Abstract
Purpose of Review
Preeclampsia complicates 5–10% of all pregnancies and is a leading cause of maternal and perinatal mortality and morbidity. The placenta plays a pivotal role in determining pregnancy outcome by supplying the fetus with oxygen and nutrients and by synthesizing hormones. Placental function is highly dependent on energy supplied by mitochondria. It is well-known that preeclampsia is originated from placental dysfunction, although the etiology of it remains elusive.
Recent Findings
During the last three decades, substantial evidence suggests that mitochondrial abnormality is a major contributor to placental dysfunction. In addition, mitochondrial damage caused by circulating bioactive factors released from the placenta may cause endothelial dysfunction and subsequent elevation in maternal blood pressure.
Summary
In this review, we summarize the current knowledge of mitochondrial abnormality in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia and discuss therapeutic approaches targeting mitochondria for treatment of preeclampsia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The mitochondrion is a double-membrane bound cellular organelle in eukaryotic cells. The widely accepted endosymbiotic theory proposes that the mitochondrion is originated from alphaproteobacterium through a process termed endosymbiosis [1]. Although being endosymbiotic origin, the mitochondrion has been evolved into an indispensable organelle for cellular functions. Producing ATP is the preeminent function of mitochondria. However, mitochondria are also involved in various other cellular processes, including biosynthesis of DNAs, proteins, and fatty acids, Ca2+ homeostasis, redox homeostasis, apoptosis, among others [2]. Mitochondria are exquisitely sensitive to external (e.g., hypoxia) and internal stress (e.g., oxidative stress/endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress) and undergo adaptation or maladaptation following stress exposure [3]. Mitochondrial homeostasis is maintained through mitochondrial biogenesis, mitochondrial fission and fusion, and mitophagy to sustain energy metabolism. Not surprisingly, mitochondrial dysfunction is implicated in a variety of human diseases [4].
The placenta, a transient organ developed during pregnancy, constitutes the interface between the maternal and fetal circulation. It plays pleiotropic roles during pregnancy such as nutrient and oxygen transport, endocrine secretion, and immunological protection that are pivotal to fetal growth and maternal well-being [5]. To fulfill its functions, the placenta has a high energy demand and is a highly metabolically active organ. Glucose is the primary energy source for ATP generation in the placenta and ~ 30% of glucose taken up from the maternal blood is consumed by the placenta [6•]. Approximately 40% of total oxygen taken up from the uteroplacental circulation is used for the metabolism in the placenta [7•]. The majority of glucose and oxygen are consumed for oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria [7•, 8].
Preeclampsia is defined as new onset hypertension (≥ 140 mmHg systolic blood pressure or ≥ 90 mmHg diastolic blood pressure) after 20 weeks’ gestation with one or more of the following conditions: (1) proteinuria; (2) other maternal organ dysfunction such as acute kidney injury, liver dysfunction, neurological complications, and hematological complications; and (3) fetal growth restriction [9]. With high morbidity and mortality, preeclampsia affects 5–10% pregnancy worldwide [10]. Preeclampsia is also associated with long-term risk of cardiovascular disease in the mother [11]. Although the etiology of preeclampsia is not fully understood, placental dysfunction appears to underpin preeclampsia. It is believed that preeclampsia occurs in two stages: impaired invasion of trophoblast culminates in incomplete remodeling of spiral arteries, resulting in narrow vessels with high resistance to uteroplacental blood flow and the subsequent placental hypoperfusion triggers hypoxia or hypoxia/reperfusion which promotes the release of antiangiogenic factors and/or inflammatory cytokines into the maternal circulation, leading to systemic inflammation and endothelial dysfunction and consequent hypertension and other clinical features [12••] (Fig. 1). Preeclampsia is heterogeneous and usually exists in two phenotypes: early-onset (delivery before 34 weeks’ gestation) and late-onset (delivery after 34 weeks’ gestation). The early-onset (placental) preeclampsia arises from abnormal placentation (i.e., inadequate invasion of trophoblasts and remodeling of spiral arteries), while the late-onset (maternal) preeclampsia is suggested to stem from existing chronic systematic inflammation and frequently occurs in women with pre-gestational obesity and diabetes [12••]. The late-onset preeclampsia accounts for ≥ 80% preeclampsia cases. However, the early-onset preeclampsia is more clinically important as it is associated with fetal growth restriction and high maternal/perinatal morbidity and mortality. An early observational study identified a high incidence of preeclampsia in a family with mitochondrial dysfunction [13••]. Since this initial finding, dysregulated mitochondria in the placenta have been demonstrated in both pregnant women with preeclampsia and animal models of preeclampsia [14]. This review intends to summarize our knowledge on the roles of mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Potential therapeutic approaches targeting mitochondria for preeclampsia will also be discussed.
