Abstract
Kidneys are complex highly organized paired organs of nearly one million nephrons each. They rigorously process about 180 l of plasma daily to keep whole body homeostasis. To effectively perform such a titanic work, kidneys rely on mechanisms able to sense dynamic changes in composition and flow rates of protourine along the renal tubule. It is envisioned that Ca2+-permeable transient receptor potential (TRP) channels, and specifically mechanosensitive TRPV4, can serve to interpret these external mechanical cues in the form of elevated intracellular Ca2+ concentration. This, in turn, initiates multiple cellular responses and adaptation mechanisms. The current review summarizes up-to-date knowledge about the sites of TRPV4 expression in renal tissue as well as discusses the functional role of the channel in cellular responses to hypotonicity and tubular flow. We will also provide insights as to how TRPV4 fits into classical polycystin mechanosensory complex in cilia and will speculate about previously underappreciated clinical implication of pharmacological TRPV4 targeting in treatment of polycystic kidney disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Mechanosensitivity is a pivotal interface employed by living organisms to survey the surrounding environment. Many cell membranes are equipped with mechanosensitive ion channels that respond to osmotic gradients, shear stress, touch, vibration, and texture. These channels are present in a great variety of life forms: from bacteria to higher plants and vertebrate animals (reviewed in [42, 63]). A number of discovered mechanosensitive channels belong to a broad family of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels [13, 63, 67, 80, 102, 118]. They share the common feature of six transmembrane domains and are repeatedly reported to participate in cellular responses to a vast array of stimuli, including temperature, chemical agents, and mechanical forces [13, 57, 63, 66, 67, 80, 102, 118]. According to their sequence similarity, TRPs can be subdivided into seven subfamilies: classical or canonical (TRPC), vanilloid (TRPV), melastatin (TRPM), ankyrin (TRPA), no mechanoreceptor potential (TRPN), polycystin (TRPP), and mucolipidin (TRPML) [102, 118]. TRPV4 (initially named VROAC, VRL-2, TRP12, and OTRPC4) is the fourth member of TRPV subfamily, which was originally identified as a mammalian homolog of the Caenorhabditis elegans osmosensory protein OSM-9 [16, 22, 47, 64, 84, 115]. Since then, TRPV4 is, perhaps, one of the most recognized mammalian mechanosensitive TRP channels, which was routinely showed to be activated by hypoosmotic challenges and mechanical shear stress arising from fluid flow [6, 22, 27, 48, 49, 53, 56, 84, 91, 115, 117]. While direct gating of TRPV4 by mechanical stimuli is debatable [11, 63, 65, 66], substantial evidence argues that TRPV4 is indispensable for a wide variety of mechanosensitive processes [1, 6, 27, 47–49, 53, 56, 64, 80, 84, 91, 117]. The channel has a tetrameric subunit arrangement and possesses a modest selectivity to Ca2+ [22, 68, 69]. TRPV4 expression is detected in many tissues including the lung, heart, brain, endothelial cells, sensory ganglia, and kidney [6, 16, 22, 47, 84, 93, 115]. In the present review, we will discuss recent advances in our understanding of a role for TRPV4 in conferring mechanosensitive properties to renal epithelial cells with a special emphasis on the distal nephron.
TRPV4 expression pattern in the kidney
Initial studies revealed that TRPV4 transcript is abundantly expressed in the kidney [16, 47, 84, 115]. High levels of TRPV4 mRNA were found in the inner cortex with only punctate distribution in the outer cortex [84]. Early immunolocalization experiments demonstrated that TRPV4 is confined to the apical border of cells lining the distal tubules [16, 84]. Further study systematically characterized TRPV4 expression pattern in mouse and rat kidneys. Abundant TRPV4 expression was detected in the cortex, medulla, and papilla. TRPV4 immunofluorescent signal indicated that the protein might be restricted to nephron segments constitutively or conditionally impermeant to water [93]. Specifically, strong immunoreactivity was observed in the thin ascending limb, thick ascending limb, and distal convoluted tubule, while moderate levels of TRPV4 were detected in the collecting duct and papillary epithelium. TRPV4 subcellular distribution in these nephron segments was regarded as predominantly basolateral [93].
Recently, our group assessed the functional TRPV4 expression in mouse kidney using a combination of immunohistochemical, fluorescent imaging, and genetic tools. We demonstrated that TRPV4 is abundantly expressed along the entire length of collecting duct system throughout the medulla and cortex [6]. TRPV4 immunostaining was confined to aquaporin-2 (AQP2)-positive nephron segments: from the connecting tubule to the papillary collecting duct. The most apparent immunoreactivity to TRPV4 was observed near the apical membrane of principal cells, whereas intercalated cells had lower levels of TRPV4 protein with more diffuse subcellular distribution [6].
The observed variations in TRPV4 expression pattern may be attributable to differences in antibody specificity, technical aspects of the employed approaches, or animal preconditioning. As far as subcellular distribution of the channel is concerned, it should be noted that so far, there is no experimental evidence demonstrating functional activity of TRPV4 on the basolateral membrane of renal epithelium. On the other hand, apical localization of the channel is consistent with previous observations [15, 27] and functional assessment of TRPV4 activity in renal cells (see further). Nevertheless, taken together, the existing data strongly favor TRPV4 abundance in the distal part of the renal nephron.
Additional evidence for TRPV4 expression in the kidney comes from the cell lines endogenously expressing the channel. Thus, TRPV4 mRNA was detected in various cultured renal cells including smooth muscle-like mouse mesangial cells and several epithelial cell lines: M-1 cortical collecting duct (CCD) cells, Madin–Darby canine kidney (MDCK), and inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD-3) cells [20, 27, 41, 117].
TRPV4 as an osmosensor in the distal nephron
Renal micropuncture studies demonstrated that tubular fluid leaving the loop of Henle is typically hypotonic. Indeed, the osmolality of the fluid entering the latter distal convoluted tubule is around 100 mOsm/kg [14, 29]. In the absence of antidiuretic hormone vasopressin, low osmolality can be maintained along the entire length of the distal nephron from the cortex to the papillary collecting duct [14, 29, 30]. Thus, depending on systemic hydration status, distal segments of renal nephron are partially or completely exposed to hypotonic luminal milieu. Numerous observations suggest that renal cells respond to hypoosmolarity with elevations of intracellular Ca2+ [24, 25, 34, 53, 55, 90, 94, 95, 99, 117]. Considering the fact that renal TRPV4 expression is primarily restricted to the distal nephron, this strongly suggests that the channel is perfectly positioned to play an essential role in cellular adaptations to decreased osmolality of the tubular fluid.
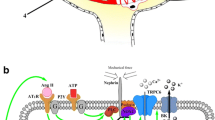
Our group convincingly demonstrated that hypotonicity stimulates endogenously expressed TRPV4 in M-1 CCD cells. Activation of TRPV4 with hypotonic medium was abolished by TRP channel inhibitor ruthenium red and after siRNA TRPV4 knockdown [117]. Of interest, hypotonicity is known to induce ATP release from many epithelia, including that of the distal nephron [73, 76]. The apically localized connexin 30 hemichannel serves as a conduit for ATP release at this site [81]. Numerous studies suggest that activation of purinergic signaling is a critical component of cellular responses to mechanical stress, such as hypotonicity [73]. We have recently documented a functional link between ATP cascade and TRPV4 in distal nephron cells [53]. We found that locally released ATP via P2Y2 receptors and phospholipase C (PLC) cascade stimulates TRPV4 for sustained elevation of intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i). Genetic ablation of TRPV4 results only in a transient elevation of [Ca2+]i due to Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum [53]. Similar mechanism was also reported in the perfused thick ascending limbs, where decreased osmolality of tubular fluid resulted in TRPV4-mediated ATP release leading to elevation of [Ca2+]i [79]. It appears that reciprocal coupling between purinergic signaling and TRPV4 activation is essential for proper mechanosensitive response in kidney cells. Indeed, distal nephrons from P2Y2−/− mice have markedly impaired responses to hypotonicity [53]. Activation of P2Y2 receptors by ATP or adenosine A1 receptors by ATP breakdown product—adenosine—inhibits vasopressin-dependent water transport in the collecting duct [76]. Consistently, P2Y2−/− mice display increased urinary concentrating ability and develop prominent hypertension associated with augmented sodium and water transport in the distal nephron [70, 76, 83, 124]. However, the precise role of TRPV4-mediated [Ca2+]i elevations in water reabsorption in the distal nephron and urinary concentrating ability remains elusive. Interestingly, in C. elegans mutants devoid of the endogenous TRPV isoform—OSM-9, TRPV4 expression restores avoidance responses to hypertonicity [49], while in mammalian cells, the channel is activated by hypotonic solutions [1, 9, 10, 25, 38, 53, 117]. This exciting discrepancy merits further investigation and, perhaps, can be attributed to different pathways regulating TRPV4 functioning in various species.
The significance of TRPV4 osmosensitivity in the collecting duct epithelium is further emphasized by an important role played by the channel in cell volume regulation and maintenance of the intracellular osmotic homeostasis. As mentioned before, the apical membrane of distal nephron cells typically faces a hypotonic tubular fluid, which can be further diluted under conditions of high water intake and subsequent water diuresis [14, 29, 30]. Exposure to a hypoosmotic environment induces cell swelling as a result of water entry along the osmotic gradient. The latter can be dramatically increased by water channels akin to AQP2 expressed on the apical membrane of principal cells in the collecting duct [24]. Dilution of the cytoplasm significantly alters the functioning of intracellular macromolecular machinery, while elevated hydrostatic pressure may compromise the integrity of the cell. Regulatory volume decrease (RVD) is a pivotal adaptation mechanism employed to preserve cellular osmotic balance in response to hypotonicity. In most cells, osmotic stress induces Ca2+ entry, which is followed by the efflux of ions and osmotically active organic solutes (reviewed in [36, 43, 44, 113]). Recent studies proposed that in renal cortical collecting duct, cell association of AQP2 and TRPV4 is required for Ca2+ entry induced by hypotonicity and subsequent RVD response [25]. Both elevation of [Ca2+]i induced by hypotonic solutions and the following RVD response were impeded after depolymerization of tubulin microtubules with colchicine and actin microfilaments with cytochalasin. This points to the importance of cytoskeleton integrity for hypotonicity-induced TRPV4-mediated [Ca2+]i increase and volume regulation in collecting duct epithelium [24, 25]. Consistently, microtubule-associated protein 7 was shown to interact with TRPV4 both in vitro and in renal cortex. This interaction enhances the channel expression on the cellular membrane [87]. A few observations indicate that N-terminal ankyrin repeat domain (ARD) is responsible for correct TRPV4 trafficking to the plasma membrane [22, 47]. It might anchor the channel to cytoskeleton or establish/constitute a mechanical link necessary for proper gating. Interestingly, deletion of ARD dramatically impairs TRPV4 mechanosensitivity [22, 47]. TRPV4 also significantly improves RVD, when expressed in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, which normally have a poor response to decreased osmolarity [5]. A functional interaction between TRPV4 and F-actin is critical for sensing hypotonicity and the onset of RVD in this model [4]. Another study demonstrated that functional interplay between TRPV4 and aquaporin-5 observed in salivary gland epithelia is critical for RVD induced by hypotonic swelling in this tissue [50].
The aforementioned experiments resonate with the initial observations in heterologous cellular systems demonstrating that TRPV4 is highly sensitive to changes in extracellular osmolality [47, 84]. Cells transfected with TRPV4 responded to hypotonic solution with elevations of [Ca2+]i. Even minor (as low as 1–10 %) fluctuations of extracellular osmolality significantly altered Ca2+ influx [47, 84]. On the contrary, increased osmolality (above 300 mOsmol/l) decreased [Ca2+]i levels and currents in the cells exhibiting spontaneous activity [84]. TRPV4-mediated currents in CHO cells were significantly increased by inflation of cell volume, achieved by positive pressure through a patch pipette [88]. The latter closely resembles cell swelling induced by hypotonicity. Subsequently, TRPV4 has been suggested to act as an osmolality sensor in the airway smooth muscle cells [38] and function as an osmotransducer in primary afferent nociceptive nerve fibers [1].
Consistent with the osmosensitive properties of the channel, TRPV4−/− mice exhibit abnormal osmotic regulation [48, 56]. Initially, these abnormalities were attributed to disruption of central TRPV4 signaling, specifically, in the sensory neurons of organum vasculosum lamina terminalis (OVLT) [48]. This hypothalamic brain nucleus, which is located outside the blood–brain barrier, regulates the secretion of antidiuretic hormone and controls the osmolality of extracellular fluid [80]. Subsequently, it was shown that modulation of OVLT neurons by tonicity or mechanical stimulation was unaffected by deletion of TRPV4, but rather requires TRPV1 [12]. The exact mechanism, by which hypertonicity modulates the activity of OVLT neurons, remains to be determined, and it is unclear whether TRPV1 and TRPV4 both contribute to this process. Finally, a recent study demonstrated that TRPV4-expressing thoracic dorsal root ganglia neurons innervating hepatic blood vessels detect physiologically pertinent decreases in blood osmolality. These hepatic sensory neurons respond even to small changes in osmolality (~15 mOsm). The evoked ionic currents have a pharmacological and biophysical profile similar to that of TRPV4 channel [45]. In TRPV4−/− mice, hepatic sensory neurons do not exhibit osmosensitive inward currents and activation of peripheral osmoreceptors is abolished [45]. The important osmosensitive role of peripherally expressed TRPV4 is further underscored by the observation that patients with liver transplants, which are, presumably, denervated, have a significantly higher baseline blood osmolality compared to a healthy control cohort [45]. Interestingly, genetic ablation of TRPV4 also significantly attenuates sensitization of nociceptive nerve fibers to mechanical and hypotonic stimuli induced by inflammatory mediators [9]. Endothelial cells in TRPV4 knockouts show a decreased response to hypotonic solutions as well [106]. Since the existing evidence arguing for the involvement of renal TRPV4 in systemic osmoregulation is scanty, future studies testing this highly probable mechanism are granted.
