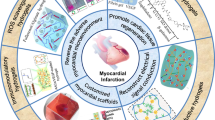
Abstract
Myocardial infarction (MI) is a leading cause of death globally. Due to limited cardiac regeneration, infarcted myocardial tissue is gradually replaced by cardiac fibrosis, causing cardiac dysfunction, arrhythmia, aneurysm, free wall rupture, and sudden cardiac death. Thus, the development of effective methods to promote cardiac regeneration is extremely important for MI treatment. In recent years, hydrogels have shown promise in various methods for cardiac regeneration. Hydrogels can be divided into natural and synthetic types. Different hydrogels have different features and can be cross-linked in various ways. Hydrogels are low in toxicity and highly stable. Since they have good biocompatibility, biodegradability, and transformability, moderate mechanical properties, and proper elasticity, hydrogels are promising biomaterials for promoting cardiac regeneration. They can be used not only as scaffolds for migration of stem cells, but also as ideal carriers for delivery of drugs, genetic materials, stem cells, growth factors, cytokines, and small molecules. In this review, the application of hydrogels in cardiac regeneration during or post-MI is discussed in detail. Hydrogels open a promising new area in cardiac regeneration for treating MI.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Myocardial infarction (MI) is a leading cause of death globally. |
Hydrogels have low toxicity and are highly stable, with good biocompatibility, biodegradability, and transformability, moderate mechanical properties, and proper elasticity, making hydrogels promising biomaterials in treating MI. |
Hydrogels can be divided into natural and synthetic types. |
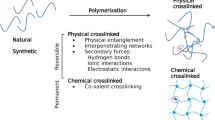
Hydrogels have different cross-linking methods. |
Hydrogels can be delivered to the heart by multiple routes. |
Hydrogels can be used as carriers for delivering drugs, stem cells, small molecules, and other treatments for MI. |
Introduction
Myocardial infarction (MI) is one of the most common cardiac diseases globally, contributing to significant morbidity and mortality. Ischemia during MI causes a significant loss of viable myocardial tissues, which impairs cardiac function. Because cardiomyocytes are terminally differentiated cells with extremely low ability for cardiac regeneration, collagen and extracellular matrix (ECM) will be synthesized to form scars and replace the infarcted myocardium. However, scars are less elastic and incompatible with cardiac contraction and dilation, leading to cardiac dysfunction and heart failure. In order to promote cardiac regeneration and mitigate cardiac remodeling after MI, numerous studies have attempted to deliver drugs, stem cells, cytokines, growth factors, and small molecules to infarcted cardiac tissues. Stem cell transplantation can promote cardiac regeneration and restore cardiac dysfunction after MI [1, 2]. However, low retention and survival rates of stem cells are two major issues limiting their efficacy. Moreover, proteins, growth factors, and small molecules have short half-lives, low bioavailability, short retention, and low stability, all of which limit their effective application as well.
Hydrogels are a category of networks with three-dimensional swollen structures. In recent years, hydrogels have been widely applied in biology and medicine. They have an incredible superabsorbent ability: when placed in a compatible liquid medium, they can absorb at least 20 times their own weight of water from the liquid media. These swelling structures can maintain specific volumes for a period of time, and they are quite stable and resistant to dissolving due to the cross-links. When an aqueous medium is absent, hydrogels will shrink [3]. Since hydrogels have high water content and share a similar flexibility as natural tissues, they are ideal biomaterials for use on natural tissues. Mounting evidence demonstrates that hydrogels not only can be applied to tissue engineering, but also can be utilized in regenerative medicine to deliver cells, drugs, and proteins due to their physical and chemical features, which can stabilize and retain those small molecules. Numerous studies have demonstrated that hydrogels coupled with growth factors, genes, drugs, and stem cells show great potential in cardiac regeneration. Single hydrogel use or combination with small molecules can significantly ameliorate cardiac dysfunction, enhance revascularization, and attenuate cardiac remodeling in animal models with MI or ischemic reperfusion (I/R) injury. Moreover, hydrogels can be easily modified and are injectable at body temperature, which facilitates their application in cardiac regeneration.
The aim of this review is to summarize current applications of hydrogels in tissue engineering and cardiac regeneration post-MI, providing readers with a general understanding of the importance of hydrogels in cardiac regeneration. This article is a review article which is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any new studies with human participants or animals performed by the author.
Features of Hydrogels in Cardiac Regeneration
Hydrogels suitable for cardiac regeneration must meet the following demands:
-
(1)
Biocompatibility and non-stimulation. Hydrogels should be biocompatible without any stimulation for local and systematic inflammation and immune response, which allows them to coexist well with tissues and promote wound healing.
-
(2)
Biodegradability. Hydrogels are foreign materials to the body. If not degraded, inflammation and immune response will be induced, which will impede tissue healing. However, a moderate rate of degradation is needed, neither too fast nor too slow. It should be gradually degraded and last for a proper period, allowing sufficient time for the delivery of molecules and tissue regeneration.
-
(3)
Transformability. Hydrogels must have the ability to transform from an aqueous phase to a solid form. As a liquid form, hydrogels can be easily delivered to the injured sites by simple covering of the tissue or direct local injection. After transformation into a solid phase by multiple cross-links and water absorption, hydrogels can provide a solid interface for tissues and cells to adhere to and regenerate.
-
(4)
Nontoxic and low injury. As a therapeutic method for wound healing and tissue regeneration, hydrogels must be nontoxic to provide an ideal microenvironment for healing.
-
(5)
Suitable mechanical properties and elasticity. The proper mechanical properties offer a scaffold for tissue regeneration, and localize the range of tissue repair. The elasticity allows the hydrogels to be highly biocompatible with local tissues, which reduces local injury and promotes wound healing. As hydrogels are easily tunable, their mechanical and elastic properties can be modified by adjustment of many factors.
-
(6)
Water absorptivity. Water plays an indispensable role in hydrogel structures and can only be isolated under extreme circumstances. Hydrogels must absorb a large amount of water to form hydrated solid hydrogels in order to achieve similar flexibility as natural tissues. In this case, low interfacial tension exists between hydrogels and tissues, which can benefit tissue regeneration.
-
(7)
Odorless and colorless. Hydrogels are odorless and transparent. The transparency allows surgical visualization and helps in evaluating the amount of hydrogel that is applied to target tissues, which enables timely adjustment during procedures.
-
(8)
High durability and stability. Hydrogels must have proper durability in different biological and physical environments. Long-standing hydrogels provide a stable microenvironment, which act as scaffolds for cell migration, proliferation, regeneration, and drug delivery.
-
(9)
Cost-effective. Most natural hydrogels are derived from natural resources, making them more cost-effective than synthetic hydrogels. Synthetic hydrogels are more expensive but have better mechanical and physical properties than natural hydrogels.
Classification of Hydrogels
There are many ways to classify hydrogels. Based on their origin, hydrogels can be classified as natural or synthetic. Based on composition, hydrogels can be defined as homopolymeric, copolymeric, or multipolymeric. According to their chemical components and physical structure, hydrogels can be defined as crystalline, semicrystalline, or amorphous (noncrystalline). Based on interactions among polymer networks, hydrogels can be classified as permanent, chemical, or physical gels [4]. Natural hydrogels have many excellent properties, including good biodegradability, easy availability, and lower toxicity and manufacturing cost.
With the rapid development of technology, natural hydrogels are continuously being replaced by synthetic hydrogels because synthetic hydrogels have stronger water absorption, longer half-life, and greater stability against temperature fluctuations in different environments. Their degradability can be tuned by structural modification, and their functionality can be modified by adjusting the ratio of ingredients, molecular weights, and cross-linking methods [4]. Synthetic hydrogels have lower immune response, which facilitates their application as artificial biocompatible materials in regenerative medicine. A summary of the hydrogel features and applications can be seen in Fig. 1.
Summary of features and applications of hydrogels in cardiac regeneration. The figure was created with BioRender.com. This picture is granted permission from BioRender for publication in Cardiology and Therapy. Abbreviations: PEG, poly(ethylene glycol); PGA, polyglycolic acid; PLA, polylactic acid; PLGA, polylactic-co-glycolic acid; PNIPAM, poly(N-isopropylacrylamide); PGCL, poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone)
Natural Hydrogels
Alginate
Alginate is a natural polysaccharide existing in the cell walls of brown seaweed. It has been widely used in the food, biomedical, and pharmaceutical fields. As its structure is quite similar to ECM, it has great biocompatibility in vivo [5]. Alginate is a polymer and forms a cross-linked hydrogel with the existence of divalent cations. Alginate hydrogels carry a low risk of inducing thrombogenesis, making it a preferred material in cardiac regeneration. However, it has poor stability and poor cell adhesion in vivo, and sometimes requires modification to improve endurance and stability [6]. Alginate cross-linked with calcium can be used for intramyocardial/intracoronary injection as a liquid solution [5, 7]. It can be produced as an epicardial patch for MI in small and large animals, and can prevent cardiac remodeling after MI, thus holding promise for use in cardiac regeneration.
Collagen
Collagen, a natural rod-type polymer, is the most abundant structural protein in mammals, representing 25–35% of the total protein in the body. It is widely distributed in connective tissue and extracellular space, acting as a scaffold. It is abundant in fibrous tissues as well. Collagen maintains tissue infrastructure and participates in cell phenotype, cell adhesion, and tissue regeneration. It is reported that ECM is one of the most common structural proteins in cardiac tissue, and collagen I is the richest in cardiac ECM. Elastin is another common structural protein in ECM to provide elastic properties. The normal ratio of elastin to collagen is about 1:10 [8, 9]. By regulating this ratio, the elastic and mechanical properties can be adjusted to tailor material properties. Because of the remarkable tissue biocompatibility and low immunogenicity, collagen has great potential in regenerative medicine. It has also been applied in 3D printing technology to generate organ and tissue growth, such as aortic valves encapsulated with human valvular interstitial cells [10]. In recent years, collagen has been utilized as a novel biomaterial for cardiac regeneration after MI. It is prepared in an injectable manner and further assembled at a certain pH or circumstance. Collagen hydrogel can be chemically cross-linked and has already been tested safe in many animal models. Blackburn et al. delivered collagen hydrogels to MI mice by intramyocardial injection and showed a remarkable improvement in cardiac dysfunction and reduction in cardiac fibrosis by around 40% relative to the control treated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) [11]. Another group of scientists applied collagen hydrogel onto the epicardial infarcted area in mice with MI and obtained similar results. Moreover, the collagen patch also decreased cardiac remodeling by decreasing fibrogenesis [12]. Araña et al. applied collagen patches together with adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) epicardially in rat and swine MI models, and discovered that collagen patches with rat ADSCs (rADSCs) could significantly promote cell engraftment and enhance cardiac function in chronic MI models. This combination reduced fibrosis and improved the formation of new vessels [13].
