Abstract
Strain ZZ-1T, a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium, motile by flagella, was isolated from phenol-contaminated soil. Strain ZZ-1T was found to grow at 15–37 °C (optimum 25–30 °C), at pH 6.0–10.0 (optimum pH 7.5) and with 0–8.0 % (w/v) NaCl (optimum 0.5 %). The isolate was found to be able to reduce nitrate to nitrite, but not to nitrogen. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that strain ZZ-1T is a member of the genus Nitratireductor, and shows high sequence similarities to Nitratireductor pacificus MCCC 1A01024T (98.5 %) and lower (<97 %) sequence similarities to all other Nitratireductor species. Chemotaxonomic analysis revealed that strain ZZ-1T possesses Q-10 as the predominant ubiquinone and Summed feature 8(C18:1 ω6c and/or C18:1 ω7c; 66.6 %), C19:0 ω8c cyclo (23.3 %), C18:0 (3.4 %), iso-C17:0 (2.3 %) and C17:0 (1.0 %) as the major fatty acids. The polar lipids of strain ZZ-1T were determined to be diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylcholine, phospholipids, aminolipids, a glycolipid and an aminophospholipid. The DNA G+C content was determined to be 64.1 mol%. Based on the draft genome sequence, the DNA–DNA hybridization estimate value between strain ZZ-1T and N. pacificus MCCC 1A01024T was 46.5 ± 3.0 % and ANI was 75.9 %. The combination of phylogenetic analysis, phenotypic characteristics, chemotaxonomic data and DNA–DNA hybridization supports the conclusion that strain ZZ-1T represents a novel species of the genus Nitratireductor, for which the name Nitratireductor soli sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is ZZ-1T (=JCM 30640T = MCCC 1K00508T).
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Labbé et al. (2004) first described the genus Nitratireductor, which forms a novel lineage in the family Phyllobacteriaceae within the α2 subgroup of the Proteobacteria (Labbé et al. 2004). Members of the genus Nitratireductor are Gram-negative, rod-shaped, strictly aerobic, light-yellow or whitish-brown pigmented bacteria. Chemotaxonomic studies have demonstrated that Nitratireductor strains contain C18:1 ω7c as the major fatty acid, C19:0 ω8c cyclo as the main cyclopropane fatty acid and Q-10 as the main respiratory quinone. Currently, the genus contains 7 species: Nitratireductor aquibiodomus, isolated from a denitrification system (Labbé et al. 2004), Nitratireductor kimnyeongensis, from seaweed (Kang et al. 2009), Nitratireductor basaltis, from black sand (Kim et al. 2009), Nitratireductor aquimarinus from a diatom culture (Jang et al. 2011), Nitratireductor indicus, from deep-sea water (Lai et al. 2011a), Nitratireductor pacificus from an enriched deep-sea sediment sample (Lai et al. 2011b) and Nitratireductor lucknowense from pesticide contaminated soil (Manickam et al. 2012) (http://www.bacterio.net/Nitratireductor.html).
During screening for phenol-degrading isolates in phenol-contaminated soil, strain ZZ-1T was isolated and characterised. The data presented here support the conclusion that strain ZZ-1T represents a novel species of the genus Nitratireductor, for which the name Nitratireductor soli sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is ZZ-1T (=JCM 30640T = MCCC 1K00508T).
Materials and methods
Bacterial strains, isolation and cultivation
During screening for phenol-degrading isolates, a light-yellow pigmented bacterium, designated ZZ-1T, was isolated from phenol-contaminated soil in Zaozhuang city, Shandong province, P. R. China (N34°42′ E117°33′). N. pacificus MCCC 1A01024T, was used as the reference strain for phenotypic characterisation. Unless indicated otherwise, the morphological, physiological and biochemical characteristics of strain ZZ-1T and the reference strain were determined using routine cultivation on TSA or TSB at 30 °C.