Extensive studies provide insights into the mechanisms underlying regulation of TRPV4 activity by hypoosmolality. The accrued evidence suggests that hypotonicity does not directly result in channel opening, but rather leads to stimulation of intracellular signaling cascades to activate TRPV4 [69, 86, 107, 111, 117]. Production of arachidonic acid metabolites—epoxyeicosatrienoids, through phospholipase A2 (PLA2)–cytochrome P450 epoxygenase (CYP450) pathway, appears to be a dominant mechanism inducing hypotonic activation of the channel [107]. Consistently, activation of TRPV4 by osmotic cell swelling is virtually abolished by four structurally unrelated PLA2 inhibitors [107]. CYP450 blockers also strongly diminish [Ca2+]i elevations induced by hypotonicity [107]. Yet, other studies indicate that phosphorylation by Src-family tyrosine kinase could also be involved in TRPV4-mediated response to anisotonic stress [112, 119]. N-terminal proline-rich domain of TRPV4 interacts with PACSIN3 protein, which strongly inhibits the basal activity of the channel and its activation by cell swelling [15, 18]. The interaction with PACSIN3 affects both the expression of the channel on the plasma membrane and its gating properties [15, 18, 22]. TRPV4 sensitivity to hypotonicity is greatly augmented at physiological temperature (+37 °C) [27, 107]. However, robust [Ca2+]i elevations in response to hypotonic solution were also observed at room temperature [53, 84, 107]. Intact intracellular environment and cytoskeleton structure appear to be important prerequisites for TRPV4-mediated responses to reduced osmolarity [4, 25, 87, 109]. Nevertheless, despite this vigorous effort, comprehensive understanding of TRPV4 regulation by hypotonicity is just beginning to emerge.
TRPV4 as a sensor of tubular fluid flow
Another focus in the field of TRPV4 functioning in the kidney is sensitivity of the channel to the tubular fluid flow. Renal tubule and particularly distal nephron is subjected to a highly variable flow of the protourine. The variations can be induced acutely by altered glomerular filtration rate [39, 46, 122], tubuloglomerular feedback [37], renal pelvic peristalsis [21], or use of diuretics; and chronically during diabetes [71], hypertensive states [3, 19], and upon variations of dietary sodium [59], potassium [8], and protein intake [78]. Luminal fluid mechanics affects the cells of the tubular lining exerting shear stress, transmural pressure, and stretch. Extensive support from the literature suggests that [Ca2+]i elevations mediate cellular responses to mechanical stimuli in the distal nephron [28, 51–53, 61, 72, 73, 116]. Indeed, the distal nephron is a well-recognized flow-sensitive tissue, where luminal flow is regarded as an important determinant of vectorial electrolyte transport [52, 58, 60, 77, 116]. Again, taking into consideration predominantly distal nephron TRPV4 expression, this strongly favors the idea that TRPV4 can participate in flow sensing.
Virtually all aspects of electrolyte transport, including K+ secretion [60, 77], Na+ reabsorption [58] and, importantly, Ca2+ influx [52, 116] were shown to be flow sensitive both in native collecting duct and cultured cells. A subsequent study demonstrated that luminal, but not basolateral, application of a TRPV4 agonist—4α-PDD—significantly enhances flow-dependent Na+ reabsorption and K+ secretion in perfused murine collecting ducts [91]. The effects of flow and 4α-PDD were abolished in TRPV4−/− mice. Interestingly, enhanced urinary K+ excretion was diminished in TRPV4 knockouts following intravenous injection of a loop diuretic—furosemide [91]. Furthermore, Ca2+ influx through TRPV4 was shown to be a critical component of purinergic response in aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron [53]. Since ATP release from distal nephron cells is known to be stimulated by mechanical stress [79, 81], purinergic signaling serves as an important facilitator of TRPV4-mediated [Ca2+]i elevations in response to flow. The most compelling evidence for a flow-sensitive nature of TRPV4 was provided by our group using ratiometric Fura 2 Ca2+ imaging in individual cells of split-opened distal nephrons. We showed that elevated fluid flow induced a rapid and sustained influx of Ca2+ in both collecting duct and connecting tubule cells [6]. Principal cells exhibited larger responses to flow when compared to intercalated cells. This is consistent with higher levels of TRPV4 expression in the former cell type [6]. Elevations of [Ca2+]i were abolished by the TRP channel inhibitor—ruthenium red, or in tubules isolated from TRPV4-deficient animals [6]. These data are in full agreement with our previous studies, demonstrating that heterologously (in HEK293 and CHO cells) and endogenously (in M-1 CCD cells) expressed TRPV4 is activated by increased flow [27, 117]. Transfection of M-1 CCD and TRPV4-expressing HEK cells with siRNA specific to TRPV4 leads to a loss of flow-induced Ca2+ influx [117]. Consistently, shear stress produced by increased viscous load activates TRPV4 in hamster oviductal ciliary cells, which natively express the channel, and TRPV4-transfected HeLa cells [2]. Endogenously expressed TRPV4 also exhibits sensitivity to flow in carotid artery endothelial cells [40, 54]. Therefore, an emerging body of evidence demonstrates that TRPV4 functions as a sensor/transducer of flow-induced mechanical stimuli in collecting duct and, likely, in other epithelia.
Little is known about the mechanisms underlying TRPV4 activation by flow/shear stress. Slow onset rate of TRPV4 responses to flow [6, 20, 117] may indicate indirect stimulation. However, direct activation of the channel by flow is not completely ruled out. Similarly to hypotonic stress, flow activation of TRPV4 in ciliated oviductal cells and cerebral arteries also seems to involve PLA2-dependent pathway [2, 54]. Increased temperature is a potent enhancer of TRPV4-mediated response to flow [117], though flow-induced Ca2+ influx via TRPV4 was repeatedly demonstrated at room temperature [6, 20, 40, 54]. In addition, channel gating is modulated by tyrosine phosphorylation [112, 119], protein kinase C [27], external and internal Ca2+ concentrations [85, 86, 105, 110], and PLC activity [23, 53]. However, these signaling cascades likely sensitize TRPV4 to mechanical stimuli rather than directly activate the channel.