Fibrin
Fibrin is a natural biopolymer derived from fibrinogen and thrombin that is involved in wound healing [14]. During the production of fibrin hydrogels, the isolated thrombin, fibrinogen, and calcium are combined. In vitro environments significantly affect the structure of fibrin hydrogels. Faster gelation can be induced by a higher thrombin concentration, whereas thicker-diameter fibers and smaller pore sizes can be obtained with low thrombin concentration. Fibrin can be utilized as a tissue sealant or a drug and growth factor delivery platform. Intramyocardial injection of fibrin hydrogel with skeletal myoblasts on rat MI models showed a significant decrease in scar size and collagen deposition, and a notable increase in arteriole density around the infarct area. Fibrin also promoted remarkable survival of skeletal myoblasts during cardiac repair [15]. Intracardial injection of fibrin with rAAV9-cyclinA2 in rat MI models was shown to significantly preserve cardiac function, decrease cardiac remodeling, and enhance vascularization [16].
Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a disaccharide with non-sulfated and unbranched features [17]. It is widely distributed in the ECM in connective tissues, and the size of a highly hydrated molecule can range from 100 to 8000 kDa [18]. As HA has strong hydrophilicity, it can absorb water of more than 1000 times its solid volume. Due to good biocompatibility and biodegradability, low immune response, and proper viscosity, HA has been widely used in biomedical fields and cardiac regeneration. HA takes part in wound repair and healing, signal transduction, cell proliferation, and tissue recovery after injury. Intramyocardial injection of HA hydrogel with engineered stromal cell-derived factor 1-α analogue (ESA) into a rat model with MI showed a significant improvement in cardiac function, revascularization, and reduced fibrosis after myocardial ischemia [19]. However, HA has poor cell adhesion and retention, which results in low cell retention and survival when used as a cell delivery material [20].
Gelatin
Gelatin is a mixture of polypeptides made from collagen, which is why it has good biocompatibility and biodegradability. Hydrogel made with gelatin is a water-soluble and biodegradable polymer that is nontoxic, and the cross-links can be induced by chemical or light cross-linking [21, 22]. It is transparent and thermo-reversible, which is opposite to collagen hydrogels. Gelatin can be easily isolated and has high solubility. It is cost-effective for processing. The ideal feature of gelatin hydrogels is that they maintain a liquid form when the temperature is above 35 °C and transform into a gel phase below this temperature. Thus, in physiological environments, gelatin hydrogel exists as a liquid form which needs chemical cross-linking for cell seeding and culture in vivo. Interestingly, gelatin hydrogel can be dried by freezing [23]. Moreover, gelatin can be bioprinted by 3D technology with other biomaterials and dissolved at 37 °C [24]. Our previous research applied hydrogels made with gelatin methacryloyl (GelMa), which showed a significantly improved survival rate and cardiac function in mouse MI models; moreover, it increased anterior wall thickness and reduced fibrosis and scar formation, indicating that gelatin-based hydrogels have good biosafety and biocompatibility, thus holding promise for treating MI [25]. Because gelatin is a good drug delivery system, biomolecules can be delivered and released by gelatin hydrogel as it is degraded in the biological environment. Reloading of drugs can be performed by rehydration or freezing [26]. Gelatin hydrogels have already been used extensively in tissue regeneration. Previous research indicated that gelatin hydrogel coupled with basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) improved cardiac function after MI in rat and canine models [22, 27]. Engineered cardiac tissue constructed with single-walled carbon nanotubes/gelatin scaffold achieved notable repair of infarcted myocardium, and demonstrated stronger contraction and electrical properties. After implantation into infarcted myocardium, engineered myocardial tissue was beneficial for heart regeneration and remodeling [28].
Matrigel
Matrigel is a soluble gelatinous protein which is secreted by mouse sarcoma cells. Matrigel is similar to the extracellular environment which has been applied for tissue regeneration in recent years. It is abundant in the basement membrane, and its major components are collagen V and laminin. Moreover, it contains many growth factors as well. Matrigel is a thermosensitive injectable biopolymer which makes itself in a liquid form at 4 °C and is self-assembled at 37 °C [29]. Matrigel is cytoprotective and can be coated with different cells for tissue regeneration, providing a good microenvironment for cellular attachment, proliferation, differentiation, and angiogenesis because it contains many growth factors [30].
Ou et al. applied Matrigel on rat MI models by intramyocardial injection into five different points in the anterior and lateral sides. Compared with control (PBS), Matrigel markedly improved left ventricular function. Although the scar size was not significantly different between these two groups, left ventricular thickness and new vessel formation were significantly increased by Matrigel treatment after MI [30]. Wang et al. discovered that human villous trophoblasts enhanced tube formation of human endothelial cells on Matrigel, and strengthened the resistance of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes against oxidative stress. The delivery of human villous trophoblasts to the cardiac ischemic area significantly restored cardiac function and decreased fibrosis in mice MI models [31]. Another study indicated that a pro-survival cocktail with Matrigel was able to provide a large graft and more mature iPS-cell-derived cardiomyocytes in ischemic cardiac tissue from rat MI models after 4 weeks of treatment, and reduced scar size following MI [32].
Silk Fibroin
Silk fibroin is another widely utilized biomaterial. It can be acquired in abundance from nature and purified by aqueous-based, nontoxic solvents at low cost [33]. Nowadays, the main source of silk is biomanufacturing and genetic engineering. Silk fibroin is an outstanding biomaterial for use in drug delivery. Sericin is a hydrophobic protein that can be used to coat silk fibroin fibers. However, because it can induce immunogenic and inflammatory responses, it is usually removed during manufacturing. The hydrogel manufactured from silk fibroin has many advantages. Because silk fibroin has excellent elasticity, the hydrogels derived from silk fibroin have robust mechanical properties and excellent elasticity [33]. Since those hydrogels are nontoxic, biocompatible, and controllable for biodegradation, with incredible chemical and thermal stability, silk fibroin is ideal for drug delivery. However, the degradation rates for hydrogels depend on the type of processing [33]. The gels can be modified into many forms and injected into tissue directly. More importantly, silk fibroin hydrogels can be 3D-printed into microporous structures with various gelation methods, which facilitates delivery of drugs and other small molecules [34]. Despite their advantages, however, silk fibroin hydrogels may induce a mild immune and inflammatory response in in vivo experiments, and due to their chemical stability, it is difficult to make chemical modifications. In a recent study, a sericin fibroin patch was placed directly on the infarcted cardiac area in rats with MI, and markedly reduced fibrogenesis, enhanced revascularization by increasing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), bFGF, and hepatic growth factors (HGF), and ameliorated cardiac dysfunction during the repair process [35].
Elastin, Chitosan, and Keratin
Elastin is a type of insoluble polymer and ECM protein which is responsible for elasticity in tissues and organs, such as blood vessels, skin, lung, and elastic ligaments. It accounts for about 70% of dry weight in the ligaments, with high elasticity. Elastin is involved in many biological processes, including elastin synthesis, fibroblast and smooth muscle cell proliferation, regulation of matrix protease activity, and tissue healing. In order to overcome its insolubility, recombinant human tropoelastin is utilized to develop synthetic elastin. Because of their ability to transition from a disorganized to an organized form with increasing temperature, elastin and tropoelastin have been used extensively as delivery systems.
Chitosan is another natural polysaccharide, which can be obtained from the deacetylation of chitin from insects. It demonstrates good biocompatibility and does not trigger immunogenicity when applied in vivo. Chitosan can also be conjugated with other molecules to form new polymers for drug and cell delivery. Research indicated that chitosan-based polymer could reduce oxidative stress and sustainably release stem cell homing factor stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) when applied in ischemic tissue during tissue repair [36]. When delivered with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSCs) in rats with MI, it significantly enhanced stem cell survival and engraftment by altering the microenvironment [37]. When cardiomyocytes were combined with collagen hydrogel, the hydrogel significantly improved the maturation and metabolism of cardiomyocytes [38].
Keratin is a common protein found in skin, hair, and other epithelial cells. Intriguingly, there is a large amount of hair discarded each year, and keratin can be extracted from it, which makes keratin a low-cost and renewable biomaterial for tissue regeneration. Because it is present naturally in the human body, keratin exhibits good biocompatibility and biodegradability. One study illustrated that hair-derived keratin biomaterials injected in infarcted hearts significantly improved revascularization, restored cardiac function, and attenuated cardiac remodeling after ischemia without exacerbation of inflammation in rats with MI [39].
Synthetic Hydrogels
Synthetic hydrogels are more promising in tissue regeneration due to their outstanding mechanical properties, morphology, and degradability. The size of pores in synthetic gels is easy to manipulate by adjusting molecular weight, copolymerization ratio, and ingredient composition. Synthetic hydrogels also exhibit better contractility and conductivity and more appropriate hardness than traditional natural hydrogels. At present, the most common synthetic hydrogels applied in cardiac regeneration include poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), polyglycolic acid (PGA), polylactic acid (PLA), polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAAM), and poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone) (PGCL).
PEG
PEG is a well-established nontoxic synthetic polymer and is widely used in the field of regeneration. PEG hydrogels are hydrophilic, injectable, bio-inert, nondegradable, and pH-sensitive [40]. PEG is a versatile hydrogel; the synthesis process is controllable and reproducible. Its physical and chemical features, including molecular weight, mechanical strength, and degradation rate, can be controlled during manufacturing, making it a cytocompatible biomaterial. Chemokine (C–C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) and C–C motif chemokine receptor 2 (CCR2) play important roles in recruiting monocytes after MI. Wang et al. developed a PEG-based micelle called PEG-distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine (PEG-DSPE) loaded with CCR2 antagonist, and applied it in mouse MI models through tail vein injection 48 h and 72 h after induction of MI. They discovered that PEG-DSPE loaded with CCR2 antagonist significantly downregulated inflammatory cells and sharply reduced infarct size [41]. Rane et al. injected PEG directly in rat models with MI after 1 week. Observation at around 1 week and 7 weeks after MI showed that the cardiac wall thickness was significantly increased in the PEG group compared with the control group. However, cardiac dysfunction was quite similar between the PEG and control groups [42].