Phenotypic characterisation
The Gram reaction was determined using the non-staining method, as described by Buck (1982). Cell morphology was determined by light phase-contrast microscopy (IX70; Olympus) and transmission electron microscopy (H7650; Hitachi). The gliding motility was determined using the hanging-drop method (Bernardet et al. 2002). Growth at various temperatures (4, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 37, 40, 45 and 50 °C), salt concentrations (0.5–10 % NaCl with increments of 0.5 %, w/v) and pH values (pH 4.0–10.5 with increments of 0.5 pH units) was assessed in TSB and after incubation for up to 5 days. The pH was maintained using four different buffers: 100 mM citric acid-sodium citrate buffer (pH 4.0–6.0), 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 5.5–8.0), 50 mM Tris–HCl buffer (pH 7.5–9.0) and 20 mM glycine-NaOH buffer (pH 8.5–10.5). Catalase and oxidase was tested according to McCarthy and Cross (1984). Growth under anaerobic conditions was determined in TSB supplemented with or without 0.1 % (w/v) nitrate using the GasPak Anaerobic System (BBL) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Hydrolysis of Tweens 20, 40 and 80 was tested according to Arden Jones et al. (1979). Other biochemical tests were carried out using the API 20 NE, API ZYM systems and 32 GN Microplates, according to the manufacturers’ instructions. N. pacificus MCCC 1A01024T was tested at the same time as strain ZZ-1T.
Sensitivity to antibiotics was tested on TSA plates using discs containing the following antibiotics: ampicillin (10 μg), streptomycin (10 μg), kanamycin (30 μg), gentamicin (10 μg), penicillin (100 μg), vancomycin (30 U), tetracycline (30 μg), piperacillin (100 μg), erythromycin (15 μg), chloramphenicol (30 μg), rifampicin (5 μg), cefoperazone (75 μg), novobiocin (30 μg), cephadrin (30 μg), clindamycin (2 μg), roxithromycin (15 μg), lincomycin (2 μg), carbenicillin (100 μg), norfloxacin (10 μg), amoxicillin (10 μg), and polymyxin B (30 μg).
Determination of 16S rRNA gene sequence and phylogenetic analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted according to standard procedures (Sambrook and Russell 2001). Amplification of the 16S rRNA gene was performed with the primer pair 27F (5′-GAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG-3′, positions 8-27 in Escherichia coli 16S rRNA) and 1492R (5′-ACGGYTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′, positions 1492–1507 in E. coli 16S rRNA), originally described by Lane (1991). Pairwise sequence similarity was calculated using a global alignment algorithm, implemented in the EzTaxon-e server (http://www.ezbiocloud.net/eztaxon; Kim et al. 2012). The 16S rRNA gene sequence alignment was performed using the CLUSTAL_X program (Thompson et al. 1997). Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the neighbour-joining method (Saitou and Nei 1987) and maximum-likelihood (Felsenstein 1981) with Kimura’s two parameter calculation model (Kimura 1980) in MEGA version 6.0 (Tamura et al. 2013). A bootstrap analysis of 1000 resamplings was used to evaluate the tree topology (Felsenstein 1985).
Genome sequencing, G+C content, DDH and ANI estimate
The draft genome sequence strain ZZ-1T was determined by Shanghai Majorbio Bio-pharm Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), using Solexa paired-end (500 bp library) sequencing technology (Illumina, SanDiego, CA, USA). The G+C content of the chromosomal DNA was determined by analysis of the draft genome sequence.
DNA–DNA hybridization (DDH) estimate value was analysed using the genome-to-genome distance calculator (GGDC2.0) with the alignment method of BLAST+ (Auch et al. 2010a, b; Meier-Kolthoff et al. 2013). The average nucleotide identity (ANI) was calculated using the algorithm of Goris et al. (2007) by the web service of EZGenome.