TRPV4 association with polycystin-2
Recent studies suggest that mechanosensitive nature of [Ca2+]i elevations in distal nephron cells could be even more complex since TRPV4 is likely a part of a larger flow-sensing apparatus. Specifically, it was shown that TRPV4 forms a mechanosensitive complex with another TRP family member—polycystin-2 (TRPP1 according to the current IUPHAR nomenclature, also widely referred to as TRPP2 or PKD2) [20, 41, 82]. The complex has a putative 2:2 stoichiometry and an alternating subunit arrangement [82]. The data demonstrate that flow-induced Ca2+ entry into cultured collecting duct cells is mediated by heteromeric TRPV4-TRPP2 channels localized to the primary cilium [20, 41]. This multifunctional apical structure is thought to work as a sensory cellular antenna in the tubular lumen, reporting velocity of the tubular flow [17, 74, 75]. The expression of dominant negative constructs for TRPV4 and TRPP2 each abolished flow-induced Ca2+ influx in M-1 CCD cells [20]. This argues that both proteins are equally important to maintain mechanosensitive responses in collecting duct renal epithelium. Interestingly, only transient [Ca2+]i responses to flow are observed in HEK293 cells heterologously expressing TRPV4 construct alone [20]. However, simultaneous expression of TRPV4 and TRPP2 results in a sustained flow-induced Ca2+ influx [20], similar to that observed by our group in native tissue [6]. This supports the concept that TRPV4 serves as a valuable component of mechanosensitive complex on the primary cilium of renal epithelium. Interestingly, TRPV4 was also shown to be coexpressed with polycystin-2 and localized to an analogous ciliary structure in murine oviduct lining cells [92] and cholangiocytes [31].
TRPV4 in polycystic kidney disease
Polycystin-2 gained its mere scientific renown as a Ca2+-permeable channel and a crucial part of the polycystin mechanosensitive complex, localized to the primary cilium of renal epithelial cells [61]. Defects in polycystin-2 or its partnering protein polycystin-1 result in the development of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) [33, 97]. With the frequency of 1:400–1,000, ADPKD is the most common in the family polycystic kidney diseases (PKD) [33, 89, 97]. PKD are characterized by formation of numerous fluid-filled cysts within the kidney [33, 89, 96, 114]. Expanding cysts invade the adjacent parenchyma, causing decline of the kidney function, eventually progressing to the end-stage renal disease (ESRD) [33, 89]. Typically diagnosed in adults, ADPKD accounts for 5–9 % of the individuals with ESRD requiring dialysis or kidney transplantation. In approximately 85 % of cases, ADPKD is caused by mutations in PKD1 gene encoding a large receptor-like protein—polycystin-1. The remaining 15 % of ADPKD patients have mutations in PKD2 gene, encoding polycystin-2 [33, 89, 97]. Polycystins were reported to interact at their carboxyl termini to form a heteromultimeric Ca2+-permeable mechanosensitive complex [32, 100, 101]. Perhaps, defects in either of the proteins preclude the binding of polycystins or render the complex inactive.
Another form of PKD closely related to mechanosensitive properties of renal epithelium is autosomal recessive PKD (ARPKD). It has the estimated incidence of 1:20,000 and causes morbidity and mortality in utero and neonates [33, 89]. The genetic basis of the disease lies in the mutations of PKHD1 gene, encoding a multidomain integral protein—fibrocystin (or polyductin) [33, 89, 123]. The function of fibrocystin merits further investigation. However, several observations suggest that the protein normally interacts with polycystin-2 as a part of the polycystin multiprotein complex, regulating [Ca2+]i response to external stimuli [31, 61, 108], and mutations in the PKHD1 gene prevent these interactions. Based on the initial studies, polycystin-1 is suggested to be a primary mechanosensor, which triggers a Ca2+ influx through polycystin-2 in response to elevated flow, while fibrocystin serves as a regulator of the mechanosensitive polycystin complex [31, 61, 108]. Nevertheless, the exact role of both polycystins and fibrocystin in the regulation of [Ca2+]i levels remains to be determined.
Despite different genetic mutations that underlie the two forms of PKD, cystic epithelia share common phenotypic abnormalities. During the disease onset and progression, renal cysts are predominantly (in ADPKD patients) [98, 103] or exclusively (individuals with ARPKD) [104, 123] derived from the collecting duct. At the cellular level, PKD progression is associated with transformation of well-differentiated slowly proliferating reabsorptive epithelia to partially dedifferentiated secretory epithelia with polarization defects and high rates of proliferation and apoptosis [89]. Experimental evidence suggests that enhanced proliferation observed during PKD is related to the inability to sense mechanical stimuli and decreased basal [Ca2+]i levels [26, 33, 61, 62, 120, 121]. This is consistent with the function of polycystin/fibrocystin complex as a regulator of [Ca2+]i in response to environmental stimuli and its suggested role in maintaining the differentiated state of the renal epithelia. However, it is unclear whether the polycystins serve as a route for Ca2+ influx per se or they trigger other mechanisms to elevate [Ca2+]i. Interestingly, a recent study suggests that polycystin-2 fails to respond to mechanical stimuli on its own and acquires mechanosensitive properties only after heteromerization with TRPV4 [20, 41]. Coimmunoprecipitation and double-immunostaining studies demonstrate physical interaction and colocalization of polycystin-2 and TRPV4 in the primary cilium [20, 41], whereas Ca2+ imaging in MDCK and M-1 CCD cells shows that TRPV4 and TRPP2 form a functional complex, which is crucial for flow sensation [20, 41]. This disputes the exclusive role of polycystin complex as a mechanosensor in CD and is consistent with cumulative evidence increasingly appreciating TRPV4 involvement in mechanosensitivity and maintenance of [Ca2+]i homeostasis in CD epithelium. Interestingly, ADPKD patients have significant defects in osmoregulation, affecting the release of vasopressin in response to increased plasma osmolality upon water deprivation [7, 35]. This phenotype is similar to that observed in TRPV4−/− mice showing a lower increase in circulating vasopressin upon hypertonic stress and being more hyperosmolar than wild-type littermates [48]. Finally, recent finding points to TRPV4 involvement in PKD progression, demonstrating that systemic stimulation of TRPV4 with a highly selective agonist—GSK1016790A—significantly inhibits cell proliferation in the liver and decreases renal cystic area and kidney-to-body weight ratio pointing to a possible clinical implication of TRPV4 targeting in PKD treatment [31]. It appears that the relationship between mechanosensitivity and PKD progression is not as straightforward, as it was originally thought. Indeed, TRPV4-deficient zebrafish and mice lack flow-induced [Ca2+]i response, but do not develop cysts [41]. Therefore, future studies are necessary to determine the extent of TRPV4 involvement in PKD progression.
