Abstract
The demand for n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3LC-PUFAs), such as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), will exceed their supply in the near future, and a sustainable source of n-3LC-PUFAs is needed. Thraustochytrids are marine protists characterized by anaerobic biosynthesis of DHA via polyunsaturated fatty acid synthase (PUFA-S). Analysis of a homemade draft genome database suggested that Parietichytrium sp. lacks PUFA-S but possesses all fatty acid elongase (ELO) and desaturase (DES) genes required for DHA synthesis. The reverse genetic approach and a tracing experiment using stable isotope-labeled fatty acids revealed that the ELO/DES pathway is the only DHA synthesis pathway in Parietichytrium sp. Disruption of the C20 fatty acid ELO (C20ELO) and ∆4 fatty acid DES (∆4DES) genes with expression of ω3 fatty acid DES in this thraustochytrid allowed the production of EPA and n-3docosapentaenoic acid (n-3DPA), respectively, at the highest level among known microbial sources using fed-batch culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, C22:6n-3) is an n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (n-3LC-PUFA) that exists in organisms ranging from certain microbes to mammals but not in higher plants1,2,3. Marine microbes, such as marine bacteria and protists (thraustochytrids), synthesize DHA from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA via polyketide-synthase like protein named PUFA synthase (PUFA-S)4,5,6. Among thraustochytrids, Schizochytrium sp.4 and Aurantiochytrium limacinum5 are known to synthesize DHA via PUFA-S, but several genes related to the fatty acid elongase (ELO)/desaturase (DES) pathway are present in the genome of A. limacinum7, and further analysis is therefore needed. Thraustochytrium sp. and T. aureum produces DHA via two distinct pathways, namely, the PUFA-S and ELO/DES pathways8,9. Although the contribution of the ELO/DES pathway to DHA production is considered to be relatively small in both Thraustochytrium10,11, quantitative data are presently limited.
n-3LC-PUFAs, such as DHA and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, C20:5n-3), are beneficial both nutritionally and pharmacologically and are used as supplements and medicines12,13,14. These n-3LC-PUFAs are industrially produced from oily fish, although the primary producers of n-3LC-PUFAs are mainly microalgae and thraustochytrids. However, there is concern that the supply of n-3LC-PUFAs will be insufficient in the future due to a decrease in fish resources resulting from climate change and overfishing15. The n-3LC-PUFA market is expected to be worth 4300 million USD by 201916, and an increase in water temperature due to global warming may result in a 10–58% loss in the globally available DHA by 210017. Thus, sustainable production of n-3LC-PUFAs using genetically engineered oilseed crops2,18 and microbial fermentation2,19,20 is needed as an alternative to production from fish oil. Among unicellular microbes, thraustochytrids have been used industrially because they can reach high cell densities with a high DHA yield21.
In addition to DHA, EPA and arachidonic acid (ARA, C20:4n-6) are other LC-PUFAs that have drawn major interest for their role in human health and nutrition22,23. The purified ethyl ester of EPA (commercial names Epadel and Vascepa) has been approved as a therapeutic agent for obstructive arteriosclerosis and hypertriglyceridemia24,25. These medicines reduce the serum triacylglycerol (TAG) level26. EPA and DHA may have different physiological and pharmacological functions in humans27. Although data remain limited, n-3 docosapentaenoic acid (n-3DPA, C22:5n-3), an intermediate metabolite of DHA in the ELO/DES pathway, is also expected to have health benefits28,29,30.
We report here that Parietichytrium sp. does not have PUFA-S and synthesizes DHA exclusively through the ELO/DES pathway. To the best of our knowledge, Parietichytrium sp. is the first example of a thraustochytrid that synthesizes a large amount of DHA through a mechanism other than the PUFA-S pathway. We have achieved the production of EPA and n-3DPA at the highest level among known microbial sources through the genetic manipulation of PUFA-S-independent DHA synthesis pathway in Parietichytrium sp.
Results
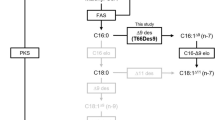
Schizochytrium sp. ATCC208884,31 and A. limacinum synthesize DHA anaerobically via PUFA-S5, whereas Thraustochytrium sp. ATCC261858 and T. aureum ATCC343049 produces DHA via both the anaerobic PUFA-S and aerobic ELO/DES pathways. These two pathways in thraustochytrids are illustrated in Fig. 1a. Differences in the DHA synthesis systems are reflected in their LC-PUFA composition (Fig. 1b). That of A. limacinum is relatively simple and consists mainly of DHA and n-6 docosapentaenoic acid (n-6DPA, C22:5n-6), whereas that of T. aureum is slightly complex, and considerable amounts of EPA and ARA are included, in addition to DHA and n-6DPA. The LC-PUFA composition of Parietichytrium sp. showed greater diversity, and the levels of n-3DPA and docosatetraenoic acid (DTA, C22:4n-6) increased (Fig. 1b). The total fatty acid compositions of three thraustochytrids are also shown in Table 1, which indicates high level of oleic acid (OA, C18:1n-9) in Parietichytrium sp. The difference in fatty acid composition, especially LC-PUFA (Fig. 1b), may indicate that Parietichytrium sp. has a different LC-PUFA biosynthetic system from those of A. limacinum and T. aureum.
a Two pathways for the synthesis of n-6DPA and DHA in thraustochytrids. One occurs via PUFA-S, directly synthesizing n-6DPA or DHA from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA in a polyketide synthase-like manner. The other is the ELO/DES pathway, in which PA is converted to DHA through six desaturation and three elongation steps. b LC-PUFA compositions of three different genera of thraustochytrids (A. limacinum, T. aureum, and Parietichytrium sp.SEK358). Each strain was cultured in 20 mL of GY medium at 28 °C for 3 days with shaking at 120 rpm. LC-PUFAs were determined by GC. c LC-PUFA profiles of WT and ∆4DES KO of Parietichytrium sp. SEK358. The data shown are the mean ± SD. (n = 3). The n values are numbers of replicates. d Generation of 13C18-labeled 22:6 (DHA) and its intermediates from the precursor 13C18-C18:1 in Parietichytrium sp. Cells of Parietichytrium sp. SEK358 were incubated at 25 °C with 0.25 mΜ 13C18-C18:1 for 24 h. The 13C18-labeled fatty acids were obtained from total lipid fractions after alkaline treatment and were determined by MRM analysis using LC-ESI MS/MS, as shown in Supplementary data set 1. Peak intensities of 13C18-labeled fatty acids were normalized to an internal standard (C12:0) (normalized intensity). The data shown are the mean ± SD. (n = 3). The n values are numbers of replicates. e Time course of the generation of 13C18-C22:6 generated from 13C18-C18:1 in Parietichytrium sp., A. limacinum, T. aureum WT, and T. aureum PUFA-S KO. Cells were incubated with 0.25 mΜ 13C18-C18:1 and collected at the indicated time points. The data shown are the mean ± SD. (n = 3). The n values are numbers of replicates. f Schematic diagrams for three types of DHA synthesis systems in thraustochytrids. DHA is synthesized only by PUFA-S in type I (e.g., A. limacinum), by the ELO/DES pathway in type III (e.g., Parietichytrium sp.), or by both the PUFA-S and ELO/DES pathways in type II (e.g., T. aureum).
