Abstract
Chitosan is a natural biopolymer modified from chitins which act as a potential biostimulant and elicitor in agriculture. It is non-toxic, biodegradable and biocompatible which favors potentially broad application. It enhances the physiological response and mitigates the adverse effect of abiotic stresses through stress transduction pathway via secondary messenger(s). Chitosan treatment stimulates photosynthetic rate, stomatal closure through ABA synthesis; enhances antioxidant enzymes via nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide signaling pathways, and induces production of organic acids, sugars, amino acids and other metabolites which are required for the osmotic adjustment, stress signaling, and energy metabolism under stresses. It is also known to form complexes with heavy metals and used as tool for phytoremediation and bioremediation of soil. Besides, this is used as antitranspirant compound through foliar application in many plants thus reducing water use and ensures protection from other negative effects. Based on such beneficial properties, chitosan is utilized in sustainable agricultural practices owing to changing climates. Our review gathers the recent information on chitosan centered upon the abiotic stress responses which could be useful in future crop improvement programs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
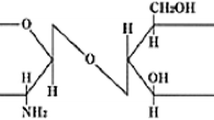
Chitosan is obtained from chitin which is considered as the second most abundant naturally occurring polysaccharides next to cellulose found in the planet (Rinaudo 2006). Chitin and cellulose feature prominent biochemical similarities found in the plant cell walls which include linear polysaccharide chain and are neutrally charged (Kurita 2006). However, unlike cellulose, chitin provides mechanical, physical and structural stability. Structurally, chitin is composed of repeating unit of saccharide monomer of N-acetylglucosamine while cellulose consists of a linear chain of several hundred to thousands of β linked d-glucose units. After deacetylation of chitin, chitosan is obtained which is composed of a linear polymer consisting of two sub-units, d-glucosamine and N-acetyl-d-glucosamine linked together by glycosidic bonds. The presence of this amine group facilitates structural modifications and synthesis of functional derivatives (Shamov et al. 2002). Chitin is basically present in arthropods exoskeleton materials such as crab, shrimp and some fungi. Commercially, chitosan is prepared by demineralization of chitin using acids followed by a deproteinization with a base (Kaya et al. 2015). The prospect for bringing values of these marine wastes has motivated research worldwide to find the use of chitin and its derivative, chitosan. Now, chitosan and its oligosaccharides have gained wide prospects in agricultural application, biomedicine and biotechnology due to their biocompatibility, biodegradability and bioactivity (Katiyar et al. 2014).
In plants, chitosan elicits numerous defense responses related to biotic and abiotic stresses. With the change in climatic conditions and increased food demand which result in an unsustainable use of synthetic chemicals, chitosan application as an elicitor has a wide prospect that would address the issues concerning stress adaptation due to abiotic and biotic stresses. Chitosan application was first studied by Allan and Hadwiger (1979). They demonstrated the effects on fungi of different cell wall compositions. Their antifungal, anti-bactericidal and anti-virucidal properties against invading pathogen and strengthening plant immune system sparked scientists to offer a varied way of application in the agricultural system. Several studies of chitosan inducing resistance mechanism under biotic stress have been extensively reviewed elsewhere (Katiyar et al. 2014; Pichyangkura and Chadchawan 2015; Sharif et al. 2018). Chitosan and its oligomers have been used in the plants to confer resistance against abiotic stresses such as water deficit, salinity, heat stress and heavy metal toxicity (Malerba and Cerana 2015). Their capacity to scavenge ROS system and ultimately improved performance under stress has attracted researchers to offer a more varied application and continue to explore this novel biopolymer.
In drought or dehydration stress, chitosan treatment alleviates the adverse effect caused by water stress by enhanced production of antioxidant enzymes (Guo et al. 2003; Yin et al. 2008), strengthening capability of water absorption through increased root growth (Zhang et al. 2002; Zeng and Luo 2012) and enhanced photosynthetic activities (Li et al. 2008). It was reported to improve soil fertility and enhance nutrient uptake by plant (Dzung 2005, 2007), increased yield and its attributes in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata), potato (Solanum tuberosum), common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) and wheat (Triticum aestivum) under control or stress conditions (Hadwiger 1989; Kowalski et al. 2007; Farouk and Amany 2012; Muriefah 2013). In common bean, when applied hydroponically, chitosan can also alter the root and shoot morphology and accumulation of minerals in plant biomass (Chatelain et al. 2014). The present review describes the mechanism and signal induced by chitosan under stresses. In particular, we focus on the application of chitosan in alleviating abiotic stresses and its abilities to improve the physiological and biochemical attributes of the plants.
Mechanism of action of chitosan
Mechanism of chitosan in plants has not been fully understood yet. However, there are many reports suggesting chitosan elicited a number of defense responses in the plants (Iriti and Faoro 2009; Mejía-Teniente et al. 2013; Malerba and Cerana 2015). Chitin-specific receptors are present in plant cell membranes which are known to elicit defense responses. When treated with chitin-based treatment, plants activate their defense mechanism since they mimic compounds related to chitin-containing organism (Iriti and Faoro 2009). Chitin elicitor binding proteins (CEBiP) have been isolated in various crops (Miya et al. 2007). These induce defense response directly affecting the chitosan-responsive differential gene expression profile interacting with the chromatin and/or it may bind with specific receptors (Hadwiger 2015). A chitosan binding glycoprotein (family of lectins) has been isolated from leaves of mustard (Brassica campestris) (Chen and Xu 2005). Also, research done on Mimosa pudica and Cassia fasciculate isolated vesicle showed rapid activation of plasma membrane H+-ATPase, suggesting the presence of chitosan receptor molecules (Amborabé et al. 2008). In addition, as reported in an experiment done on A. thaliana knockout mutants, chitosan can induce a receptor-like kinase gene, MAP kinase pathway and lysin motif receptor-like kinase, chitin elicitor receptor kinase 1 (CERK1) which can bind with chitin and chitosan (Petutschnig et al. 2010). On the other hand, Povero et al. (2011) reported that in A. thaliana seedlings, chitosan signaling does not use CERK1 and is perceived through a CERK1-independent pathway. Thus, chitosan binding receptors is still uncertain and remains “a Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern (PAMP) in search of a Pattern Recognition Receptor (PRR)” (Iriti and Faoro 2009).
Chitosan and its derivatives exhibit numerous eliciting compounds in several plants (Pichyangkura and Chadchawan 2015; Malerba and Cerana 2015). Under biotic stress, plants exhibited defense response including production of phytoalexin, pathogenesis-related proteins such as chitinase and β-glucanase, proteinase inhibitors, callose formation, lignin biosynthesis and induction of stress-responsive genes. However, upon treatment with chitosan and its oligomers, these defense-related compounds are found to increase, facilitating the use of chitosan and its derivatives as strong antimicrobial compounds and elicitors for plant protection (Katiyar et al. 2014). Induction of chitinase and glucanase enzymes by chitosan treatment has been reported in several crops, including peach (Prunupersica L. Batsch; Ma et al. 2013), tomato (Sathiyabama et al. 2014), dragon-fruit (Hylocereus undatus; Ali et al. 2014). Chitinase and glucanase are compounds associated with resistance to pathogen, however, in rice seedling, different molecular weight chitosan exhibit different level of pathogenesis-related protein, suggesting chitosan has varied functionality depending upon its type (Lin et al. 2005). Further, Low molecular weight chitosan (5 kDa) was able to induce phytoalexin and other pathogenesis-related compounds, chitinase, β-glucanase, lipoxygenase and activated the generation of ROS species, Also, changes in the composition of sterol was found to produce adverse effect against infester (Vasiukova et al. 2001). Seed treatment with depolymerized chitosan and its oligosaccharides was reported to increase the chitinase activity in seedlings by 30–50% (Hirano et al. 1990). Some of the defense responses elicited by chitosan are summarized in Table 1.
