Abstract
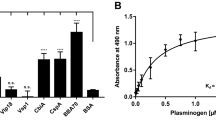
An important aspect of host-pathogen interactions is the interference of secreted proteins with the fibrinolytic system. Herein, we describe a modified ELISA method used to evaluate the interaction of a recombinant Schistosoma mansoni protein with plasminogen (PLG). Using this protocol, we demonstrated that a secreted protein, recombinant venom allergen-like protein 18 (rSmVAL18) acts as a plasminogen receptor increasing its activation into plasmin in the presence of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA). PLG binding was determined by immobilizing human PLG in the plate and incubating with the recombinant protein; competitive binding with a lysine analog demonstrated the interaction of the protein lysine residues with PLG Kringle domains. To assess the activation of S. mansoni recombinant protein-bound PLG, the amidolytic activity of generated plasmin was measured using the d-Val-Leu-Lys 4-nitroanilide dihydrochloride substrate.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbosa AS, Abreu PA, Neves FO et al (2006) A newly identified leptospiral adhesin mediates attachment to laminin. Infect Immun 74(11):6356–6364
Fernandes RS, Fernandes LG, de Godoy AS et al (2018) Schistosoma mansoni venom allergen-like protein 18 (SmVAL18) is a plasminogen-binding protein secreted during the early stages of mammalian-host infection. Mol Biochem Parasitol 221:23–31
Figueiredo BC, Da'dara A, Oliveira SC et al (2015) Schistosomes enhance plasminogen activation: the role of Tegumental Enolase. PLoS Pathog 11(12):e1005335
Lin YP, Lee DW, McDonough SP et al (2009) Repeated domains of leptospira immunoglobulin-like proteins interact with elastin and tropoelastin. J Biol Chem 284(29):19380–19391
Lahteenmaki K, Kuusela P, Korhonen TK (2001) Bacterial plasminogen activators and receptors. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25(5):531–552
Lahteenmaki K, Virkola R, Pouttu R et al (1995) Bacterial plasminogen receptors: in vitro evidence for a role in degradation of the mammalian extracellular matrix. Infect Immun 63(9):3659–3664
Vieira ML, Vasconcellos SA, Gonçalves AP et al (2009) Plasminogen acquisition and activation at the surface of leptospira species lead to fibronectin degradation. Infect Immun 77(9):4092–4101
Ramajo-Hernandez A, Pérez-Sánchez R, Ramajo-Martín V et al (2007) Schistosoma bovis: plasminogen binding in adults and the identification of plasminogen-binding proteins from the worm tegument. Exp Parasitol 115(1):83–91
de la Torre-Escudero E, Manzano-Román R, Pérez-Sánchez R et al (2010) Cloning and characterization of a plasminogen-binding surface-associated enolase from Schistosoma bovis. Vet Parasitol 173(1–2):76–84
Yang J, Qiu C, Xia Y et al (2010) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of Schistosoma japonicum enolase which is highly expressed at the schistosomulum stage. Parasitol Res 107(3):667–677
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP, grants 2012/23124-4, 2010/18486-9, 2014/50981-0 and 2017/06731-8), CNPq (grants 301229/2017-1 and 441449/2014-0) and Fundação Butantan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Fernandes, L.G.V., Fernandes, R.S., Nascimento, A.L.T.O., Leite, L.C.C. (2020). A Modified ELISA Method to Evaluate the Interaction of Schistosoma mansoni Proteins with Plasminogen. In: Timson, D.J. (eds) Schistosoma mansoni. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2151. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0635-3_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-0635-3_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-0634-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-0635-3
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols