Abstract
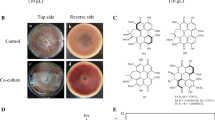
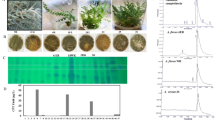
Fermentation technology using endophytes is considered a potential alternative approach for producing pharmaceutical compounds like podophyllotoxin (PTOX). In this study, fungus TQN5T (VCCM 44284) was selected from endophytic fungi isolated from Dysosma versipellis in Vietnam for PTOX production through TLC. The presence of PTOX in TQN5T was further confirmed by HPLC. Molecular identification indicated TQN5T as Fusarium proliferatum with 99.43% identity. This result was asserted by morphological characteristics such as white cottony, filamentous colony, layer and branched mycelium, and clear hyphae septa. Cytotoxic assay indicated both biomass extract and culture filtrate of TQN5T presented strong cytotoxicity on LU-1 and HepG2 with IC50 of 0.11, 0.20, 0.041, and 0071, respectively, implying anti-cancer compounds were accumulated in the mycelium and secreted into the medium. Further, the production of PTOX in TQN5T was investigated in the fermentation condition supplemented with 10 µg/ml of host plant extract or phenylalanine as elicitors. The results revealed a significantly higher amount of PTOX in the PDB + PE and PDB + PA at all studied time points in comparison with PDB (control). Especially, after 168 h of culture, PTOX content in the PDB with plant extract reached the peak with 314 µg/g DW which is 10% higher than the best yield of PTOX in previous studies, denoting F. proliferatum TQN5T as a promising PTOX producer. This is the first study on enhancing the PTOX production in endophytic fungi by supplementing phenylalanine—a precursor for PTOX biosynthesis in plants into fermented media, suggesting a common PTOX biosynthetic pathway between host plant and endophytes.
Key points
• Fusarium proliferatum TQN5T was proven for PTOX production.
• Both mycelia extract and spent broth extract of Fusarium proliferatum TQN5T presented strong cytotoxicity on cancer cell lines LU-1 and HepG2.
• The supplementation of 10 µg/ml host plant extract and phenylalanine into fermentation media of F. proliferatum TQN5T improved the yield of PTOX.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All information and data related to the study are provided in the main manuscript.
References
Andrea S, Gary S, Donald S (1993) Taxol and taxane production by Taxomyces andreanae, an endophytic fungus of Pacific yew. Science 5105(260):214–216. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8097061
Astuti P, Sudarsono S, Nisak K, Nugroho GW (2014) Endophytic fungi isolated from Coleus amboinicus Lour exhibited antimicrobial activity. Adv Pharm Bull 4:599–605. https://doi.org/10.5681/apb.2014.088
Broomhead AJ, Dewick PM (1990) Aryltetralin lignans from Linum flavum and Linum capitatum. Phytochemistry 29:3839–3844. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(90)85343-E
Bui TV, Nguyen AVT, Chu HTT, Do GH, Truong LT, Nguyen TKT, Nguyen DT (2022) A new 2, 3-dioxygenated flavanone and other constituents from Dysosma difformis. Rec Nat Prod 1:84–91. https://doi.org/10.25135/rnp.256.21.03.2017
Carvalho R, Corrêa G, Augusto S, Thatiane R, Mota R, Lúcio J (2014) Endophytic fungi: expanding the arsenal of industrial enzyme producers. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 1467–1478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1496-2
Changxing L, Galani S, Hassan F, Rashid Z, Naveed M (2020) Biotechnological approaches to the production of plant-derived promising anticancer agents: an update and overview. Biomed Pharmacother 132:110918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110918
Chen JY, Tang YA, Li WS, Chiou YC, Shieh JM, Wang YC (2013) A synthetic podophyllotoxin derivative exerts anti-cancer effects by inducing mitotic arrest and pro-apoptotic ER stress in lung cancer preclinical models. PLoS One 8:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0062082
Cheng Z, Xu W, Wang Y, Bai S, Liu L, Luo Z (2019) Two new meroterpenoids and two new monoterpenoids from the deep sea-derived fungus Penicillium sp. YPGA11. Fitoterapia 133:120–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2018.12.022
Cortese F, Bhattacharyya B, Wolff J (1977) Podophyllotoxin as a probe for the colchicine site of tubulin. J Biol Chem 252:1134–1140. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(17)40631-4
Dame ZT, Silima B, Gryzenhout M (2015) Bioactive compounds from the endophytic fungus Fusarium proliferatum. Nat Prod Res 30:1301–1304. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2015.1053089