Determination of fatty acid, polar lipid analysis and isoprenoid ubiquinone
For chemotaxonomic determination, cells of strain ZZ-1T and the reference strain were grown on TSB and harvested at the mid-exponential phase by centrifugation, washed with distilled water and freeze-dried. The fatty acid profiles were determined according to the method of manufacturer’s instructions of the Sherlock Microbial Identification System (MIDI Corporation; Sasser 1990). The fatty acid methyl esters were obtained from cells by saponification, methylation and extraction, and separated in a gas chromatograph (Agilent 6890N). Peaks were automatically integrated and fatty acid names and percentages were determined using the MIDI Sherlock MIS system (Library: TSBA6; Version, 6.0B). The polar lipid analysis of strain ZZ-1T was performed at the Identification Service of the Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen (DSMZ, Braunschweig, Germany) as described by Tindall (1990a, b). Analysis of the respiratory quinone was carried out by the Identification Service of the Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen (DSMZ, Braunschweig, Germany). Quinones were extracted according to Collins et al. (1977) and separated by HPLC (Tamaoka et al. 1983).
Results and discussion
Phenotypic characteristics
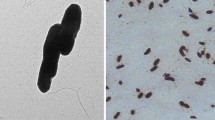
Strain ZZ-1T was found to be a Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that is motile by flagella. Cells were observed to be approximately 0.5–0.8 µm in width and 1.2–1.6 μm in length (see Supplementary Materials Fig. S1). Growth was observed at 0–8 % NaCl, at pH 6.0–10.0 and 15–37 °C, Strain ZZ-1T was found to be sensitive to ampicillin, gentamicin, penicillin, tetracycline, piperacillin, erythromycin, chloramphenicol, rifampicin, novobiocin, clindamycin, roxithromycin, lincomycin, carbenicillin, amoxicillin and polymyxin B; and to be resistant to streptomycin, kanamycin, vancomycin, cefoperazone, cephadrin and norfloxacin. Other characteristics are given in Table 1.
16S rRNA gene sequence analysis
A nearly full-length 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain ZZ-1T was determined (1448 nt, GenBank accession number KP639570). In the neighbour-joining phylogenetic tree (Fig. 1), strain ZZ-1T grouped among Nitratireductor species and formed a subclade with N. pacificus MCCC 1A01024T. According to sequence similarity calculations, the strain is closely related to N. pacificus MCCC 1A01024T (98.5 %) and showed <97 % similaries with other currently described Nitratireductor species. Phylogenetic trees inferred by the maximum-likelihood method are shown in Fig. S2 (see Supplementary Materials Fig. S2). This branching pattern demonstrated that strain ZZ-1T represents a novel species within the genus Nitratireductor.
Phylogenetic tree constructed by the neighbour-joining method based on 16S rRNA gene sequences of strain ZZ-1T and close relatives. Rhizobium leguminosarum USDA 2379T (U29386) was used as outgroup. Dots indicated that the corresponding nodes were also recovered in the trees generated with maximum-parsimony algorithms. Bootstrap values, generated from 1000 re-samplings, at or above 50 % are indicated at the branch points. Bar, 0.005 nucleotide substitutions per nucleotide position
Genome sequencing, DNA G+C content, DDH and ANI estimate chemotaxonomic characteristics
The draft genome of strains ZZ-1T consists of 5,125,897 bp in length. The accession number for strain ZZ-1T is LFVY00000000. The draft genome sequence of N. pacificus MCCC 1A01024T (NZ_AMRM00000000.1) was obtained from NCBI. The chromosomal DNA G+C content of strain ZZ-1T was determined to be 64.1 mol%, which is close to the value determined for N. pacificus MCCC 1A01024T (63 mol%). The DDH estimated value between strain ZZ-1T and N. pacificus MCCC 1A01024T was 46.5 ± 3.0 %, which is below the standard cut-off value (70 %) (Wayne et al. 1987). The ANI value between strain ZZ-1T and N. pacificus MCCC 1A01024T was 75.9 %, which is below standard ANI criteria for species identity (95–96 %) (Richter and Rossello-Mora 2009). These data confirm that strain ZZ-1T represents a novel species of the genus Nitratireductor.
