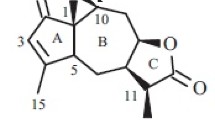
One novel sesquiterpene lactone, sonchifoliactone A1 (1), along with one known compound, sonchifoliactone A (2), were isolated from the water extract of the whole plant of Ixeris sonchifolia Hance. The structures of these compounds were elucidated through spectroscopic techniques including HR-MS and 2D NMR.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Ixeris sonchifolia Hance is a bitter, perennial herb known as kudiezi or mantianxing that belongs to the genus Ixeris of the Cichorieae tribe of the Asteraceae. It is widely distributed and cultivated in northeastern areas of China, Japan, and Korea [1]. In Chinese folklore, it has been used to treat cardiovascular diseases. Previous phytochemical investigations on plants of the genus Ixeris showed that the active principles were mainly flavonoids, sesquiterpene lactones, triterpenoid saponins [2–6].
Isolation studies on the water extract of the whole plant of Ixeris sonchifolia Hance resulted in the isolation of one novel sesquiterpene lactone, named sonchifoliactone A1 (1), along with one known sesquiterpene lactone, named sonchifoliactone A (2) [7].

Compound 1 was obtained as a white amorphous powder. Its molecular formula was determined as C19H23NO5 at m/z 344.1500 (calcd 344.1492) [M – H]– by HR-ESI-MS. All proton and carbon signals of compound 1 were completely assigned with the aid of two-dimensional NMR experiments such as COSY, DEPT, HMQC, and HMBC (Fig. 1). All proton and carbon signals of compound 1 were quite similar to those of compound 2 (Table 1). However, the proton and carbon signals assignable to 13-exomethyl of compound 2 were changed in the 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra of compound 2. Instead, several new proton and carbon signals were found assignable to an N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (Table 1). These results implied that an N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone was added to 13-exomethyl of 2 to yield compound 1. This was supported by the HMBC correlations of H-13α(δ 3.56) with C-12 carbonyl carbon (δ 176.5) and also by the correlation between H-13α with C-2′ (δ 175.2) and C-5′ (δ 48.0) of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone. Their stereochemistry was considered to be H-5α, H-6β, since the naturally occurring guaianolides have α-orientation at H-7 [8]. The configuration of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone is α, as judged from the coupling constant (J = 15.9 Hz) between H-7 and H-11 [9]. From these spectroscopic data, compound 1 was tentatively named sonchifoliactone A1.
Experimental
General Experimental Procedures. IR spectra were determined on an IFS 55 infrared spectrophotometer with KBr disks. The 1H and 13C NMR data were recorded on a Bruker Biospin NMR spectrometer with TMS as the internal standard. Mass spectra were obtained on a LTQ-Orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometer. Column chromatography was performed on silica gel (200–300 mesh; Qingdao Haiyang Chemicals) and Sephadex LH-20 (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany).
Plant Material. The whole plants of I. sonchifolia were collected from Haicheng City, Liaoning Province of China in September 2013. It was identified by Prof. Jian-Qiu Lu, Center of Scientific Experiment, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine. A voucher specimen (No. 20130901) was deposited in the same department.
Extraction and Isolation. The whole plants of I. sonchifolia (10 kg) were ground and extracted with water (3 × 60 L) for 1 h each time, and then the filtrate extracts were combined and loaded on a glass column (10 × 1500 cm) containing 3000 g D101 macroporous resin. First, water was used to remove the unabsorbed substances until the eluted solution became nearly colorless, and then different concentrations of aqueous ethanol (10%, 30%, 50%, and 95%) were used to elute the column. All of the fraction were concentrated under reduced pressure to give a black residue. The fraction eluted with 95% aqueous ethanol was subject to silica gel column chromatography using CH2Cl2–MeOH (100:1–0:1, v/v) as eluent to obtain six fractions (Fr. E1–E6). Fraction E3 was purified by Sephadex LH-20 using CH2Cl2–MeOH (1:1, v/v) repeatedly to yield compound 2. Compound 1 was obtained from Fr. E4 using Sephadex LH-20 eluting with CH2Cl2–MeOH (1:1, v/v).
Sonchifoliactone A1 (1). White amorphous powder. UV spectrum (MeOH, λmax, nm): 274. IR (KBr, ν, cm–1): 3446, 2924, 2853, 1669, 1663, 1653, 1635, 1457, 1400. HR-ESI-MS m/z 344.1500 [M – H]– (calcd for C19H22NO5, 344.1492). For 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1.
Sonchifoliactone A (2). White needle crystals. UV spectrum (MeOH, λmax, nm): 276. IR (KBr, ν, cm–1): 3473, 2975, 2926, 2875, 1766, 1672, 1623, 1216, 1185, 989. HR-ESI-MS m/z 261.1133 [M – H]– (calcd for C15H17O4, 261.1121). For 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1.
References
Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Encyclopedia of Chinese Materia Medica, Vol. 2, Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2006, 1783 pp.
J. Y. Ma, Z. T. Wang, L. S. Xu, G. J. Xu, and Q. X. Wang, J. Chin. Pharm. Univ., 29, 94 (1998).
X. Z. Feng, S. X. Xu, W. Li, and Y. Sha, Chin. J. Med. Chem., 10, 143 (2000).
N. Zhang, A. L. Lv, and Z. Zheng, J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res., 10, 211 (2008).
W. Z. Zhang, X. L. Li, L. G. Shi, J. L. Wang, M. Zhao, D. F. Zhao, and S. J. Zhang, J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res., 10, 1087 (2008).
Y. C. Zhang, L. Zhou, and K. Y. Ng, J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res., 11, 294 (2009).
A. N. D. Gutierrez, E. E. Sigstad, C. A. Catalan, A. B. Gutierrez, and W. Herz, Phytochemistry, 29, 1219 (1990).
K. Nishimura, T. Miyase, A. Ueno, T. Noro, M. Kuroyanagi, and S. Fukushima, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 34, 2518 (1986).
F. Bohlmann and P. Singh, Phytochemistry, 21, 2119 (1982).
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Basic Research and Development Program of China (973 Program, No. 2012CB518406).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 2, March–April, 2016, pp. 206–207.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, W., Zhang, J., Li, Y. et al. A Novel Sesquiterpene Lactone from Ixeris sonchifolia . Chem Nat Compd 52, 234–236 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-016-1603-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-016-1603-x