Signaling induced by chitosan
Signaling induced by chitosan molecule includes specific cellular receptors which are then transduced by secondary messenger(s) such as reactive oxygen species (ROS), H2O2, Ca2+, nitric oxide (NO) and phytohormones inside the cell to induce physiological responses. The inhibitory effect of radicals like superoxide anion and lipid free radical by chitosan treatment has been previously reported by Li et al. (2002). Decrease in molecular weight and increase in deacetylation degree increased the inhibition of superoxide anion and lipid-free radicals. Pongprayoon et al. (2013) reported that H2O2 acts as a signal molecule to induce resistance to osmotic stress in two rice cultivars, LPT123 and LPT123-TC171 mutated line, by increasing plant growth and improved photosynthetic pigments during osmotic stress. Further, it has been confirmed in wheat to improve membrane stability through activation of antioxidant system (He et al. 2009), and in soybean to increase oligosaccharides synthesis and enhance drought tolerance (Ishibashi et al. 2011). Ca2+ regulates callose synthase activity in both monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous species in response to chitosan elicitation (Kohle et al. 1985; Faoro et al. 2008), mediates programmed cell death in soybean cells (Zuppini et al. 2003) while treatment with a calcium channel inhibitor delayed the cell death kinetic in tobacco plants infected with tobacco necrosis virus (Iriti et al. 2006).
Nitric oxide (NO) signaling has been investigated in pearl millet seedlings treated with chitosan where exogenous NO inhibitor LNAME (N-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester hydrochloride) or NO scavenger c-PTIO [2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethylimidazoline-1-oxy-3-oxide potassium salt] reduced the degree of protection from pathogen attack (Hadwiger 2013). Chitosan also induced jasmonic acid (JA) accumulation in rice (Rakwal et al. 2002) and Phaseolus vulgaris (Iriti and Faoro 2009). A cDNA microarray/semiquantitative RT-PCR analyses of Brassica napus gene expression showed that JA/ethylene plays a signaling role in chitosan mediated plant defense response (Yin et al. 2006). Transcriptional activation of gene encoding phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) and protease inhibitors was induced by both chitosan and jasmonic acid (Doares et al. 1995; Khan et al. 2003). Chitosan may trigger JA and ABA synthesis (Iriti and Faoro 2008). In rice seedlings, there was increase in JA and 12-oxo-phytodieonic acid accumulation via octadecanoid pathway when treated with chitosan (Rakwal et al. 2002), while ABA was also induced via hydrogen peroxide signaling leading to stomatal closure (Pichyangkura and Chadchawan 2015). JA and ABA have similar activities which play a significant role in the regulation of water use by plants (Leung and Giraudat 1998). Additionally, chitosan application results in enhanced defense responses involving activation of hydrogen peroxide through octadecanoid pathway and NO in the chloroplast, MAP-kinase activation, oxidative burst and hypersensitive responses (Rakwal et al. 2002; Lin et al. 2005; Dwivedi and Singh 2014; Pichyangkura and Chadchawan 2015). These entire signaling molecules contribute to the adaptive mechanism in chitosan treated plants in response to stress. Below is the summarized view of different secondary messengers induced by chitosan in plants subjected to stresses (Fig. 1).
Chitosan induces ABA activity leading to stomatal closure
Chitosan induced ABA activity was demonstrated in tobacco plants where ABA inhibitor (nordihydroguaiaretic acid) treated before chitosan application was able to reduce callose synthesis and conferred resistance against tobacco necrosis virus (Iriti and Faoro 2009). Also, ABA content was increased upon treatment with chitosan on bean leaves, proving the involvement of ABA in stomatal closure (Iriti et al. 2009). The mechanism behind chitosan induced stomatal closure which led to the closure of stomata is not well understood yet. However, transcriptomics and phenotypic analysis of ABA and chitosan treated plants suggest that the effect of chitosan is partially due to the activation of ABA signaling pathway (Azinheiro et al. 2014) where ABA plays an important role in the regulation of stomatal closure (Kim et al. 2010; Kumar et al. 2016; Kuyyogsuy et al. 2018). Chitosan mediated role of ABA synthesis leading to stomatal closure has been depicted in Fig. 2. Also, studies have already reported that stomatal closure and reduced transpiration were induced by abscisic acid (Leung and Giraudat 1998). Increase in H2O2 accumulation and induction of stomatal closure was observed upon treatment with chitosan (Lee et al. 1999). NO acts as a secondary messenger and it is known to induce PA (phosphatidic acid) accumulation under pathogen attack. In tomato cell cultures upon treatment with NO inhibitor, cPTIO, and chitosan together, there was decreased level of PA accumulation (Raho et al. 2011). PA interacts with ABI1 which is a negative regulator of ABA, and induces ABA-mediated stomatal closure through phospholipase C and diacylglycerol kinase (DGK) pathways (Zhang et al. 2002). This proves that NO signaling inside the cell is induced by responses to both biotic and abiotic stresses. NO was shown to act downstream of ROS production which is similar to the effects of ABA or methyl jasmonate (MJ) on closure of stomata (Srivastava et al. 2009). Chitosan treated pepper plant was able to use 26–43% less water than control plant by inducing stomatal closure (Bittelli et al. 2001). This provided clear evidence that chitosan can be effective antitranspirant compound by reducing transpiration via stomatal closure. Similar effect has been described in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) (Khokon et al. 2010) and barley (Hordeum vulgare) (Koers et al. 2011).
Role of chitosan mediated responses in stomata closing mechanism via ABA biosynthesis at cellular level. The signaling induced by chitosan involves hydrogen peroxide via octadecanoid pathway and nitric oxide. Hydrogen peroxide induces both the ABA synthesis and ROS scavenging mechanism while nitric oxide regulates phosphatidic acid (PA) via phospholipase C (PLC) and diacylglyceral kinase (DGK) (PLC/DGK) pathway, and initiates ABA synthesis leading to closure of stomata and activates biotic and abiotic stress responsive genes (Pichyangkura and Chadchawan 2015)
A negative effect of antitranspirant application could hamper plant productivity. However, upon foliar treatment with chitosan, there was significant decrease in stomatal conductance and maximal photosynthetic activity with no significant change in internal CO2 concentration, which may suggest that decreasing assimilation was not only due to decrease in CO2 transfer from the atmosphere (Iriti et al. 2009). But, it might be the decrease in carboxylation efficiency which does not affect stomatal limitation (Rouhi et al. 2007). Further, Iriti et al. (2009) compared the antitranspirant activity between chitosan treatment and Vapor Gard (commercial antitranspirant). Vapor Gard results in better antitranspirant activity than chitosan treatment. Also, the WUE was higher in case of VP associated with low internal CO2 concentration in leaves which led to lower photosynthetic rate and carbon gain. However, in chitosan treated plant, there was no significant increase in water use efficiency (WUE) but ensured enhanced photosynthetic activity than Vapor Gard since chitosan treated plant resulted in better regulation of stomata as compared to control, while in VP, it formed thin antitranspirant film on the leaves and did not affect the stomatal opening which suggests that photosynthetic activity and stomatal conductance changes proportionally, thus reducing assimilated carbon as water consumption decreases. The authors also suggested that chitosan application as an antitranspirant compound would be more suitable in plant subjected to minor or occasional drought events. In these conditions, chitosan-treated plants would let their innate physiological mechanism to rapidly recover a maximal carbon uptake while maintaining biomass and yield (Bittelli et al. 2001).
Chitosan influence on abiotic stress
Chitin and its derivatives have evolved as natural polymers which elicit beneficial responses in plants. However, their functionality is dependent on its structure, concentration, species and developmental stage of the plant. They are reported to possess antioxidant activity due to their presence of hydroxylated amino group which offers an effective scavenger of ROS (Xie et al. 2001; Sun et al. 2008). Interesting results were obtained with chitosan treated plants against various abiotic stresses (Table 2).