Concluding remarks
During the last decade, our understanding of the role that TRPV4 plays in the kidney has greatly advanced. Multiple studies identified the distal part of the renal nephron as a primary segment expressing TRPV4. A combination of new approaches in knockout and transgenic animals with numerous techniques probing TRPV4 expression, subcellular localization, and function revealed that TRPV4 is paramount for sensitivity of distal nephron epithelium to decreased osmolarity and flow-induced shear stress. Substantial evidence argues that the channel is involved in local regulation of transmural ion transport in the distal nephron by flow and hypotonicity. Recent studies revise the current scientific paradigm and shift it towards the idea that TRPV4 is a vital part of a larger multimolecular mechanosensitive complex, which requires orchestrated interaction of multiple components to maintain a proper mechanosensitive response. Figure 1 summarizes the evidence supporting this idea. It includes but, perhaps, is not limited to modulation of TRPV4 sensitivity to hypoosmolarity by epoxyeicosatrienoic acids or PACSIN3 protein and reciprocal activation of TRPV4 by purinergic cascade. Finally, heteromerization of TRPV4 with other proteins akin to polycystin-2 leads to formation of new complexes with a unique set of features. This opens another exciting chapter in the field of renal mechanosensitive signaling. It appears that until now, the physiological role of TRPV4 in the kidney was underappreciated as polycystin complex and, specifically, polycystin-2 was considered to be a major Ca2+-permeable channel, implicated in mechanosensation. While direct experimental evidence demonstrating polycystin-2 mechanosensitive properties is scanty, a mounting body of evidence clearly demonstrates that TRPV4 is pivotal to mechanosensitivity of CD cells and maintenance of [Ca2+]i balance under normal physiological conditions. Moreover, stimulation of the channel in the animals with ARPKD drastically attenuates renal manifestations of this devastating disease. Beneficial actions of TRPV4 activation on disease progression make the channel an attractive pharmacological target for development of effective therapeutic approaches in PKD treatment.
Proposed scheme, illustrating the involvement of TRPV4 in mechanosensitivity in the distal nephron cells. PLA 2 phospholipase A2, AA arachidonic acid, CYP450 cytochrome P450 epoxygenase, EETs epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, PC-1 polycystin-1, PKC protein kinase C, PLC phospholipase C, P2Y2R P2Y2 receptor, Cx30 connexin 30 hemichannel. The blue octagon represents the proline-rich domain. In the kidney, TRPV4 forms a heteromeric channel with polycystin-2 (TRPP2), which is a part of a larger mechanosensitive complex also involving of PC-1. Mechanical stress stimulates PLA2–CYP450 pathway, which metabolizes AA to EETs. EETs activate TRPV4 channel to elicit Ca2+ influx in response to hypotonicity or elevated flow. This activation can be prevented by interaction of TRPV4 N-terminal proline-rich domain with PACSIN3 protein. On the other hand, mechanical stimuli induce ATP release from distal nephron cells through Cx30 hemichannels. Locally released ATP binds to purinergic P2Y2 receptors on the apical membrane of renal epithelium. This leads to Gq/11-dependent activation of PLC and, likely, PKC and further augmenting TRPV4 activity
References
Alessandri-Haber N, Yeh JJ, Boyd AE, Parada CA, Chen X, Reichling DB, Levine JD (2003) Hypotonicity induces TRPV4-mediated nociception in rat. Neuron 39:497–511
Andrade YN, Fernandes J, Vazquez E, Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Arniges M, Sanchez TM, Villalon M, Valverde MA (2005) TRPV4 channel is involved in the coupling of fluid viscosity changes to epithelial ciliary activity. J Cell Biol 168:869–874
Baer PG, Bianchi G, Liliana D (1978) Renal micropuncture study of normotensive and Milan hypertensive rats before and after development of hypertension. Kidney Int 13:452–466
Becker D, Bereiter-Hahn J, Jendrach M (2009) Functional interaction of the cation channel transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) and actin in volume regulation. Eur J Cell Biol 88:141–152
Becker D, Blase C, Bereiter-Hahn J, Jendrach M (2005) TRPV4 exhibits a functional role in cell-volume regulation. J Cell Sci 118:2435–2440
Berrout J, Jin M, Mamenko M, Zaika O, Pochynyuk O, O'Neil RG (2012) Function of transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4 (TRPV4) as a mechanical transducer in flow-sensitive segments of renal collecting duct system. J Biol Chem 287:8782–8791
Bichet DG (2012) A defect in vasopressin secretion in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int 82:1051–1053
Cheema-Dhadli S, Lin SH, Keong-Chong C, Kamel KS, Halperin ML (2006) Requirements for a high rate of potassium excretion in rats consuming a low electrolyte diet. J Physiol 572:493–501
Chen X, Alessandri-Haber N, Levine JD (2007) Marked attenuation of inflammatory mediator-induced C-fiber sensitization for mechanical and hypotonic stimuli in TRPV4−/− mice. Mol Pain 3:31
Chen L, Liu C, Liu L (2009) Osmolality-induced tuning of action potentials in trigeminal ganglion neurons. Neurosci Lett 452:79–83
Christensen AP, Corey DP (2007) TRP channels in mechanosensation: direct or indirect activation? Nat Rev Neurosci 8:510–521
Ciura S, Liedtke W, Bourque CW (2011) Hypertonicity sensing in organum vasculosum lamina terminalis neurons: a mechanical process involving TRPV1 but not TRPV4. J Neurosci 31:14669–14676
Clapham DE, Julius D, Montell C, Schultz G (2005) International Union of Pharmacology. XLIX. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of transient receptor potential channels. Pharmacol Rev 57:427–450
Clapp JR, Robinson RR (1966) Osmolality of distal tubular fluid in the dog. J Clin Invest 45:1847–1853
Cuajungco MP, Grimm C, Oshima K, D'hoedt D, Nilius B, Mensenkamp AR, Bindels RJ, Plomann M, Heller S (2006) PACSINs bind to the TRPV4 cation channel. PACSIN 3 modulates the subcellular localization of TRPV4. J Biol Chem 281:18753–18762
Delany NS, Hurle M, Facer P, Alnadaf T, Plumpton C, Kinghorn I, See CG, Costigan M, Anand P, Woolf CJ, Crowther D, Sanseau P, Tate SN (2001) Identification and characterization of a novel human vanilloid receptor-like protein, VRL-2. Physiol Genomics 4:165–174
Delmas P (2004) Polycystins: from mechanosensation to gene regulation. Cell 118:145–148
D'hoedt D, Owsianik G, Prenen J, Cuajungco MP, Grimm C, Heller S, Voets T, Nilius B (2008) Stimulus-specific modulation of the cation channel TRPV4 by PACSIN 3. J Biol Chem 283:6272–6280