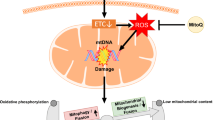
Association of mitochondrial dysfunction with preeclampsia. Preeclampsia is proposed to occur in two stages. In the first stage, incomplete spiral artery remodeling causes reduced placental perfusion. In the second stage, the resultant placental hypoxia/ischemia or hypoxia/reoxygenation induces oxidative stress which in turn boosts the release of bioactive factors, leading to endothelial dysfunction and ultimately clinical symptoms such as hypertension and proteinuria. Accumulating evidence suggests mitochondrial dysfunction plays a central role in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Placental hypoxia/ischemia-induced mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS) overproduction apparently is the major player of mitochondrial dysfunction by promoting mtDNA damage and mtDNA release into the circulation, altering mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy, and increasing apoptosis. mtROS also stabilizes HIF-1 in the placenta which then reprograms metabolism and stimulates sFlt-1 expression and release into the circulation. sFlt-1 and mtDNA along with other bioactive factors initiate systemic inflammation and endothelial dysfunction, engendering preeclamptic phenotype
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Placenta and Preeclampsia
Metabolism Reprogramming in Preeclampsia
Eukaryotic cells derive their chemical energy ATP from nutrients such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins through glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation (Fig. 2). Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol converting glucose into pyruvate in the presence of oxygen or into lactate in the absence of oxygen and produces 2 mol of ATP per mole of glucose. In contrast, the oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria theoretically generates 36 mol of ATP per mole of glucose and produce up to 95% of ATP to sustain cellular activity. This process is fulfilled by the coupling the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle (also known as Krebs cycle) in the mitochondrial matrix to the electron transport chain (ETC) embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The TCA cycle functions as the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules. Acetyl-CoA bridges glycolysis of glucose/β-oxidation of fatty acids/deamination of amino acids and the TCA cycle. Through the enzymatic reactions in the cycle, electrons are harvested to form NADH and FADH2 and are subsequently passed onto the ETC. Energy released during the shuttling of electrons across complexes I–IV is used to pump protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space and establish an electrochemical gradient across the inner membrane. Protons then flow through ATP synthase (complex V) to drive the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. Oxygen serves as the final electron acceptor at the end of ETC and reacts with protons to form water. It is estimated that ~ 90% of intracellular oxygen is consumed by oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria [15].