PGA
PGA is a degradable polymer first investigated in the field of biomedicine. Rapid degradation and insolubility in many common solvents limit the use of PGA [43]. Ke et al. applied embryonic stem cells (ESCs) together with PGA patches onto the ischemic and para-ischemic myocardium, and ultimately discovered that ESCs plus PGA patches significantly improved blood pressure and left ventricular function; the survival of ESCs was also higher than in MI and MI plus PGA groups, suggesting that PGA could serve as a good platform for repair in ischemic heart disease [44].
PLA
PLA is a biopolymer obtained from multiple renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. It is an aliphatic ester of lactic acid widely manufactured because of its easy industrial production. PLA has many advantages. It has low toxicity, good biocompatibility and biodegradability, and proper mechanical strength, and exhibits a low inflammatory response applied in vivo. PLA is also injectable and compressible, which makes it applicable for wide use. In addition, the cost to produce PLA is relatively low in comparison with other traditional polymers. PLA is highly bioabsorbable and generally does not trigger fibrosis and adhesions during in vivo experiments. Moreover, it is transparent and aids in ideal visualization during surgery [45]. However, PLA has low hydrophilicity and prolonged degradation time. Its hydrolytic degradation is affected by many factors, such as its additives, chemical constituents, molecular weight, morphology, porosity, site of action, and water permeability and solubility. Modification techniques are utilized to reduce its degradation time. Radiation can be used to create radicals to enhance branching and cross-linking. Shortening the polymer can induce more rapid degradation. A study utilizing PLA and PLGA nanoparticles as delivery systems for sirolimus during percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) found that these delivery systems exhibited good biocompatibility and biosafety to local cardiac tissues, and significantly decreased the neointima compared with the control group in swine models [46].
PLGA
PLGA is another extensively utilized biodegradable and biocompatible biopolymer, which has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in drug delivery. The degradation rate of PLGA is controllable, and it can be used as a drug and cell carrier. When synthesized in the form of nanoparticles, it allows slow and sustained drug release into interstitial spaces due to its good permeability [47]. Al Kindi et al. applied a PLGA microparticle (PLGA-MPs) system loaded with milrinone by intravenous injection into rat models with MI, and showed that this combination could significantly improve cardiac dysfunction and release higher milrinone concentrations than PLGA-MPs alone or milrinone alone. Moreover, PLGA-MPs loaded with milrinone exhibited lower inflammation than the other two groups [48]. Ishimaru et al. applied a selective prostacyclin receptor agonist, ONO1301, polymerized with PLGA in a hamster model with dilated cardiomyopathy, and discovered that it enhanced capillary generation and inhibited left ventricular remodeling by upregulation of HGF, VEGF, and stromal cell-derived factor-1. The survival rate was much higher in the treatment group than in the control and sham groups [49].
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM)-Based Gels
PNIPAM is a smart material with thermo-responsive characteristics. With changes in temperature, the conformation of PNIPAM will change from coil to globule, enabling it to be widely used in the field of biomedicine. PNIPAM can undergo a reversible hydrophilic-to-hydrophobic transition at 32 °C in liquid solution. When it is utilized for drug release, the temperature should be increased above 32 °C. It has been reported that PNIPAM is not appropriate for use in in vivo experiments because of rapid aggregation during the injection, so chemical modifications are required. In recent years, PNIPAM-based hydrogels have been widely used as drug delivery systems for biomedical applications, enabling the controlled release of drugs in a target organ. PNIPAM hydrogels are usually manufactured by interaction with cross-linkers with a coil-to-globule transition, which leads to a quick decrease in the volume of the gel and rapid release of entrapped drugs, in line with a linear and diffusion controlled release [50, 51]. An injectable, pH- and temperature-sensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-propylacrylic acid-co-butylacrylate) hydrogel was synthesized and proved to enhance angiogenesis in infarcted myocardium. This hydrogel can approach therapeutic angiogenesis by providing spatial and temporal control of angiogenic growth factor delivery [52].
PGCL
PGCL is an elastic synthetic hydrogel with great mechanical properties, biodegradability, and biocompatibility. PGCL has good elasticity; it can be extended by more than 250% with recovery greater than 98% after being stretched. Moreover, PGCL hydrogel shows a permanent deformation of less than 4%, with extensions around 5–20% at a frequency of 0.1 Hz. In addition, the average molecular weight is around 121,000 g/mol, endowing PGCL with excellent mechanical properties and proper pore size for drug and cell delivery. PGCL is a permeable layer and plays an important role in cell migration and nutrition diffusion [53]. With these advantages, it can be used as a cardiac patch to be implanted onto the surface of the myocardium, and is harmonious with the contraction and dilation of the cardiac tissue. Studies have indicated that bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells (BMMNCs) can be seeded on the PGCL patch onto the epicardial myocardium in rat models with MI, leading to improved BMMNC migration to the infarcted myocardium using this patch. Moreover, left ventricular function was reportedly restored and revascularization was enhanced by treatment with PGCL gel plus BMMNCs or only PGCL hydrogel compared to the control group [54].
Cross-Linking Methods
Based on the cross-linking methods, hydrogels can be divided into physical and chemical cross-linked hydrogels. The cross-linking methods are dependent on the application and function of hydrogels.
Physical Cross-Linking
The physical cross-linking method is a transient junction defined as preparation in mild conditions without the use of chemical modification. Because of the lack of cross-linkers during the fabrication, physical hydrogels are usually homogeneous and demonstrate low toxicity and excellent biocompatibility. Alginate, collagen, gelatin, and HA are the polymers most frequently utilized to generate physical hydrogels. However, since the links between polymers are weak, those hydrogels are regarded as reversible gels and are less stable during the application, so they are likely to be degraded earlier by their corresponding proteolytic enzymes. The features of physically cross-linked hydrogels, like gelation time, pore size, and degradation rate, are inflexible, resulting in inconsistent performance during in vivo experiments [55]. Each kind of physical hydrogel has some drawbacks. For example, gelatin can only be dissolved at high temperature. Due to the reversible physical interactions between polymers, those physically cross-linked hydrogels demonstrate poor mechanical properties. Thus, many properties must be modified during manufacturing. Pressure, light, ions, temperature, electricity, and magnetism are the most common physical cross-linking methods, which divide hydrogels into pressure-cross-linked, photo-cross-linked, thermo-responsive, and ionic cross-linked hydrogels [56].
Chemical Cross-Linking
Chemical cross-linking is the most common way to increase the mechanical properties of hydrogels. Hydrogels generated in this way are usually nonhomogeneous and much more stable than those synthesized by physical cross-linking, because chemical cross-linking makes a permanent junction due to covalent bonds which can be modified by various chemicals. Thus, chemically cross-linked hydrogels can be considered irreversible hydrogels. If the polymers comprise amine, hydroxy, or hydrazide groups, glutaraldehyde can be cross-linked with these groups to generate covalent bonds. The physical properties of diffusion, swelling, elasticity, pore size, and mechanical strength are quite flexible and dependent on the temperature, degree of cross-linking, and manufacturing method. Common methods for the preparation of hydrogels by chemical cross-linking include pH cross-linking, Schiff-base cross-linking, and enzymatic cross-linking.
Delivery Methods
An ideal hydrogel for cardiac repair requires easy delivery, accurate targeting, and minimum injury to the local tissue. The natural injectable hydrogels currently approved by FDA are alginate, collagen, chitosan, chondroitin, dextran, fibrin, gelatin, HA, and silk. Synthetic hydrogels like PEG, PGA, PLA, PLGA, and PNIPAM are injectable as well. This feature facilitates endocardial, epicardial, and intracoronary delivery methods to treat MI. Injectable gels can be delivered as a single bolus or multiple injections. A single bolus is generally used for small animals, whereas multiple delivery can be applied to large animals. The volume for the injection is optimized by different needs and animal models. One study suggested injection volumes as follows: 10–50 µl for the mouse model, 50–250 µl for the rat model, 200 µl for the rabbit model, 1–4 ml for the porcine model, and 1.3–6 ml for the ovine model [57]. MI is followed by cardiomyocyte necrosis, inflammation, fibrosis and scar formation, and chamber dilation. Delivering hydrogels at different time points affects different pathological processes. MI cannot be reversed at late stages. Immediate injection of hydrogel after MI is not applicable in clinical practice since patients cannot be treated instantaneously after the MI. Thus, choosing the right time point for hydrogel delivery is crucial for therapeutic effectiveness in experiments and in clinical practice [57].
Intracoronary Delivery
Intracoronary delivery is a very common method for delivery of injectable hydrogel into cardiac tissue. Both the coronary artery and venous system can be applied for hydrogel delivery. The ideal hydrogel that can be delivered by this method is required to be non-thrombogenic and without bloodstream leakage. Typically, intracoronary delivery utilizes a catheter setup, and the hydrogel is delivered by trained interventional staff. This method does not cause direct damage to surrounding tissues. However, the gel inevitably leaks into the bloodstream, which makes this strategy much more challenging [58]. Moreover, the delivery cannot be precisely controlled, which requires sophisticated instruments to monitor the effect. Another problem is that hydrogel cannot efficiently reach the whole infarcted area because of vasculature damage during the infarction [59].
Epicardial Delivery (Injection/Spray)
Epicardial injection requires the gel to maintain a liquid form before injection, and transfer into a solid phase after delivery. This method requires the removal of the pericardium and demands open-chest surgery. By epicardial delivery, it is easy to deliver a limited amount of gel to damaged tissue. However, it is much more invasive and raises the risk of operation. Although, to our knowledge, there is no spray hydrogel for MI treatment, one study introduced an absorbable hydrogel which could be sprayed onto the mediastinal surface during congenital heart defect surgery in infants. This method notably reduced mediastinal adhesions after surgery [60]. Spraying of hydrogels in cardiac regeneration may also be realized in the future.