El-elimat T, Raja HA, Graf TN, Faeth SH, Cech NB, Oberlies NH (2014) Flavonolignans from Aspergillus iizukae, a fungal endophyte of milk thistle (Silybum marianum). J Nat Prod 77:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1021/np400955q
Fan H, Xuan J, Zhang K, Jiang J (2018) Analytical methods anticancer component identification from the extract of Dysosma versipellis and Glycyrrhiza uralensis based on support vector regression and mean impact value. Anal Methods 10:371–380. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7AY02465G
Fan HY, Zhu ZL, Xian HC, Wang HF, Chen BJ, Tang YJ, Tang YL, Liang XH (2021) Insight into the molecular mechanism of podophyllotoxin derivatives as anticancer drugs. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.709075
Gakuubi MM, Munusamy M, Liang ZX, Ng SB (2021) Fungal endophytes: a promising frontier for discovery of novel bioactive compounds. J Fungi 7:786–810. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7100786
Gupta S, Chaturvedi P, Kulkarni MG, Van Staden J (2020) A critical review on exploiting the pharmaceutical potential of plant endophytic fungi. Biotechnol Adv 39:107462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107462
Hammonds TR, Denyer SP, Jackson DE, Irving WL (1996) Studies to show that with podophyllotoxin the early replicative stages of herpes simplex virus type 1 depend upon functional cytoplasmic microtubules. J Med Microbiol 45:167–172. https://doi.org/10.1099/00222615-45-3-167
Hu LL, Liao BY, Wei JX, Ling YL, Wei YX, Liu ZL, Luo XQ, Wang JL (2020) Podophyllotoxin exposure causes spindle defects and DNA damage-induced apoptosis in mouse fertilized oocytes and early embryos. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.600521
Huang JX, Zhang J, Zhang XR, Zhang K, Zhang X, He XR (2014) Mucor fragilis as a novel source of the key pharmaceutical agents podophyllotoxin and kaempferol. Pharm Biol 52:1237–1243. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2014.885061
Karuppaiya P (2019) Enhanced production of podophyllotoxin, kaempferol, and quercetin from callus culture of Dysosma pleiantha (Hance) Woodson: an endangered medicinal plant. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 67:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1810
Karuppaiya P, Sheng H (2017) Therapeutic values, chemical constituents and toxicity of Taiwanese Dysosma pleiantha – a review. Toxicol Lett 236:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.05.004
Kašparováa M, Martina J, Tůmováa L, Spilkováa J (2017) Production of podophyllotoxin by plant tissue cultures of Juniperus virginiana. Nat Prod Commun 12:14–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X1701200129
Klich MA (2002) Identification of common Aspergillus species. Centraal bureau voor Schim, Utrecht
Kour A, Shawl AS, Rehman S, Sultan P, Qazi PH, Suden P, Khajuria RK, Verma V (2008) Isolation and identification of an endophytic strain of Fusarium oxysporum producing podophyllotoxin from Juniperus recurva. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1115–1121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-007-9582-5
Kusari S, Spiteller M (2011) Are we ready for industrial production of bioactive plant secondary metabolites utilizing endophytes? Nat Prod Rep 28:1203–1207. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1np00030f
Kusari S, Lamshöft M, Spiteller M (2009) Aspergillus fumigatus Fresenius, an endophytic fungus from Juniperus communis L. Horstmann as a novel source of the anticancer pro-drug deoxypodophyllotoxin. J Appl Microbiol 107:1019–1030. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04285.x
Kusari S, Singh S, Jayabaskaran C (2014) Biotechnological potential of plant-associated endophytic fungi: hope versus hype. Trends Biotechnol 32:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.03.009
Li YC, Tao WY, Cheng L (2009) Paclitaxel production using co-culture of Taxus suspension cells and paclitaxel-producing endophytic fungi in a co-bioreactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:233–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-1856-4
Li M, Yu R, Bai X, Wang H, Zhang H (2020) Fusarium: a treasure trove of bioactive secondary metabolites. Nat Prod Rep 37:1568–1588. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0np00038h
Liang Z, Zhang J, Zhang X, Li J, Zhang X, Zhao C (2016) Endophytic fungus from Sinopodophyllum emodi (Wall.) Ying that produces podophyllotoxin. J Chromatogr Sci 54:175–178. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmv124
Luo J, Kong W, Yang M (2014) HJC, a new arylnaphthalene lignan isolated from Justicia procumbens, causes apoptosis and caspase activation in K562 leukemia cells. J Pharmacol Sci 125:355–363. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.13211FP
Lv M, Xu H (2011) Recent advances in semisynthesis, biosynthesis, biological activities, mode of action, and structure-activity relationship of podophyllotoxins: an update (2008–2010). Med Chem 2:901–909. https://doi.org/10.2174/138955711796575461
Marques JV, Kim K, Lee C, Costa MA, May GD, Crow JA, Davin LB, Lewis NG (2013) Next generation sequencing in predicting gene function in podophyllotoxin biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 288:466–479. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.400689
Mishra S, Sahu PK, Agarwal V, Singh N (2021) Exploiting endophytic microbes as micro-factories for plant secondary metabolite production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:6579–6596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11527-0
Mohammad N (2012) Fusarium solani, P1, a new endophytic podophyllotoxin-producing fungus from roots of Podophyllum hexandrum. African J Microbiol Res 6:2493–2499. https://doi.org/10.5897/ajmr11.1596
Moradi MR, Hassanian SM, Ghobadi N, Ferns GA, Karimi A, Jazayeri MH, Nasiri M, Avan A, Khazaei M (2018) Targeting the death receptor signaling pathway as a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of colorectal cancer. J Cell Physiol 233:6538–6549. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26640
Nguyen DL (1982) Fungi. Science and Engineering, Hanoi
Oh HN, Kwak AW, Lee MH, Kim E, Yoon G, Cho SS, Liu K, Chae JI, Shim JH (2021) Targeted inhibition of c-MET by podophyllotoxin promotes caspase-dependent apoptosis and suppresses cell growth in gefitinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Phytomedicine 80:153355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153355
Pham NK, Pham TH, Nguyen QN, Floden A, Ninh TP, Tran TVT, Phan LK (2020) Characterisation of Dysosma tonkinense (Gagnep.) M. Hiroe (Berberidaceae) based on morphological characteristics and ITS sequences. Nord J Bot 38:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/njb.02537
Pu Y, Jin P, Liu L, Pu Q, Wu F (2021) Dysosma versipellis extract inhibits esophageal cancer progression through the Wnt signaling pathway. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med 2021:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/1221899
Puri SC, Nazir A, Chawla R, Arora R, Riyazulhasan S, Amna T, Ahmed B, Verma V, Singh S, Sagar R, Sharma A, Kumar R, Sharma RK, Qazi GN (2006) The endophytic fungus Trametes hirsuta as a novel alternative source of podophyllotoxin and related aryl tetralin lignans. J Biotechnol 122:494–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.10.015
Rai N, KumariKeshri P, Verma A, Kamble SC, Mishra P, Barik S, Kumar SS, Gautam V (2021) Plant associated fungal endophytes as a source of natural bioactive compounds. Mycology 12:139–159. https://doi.org/10.1080/21501203.2020.1870579
Saha P, Talukdar AD, Choudhury MD, Nath D (2019) Bioprospecting for fungal-endophyte-derived natural products for drug discovery. In: Singh B (eds) Advances in endophytic fungal research. Fungal biology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03589-1_3
Sahu PK, Mishra S (2021) Effect of hybridization on endophytes: the endo-microbiome dynamics. Symbiosis 84:369–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-021-00760-w
Sang CY, Xu XH, Qin WW, Liu JF, Hui L, Chen SW (2013) DPMA, a deoxypodophyllotoxin derivative, induces apoptosis and anti-angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Bioorganic Med Chem Lett 23:6650–6655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.10.048
Shah Z, Gohar UF, Jamshed I, Mushtaq A, Mukhtar H, Zia UHM, Toma SI, Manea R, Moga M, Popovici B (2021) Podophyllotoxin: history, recent advances and future prospects. Biomolecules 11:1–27. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040603
Sharma H, Rai AK, Dahiya D, Chettri R, Singh P (2021) Exploring endophytes for in vitro synthesis of bioactive compounds similar to metabolites produced in vivo by host plants. 7:175–199. https://doi.org/10.3934/microbiol.2021012
Skehan P, Storeng R, Scudiero D, Monks A, McMahon J, Vistica D, Warren JT, Bokesch H, Kenney S, Boyd MR (1990) New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J Natl Cancer Inst 82:1107–1112. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/82.13.1107