Thus, we examined draft genome databases of A. limacinum (provided by the U.S. Department of Energy, Joint Genome Institute, USA), T. aureum (this study) and Parietichytrium sp. (this study) (Table 2) and found that the three thraustochytrid species share the fatty acid synthase (FAS) gene that functions in the synthesis of palmitic acid (C16:0, PA). The PUFA-S gene was found in A. limacinum and T. aureum but not in Parietichytrium sp., suggesting that Parietichytrium sp. does not synthesize DHA via PUFA-S. On the other hand, the ∆4DES gene, which is responsible for the conversion of n-3DPA to DHA and is essential for DHA synthesis in the ELO/DES pathway32, was found in T. aureum and Parietichytrium sp. but not in A. limacinum. These results are basically consistent with previous reports that A. limacinum can synthesize DHA via the PUFA-S pathway, and Thraustochytrium (Thraustochytrium sp. and T. aureum) can synthesize DHA via both the PUFA-S and ELO/DES pathways5,9. In addition, the present genome analysis strongly suggested that Parietichytrium sp. synthesizes DHA only through a PUFA-S-independent pathway.
To disclose the PUFA-S independent pathway for DHA synthesis, we cloned all ELO and DES genes constituting ELO/DES pathway of Parietichytrium sp. (Supplementary Fig. S1). This pathway consists of three ELOs (tentatively designated ELO-1, ELO-2, and ELO-3) and six DESs (DES-1, DES-2, DES-3, DES-4, DES-5, and DES-6). We analyzed the substrate specificity of each enzyme by analysis of fatty acid profiles in budding yeasts after expression of each ELO or DES gene. As a result, we found that DES-1, DES-2, DES-3, DES-4, DES-5, and DES-6 were Δ9DES, Δ12DES (ω6DES), Δ6DES, Δ5DES, Δ4DES, and Δ17/19DES (ω3DES), respectively, and ELO-1, ELO-2, and ELO-3 were C16ELO, C18/C20ELO (Δ6ELO), and C20ELO (Δ5ΕLO), respectively (Supplementary Fig. S1a, b). All the ELO/DES genes examined were actually expressed in Parietichytrium sp.; however, their expression levels varied; the expression of DES-1, DES-2, and DES-3 was high, that of ELO-1, ELO-2, ELO-3, and DES-4 was moderate, and that of DES-5 and DES-6 was low (Supplementary Fig. S1c).
To address whether Parietichytrium sp. synthesizes DHA only through the ELO/DES pathway, we generated a ∆4DES-deficient mutant (∆4DES KO) of Parietichytrium sp. and compared the fatty acid composition between the mutant and wildtype (WT). As shown in Fig. 1c, the ∆4DES KO of Parietichytrium sp. completely lacked DHA and n-6DPA, whereas the amount of n-3DPA and DTA (C22:4n-6), which are precursors of DHA and n-6DPA in the ELO/DES pathway (Fig. 1a), respectively, markedly increased. The profiles of gas chromatography (GC) of Parietichytrium sp. WT and its ∆4DES KO mutant is also shown in Supplementary Fig. S2. These results indicate that DHA and n-6DPA are generated through only the ELO/DES pathway in Parietichytrium sp., in which Δ4DES is the sole enzyme that converts n-3DPA to DHA and DTA to n-6DPA. In contrast to Parietichytrium sp., DHA and n-6DPA were still present in the Δ4DES KO of T. aureum, and these LC-PUFAs were lost when both the PUFA-S and Δ4DES genes were disrupted (Supplementary Fig. S3a).
To confirm that Parietichytrium sp. produces DHA through the ELO/DES pathway, we traced the DHA synthesis of Parietichytrium sp. using 13C-labeled OA (13C18-C18:1) as a precursor. Parietichytrium sp. was cultured in GY medium containing 13C18-C18:1, and total fatty acids were extracted from the cells after cultivation for 24 h. The fatty acid fraction was then analyzed by LC-ESI MS/MS as described in the Methods, and multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) conditions for 13C-labeled fatty acids are described in Supplementary data set 1. We were able to detect the precursor 13C18-C18:1 and end product 13C18-labeled DHA (13C18-C22:6) as well as intermediates during DHA synthesis by the ELO/DES pathway (Fig. 1d). The production of 13C18-C22:6 in Parietichytrium sp. reached a plateau at 9–24 h and began to decline after 24 h (Fig. 1e). The time-course for the generation of intermediates of DHA synthesis in Parietichytrium sp. is shown in Supplementary Fig. S4. In T. aureum WT, the production of 13C18-C22:6 was much lower than that of Parietichytrium sp.; however, it significantly increased when the PUFA-S gene was disrupted (T. aureum PUFA-S KO, Fig. 1e), suggesting that the ELO/DES pathway is a supplementary or auxiliary system for the PUFA-S pathway in DHA synthesis in T. aureum. No 13C18-C22:6 was produced in A. limacinum under the same conditions, indicating that DHA is not produced by the ELO/DES pathway in A. limacinum (Fig. 1e). It was reported, however, that several genes related to the ELO/DES pathway are present in the genome of A. limacinum7, and thus, a tracing experiment using stable isotope-labeled PA (d31–C16:0) was conducted to determine which step of the ELO/DES pathway in A. limacinum does not function in vivo. We found that d31–C18:0 and d29–C18:1 were generated in Parietichytrium sp. and T. aureum (WT) when d31–C16:0 was added to each culture; however, in A. limacinum d29–C18:1 could not be detected at all, although a small amount of d31–C16:0 was converted to d31–C18:0 (Supplementary Fig. S3b, c). This result indicates that the machinery for the conversion of C16:0 to C18:1 is not fully functional in A. limacinum, and in particular, Δ9DES, which is responsible for the conversion of C18:0 to C18:1, does not function in vivo. The fact that the C16ELO homolog exists in the A. limacinum draft genome database but the Δ9DES homolog does not, which is consistent with the results obtained in this study. Thus, we conclude that the ELO/DES pathway does not function in vivo due at least to the lack of Δ9DES function and that DHA is exclusively generated through the PUFA-S pathway in A. limacinum.
These results indicate that thraustochytrids can be classified into three types according to their DHA synthesis system: type I, which synthesizes DHA via only the PUFA-S pathway, such as A. limacinum; type II, which has both PUFA-S and ELO/DES pathways, such as T. aureum; and type III, which synthesizes DHA via only the ELO/DES pathway, such as Parietichytrium sp. (Fig. 1f).
