen LY, Sukontason K, Sukontason K, Kang SY (2002) Clonorchis sinensis: glutathione S-transferase as a serodiagnostic antigen for detecting IgG and IgE antibodies. Exp Parasitol 101:231–233
Hong SJ, Shin JK, Kang SY, Ryu JR (2003a) Ultrastructural localization of phosphoglycerate kinase in adult Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 90:369–371
Hong ST, Choi MH, Kim CH, Chung BS, Ji Z (2003b) The Kato-Katz method is reliable for diagnosis of Clonorchis sinensis infection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 47:345–347
Honjo S, Srivatanakul P, Sriplung H, Kikukawa H, Hanai S, Uchida K, Todoroki T, Jedpiyawongse A, Kittiwatanachot P, Sripa B, Deerasamee S, Miwa M (2005) Genetic and environmental determinants of risk for cholangiocarcinoma via Opisthorchis viverrini in a densely infested area in Nakhon Phanom, northeast Thailand. Int J Cancer 117:854–860
Hotez PJ, Alibek K (2011) Central Asia’s hidden burden of neglected tropical diseases. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 5:e1224
Hou PC (1956) The relationship between primary carcinoma of the liver and infestation with Clonorchis sinensis. J Pathol Bacteriol 72:239–246
Hu F, Yu X, Ma C, Zhou H, Zhou Z, Li Y, Lu F, Xu J, Wu Z, Hu X (2007) Clonorchis sinensis: expression, characterization, immunolocalization and serological reactivity of one excretory/secretory antigen-LPAP homologue. Exp Parasitol 117:157–164
Huang Y, Zhou Z, Hu X, Wei Q, Xu J, Wu Z, Yu X (2007) A novel tegumental protein 31.8 kDa of Clonorchis sinensis: sequence analysis, expression, and immunolocalization. Parasitol Res 102:77–81
Huang SY, Zhao GH, Fu BQ, Xu MJ, Wang CR, Wu SM, Zou FC, Zhu XQ (2012) Genomics and molecular genetics of Clonorchis sinensis: current status and perspectives. Parasitol Int 61:71–76
Huang Y, Huang D, Geng Y, Fang S, Yang F, Wu C, Zhang H, Wang M, Zhang R, Wang X, Wu S, Cao J, Zhang R (2017) An integrated control strategy takes Clonorchis sinensis under control in an endemic area in south China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 17:791–798
Hutadilok N, Ruenwongsa P (1983) Liver collagen turnover in hamsters during infection by the human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini. Mol Biochem Parasitol 8:71–77
IARC (2012) Biological agents: a review of human carcinogens. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 100B:341–370
Inoue S, Kawanishi S (1995) Oxidative DNA damage induced by simultaneous generation of nitric oxide and superoxide. FEBS Lett 371:86–88
Itoh M, Pairojkul C, Thamawit W, Sithithaworn P, Tiwawech D, Uttaravicien T, Shirai T, Ito N (1994) Association of antibodies to Opisthorchis viverrini with hepatobiliary disease in northeastern Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg 51:424–429
Jeong YI, Shin HE, Lee SE, Cheun HI, Ju JW, Kim JY, Park MY, Cho SH (2016) Prevalence of Clonorchis sinensis infection among residents along 5 major rivers in the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 54:215–219
Jittimanee J, Sermswan RW, Kaewraemruaen C, Barta JR, Macinnes JI, Maleewong W, Wongratanacheewin S (2012) Protective immunization of hamsters against Opisthorchis viverrini infection is associated with the reduction of TGF-beta expression. Acta Trop 122:189–195
Johansen MV, Sithithaworn P, Bergquist R, Utzinger J (2010) Towards improved diagnosis of zoonotic trematode infections in Southeast Asia. Adv Parasitol 73:171–195
Jones MK, Gobert GN, Zhang L, Sunderland P, McManus DP (2004) The cytoskeleton and motor proteins of human schistosomes and their roles in surface maintenance and host-parasite interactions. Bioessays 26:752–765
Jongsuksuntigul P (2002) Parasitic diseases in Northeast Thailand. In: Seminar in parasitic diseases in Northeast Thailand. Klang Nana Tham, Khon Kaen, pp 3–18
Jongsuksuntigul P, Imsomboon T (2003) Opisthorchiasis control in Thailand. Acta Trop 88:229–232
Jongsuksuntigul P, Chaychumsri W, Techamontrikul P, Cheeradit P, Suratawanich P (1992) Studies on prevalence and intensity of intestinal helminthiasis and liver fluke in Thailand in 1991. J Med Assoc Thai 2:80–95
Joo KR, Bang SJ (2005) A bile based study of Clonorchis sinensis infections in patients with biliary tract diseases in Ulsan, Korea. Yonsei Med J 46:794–798
Joo CY, Chung MS, Kim SJ, Kang CM (1997) Changing patterns of Clonorchis sinensis infections in Kyongbuk, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 35:155–164
Ju JW, Joo HN, Lee MR, Cho SH, Cheun HI, Kim JY, Lee YH, Lee KJ, Sohn WM, Kim DM, Kim IC, Park BC, Kim TS (2009) Identification of a serodiagnostic antigen, legumain, by immunoproteomic analysis of excretory-secretory products of Clonorchis sinensis adult worms. Proteomics 9:3066–3078
Kaewkes S (2003) Taxonomy and biology of liver flukes. Acta Trop 88:177–186
Kaewkes S, Kaewkes W, Boonmars T, Sripa B (2012a) Effect of light intensity on Opisthorchis viverrini cercarial shedding levels from Bithynia snails—a preliminary study. Parasitol Int 61:46–48
Kaewkes W, Kaewkes S, Tesana S, Laha T, Sripa B (2012b) Fecal bacterial contamination in natural water reservoirs as an indicator of seasonal infection by Opisthorchis viverrini in snail intermediate hosts. Parasitol Int 61:49–51
Kaewkong W, Choochote W, Kanla P, Maleewong W, Intapan PM, Wongkham S, Wongkham C (2012a) Chromosomes and karyotype analysis of a liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini, by scanning electron microscopy. Parasitol Int 61:504–507
Kaewkong W, Imtawil K, Maleewong W, Intapan PM, Sri-Aroon P, Wongkham S, Wongkham C (2012b) Genome size estimation of liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini by real-time polymerase chain reaction based method. Parasitol Int 61:77–80
Kaewpitoon N, Kaewpitoon SJ, Ueng-arporn N, Rujirakul R, Churproong S, Matrakool L, Auiwatanagul S, Sripa B (2012) Carcinogenic human liver fluke: current status of Opisthorchis viverrini metacercariae in Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 13:1235–1240
Kaewpitoon N, Kootanavanichpong N, Kompor P, Chavenkun W, Kujapun J, Norkaew J, Ponphimai S, Matrakool L, Tongtawee T, Panpimanmas S, Rujirakul R, Padchasuwan N, Pholsripradit P, Eksanti T, Phatisena T, Loyd RA, Kaewpitoon SJ (2015) Review and current status of Opisthorchis viverrini infection at the community level in Thailand. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16:6825–6830
Kang TH, Yun DH, Lee EH, Chung YB, Bae YA, Chung JY, Kang I, Kim J, Cho SY, Kong Y (2004) A cathepsin F of adult Clonorchis sinensis and its phylogenetic conservation in trematodes. Parasitology 128:195–207
Kang S, Sultana T, Loktev VB, Wongratanacheewin S, Sohn WM, Eom KS, Park JK (2008) Molecular identification and phylogenetic analysis of nuclear rDNA sequences among three opisthorchid liver fluke species (Opisthorchiidae: Trematoda). Parasitol Int 57:191–197
Katokhin AV, Shekhovtsov SV, Konkow S, Yurlova NI, Serbina EA, Vodianitskai SN, Fedorov KP, Loktev VB, Muratov IV, Ohyama F, Makhnev TV, Pel'tek SE, Mordvinov VA (2008) Assessment of the genetic distinctions of Opisthorchis felineus from O. viverrini and Clonorchis sinensis by ITS2 and CO1 sequences. Dokl Biochem Biophys 421:214–217
Keiser J, Utzinger J (2005) Emerging foodborne trematodiasis. Emerg Infect Dis 11:1507–1514
Kenny PA, Bissell MJ (2003) Tumor reversion: correction of malignant behavior by microenvironmental cues. Int J Cancer 107:688–695