Endocardial Delivery
Endocardial delivery can be performed by means of catheter technology. It can directly deliver the gel to the target infarcted area [57]. But this technology is not commonly performed because it requires specialized training and imaging techniques. Moreover, the heart is moving during the delivery, causing leakage of the gel into the ventricle. Some research demonstrates that alginate, collagen, fibrin, ECM, and other biomaterials can be bioengineered into cardiac patches. These patches can be placed endoventricularly as well.
Pericardial Delivery (Implantation)
Pericardial delivery is a convenient way to deliver hydrogel to the infarcted myocardium. Currently, the biocompatible and non-immunogenic cardiac patch is widely utilized in animal MI models. Alginate, collagen, ECM, and fibrin are good choices. Many synthetic hydrogels, such as PGCL, have good elasticity and mechanical properties and can be applied as a cardiac patch onto the infarcted myocardium, providing a temporary scaffold for stem cell migration and growth, and presenting a harmonious and consistent stretch and recoil during normal cardiac cycles to aid recovery from MI [54]. Moreover, a cardiac patch provides an electric-conductible scaffold to facilitate electrical conduction between ischemic and normal cardiac tissues. A 3D-bioprinted cardiac patch based on decellularized ECM bioink with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and VEGF was directly implanted in the infarcted myocardium, and showed significant improvement of cardiac function, new capillary and muscle formation, and reduction of cardiac remodeling after MI [61]. The disadvantage of the cardiac patch is that it requires open-chest operation, which increases the risks related to the surgery. In addition, the cardiac patch requires appropriate thickness and similar mechanical strength and elasticity as the myocardium, which should be taken into consideration during manufacturing.
Intracardial Delivery
Alginate, fibrin, hyaluronic acid, and Matrigel can be delivered by intracardial injection. Those hydrogels should be in liquid form for storage and transformed into a solid phase when reaching the targeted tissue. The transformation rate should be neither too quick nor too slow. Intracardial injection can specifically target the ischemic heart tissue with specific doses and different positions in and around the ischemic tissues, and it is safe and minimally invasive. But in most cases, this method still requires an opening of the chest to enable a clear view of the heart, which leads to the risks associated with surgery. Moreover, it will result in leak during the intracardial injection.
The Application of Natural and Synthetic Hydrogels in MI Models
The application of natural and synthetic hydrogels in MI models has been well studied in recent years (Table 1). As a natural hydrogel, alginate is commonly used to test its roles in rodent MI models. Some studies have indicated that alginate can improve cardiac function, increase scar thickness, and attract myofibroblasts after intramyocardial injection, whereas other studies have demonstrated that alginate alone produces no improvement in cardiac function [5, 62, 63]. Collagen is another natural hydrogel that is used in rodent and swine models with MI. Studies found that collagen hydrogel is most effective when administered early after the onset of ischemia. Transplantation of collagen patches with ADSCs in rat and swine MI models was shown to significantly improve cardiac function, decrease fibrosis, and enhance angiogenesis and cardiac remodeling as well [11,12,13]. Fibrin is another good natural hydrogel material. Studies indicate that hydrogel made with fibrin can enhance the survival of cell transplant, reduce infarct area, and promote blood flow to the ischemic myocardium [15]. Fibrin-rAAV9-CyclinA2 is effective in preventing cardiac remodeling and preserving cardiac function after MI [16]. BMSC-fibrin patch significantly ameliorated cardiac dysfunction, reduced cardiac remodeling, and increase angiogenesis after MI [64]. Gelatin-based natural hydrogel has been shown to be protective for the heart after MI in both rat and canine models [22, 27, 65]. HA-gelatin hydrogel has been demonstrated to be effective and protective in cell activity and improving cardiac dysfunction after MI in both mice and rats [19, 66]. Moreover, a biopolymer made with Matrigel, fibrin, and collagen has proved to be promising in treating MI in rat cardiac ischemia–reperfusion injury, enhancing the infiltration of myofibroblasts into the infarct area. In addition, Matrigel-based hydrogel shows good recruitment of stem cells and angiogenesis and improves iPS cell survival in ischemic cardiac tissue [30, 32, 67]. Silk fibroin or coupling with HA and BMSCs exhibits increased angiogenesis, elevated growth factors, decreased apoptosis, and reduced cardiac remodeling after MI in mice and rats [35, 68, 69]. Moreover, synthetic hydrogels or combination with natural hydrogels have been shown to be promising in rabbit, mouse, and rat MI models with BMSCs or tPA, or cell contractility inhibitors [70,71,72]. Moreover, synthetic hydrogels combined with peptides, hydrazides, aldehydes, and siRNA have been shown to be protective for cardiac function and remodeling after MI in rat and mouse MI models [73, 74]. Other synthetic hydrogels such as PCL, PEG or PGCL, or PLGA, poly(NIPAAm-co-VPco-MAPLA-co-MATEMPO), coupled with BMSCs, VEGF, IGF-1, MSCs, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavengers is also protective for cardiac function, cardiac remodeling, and angiogenesis in mouse, rat, and rabbit MI models [8, 42, 54, 76,77,78,79,80].
The Pros and Cons of Natural Hydrogels
Different natural hydrogels each have their own advantages and disadvantages. Alginate offers the advantages of non-thrombogenic, biocompatible, and bio-inert characteristics. However, its cell adhesion is limited, which requires modification [5, 6, 81]. Chitosan is non-immunogenic, with low toxicity and good biocompatibility, and can be conjugated with other molecules for delivery. However, its mechanical properties are non-controllable [38]. Collagen is one of the most widely used natural hydrogels due to its low immunogenicity, good availability, remarkable biocompatibility, good biodegradability, and sufficient mechanical stability, and its tensile strength can be modified by varying the collagen amount and by cross-linking. Collagen enhances stem cell engraftment and requires fewer cells to be transplanted. Moreover, collagen can easily change shapes and can be used for 3D-printed tissues. The disadvantages are that its mechanical properties are not controllable, collagen lacks mechanical robustness, and cell migration is limited because of the high weight fraction of the gel [8, 13, 82]. Elastin is soft and stretchable, with good cell–matrix interactions, elasticity, and biocompatibility. However, elastin requires a specific temperature during aggregation or self-assembly, and its insolubility, easy calcification, and poor mechanical stability limit its applications [83, 84]. Fibrin has good biocompatibility and biodegradability; it can be easily cross-linked with cells and can be injected in vivo into tissues. Fibrin can be easily modified to many shapes and morphologies, and can thus provide a good drug delivery system with great extensibility. However, stiffness and rapid degradation are two major drawbacks of fibrin [85, 86]. Gelatin has good solubility and ideal biocompatibility and biodegradability. The isolation of gelatin is simple at very low cost. Since gelatin is nontoxic and has good compatibility in vivo, it can be used for 3D printing and in vivo experiments, and is ideal for drug delivery. The drawback for gelatin is that it has a prolonged existence in vivo [22]. Hyaluronic acid (HA) is non-immunogenic and has excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability. Its disadvantages are rapid degradation and poor retention in cells [20]. Matrigel is a soluble natural hydrogel and has good attachment for cells, which promotes cellular attachment, proliferation, differentiation, and angiogenesis. It is cytoprotective and less invasive, and can be used to deliver many growth factors. However, it undergoes a fast transition to a solid at 37 °C due to structural weakness, and can only be used for short-term analysis [29, 30]. Keratin has wide availability and can be easily obtained. Its primary advantages are its low cost, renewability, good biocompatibility and biodegradability, high stability, and no inflammatory or immunogenic response. However, it is insoluble, and the chemicals used to increase its solubility are toxic [87]. Silk fibroin is abundant in nature and thus low-cost. It has robust mechanical and elastic properties and is highly stable. Because it is nontoxic and highly biocompatible, it can be used for 3D printing. Its shortcomings include mild immune and inflammatory response, difficulty in chemical modification, and degradation rate dependent on processing methods [33, 34]. The pros and cons of natural hydrogels are summarized in Table 2.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Synthetic Hydrogels
Synthetic hydrogels have advantages and disadvantages as well (Table 3). PEG is a nontoxic synthetic hydrogel that can be modified by different methods and used to carry multiple drugs, ECMs, and growth factors due to its high biocompatibility and water solubility. Its synthesis and degradation are controllable and reproducible, which makes it an ideal material for drug delivery. However, its applications are limited because of poor degradation, which requires high temperature or modification [40, 88]. PGA is a biocompatible and biodegradable synthetic hydrogel, and is a commonly used biomaterial. However, the drawbacks of PGA are rapid degradation rate and insolubility [43, 44]. PLA has renewable resources, and it has many advantages, such as good biocompatibility, biodegradability, and bioabsorbability, low toxicity, proper mechanical strength, and mild inflammatory response, and it is transparent, low-cost, easily produced, and compressible, and can be injected in vivo. The disadvantages are low hydrophilicity and long-term degradation [4]. PLGA is a biodegradable and biocompatible biomaterial with a controllable degradation rate, and can be used as a nontoxic carrier for drugs and tissues. However, PLGA can induce inflammation [89]. PNIPAM is a thermosensitive biomaterial that is suitable for controlled drug release. The drawbacks for PNIPAM are its rapid aggregation and need for chemical modification [50]. PGCL is a biomaterial with good mechanical strength, biodegradability, and biocompatibility. Its elasticity and proper pore size are also suitable for drug and cell delivery [53].
Comparisons Between Natural and Synthetic Hydrogels
Both natural and synthetic hydrogels have their advantages and disadvantages (Table 4). Natural hydrogels are biocompatible and can provide a similar microenvironment as native tissue. They are widely available, with easy processing at low cost. However, natural hydrogels have weak mechanical properties and sometimes are difficult to modify and purify, and variations can be seen from batch to batch. Synthetic hydrogels have good biocompatibility, biodegradability, and bioresorbability. They are easily modified and have good reproducibility, controlled degradation time, and ideal mechanical properties. The drawbacks are that synthetic hydrogels are costly and the manufacturing process is complicated.
Hydrogels Can Serve as a Delivery System
As an ideal delivery system for small molecules and stem cells, hydrogels must be resistant to enzyme degradation, have the ability to target specific tissues, and allow the controllable release of relevant molecules. Below are different cellular and molecular ingredients which have been applied in animal models with MI and show promise for treating MI in humans.