Drought stress
Drought stress or deficit irrigation limits the agricultural production causing many deleterious effects on plant health which mainly include the production of reactive oxygen species causing lipid peroxidation of membrane and interaction with other macromolecules, leading to reduced plant growth and yield (Yang et al. 2009; Bistgani et al. 2017). However, application of chitosan stimulated plant growth and increased the availability and uptake of water and essential nutrients, thereby contributing to enhanced reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging activities (Guan et al. 2009). Chitosan treatment in white clover (Trifolium repens) (pretreated with Hoagland’s solution containing 1.0 mg/ml chitosan, 2 days before induction of dehydration stress) alleviated drought stress and increased production of stress protective metabolites (Li et al. 2017). Foliar application of chitosan (200–400 μL/L) sprayed three times before flowering stage, 50% flowering and full bloom, reduced the negative impact of drought condition on the oil yield and dry matter of Thymus daenensis Celak (Bistgani et al. 2017). Also, chitosan application (0.2–0.4 g/L) under drought stress, foliar sprayed three times before flowering and 2 weeks later, increased plant growth attributes in two species of sweet basil (Ocimum ciliatum and O. basilicum) (Pirbalouti et al. 2017). Foliar application of chitosan at a concentration of 250 mg/L in cowpea improved growth and yield parameters in both drought stress and non-stress conditions (Farouk and Amany 2012). Similar observation was made where chitosan induced drought resistance in rice (Boonlertnirun et al. 2007), apple (Yang et al. 2009) and coffee (Dzung et al. 2011). Besides, plants soaked and sprayed with 0.05% chitosan reversed the harmful effects caused by ozone as compared to control treatment (Phothi and Theerakarunwong 2017).
Influence on biochemical activities
Under drought stress, proline accumulation increases. Proline is a vital osmoprotectant responsible for osmotic adjustment, quenching of ROS and maintenance of redox balance under abiotic stresses (Matysik et al. 2002; Ashraf and Foolad 2007; Hidangmayum and Dwivedi 2018). Under severe drought stress, metabolic factor such as free proline content in leaves significantly increased (Din et al. 2011) as a part of an adaptive mechanism. Proline accumulation contributes to reduced water loss by lowering the leaf water potential. It also favors the water transport to leaves and increases their turgor. Amino acids such as isoleucine, threonine, lysine and aspartic acid were also identified as osmoregulants and supply nutrition when plants suffer from abiotic and biotic stresses (Joshi et al. 2010; Chang et al. 2014; Du et al. 2015; Singh and Dwivedi 2016). Studies done on white clover when subjected to drought stress reported that chitosan treatment enhanced the production of metabolites and amino acids such as proline, GABA, aspartic acid, valine, serine, lysine, threonine, isoleucine and phenylalanine (Li et al. 2017). Treatment with chitosan increased the accumulation of proline level in thyme plant (Bistgani et al. 2017). However, in safflower, low concentration of chitosan (0.05–0.4%) decreased proline level, but at high concentration, increased its level (Mahdavi et al. 2011). Similarly, in Ricinus communis, it did not influence proline level (Karimi et al. 2012). Thus, the effect of chitosan on different plant species may follow different mechanisms.
Membrane integrity is often disturbed when the plant is subjected to water deficit condition. Membrane relative permeability and MDA (malondialdehyde) concentration are used to represent membrane stability. In water deficit condition, there is an increase in MDA level which is a product of lipid peroxidation and may cause membrane leakage due to the accumulation of free radicals. However, chitosan functions as a positive regulator in osmotic adjustment and eliminate the adverse effect of drought stress symptoms. Many researchers have reported that pretreatment with chitosan in bean, potato, thyme, Hydrilla verticillata, apple seedlings decreased lipid peroxidation, eliminated ROS and increased membrane stability (Xu et al. 2007; Yang et al. 2009; Jiao et al. 2012; Karimi et al. 2012; Bistgani et al. 2017). Due to the presence of abundant hydroxyl and amino groups present in chitosan, these react with ROS and form stable, non-toxic macromolecular radicals. Chitosan can scavenge OH and O2− radicals and possesses DNA-protective properties (Prashanth et al. 2007). Enhanced level of SOD and catalase enzyme activities promote the production of MDA and reduces lipid peroxidation in apple seedlings subjected to drought stress (Yang et al. 2009). Yin et al. (2002) and Sun et al. (2004) also reported that superoxide anion can be scavenged by chitosan and SOD. The ability to scavenge by chitosan may be attributed to its structure, which consists of hydroxyl and amino groups available to react with ROS (Xie et al. 2001; Li et al. 2002; Sun et al. 2004).
In response to drought, accumulation of total soluble sugar increases due to the breakdown of polysaccharides which help in the maintenance of turgor (Nazarli et al. 2011). Soluble sugars contribute to drought tolerance of peas, sugar beets and black poplars (Liu et al. 2011). Sugar such as glucose and fructose contribute to drought-resistance including signal transduction to modulate plant growth, development and stress responses (Rolland et al. 2006). In chitosan treated plants, these carbohydrates increase glucose, fructose, mannose, trehalose, sorbitol, myoinositol, while other detected sugars also up-regulated many genes involved in carbohydrate transport and metabolism in leaves of white clover (Li et al. 2017). These might contribute to improved drought resistance via increase in osmotic adjustment and maintenance of carbon balance in response to dehydration stress.
Also, drought stress impairs the photosynthetic ability, thus reducing chlorophyll synthesis. This might be due to destruction of chlorophyll pigment complexes encoded by the cab gene family (Allakhverdiev et al. 2003; Farouk and Amany 2012), or destruction of light-harvesting protein complexes or by oxidative damage incurred on chloroplast lipids, pigments and proteins (Lai et al. 2007). However, chitosan has been found to alleviate these effects in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.), where chlorophylls and total carbohydrate increased when sprayed with chitosan at 250 mg/L (Farouk and Amany 2012). Similarly, increased photosynthesis level was observed when maize, soybean and bean were treated with chitin oligosaccharides (Khan et al. 2002; Sheikha and Al-Malki 2011). This may be due to increase in nitrogen and potassium content in plant shoot which helps in increasing the number of chloroplast per cell, thus contributing to increased synthesis of chlorophyll (Possingham 1980). Also, higher availability of amino compounds released by chitosan treatment (Chibu and Shibayama 2001) contributes to stimulation of chlorophyll synthesis. Proline and photosynthetic complexes are both synthesized from the same substrate, so increase in production of proline leads to decrease in synthesis of photosynthetic pigments under drought (Paleg and Aspinall 1981).
Salinity stress
Salinity affects whole plant, both physiologically and biochemically, and in severe cases, it also inhibits plant uptake of nutrients and water either due to low external osmotic potential or toxic effect caused by higher accumulation of Na+ and Cl− ions as a result of direct ionic effects. Salt stress results in biochemical alteration and induces ROS which hampers the cellular machinery leading to oxidative stress. Various studies have found that higher accumulation of MDA was observed in salt-affected plant which is primarily due to lipid peroxidation of membrane caused by ion toxicity. However, several researchers have reported that treatment with chitosan at low concentration could alleviate the negative effects caused by salt stress. Low concentration chitosan treated seeds of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) and sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) are able to alleviate the oxidative stress caused by salt stress by reducing enzyme activities in both crops (Jabeen and Ahmad 2013). Similarly, pretreatment with chitosan during salinity stress results in increased antioxidant enzyme activities and lower level of MDA content which ultimately reduces the negative effect caused by salt stress in Oryza sativa (Martínez et al. 2015), Zea mays (Al-Tawaha et al. 2018), Vigna radiata (Ray et al. 2016), Trachyspermum ammi (Mahdavi and Rahimi 2013) and Plantago ovata (Mahdavi 2013). Further, hydroponic experiment done on wheat showed that 0.0625% oligochitosan treated seed resulted in positive effects by significantly increasing antioxidant enzyme (SOD, POD and CAT) during salt induced stress and was able to alleviate the oxidative stress (Ma et al. 2012). Oligochitosan is one of the effective oligosaccharides comprising of β-1, 4-linked 2-amino-d-glucose units and contains small amounts of 2-acetomido-d-glucose unit which are obtained by degradation of chitosan.