The major LC-PUFAs of Parietichytrium sp. were DHA and n-6DPA, and the levels of EPA and ARA were relatively low (Fig. 1b and Table 1). Disruption of the gene encoding ELO-3 (C20ELO) in Parietichytrium sp. resulted in a reduction in DHA and n-6DPA levels and a marked increase in EPA and ARA levels (Fig. 2a). The GC profiles are also shown in supplementary Fig. S5. A small amount of DHA and n-6DPA remained in the ELO-3 gene-deficient mutant (C20ELO KO), probably because ELO-2 (C18/C20ELO) partially compensated for the defect of ELO-3 (C20ELO) in C20ELO KO. The expression level of DES-6 (ω3DES) in Parietichytrium sp. was markedly low (Supplementary Fig. S1c); therefore, we examined whether heterologous expression of ω3DES could increase the amount of EPA in C20ELO KO cells. Prior to this experiment, we searched for suitable ω3DES genes and potent promoters, by which ARA is expected to be efficiently converted to EPA in vivo. Among the three ω3DESs tested, ω3DES from Saprolegnia diclina33 most efficiently converted ARA to EPA (Supplementary Fig. S6a). We also found that the Smp1 promoter (Smp1P) from Sicyoidochytrium minutum DNA virus (SmDNAV)34 exhibited several times higher expression efficiency than the conventional ubiquitin promoter35 when the neomycin resistance gene (NeoR) was used as a marker gene (Supplementary Fig. S6b, c). Thus, we expressed the S. diclina ω3DES gene in C20ELO KO cells using an overexpression construct driven by the Smp1 promoter (Supplementary Fig. S6d). As a result, the EPA level in the mutant (C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE) increased 6-fold compared with that in the WT (Fig. 2a). The growth of two mutants (C20ELO KO and C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE) was compared with that of the WT in flask culture. The growth in log phase of the three strains was almost the same based on either total biomass (dry cell weight, DCW) or glucose consumption; however, the growth of the two mutants rapidly declined compared with that of the WT after day 3 under the culture conditions used (Fig. 2b). Similar to the growth, the total fatty acid (TFA) content of these mutants also decreased much faster than that of the WT after day 3 (Fig. 2c). Figure 2d and e show the time-courses of the production of ARA and EPA, respectively, in the WT and two mutants. In C20ELO KO, the production of ARA was much higher than that in the WT, but the production of EPA was lower than that of ARA. However, the production of EPA exceeded that of ARA in C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE throughout cultivation and reached 350 mg/L at day 3, indicating that S. diclina ω3DES efficiently converted ARA to EPA in this mutant. The increase in ARA and EPA in C20ELO KO and the conversion of ARA to EPA in C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE were observed in both the phospholipid (phosphatidylcholine, PC) and neutral lipid (TAG) fractions by LC-ESI MS/MS analysis (Supplementary Fig. S7).
a LC-PUFA profiles of WT, C20ELO KO, and C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE of Parietichytrium sp. in flask culture. Fatty acids were extracted from the 2-day cultured Parietichytrium sp. and used for GC analysis. b Growth characteristics of each strain. Glucose consumption and DCW were measured. c Time course of TFA production in each strain. d Time course of the production of C20:4n-6 (ARA) in each strain. e Time course of the production of C20:5 (EPA) in each strain. f LC-PUFA profiles of WT, Δ4DES KO, and Δ4DES KO/ω3DES OE of Parietichytrium sp. in flask culture. Fatty acids were extracted from the 3-day cultured Parietichytrium sp. and used for GC analysis. g Growth characteristics (glucose consumption and DCW) of each strain. h Time course of TFA production in each strain. i Time course of the production of C22:4n-6 (DTA) in each strain. j Time course of the production of C22:5n-3 (n-3DPA) in each strain. All data shown are the mean ± SD. (n = 3). The n values are numbers of replicates. WT, C20ELO KO, C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE, Δ4DES KO, and Δ4DES KO/ω3DES OE strains used in flask culture were derived from Parietichytrium sp. SEK358.
Disruption of the gene encoding DES-5 (Δ4DES) in Parietichytrium sp. resulted in marked accumulation of n-3DPA and DTA, with complete loss of DHA and n-6DPA (Fig. 2f). Similar to C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE, the expression of S. diclina ω3DES in Δ4DES KO facilitated the conversion of n-6LC-PUFA (DTA) to n-3LC-PUFA (n-3DPA), resulting in a 11-fold increase in n-3DPA production compared with that in the WT (Fig. 2f). Unlike C20ELO disruption, Δ4DES disruption did not cause notable growth inhibition of the mutant (Fig. 2g). After day 3, a decrease in TFA was observed in the two mutants (Δ4DES KO and Δ4DES KO/ω3DES OE), but the extent of this decrease was similar to that in the WT (Fig. 2h). Figure 2i and j show the production of DTA and n-3DPA, respectively, in the flask culture. The production of n-3DPA was always higher than that of DTA in Δ4DES KO/ω3DES OE mutant during the course of cultivation (Fig. 2j) and reached 300 mg/L at days 3 and 4. LC-ESI MS/MS confirmed that the n-3DPA level of PC and TAG increased in both mutants (Supplementary Fig. S8).
The amounts of TFA and biomass (DCW) decreased from day 3 when the glucose in the medium was exhausted in flask culture (Fig. 2b, g), suggesting that the decrease in TFA and biomass was due to the depletion of glucose in the medium. In addition, the air supply may be insufficient in flask culture, which can inhibit the production of LC-PUFAs in Parietichytrium sp. because LC-PUFAs are exclusively produced via the ELO/DES pathway, in which DES requires molecular oxygen for its reaction. Thus, we examined the effects of air supply on the production of LC-PUFAs using three different concentrations of dissolved oxygen (DO) in flask culture (Supplementary Fig. S10). As a result, an increase in the oxygen supply significantly increased the proportion of LC-PUFAs in TFA of Parietichytrium sp. but not in TFA of A. limacinum (Fig. 3a), which synthesizes LC-PUFAs only via an anaerobic PUFA-S pathway. These results suggest that LC-PUFA production in Parietichytrium sp. can be improved by increasing the glucose and oxygen supply in fed-batch culture.
a LC-PUFA levels of Parietichytrium sp. and A. limacinum cultured in the GY medium with different air supply. b LC-PUFA profiles of WT, C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE, and Δ4DES KO/ω3 DES OE of Parietichytrium sp. SEK358 in fed-batch culture. DCW and TFA of fed-batch culture (1 L jar fermenter) of c C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE and d Δ4DES KO/ω3 DES OE. The glucose concentration, DO level, and pH of the medium were monitored and maintained, as described in the “Methods” section. e Production of EPA using C20ELO KO and C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE in fed-batch culture. f Production of n-3DPA using Δ4DES KO and Δ4DES KO/ω3DES OE in fed-batch culture. C20ELO KO and C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE strains for EPA production, and Δ4DES KO and Δ4DES KO/ω3DES OE strains for n-3DPA production used in fed batch culture were derived from Parietichytrium sp. SEK364 and SEK358, respectively. Because SEK364 and SEK358 mutants showed superior production of EPA and n-3DPA, respectively, in fed batch culture under the conditions used. The LC-PUFA profiles of both mutant strains are very similar (Supplementary Fig. S12a, b). All data shown are the mean ± SD. (n = 3). The n values are numbers of replicates.