Stem Cell Delivery
Stem cell therapy is a promising method for cardiac tissue regeneration, since stem cells have great potential to differentiate into cardiac cells. Stem cells can be acquired from a wide range of approaches, such as direct separation from embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells. In recent years, multiple stem cells have been investigated, such as adipose-derived stromal cells (ASCs), cardiomyocytes (CMs), epithelial cells (ECs), cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs), endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), embryonic stem cells (ESCs), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMMSCs). As stem cells have the propensity to form tumors, undifferentiated stem cells are often not applied directly during clinical transplants. Moreover, the retention and survival of stem cells in ischemic tissue is very limited, which poses significant challenges in their clinical use for cardiac regeneration.
In recent research, scientists have discovered that multiple hydrogels can be applied as important delivery systems for stem cell retention. They provide an ideal microenvironment for stem cells to maintain their stemness, promoting their survival and differentiation. MSCs have been found useful in the therapeutic treatment of MI. One study reported that MSC retention and impulse conduction could be enhanced by alginate hydrogels in swine MI models [90]. Another study indicated that retention of MSCs could be realized by using a novel injectable thermosensitive hydrogel, which is made from copolymer with N-isopropylacrylamide/acrylic acid/2-hydroxylethyl methacrylate-poly(ɛ-caprolactone) coupled with type I collagen. This hydrogel was shown to significantly promote the survival of the grafted MSCs, stimulate neovascularization, attenuate fibrosis, and further improve cardiac function in the MI models [91]. Francis et al. discovered that an original hydrogel derived from the human placenta (hpECM) was helpful in cardiac regeneration. It showed versatility as it comprised numerous collagens, fibronectin, glycoproteins, laminin, growth factors, and several known pro-regenerative, pro-angiogenic, and stem cell-recruiting factors. Furthermore, it could induce human iPSC-derived CMs to be electrically synchronized at a faster speed than traditional methods. Compared with the sham group, rat MI models with hpECM injection showed a significant decrease in scar size and promotion of normal electrical conductivity in the surviving tissues, indicating that hydrogel is promising in cardiac regeneration [92].
Drug Delivery System (DDS)
A DDS is a device which can be loaded with therapeutic compounds and delivered to the animal or human body in order to enhance the safety and efficiency of the delivery of drugs to a target site or tissue with controllable delivery time and rate. Drug efficacy can be significantly affected by the delivery method. For achieving the desired concentration of a drug in the body, hydrogels have shown significant advantages over traditional methods, with moderate pore size for better drug delivery and protection of drugs from degradation in the body. Moreover, they can facilitate the gradual release of the drug to the target tissues and reduce drug delivery times. Currently, alginate, chitosan, cellulose, dextran, PLA, and PLGA can all be applied as a DDS because of their biocompatibility and biodegradability. The selection of the appropriate DDS is dependent on the features of polymers and target drugs and tissues.
Cytokines
Multiple cytokines have been applied to MI models. Growth factors are most common for regulating cell fate and function during regeneration, such as fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), nerve growth factor (NGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-β1), and vascular endothelial growth factor 165 (VEGF165). However, the delivery of growth factors requires a moderate release speed rather than a burst release profile. Hydrogels and nanoparticles perform important roles during growth factor release. They can control the release speed in a sustained manner [93]. Moreover, these materials can increase the stability and specificity of growth factors. All those growth factors have already been applied with different hydrogels in the investigation of MI models, and most of the research has exhibited exciting discoveries that various hydrogels can provide an ideal platform for growth factors to release and facilitate the restoration of cardiac function after MI.
Nucleic Acids and Plasmids
Gene delivery and therapy can be realized by hydrogels. Introducing genomic materials into a target tissue is beneficial for individuals. Small nucleic acids and plasmids can be conjugated to different hydrogel-based DDS to reach the therapeutic target. Some scientists have applied hydrogels as a tool to release siRNA against MMP2(siMMP2). MMP2 is responsible for cardiac remodeling after MI. When responding to proteases, hydrogels were eroded and released active siRNA, which further knocked down MMP2 in primary CFs. In a rat model of MI after 4 weeks, hydrogels delivering siMMP2 improved myocardial thickness in the infarct area and made a significant improvement in increasing ejection fraction (EF), stroke volume (SV), and cardiac output (CO) compared to hydrogels with control siRNA [74]. Wang et al. applied a soft hydrogel (based on PEG-HA) having similar myocardial conductivity loaded with a plasmid DNA encoding endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOs) nano-complexes coupled with ADSCs to treat MI. This hydrogel-based plasmid delivery system was directly injected into the infarcted myocardium in rats with MI. Expression of eNOs in myocardial tissue significantly increased with enhanced expression of proangiogenic growth factors. Moreover, a remarkable increase in EF, less fibrogenesis, smaller infarction size, and greater revascularization were demonstrated with this treatment [94]. Combination with conductive injectable hydrogel, stem cells, and gene-encoding plasmid might become an ideal therapeutic strategy for MI in the future.
Peptides
Hydrogels can be utilized to carry peptides to prevent cardiac functional loss in MI models. By injection into the peri-infarct/MI zone on rat models with MI, a chitosan-collagen-based hydrogel immobilized with pro-survival angiopoietin-1-derived peptide was shown to better attenuate post-MI cardiac remodeling than gel without peptide or gel with PBS groups. This hydrogel remained in situ for 2 weeks and degraded around the third week. The combination significantly ameliorated cardiac dysfunction and scar thickness. Moreover, more CMs were detected in the MI zone after hydrogel application, without inducing an inflammatory response [95].
ECM is degraded by increasing matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) after MI, which can lead to a decrease in tissue mechanical properties. Mitigating the degradation of ECM in the early stage of MI can restore cardiac function. Ma et al. used a thermosensitive hydrogel based on the polymerization of NIPAM, HEMA, and acrylate-oligolactide carried with an MMP-2-specific inhibitor, CTTHWGFTLC (CTT), to continuously release CTT in the heart tissue. This system demonstrated that it could successfully prevent ECM degradation and improve cardiac dysfunction in rat MI models [96].
Oxygen Delivery System
After MI, the lack of oxygen in the local cardiac tissue makes cardiomyocytes vulnerable to cell death. Controlled oxygen release to the infarcted area may be a potential way to protect the ischemic cardiac cells and promote cardiac repair. Current oxygen delivery methods cannot effectively diffuse oxygen into the infarcted area due to low blood flow in the ischemic area. Fan et al. developed a new oxygen delivery system using hydrogels with features of thermosensitive, fast gelation combined with oxygen-releasing microspheres. It was shown to consistently release oxygen and specifically diffuse to infarcted cardiac tissue. This system was able to release oxygen continuously for 4 weeks, which significantly improved the survival of cardiac cells under ischemic conditions with 1% O2, which was equivalent to the concentration of infarcted cardiac tissue. After the application of this system on infarcted hearts for 4 weeks, cell survival was improved, and the number of macrophages decreased significantly. Moreover, collagen deposition and myofibroblast density were prominently reduced and angiogenesis was significantly improved, which greatly improved cardiac function [97].
Hydrogels Can Modulate the Microenvironment, Signal Transduction, and Endogenous Cell Response
A large number of biofunctional additives can be added to hydrogels in order to enhance their biological effects. These additives can be cytokines, nucleic acids, extracellular ligands, and short peptides [98], and can be performed as biochemical and biophysical signals, and provide an ideal microenvironment. In addition, they can determine and modulate cell fate and function during regeneration. More interestingly, hydrogels can modulate the microenvironment for tissue regeneration. A relevant study indicates that hydrogel together with antioxidants and anti-inflammatory factors can inhibit target tissue oxidation and inflammation [99, 100]. The heart has the ability to transduce orchestrated electrical activity during its normal function. After MI, collagen and fibrotic scar are often formed and severely affect electrical activity transduction. Hydrogels provide a good platform for electrical signal transduction after ischemic events. Many studies are engaged in developing novel hydrogels to lower the electrical impedance in the cellular environments and enhance the survival and maturation of engineered heart tissue. In this way, the excitability and attachment of the cardiac cells and tissue can be significantly improved. Some studies demonstrate that polymer hydrogels (polypyrrole (PPy)-chitosan hydrogel) can prominently enhance cell electrical signal transduction and ameliorate cardiac dysfunction when applied to the ischemic and infarct cardiac tissue. Collagen and fibrotic scar formation during MI severely affects impulse and electrical activity transduction. Some scientists have established hybrid properties with nano-electrics and cardiac tissues to sense the spatial electrical signal in the microenvironment, which is much more promising in drug testing in a real-time manner [101].
Hydrogels can also modulate endogenous cell response. During tissue regeneration, injured tissue response relies on the surrounding cell response, which is determined by the cell types and populations. As hydrogels can be utilized as a delivery platform for stem cells or cytokines, these combinations provide basic elements for cell survival and engraftment. They also enhance the cell–cell interaction, promoting communication of information between cells [98].
New Technology Applied in Hydrogels
3D and 4D Bioprinting
Three-dimensional printing is an emerging and promising field for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. It can generate 3D tissues or organs for application in vivo. Moreover, 3D-printed structures can be used to test the safety and efficiency of the DDS. The bioink used in 3D printing contains various types of cells and biomaterials, and can transform from a liquid phase into a solid form to generate functional 3D architectures under the precise control of pre-designed computer software. Different cell types can be utilized for 3D bioprinting in cardiac regeneration, including endothelial cells, cardiomyocytes, fibroblast cells, mesenchymal cells, and smooth muscle cells [102].
Biomaterials for 3D bioprinting are utilized as a scaffold to support 3D architecture and nutrient transfer, sometimes as a natural ECM environment in the heart. The ideal material for bioprinting must be easily tunable, with specific viscosity, the ability to transform from a liquid form to a solid form, must be nontoxic, with good biocompatibility without inducing inflammation or immune response, and must have proper mechanical properties (stiffness, elasticity, strength), biodegradability, and appropriate pore size. The viscosity of bioink determines the resolution, mechanical strength, and outer appearance. Alginate, agarose, chitosan, collagen, HA, and decellularized ECM can be used as biomaterial for 3D bioprinting [102].
Recently, Maiullari et al. developed a PEG-based hydrogel with induced pluripotent cell-derived cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CMs) and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), and applied 3D technology to encapsulate cells within the hydrogel. A 3D cardiac tissue was generated and applied in non-obese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD-SCID) mice. Their research showed that these 3D-bioprinted multicellular structures could mature in vivo and aided in vascularization. This method shows potential for enabling revascularization of ischemic tissue and organs [103]. Other scientists applied 3D-bioprinted myocardium cultured with HUVECs and human mesenchymal cells based on HA/gelatin hydrogel patch in mice models with MI after 8 weeks, which significantly reduced cardiac adverse remodeling and restored cardiac performance [104].