Influence on biochemical activities
In salt stress, plant exhibits a significant reduction in chlorophyll content due to the instability of protein complexes and accumulation of chlorophyllase (chlorophyll-degrading enzyme) (Reddy and Vora 1986). On the other hand, excessive accumulation of Na+ caused by direct ionic effect induces stomatal closure which may reduce internal CO2 and lead to the reduction of photosynthesis rate. However, upon seed treatment with oligochitosan (0.0625%), photosynthetic rate and stomatal conductance were found to increase in wheat since photosynthesis is dependent on the stomatal movement and protein associated with chlorophyll metabolism (Ma et al. 2012). While in other study, foliar application of chitosan resulted in reduced stomatal conductance and photosynthetic rate with no change in internal CO2 concentration (Iriti et al. 2009). These contrasting results might be due to the fact that chitosan functionality is dependent on various factors such as method of application, degree of deacetylation, molecular weight and different species perceiving different responses. However, in this condition, the method of application is critical as foliar treatment results in reduced stomatal conductance and photosynthetic rate, while in seed treatment, the reverse was shown. Production of ROS is obvious in plant subjected to stresses as discussed earlier. Plants have acquired their innate ROS scavenging mechanism by the production of enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant compounds. SOD, POD, and CAT are enzymatic antioxidants which are found to increase when plants are subjected to salt stress (Jabeen and Ahmad 2013). Higher accumulation of these enzymes indicates efficient detoxification of ROS. Chitosan treated plants were found to increase these enzymes and play an important role in alleviating salt stress through enhanced antioxidant enzymes (Ma et al. 2012; Jabeen and Ahmad 2013). Similarly, lipid peroxidation caused by accumulation of MDA was found in salt-induced stress condition (Meloni et al. 2003). However, upon treatment with chitosan and its derivatives, there was reduction in MDA content ultimately stabilizing membrane damage which could be the reason to confer tolerance against salt stress (Jabeen and Ahmad 2013). Enhanced level of proline was also observed in salt stress which might be due to the induction of proline biosynthesis or decrease in oxidation of proline to glutamate or reduction in utilization of protein synthesis or increase in protein turnover (Khan et al. 2010). Interestingly, seed soaked with oligochitosan at 0.0625% for 5 h, led to significant increase in proline level (Ma et al. 2012). Similar observation was reported in pre-sowing seed treatment of chitosan in safflower and sunflower, where increasing chitosan concentration was found to enhance proline level, while the decrease in proline content was found at low concentration (0.25%) of chitosan (Jabeen and Ahmad 2013).
Heavy metal toxicity
Several studies confirmed that chitosan has the ability to form complexes with non-nutrient elemental ions including a number of heavy metals due to presence of functional amino and hydroxyl group; it has recently been reported to alleviate toxic effects of cadmium through foliar application of different molecular weight chitosan such as 10 kDa, 5 kDa and 1 kDa in a hydroponically grown edible rape (Brassica rapa L.) (Zong et al. 2017a). Similarly, in the same experiment done under greenhouse conditions, a protective effect of cadmium (Cd) toxicity was observed (Zong et al. 2017b). Kamari et al. (2011, 2012) also reported that chitosan could bind Ag, Zn, Cd, and Pb and provided evidence of metal accumulation in perennial rye grass and rapeseed under chitosan application. Additionally, Vasconcelos (2014) extensively reviewed the impact of chitosan and chitosan oligosaccharides in phytoremediation and biofortification programmes. These findings provide a potential mechanism to alleviate phytotoxicity under heavy metal stresses, and also it can be hypothesized that since chitosan and its oligomers can take up a higher concentration of toxic elements, it could be possible that they also increase the absorption of essential minerals.
Influence on biochemical activities
Under heavy metal stress, heavy metal toxicity in shoot and roots leads to cellular dysfunction and metabolism. Cadmium (Cd) toxicity is reported to suppress stomatal conductance and photosynthesis while foliar application of chitosan tends to alleviate these effects and increase stomatal conductance, gas exchange and promote photosynthesis (Zong et al. 2017a). However, it was inconsistent with the earlier report where foliar application of chitosan induced stomatal closure and reduced transpiration in pepper (Bittelli et al. 2001). This might be due to chitosan’s response following different mechanisms in different species. SOD, POD and CAT content which were reported to increase under Cd stress, further increases when treated with chitosan. However, ascorbic acid was found to be reduced when subjected to Cd stress which might be due to its potential mechanism to directly scavenge ROS, indicating its role as first line of defense against oxidative stresses. While chitosan treatment significantly increased ascorbic acid in Cd stress plant, glutathione level was found to increase under Cd stress but remained unchanged under chitosan treatment as reported by Zong et al. (2017a). This shows that glutathione has no effect under chitosan treatment.
Heat stress
Heat stress is often considered a complicated issue as it usually coincides with drought stress and it’s difficult to monitor these two stresses (McKersie and Lesheim 2013). It has been reported that foliar spraying of chitosan in combination of zinc and humic acid on dry bean could tolerate heat stress under late sown plants (Ibrahim and Ramadan 2015). There is a dearth of published information regarding chitosan application under heat stress. However, there are reports that suggest ABA can trigger heat shock-related genes (Choi et al. 2013) like overexpression of ABF3 (Abscisic acid responsive-element-binding factor 3) could alleviate heat stress tolerance. Therefore, use of chitosan could overcome high-temperature stress by inducing ABA activity which is linked with the previous report on stomatal closure (Bittelli et al. 2001), and further induces defense-related ABA-responsive genes.
Application of chitosan nanoparticle in plants
Apart from biomedical application, chitosan nanoparticles have evolved as a promising alternative for various carrier molecules because of their proven biocompatibility, biodegradability, adsorption abilities and low-toxicity, thus offering a great tool for inducing multifaceted disease resistance (Malerba and Cerana 2015). Chitosan nanoparticle preparation requires a simple procedure which makes them versatile and user-friendly drug delivery (Kashyap et al. 2015). Oliveira et al. (2016) reported that chitosan nanoparticle containing S-nitroso-mercaptosuccinic acid (S-nitroso-MSA), in which nitric oxide (NO) was able to control release, could alleviate the potential harm caused by salt stress in maize plant. NO is involved in plant response to various abiotic stresses such as salinity, drought, heavy metal and extreme temperatures, and it offers beneficial effect on physiological and biochemical processes of plant growth and development (Singh et al. 2018). Chitosan nanoparticle encapsulated with NO donor (S-nitroso-MSA) is able to mitigate the effects of salinity in maize plant. This might be due to slower release of NO by the nanoformulation (Oliveira et al. 2016). Also, the encapsulated S-nitroso-MSA in chitosan domain may protect the NO donor from heat and decomposition (Seabra et al. 2014). Encapsulations of active ingredient in the chitosan domain offer a wise strategy in the promotion of sustainable agricultural practices and their control release facilitates an efficient gene delivery system for plant transformation (Kashyap et al. 2015). Chandra and his colleagues demonstrated the effects of chitosan nanoparticle on plant system where they found that chitosan nanoparticles induced significant plant innate immune responses and various defense-related enzymes. They also suggested that chitosan nanoparticles could be better strategies for phytosanitation and disease management in sustainable agriculture as compared to natural chitosan (Chandra et al. 2015).