Khampoosa P, Jones MK, Lovas EM, Piratae S, Kulsuntiwong J, Prasopdee S, Srisawangwong T, Laha T, Sripanidkulchai B, Thitapakorn V, Tesana S (2018) Egg-hatching mechanism of human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini: a role for leucine aminopeptidases from the snail host, Bithynia siamensis goniomphalos. J Parasitol 104:388–397
Khan SA, Miras A, Pelling M, Taylor-Robinson SD (2007) Cholangiocarcinoma and its management. Gut 56:1755–1756
Khuntikeo N, Sithithaworn P, Loilom W, Namwat N, Yongvanit P, Thinkhamrop B, Kiatsopit N, Andrews RH, Petney TN (2016) Changing patterns of prevalence in Opisthorchis viverrini sensu lato infection in children and adolescents in northeast Thailand. Acta Trop 164:469–472
Khuntikeo N, Thinkhamrop B, Bundhamcharoen K, Andrews RH, Grundy-Warr C, Yongvanit P, Loilome W, Chamadol N, Kosuwan W, Sithithaworn P, Petney TN (2018) The socioeconomic burden of cholangiocarcinoma associated with Opisthorchis viverrini sensu lato infection in northeast Thailand: a preliminary analysis. Adv Parasitol 102:141–163
Kiatsopit N, Sithithaworn P, Sithithaworn J, Boonmars T, Tesana S, Pitaksakulrat O, Saijuntha W, Petney TN, Andrews RH (2011) Genetic relationships within the Opisthorchis viverrini species complex with specific analysis of O. viverrini from Savannakhet, Lao PDR by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Parasitol Res 108:211–217
Kiatsopit N, Sithithaworn P, Saijuntha W, Boonmars T, Tesana S, Sithithaworn J, Petney TN, Andrews RH (2012) Exceptionally high prevalence of infection of Bithynia siamensis goniomphalos with Opisthorchis viverrini cercariae in different wetlands in Thailand and Lao PDR. Am J Trop Med Hyg 86:464–469
Kiatsopit N, Sithithaworn P, Saijuntha W, Petney TN, Andrews RH (2013) Opisthorchis viverrini: implications of the systematics of first intermediate hosts, Bithynia snail species in Thailand and Lao PDR. Infect Genet Evol 14:313–319
Kiatsopit N, Sithithaworn P, Saijuntha W, Pitaksakulrat O, Petney TN, Webster JP, Andrews RH (2014) Analysis of the population genetics of Opisthorchis viverrini sensu lato in the Nam Ngum River wetland, Lao PDR, by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Parasitol Res 113:2973–2981
Kim YI, Yu ES, Kim ST (1989) Intraductal variant of peripheral cholangiocarcinoma of the liver with Clonorchis sinensis infection. Cancer 63:1562–1566
Kim TI, Na BK, Hong SJ (2009a) Functional genes and proteins of Clonorchis sinensis. Korean J Parasitol 47(Suppl):S59–S68
Kim TS, Cho SH, Huh S, Kong Y, Sohn WM, Hwang SS, Chai JY, Lee SH, Park YK, Oh DK, Lee JK, Working Groups in National Institute of Health, Korea Association of Health, Promotion (2009b) A nationwide survey on the prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections in the Republic of Korea, 2004. Korean J Parasitol 47:37–47
Kim TY, Lee YS, Yun JH, Kim JJ, Choi WH, Oh IH, Song HO, Chu JP (2010) A case of probable mixed-infection with Clonorchis sinensis and Fasciola sp.: CT and parasitological findings. Korean J Parasitol 48:157–160
Kim JH, Choi MH, Bae YM, Oh JK, Lim MK, Hong ST (2011) Correlation between discharged worms and fecal egg counts in human clonorchiasis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 5:e1339
King S, Scholz T (2001) Trematodes of the family Opisthorchiidae: a minireview. Korean J Parasitol 39:209–221
Kirby GM, Pelkonen P, Vatanasapt V, Camus AM, Wild CP, Lang MA (1994) Association of liver fluke (Opisthorchis viverrini) infestation with increased expression of cytochrome P450 and carcinogen metabolism in male hamster liver. Mol Carcinog 11:81–89
Kobayashi J, Vannachone B, Xeutvongsa A, Manivang K, Ogawa S, Sato Y, Pholsena K (1996) Prevalence of intestinal parasitic infection among children in two villages in Lao PDR. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 27:562–565
Kobayashi J, Vannachone B, Sato Y, Manivong K, Nambanya S, Inthakone S (2000) An epidemiological study on Opisthorchis viverrini infection in Lao villages. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 31:128–132
Komalamisra C (1999) Chromosomes and C-banding of Opisthorchis viverrini. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 30:576–579
Kwon YD, Cho PY, Hong SJ (2005) Clonorchis sinensis: molecular cloning and localization of myosin regulatory light chain. Parasitol Res 97:21–26
Laha T, Pinlaor P, Mulvenna J, Sripa B, Sripa M, Smout MJ, Gasser RB, Brindley PJ, Loukas A (2007) Gene discovery for the carcinogenic human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini. BMC Genomics 8:189
Lai DH, Wang QP, Chen W, Cai LS, Wu ZD, Zhu XQ, Lun ZR (2008) Molecular genetic profiles among individual Clonorchis sinensis adults collected from cats in two geographic regions of China revealed by RAPD and MGE-PCR methods. Acta Trop 107:213–216
Lai DH, Hong XK, Su BX, Liang C, Hide G, Zhang X, Yu X, Lun ZR (2016) Current status of Clonorchis sinensis and clonorchiasis in China. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 110:21–27
Laithavewat L, Grundy-Warr C, Khuntikeo N, Andrews RH, Petney TN, Yongvanit P, Banchonhattakit P, Sithithaworn P (2018) Analysis of a school-based health education model to prevent opisthorchiasis and cholangiocarcinoma in primary school children in northeast Thailand. Glob Health Promot. https://doi.org/10.1177/1757975918767622
Lan-Anh NT, Phuong NT, Murrell KD, Johansen MV, Dalsgaard A, Thu LT, Kim-Chi TT, Thamsborg SM (2009) Animal reservoir hosts and fish-borne zoonotic trematode infections on fish farms, Vietnam. Emerg Infect Dis 15:540–546
Laoprom N, Saijuntha W, Sithithaworn P, Wongkham S, Laha T, Ando K, Andrews RH, Petney TN (2009) Biological variation within Opisthorchis viverrini sensu lato in Thailand and Lao PDR. J Parasitol 95:1307–1313
Laoprom N, Sithithaworn P, Ando K, Sithithaworn J, Wongkham S, Laha T, Klinbunga S, Webster JP, Andrews RH (2010) Microsatellite loci in the carcinogenic liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini and their application as population genetic markers. Infect Genet Evol 10:146–153
Laoprom N, Sithithaworn P, Andrews RH, Ando K, Laha T, Klinbunga S, Webster JP, Petney TN (2012) Population genetic structuring in Opisthorchis viverrini over various spatial scales in Thailand and Lao PDR. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6:e1906
Laoprom N, Kiatsopit N, Sithithaworn P, Kopolrat K, Namsanor J, Andrews RH, Petney TN (2016) Cercarial emergence patterns for Opisthorchis viverrini sensu lato infecting Bithynia siamensis goniomphalos from Sakon Nakhon Province, Thailand. Parasitol Res 115:3313–3321
Lazutkina EA, Andreyev NI, Andreyeva SI, Gloer P, Vinarski MV (2009) On the taxonomic state of Bithynia troschelii var. sibirica Westerlund, 1886, a Siberian endemic bithyniid snail (Gastropoda: Bithyniidae). Mollusca 27:113–122
Le TH, Van De N, Blair D, Sithithaworn P, McManus DP (2006) Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini: development of a mitochondrial-based multiplex PCR for their identification and discrimination. Exp Parasitol 112:109–114
Le TH, Nguyen NT, Truong NH, De NV (2012) Development of mitochondrial loop-mediated isothermal amplification for detection of the small liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini (Opisthorchiidae; Trematoda; Platyhelminthes). J Clin Microbiol 50:1178–1184