We examined the conditions for fed-batch culture of Parietichytrium sp. mutant strains. A good yield of EPA production in a 1 L fed-batch culture was obtained using a medium containing 3% glucose and 2% yeast extract in 50% artificial sea water supplemented with a vitamin mixture and an element solution. Of note, the addition of inorganic nitrogen compounds such as monosodium glutamate, ammonium sulfate, and potassium phosphates as a feed solution was effective for increasing DCW and TFA, leading to an increase of EPA production (Supplementary Fig. S11). Under these conditions, the C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE and Δ4DES KO/ω3DES OE mutants showed increased proportions of EPA and n-3DPA, respectively, in LC-PUFAs compared with WT (Fig. 3b). The levels of DCW and TFA in the C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE mutant continuously increased during the culture period to reach approximately 144 g/L and 76 g/L, respectively, after 214 h in batch culture (Fig. 3c). Similarly, approximately 84 g/L DCW and 43 g/L TFA were obtained after 190 h when the Δ4DES KO/ω3DES OE mutant was used for fed-batch culture (Fig. 3d). The yield of EPA and n-3DPA was increased by ω3DES overexpression, and the yield of EPA reached approximately 11.4 g/L (15% of TFA) after 214 h using the C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE mutant (Fig. 3e) and that of n-3DPA reached approximately 4.8 g/L (11% of TFA) after 190 h using Δ4DES KO/ω3DES OE mutant (Fig. 3f). The yield of EPA and n-3DPA in Parietichytrium sp. mutants markedly increased in fed-batch culture compared with flask culture due to the elimination of two negative factors (glucose depletion and insufficient air supply) in flask culture. Collectively, the use of gene manipulation and fed-batch culture in this study made Parietichytrium sp. suitable for mass production of EPA and n-3DPA.
Discussion
Thraustochytrids have been characterized by anaerobic biosynthesis of DHA via PUFA-S, which is considered to be obtained from marine bacteria by horizontal gene transfer4,11. In contrast to the previously known thraustochytrids, Parietichytrium sp. has no PUFA-S gene and synthesizes DHA solely via the ELO/DES pathway (type III LC-PUFA synthesis system), as shown in this study. The distribution of type III LC-PUFA synthesis systems in thraustochytrids, and the relationship of thraustochytrid species possessing different LC-PUFA synthesis systems remain unknown. However, we consider that the genus Parietichytrium has the characteristic of having a type III LC-PUFA synthesis pathway, because all strains of Parietichytrium sp. tested (Supplementary Fig. S12c) showed the characteristic GC profile of type III pathway, as shown in Fig. 1b.
LC-PUFA synthesis pathways similar to type III have been found in molds, such as Mortierella alpina36, and photosynthetic haptophytes, such as Pavlova lutheri37. However, M. alpina does not synthesize DHA due to the lack of ∆4DES, and P. lutheri primarily synthesizes EPA rather than DHA. Thus, the Parietichytrium sp. type III pathway can be thought of as a prototype of an aerobic DHA-synthesizing system. The evolutionary implications of the existence of three LC-PUFA synthesis systems among thraustochytrid species (Fig. 1f) are currently unknown. However, it is of interest that the PUFA-S system, which yields a simple LC-PUFA composition (Fig. 1b), disappeared, and the ELO/DES pathway responsible for the molecular diversity of LC-PUFAs was selected during evolution. In mammals, the diversity of LC-PUFAs plays a role in the diversity of membrane lipids, which are involved in membrane fluidity and functions38.
In this study, we developed a new promoter, Smp1P, derived from SmDNAV, which is a double-stranded DNA virus capable of infecting thraustochytrids34. Smp1P is a promoter of the immediate-early gene of SmDNAV. The immediate-early gene promoter of double-stranded DNA viruses is often used in eukaryotic expression systems as a promoter with high transcription activity. The relative expression level of a marker protein (NeoR) under Smp1P was much higher than that under the ubiquitin promoter used in a previous study35,39 (Supplementary Fig. S6b, c). Smp1P can be used for gene expression in not only Parietichytrium sp. but also other species of thraustochytrids, and thus will aid in the construction of highly efficient transformation systems for a wide range of thraustochytrids.
The yields of EPA and n-3DPA obtained via microbial production reported thus far are listed in Supplementary Table S1. Some marine microalgae are known to produce considerable amounts of EPA40. When the filamentous fungus M. alpina was cultured under low-temperature conditions, high expression of the ω3DES gene was induced, and the EPA content reached 26.4% of the TFA content and 1.8 g/L of culture fluid41. Recently, Wang et al. reported that Aurantiochytrium sp. transformed with a bacterial EPA-producing PUFA-S gene cluster produced 2.7 g/L EPA42. To date, the highest yield of EPA was achieved by engineered Yarrowia lipolytica, which was transformed with several heterologous genes that constitute the ELO/DES pathway required for EPA synthesis43. The engineered oil yeasts eventually produced EPA at 55.6% of the TFA content, 120.7 mg/g of DCW and 5.5 g/L of culture fluid, by inactivating the PEX10 gene, which is involved in peroxisomal β-oxidation. Compared with the engineered Y. lipolytica, the Parietichytrium sp. mutant (C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE) had a lower EPA proportion in terms of TFA and DCW (15.6% of the TFA content and 78.9 mg/g of DCW); however, the mutant exhibited higher production of EPA per liter of culture (approximately 11.4 g/L), exhibiting the highest level of microbial production of EPA to date via a different approach from Y. lipolytica engineering. Compared to the engineered Y. lipolytica oils, the Parietichytrium oils contain a significant amount of n-6PUFAs, so further work may be needed to make the Parietichytrium oils more useful for human and fish supplements.
The physiological function of n-3DPA is not fully understood, although this LC-PUFA is present in the plasma, brain, retina, and heart of mammals30. Recent studies have reported that n-3DPA is converted to novel n-3 immunoresolvents in vivo and exhibits numerous physiological functions, such as anti-inflammatory and proresolving activities29,44,45. To date, there have been few reports on the details of microbial production of n-3DPA, other than reports of certain diatoms, thraustochytrids or Y. lipolytica employing designed myxobacterial PUFA-S46 (Supplementary Table S1). We achieved the production of n-3DPA at 11% of the TFA content, 57 mg/g of DCW, and 4.8 g/L of culture using the mutant Parietichytrium sp. (Δ4DES KO/ω3DES OE). To the best of our knowledge, this is the highest yield of n-3DPA obtained by microbial fermentation. Mass production of n-3DPA enables the supply of pure n-3DPA, which will help to clarify the physiological and pharmacological properties of n-3DPA. Furthermore, Parietichytrium sp., which naturally possesses all genes required for DHA synthesis in its genome, will enable the production of desired LC-PUFAs other than EPA and n-3DPA by disrupting the target gene in the ELO/DES pathway.