Soliman SSM, Mosa KA, El-keblawy AA, Husseiny MI (2017) Exogenous and endogenous increase in fungal GGPP increased fungal Taxol production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:7523–7533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8509-9
Sudo K, Konno K, Shigeta S, Yokota T (1998) Inhibitory effects of podophyllotoxin derivatives on herpes simplex virus replication. Antivir Chem Chemother 9:263–267. https://doi.org/10.1177/095632029800900307
Tan RX, Zou WX (2001) Endophytes: a rich source of functional metabolites. Nat Prod Rep 18:448–459. https://doi.org/10.1039/b100918o
Tan X, Zhou Y, Zhou X, Xia X, Wei Y, He L, Tang H, Yu L (2018) Diversity and bioactive potential of culturable fungal endophytes of Dysosma versipellis; a rare medicinal plant endemic to China. Sci Rep 8:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24313-2
Toghueo K (2020) Bioprospecting endophytic fungi from Fusarium genus as sources of bioactive metabolites. Mycology 11:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/21501203.2019.1645053
Tran HT, Nguyen GT, Nguyen HHT, Tran HT, Tran QH, Tran QH, Ninh NT, Do PT, Chu HH, Pham NB (2022) Isolation and cytotoxic potency of endophytic fungi associated with Dysosma difformis, a study for the novel resources of podophyllotoxin. Mycobiology 50:389–398. https://doi.org/10.1080/12298093.2022.2126166
Uzma F, Mohan CD, Hashem A, Konappa NM, Salomone S (2018) Endophytic fungi-alternative sources of cytotoxic compounds: a review. Front Pharmacol 9:1–37. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00309
Venugopalan A, Potunuru UR, Dixit M, Srivastava S (2016) Reprint of: Effect of fermentation parameters, elicitors and precursors on camptothecin production from the endophyte Fusarium solani. Bioresour Technol 213:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.023
Wang Y, Sun H, Xiao Z, Zhang D, Bao X, Wei N (2017) XWL-1-48 exerts antitumor activity via targeting topoisomerase II and enhancing degradation of Mdm2 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10577-7
Waskiewicz A, Golinski P, Karolewski Z, Irzykowska L, Bocianowski J, Kostecki M, Weber Z (2010) Formation of fumonisins and other secondary metabolites by Fusarium oxysporum and F. proliferatum: a comparative study. Food Addit Contam 27:608–615. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440040903551947
Xianzhi Y, Shiping G, Lingqi Z, Hua S (2003) Select of producing podophyllotoxin endophytic fungi from podophyllin plant. Nat Prod Res Dev 15:419–422. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2003.05.012
Xiong Z, Yang Y, Zhao N, Wang Y (2013) Diversity of endophytic fungi and screening of fungal paclitaxel producer from Anglojap yew. Taxus x Media BMC Microbiol 13:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-13-71
Yang C, Xie Q, Zeng X, Tao N, Xu Y, Chen Y, Wang J, Zhang L (2019) Novel hybrids of podophyllotoxin and formononetin inhibit the growth, migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. Bioorg Chem 85:445–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.02.019
Yu PZ, Wang LP, Chen ZN (1991) A new podophyllotoxin-type lignan from Dysosma versipellls var Tomentosa. J Nat Prod 54:1422–1424. https://doi.org/10.1021/np50077a034
Zhang X, Rakesh KP, Shantharam CS, Manukumar HM, Asiri AM, Marwani HM, Qin HL (2018) Podophyllotoxin derivatives as an excellent anticancer aspirant for future chemotherapy: a key current imminent needs. Bioorganic Med Chem 26:340–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2017.11.026
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Thao Thi Do for the cytotoxic assay. We also thank to Dr. Hieu Dang Hoang for his contribution to edit manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by funding from the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST), under Grant: TDCN.01/ 20-22.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NBP designed the study. HTHN, HTT, HTT, and ANH performed the experiments. QHT analyzed data. GTN analyzed data and wrote manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All experiments are not related to human participants or animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Giang Thu Nguyen and Ha Thi Hong Nguyen have the equal contributions to this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, G.T., Nguyen, H.T.H., Tran, H.T. et al. Enhanced podophyllotoxin production of endophyte Fusarium proliferatum TQN5T by host extract and phenylalanine. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 5367–5378 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12659-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12659-1