Lee SU, Huh S (2004) Variation of nuclear and mitochondrial DNAs in Korean and Chinese isolates of Clonorchis sinensis. Korean J Parasitol 42:145–148
Lee JH, Rim HJ, Bak UB (1993) Effect of Clonorchis sinensis infection and dimethylnitrosamine administration on the induction of cholangiocarcinoma in Syrian golden hamsters. Korean J Parasitol 31:21–30
Lee JH, Yang HM, Bak UB, Rim HJ (1994) Promoting role of Clonorchis sinensis infection on induction of cholangiocarcinoma during two-step carcinogenesis. Korean J Parasitol 32:13–18
Lee JS, Kim IS, Sohn WM, Lee J, Yong TS (2006) Vaccination with DNA encoding cysteine proteinase confers protective immune response to rats infected with Clonorchis sinensis. Vaccine 24:2358–2366
Leiper RT (1915) Notes of the occurrence of parasites presumably rare in man. J R Army Med Corps 24:569–575
Li S, Shin JG, Cho PY, Kim TI, Hong ST, Hong SJ (2011) Multiple recombinant antigens of Clonorchis sinensis for serodiagnosis of human clonorchiasis. Parasitol Res 108:1295–1302
Li Y, Hu X, Liu X, Huang Y, Xu J, Zhao J, Wu Z, Yu X (2012) Serological diagnosis of clonorchiasis: using a recombinant propeptide of cathepsin L proteinase from Clonorchis sinensis as a candidate antigen. Parasitol Res 110:2197–2203
Lin R, Li X, Lan C, Yu S, Kawanaka M (2005) Investigation on the epidemiological factors of Clonorchis sinensis infection in an area of south China. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 36:1114–1117
Liu WQ, Liu J, Zhang JH, Long XC, Lei JH, Li YL (2007) Comparison of ancient and modern Clonorchis sinensis based on ITS1 and ITS2 sequences. Acta Trop 101:91–94
Liu GH, Li B, Li JY, Song HQ, Lin RQ, Cai XQ, Zou FC, Yan HK, Yuan ZG, Zhou DH, Zhu XQ (2012) Genetic variation among Clonorchis sinensis isolates from different geographic regions in China revealed by sequence analyses of four mitochondrial genes. J Helminthol 86:479–484
Lohachit C (2004-2005) Ecological studies of Bithynia siamensis goniomphalos, a snail intermediate host of Opisthorchis viverrini, in Khon Kaen Province, Northeast Thailand. Malacol Rev 37(38):1–26
Looss A (1907) On some parasites in the museum of the School of Tropical Medicine, Liverpool. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 1:123–152
Lovis L, Mak TK, Phongluxa K, Soukhathammavong P, Sayasone S, Akkhavong K, Odermatt P, Keiser J, Felger I (2009) PCR diagnosis of Opisthorchis viverrini and Haplorchis taichui infections in a Lao community in an area of endemicity and comparison of diagnostic methods for parasitological field surveys. J Clin Microbiol 47:1517–1523
Lovis L, Mak TK, Phongluxa K, Aye Soukhathammavong P, Vonghachack Y, Keiser J, Vounatsou P, Tanner M, Hatz C, Utzinger J, Odermatt P, Akkhavong K (2012) Efficacy of praziquantel against Schistosoma mekongi and Opisthorchis viverrini: a randomized, single-blinded dose-comparison trial. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6:e1726
Lowe S, Browne M, Boudjelas S, De Poorter M (2000) 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species A selection from the Global Invasive Species Database. In: The Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG) a specialist group of the Species Survival Commission (SSC) of the World Conservation Union (IUCN). Hollands Printing Ltd, Auckland
Lun ZR, Gasser RB, Lai DH, Li AX, Zhu XQ, Yu XB, Fang YY (2005) Clonorchiasis: a key foodborne zoonosis in China. Lancet Infect Dis 5:31–41
Mairiang E, Elkins DB, Mairiang P, Chaiyakum J, Chamadol N, Loapaiboon V, Posri S, Sithithaworn P, Haswell-Elkins M (1992) Relationship between intensity of Opisthorchis viverrini infection and hepatobiliary disease detected by ultrasonography. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:17–21
Mairiang E, Laha T, Bethony JM, Thinkhamrop B, Kaewkes S, Sithithaworn P, Tesana S, Loukas A, Brindley PJ, Sripa B (2012) Ultrasonography assessment of hepatobiliary abnormalities in 3359 subjects with Opisthorchis viverrini infection in endemic areas of Thailand. Parasitol Int 61:208–211
Manivong K, Komalamisra C, Waikagul J, Radomyos P (2009) Opisthorchis viverrini metacercariae in cyprinoid fish from three rivers in Khammouane Province, Lao PDR. J Trop Med Parasitol 32:23–29
Mas-Coma S, Bargues MD (1997) Human liver flukes: a review. Res Rev Parasitol 57:144–225
Mazidur Rahman SM, Choi MH, Bae YM, Hong ST (2012) Coproantigen capture ELISA for detection of Clonorchis sinensis infection in experimentally infected rats. Parasitol Int 61:203–207
Miyamoto K, Kirinoki M, Matsuda H, Hayashi N, Chigusa Y, Sinuon M, Chuor CM, Kitikoon V (2014) Field survey focused on Opisthorchis viverrini infection in five provinces of Cambodia. Parasitol Int 63:366–373
Molina CD, Molina MM, Molina JM (1988) Intestinal parasites in southeast Asian refugees two years after immigration. West J Med 149:422–425
Mordvinov VA, Yurlova NI, Ogorodova LM, Katokhin AV (2012) Opisthorchis felineus and Metorchis bilis are the main agents of liver fluke infection of humans in Russia. Parasitol Int 61:25–31
Mulvenna J, Sripa B, Brindley PJ, Gorman J, Jones MK, Colgrave ML, Jones A, Nawaratna S, Laha T, Suttiprapa S, Smout MJ, Loukas A (2010) The secreted and surface proteomes of the adult stage of the carcinogenic human liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini. Proteomics 10:1063–1078
Nagano I, Pei F, Wu Z, Wu J, Cui H, Boonmars T, Takahashi Y (2004) Molecular expression of a cysteine proteinase of Clonorchis sinensis and its application to an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunodiagnosis of clonorchiasis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 11:411–416
Nakeeb A, Pitt HA, Sohn TA, Coleman J, Abrams RA, Piantadosi S, Hruban RH, Lillemoe KD, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL (1996) Cholangiocarcinoma. A spectrum of intrahepatic, perihilar, and distal tumors. Ann Surg 224:463–473
Namsanor J, Sithithaworn P, Kopolrat K, Kiatsopit N, Pitaksakulrat O, Tesana S, Andrews RH, Petney TN (2015) Seasonal transmission of Opisthorchis viverrini sensu lato and a Lecithodendriid trematode species in Bithynia siamensis goniomphalos snails in Northeast Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg 93:87–93
Nawa Y, Doanh PN, Thaenkham U (2015) Is Opisthorchis viverrini an avian liver fluke? J Helminthol 89:255–256
Naylor RL, Goldburg RJ, Primavera JH, Kautsky N, Beveridge MC, Clay J, Folke C, Lubchenco J, Mooney H, Troell M (2000) Effect of aquaculture on world fish supplies. Nature 405:1017–1024
Ngern-klun R, Sukontason KL, Tesana S, Sripakdee D, Irvine KN, Sukontason K (2006) Field investigation of Bithynia funiculata, intermediate host of Opisthorchis viverrini in northern Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 37:662–672
Ngoen-Klan R, Piangjai S, Somwang P, Moophayak K, Sukontason K, Sukontason KL, Sampson M, Irvine K (2010) Emerging helminths infection in snails and cyprinoid fish in sewage treatment wetlands waters in Cambodia. Asian J Water Environ Pollut 7:13–21
Nguyen TT, Arimatsu Y, Hong SJ, Brindley PJ, Blair D, Laha T, Sripa B (2015) Genome-wide characterization of microsatellites and marker development in the carcinogenic liver fluke Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 114:2263–2272
Ogorodova LM, Freidin MB, Sazonov AE, Fedorova OS, Gerbek IE, Cherevko NA, Lebedeva NY (2007) A pilot screening of prevalence of atopic states and opisthorchosis and their relationship in people of Tomsk Oblast. Parasitol Res 101:1165–1168