Methods
Thraustochytrid strains
T. aureum ATCC 34304 was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (USA). Parietichytrium sp. SEK358, SEK36447, I65-24A, and A. limacinum mh018648 were isolated from seawater from the Ishigaki Islands, Iriomote Islands, Ishigaki Islands, and Yaeyama Islands, Okinawa, Japan, respectively. Parietichytrium sp. SEK364 was identified as Parietichytrium sarkarianum by analyses of 18S rRNA gene, morphology and cultural properties47. The Parietichytrium strains used in each experiment are indicated in the legend of each Figure and Table.
Culture of thraustochytrids
Thraustochytrid strains were grown in 20 mL of GY medium [3% glucose and 1% yeast extract in 50% artificial sea water(3% NaCl, 0.07% KCl, 1.08% MgCl2 6H2O, 0.54% MgSO4 7H2O, 0.1% CaCl2 2H2O)] with 0.1% vitamin mixture (0.2% vitamin B1, 0.001% vitamin B2, and 0.001% vitamin B12) and 0.2% trace elements (3% EDTA di-sodium, 0.15% FeCl3·6H2O, 3.4% H3BO4, 0.43% MnCl2·4H2O, 0.13% ZnSO4·7H2O, 0.026% CoCl2·6H2O, 0.013% NiSO4·6H2O, 0.001% CuSO4·5H2O, and 0.0025% Na2MoO4·2H2O) in a 100 mL flask at 25 °C with rotation at 150 rpm. Potato dextrose agar (PDA) plates (0.8% potato dextrose agar, 50% artificial sea water, 2% agar) containing appropriate antibiotics were used to select Parietichytrium sp. and T. aureum mutants. The growth of these strains was monitored by measuring the optical density at 600 nm (OD 600), dry cell weight (DCW), and consumption of glucose in the medium. The glucose concentration was measured by the Glucose CII test (FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Co., Japan) and the concentration of dissolved oxygen (DO) was measured by a DO meter.
GC analysis to determine the fatty acid composition
Cells were cultured in a 100 mL flask containing 40 mL of GY medium at 25 °C with shaking at 150 rpm. Two mL of culture fluid was harvested, and cells were collected by centrifugation (2500 × g, 3 min), dried by lyophilization, and their DCW was measured. The fatty acids were extracted as fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) from dried cells as described in ref. 49. FAMEs were analyzed by GC-2014 (Shimadzu) equipped with an ULBON HR SS-10 column (Shinwa Chemical Industries). The column temperature was programmed to increase from 160 to 200 °C by 2 °C/min, and then from 200 to 220 °C by 5 °C/min.
Genome sequencing and assembly
Genomic DNA from thraustochytrids was extracted by the standard phenol–chloroform method. The draft genome sequences of T. aureum ATCC 34304 and Parietichytrium sp. I65-24A were obtained using a 454 GS FLX system (Roche Diagnostics) and assembled using Newbler assembler version 2.7 software (Roche Diagnostics). The genomic DNA from T. aureum was sequenced using a paired-end sequencing strategy, and a total of 369 Mbp was obtained from 1,046,218 reads (approximately 9-fold coverage). Assembly of all reads resulted in 14,205 contigs (>500 bp) and 463 scaffolds. The genomic DNA from Parietichytrium sp. was sequenced using a whole-genome shotgun and a paired-end sequencing strategy, and a total of 1556 Mbp was obtained from 4,511,709 reads (approximately 29-fold coverage). Assembly of all reads resulted in 11,544 contigs (>500 bp) and 360 scaffolds. The draft genome sequences of Parietichytrium sp. and T. aureum have been deposited into DDBJ under accession numbers BLSF01000001 to BLSF01000360 and BLSG01000001 to BLSG01000463, respectively.
Expression of DES and ELO genes in S. cerevisiae
The candidate genes for ELO and DES were extracted from the Parietichytrium draft genome database by local BLAST using previously known ELO/DES genes as query sequences. The ORFs of the putative ELO (ELO-1, ELO-2, and ELO-3) and DES (DES-1, DES-2, DES-3, DES-4, DES-5, and DES-6) were amplified by PCR using cDNA or genomic DNA of Parietichytrium, and inserted into the MCS of pYES2/CT (Invitrogen). The ω3DES of S. diclina33 and M. alpina50 were obtained from genomic DNA and cDNA, respectively, by PCR, and inserted into pYES2/CT. The expression vectors were introduced into S. cerevisiae INVSc1 (Invitrogen) using the lithium acetate method51. The transformants were selected by plating on synthetic agar plates lacking uracil (SC-ura). S. cerevisiae transformants harboring ELO and DES were cultured in SC-ura medium containing 2% glucose at 25 °C for 1 day, and then cultured for an additional 1 day in SC-ura medium containing 2% galactose and 50 μM fatty acids (substrate), as described in Supplementary Fig. S1a. The cells were collected by centrifugation at 2000 × g for 10 min and lyophilized. The fatty acid profiles were obtained by GC analysis. ELO or DES activity was expressed as follows: activity (%) = product area × 100/(substrate area + product area).
Quantitative real-time PCR
Real-time PCR was performed using an Mx3000P qPCR System (Agilent Technologies) with TB Green Premix Ex Taq II (Tli RNaseH Plus) (Takara-Bio) using cDNA from Parietichytrium (2 days culture) as a template. The copy numbers of three ELO and six DES were measured using plasmids containing the ORF of each gene as a standard.