Another printing technology, 4D bioprinting is much more advanced than 3D bioprinting because it is integrated with time. In order to create tissue structures that resemble nature, 4D bioprinting provides a dynamic way to produce structural and cell changes over a period of time. One way to create the 4D architecture is to seed 4D-bioprinted tissue into a desired shape, such as a tube like a blood vessel [105]. Another way is to promote the self-assembly of tissues through stimulation. Kaji et al. found that myocytes could conjugate gap junctions under chemical stimuli [106]. This 4D bioprinting technology holds promise in the field of cardiac regeneration, and will facilitate further novel work in the future.
Cooperation Between Hydrogels and Artificial Intelligence
Another thermally responsive, injectable hydrogel with relative stiffness, poly(NIPAAm-co-VP-co-MAPLA), was fabricated based on N-isopropylacrylamide and N-vinylpyrrolidone (VP gel). Optimized gel injected by a robot into the ventricular wall in vitro on beating infarcted porcine hearts showed that this thermosensitive gel injected using a temperature-controlled robotic system achieved an accurate injected location and reliable depth without any occlusion, thus showing great potential for therapeutic application in patient-specific planning strategies [107].
Biosensing and Diagnosis
In recent years, hydrogels have also been applied as biosensors or diagnostic tools for cardiac disorders such as arrhythmia [108]. In the future, additional kinds of hydrogels must be developed in these fields.
Prospective Hydrogel Applications in Cardiac Regeneration
Hydrogels are promising biomaterials for cardiac regeneration. Additional biomaterials with ideal physical and chemical properties will be developed in the future. Numerous studies are needed to confirm the therapeutic efficacy of hydrogels in animals and humans with MI. Hydrogels play significant roles in cardiac regeneration and tissue engineering, and pave the way for future therapeutic treatments of MI.
Limitations
Numerous newly developed hydrogels and applications of artificial intelligence in delivering hydrogels have not been mentioned. The signaling pathways and mechanisms of each hydrogel are not discussed in detail due to space limitations.
Conclusion
Hydrogels are promising biomaterials in tissue engineering and cardiac regeneration, which can be used in the future for treatment of MI.
Data Availability
Since this is a review article, data sharing is not applicable, as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Feygin J, Mansoor A, Eckman P, Swingen C, Zhang J. Functional and bioenergetic modulations in the infarct border zone following autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007;293:H1772–80.
Berry MF, Engler AJ, Woo YJ, Pirolli TJ, Bish LT, Jayasankar V, Morine KJ, Gardner TJ, Discher DE, Sweeney HL. Mesenchymal stem cell injection after myocardial infarction improves myocardial compliance. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;290:H2196–203.
Ahmed EM. Hydrogel: preparation, characterization, and applications: a review. J Adv Res. 2015;6:105–21.
Hamad K, Kaseem M, Yang HW, Deri F, Ko YG. Properties and medical applications of polylactic acid: a review. DOAJ Express Polym Lett. 2015;9:435–55.
Landa N, Miller L, Feinberg MS, Holbova R, Shachar M, Freeman I, Cohen S, Leor J. Effect of injectable alginate implant on cardiac remodeling and function after recent and old infarcts in rat. Circulation. 2008;117:1388–96.
Deng B, Shen L, Wu Y, Shen Y, Ding X, Lu S, Jia J, Qian J, Ge J. Delivery of alginate-chitosan hydrogel promotes endogenous repair and preserves cardiac function in rats with myocardial infarction. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103:907–18.
Leor J, Tuvia S, Guetta V, Manczur F, Castel D, Willenz U, Petnehazy O, Landa N, Feinberg MS, Konen E, Goitein O, Tsur-Gang O, Shaul M, Klapper L, Cohen S. Intracoronary injection of in situ forming alginate hydrogel reverses left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in Swine. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54:1014–23.
Liu Y, Xu Y, Wang Z, Wen D, Zhang W, Schmull S, Li H, Chen Y, Xue S. Electrospun nanofibrous sheets of collagen/elastin/polycaprolactone improve cardiac repair after myocardial infarction. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8:1678–94.
Merna N, Robertson C, La A, George SC. Optical imaging predicts mechanical properties during decellularization of cardiac tissue. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013;19:802–9.
van der Valk DC, van der Ven CFT, Blaser MC, Grolman JM, Wu PJ, Fenton OS, Lee LH, Tibbitt MW, Andresen JL, Wen JR, Ha AH, Buffolo F, van Mil A, Bouten CVC, Body SC, Mooney DJ, Sluijter JPG, Aikawa M, Hjortnaes J, Langer R, Aikawa E. Engineering a 3D-bioprinted model of human heart valve disease using nanoindentation-based biomechanics. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018;8(5):296.
Blackburn NJ, Sofrenovic T, Kuraitis D, Ahmadi A, McNeill B, Deng C, Rayner KJ, Zhong Z, Ruel M, Suuronen EJ. Timing underpins the benefits associated with injectable collagen biomaterial therapy for the treatment of myocardial infarction. Biomaterials. 2015;39:182–92.
Serpooshan V, Zhao M, Metzler SA, Wei K, Shah PB, Wang A, Mahmoudi M, Malkovskiy AV, Rajadas J, Butte MJ, Bernstein D, Ruiz-Lozano P. The effect of bioengineered acellular collagen patch on cardiac remodeling and ventricular function post myocardial infarction. Biomaterials. 2013;34:9048–55.
Araña M, Gavira JJ, Pena E, Gonzalez A, Abizanda G, Cilla M, Perez MM, Albiasu E, Aguado N, Casado M, Lopez B, Gonzalez S, Soriano M, Moreno C, Merino J, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Diez J, Doblare M, Pelacho B, Prosper F. Epicardial delivery of collagen patches with adipose-derived stem cells in rat and minipig models of chronic myocardial infarction. Biomaterials. 2014;35:143–51.
Radhakrishnan J, Krishnan UM, Sethuraman S. Hydrogel based injectable scaffolds for cardiac tissue regeneration. Biotechnol Adv. 2014;32:449–61.
Christman KL, Vardanian AJ, Fang Q, Sievers RE, Fok HH, Lee RJ. Injectable fibrin scaffold improves cell transplant survival, reduces infarct expansion, and induces neovasculature formation in ischemic myocardium. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:654–60.
Cao W, Chang YF, Zhao AC, Chen BD, Liu F, Ma YT, Ma X. Synergistic cardioprotective effects of rAAV9-CyclinA2 combined with fibrin glue in rats after myocardial infarction. J Mol Histol. 2017;48:275–83.
Prestwich GD. Hyaluronic acid-based clinical biomaterials derived for cell and molecule delivery in regenerative medicine. J Control Release. 2011;155:193–9.
Tan H, Ramirez CM, Miljkovic N, Li H, Rubin JP, Marra KG. Thermosensitive injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogel for adipose tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2009;30:6844–53.
MacArthur JW Jr, Purcell BP, Shudo Y, Cohen JE, Fairman A, Trubelja A, Patel J, Hsiao P, Yang E, Lloyd K, Hiesinger W, Atluri P, Burdick JA, Woo YJ. Sustained release of engineered stromal cell-derived factor 1-α from injectable hydrogels effectively recruits endothelial progenitor cells and preserves ventricular function after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2013;128:S79-86.
Cheng K, Blusztajn A, Shen D, Li TS, Sun B, Galang G, Zarembinski TI, Prestwich GD, Marban E, Smith RR, Marban L. Functional performance of human cardiosphere-derived cells delivered in an in situ polymerizable hyaluronan-gelatin hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2012;33:5317–24.
Tabata Y, Yamada K, Miyamoto S, Nagata I, Kikuchi H, Aoyama I, Tamura M, Ikada Y. Bone regeneration by basic fibroblast growth factor complexed with biodegradable hydrogels. Biomaterials. 1998;19:807–15.
Kumagai M, Minakata K, Masumoto H, Yamamoto M, Yonezawa A, Ikeda T, Uehara K, Yamazaki K, Ikeda T, Matsubara K, Yokode M, Shimizu A, Tabata Y, Sakata R, Minatoya K. A therapeutic angiogenesis of sustained release of basic fibroblast growth factor using biodegradable gelatin hydrogel sheets in a canine chronic myocardial infarction model. Heart Vessels. 2018;33:1251–7.
Kang HW, Tabata Y, Ikada Y. Fabrication of porous gelatin scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 1999;20:1339–44.
Lee W, Lee V, Polio S, Keegan P, Lee JH, Fischer K, Park JK, Yoo SS. On-demand three-dimensional freeform fabrication of multi-layered hydrogel scaffold with fluidic channels. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2010;105:1178–86.
Ptaszek LM, Portillo Lara R, Shirzaei Sani E, Xiao C, Roh J, Yu X, Ledesma PA, Hsiang YuC, Annabi N, Ruskin JN. Gelatin methacryloyl bioadhesive improves survival and reduces scar burden in a mouse model of myocardial infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020;9: e014199.
Yamamoto M, Ikada Y, Tabata Y. Controlled release of growth factors based on biodegradation of gelatin hydrogel. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2001;12:77–88.
Li Z, Masumoto H, Jo JI, Yamazaki K, Ikeda T, Tabata Y, Minatoya K. Sustained release of basic fibroblast growth factor using gelatin hydrogel improved left ventricular function through the alteration of collagen subtype in a rat chronic myocardial infarction model. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;66:641–7.
Zhou J, Chen J, Sun H, Qiu X, Mou Y, Liu Z, Zhao Y, Li X, Han Y, Duan C, Tang R, Wang C, Zhong W, Liu J, Luo Y, Mengqiu Xing M, Wang C. Engineering the heart: evaluation of conductive nanomaterials for improving implant integration and cardiac function. Sci Rep. 2014;4:3733.
Cavo M, Caria M, Pulsoni I, Beltrame F, Fato M, Scaglione S. A new cell-laden 3D Alginate-Matrigel hydrogel resembles human breast cancer cell malignant morphology, spread and invasion capability observed “in vivo.” Sci Rep. 2018;8:5333.