Chemotaxonomic characteristics
Chemotaxonomic analysis revealed that strain ZZ-1T possesses Q-10 as the predominant ubiquinone. This is consistent with the members of the genus Nitratireductor (Labbé et al. 2004). The fatty acid profiles of strain ZZ-1T and N. pacificus MCCC 1A01024T are shown in Table 2. The major fatty acids of strain ZZ-1T are (> 1 %) Summed feature 8(C18:1 ω6c and/or C18:1 ω7c; 66.6 %), C19:0 ω8c cyclo (23.3 %), C18:0 (3.4 %), iso-C17:0 (2.3 %) and C17:0 (1.0 %). The profile for strain ZZ-1T was similar to that of N. pacificus MCCC 1A01024T, but some qualitative and quantitative differences in proportions could be observed. Compared to N. pacificus MCCC 1A01024T, strain ZZ-1T was found to possess a high level of C19:0 ω8c cyclo, whilst iso-C17:0 3-OH was not detected in strain ZZ-1T. The polar lipids were found to comprise of diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylcholine, phospholipids, aminolipids, a glycolipid and an aminophospholipid (Supplementary Materials Fig. S3).
Taxonomic conclusion
The results of the phylogenetic analysis, phenotypic analysis, and chemotaxonomic studies presented above support the conclusion that strain ZZ-1T belongs to the genus Nitratireductor. However, phylogenetic distinctiveness, some phenotypic differences (Table 1) and its low DDH and ANI values when compared with the type strain of the closely related species N. pacificus confirmed that strain ZZ-1T represents a species distinct from the recognised Nitratireductor species. Therefore, strain ZZ-1T represents a novel species of the genus Nitratireductor, for which the name Nitratireductor soli sp. nov. is proposed.
Description of Nitratireductor soli sp. nov
Nitratireductor soli (so′li. L. neut. gen. n. soli of soil, the source of the type strain)
Cells are Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped and motile by flagella. Cells are approximately 0.5–0.8 µm in width and 1.2–1.6 μm in length. After 2 days of incubation on TSA, colonies are 1.5 mm in diameter, smooth, circular, convex and pale yellow. Growth occurs at 15–37 °C (optimum 25–30 °C), at pH 6.0–10.0 (optimum pH 7.5) and in 0–8 % (w/v) NaCl (optimum 0.5 %). Positive for oxidase, catalase, nitrate reduction, indole production, hydrolysis of Tweens 20 and 80 (weak), d-glucose fermentation, aesculin hydrolysis and N-acetyl-glucosamine utilisation, but negative for arginine dihydrolase, gelatin hydrolysis or urease. With the API ZYM system, positive for alkaline phosphatase, esterase (C4), esterase lipase (C8), lipase (C14) (weakly), cystine aminopeptidase, acid phosphatase, leucine aminopeptidase, valine aminopeptidase, α-chymotrypsin, naphthol-AS-BI-phosphoamidase α-glucosidase, β-glucosidase, β-glucuronidase (weakly), N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase; negative for α-galactosidase, β-galactosidase, α-mannosidase and α-fucosidase. With the API 20 NE system, utilises N-acetyl-glucosamine, d-maltose and malic acid but not d-glucose, l-arabinose, d-mannose, d-mannitol, potassium gluconate, capric acid, phenylacetic acid or adipic acid. With the API 32 GN Microplates, utilises d-ribose, suberic acid, potassium 5-ketogluconate, l-serine, l-arabinose, citrate and l-histidine as sole carbon sources but does not utilise, l-rhamnose, inositol, sucrose, malate, itaconic acid, 3-hydroxybenzoic acid, glycogen, d-mannitol, d-glucose, d-mannose, d-maltose, propionate, adipic acid, phenyl acetate, acetate, citrate, gluconate, malonate, lactic acid, l-alanine, caprate, salicoside, d-melibiose, l-fucose, d-sorbitol, propionic acid, potassium 2-ketogluconate, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, valeric acid, succinic acid or l-proline as sole carbon sources. The quinone system contains large amounts of Q-10 and the major fatty acids are Summed feature 8* (C18:1 ω6c and/or C18:1 ω7c), C19:0 ω8c cyclo, C18:0 and iso-C17:0. The polar lipids are diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylcholine, phospholipids, aminolipids, a glycolipid and an aminophospholipid. The DNA G+C content of the type strain is 64.1 mol%.