Disruption of genes in Parietichytrium sp. and T. aureum
The genes of Δ4DES and C20ELO in Parietichytrium sp., and Δ4DES and PUFA-S in T. aureum were disrupted by homologous recombination using targeting constructs (Supplementary Fig. S13) as described in the previous report35. The linearized knockout targeting constructs containing antibiotic resistance gene were obtained by PCR, introduced into thraustochytrids with a PDS-1000/He (BioRad) using 1550 psi (for Parietichytrium sp.) or 1100 psi (for T. aureum) rupture disks, and then cultured on PDA plate containing appropriate antibiotics. After transfection, ∆4DES and C20ELO KO mutants of Parietichytrium sp. SEK358 (Supplementary Fig. S13a, b) were selected on PDA medium containing 0.5 mg/mL of G418. Two different selection markers were used for disruption of the target genes of Parietichytrium sp. SEK364 and T. aureum (Supplementary Fig. S13c–e). After transfection of C20ELO knockout construct containing NeoR (Supplementary Fig. S13c), Parietichytrium sp. SEK364 was cultured on 2 mg/mL G418, then first allele knockout strain was selected by PCR. For the disruption of second allele of C20ELO of Parietichytrium sp. SEK364, hygromycin resistance gene (HygR) containing knockout construct (Supplementary Fig. S13c) was introduced into first allele knockout strain, then cultured on 2 mg/mL hygromycin containing PDA. The first allele of Δ4DES in T. aureum was replaced with the knockout construct containing the Blasticidin S resistance gene (BlaR) expression cassette (first allele KO construct) and selected on PDA medium containing 0.2 mg/mL of Blasticidin S (Supplementary Fig. S13d). The second allele was replaced with the construct containing the GFP-fused zeocin resistance gene (ZeoR) expression cassette (second allele KO construct) and selected on PDA medium containing 20 mg/mL of zeocin (Supplementary Fig. S13d). In addition to zeocin resistance, fluorescence derived from GFP-ZeoR was used as indicator to select transfectants because of low antibiotic efficiency of zeocin. The first allele of PUFA-S in T. aureum was replaced with the disruption construct containing NeoR expression cassette (first allele KO construct, Supplementary Fig. S13e) and selected on PDA medium containing 2 mg/mL of G418. The second allele was replaced with the construct containing the hygromycin resistance gene (HygR) expression cassette (second allele KO construct, Supplementary Fig. S13e) and selected on PDA medium containing 2 mg/mL of hygromycin, generating the PUFA-S KO strain. The PUFA-S-disrupted and Δ4DES-disrupted mutant (PUFA-S/D4DES KO) was obtained by introducing the Δ4DES knockout construct into the PUFA-S KO strain. The mutants were selected by PCR, and the gene disruption of mutants was confirmed by Southern blot analysis using WT DNA as a control.
Development of a high-expression promoter for Parietichytrium sp
To overexpress ω3DES, which is a bottleneck for EPA or n-3DPA production by Parietichytrium, we developed high-expression promoters in this study. SmDNAV is a double-stranded DNA virus infecting S. minutum34. To identify the immediate early genes of SmDNAV, DNA microarray was performed in SmDNAV-infected S. minutum treated with or without cycloheximide. The 1 kbp upstream sequence of immediate early genes was isolated from the genomic DNA of SmDNAV and inserted upstream of NeoR. Then, the promoter activity was assessed by the transformation efficiency or mRNA expression level of NeoR, which was quantified by real-time PCR. The promoter region demonstrating the highest transcriptional activity was used as the SmDNAV-derived promoter (Smp1P) in this study.
Generation of ω3DES-overexpressing mutants
The codon optimized ω3DES gene of S. diclina was chemically synthesized (Biomatik), and inserted between the Smp1 or EF1α promoter and ubiquitin terminator (Supplementary Fig. S6d). The linearized expression construct was prepared by PCR using the plasmid as a template, and then introduced into Δ4DES KO and C20ELO KO strains of Parietichytrium sp. by biolistic transformation with a PDS-1000/He (BioRad). C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE was selected by 1 mg/mL of Blasticidin-containing PDA. ∆4DES KO/ω3DES OE was selected by 1 mg/mL hygromycin-containing PDA.
Tracing the metabolism of stable isotope-labeled fatty acids
Deuterium-labeled palmitic acid (d31-C16:0) and 13C18-labeled oleic acid (13C18-C18:1) were purchased from Cambridge Isotope Laboratories, Inc. 13C18-C18:1 was added to the medium at a final concentration of 0.25 mM. Cells were collected 4, 8, 24, and 48 h after adding stable isotope-labeled fatty acids. The cell pellet and supernatant were separated by centrifugation at 5,000 × g for 3 min. The cell pellet was dissolved in 200 µL of distilled water. Then, the pellet was crushed at 3000 rpm for 60 s using a bead beater (μT-12, TAITEC) with glass beads (diameter: 0.4 mm, AS ONE Corp.) and kept on ice for 60 s. This procedure was repeated three times to prepare the cell lysate. Cellular lipids were extracted from 90 µL of cell lysate by adding 375 μL of chloroform/methanol (1:2, v/v) containing 50 µM internal standard (C12:0). For saponification, 10 µL of 4 M KOH was added. After incubation at 37 °C for 3 h, 10 µL of 2 M acetic acid, 125 µL of chloroform, and 125 µL of water were added, and the organic phase was separated by centrifugation at 17,500 × g for 3 min. Then, 150 μL of the organic phase was transferred to vials, and the stable isotope-labeled fatty acids were measured using LC-ESI MS/MS (3200 QTRAP, SCIEX) equipped with an InertSustain C18 column (2.1 × 150 mm, 5 μm, GL Sciences) using a gradient starting with 10% solvent B (methanol with 2.5 mM ammonium acetate) in solvent A (distilled water with 2.5 mM ammonium acetate) and reaching 90% solvent B for 1 min, followed by 95% solvent B for 15 min. The column was equilibrated for 5 min before the next run. Isotope-labeled fatty acids were detected by MRM or pseudo-MRM, for which the conditions are described in Supplementary data set 1.
LC-ESI MS/MS to determine the lipid composition
The cell pellet and supernatant were separated by centrifugation at 5000 × g for 3 min, and the DCW was measured after the pellet was lyophilized. The 2 mg of dried cells was dissolved in 300 μL of chloroform/methanol (2:1, v/v) containing 10 μM PC22:0 (11:0/11:0), 10 μM LPC13:0, and 20 μM TG36:0 (12:0/12:0/12:0) as internal standards, and then crushed by sonication for 60 s and kept on ice for 60 s. This procedure was repeated three times. After incubation at 25 °C for 30 min, the supernatant and cell debris were separated by centrifugation at 17,500 × g for 3 min. The 240 μL of supernatant was mixed with 60 μL of water, and then centrifuged at 17,500 × g for 3 min. Forty microliters of the organic phase was transferred into autoinjector vials containing 960 μL of 2-propanol, and then the cellular lipids were measured by LC-ESI MS/MS using a high-performance liquid chromatography system (1200 series, Agilent Technologies) equipped with a mass spectrometer (3200 QTRAP LC-MS/MS system). A binary solvent gradient with a flow rate of 200 μL/min was used to separate phospholipids and neutral lipids by reversed-phase chromatography using an InertSustain C18 column (2.1 × 150 mm, 5 μm)39,52. The gradient was started with 0% solvent B1 (2-propanol with 0.1% formic acid and 0.028% ammonia) in solvent A1 (acetonitrile/methanol/water, 19:19:2, v/v/v containing 0.1% formic acid and 0.028% ammonia) and was maintained for 3 min. The gradient reached 40% B for 24 min, then 50% B for 26 min, and was maintained for 3 min. The gradient was returned to the starting conditions for 1 min and the column was equilibrated for 7 min before the next run. LPC, PC, LPE, PE, diacylglycerol (DAG), and TAG containing C16:0, C18:0, C18:1, C18:2, C18:3, C20:3, C20:4, C20:5, C22:4, C22:5, and C22:6 fatty acids were detected using MRM. The peak intensity of each glycerolipid species was analyzed using MultiQuant 3.0.1 (SCIEX). MRM conditions are described in Supplementary data set 1.
