Abstract
Quantum teleportation has provided us with an interesting way to transmit an arbitrary quantum state using one maximal entangled state and two classical bits of information. A variety of theoretical suggestions and experimental efforts have been made in this realm. In practical implementations of the teleportation protocol, quantum noise is an unavoidable factor. In this paper, we investigate the probabilistic quantum teleportation of two-particle. The fidelity of quantum state is calculated in detail, after suffering from the quantum noise. The relationship between quantum noise, quantum channel and quantum state fidelity is obtained. The effect of noise on the teleportation is analyzed.
Access provided by CONRICYT-eBooks. Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
Quantum teleportation is a technique for the direct transmission of quantum states between the correspondents. In 1993, Bennett et al. [1] proposed the concept of quantum teleportation. At present, the technology has made numerous achievements in both theory [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15] and experiment [16,17,18]. It has been studied from the original single particle quantum teleportation to many particle quantum teleportation and continuous variable quantum teleportation; from accurate quantum teleportation (the value of fidelity is 1) to the precise quantum teleportation (the value of fidelity is less than 1). All quantum teleportation protocols need establish a quantum channel by the entangled state. In this process, the particles of the entangled channel are susceptible to the interference by the quantum noise.
In this paper, we take the probability teleportation of two particle entangled state [19] as an example. and analyze the effects of several common quantum noises [20, 21] on the quantum channel. We have obtained the relationship between the quantum fidelity, the parameters of noise and the state parameters of channel. It has an important reference value for the practical application of the quantum teleportation.
2 Preparation
2.1 Fidelity and Quantum Noise
To quantify the efficiency of the probabilistic teleportation protocol we use the fidelity. The fidelity is
The action of the noise on the qubit, described by the density matrix \(\rho \), is (Table 1)
2.2 Examples of Quantum Teleportation
The quantum teleportation of the participant are Alice and Bob. The quantum state that Alice wants to transmit is \(|\varphi \rangle _{12}\). And the quantum entanglement channel is \(|\phi \rangle _{34}\).
where x and y are non negative real numbers, and \(x^2+y^2=1\); also a and b are non negative real numbers, and \(a^2+b^2=1\). We can suppose \(0<b\le a<1.\)
Suppose Alice prepared entangled state \(|\phi \rangle _{34}\), then sends Bob the qubit 4 by optical fiber to set up communication channel. In this process, the qubit 4 is easier affected by noise. So when noise act on the qubit 4, we study the influence of noise for the quantum teleportation.
Without noise, composite system composed of qubits 1, 2, 3, 4 is:
the quantum state of Eq. (3) can be written as
where \(|\phi ^\pm \rangle \) and \(|\psi ^\pm \rangle \) are Bell states.
Without noise, the quantum channel is \(|\phi \rangle _{34}\). And the density matrix is
3 The Presence of Quantum Noise on the Teleportation
3.1 Bit Flip
After suffering from the noise named bit flip, the density matrix of \(|\phi \rangle _{34}\) is
so the quantum channel has changed as
and the composite system has changed as
obviously, the fidelity of the composite system is \(F_1=(1-p)\times 1+p\times 0=1-p\).
3.2 Phase Flip
After suffering from the noise named phase flip, the density matrix of \(|\phi \rangle _{34}\) is
so the quantum channel has changed as
and the composite system has changed as
obviously, the fidelity of the composite system is
3.3 Depolarizing
After suffering from the noise named depolarizing, the density matrix of \(|\phi \rangle _{34}\) is
so the quantum channel has changed as
and the composite system has changed as
obviously, the fidelity of the composite system is
3.4 Amplitude Damping
After suffering from the noise named amplitude damping, the density matrix of \(|\phi \rangle _{34}\) is
so the quantum channel has changed as
and the composite system has changed as
obviously, the fidelity of the composite system is
4 Analysis
In the process of quantum teleportation, the fidelity of the composite system is \(F_1=1-p\), after the channel suffering from the noise named bit flip. So, we clearly known the fidelity \(F_1\) decreases with the increase of the noise parameters p. If \(p=0\), means there is no noise, the value of fidelity is 1.

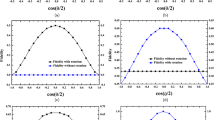
In the process of quantum teleportation, the fidelity of the composite system is \(F_2=1+(a^2-\frac{3}{2})p\), after the channel suffering from the noise named phase flip. In this equation, we known \(0<b\le a<1\), and \(a^2+b^2=1\). So we get \(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\le a<1\). According to the figure (a), suppose a is constant, the fidelity \(F_2\) decreases with the increase of the noise parameters p; suppose p is constant, the fidelity \(F_2\) increases with the increase of a. However, if a close to 1, the entangled state will be unstable. similarly, if \(p=0\), the value of fidelity is 1.
In the process of quantum teleportation, the fidelity of the composite system is \(F_3=1-\frac{1}{8}(7-a^2)p\), after the channel suffering from the noise named depolarizing. In this equation, we known \(\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\le a<1\) and \(0\le p\le 1\). According to the figure (b), suppose a is constant, the fidelity \(F_3\) decreases with the increase of the noise parameters p; suppose p is constant, the fidelity \(F_3\) increases with the increase of a. Also a can not be close to 1, and if \(p=0\), the value of fidelity is 1.