Chitosan as a different formulation of bio-fertilizer
Chitosan has attracted scientists for its use as bio-fertilizer due to its biodegradability and non-toxic nature which could be an alternative for synthetic fertilizers with less impact on environmental contamination. Chitosan as a bio-fertilizer has been reported to stimulate crop yield; in potato infested with late blight it significantly reduced the tuber infestation and increased plant nutrient uptake (O’Herlihy et al. 2003). In another study, combination of chitosan (1%) and fertilizer increased the nitrogen and phosphorous content in the roots and shoots of Eustoma grandiflorum (Raf) compared to non-treated ones (Ohta et al. 2000). Similar results were recorded when chitosan was used as bio-fertilizer in different crops, for instance, chitosan in combination with N, P, K reduced the effect of Botrytis cinerea-causing grey mold disease in begonia × hiemalis Fotsch (Chen et al. 2016); irrigation with chitosan has shown to reduce root-knot nematodes and Pochonia chlamydosporia infection (Escudero et al. 2017). These results prove that chitosan has a potential role as bio-fertilizer application.
Conclusion and future prospect
The most commonly reported utilization of chitosan has been in the biomedical industry. Due to its proven biodegradable, biocompatibility, non-toxic and non-allergenic nature, chitosan application offers a wide possibility for use as a bioactive material (Katiyar et al. 2011, 2015). However, application of chitosan in plants has been less diverse, especially under abiotic stresses. As far as drought is concerned, chitosan induces numerous beneficial responses in plants such as antitranspirant, activation of ROS scavenging system, enhanced stomatal conductance, improved root growth and overall plant development. It is non-toxic and environmental friendly which will gain much value in the use of sustainable agricultural practices. However, the heterogeneity of preparation is still unavoidable which can greatly affect the physical properties of chitosan. Despite the work done till date, the mode of action of chitosan in the plant system is not understood in totality. So, further transcriptomic and proteomic studies of abiotic stress responsive genes and proteins need to be identified to provide a better use of chitosan in the abiotic stress management.
References
Agrawal GK, Rakwal R, Tamogami S, Yonekura M, Kubo A, Saji H (2002) Chitosan activates defence/stress response(s) in the leaves of Oryza sativa seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:1061–1069
Ali A, Zahid N, Manickam S, Siddiqui Y, Alderson PG, Maqbool M (2014) Induction of lignin and pathogenesis related proteins in dragon fruit plants in response to submicron chitosan dispersions. Crop Prot 63:83–88
Allakhverdiev I, Hayashi H, Nishiyama Y, Ivanov AG, Aliev JA, Klimov VV, Murata N, Carpentier R (2003) Glycinebetaine protects the D1/D2/Cytb559 complex of photosystem II against photo-induced and heat-induced inactivation. J Plant Physiol 160:41–49
Allan CR, Hadwiger LA (1979) The fungicidal effect of chitosan on fungi of varying cell wall composition. Exp Mycol 3:285–287
Al-Tawaha AR, Turk MA, Al-Tawaha ARM et al (2018) Using chitosan to improve growth of maize cultivars under salinity conditions. Bulg J Agric Sci 24(3):437–442
Amborabé BE, Bonmort J, Fleurat-Lessard P, Roblin G (2008) Early events induced by chitosan on plant cells. J Exp Bot 59:2317–2324
Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2007) Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance. Environ Exp Bot 59:206–216
Azinheiro S, Avelelas F, Leandro SM, Rodrigues AA (2014) Role for ABA in the plants response to chitosan. Front Mar Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/conf.fmars.2014.02.00069
Bistgani ZE, Siadat SA, Bakhshandeh A, Pirbalouti AG, Hashemi M (2017) Interactive effects of drought stress and chitosan application on physiological characteristics and essential oil yield of Thymus daenensis Celak. Crop J 5(5):407–415
Bittelli M, Flury M, Campbell GS, Nichols EJ (2001) Reduction of transpiration through foliar application of chitosan. Agric For Meteorol 107:167–175
Boonlertnirun S, Sarobol E, Meechoui S, Sooksathan I (2007) Drought Recovery and grain yield potential of rice after chitosan application. Kasetsart J 41:1–6
Chakraborty M, Karun A, Mitra A (2008) Accumulation of phenilpropanoid derivatives in chitosan-induced cell suspension culture of Cocos nucifera. J Plant Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph2008.02.004
Chandra S, Chakraborty N, DasguptaA SJ, Panda K, Acharya K (2015) Chitosan nanoparticles: a positive modulator of innate immune responses in plants. Sci Rep 5:15195
Chang B, Yang L, Cong W, Zu Y, Tang Z (2014) The improved resistance to high salinity induced by trehalose is associated with ionic regulation and osmotic adjustment in Catharanthus roseus. Plant Physiol Biochem 77:140–148
Chatelain PG, Pintado ME, Vasconcelos MW (2014) Evaluation of chitooligosaccharide application on mineral accumulation and plant growth in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Sci 215–216:134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.11.009
Chen HP, Xu LL (2005) Isolation and characterization of a novel chitosan-binding protein from non-heading Chinese cabbage leaves. J Integr Plant Biol 47:452–456
Chen YE, Yuan S, Liu HM, Chen ZY, Zhang YH, Zhang HY (2016) A combination ofchitosan and chemical fertilizers improves growth and disease resistance in Begonia hiemalis Fotsch. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 57:1–10
Chibu H, Shibayama H (2001) Effects of chitosan applications on the growth of several crops. In: Uragami T, Kurita K, Fukamizo T (eds) Chitin and chitosan in life science. Yamaguchi pp 235–239
Choi YS, Kim YM, Hwang OJ, Han YJ, Kim SY, Kim JI (2013) Overexpression of Arabidopsis ABF3 gene confers enhanced tolerance to drought and heat stress in creeping bentgrass. Plant Biotechnol Rep 7:165–173
Croteau R, Gurkewitz S, Johnson MA, Fisk HJ (1987) Monoterpene and diterpene biosynthesis in lodgepole pine saplings infected with Ceratocystis clavigera or treated with carbohydrate elicitors. Plant Physiol 85:1123–1128
Din J, Khan SU, Ali I, Gurmani AR (2011) Physiological and agronomic response of canola varieties to drought stress. J Anim Plant Sci 21(1):78–82
Doares SH, Syrovets T, Wieler EW, Ryan A (1995) Oligogalacturonides and chitosan activate plant defensive gene through the octadecanoid pathway. Proc Natl Acad USA 92:4095–4098
Du B, Jansen K, Kleiber A, Eiblmeier M, Kammerer B, Ensminger I, Gessler A, Rennenberg H, Kreuzwieser JA (2015) Coastal and an interior Douglas fir provenance exhibit different metabolic strategies to deal with drought stress. Tree Physiol 36:148
Dwivedi P, Singh BN (2014) Nitric oxide as a signalling agent in plant. In Singh AL (ed) Advances in crop physiol, pp 63–78
Dzung NA (2005) Application of chitin, chitosan and their derivatives for agriculture in Vietnam. J Chitin Chitosan 10(3):109–113
Dzung NA (2007) Chitosan and their derivatives as prospective biosubstances for developing sustainable eco-agriculture. In Senel S, Varum KM, Sumnu MM, Hincal AA (eds) Advances in chitin science X, pp 453–459
Dzung NA, Khanh VTP, Dzung TT (2011) Research on impact of chitosan oligomers on biophysical characteristics, growth, development and drought resistance of coffee. Carbohydr Polym 84:751–755
El-Hassni M, El-Hadrami A, Daayf F, Chérif M, Ait-Barka E, El-Hadrami I (2004) Chitosan, antifungal product against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. albedinis and elicitor of defense reactions in date palm roots. Phytopathol Mediterr 43:195–204