Ohshima H, Bartsch H (1994) Chronic infections and inflammatory processes as cancer risk factors: possible role of nitric oxide in carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 305:253–264
Onsurathum S, Pinlaor P, Charoensuk L, Haonon O, Chaidee A, Intuyod K, Laummaunwai P, Boonmars T, Kaewkes W, Pinlaor S (2016a) Contamination of Opisthorchis viverrini and Haplorchis taichui metacercariae in fermented fish products in northeastern Thailand markets. Food Control 59:493–498
Onsurathum S, Pinlaor P, Haonon O, Chaidee A, Charoensuk L, Intuyod K, Boonmars T, Laummaunwai P, Pinlaor S (2016b) Effects of fermentation time and low temperature during the production process of Thai pickled fish (pla-som) on the viability and infectivity of Opisthorchis viverrini metacercariae. Int J Food Microbiol 218:1–5
Park GM (2007) Genetic comparison of liver flukes, Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini, based on rDNA and mtDNA gene sequences. Parasitol Res 100:351–357
Park GM, Yong TS (2001) Geographical variation of the liver fluke, Clonorchis sinensis, from Korea and China based on the karyotypes, zymodeme and DNA sequences. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 32(Suppl 2):12–16
Park GM, Im K, Huh S, Yong TS (2000a) Chromosomes of the liver fluke, Clonorchis sinensis. Korean J Parasitol 38:201–206
Park GM, Yong TS, Im K, Lee KJ (2000b) Isozyme electrophoresis patterns of the liver fluke, Clonorchis sinensis from Kimhae, Korea and from Shenyang, China. Korean J Parasitol 38:45–48
Parkin DM (2006) The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer 118:3030–3044
Parkin DM, Srivatanakul P, Khlat M, Chenvidhya D, Chotiwan P, Insiripong S, L'Abbe KA, Wild CP (1991) Liver cancer in Thailand. I. A case-control study of cholangiocarcinoma. Int J Cancer 48:323–328
Parkin DM, Ohshima H, Srivatanakul P, Vatanasapt V (1993) Cholangiocarcinoma: epidemiology, mechanisms of carcinogenesis and prevention. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2:537–544
Parvathi A, Sanath Kumar H, Kenchanna Prakasha B, Lu J, Xu X, Hu W, Feng Z, Karunasagar I, Karunasagar I (2007) Clonorchis sinensis: development and evaluation of a nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay. Exp Parasitol 115:291–295
Parvathi A, Umesha KR, Kumar S, Sithithaworn P, Karunasagar I, Karunasagar I (2008) Development and evaluation of a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay for the detection of Opisthorchis viverrini in fish. Acta Trop 107:13–16
Patz JA, Githeko AK, McCarty JP, Hussein S, Confalonieri U, de Wet N (2003) Climate change and infectious diseases. In: McMichael AJ, Campbell-Lendrum DH, Corvalán CF, Ebi KL, Githeko A, Scheraga JD, Woodward A (eds) Climate change and human health: risks and responses. World Health Organization, Malta, pp 103–132
Patz JA, Daszak P, Tabor GM, Aguirre AA, Pearl M, Epstein J, Wolfe ND, Kilpatrick AM, Foufopoulos J, Molyneux D, Bradley DJ, Members of the Working Group on Land Use Change and Disease Emergence (2004) Unhealthy landscapes: Policy recommendations on land use change and infectious disease emergence. Environ Health Perspect 112:1092–1098
Pauly A, Schuster R, Steuber S (2003) Molecular characterization and differentiation of opisthorchiid trematodes of the species Opisthorchis felineus (Rivolta, 1884) and Metorchis bilis (Braun, 1790) using polymerase chain reaction. Parasitol Res 90:409–414
Petney TN, Andrews RH (1998) Multiparasite communities in animals and humans: frequency, structure and pathogenic significance. Int J Parasitol 28:377–393
Petney T, Sithithaworn P, Andrews R, Kiatsopit N, Tesana S, Grundy-Warr C, Ziegler A (2012) The ecology of the Bithynia first intermediate hosts of Opisthorchis viverrini. Parasitol Int 61:38–45
Petney TN, Andrews RH, Saijuntha W, Wenz-Mucke A, Sithithaworn P (2013) The zoonotic, fish-borne liver flukes Clonorchis sinensis, Opisthorchis felineus and Opisthorchis viverrini. Int J Parasitol 43:1031–1046
Petney TN, Andrews RH, Saijuntha W, Tesana S, Prasopdee S, Kiatsopit N, Sithithaworn P (2018) Taxonomy, ecology and population genetics of Opisthorchis viverrini and its intermediate hosts. Adv Parasitol 101:1–39
Phalee A, Wongsawad C, Chuboon S (2008) Occurrence of Metacercariae in Cyprinoid Fish from Khumtakla District, Sakonnakorn Province. In: 34th Congress on Science and Technology of Thailand. Queen Sirikit National Convention Center, Thailand
Phan VT, Ersboll AK, Nguyen KV, Madsen H, Dalsgaard A (2010a) Farm-level risk factors for fish-borne zoonotic trematode infection in integrated small-scale fish farms in northern Vietnam. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 4:e742
Phan VT, Ersboll AK, Nguyen TT, Nguyen KV, Nguyen HT, Murrell D, Dalsgaard A (2010b) Freshwater aquaculture nurseries and infection of fish with zoonotic trematodes, Vietnam. Emerg Infect Dis 16:1905–1909
Phung LT, Loukas A, Brindley PJ, Sripa B, Laha T (2014) Retrotransposon OV-RTE-1 from the carcinogenic liver flukes Opisthorchis viverrini: Potential target for DNA-based diagnosis. Infect Genet Evol 21:443–451
Pinlaor S, Prakobwong S, Hiraku Y, Kaewsamut B, Dechakhamphu S, Boonmars T, Sithithaworn P, Pinlaor P, Ma N, Yongvanit P, Kawanishi S (2008) Oxidative and nitrative stress in Opisthorchis viverrini-infected hamsters: an indirect effect after praziquantel treatment. Am J Trop Med Hyg 78:564–573
Pinlaor S, Onsurathum S, Boonmars T, Pinlaor P, Hongsrichan N, Chaidee A, Haonon O, Limviroj W, Tesana S, Kaewkes S, Sithithaworn P (2013) Distribution and abundance of Opisthorchis viverrini metacercariae in cyprinid fish in Northeastern Thailand. Korean J Parasitol 51:703–710
Pitaksakulrat O, Sithithaworn P, Laoprom N, Laha T, Petney TN, Andrews RH (2013) A cross-sectional study on the potential transmission of the carcinogenic liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini and other fishborne zoonotic trematodes by aquaculture fish. Foodborne Pathog Dis 10:35–41
Pitaksakulrat O, Webster BL, Webster JP, Laha T, Saijuntha W, Lamberton PHL, Kiatsopit N, Andrews RH, Petney TN, Sithithaworn P (2018) Phylogenetic relationships within the Opisthorchis viverrini species complex with specific analysis of O. viverrini sensu lato from Sakon Nakhon, Thailand by mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequencing. Infect Genet Evol 62:86–94
Poirier MJ (1886) Trematodes nouveaux ou peu connus. Bull Soc Philom 7:20–40
Polyakov AV, Katokhin AV, Bocharova TA, Romanov KV, L'vova MN, Bonina OM, Yurlova NI, Mordvinov VA (2010) Comparative analysis of karyotypes of Opisthorchis felineus from West Siberia. Contemp Probl Ecol 3:1–3
Poopyruchpong N, Viyanant V, Upatham ES, Srivatanakul P (1990) Diagnosis of opisthorchiasis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using partially purified antigens. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 8:27–31
Pozio E, Armignacco O, Ferri F, Gomez Morales MA (2013) Opisthorchis felineus, an emerging infection in Italy and its implication for the European Union. Acta Trop 126:54–62
Prakobwong S, Suwannatrai A, Sancomerang A, Chaipibool S, Siriwechtumrong N (2017) A large scale study of the epidemiology and risk factors for the carcinogenic liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini in Udon Thani Province, Thailand. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 18:2853–2860