DiBona GF, Rios LL (1978) Mechanism of exaggerated diuresis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol 235:409–416
Du J, Wong WY, Sun L, Huang Y, Yao X (2012) Protein kinase G inhibits flow-induced Ca2+ entry into collecting duct cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1172–1180
Dwyer TM, Schmidt-Nielsen B (2003) The renal pelvis: machinery that concentrates urine in the papilla. News Physiol Sci 18:1–6
Everaerts W, Nilius B, Owsianik G (2010) The vanilloid transient receptor potential channel TRPV4: from structure to disease. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 103:2–17
Fernandes J, Lorenzo IM, Andrade YN, Garcia-Elias A, Serra SA, Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Valverde MA (2008) IP3 sensitizes TRPV4 channel to the mechano- and osmotransducing messenger 5′-6′-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid. J Cell Biol 181:143–155
Galizia L, Flamenco MP, Rivarola V, Capurro C, Ford P (2008) Role of AQP2 in activation of calcium entry by hypotonicity: implications in cell volume regulation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294:F582–F590
Galizia L, Pizzoni A, Fernandez J, Rivarola V, Capurro C, Ford P (2012) Functional interaction between AQP2 and TRPV4 in renal cells. J Cell Biochem 113:580–589
Gallagher AR, Germino GG, Somlo S (2010) Molecular advances in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 17:118–130
Gao X, Wu L, O'Neil RG (2003) Temperature-modulated diversity of TRPV4 channel gating: activation by physical stresses and phorbol ester derivatives through protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem 278:27129–27137
Geyti CS, Odgaard E, Overgaard MT, Jensen ME, Leipziger J, Praetorius HA (2008) Slow spontaneous [Ca2+]i oscillations reflect nucleotide release from renal epithelia. Pflugers Arch 455:1105–1117
Gottschalk CW (1961) Micropuncture studies of tubular function in the mammalian kidney. Physiologist 4:35–55
Gottschalk CW, Mylle M (1959) Micropuncture study of the mammalian urinary concentrating mechanism: evidence for the countercurrent hypothesis. Am J Physiol 196:927–936
Gradilone SA, Masyuk TV, Huang BQ, Banales JM, Lehmann GL, Radtke BN, Stroope A, Masyuk AI, Splinter PL, Larusso NF (2010) Activation of Trpv4 reduces the hyperproliferative phenotype of cystic cholangiocytes from an animal model of ARPKD. Gastroenterology 139:304–314
Hanaoka K, Qian F, Boletta A, Bhunia AK, Piontek K, Tsiokas L, Sukhatme VP, Guggino WB, Germino GG (2000) Co-assembly of polycystin-1 and −2 produces unique cation-permeable currents. Nature 408:990–994
Harris PC, Torres VE (2009) Polycystic kidney disease. Annu Rev Med 60:321–337
Hirsch J, Leipziger J, Frobe U, Schlatter E (1993) Regulation and possible physiological role of the Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channel of cortical collecting ducts of the rat. Pflugers Arch 422:492–498
Ho TA, Godefroid N, Gruzon D, Haymann JP, Marechal C, Wang X, Serra A, Pirson Y, Devuyst O (2012) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is associated with central and nephrogenic defects in osmoregulation. Kidney Int 82:1121–1129
Hoffmann EK, Lambert IH, Pedersen SF (2009) Physiology of cell volume regulation in vertebrates. Physiol Rev 89:193–277
Holstein-Rathlou NH, Marsh DJ (1990) A dynamic model of the tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism. Am J Physiol 258:F1448–F1459
Jia Y, Wang X, Varty L, Rizzo CA, Yang R, Correll CC, Phelps PT, Egan RW, Hey JA (2004) Functional TRPV4 channels are expressed in human airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 287:L272–L278
Karlsen FM, Holstein-Rathlou NH, Leyssac PP (1995) A re-evaluation of the determinants of glomerular filtration rate. Acta Physiol Scand 155:335–350
Kohler R, Heyken WT, Heinau P, Schubert R, Si H, Kacik M, Busch C, Grgic I, Maier T, Hoyer J (2006) Evidence for a functional role of endothelial transient receptor potential V4 in shear stress-induced vasodilatation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:1495–1502
Kottgen M, Buchholz B, Garcia-Gonzalez MA, Kotsis F, Fu X, Doerken M, Boehlke C, Steffl D, Tauber R, Wegierski T, Nitschke R, Suzuki M, Kramer-Zucker A, Germino GG, Watnick T, Prenen J, Nilius B, Kuehn EW, Walz G (2008) TRPP2 and TRPV4 form a polymodal sensory channel complex. J Cell Biol 182:437–447
Kung C (2005) A possible unifying principle for mechanosensation. Nature 436:647–654
Lambert IH, Hoffmann EK, Pedersen SF (2008) Cell volume regulation: physiology and pathophysiology. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 194:255–282
Lang F, Busch GL, Ritter M, Volkl H, Waldegger S, Gulbins E, Haussinger D (1998) Functional significance of cell volume regulatory mechanisms. Physiol Rev 78:247–306
Lechner SG, Markworth S, Poole K, Smith ES, Lapatsina L, Frahm S, May M, Pischke S, Suzuki M, Ibanez-Tallon I, Luft FC, Jordan J, Lewin GR (2011) The molecular and cellular identity of peripheral osmoreceptors. Neuron 69:332–344
Leyssac PP, Karlsen FM, Holstein-Rathlou NH, Skott O (1994) On determinants of glomerular filtration rate after inhibition of proximal tubular reabsorption. Am J Physiol 266:R1544–R1550
Liedtke W, Choe Y, Marti-Renom MA, Bell AM, Denis CS, Sali A, Hudspeth AJ, Friedman JM, Heller S (2000) Vanilloid receptor-related osmotically activated channel (VR-OAC), a candidate vertebrate osmoreceptor. Cell 103:525–535
Liedtke W, Friedman JM (2003) Abnormal osmotic regulation in trpv4−/− mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:13698–13703
Liedtke W, Tobin DM, Bargmann CI, Friedman JM (2003) Mammalian TRPV4 (VR-OAC) directs behavioral responses to osmotic and mechanical stimuli in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(Suppl 2):14531–14536
Liu X, Bandyopadhyay BC, Nakamoto T, Singh B, Liedtke W, Melvin JE, Ambudkar I (2006) A role for AQP5 in activation of TRPV4 by hypotonicity: concerted involvement of AQP5 and TRPV4 in regulation of cell volume recovery. J Biol Chem 281:15485–15495
Liu W, Morimoto T, Woda C, Kleyman TR, Satlin LM (2007) Ca2+ dependence of flow-stimulated K secretion in the mammalian cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F227–F235
Liu W, Xu S, Woda C, Kim P, Weinbaum S, Satlin LM (2003) Effect of flow and stretch on the [Ca2+]i response of principal and intercalated cells in cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 285:F998–F1012
Mamenko M, Zaika O, Jin M, O'Neil RG, Pochynyuk O (2011) Purinergic activation of Ca2+-permeable TRPV4 channels is essential for mechano-sensitivity in the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron. PLoS One 6:e22824