Ou L, Li W, Zhang Y, Wang W, Liu J, Sorg H, Furlani D, Gabel R, Mark P, Klopsch C, Wang L, Lutzow K, Lendlein A, Wagner K, Klee D, Liebold A, Li RK, Kong D, Steinhoff G, Ma N. Intracardiac injection of matrigel induces stem cell recruitment and improves cardiac functions in a rat myocardial infarction model. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15:1310–8.
Wang Z, Dong N, Niu Y, Zhang Z, Zhang C, Liu M, Zhou T, Wu Q, Cheng K. Transplantation of human villous trophoblasts preserves cardiac function in mice with acute myocardial infarction. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21:2432–40.
Ogasawara T, Okano S, Ichimura H, Kadota S, Tanaka Y, Minami I, Uesugi M, Wada Y, Saito N, Okada K, Kuwahara K, Shiba Y. Impact of extracellular matrix on engraftment and maturation of pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes in a rat myocardial infarct model. Sci Rep. 2017;7:8630.
Yucel T, Lovett ML, Kaplan DL. Silk-based biomaterials for sustained drug delivery. J Control Release. 2014;190:381–97.
Sun L, Parker ST, Syoji D, Wang X, Lewis JA, Kaplan DL. Direct-write assembly of 3D silk/hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone co-cultures. Adv Healthc Mater. 2012;1:729–35.
Chi NH, Yang MC, Chung TW, Chou NK, Wang SS. Cardiac repair using chitosan-hyaluronan/silk fibroin patches in a rat heart model with myocardial infarction. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;92:591–7.
Wang B, Guo Y, Chen X, Zeng C, Hu Q, Yin W, Li W, Xie H, Zhang B, Huang X, Yu F. Nanoparticle-modified chitosan-agarose-gelatin scaffold for sustained release of SDF-1 and BMP-2. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:7395–408.
Liu Z, Wang H, Wang Y, Lin Q, Yao A, Cao F, Li D, Zhou J, Duan C, Du Z, Wang Y, Wang C. The influence of chitosan hydrogel on stem cell engraftment, survival and homing in the ischemic myocardial microenvironment. Biomaterials. 2012;33:3093–106.
Reis LA, Chiu LL, Liang Y, Hyunh K, Momen A, Radisic M. A peptide-modified chitosan-collagen hydrogel for cardiac cell culture and delivery. Acta Biomater. 2012;8:1022–36.
Shen D, Wang X, Zhang L, Zhao X, Li J, Cheng K, Zhang J. The amelioration of cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction by the injection of keratin biomaterials derived from human hair. Biomaterials. 2011;32:9290–9.
Wang JZ, You ML, Ding ZQ, Ye WB. A review of emerging bone tissue engineering via PEG conjugated biodegradable amphiphilic copolymers. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;97:1021–35.
Wang J, Seo MJ, Deci MB, Weil BR, Canty JM, Nguyen J. Effect of CCR2 inhibitor-loaded lipid micelles on inflammatory cell migration and cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Int J Nanomed. 2018;13:6441–51.
Rane AA, Chuang JS, Shah A, Hu DP, Dalton ND, Gu Y, Peterson KL, Omens JH, Christman KL. Increased infarct wall thickness by a bio-inert material is insufficient to prevent negative left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 2011;6: e21571.
Ulery BD, Nair LS, Laurencin CT. Biomedical applications of biodegradable polymers. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys. 2011;49:832–64.
Ke Q, Yang Y, Rana JS, Chen Y, Morgan JP, Xiao YF. Embryonic stem cells cultured in biodegradable scaffold repair infarcted myocardium in mice. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2005;57:673–81.
Li J, Ren G, Zhang W. Reduction of abdominal adhesions with elecrospun fiber membranes in rat models. J Invest Surg. 2018;31:210–7.
Zago AC, Raudales JC, Attizzani G, Matte BS, Yamamoto GI, Balvedi JA, Nascimento L, Kosachenco BG, Centeno PR, Zago AJ. Local delivery of sirolimus nanoparticles for the treatment of in-stent restenosis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;81:E124–9.
Luo L, Chen B, Huang Y, Liang Z, Li S, Yin Y, Chen J, Wu W. Cardioprotective activity of placental growth factor combined with oral supplementation of l-arginine in a rat model of acute myocardial infarction. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016;10:3483–92.
Al Kindi H, Paul A, You Z, Nepotchatykh O, Schwertani A, Prakash S, Shum-Tim D. Sustained release of milrinone delivered via microparticles in a rodent model of myocardial infarction. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;148:2316–23.
Ishimaru K, Miyagawa S, Fukushima S, Saito A, Sakai Y, Ueno T, Sawa Y. Synthetic prostacyclin agonist, ONO1301, enhances endogenous myocardial repair in a hamster model of dilated cardiomyopathy: a promising regenerative therapy for the failing heart. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013;146:1516–25.
Okuyama Y, Yoshida R, Sakai K, Okano T, Sakurai Y. Swelling controlled zero order and sigmoidal drug release from thermo-responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-butyl methacrylate) hydrogel. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1993;4:545–56.
Jones DS, Lorimer CP, McCoy CP, Gorman SP. Characterization of the physicochemical, antimicrobial, and drug release properties of thermoresponsive hydrogel copolymers designed for medical device applications. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;85:417–26.
Garbern JC, Minami E, Stayton PS, Murry CE. Delivery of basic fibroblast growth factor with a pH-responsive, injectable hydrogel to improve angiogenesis in infarcted myocardium. Biomaterials. 2011;32:2407–16.
Lee SH, Kim BS, Kim SH, Choi SW, Jeong SI, Kwon IK, Kang SW, Nikolovski J, Mooney DJ, Han YK, Kim YH. Elastic biodegradable poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone) scaffold for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003;66:29–37.
Piao H, Kwon JS, Piao S, Sohn JH, Lee YS, Bae JW, Hwang KK, Kim DW, Jeon O, Kim BS, Park YB, Cho MC. Effects of cardiac patches engineered with bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells and PGCL scaffolds in a rat myocardial infarction model. Biomaterials. 2007;28:641–9.
Parhi R. Cross-linked hydrogel for pharmaceutical applications: a review. Adv Pharm Bull. 2017;7:515–30.
Saludas L, Pascual-Gil S, Prosper F, Garbayo E, Blanco-Prieto M. Hydrogel based approaches for cardiac tissue engineering. Int J Pharm. 2017;523:454–75.
Johnson TD, Christman KL. Injectable hydrogel therapies and their delivery strategies for treating myocardial infarction. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2013;10:59–72.
Dib N, Campbell A, Jacoby DB, Zawadzka A, Ratliff J, Miedzybrocki BM, Gahremanpour A, Diethrich EB, Opie SR. Safety and feasibility of percutaneous autologous skeletal myoblast transplantation in the coil-infarcted swine myocardium. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2006;54:71–7.
Chachques JC, Azarine A, Mousseaux E, El Serafi M, Cortes-Morichetti M, Carpentier AF. MRI evaluation of local myocardial treatments: epicardial versus endocardial (Cell-Fix catheter) injections. J Interv Cardiol. 2007;20:188–96.
Hasaniya N, Razzouk A, Newcombe J, Hassneiah D, Heimes J, Gysbers J, Martens T, Bailey L. An absorbable hydrogel spray reduces postoperative mediastinal adhesions after congenital heart surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018;105:837–42.
Jang J, Park HJ, Kim SW, Kim H, Park JY, Na SJ, Kim HJ, Park MN, Choi SH, Park SH, Kim SW, Kwon SM, Kim PJ, Cho DW. 3D printed complex tissue construct using stem cell-laden decellularized extracellular matrix bioinks for cardiac repair. Biomaterials. 2017;112:264–74.
Follin B, Ghotbi AA, Clemmensen AE, Bentsen S, Juhl M, Sondergaard RH, Lund LD, Haack-Sorensen M, Hasbak P, Cohen S, Ripa RS, Kastrup J, Ekblond A, Kjaer A. Retention and functional effect of adipose-derived stromal cells administered in alginate hydrogel in a rat model of acute myocardial infarction. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:7821461.
Rocca DG, Willenberg BJ, Qi Y, Simmons CS, Rubiano A, Ferreira LF, Huo T, Petersen JW, Ruchaya PJ, Wate PS, Wise EA, Handberg EM, Cogle CR, Batich CD, Byrne BJ, Pepine CJ. An injectable capillary-like microstructured alginate hydrogel improves left ventricular function after myocardial infarction in rats. Int J Cardiol. 2016;220:149–54.
Blondiaux E, Pidial L, Autret G, Rahmi G, Balvay D, Audureau E, Wilhelm C, Guerin CL, Bruneval P, Silvestre JS, Menasche P, Clement O. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell-loaded fibrin patches act as a reservoir of paracrine factors in chronic myocardial infarction. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11:3417–27.
Nakajima K, Fujita J, Matsui M, Tohyama S, Tamura N, Kanazawa H, Seki T, Kishino Y, Hirano A, Okada M, Tabei R, Sano M, Goto S, Tabata Y, Fukuda K. Gelatin hydrogel enhances the engraftment of transplanted cardiomyocytes and angiogenesis to ameliorate cardiac function after myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 2015;10: e0133308.
Smith RR, Marban E, Marban L. Enhancing retention and efficacy of cardiosphere-derived cells administered after myocardial infarction using a hyaluronan-gelatin hydrogel. Biomatter. 2013. https://doi.org/10.4161/biom.24490.
Huang NF, Yu J, Sievers R, Li S, Lee RJ. Injectable biopolymers enhance angiogenesis after myocardial infarction. Tissue Eng. 2005;11:1860–6.
Song Y, Zhang C, Zhang J, Sun N, Huang K, Li H, Wang Z, Huang K, Wang L. An injectable silk sericin hydrogel promotes cardiac functional recovery after ischemic myocardial infarction. Acta Biomater. 2016;41:210–23.
Chi NH, Yang MC, Chung TW, Chen JY, Chou NK, Wang SS. Cardiac repair achieved by bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells/silk fibroin/hyaluronic acid patches in a rat of myocardial infarction model. Biomaterials. 2012;33:5541–51.
Jiang XJ, Wang T, Li XY, Wu DQ, Zheng ZB, Zhang JF, Chen JL, Peng B, Jiang H, Huang C, Zhang XZ. Injection of a novel synthetic hydrogel preserves left ventricle function after myocardial infarction. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;90:472–7.