Prasopdee S, Kulsantiwong J, Piratae S, Khampoosa P, Thammasiri C, Suwannatrai A, Laha T, Grams R, Loukas A, Tesana S (2015) Temperature dependence of Opisthorchis viverrini infection in first intermediate host snail, Bithynia siamensis goniomphalos. Acta Trop 141:112–117
Prommas C (1927) Report of a case of Opisthorchis felineus in siam. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 21:9–10
Pumidonming W, Katahira H, Igarashi M, Salman D, Abdelbaset AE, Sangkaeo K (2018) Potential risk of a liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini infection brought by immigrants from prevalent areas: a case study in the lower Northern Thailand. Acta Trop 178:213–218
Qian MB, Chen YD, Yan F (2013) Time to tackle clonorchiasis in China. Infect Dis Poverty 2:4
Qiao T, Zheng PM, Ma RH, Luo XB, Luo ZL (2012) Development of a real-time PCR assay for the detection of Clonorchis sinensis DNA in gallbladder bile and stone samples from patients with cholecystolithiasis. Parasitol Res 111:1497–1503
Radomyos P, Radomyos B, Tungtrongchitr A (1994) Multi-infection with helminths in adults from northeast Thailand as determined by post-treatment fecal examination of adult worms. Trop Med Parasitol 45:133–135
Rahman SM, Bae YM, Hong ST, Choi MH (2011) Early detection and estimation of infection burden by real-time PCR in rats experimentally infected with Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 109:297–303
Ramsay RJ, Sithithaworn P, Prociv P, Moorhouse DE, Methaphat C (1989) Density-dependent fecundity of Opisthorchis viverrini in humans, based on faecal recovery of flukes. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 83:241–242
Riganti M, Pungpak S, Punpoowong B, Bunnag D, Harinasuta T (1989) Human pathology of Opisthorchis viverrini infection: a comparison of adults and children. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 20:95–100
Rim HJ (2005) Clonorchiasis: an update. J Helminthol 79:269–281
Rim HJ, Yoo KS (1979) Chemotherapeutic effect of praziquantel (Embay 8440) in the treatment of Clonorchiasis sinensis. Korea Univ Med J 16:459–470
Rim HJ, Sohn WM, Yong TS, Eom KS, Chai JY, Min DY, Lee SH, Hoang EH, Phommasack B, Insisengmay S (2008) Fishborne trematode metacercariae detected in freshwater fish from Vientiane Municipality and Savannakhet Province, Lao PDR. Korean J Parasitol 46:253–260
Rim HJ, Sohn WM, Yong TS, Eom KS, Chai JY, Min DY, Lee SH, Hoang EH, Phommasack B, Insisiengmay S (2013) Fishborne trematode metacercariae in Luang Prabang, Khammouane, and Saravane Province, Lao PDR. Korean J Parasitol 51:107–114
Rivolta S (1884) Sopra una specie di Distoma nel gatto e nel cane. Giorn Anat Fisiol Patol Anim 16:20–28
Ruangkunaporn Y, Akai PS, Chongsa-nguan M, Sri-Yeythong S, Kitikoon V, Chaicumpa W (1994) Changes in serum antibodies to Opisthorchis viverrini in humans and hamsters following treatment of opisthorchiasis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 12:83–84
Ruangsittichai J, Viyanant V, Vichasri-Grams S, Sobhon P, Tesana S, Upatham ES, Hofmann A, Korge G, Grams R (2006) Opisthorchis viverrini: identification of a glycine-tyrosine rich eggshell protein and its potential as a diagnostic tool for human opisthorchiasis. Int J Parasitol 36:1329–1339
Sadun EH (1955) Studies on Opisthorchis viverrini in Thailand. Am J Hyg 62:81–115
Saijuntha W, Sithithaworn P, Wongkham S, Laha T, Pipitgool V, Petney TN, Andrews RH (2006a) Genetic markers for the identification and characterization of Opisthorchis viverrini, a medically important food borne trematode in Southeast Asia. Acta Trop 100:246–251
Saijuntha W, Sithithaworn P, Wongkham S, Laha T, Pipitgool V, Petney TN, Chilton NB, Andrews RH (2006b) Enzyme markers to identify and characterize Opisthorchis viverrini in Thailand and Lao PDR. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 37(Suppl 3):43–47
Saijuntha W, Sithithaworn P, Wongkham S, Laha T, Pipitgool V, Tesana S, Chilton NB, Petney TN, Andrews RH (2007) Evidence of a species complex within the food-borne trematode Opisthorchis viverrini and possible co-evolution with their first intermediate hosts. Int J Parasitol 37:695–703
Saijuntha W, Sithithaworn P, Wongkham S, Laha T, Satrawaha R, Chilton NB, Petney TN, Andrews RH (2008) Genetic variation at three enzyme loci within a Thailand population of Opisthorchis viverrini. Parasitol Res 103:1283–1287
Saijuntha W, Sithithaworn P, Chilton NB, Petney TN, Klinbunga S, Satrawaha R, Webster JP, Andrews RH (2009) Impact of temporal changes and host factors on the genetic structure of a population of Opisthorchis viverrini sensu lato in Khon Kaen Province (Thailand). Parasitology 136:1057–1063
Saijuntha W, Duenngai K, Tangkawattana S, Petney TN, Andrews RH, Sithithaworn P (2018) Recent advances in the diagnosis and detection of Opisthorchis viverrini sensu lato in human and intermediate hosts for use in control and elimination programs. Adv Parasitol 101:177–214
Saksirisampant W, Wiwanitkit V, Akrabovorn P, Nuchprayoon S (2002) Parasitic infections in Thai workers that pursue overseas employment: the need for a screening program. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 33(Suppl 3):110–112
Sanpool O, Intapan PM, Thanchomnang T, Janwan P, Lulitanond V, Doanh PN, Van Hien H, Dung do T, Maleewong W, Nawa Y (2012) Rapid detection and differentiation of Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini eggs in human fecal samples using a duplex real-time fluorescence resonance energy transfer PCR and melting curve analysis. Parasitol Res 111:89–96
Sanpool O, Aung WPP, Rodpai R, Maleewong W, Intapan PM (2018) Human liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini (Trematoda, Opisthorchiidae) in Central Myanmar: new records of adults and metacercariae identified by morphology and molecular analysis. Acta Trop 185:149–155
Saowakontha S, Pipitgool V, Pariyanonda S, Tesana S, Rojsathaporn K, Intarakhao C (1993) Field trials in the control of Opisthorchis viverrini with an integrated programme in endemic areas of northeast Thailand. Parasitology 106(Pt 3):283–288
Satarug S, Lang MA, Yongvanit P, Sithithaworn P, Mairiang E, Mairiang P, Pelkonen P, Bartsch H, Haswell-Elkins MR (1996) Induction of cytochrome P450 2A6 expression in humans by the carcinogenic parasite infection, Opisthorchiasis viverrini. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 5:795–800
Satarug S, Haswell-Elkins MR, Sithithaworn P, Bartsch H, Ohshima H, Tsuda M, Mairiang P, Mairiang E, Yongvanit P, Esumi H, Elkins DB (1998) Relationships between the synthesis of N-nitrosodimethylamine and immune responses to chronic infection with the carcinogenic parasite, Opisthorchis viverrini, in men. Carcinogenesis 19:485–491
Sato M, Thaenkham U, Dekumyoy P, Waikagul J (2009) Discrimination of O. viverrini, C. sinensis, H. pumilio and H. taichui using nuclear DNA-based PCR targeting ribosomal DNA ITS regions. Acta Trop 109:81–83
Sawangsoda P, Sithithaworn J, Tesana S, Pinlaor S, Boonmars T, Mairiang E, Yongvanit P, Duenngai K, Sithithaworn P (2012) Diagnostic values of parasite-specific antibody detections in saliva and urine in comparison with serum in opisthorchiasis. Parasitol Int 61:196–202
Sayasone S, Odermatt P, Phoumindr N, Vongsaravane X, Sensombath V, Phetsouvanh R, Choulamany X, Strobel M (2007) Epidemiology of Opisthorchis viverrini in a rural district of southern Lao PDR. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 101:40–47