Escudero N, Lopez-Moya F, Ghahremani Z, Zavala-Gonzalez EA, Alaguero-Cordovilla A et al (2017) Chitosan increases tomato root colonization by Pochonia chlamydosporia and their combination reduces root-knot nematode damage. Front Plant Sci 8:1415
Faoro F, Iriti M (2007) Callose synthesis as a tool to screen chitosan efficacy in inducing plantresistance to pathogens. Caryologia 60:121–124
Faoro F, Maffi D, Cantu D, Iriti M (2008) Chemical-induced resistance against powdery mildewin barley: the effects of chitosan and benzothiadiazole. Biocontrol 53:387–401
Farouk S, Amany AR (2012) Improving growth and yield of cowpea by foliar application of chitosan under water stress. Egypt J Biol 14(1):14–16
Farouk S, Mosa AA, Taha AA, Ibrahim Heba M, Gahmery AM (2011) Protective effect of humic acid and chitosan on radish (Raphanus sativus L. var. sativus) plants subjected to cadmium stress. J Stress Physiol Biochem 7(2):99–116
Guan YJ, Hu J, Wang X, Shao C (2009) Seed priming with chitosan improves maize germination and seedling growth in relation to physiological changes under low temperature stress. J Zhejiang Univ Sci 10(6):427–433
Guo HL, Du YG, Bai XF, Zhao XM (2003) Effects of active oxygen on suspended cotton cell culture by oligochitosan. Chin J Mar Drugs 1:11–12
Hadwiger LA (1989) Method for treating cereal crop Seed with chitosan to enhance yield, root growth, and stem Strength. U.S. Patent US4978381 A
Hadwiger LA (2013) Multiple effects of chitosan on plant systems: solid science or hype. Plant Sci 208:42–49
Hadwiger LA (2015) Anatomy of a nonhost disease resistance response of pea to Fusarium solani: PR gene elicitation via DNase, chitosan and chromatin alterations. Front Plant Sci 6:373
Hadwiger LA, Ogawa T, Kuyama H (1994) Chitosan polymer sizes effective in inducing phytoalexin accumulation and fungal suppression are verified with synthesized oligomers. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 7:531–533
He L, Gao Z, Li R (2009) Pretreatment of seed with H2O2 enhances drought tolerance of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedlings. Afr J Biotechnol 8:6151–6157
Hidangmayum A, Dwivedi P (2018) Plant responses to Trichoderma spp. and their tolerance to abiotic stresses: a review. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 7(1):758–766
Hirano S, Yamamoto T, Hayashi M, Nishida T, Inui H (1990) Chitinase activity in seeds coated with chitosan derivatives. Agric Biol Chem 54(10):2719–2720
Ibrahim EA, Ramadan WA (2015) Effect of zinc foliar spray alone and combined with humic acid or/and chitosan on growth, nutrient elements content and yield of dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) plants sown at different dates. Sci Hortic 184:101–105
Iriti M, Faoro F (2008) Abscisic acid mediates the chitosan-induced resistance in plant against viral disease. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:1106–1111
Iriti M, Faoro F (2009) Chitosan as a MAMP, searching for a PRR. Plant Signal Behav 4(1):66–68
Iriti M, Sironi M, Gomarasca S, Casazza AP, Soave C, Faoro F (2006) Cell death-mediated antiviral effect of chitosan in tabacco. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:893–900
Iriti M, Picchi V, Rossoni M, Gomarasca S, Ludwig N, Gargano M, Faoro F (2009) Chitosan antitranspirant activity is due to abscisic acid-dependent stomatal closure. Environ Exp Bot 66:493–500
Ishibashi Y, Yamagguchi H, Yuasa T, Iwaya-Inoue M, Arima S, Zheng S (2011) Hydrogen peroxidase spraying alleviates drought stress in soybean plants. J Plant Physiol 168:1562–1567
Jabeen N, Ahmad R (2013) The activity of antioxidant enzymes in response to salt stress in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) and sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) seedlings raised from seed treated with chitosan. J Sci Food Agric 93(7):1699–1705
Jiao Z, Li Y, Li J, Xu X, Li H, Lu D, Wang J (2012) Effects of exogenous chitosan on physiological characteristics of potato seedlings under drought stress and rehydration. Potato Res 55:293–301
Joshi V, Joung JG, Fei Z, Jander G (2010) Interdependence of threonine, methionine and isoleucine metabolism in plants: accumulation and transcriptional regulation under abiotic stress. Amino Acids 39:933–947
Kamari A, Pulford ID, Hargreaves JS (2011) Binding of heavy metal contaminants onto chitosans—an evaluation for remediation of metal contaminated soil and water. J Environ Manag 92:2675–2682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.06.005
Kamari A, Pulford ID, Hargreaves JS (2012) Metal accumulation in Lolium perenne and Brassica napus as affected by application of chitosans. Int J Phytoremediation 14:894–907. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2011.636401
Karimi S, Abbaspour H, Sinaki JM, Makarian H (2012) Effects of water deficit and chitosan spraying on osmotic adjustment and soluble protein of cultivars castor bean (Ricinus communis L.). J Physiol Biochem 8:160–169
Kashyap PL, Xiang X, Heiden P (2015) Chitosan nanoparticle based delivery systems for sustainable agriculture. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.02.039
Katiyar D, Singh B, Lall AM, Haldar C (2011) Efficacy of chitooligosaccharides for the management of diabetes in alloxan induced mice: a correlative study with antihyperlipidemic and antioxidative activity. Eur J Pharmaceut Sci 44:534–543
Katiyar D, Hemantaranjan A, Singh B, Bhanu NA (2014) A future perspective in crop protection: chitosan and its oligosaccharides. Adv Plants Agric Res 1:06
Katiyar D, Hemantaranjan A, Singh B (2015) Chitosan as a promising natural compound to enhance potential physiological responses in plant: a review. Indian J Plant Physiol 20(1):1–9
Kaya M, Mujtaba M, Bulut E, Akyuz B, Zelencova L, Sofi K (2015) Fluctuation in physicochemical propertiesof chitins extracted from different body parts of honeybee. Carbohydr Polym 132:9–16
Khan WM, Prithiviraj B, Smiyh DL (2002) Effect of foliar application of chitinoligosaccharides on photosynthesis of maize and soybean. Photosynthetica 40(621–624):87
Khan W, Prithiviraj B, Smith DL (2003) Chitosan and chitin oligomers increase phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and tyrosine ammonia-lyase activities in soybean leaves. J Plant Physiol 160:859–863
Khan MN, Siddiqui MH, Mohammad F, Naeem M, Khan MMA (2010) Calcium chloride and gibberellic acid protect linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) from NaCl stress by inducing antioxidative defence system and osmoprotectant accumulation. Acta Physiol Plant 32:121–132
Khokon MAR, Uraji M, Munemasa S, Okuma E, Nakamura Y, Mori IC, Murata Y (2010) Chitosan-induced stomatal closure accompanied by peroxidase-mediated reactive oxygen species production in Arabidopsis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 74:2313–2315
Kim TH, Bohmer M, Hu H, Nishimura N, Schroeder JI (2010) Guard cell signal transduction network: advances in understanding abscisic acid, CO2, and Ca2+ signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:561–591
Koers S, Guzel-Deger A, Marten I, Roelfsema MRG (2011) Barley mildew and its elicitor chitosan promote closed stomata by stimulating guard-cell S-type anion channels. Plant J 68:670–680
Kohle H, Jeblick W, Poten F, Blaschek W, Kauss H (1985) Chitosan-elicited callose synthesis in soybean cells as a Ca2+-dependent process. Plant Physiol 77:544–551
Kowalski B, Terry FJ, Herrera L, Peñalver DA (2007) Application of soluble chitosan in vitro and in the greenhouse to increase yield and seed quality of potato minitubers. Potato Res 49:167–176
Krupa-Małkiewicz M, Fornal N (2018) Application of chitosan in vitro to minimize the adverse effects of salinity in Petunia × atkinsiana D. don. J Ecol Eng 19(1):143–149