Marrelli SP, O'Neil RG, Brown RC, Bryan RM Jr (2007) PLA2 and TRPV4 channels regulate endothelial calcium in cerebral arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292:H1390–H1397
McCarty NA, O'Neil RG (1992) Calcium signaling in cell volume regulation. Physiol Rev 72:1037–1061
Mizuno A, Matsumoto N, Imai M, Suzuki M (2003) Impaired osmotic sensation in mice lacking TRPV4. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285:C96–C101
Montell C (2005) The TRP superfamily of cation channels. Sci STKE 2005: re3
Morimoto T, Liu W, Woda C, Carattino MD, Wei Y, Hughey RP, Apodaca G, Satlin LM, Kleyman TR (2006) Mechanism underlying flow stimulation of sodium absorption in the mammalian collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F663–F669
Mozaffari MS, Jirakulsomchok S, Shao ZH, Wyss JM (1991) High-NaCl diets increase natriuretic and diuretic responses in salt-resistant but not salt-sensitive SHR. Am J Physiol 260:F890–F897
Muto S (2001) Potassium transport in the mammalian collecting duct. Physiol Rev 81:85–116
Nauli SM, Alenghat FJ, Luo Y, Williams E, Vassilev P, Li X, Elia AE, Lu W, Brown EM, Quinn SJ, Ingber DE, Zhou J (2003) Polycystins 1 and 2 mediate mechanosensation in the primary cilium of kidney cells. Nat Genet 33:129–137
Nauli SM, Rossetti S, Kolb RJ, Alenghat FJ, Consugar MB, Harris PC, Ingber DE, Loghman-Adham M, Zhou J (2006) Loss of polycystin-1 in human cyst-lining epithelia leads to ciliary dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1015–1025
Nilius B, Honore E (2012) Sensing pressure with ion channels. Trends Neurosci 35:477–486
Nilius B, Prenen J, Wissenbach U, Bodding M, Droogmans G (2001) Differential activation of the volume-sensitive cation channel TRP12 (OTRPC4) and volume-regulated anion currents in HEK-293 cells. Pflugers Arch 443:227–233
Pedersen SF, Kapus A, Hoffmann EK (2011) Osmosensory mechanisms in cellular and systemic volume regulation. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1587–1597
Pedersen SF, Nilius B (2007) Transient receptor potential channels in mechanosensing and cell volume regulation. Methods Enzymol 428:183–207
Pedersen SF, Owsianik G, Nilius B (2005) TRP channels: an overview. Cell Calcium 38:233–252
Plant TD, Strotmann R (2007) TRPV4. Handb Exp Pharmacol 179:189–205
Plant TD, Strotmann R (2007) TRPV4: a multifunctional nonselective cation channel with complex regulation. In: Liedtke WB, Heller S (eds) TRP ion channel function in sensory transduction and cellular signaling cascades. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 129–140
Pochynyuk O, Bugaj V, Rieg T, Insel PA, Mironova E, Vallon V, Stockand JD (2008) Paracrine regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel in the mammalian collecting duct by purinergic P2Y2 receptor tone. J Biol Chem 283:36599–36607
Pollock CA, Lawrence JR, Field MJ (1991) Tubular sodium handling and tubuloglomerular feedback in experimental diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol 260:F946–F952
Praetorius HA, Leipziger J (2009) Released nucleotides amplify the cilium-dependent, flow-induced [Ca2+]i response in MDCK cells. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 197:241–251
Praetorius HA, Leipziger J (2010) Intrarenal purinergic signaling in the control of renal tubular transport. Annu Rev Physiol 72:377–393
Praetorius HA, Spring KR (2003) The renal cell primary cilium functions as a flow sensor. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 12:517–520
Praetorius HA, Spring KR (2005) A physiological view of the primary cilium. Annu Rev Physiol 67:515–529
Rieg T, Vallon V (2009) ATP and adenosine in the local regulation of water transport and homeostasis by the kidney. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:R419–R427
Satlin LM (2004) Developmental regulation of expression of renal potassium secretory channels. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 13:445–450
Seney FD Jr, Persson EG, Wright FS (1987) Modification of tubuloglomerular feedback signal by dietary protein. Am J Physiol 252:F83–F90
Silva GB, Garvin JL (2008) TRPV4 mediates hypotonicity-induced ATP release by the thick ascending limb. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 295:F1090–F1095
Sinke AP, Deen PM (2011) The physiological implication of novel proteins in systemic osmoregulation. FASEB J 25:3279–3289
Sipos A, Vargas SL, Toma I, Hanner F, Willecke K, Peti-Peterdi J (2009) Connexin 30 deficiency impairs renal tubular ATP release and pressure natriuresis. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:1724–1732
Stewart AP, Smith GD, Sandford RN, Edwardson JM (2010) Atomic force microscopy reveals the alternating subunit arrangement of the TRPP2-TRPV4 heterotetramer. Biophys J 99:790–797
Stockand JD, Mironova E, Bugaj V, Rieg T, Insel PA, Vallon V, Peti-Peterdi J, Pochynyuk O (2010) Purinergic inhibition of ENaC produces aldosterone escape. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1903–1911
Strotmann R, Harteneck C, Nunnenmacher K, Schultz G, Plant TD (2000) OTRPC4, a nonselective cation channel that confers sensitivity to extracellular osmolarity. Nat Cell Biol 2:695–702
Strotmann R, Schultz G, Plant TD (2003) Ca2+-dependent potentiation of the nonselective cation channel TRPV4 is mediated by a C-terminal calmodulin binding site. J Biol Chem 278:26541–26549
Strotmann R, Semtner M, Kepura F, Plant TD, Schoneberg T (2010) Interdomain interactions control Ca2+-dependent potentiation in the cation channel TRPV4. PLoS One 5:e10580
Suzuki M, Hirao A, Mizuno A (2003) Microtubule-associated [corrected] protein 7 increases the membrane expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4). J Biol Chem 278:51448–51453
Suzuki M, Mizuno A, Kodaira K, Imai M (2003) Impaired pressure sensation in mice lacking TRPV4. J Biol Chem 278:22664–22668
Sweeney WE Jr, Avner ED (2006) Molecular and cellular pathophysiology of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). Cell Tissue Res 326:671–685
Tamma G, Procino G, Svelto M, Valenti G (2007) Hypotonicity causes actin reorganization and recruitment of the actin-binding ERM protein moesin in membrane protrusions in collecting duct principal cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C1476–C1484
Taniguchi J, Tsuruoka S, Mizuno A, Sato J, Fujimura A, Suzuki M (2007) TRPV4 as a flow sensor in flow-dependent K+ secretion from the cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292:F667–F673
Teilmann SC, Byskov AG, Pedersen PA, Wheatley DN, Pazour GJ, Christensen ST (2005) Localization of transient receptor potential ion channels in primary and motile cilia of the female murine reproductive organs. Mol Reprod Dev 71:444–452