Schad GA, Anderson RM (1985) Predisposition to hookworm infection in humans. Science 228:1537–1540
Scholz T (2008) Family Opistorchiidae Looss, 1899. In: Bray RA, Gibson DI, Jones A (eds) Keys to the Trematoda. CAB International and Natural History Museum, London, pp 9–49
Scholz T, Ditrich O, Giboda M (1991) Differential diagnosis of opisthorchiid and heterophyid metacercariae (Trematoda) infecting flesh of cyprinid fish from Nam Ngum Dam Lake in Laos. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 22(Suppl):171–173
Schuster R (2002) Leberegelbefall. Denisia 184:291–315
Shekhovtsov SV, Katokhin AV, Romanov KV, Besprozvannykh VV, Fedorov KP, Yurlova NI, Serbina EA, Sithithaworn P, Kolchanov NA, Mordvinov VA (2009) A novel nuclear marker, Pm-int9, for phylogenetic studies of Opisthorchis felineus, Opisthorchis viverrini, and Clonorchis sinensis (Opisthorchiidae, Trematoda). Parasitol Res 106:293–297
Shekhovtsov SV, Katokhin AV, Kolchanov NA, Mordvinov VA (2010) The complete mitochondrial genomes of the liver flukes Opisthorchis felineus and Clonorchis sinensis (Trematoda). Parasitol Int 59:100–103
Shen C, Kim J, Lee JK, Bae YM, Choi MH, Oh JK, Lim MK, Shin HR, Hong ST (2007) Collection of Clonorchis sinensis adult worms from infected humans after praziquantel treatment. Korean J Parasitol 45:149–152
Shimalov VV, Shimalov VT (2003) Helminth fauna of the red fox (Vulpes vulpes Linnaeus, 1758) in southern Belarus. Parasitol Res 89:77–78
Shin HR, Lee CU, Park HJ, Seol SY, Chung JM, Choi HC, Ahn YO, Shigemastu T (1996) Hepatitis B and C virus, Clonorchis sinensis for the risk of liver cancer: a case-control study in Pusan, Korea. Int J Epidemiol 25:933–940
Shin HR, Oh JK, Lim MK, Shin A, Kong HJ, Jung KW, Won YJ, Park S, Park SJ, Hong ST (2010) Descriptive epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma and clonorchiasis in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 25:1011–1016
Sirisinha S, Sahassananda D, Bunnag D, Rim HJ (1990) Immunological analysis of Opisthorchis and Clonorchis antigens. J Helminthol 64:133–138
Sirisinha S, Chawengkirttikul R, Sermswan R, Amornpant S, Mongkolsuk S, Panyim S (1991) Detection of Opisthorchis viverrini by monoclonal antibody-based ELISA and DNA hybridization. Am J Trop Med Hyg 44:140–145
Sirisinha S, Chawengkirttikul R, Haswell-Elkins MR, Elkins DB, Kaewkes S, Sithithaworn P (1995) Evaluation of a monoclonal antibody-based enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for the diagnosis of Opisthorchis viverrini infection in an endemic area. Am J Trop Med Hyg 52:521–524
Sithithaworn P, Haswell-Elkins M (2003) Epidemiology of Opisthorchis viverrini. Acta Trop 88:187–194
Sithithaworn P, Tesana S, Pipitgool V, Kaewkes S, Pairojkul C, Sripa B, Paupairoj A, Thaiklar K (1991) Relationship between faecal egg count and worm burden of Opisthorchis viverrini in human autopsy cases. Parasitology 102(Pt 2):277–281
Sithithaworn P, Pipitgool V, Srisawangwong T, Elkins DB, Haswell-Elkins MR (1997) Seasonal variation of Opisthorchis viverrini infection in cyprinoid fish in north-east Thailand: implications for parasite control and food safety. Bull World Health Organ 75:125–131
Sithithaworn P, Sukavat K, Vannachone B, Sophonphong K, Ben-Embarek P, Petney T, Andrews R (2006) Epidemiology of food-borne trematodes and other parasite infections in a fishing community on the Nam Ngum reservoir, Lao PDR. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 37:1083–1090
Sithithaworn P, Nuchjungreed C, Srisawangwong T, Ando K, Petney TN, Chilton NB, Andrews RH (2007a) Genetic variation in Opisthorchis viverrini (Trematoda: Opisthorchiidae) from northeast Thailand and Laos PDR based on random amplified polymorphic DNA analyses. Parasitol Res 100:613–617
Sithithaworn P, Yongvanit P, Tesana S, Pairojkul C (2007b) Liver flukes. In: Murrell KD, Bernard F (eds) Food-borne parasitic zoonoses. Springer, Berlin, pp 3–52
Sithithaworn P, Andrews RH, Nguyen VD, Wongsaroj T, Sinuon M, Odermatt P, Nawa Y, Liang S, Brindley PJ, Sripa B (2012a) The current status of opisthorchiasis and clonorchiasis in the Mekong Basin. Parasitol Int 61:10–16
Sithithaworn P, Andrews RH, Petney TN, Saijuntha W, Laoprom N (2012b) The systematics and population genetics of Opisthorchis viverrini sensu lato: implications in parasite epidemiology and bile duct cancer. Parasitol Int 61:32–37
Sithithaworn P, Yongvanit P, Duenngai K, Kiatsopit N, Pairojkul C (2014) Roles of liver fluke infection as risk factor for cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 21:301–308
Smout MJ, Laha T, Mulvenna J, Sripa B, Suttiprapa S, Jones A, Brindley PJ, Loukas A (2009) A granulin-like growth factor secreted by the carcinogenic liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini, promotes proliferation of host cells. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000611
Sohn WM, Yong TS, Eom KS, Pyo KH, Lee MY, Lim H, Choe S, Jeong HG, Sinuon M, Socheat D, Chai JY (2012) Prevalence of Opisthorchis viverrini infection in humans and fish in Kratie Province, Cambodia. Acta Trop 124:215–220
Song L, Xu Z, Yu X (2007) Molecular cloning and characterization of a phosphoglycerate mutase gene from Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 101:709–714
Sornmani S, Schelp FP, Vivatanasesth P, Patihatakorn W, Impand P, Sitabutra P, Worasan P, Preuksaraj S (1984) A pilot project for controlling O. viverrini infection in Nong Wai, Northeast Thailand, by applying praziquantel and other measures. Arzneimittelforschung 34:1231–1234
Sri-Aroon P, Butraporn P, Limsomboon J, Kerdpuech Y, Kaewpoolsri M, Kiatsiri S (2005) Freshwater mollusks of medical importance in Kalasin Province, northeast Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 36:653–657
Sri-Aroon P, Intapan PM, Lohachit C, Phongsasakulchoti P, Thanchomnang T, Lulitanond V, Hiscox A, Phompida S, Sananikhom P, Maleewong W, Brey PT (2011) Molecular evidence of Opisthorchis viverrini in infected bithyniid snails in the Lao People's Democratic Republic by specific hybridization probe-based real-time fluorescence resonance energy transfer PCR method. Parasitol Res 108:973–978
Sripa B (2003) Pathobiology of opisthorchiasis: an update. Acta Trop 88:209–220
Sripa B, Kaewkes S, Sithithaworn P, Mairiang E, Laha T, Smout M, Pairojkul C, Bhudhisawasdi V, Tesana S, Thinkamrop B, Bethony JM, Loukas A, Brindley PJ (2007) Liver fluke induces cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS Med 4:e201
Sripa B, Mairiang E, Thinkhamrop B, Laha T, Kaewkes S, Sithithaworn P, Tessana S, Loukas A, Brindley PJ, Bethony JM (2009) Advanced periductal fibrosis from infection with the carcinogenic human liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini correlates with elevated levels of interleukin-6. Hepatology 50:1273–1281
Sripa B, Brindley PJ, Mulvenna J, Laha T, Smout MJ, Mairiang E, Bethony JM, Loukas A (2012) The tumorigenic liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini-multiple pathways to cancer. Trends Parasitol 28:395–407
Stensvold CR, Saijuntha W, Sithithaworn P, Wongratanacheewin S, Strandgaard H, Ornbjerg N, Johansen MV (2006) Evaluation of PCR based coprodiagnosis of human opisthorchiasis. Acta Trop 97:26–30
Sukontason K, Piangjai S, Muangyimpong Y, Sukontason K, Methanitikorn R, Chaithong U (1999) Prevalence of trematode metacercariae in cyprinoid fish of Ban Pao district, Chiang Mai Province, northern Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 30:365–370