In the process of quantum teleportation, the fidelity of the composite system is \(F_4=\frac{1}{2}(1-b^2p)\), after the channel suffering from the noise named amplitude damping. In this equation, we known \(0<b\le \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\) and \(0< p\le 1\). In another case, if \(p=0\), the value of fidelity \(F_4\) is 1. According to the figure (c), suppose b is constant, the fidelity \(F_4\) decreases with the increase of the noise parameters p; suppose p is constant, the fidelity \(F_4\) decreases with the increase of b. And b can not be close to 0.
5 Conclusion
We have calculated the fidelity of quantum state, and analysis of the effect of quantum noise on the quantum teleportation. It is useful for the practical application of the quantum teleportation. Next, we will study the situations that the quantum states suffer from the different noise at the same time.
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Grepeau, C., et al.: Teleporting an unknown quantum stage via dual classical and Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen channels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1895 (1993)
Karlsson, A., Bourennane, M.: Quantum teleportation using three-particle entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 58, 4394 (1998)
Shi, B.S., Tomita, A.: Teleportation of an unknown state by W state. Phys. Lett. A 296, 161 (2002)
Liu, J., Mo, Z., Sun, S.: Quantum state sharing for networks using the GHZ channel. In: International Conference on Oriental Thinking and Fuzzy Logic, pp. 533–540. Springer International Publishing (2016)
Lin, X., Li, H.C.: Probabilistic teleportation of an arbitrary three-particle state. Chin. Phys. 14, 1724 (2005)
Cola, M.M., Paris, M.G.A.: Teleportation of bipartite states using a single entangled pair. Phys. Lett. A 337, 10 (2005)
Liu, J., Mo, Z., Sun, S.: Controlled dense coding using the maximal slice states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(4), 2182–2188 (2016)
Son, W., Lee, J., Kim, M.S., et al.: Conclusive teleportation of a d-dimensional unknown state. Phys. Rev. A 64, 064304 (2001)
Lee, J., Kim, M.S.: Entanglement teleportation via Werner states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 4236 (2000)
Lu, H.: Probabilistic teleportation of the three-particle entangled state via entanglement Swapping. Chin. Phys. Lett. 18, 1004 (2001)
Wang, M.Y., Yan, F.L.: Teleporting a quantum state from a subset of the whole Hilbert space. Phys. Lett. A 355, 94–97 (2006)
Li, L.Z., Qiu, D.W.: The states of W-class as shared resources for perfect teleportation and superdense coding. J. Phys. A Mathe. Theor. 40, 10871 (2007)
Zha, X.W., Song, H.Y.: Non-Bell-pair quantum channel for teleportirng an arbitrary two-qubit state. Phys. Lett. A 369, 377 (2007)
Venuti, L.C., Boschi, C.D.E., Roncaglia, M.: Qubit teleportation and transfer across antiferromagnetic spin chains. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 060401 (2007)
Zhou, P., Li, X.H., Deng, F.G., et al.: Multiparty-controlled teleportation of an arbitrary m-qubit state with a pure entangled quantum channel. J. Phys. A Mathe. Theor. 40, 13121 (2007)
van Houwelingen, J.A.W., Beveratos, A., Brunner, N., et al.: Experimental quantum teleportation with a three-Bell-state analyzer. Phys. Rev. A 74, 022303 (2006)
Cao, Z.L., Yang, M., Guo, G.C.: The scheme for realizing probabilistic teleportation of atomic states and purifying the quantum channel on cavity QED. Phys. Lett. A 308, 349 (2003)
Landry, O., van Houwelingen, J.A.W., Beveratos, A., et al.: Quantum teleportation over the Swisscom telecommunication network. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 24, 398 (2007)
Wen, Q.Y., Guo, F.Z., Zhu, F.C.: Design and analysis of quantum secure communication protocol, pp. 197–238. Science Press, Beijing (2009)
Mertz, M., Kampermann, H., Shadman, Z., et al.: Quantum key distribution with finite resources: taking advantage of quantum noise. Phys. Rev. A 87, 042312 (2013)
Fortes, R., Rigolin, G.: Fighting noise with noise in realistic quantum teleportation. Phys. Rev. A 92, 012338 (2015)
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11671284), Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education(Grant No.20135134110003), Sichuan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 2015JY0002) and the Research Foundation of the Education Department of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 15ZA0032).
Recommender: Ming-qiang Bo, Professor. Institute of Information and Quantum Information, Sichuan Normal University, Chengdu, 610066, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Li, Yc., Mo, Zw., Sun, Sq. (2018). Analysis for the Presence of Quantum Noise on the Teleportation. In: Cao, BY. (eds) Fuzzy Information and Engineering and Decision. IWDS 2016. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 646. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66514-6_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-66514-6_14
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-66513-9
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-66514-6
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)