Tian W, Salanova M, Xu H, Lindsley JN, Oyama TT, Anderson S, Bachmann S, Cohen DM (2004) Renal expression of osmotically responsive cation channel TRPV4 is restricted to water-impermeant nephron segments. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F17–F24
Tinel H, Kinne-Saffran E, Kinne RK (2000) Calcium signalling during RVD of kidney cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 10:297–302
Tinel H, Kinne-Saffran E, Kinne RH (2002) Calcium-induced calcium release participates in cell volume regulation of rabbit TALH cells. Pflugers Arch 443:754–761
Torres VE, Harris PC (2011) Polycystic kidney disease in 2011: connecting the dots toward a polycystic kidney disease therapy. Nat Rev Nephrol 8:66–68
Torres VE, Harris PC, Pirson Y (2007) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet 369:1287–1301
Torres VE, Wang X, Qian Q, Somlo S, Harris PC, Gattone VH (2004) Effective treatment of an orthologous model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nat Med 10:363–364
Urbach V, Leguen I, O'Kelly I, Harvey BJ (1999) Mechanosensitive calcium entry and mobilization in renal A6 cells. J Membr Biol 168:29–37
Vandorpe DH, Chernova MN, Jiang L, Sellin LK, Wilhelm S, Stuart-Tilley AK, Walz G, Alper SL (2001) The cytoplasmic C-terminal fragment of polycystin-1 regulates a Ca2+-permeable cation channel. J Biol Chem 276:4093–4101
Vandorpe DH, Wilhelm S, Jiang L, Ibraghimov-Beskrovnaya O, Chernova MN, Stuart-Tilley AK, Alper SL (2002) Cation channel regulation by COOH-terminal cytoplasmic tail of polycystin-1: mutational and functional analysis. Physiol Genomics 8:87–98
Venkatachalam K, Montell C (2007) TRP channels. Annu Rev Biochem 76:387–417
Verani RR, Silva FG (1988) Histogenesis of the renal cysts in adult (autosomal dominant) polycystic kidney disease: a histochemical study. Mod Pathol 1:457–463
Verani R, Walker P, Silva FG (1989) Renal cystic disease of infancy: results of histochemical studies. A report of the Southwest Pediatric Nephrology Study Group. Pediatr Nephrol 3:37–42
Voets T, Prenen J, Vriens J, Watanabe H, Janssens A, Wissenbach U, Bodding M, Droogmans G, Nilius B (2002) Molecular determinants of permeation through the cation channel TRPV4. J Biol Chem 277:33704–33710
Vriens J, Owsianik G, Fisslthaler B, Suzuki M, Janssens A, Voets T, Morisseau C, Hammock BD, Fleming I, Busse R, Nilius B (2005) Modulation of the Ca2+ permeable cation channel TRPV4 by cytochrome P450 epoxygenases in vascular endothelium. Circ Res 97:908–915
Vriens J, Watanabe H, Janssens A, Droogmans G, Voets T, Nilius B (2004) Cell swelling, heat, and chemical agonists use distinct pathways for the activation of the cation channel TRPV4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:396–401
Wang S, Zhang J, Nauli SM, Li X, Starremans PG, Luo Y, Roberts KA, Zhou J (2007) Fibrocystin/polyductin, found in the same protein complex with polycystin-2, regulates calcium responses in kidney epithelia. Mol Cell Biol 27:3241–3252
Watanabe H, Davis JB, Smart D, Jerman JC, Smith GD, Hayes P, Vriens J, Cairns W, Wissenbach U, Prenen J, Flockerzi V, Droogmans G, Benham CD, Nilius B (2002) Activation of TRPV4 channels (hVRL-2/mTRP12) by phorbol derivatives. J Biol Chem 277:13569–13577
Watanabe H, Vriens J, Janssens A, Wondergem R, Droogmans G, Nilius B (2003) Modulation of TRPV4 gating by intra- and extracellular Ca2+. Cell Calcium 33:489–495
Watanabe H, Vriens J, Prenen J, Droogmans G, Voets T, Nilius B (2003) Anandamide and arachidonic acid use epoxyeicosatrienoic acids to activate TRPV4 channels. Nature 424:434–438
Wegierski T, Lewandrowski U, Muller B, Sickmann A, Walz G (2009) Tyrosine phosphorylation modulates the activity of TRPV4 in response to defined stimuli. J Biol Chem 284:2923–2933
Wehner F, Olsen H, Tinel H, Kinne-Saffran E, Kinne RK (2003) Cell volume regulation: osmolytes, osmolyte transport, and signal transduction. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 148:1–80
Wilson PD, Goilav B (2007) Cystic disease of the kidney. Annu Rev Pathol 2:341–368
Wissenbach U, Bodding M, Freichel M, Flockerzi V (2000) Trp12, a novel Trp related protein from kidney. FEBS Lett 485:127–134
Woda CB, Leite M Jr, Rohatgi R, Satlin LM (2002) Effects of luminal flow and nucleotides on [Ca(2+)](i) in rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F437–F446
Wu L, Gao X, Brown RC, Heller S, O'Neil RG (2007) Dual role of the TRPV4 channel as a sensor of flow and osmolality in renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293:F1699–F1713
Wu LJ, Sweet TB, Clapham DE (2010) International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXVI. Current progress in the mammalian TRP ion channel family. Pharmacol Rev 62:381–404
Xu H, Zhao H, Tian W, Yoshida K, Roullet JB, Cohen DM (2003) Regulation of a transient receptor potential (TRP) channel by tyrosine phosphorylation. SRC family kinase-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of TRPV4 on TYR-253 mediates its response to hypotonic stress. J Biol Chem 278:11520–11527
Yamaguchi T, Hempson SJ, Reif GA, Hedge AM, Wallace DP (2006) Calcium restores a normal proliferation phenotype in human polycystic kidney disease epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:178–187
Yang J, Zhang S, Zhou Q, Guo H, Zhang K, Zheng R, Xiao C (2007) PKHD1 gene silencing may cause cell abnormal proliferation through modulation of intracellular calcium in autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. J Biochem Mol Biol 40:467–474
Yip KP, Holstein-Rathlou NH, Marsh DJ (1993) Mechanisms of temporal variation in single-nephron blood flow in rats. Am J Physiol 264:F427–F434
Zerres K, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Steinkamm C, Becker J, Mucher G (1998) Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. J Mol Med (Berl) 76:303–309
Zhang Y, Sands JM, Kohan DE, Nelson RD, Martin CF, Carlson NG, Kamerath CD, Ge Y, Klein JD, Kishore BK (2008) Potential role of purinergic signaling in urinary concentration in inner medulla: insights from P2Y2 receptor gene knockout mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 295:F1715–F1724
Acknowledgments
The research in Pochynyuk’s lab is supported by the National Institutes of Health DK095029.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pochynyuk, O., Zaika, O., O’Neil, R.G. et al. Novel insights into TRPV4 function in the kidney. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 465, 177–186 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1190-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1190-z