The type strain is Nitratireductor soli ZZ-1T (=JCM 30640T = MCCC 1K00508T), which was isolated from phenol-contaminated soil from Zaozhuang city, Shandong province, P. R. China. The Genbank/EMBL/DDBJ accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of strain ZZ-1T is KP639570. The accession number for the draft genome of strain ZZ-1T is LFVY00000000.
Abbreviations
- MCCC:
-
Marine Culture Collection of China
- ANI:
-
Average nucleotide identity
- DDH:
-
DNA–DNA hybridization
- MSM:
-
Mineral salts medium
References
Arden Jones MP, McCarthy AJ, Cross T (1979) Taxonomic and serologic studies on Micropolyspora faeni and Micropolyspora strains from soil bearing the specific epithet rectivirgula. J Gen Microbiol 115:343–354
Auch AF, Klenk HP, Goker M (2010a) Standard operating pro-cedure for calculating genome-to-genome distances based on high-scoring segment pairs. Stand Genomic Sci 2:142–148
Auch AF, von Jan M, Klenk HP, Goker M (2010b) Digital DNA–DNA hybridization for microbial species delinea-tion by means of genome-to-genome sequence compari-son. Stand Genomic Sci 2:117–134
Bernardet JF, Nakagawa Y, Holmes B (2002) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Flavobacteriaceae and emended description of the family. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1049–1070
Buck JD (1982) Nonstaining (KOH) method for determination of gram reactions of marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:992–993
Collins MD, Pirouz T, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1977) Distribution of menaquinones in Actinomycetes and Corynebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 100:221–230
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA–DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91
Jang GI, Hwang CY, Cho BC, Shao ZZ (2011) Nitratireductor aquimarinus sp. nov., isolated from a culture of the diatom Skeletonema costatum, and emended description of the genus Nitratireductor. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2676–2681
Kang HS, Yang HL, Lee SD (2009) Nitratireductor kimnyeongensis sp. nov., isolated from seaweed. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1036–1039
Kim KH, Roh SW, Chang HW, Nam YD, Yoon JH, Jeon CO, Oh HM, Bae JW (2009) Nitratireductor basaltissp. nov., isolated from black beach sand. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:135–138
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Labbé N, Parent S, Villemur R (2004) Nitratireductor aquibiodomus gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel α-proteobacterium from the marine denitrification system of the Montreal Biodome (Canada). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:269–273
Lai Q, Yu Z, Yuan J, Sun F, Shao Z (2011a) Nitratireductor indicus sp. nov., isolated from deep-sea water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:295–298
Lai Q, Yu Z, Wang J, Zhong H, Sun F, Wang L, Shao Z (2011b) Nitratireductor pacificus sp. nov., isolated from a pyrene-degrading consortium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1386–1391
Lane DL (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt ER, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 115–175
Manickam N, Pareek S, Kaur I, Singh NK, Mayilraj S (2012) Nitratireductor lucknowense sp. nov., a novel bacterium isolated from a pesticide contaminated soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 101:125–131
McCarthy AJ, Cross T (1984) A taxonomic study of Thermomonospora and other monosporic Actinomycetes. J Gen Microbiol 130:5–25
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Goker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60
Richter M, Rossello-Mora R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19126–19131
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids, MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI, Newark
Tamaoka J, Katayama-Fujimura Y, Kuraishi H (1983) Analysis of bacterial menaquinone mixtures by high performance liquid chromatography. J Appl Bacteriol 54:31–36
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evo 30:2725–2729
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL-X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tindall BJ (1990a) A comparative study of the lipid composition of Halobacterium saccharovorum from various sources. Syst Appl Microbiol 13:128–130
Tindall BJ (1990b) Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol Letts 66:199–202
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR (1987) International committee on systematic bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Zaozhuang University, China (2014BS14), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (ZR2014DP005), and the National natural science foundation of China (Grant No. 31270157). We acknowledge Dr. Qi-Liang Lai (Key Laboratory of Marine Biogenetic Resources, Third Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, Xiamen, China) for genome analysis and submission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Qing Chen and Hai-Yan Ni have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Q., Ni, HY., Zhuang, W. et al. Nitratireductor soli sp. nov., isolated from phenol-contaminated soil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 108, 1139–1146 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0567-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0567-3