Fed-batch culture of Parietichytrium sp
Mutant strains of Parietichytrium sp. SEK364 (C20ELO KO and C20ELO KO/ω3DES OE) Parietichytrium sp. SEK358 (Δ4DES KO and Δ4DES KO/ω3DES OE) were precultured in 500-mL flasks containing 100 mL of GY medium at 28 °C with shaking at 120 rpm. After glucose consumption, the cells were transferred to a Small Scale Bioreactor BMP-Z (ABLE Co. & Biott Co., Ltd) equipped with a 1 L vessel containing 400 mL of GY medium, the temperature and pH of which were maintained at 28 °C and 6.8 ± 0.2, respectively. The DO level in the medium was maintained above 10% by adjusting the agitation speed (from 600 to 1200 rpm) and air flow rate (from 0.25 to 0.5 L/min). The glucose concentration was continuously monitored and maintained below 60 g/L throughout cultivation by adding feed solution (50% glucose). Samples were collected at the time points indicated in Fig. 3, and the DCW, TFA, EPA, and n-3DPA levels were measured by the method described in “Methods” section.
Statistics and reproducibility
The results are expressed as mean ± SD.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
The authors declare that all data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary information (Figs. S1–S13 and Table S1), supplementary data 1, 2 or from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Accession number of genes encoding ELO-1, ELO-2, ELO-3, DES-1, DES-2, DES-3, DES-4, DES-5, DES-6, and Smp1 promoter are LC530191, LC530192, LC530193, LC530194, LC530195, LC530196, LC530197, LC530198, LC530199, and LC599980 in DDBJ databases, respectively. The draft genome sequences of Parietichytrium sp. and Thraustochytrium aureum have been deposited into DDBJ as accession numbers BLSF01000001 to BLSF01000360 and BLSG01000001 to BLSG01000463, respectively.
References
Abedi, E. & Sahari, M. A. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid sources and evaluation of their nutritional and functional properties. Food Sci. Nutr. 2, 443–463 (2014).
Venegas-Caleron, M., Sayanova, O. & Napier, J. A. An alternative to fish oils: metabolic engineering of oil-seed crops to produce omega-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Prog. Lipid Res. 49, 108–119 (2010).
Hashimoto, M. et al. Docosahexaenoic acid: one molecule diverse functions. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 37, 579–597 (2017).
Metz, J. G. et al. Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids by polyketide synthases in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Science 293, 290–293 (2001).
Morabito, C. et al. The lipid metabolism in thraustochytrids. Prog. Lipid Res. 76, 101007 (2019).
Yoshida, K. et al. Bacterial long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids: their biosynthetic genes, functions, and practical use. Mar. Drugs 14, 94 (2016).
Liang, Y. et al. Transcriptomic profiling and gene disruption revealed that two genes related to Pufas/DHA biosynthesis may be essential for cell growth of Aurantiochytrium sp. Mar. Drugs 16, 310 (2018).
Qiu, X. Biosynthesis of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22:6-4, 7,10,13,16,19): two distinct pathways. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 68, 181–186 (2003).
Matsuda, T. et al. Analysis of ∆12-fatty acid desaturase function revealed that two distinct pathways are active for the synthesis of PUFAs in T. aureum ATCC 34304. J. Lipid Res. 53, 1210–1222 (2012).
Meesapyodsuk, D. & Qiu, X. Biosynthetic mechanism of very long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in Thraustochytrium sp. 26185. J. Lipid Res. 57, 1854–1864 (2016).
Qiu, X., Xie, X. & Meesapyodsuk, D. Molecular mechanisms for biosynthesis and assembly of nutritionally important very long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in microorganisms. Prog. Lipid Res. 79, 101047 (2020).
Siriwardhana, N., Kalupahana, N. S. & Moustaid-Moussa, N. Health benefits of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 65, 211–222 (2012).
Wall, R., Ross, R. P., Fitzgerald, G. F. & Stanton, C. Fatty acids from fish: the anti-inflammatory potential of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids. Nutr. Rev. 68, 280–289 (2010).
Jacobson, T. A., Glickstein, S. B., Rowe, J. D. & Soni, P. N. Effects of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and other lipids: a review. J. Clin. Lipidol. 6, 5–18 (2012).
Tocher, D. Issues surrounding fish as a source of omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Lipid Technol. 21, 13–16 (2009).
Aasen, I. M. et al. Thraustochytrids as production organisms for docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), squalene, and carotenoids. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 100, 4309–4321 (2016).
Colombo, S. M., Rodgers, T. F. M., Diamond, M. L., Bazinet, R. P. & Arts, M. T. Projected declines in global DHA availability for human consumption as a result of global warming. Ambio 49, 865–880 (2020).
Wu, G. et al. Stepwise engineering to produce high yields of very long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in plants. Nat. Biotechnol. 23, 1013–1017 (2005).
Gong, Y. et al. Metabolic engineering of microorganisms to produce omega-3 very long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Prog. Lipid Res. 56, 19–35 (2014).
Walsh, T. A. et al. Canola engineered with a microalgal polyketide synthase-like system produces oil enriched in docosahexaenoic acid. Nat. Biotechnol. 34, 881–887 (2016).
Gupta, A., Barrow, C. J. & Puri, M. Omega-3 biotechnology: thraustochytrids as a novel source of omega-3 oils. Biotechnol. Adv. 30, 1733–1745 (2012).
Calder, P. C. Long-chain fatty acids and inflammation. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 71, 284–289 (2012).
Janssen, C. I. & Kiliaan, A. J. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFA) from genesis to senescence: the influence of LCPUFA on neural development, aging, and neurodegeneration. Prog. Lipid Res. 53, 1–17 (2014).
Brinton, E. A. & Mason, R. P. Prescription omega-3 fatty acid products containing highly purified eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). Lipids Health Dis. 16, 23 (2017).
Bhatt, D. L. et al. Cardiovascular risk reduction with icosapent ethyl for hypertriglyceridemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 380, 11–22 (2019).
Yokoyama, M. et al. Effects of eicosapentaenoic acid on major coronary events in hypercholesterolaemic patients (JELIS): a randomised open-label, blinded endpoint analysis. Lancet 369, 1090–1098 (2007).
Dyall, S. C. Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and the brain: a review of the independent and shared effects of EPA, DPA and DHA. Front. Aging Neurosci. 7, 52 (2015).