Sun J, Xu J, Liang P, Mao Q, Huang Y, Lv X, Deng C, Liang C, de Hoog GS, Yu X (2011) Molecular identification of Clonorchis sinensis and discrimination with other opisthorchid liver fluke species using multiple Ligation-depended Probe Amplification (MLPA). Parasit Vectors 4:98
Suttiprapa S, Sotillo J, Smout M, Suyapoh W, Chaiyadet S, Tripathi T, Laha T, Loukas A (2018) Opisthorchis viverrini proteome and host-parasite interactions. Adv Parasitol 102:45–72
Suwannahitatorn P, Klomjit S, Naaglor T, Taamasri P, Rangsin R, Leelayoova S, Mungthin M (2013) A follow-up study of Opisthorchis viverrini infection after the implementation of control program in a rural community, central Thailand. Parasit Vectors 6:188
Suwannatrai A, Suwannatrai K, Haruay S, Piratae S, Thammasiri C, Khampoosa P, Kulsantiwong J, Prasopdee S, Tarbsripair P, Suwanwerakamtorn R, Sukchan S, Boonmars T, Malone JB, Kearney MT, Tesana S (2011) Effect of soil surface salt on the density and distribution of the snail Bithynia siamensis goniomphalos in northeast Thailand. Geospat Health 5:183–190
Suwannatrai A, Pratumchart K, Suwannatrai K, Thinkhamrop K, Chaiyos J, Kim CS, Suwanweerakamtorn R, Boonmars T, Wongsaroj T, Sripa B (2017) Modeling impacts of climate change on the potential distribution of the carcinogenic liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini, in Thailand. Parasitol Res 116:243–250
Tang Y, Cho PY, Kim BS, Hong SJ (2005) Molecular cloning and characterization of vitelline precursor protein B1 from Clonorchis sinensis. J Parasitol 91:1374–1378
Tatonova YV, Chelomina GN, Besprosvannykh VV (2012) Genetic diversity of nuclear ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 rDNA sequence in Clonorchis sinensis Cobbold, 1875 (Trematoda: Opisthorchidae) from the Russian Far East. Parasitol Int 61:664–674
Tatonova YV, Chelomina GN, Besprozvannykh VV (2013) Genetic diversity of Clonorchis sinensis (Trematoda: Opisthorchiidae) in the Russian southern Far East based on mtDNA cox1 sequence variation. Folia Parasitol 60:155–162
Tesana S, Srisawangwonk T, Kaewkes S, Sithithaworn P, Kanla P, Arunyanart C (1991) Eggshell morphology of the small eggs of human trematodes in Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 22:631–636
Tesana S, Thapsripair P, Thammasiri C, Prasopdee S, Suwannatrai A, Harauy S, Piratae S, Khampoosa P, Kulsantiwong J, Donthaisong C, Chalokepanrat P, Viyanant V, Malone JB (2012) Effects of Bayluscide on Bithynia siamensis goniomphalos, the first intermediate host of the human liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini, in laboratory and field trials. Parasitol Int 61:52–55
Thaenkham U, Nuamtanong S, Vonghachack Y, Yoonuan T, Sanguankiat S, Dekumyoy P, Prommasack B, Kobayashi J, Waikagul J (2011) Discovery of Opisthorchis lobatus (Trematoda: Opisthorchiidae): a new record of small liver flukes in the Greater Mekong Sub-region. J Parasitol 97:1152–1158
Thaewnongiew K, Singthong S, Kutchamart S, Tangsawad S, Promthet S, Sailugkum S, Wongba N (2014) Prevalence and risk factors for Opisthorchis viverrini infections in upper Northeast Thailand. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15:6609–6612
Toledo R, Bernal MD, Marcilla A (2011) Proteomics of foodborne trematodes. J Proteomics 74:1485–1503
Touch S, Komalamisra C, Radomyos P, Waikagul J (2009) Discovery of Opisthorchis viverrini metacercariae in freshwater fish in southern Cambodia. Acta Trop 111:108–113
Touch S, Yoonuan T, Nuamtanong S, Homsuwan N, Phuphisut O, Thaenkham U, Waikagul J (2013) Seasonal variation of Opisthorchis viverrini metacercarial infection in cyprinid fish from Southern Cambodia. J Trop Med Parasitol 36:1–7
Traub RJ, Macaranas J, Mungthin M, Leelayoova S, Cribb T, Murrell KD, Thompson RC (2009) A new PCR-based approach indicates the range of Clonorchis sinensis now extends to Central Thailand. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 3:e367
Traverso A, Repetto E, Magnani S, Meloni T, Natrella M, Marchisio P, Giacomazzi C, Bernardi P, Gatti S, Gomez Morales MA, Pozio E (2012) A large outbreak of Opisthorchis felineus in Italy suggests that opisthorchiasis develops as a febrile eosinophilic syndrome with cholestasis rather than a hepatitis-like syndrome. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 31:1089–1093
Tyson GL, El-Serag HB (2011) Risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 54:173–184
Upatham ES, Sukhapanth N (1980) Field studies on the bionomics of Bithynia siamensis siamensis and the transmission of Opisthorchis viverrini in Bangna, Bangkok, Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 11:355–358
Upatham ES, Viyanant V, Kurathong S, Brockelman WY, Menaruchi A, Saowakontha S, Intarakhao C, Vajrasthira S, Warren KS (1982) Morbidity in relation to intensity of infection in Opisthorchiasis viverrini: study of a community in Khon Kaen, Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg 31:1156–1163
Upatham ES, Viyanant V, Kurathong S, Rojborwonwitaya J, Brockelman WY, Ardsungnoen S, Lee P, Vajrasthira S (1984) Relationship between prevalence and intensity of Opisthorchis viverrini infection, and clinical symptoms and signs in a rural community in north-east Thailand. Bull World Health Organ 62:451–461
Upatham ES, Brockelman WY, Viyanant V, Lee P, Kaengraeng R, Prayoonwiwat B (1985) Incidence of endemic Opisthorchis viverrini infection in a village in northeast Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg 34:903–906
Upatham ES, Viyanant V, Brockelman WY, Kurathong S, Lee P, Kraengraeng R (1988) Rate of re-infection by Opisthorchis viverrini in an endemic northeast Thai community after chemotherapy. Int J Parasitol 18:643–649
Van Hellemond JJ, Retra K, Brouwers JF, van Balkom BW, Yazdanbakhsh M, Shoemaker CB, Tielens AG (2006) Functions of the tegument of schistosomes: clues from the proteome and lipidome. Int J Parasitol 36:691–699
Van CD, Doungchawee G, Suttiprapa S, Arimatsu Y, Kaewkes S, Sripa B (2017) Association between Opisthorchis viverrini and Leptospira spp. infection in endemic Northeast Thailand. Parasitol Int 66:503–509
Vichasri S, Viyanant V, Upatham ES (1982) Opisthorchis viverrini: intensity and rates of infection in cyprinoid fish from an endemic focus in Northeast Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 13:138–141
Vinogradoff K (1892) On a new species of distomum (Distomum sibericum) in the human liver (in Russian). Zentralblatt für allgemeine Pathologie u pathologische Anatomie 3:910–911
Viyanant V, Brockelman WY, Lee P, Ardsungnoen S, Upatham ES (1983) A comparison of a modified quick-Kato technique and the Stoll dilution method for field examination for Opisthorchis viverrini eggs. J Helminthol 57:191–195
Waikagul J (1998) Opisthorchis viverrini metacercaria in Thai freshwater fish. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 29:324–326
Waikagul J, Dekumyoy P, Chaichana K, Thairungroje Anantapruti M, Komalamisra C, Kitikoon V (2002) Serodiagnosis of human opisthorchiasis using cocktail and electroeluted Bithynia snail antigens. Parasitol Int 51:237–247
Wang X, Chen W, Huang Y, Sun J, Men J, Liu H, Luo F, Guo L, Lv X, Deng C, Zhou C, Fan Y, Li X, Huang L, Hu Y, Liang C, Hu X, Xu J, Yu X (2011) The draft genome of the carcinogenic human liver fluke Clonorchis sinensis. Genome Biol 12:R107