Kumar P, Singh BN, Dwivedi P (2016) Managing plant hormones to improve plant adaptability to future environmental stresses: a deeper insight into abscisic acid signaling in response to temperature and heavy metal stress. Sustaining Future Food Security in the Changing Environment [Nova Scientific Publishers, USA]
Kurita K (2006) Chitin and chitosan: functional biopolymers from marine crustaceans. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 8:203–226
Kuyyogsuy A, Deenamo N, Khompatara K, Ekchaweng K, Churngchow N (2018) Chitosan enhances resistance in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis), through the induction of abscisic acid (ABA). Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 102:67–78
Lafontaine JP, Benhamou N (1996) Chitosan treatment: an emerging strategy for enhancing resistance of greenhouse tomato plants to infection by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. radicislycopersici. Biocontrol Sci Technol 6:111–124
Lai Q, Zhi-yi B, Zhu-Jun Z, Qiong-Qiu Q, Bi-Zeng M (2007) Effects of osmotic stress on antioxidant enzymes activities in leaf discs of PSAG12-IPT modified gerbera. J Zheijang Univ Sci 8(7):458–464. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2007.B0458
Lee S, Choi H, Suh S, Doo IS, Oh KY, Choi EJ, Taylor ATS, Low PS, Lee Y (1999) Oligogalacturonic acid and chitosan reduce stomatal aperture by Inducing the evolution of reactive oxygen species from guard cells of tomato and Commelina communis. Plant Physiol 121:147–152
Leung J, Giraudat J (1998) Abscisic acid and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:199–222
Li WJ, Jiang X, Xue PH, Chen SM (2002) Inhibitory effects of chitosan on superoxide anion radicals and lipid free radicals. Chin Sci Bull 47:887–889. https://doi.org/10.1360/02tb9198
Li Y, Zhao XM, Xia XY, Luan YS, Du YG, Li FL (2008) Effects of oligochitosan on photosynthetic parameter of Brassica napus seedlings under drought stress. Acta Agron Sin 34:326–329
Li Z, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Merewitz E, Peng Y, Ma X, Yan Y (2017) Metabolic pathways regulated by chitosan contributing to drought resistance in white clover. J Proteome Res 16(8):3039–3052
Lin W, Hu X, Zhang W, Rogers WJ, Cai W (2005) Hydrogen peroxide mediates defence responses induced by chitosans of different molecular weights in rice. J Plant Physiol 162:937–944
Liu C, Liu Y, Guo K, Fan D, Li G, Zheng Y, Yu L, Yang R (2011) Effect of drought on pigments, osmotic adjustment and antioxidant enzymes in six woody plant species in karst habitats of southwestern China. Environ Exp Bot 71:174–183
Lizama-Uc G, Estrada-Mota IA, Caamal-Chan MG, Souza-Perera R, Oropeza-Salìn C, Islas-Flores I, Zuñiga-Aguillar JJ (2007) Chitosan activates a MAP-kinase pathway and modifies abundance of defence-related transcripts in calli of Cocus nucifera L. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 70:130–141
Ma L, Li Y, Yu C, Wang Y, Li X, Li N, Bu N (2012) Alleviation of exogenous oligochitosan on wheat seedlings growth under salt stress. Protoplasma 249(2):393–399
Ma Z, Yang L, Yan H, Kennedy JF, Meng X (2013) Chitosan and oligochitosanenhance the resistance of peach fruit to brown rot. Carbohydr Polym 94:272–277
Mahdavi B (2013) Seed germination and growth responses of Isabgol (Plantago ovata Forsk) to chitosan and salinity. Int J Agric Crop Sci 5:1084–1088
Mahdavi B, Rahimi A (2013) Seed priming with chitosan improves the germination and growth performance of ajowan (Carum copticum) under salt stress. EurAsian J BioSci 7:69–76. https://doi.org/10.5053/ejobios.2013.7.0.9
Mahdavi B, Sanavy SAMM, Aghaalikhani M, Sharifi M, Dolatabadian A (2011) Chitosan improves osmotic potential tolerance in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) seedlings. J Crop Improv 4:728–741
Malekpoor F, Pirbalouti G, Salimi A (2016) Effect of foliar application of chitosan on morphological and physiological characteristics of basil under reduced irrigation. Res Crops 17(2):354–359. https://doi.org/10.5958/2348-7542.2016.00060.7
Malerba M, Cerana R (2015) Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species indefense/stress responses activated by chitosan in sycamore cultured cells. Int J Mol Sci 16:3019–3034
Martínez G, Reyes G, Falcón R, Núñez V (2015) Effect of seed treatment with chitosan on the growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings cv. INCA LP-5 in saline medium. Cultivos Tropicales 36(1):143–150
Matysik J, Bhalu BA, Mohanty P, Bohrweg N (2002) Molecular mechanisms of quenching of reactive oxygen species by proline under stress in plants. Curr Sci 82:525–532
McKersie BD, Lesheim Y (2013) Stress and stress coping in cultivated plants. Springer, Berlin
Mejía-Teniente L, Duran-Flores FD, Chapa-Oliver AM, Torres-Pacheco I, Cruz-Hernández A, González-Chavira MM, Ocampo-Velázquez RV, Guevara-González RG (2013) Oxidative and molecular responses in Capsicum annuum L. after hydrogen peroxide, salicylic acid and chitosan foliar applications. Int J Mol Sci 14:10178–10196
Meloni DA, Oliva MA, Martinez CA, Cambraia J (2003) Photosynthesis and activity of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and glutathione reductase in cotton under salt stress. Environ Exp Bot 49:69–76
Miya A, Albert P, Shinya T, Desaki Y, Ichimura K, Shirasu K, Narusaka Y, Kawakami N, Kaku H, Shibuya N (2007) CERK1, a LysM receptor kinase, is essential for chitin elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19613–19618
Muriefah SS (2013) Effect of chitosan on common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) plants grown under water stress conditions. Int Res J Agric Sci Soil Sci 3:192–199
Nazarli A, Faraji F, Zardashti MR (2011) Effect of drought stress and polymer on osmotic adjustment and photosynthetic pigments of sunflower. Cercetări Agronomice în Moldova 44(1):35–42
O’Herlihy EA, Duffy EM, Cassells AC (2003) The effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and chitosan sprays on yield and late blight resistance in potato crops from microplants. Folia Geobot 38:201–207
Ohta K, Atarashi H, Shimatani Y, Matsumoto S, Asao T, Hosoki T (2000) Effects of chitosan with or withoutnitrogen treatments on seedling growth in Eustoma grandiflorum (Raf.) Shinn. Cv. KairyouWakamurasaki. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 69:63–65
Oliveira HC, Gomes BC, Pelegrino MT, Seabra AB (2016) Nitric oxide-releasing chitosan nanoparticles alleviate the effects of salt stress in maize plants. Nitric Oxide 61:10–19
Paleg LG, Aspinall D (1981) The physiology and biochemistry of drought resistance in plants. Academic Press, New York
Pearce RB, Ride JP (1982) Chitin and related compounds as elicitors of the lignification response in wounded wheat leaves. Physiol Plant Pathol 20:119–123
Petutschnig EK, Jones AME, Serazetdinova L, Lipka U, Lipka V (2010) The Lysin Motif Receptor-like Kinase (LysM-RLK) CERK1 is a major chitin-binding protein in Arabidopsis thaliana and subject to chitin-induced phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 285:28902–28911
Phothi R, Theerakarunwong CD (2017) Effect of chitosan on physiology, photosynthesis and biomass of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under elevated ozone. Aust J Crop Sci 11:624–630
Pichyangkura R, Chadchawan S (2015) Biostimulant activity of chitosan in horticulture. Sci Hort 196:49–65
Pirbalouti AG, Malekpoor F, Salimi A, Golparvar A (2017) Exogenous application of chitosan on biochemical and physiological characteristics, phenolic content and antioxidant activity of two species of basil (Ocimum ciliatum and Ocimum basilicum) under reduced irrigation. Sci Hortic 217:114–122