Byelashov, O. A., Sinclair, A. J. & Kaur, G. Dietary sources, current intakes, and nutritional role of omega-3 docosapentaenoic acid. Lipid Technol. 27, 79–82 (2015).
Kaur, G., Cameron-Smith, D., Garg, M. & Sinclair, A. J. Docosapentaenoic acid (22:5n-3): a review of its biological effects. Prog. Lipid Res. 50, 28–34 (2011).
Drouin, G., Rioux, V. & Legrand, P. The n-3 docosapentaenoic acid (DPA): a new player in the n-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid family. Biochimie 159, 36–48 (2019).
Hauvermale, A. et al. Fatty acid production in Schizochytrium sp.: involvement of a polyunsaturated fatty acid synthase and a type I fatty acid synthase. Lipids 41, 739–747 (2006).
Qiu, X., Hong, H. & MacKenzie, S. L. Identification of a Delta 4 fatty acid desaturase from Thraustochytrium sp. involved in the biosynthesis of docosahexanoic acid by heterologous expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Brassica juncea. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 31561–31566 (2001).
Pereira, S. L. et al. A novel omega3-fatty acid desaturase involved in the biosynthesis of eicosapentaenoic acid. Biochem. J. 378, 665–671 (2004).
Takao, Y., Nagasaki, K. & Honda, D. Squashed ball-like dsDNA virus infecting a marine fungoid protist Sicyoidochytrium minutum (Thraustochytriaceae, Labyrinthulomycetes). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 49, 101–108 (2007).
Sakaguchi, K. et al. Versatile transformation system that is applicable to both multiple transgene expression and gene targeting for Thraustochytrids. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78, 3193–3202 (2012).
Sakuradani, E., Ando, A., Shimizu, S. & Ogawa, J. Metabolic engineering for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids by oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina 1S-4. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 116, 417–422 (2013).
Guiheneuf, F., Ulmann, L., Mimouni, V. & Tremblin, G. Use of radiolabeled substrates to determine the desaturase and elongase activities involved in eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid biosynthesis in the marine microalga Pavlova lutheri. Phytochemistry 90, 43–49 (2013).
Harayama, T. & Riezman, H. Understanding the diversity of membrane lipid composition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 281–296 (2018).
Watanabe, T. et al. Regulation of TG accumulation and lipid droplet morphology by the novel TLDP1 in Aurantiochytrium limacinum F26-b. J. Lipid Res. 58, 2334–2347 (2017).
Tocher, D. R., Betancor, M. B., Sprague, M., Olsen, R. E. & Napier, J. A. Omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, EPA and DHA: bridging the gap between supply and demand. Nutrients 11, 89 (2019).
Okuda, T. et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) production by an oleaginous fungus Mortierella alpina expressing heterologous the Δ17-desaturase gene under ordinary temperature. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 117, 1919–1927 (2015).
Wang, S. et al. Optimizing eicosapentaenoic acid production by grafting a heterologous polyketide synthase pathway in the thraustochytrid Aurantiochytrium. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68, 11253–11260 (2020).
Xue, Z. et al. Production of omega-3 eicosapentaenoic acid by metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica. Nat. Biotechnol. 31, 734–740 (2013).
Dalli, J., Colas, R. A. & Serhan, C. N. Novel n-3 immunoresolvents: structures and actions. Sci. Rep. 3, 1940 (2013).
Hansen, T. V., Dalli, J. & Serhan, C. N. The novel lipid mediator PD1n-3 DPA: an overview of the structural elucidation, synthesis, biosynthesis and bioactions. Prostaglandins Lipid Mediat. 133, 103–110 (2017).
Gemperlein, K. et al. Polyunsaturated fatty acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica employing designed myxobacterial PUFA synthases. Nat. Commun. 10, 4055 (2019).
Yokoyama, R., Salleh, B. & Honda, D. Taxonomic rearrangement of the genus Ulkenia sensu lato based on morphology, chemotaxonomical characteristics, and 18S rRNA gene phylogeny (Thraustochytriaceae, Labyrinthulomycetes): emendation for Ulkenia and erection of Parietichytrium, and Sicyoidochytrium gen. nov. Mycoscience 48, 329–341 (2007).
Nagano, N., Taoka, Y., Honda, D. & Hayashi, M. Optimization of culture conditions for growth and docosahexaenoic acid production by a marine thraustochytrid, Aurantiochytrium limacinum mh0186. J. Oleo Sci. 58, 623–628 (2009).
Ichihara, K. & Fukubayashi, Y. Preparation of fatty acid methyl esters for gas-liquid chromatography. J. Lipid Res. 51, 635–640 (2010).
Sakuradani, E., Abe, T., Iguchi, K. & Shimizu, S. A novel fungal omega3-desaturase with wide substrate specificity from arachidonic acid-producing Mortierella alpina 1S-4. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 66, 648–654 (2005).
Ito, H., Fukuda, Y., Murata, K. & Kimura, A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J. Bacteriol. 153, 163–168 (1983).
Ikeda, K., Oike, Y., Shimizu, T. & Taguchi, R. Global analysis of triacylglycerols including oxidized molecular species by reverse-phase high resolution LC/ESI-QTOF MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 877, 2639–2647 (2009).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The Science and Technology Research Promotion program for Agriculture, Fisheries and Food Industry, Japan (26050A). We acknowledge E. Abe, S. Kim (Kyushu University), N. Nagano, Y. Taoka, A. Matsuda (University of Miyazaki), M. Ueda and Y. Takeuchi (Konan University) for their technical assistance and valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: M.I., R.H. and K.S.; Funding acquisition: M.I.; Project administration, M.I. and Y.O.; Investigation, Y.I., H.G., R.H., K.S., T.S., Yu.I., S.M., I.S., M.T., M.K., K.T. and N.O.; Resources, D.H., M.H. and Y.T.; Validation: M.I., Y.I. and H.G.; Visualization, H.G., Y.I., T.S. and N.O.; Writing: M.I., Y.I. and H.G.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Communications Biology thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Primary Handling Editors: Jesmond Dalli and Karli Montague-Cardoso. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Ishibashi, Y., Goda, H., Hamaguchi, R. et al. PUFA synthase-independent DHA synthesis pathway in Parietichytrium sp. and its modification to produce EPA and n-3DPA. Commun Biol 4, 1378 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02857-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02857-w
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Transcriptomics aids in uncovering the metabolic shifts and molecular machinery of Schizochytrium limacinum during biotransformation of hydrophobic substrates to docosahexaenoic acid
Microbial Cell Factories (2024)
-
Accumulation of docosapentaenoic acid (n-3 DPA) in a novel isolate of the marine ichthyosporean Sphaeroforma arctica
Biotechnology Letters (2024)
-
Efficient co-production of EPA and DHA by Schizochytrium sp. via regulation of the polyketide synthase pathway
Communications Biology (2022)