Wang YC, Feng CC, Sithithaworn P (2013) Environmental determinants of Opisthorchis viverrini prevalence in northeast Thailand. Geospat Health 8:111–123
Wang D, Young ND, Korhonen PK, Gasser RB (2018) Clonorchis sinensis and Clonorchiasis: the relevance of exploring genetic variation. Adv Parasitol 100:155–208
Watthanakulpanich D, Waikagul J, Dekumyoy P, Anantaphruti MT (2003) Studies on concomitant antigens of Bithynia funiculata for detection of antibody to Opisthorchis viverrini: effect of different centrifugal speeds on antigen preparation. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Publ Health 34(Suppl 2):114–120
Watwiengkam N, Sithithaworn J, Duenngai K, Sripa B, Laha T, Johansen MV, Sithithaworn P (2013) Improved performance and quantitative detection of copro-antigens by a monoclonal antibody based ELISA to diagnose human opisthorchiasis. Acta Trop 128:659–665
Wegner DH (1984) The profile of the trematodicidal compound praziquantel. Arzneimittelforschung 34:1132–1136
WHO (1995) Control of foodborne trematode infections. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wongratanacheewin S, Pumidonming W, Sermswan RW, Maleewong W (2001) Development of a PCR-based method for the detection of Opisthorchis viverrini in experimentally infected hamsters. Parasitology 122:175–180
Wongratanacheewin S, Pumidonming W, Sermswan RW, Pipitgool V, Maleewong W (2002) Detection of Opisthorchis viverrini in human stool specimens by PCR. J Clin Microbiol 40:3879–3880
Wongratanacheewin S, Sermswan RW, Sirisinha S (2003) Immunology and molecular biology of Opisthorchis viverrini infection. Acta Trop 88:195–207
Wongsaroj T, Sakolvaree Y, Chaicumpa W, Maleewong W, Kitikoon V, Tapchaisri P, Chongsa-nguan M, Cross JH (2001) Affinity purified oval antigen for diagnosis of Opisthorchiasis viverrini. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 19:245–258
Wongsawad C, Wongsawad P, Anuntalabhochai S, Chai JY, Sukontason K (2013) Occurrence and molecular identification of liver and minute intestinal flukes metacercariae in freshwater fish from Fang-Mae Ai Agricultural Basin, Chiang Mai province, Thailand. Asian Biomed 7:97–104
Worasith C, Kamamia C, Yakovleva A, Duenngai K, Wangboon C, Sithithaworn J, Watwiengkam N, Namwat N, Techasen A, Loilome W, Yongvanit P, Loukas A, Sithithaworn P, Bethony JM (2015) Advances in the diagnosis of human opisthorchiasis: development of Opisthorchis viverrini antigen detection in urine. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 9:e0004157
Wykoff DE, Harinasuta C, Juttijudata P, Winn MM (1965) Opisthorchis viverrini in Thailand-the life cycle and comparison with O. felineus. J Parasitol 51:207–214
Xiao JY, Gao JF, Cai LS, Dai Y, Yang CJ, Luo L, Agatsuma T, Wang CR (2013) Genetic variation among Clonorchis sinensis isolates from different hosts and geographical locations revealed by sequence analysis of mitochondrial and ribosomal DNA regions. Mitochondrial DNA 24:559–564
Xu M, Jiang Z, Huang W, Yin J, Ou S, Jiang Y, Meng L, Cao S, Yu A, Cao J, Shen Y (2018) Altered gut microbiota composition in subjects infected with Clonorchis sinensis. Front Microbiol 9:2292
Yang G, Jing C, Zhu P, Hu X, Xu J, Wu Z, Yu X (2006) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel lactate dehydrogenase gene from Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 99:55–64
Yongvanit P, Pinlaor S, Bartsch H (2012) Oxidative and nitrative DNA damage: key events in opisthorchiasis-induced carcinogenesis. Parasitol Int 61:130–135
Yossepowitch O, Gotesman T, Assous M, Marva E, Zimlichman R, Dan M (2004) Opisthorchiasis from imported raw fish. Emerg Infect Dis 10:2122–2126
Young ND, Campbell BE, Hall RS, Jex AR, Cantacessi C, Laha T, Sohn WM, Sripa B, Loukas A, Brindley PJ, Gasser RB (2010) Unlocking the transcriptomes of two carcinogenic parasites, Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis viverrini. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 4:e719
Zadesenets KS, Karamysheva TV, Katokhin AV, Mordvinov VA, Rubtsov NB (2012a) Distribution of repetitive DNA sequences in chromosomes of five opisthorchid species (Trematoda, Opisthorchiidae). Parasitol Int 61:84–86
Zadesenets KS, Katokhin AV, Mordvinov VA, Rubtsov NB (2012b) Comparative cytogenetics of opisthorchid species (Trematoda, Opisthorchiidae). Parasitol Int 61:87–89
Zadesenets KS, Katokhin AV, Mordvinov VA, Rubtsov NB (2012c) Telomeric DNA in chromosomes of five opisthorchid species. Parasitol Int 61:81–83
Zavoikin VD, Zelia OP, Bronshtein AM, Sokerina OA, Iarotskii LS, Firsova RA, Mikhailov MM, Gerasimov IV (1994) The procedure for the wide use of praziquantel in a complex of measures to control opisthorchiasis. 1. The tolerance and efficacy of different doses of biltricide during outpatient use in foci. Med Parazitol 24–27
Zhang HM, Jiang H, Xu B, Tan CP (2007) Preliminary survey on the infection status of freshwater fish with metacercariae of Metorchis orientalis in Guangxi province. In: The 1st International symposium on geospatial health, Lijiang, Yunnan, China, pp 39–41
Zheng N, Xu J, Wu Z, Chen J, Hu X, Song L, Yang G, Ji C, Chen S, Gu S, Ying K, Yu X (2005) Clonorchis sinensis: molecular cloning and functional expression of novel cytosolic malate dehydrogenase. Exp Parasitol 109:220–227
Zheng N, Huang B, Xu J, Huang S, Chen J, Hu X, Ying K, Yu X (2006) Enzymatic and physico-chemical characteristics of recombinant cMDH and mMDH of Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 99:174–180
Zheng N, Huang B, Xu J, Huang S, Chen J, Hu X, Ji C, Ying K, Yu X (2008) Cloning and expression of mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase of Clonorchis sinensis. Parasitol Res 102:989–995
Zheng M, Hu K, Liu W, Hu X, Hu F, Huang L, Wang P, Hu Y, Huang Y, Li W, Liang C, Yin X, He Q, Yu X (2011) Proteomic analysis of excretory secretory products from Clonorchis sinensis adult worms: molecular characterization and serological reactivity of a excretory-secretory antigen-fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Parasitol Res 109:737–744
Zhigileva ON, Zenovkina DV, Zamyatina TA (2013) Genetic variability and population differentiation of Opisthorchis felineus (Trematoda) in Western Siberian rivers. Russ J Genet Appl Res 3:371–377
Zhou Z, Hu X, Huang Y, Hu H, Ma C, Chen X, Hu F, Xu J, Lu F, Wu Z, Yu X (2007) Molecular cloning and identification of a novel Clonorchis sinensis gene encoding a tegumental protein. Parasitol Res 101:737–742
Zhou Z, Xia H, Hu X, Huang Y, Li Y, Li L, Ma C, Chen X, Hu F, Xu J, Lu F, Wu Z, Yu X (2008) Oral administration of a Bacillus subtilis spore-based vaccine expressing Clonorchis sinensis tegumental protein 22.3 kDa confers protection against Clonorchis sinensis. Vaccine 26:1817–1825
Ziegler AD, Andrews RH, Grundy-Warr C, Sithithaworn P, Petney TN (2011) Fighting liverflukes with food safety education. Science 331:282–283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Saijuntha, W., Sithithaworn, P., Kiatsopit, N., Andrews, R.H., Petney, T.N. (2019). Liver Flukes: Clonorchis and Opisthorchis. In: Toledo, R., Fried, B. (eds) Digenetic Trematodes. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1154. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-18616-6_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-18616-6_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-18615-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-18616-6
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)