Pongprayoon W, Roytrakul S, Pichayangkura R, Chadchawan S (2013) The role of hydrogen peroxide in chitosan-induced resistance to osmotic stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Growth Regul 70:159–173
Possingham JV (1980) Plastid replication and development in the life cycle of higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 31:113–129
Povero G, Loreti E, Pucciariello C, Santaniello A, Di Tommaso D, Di Tommaso G, Kapetis D, Zolezzi F, Piaggesi A, Perata P (2011) Transcript profiling of chitosan-treated Arabidopsis seedings. J Plant Res 124:619–629
Prashanth HKV, Dharmesh SM, Rao KS, Tharanathan RN (2007) Free radical-induced chitosan depolymerized products protect calf thymus DNA from oxidative damage. Carbohydr Res 342:190–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2006.11.010
Raho N, Ramirez L, Lanteri ML, Gonorazky G, Lamattina L, Ten Have A, Laxalt AM (2011) Phosphatidic acid production in chitosan-elicited tomato cells, via both phospholipase D and phospholipase C/diacylglycerol kinase, requires nitric oxide. J Plant Physiol 168(6):534–539
Rakwal R, Tamogami S, Agrawal GK, Iwahashi H (2002) Octadecanoid signaling component “burst” in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedling leaves upon wounding by cut and treatment with fungal elicitor chitosan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 295(5):1041–1045
Ray SR, Bhuiyan MJH, Hossain MA, Hasan AK, Sharmin S (2016) Chitosan ameliorates growth and biochemical attributes in mungbean varieties under saline condition. Res Agric Livest Fish 3(1):45–51
Reddy MP, Vora AB (1986) Salinity induced changes in pigment composition and chlorophyllase activity of wheat. Indian J Plant Physiol 29(4):331–334
Rinaudo M (2006) Chitin and chitosan: properties and application. Prog Polym Sci 31(7):603–632
Rolland F, Baenagonzalez E, Sheen J (2006) Sugar sensing and signaling in plants: conserved and novel mechanisms. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:675–709
Romanazzi G, Nigro F, Ippolito A, Di Venere D, Salerno M (2002) Effects of pre- and post-harvest chitosan treatments to control storage grey mold of table grapes. J Food Sci 67:1862–1867
Rouhi V, Samson R, Lemeur R, Van Damme P (2007) Photosynthetic gas-exchange characteristics in three different almond species during drought stress and subsequent recovery. Environ Exp Bot 59(2):117–129
Sathiyabama M, Akila G, Einstein Charles R (2014) Chitosan-induced defence responses in tomatoplants against early blight disease caused by Alternaria solani (Ellis and Martin) Sorauer. Arch Phytopathol Plant Prot 47:1777–1787
Seabra AB, Rai M, Durán N (2014) Nano carriers for nitric oxide delivery and its potential applications in plant physiological process: a mini review. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 23:1–10
Shamov M, Bratskaya SY, Avramenko V (2002) Interaction of carboxylic acids with chitosan: effect of pK and hydrocarbon chain length. J Colloid Interface Sci 249:316–321
Sharif R, Mujtaba M, Ur Rahman M, Shalmani A, Ahmad H, Anwar T, Tianchan D, Wang X (2018) The multifunctional role of chitosan in horticultural crops: a review. Molecules 23(4):872
Sheikha SA, Al-Malki FM (2011) Growth and chlorophyll responses of bean plants to chitosan applications. Eur J Sci Res 50(1):124–134
Singh BN, Dwivedi P (2016) Sugar, amino acids and nitrate as nitrogenous source of fertilization influence growth of Xanthomonasoryzae pv. oryzae and Aspergillus species in hypersensitive response development of tobacco crop. Int J Plant Reprod Biol 8:88–93
Singh BN, Dwivedi P, Sarma BK, Singh GS, Singh HB (2018) Trichoderma asperellum T42 reprograms tobacco for enhanced nitrogen utilization efficiency and plant growth when fed with N nutrients. Front Plant Sci 9:163. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00163
Srivastava N, Gonugunta VK, Puli MR, Raghavendra AS (2009) Nitric oxide production occurs downstream of reactive oxygen species in guard cells during stomatal closure induced by chitosan in abaxial epidermis of Pisum sativum. Planta 229(4):757–765
Sun T, Xie WM, Xu PX (2004) Superoxide anion scavenging activity of graft chitosan derivatives. Carbohydr Polym 58:379–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2004.06.042
Sun T, Yao Q, Zhou D, Mao F (2008) Antioxidant activity of N-carboxymethyl chitosan oligosaccharides. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:5774–5776
Vasconcelos MW (2014) Chitosan and chitooligosaccharide utilization in phytoremediation and biofortification programs: current knowledge and future perspectives. Front Plant Sci 5:616
Vasiukova NI, Zinoveva SV, Iiinskaia LI, Perekhod EA, Chalenko GI et al (2001) Modulation of plant resistance to diseases by water-soluble chitosan. Prikladnaia Biokhimiia Mikrobiologiia 37(1):115–122
Wang W, Li S, Zhao X, Du Y, Lin B (2008) Oligochitosan induces cell death and hydrogen peroxide accumulation in tobacco suspension cells. Pestic Biochem Physiol 90:106–113
Xie WM, Xu PX, Liu Q (2001) Antioxidant activity of water-soluble chitosan derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 11:1699–1701. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-894X(01)002852
Xu QJ, Nian YG, Jin XC, Yan CZ, Liu J, Jiang GM (2007) Effects of chitosan on growth of an aquatic plant (Hydrilla verticillata) in polluted waters with different chemical oxygen demands. J Environ Sci 19:217–222
Yahyaabadi HM, Asgharipour MR, Basiri M (2016) Role of chitosan in improving salinity resistance through some morphological and physiological characteristics in fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). J Sci Technol Greenhouse Cult 7(25):165–174
Yang F, Hu J, Li J, Wu X, Qian Y (2009) Chitosan enhances leaf membrane stability and antioxidant enzyme activities in apple seedlings under drought stress. Plant Growth Regul 58:131–136
Yin XQ, Lin Q, Zhang Q, Yang LC (2002) O2- scavenging activity of chitosan and its metal complexes. Chin J Appl Chem 19:325–328
Yin H, Li S, Zhao X, Du Y, Ma X (2006) cDNA microarray analysis of gene expression in Brassica napus treated with oligochitosan elicitor. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:910–916
Yin H, Bai XF, Du YG (2008) The primary study of oligochitosan inducing resistance to Sclerotinia scleraotiorum on B. napus. J Biotechnol 136:600–601
Zeng D, Luo X (2012) Physiological effects of chitosan coating on wheat growth and activities of protective enzyme with drought tolerance. Open J Soil Sci 2:282–288
Zhang XK, Tang ZL, Zhan L et al (2002) Influence of chitosan on induction rapeseed resistance. Agric Sci China 35:287–290
Zong H, Li K, Liu S, Song L, Xing R, Chen X, Li P (2017a) Improvement in cadmium tolerance of edible rape (Brassica rapa L.) with exogenous application of chitooligosaccharide. Chemosphere 181:92–100
Zong H, Liu S, Xing R, Chen X, Li P (2017b) Protective effect of chitosan on photosynthesis and antioxidative defense system in edible rape (Brassica rapa L.) in the presence of cadmium. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 138:271–278
Zuppini A, Baldan B, Millioni R, Favaron F, Navazio L, Mariani P (2003) Chitosan induces Ca2+ mediated programmed cell death in soybean cells. New Phytol 161:557–568
Acknowledgements
We thank all the researchers working on chitosan application in plant science for improving our understanding of this novel bio-polymer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hidangmayum, A., Dwivedi, P., Katiyar, D. et al. Application of chitosan on plant responses with special reference to abiotic stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 25, 313–326 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-018-0633-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-018-0633-1