Chen J, Guo R, Zhou Q, Wang T. Injection of composite with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and a novel synthetic hydrogel after myocardial infarction: a protective role in left ventricle function. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2014;30:173–80.
Mihalko E, Huang K, Sproul E, Cheng K, Brown AC. Targeted treatment of ischemic and fibrotic complications of myocardial infarction using a dual-delivery microgel therapeutic. ACS Nano. 2018;12:7826–37.
Li H, Gao J, Shang Y, Hua Y, Ye M, Yang Z, Ou C, Chen M. Folic acid derived hydrogel enhances the survival and promotes therapeutic efficacy of iPS cells for acute myocardial infarction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:24459–68.
Wang LL, Chung JJ, Li EC, Uman S, Atluri P, Burdick JA. Injectable and protease-degradable hydrogel for siRNA sequestration and triggered delivery to the heart. J Control Release. 2018;285:152–61.
Zhou J, Yang X, Liu W, Wang C, Shen Y, Zhang F, Zhu H, Sun H, Chen J, Lam J, Mikos AG, Wang C. Injectable OPF/graphene oxide hydrogels provide mechanical support and enhance cell electrical signaling after implantation into myocardial infarct. Theranostics. 2018;8:3317–30.
Xu G, Wang X, Deng C, Teng X, Suuronen EJ, Shen Z, Zhong Z. Injectable biodegradable hybrid hydrogels based on thiolated collagen and oligo(acryloyl carbonate)-poly(ethylene glycol)-oligo(acryloyl carbonate) copolymer for functional cardiac regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2015;15:55–64.
Rufaihah AJ, Vaibavi SR, Plotkin M, Shen J, Nithya V, Wang J, Seliktar D, Kofidis T. Enhanced infarct stabilization and neovascularization mediated by VEGF-loaded PEGylated fibrinogen hydrogel in a rodent myocardial infarction model. Biomaterials. 2013;34:8195–202.
Rabbani S, Soleimani M, Sahebjam M, Imani M, Haeri A, Ghiaseddin A, Nassiri SM, MajdArdakani J, Tajik Rostami M, Jalali A, Ahmadi Tafti SH. Simultaneous delivery of Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal stem cells and insulin-like growth factor-1 in acute myocardial infarction. Iran J Pharm Res. 2018;17:426–41.
Zhou Q, Zhou JY, Zheng Z, Zhang H, Hu SS. A novel vascularized patch enhances cell survival and modifies ventricular remodeling in a rat myocardial infarction model. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;140(1388–96):e1-3.
Zhu Y, Matsumura Y, Velayutham M, Foley LM, Hitchens TK, Wagner WR. Reactive oxygen species scavenging with a biodegradable, thermally responsive hydrogel compatible with soft tissue injection. Biomaterials. 2018;177:98–112.
Della Rocca DG, Willenberg BJ, Ferreira LF, Wate PS, Petersen JW, Handberg EM, Zheng T, Steindler DA, Terada N, Batich CD, Byrne BJ, Pepine CJ. A degradable, bioactive, gelatinized alginate hydrogel to improve stem cell/growth factor delivery and facilitate healing after myocardial infarction. Med Hypotheses. 2012;79:673–7.
Antoine EE, Vlachos PP, Rylander MN. Review of collagen I hydrogels for bioengineered tissue microenvironments: characterization of mechanics, structure, and transport. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014;20:683–96.
Daamen WF, Nillesen ST, Wismans RG, Reinhardt DP, Hafmans T, Veerkamp JH, van Kuppevelt TH. A biomaterial composed of collagen and solubilized elastin enhances angiogenesis and elastic fiber formation without calcification. Tissue Eng Part A. 2008;14:349–60.
Rincon AC, Molina-Martinez IT, de Las HB, Alonso M, Bailez C, Rodriguez-Cabello JC, Herrero-Vanrell R. Biocompatibility of elastin-like polymer poly(VPAVG) microparticles: in vitro and in vivo studies. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;78:343–51.
Bjork JW, Johnson SL, Tranquillo RT. Ruthenium-catalyzed photo cross-linking of fibrin-based engineered tissue. Biomaterials. 2011;32:2479–88.
Le Guehennec L, Goyenvalle E, Aguado E, Pilet P, Spaethe R, Daculsi G. Influence of calcium chloride and aprotinin in the in vivo biological performance of a composite combining biphasic calcium phosphate granules and fibrin sealant. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2007;18:1489–95.
Reichl S. Films based on human hair keratin as substrates for cell culture and tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2009;30:6854–66.
Klouda L. Thermoresponsive hydrogels in biomedical applications: A seven-year update. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;97:338–49.
Balakrishnan P, Geethamma VG, Sreekala MS, Thomas S. Polymeric biomaterials: State-of-the-art and new challenges. Fundam Biomater Polym. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102194-1.00001-3.
Panda NC, Zuckerman ST, Mesubi OO, Rosenbaum DS, Penn MS, Donahue JK, Alsberg E, Laurita KR. Improved conduction and increased cell retention in healed MI using mesenchymal stem cells suspended in alginate hydrogel. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2014;41:117–27.
Xia Y, Zhu K, Lai H, Lang M, Xiao Y, Lian S, Guo C, Wang C. Enhanced infarct myocardium repair mediated by thermosensitive copolymer hydrogel-based stem cell transplantation. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015;240:593–600.
Francis MP, Breathwaite E, Bulysheva AA, Varghese F, Rodriguez RU, Dutta S, Semenov I, Ogle R, Huber A, Tichy AM, Chen S, Zemlin C. Human placenta hydrogel reduces scarring in a rat model of cardiac ischemia and enhances cardiomyocyte and stem cell cultures. Acta Biomater. 2017;52:92–104.
Lim TC, Rokkappanavar S, Toh WS, Wang LS, Kurisawa M, Spector M. Chemotactic recruitment of adult neural progenitor cells into multifunctional hydrogels providing sustained SDF-1α release and compatible structural support. FASEB J. 2013;27:1023–33.
Wang W, Tan B, Chen J, Bao R, Zhang X, Liang S, Shang Y, Liang W, Cui Y, Fan G, Jia H, Liu W. An injectable conductive hydrogel encapsulating plasmid DNA-eNOs and ADSCs for treating myocardial infarction. Biomaterials. 2018;160:69–81.
Reis LA, Chiu LL, Wu J, Feric N, Laschinger C, Momen A, Li RK, Radisic M. Hydrogels with integrin-binding angiopoietin-1-derived peptide, QHREDGS, for treatment of acute myocardial infarction. Circ Heart Fail. 2015;8:333–41.
Fan Z, Fu M, Xu Z, Zhang B, Li Z, Li H, Zhou X, Liu X, Duan Y, Lin PH, Duann P, Xie X, Ma J, Liu Z, Guan J. Sustained release of a peptide-based matrix metalloproteinase-2 inhibitor to attenuate adverse cardiac remodeling and improve cardiac function following myocardial infarction. Biomacromol. 2017;18:2820–9.
Fan Z, Xu Z, Niu H, Gao N, Guan Y, Li C, Dang Y, Cui X, Liu XL, Duan Y, Li H, Zhou X, Lin PH, Ma J, Guan J. An injectable oxygen release system to augment cell survival and promote cardiac repair following myocardial infarction. Sci Rep. 2018;8:1371.
Toh WS, Loh XJ. Advances in hydrogel delivery systems for tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;45:690–7.
Li J, Shu Y, Hao T, Wang Y, Qian Y, Duan C, Sun H, Lin Q, Wang C. A chitosan-glutathione based injectable hydrogel for suppression of oxidative stress damage in cardiomyocytes. Biomaterials. 2013;34:9071–81.
Su J, Hu BH, Lowe WL Jr, Kaufman DB, Messersmith PB. Anti-inflammatory peptide-functionalized hydrogels for insulin-secreting cell encapsulation. Biomaterials. 2010;31:308–14.
Tian B, Liu J, Dvir T, Jin L, Tsui JH, Qing Q, Suo Z, Langer R, Kohane DS, Lieber CM. Macroporous nanowire nanoelectronic scaffolds for synthetic tissues. Nat Mater. 2012;11:986–94.
Ong CS, Nam L, Ong K, Krishnan A, Huang CY, Fukunishi T, Hibino N. 3D and 4D bioprinting of the myocardium: current approaches, challenges, and future prospects. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:6497242.
Maiullari F, Costantini M, Milan M, Pace V, Chirivi M, Maiullari S, Rainer A, Baci D, Marei HE, Seliktar D, Gargioli C, Bearzi C, Rizzi R. A multi-cellular 3D bioprinting approach for vascularized heart tissue engineering based on HUVECs and iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes. Sci Rep. 2018;8:13532.
Gaetani R, Feyen DA, Verhage V, Slaats R, Messina E, Christman KL, Giacomello A, Doevendans PA, Sluijter JP. Epicardial application of cardiac progenitor cells in a 3D-printed gelatin/hyaluronic acid patch preserves cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Biomaterials. 2015;61:339–48.
Kirillova A, Maxson R, Stoychev G, Gomillion CT, Ionov L. 4D Biofabrication using shape-morphing hydrogels. Adv Mater. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201703443.
Kaji H, Takii Y, Nishizawa M, Matsue T. Pharmacological characterization of micropatterned cardiac myocytes. Biomaterials. 2003;24:4239–44.
Zhu Y, Wood NA, Fok K, Yoshizumi T, Park DW, Jiang H, Schwartzman DS, Zenati MA, Uchibori T, Wagner WR, Riviere CN. Design of a coupled thermoresponsive hydrogel and robotic system for postinfarct biomaterial injection therapy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;102:780–6.
Moric-Janiszewska E, Hibner G. Microarray analysis in cardiac arrhythmias: a new perspective? Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2013;36:911–7.
Funding
No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xuejing Yu is the only one who contributed to the conception, literature searching and writing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Xuejing Yu has no conflicts of interest in this work and has nothing to disclose.
Ethical Approval
Since this is a review article, it is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any new studies with human participants or animals performed by the author. Therefore, no ethical approval is required.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X. Application of Hydrogels in Cardiac Regeneration. Cardiol Ther 12, 637–674 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40119-023-00339-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40119-023-00339-0