source of cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). Leakage of electrons at complexes I and III from the ETC leads to partial reduction of oxygen to form superoxide (O2•−). O2•− is rapidly converted to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by superoxide dismutases (SODs), which is then reduced to water by glutathione peroxidases (GPXs) and peroxiredoxins (PRXs). The production of ROS at complexes I and III are increased in hypoxic conditions
Cell bioenergetics in the placenta. Placental function depends on constant energy supply. Mitochondria act as the energy center to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell. The primary energy substrate in placental cells is glucose with some contribution from fatty acids. Under aerobic conditions, glucose is converted to acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) through glycolysis. Fatty acids can undergo β-oxidation to produce acetyl-CoA in mitochondria. Acetyl-CoA is fed to the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle) and the cycle reduce NAD+ to NADH and FAD to FADH2. High-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed onto and flow through the ETC. The energy carried by those electrons is used to pump protons (H+) from the matrix to the intermembrane space, resulting in a proton gradient. Oxygen acts as the terminal electron acceptor and reacts with protons to form water at the end of the ETC. Protons then flow back to the matrix through Complex V (the ATP synthase) and the energy from this influx is used to drive ATP synthesis. When placental hypoxia/ischemia occurs, the placenta undergoes metabolic reprogramming and glycolysis becomes the dominant pathway of bioenergetics. Intriguingly, mitochondria are the major
In the early gestation, the implantation and placental development are dependent on glycolysis to supply ATP due to low oxygen concentration at the implantation site [16]. With the establishment of the uteroplacental circulation and an increase in oxygen level in the placenta at the beginning of the second trimester [17••], the oxidative metabolism becomes the prevailing pathway to generate ATP in the placenta [7•, 8] (Fig. 2). However, aerobic glycolysis still occurs in the placenta to produce lactate which is used by the fetus as an energy source, consuming one fifth of glucose taken up from the uteroplacental circulation [18].
Apparently, mitochondrial bioenergetics in the placenta is altered in preeclampsia. ATP production is reduced in preeclamptic placentas [19, 20] and in the placenta of a mouse model induced by overexpressing sFlt-1 [21]. The preeclamptic placenta displays a hypoxic phenotype [22••]. To promote survival, mammalian cells undergo hyoxia-inducible factor (HIF)‐1‐dependent reprogramming of glucose metabolism to cope with the deficiency of oxygen (Fig. 1). Glycolysis is boosted by the HIF-1-induced upregulation of glucose transporters and glycolytic enzymes while the oxidative metabolism is suppressed by preventing the conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA through HIF-1-mediated induction of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1) which deactivates pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) [23••, 24]. In addition, HIF-1 also upregulates lactate dehydrogenase, enhancing the conversion of pyruvate to lactate. Glucose transporter 1 (GLUT-1) and key enzymes such as phosphofructokinase (PFK) and hexokinase II (HKII) are upregulated in the preeclamptic placenta [25••]. Proteomic analysis reveals that several enzymes in the TCA cycle including pyruvate dehydrogenase E1 subunit α1 (PDHA1), oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (OGDH, also known as α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (KGDH)), and malate dehydrogenase 2 (MDH2) are downregulated in preeclamptic placentas [26, 27]. Moreover, preeclampsia also suppresses the expression and/or activities of ETC complexes I–IV and ATPase in the placenta [26,27,28,29,30,31]. However, there are reports suggesting that oxidative phosphorylation in the early-onset preeclamptic placenta is reduced without altering the expression of ETC complexes [32••, 33]. Intriguingly, protein abundance of mitochondrial complexes II and III and mitochondrial respiration are increased in the late-onset preeclamptic placenta, suggesting a metabolic adaptation [32••, 34]. Fatty acid β-oxidation primarily occurs in the mitochondrial matrix. Preeclampsia decreases abundance/activity of long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (LCAD) and hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase trifunctional multienzyme complex subunits α/β (HADHA/HADGB) and fatty acid oxidation in the placenta [20, 35]. The suppression of fatty acid oxidation in preeclamptic placentas is probably mediated by oxidative stress as fatty acid oxidation is reduced by H2O2 in placental explants [36]. The metabolic reprogramming also occurs in placentas of high-altitude pregnancy, which is associated with ~ threefold increase in the incidence of preeclampsia [37•]. Similar changes have also been observed in vitro/ex vivo hypoxia- or hypoxia/reoxygenation-treated placental explants and trophoblast cell lines [38, 39••] and in placentas of hypoxia-exposed rodents [24, 40•, 41, 42]. Furthermore, hypoxia-responsive microRNA 210 (miR-210) is elevated in the preeclamptic placenta and impairs mitochondrial respiration by targeting and downregulating iron-sulfur cluster assembly enzyme (ISCU) [29]. This reprogramming is believed to reduce placental oxygen consumption and to ensure adequate oxygen to be delivered to the fetus at the expense of glucose availability [37•]. Moreover, severe preeclampsia could diminish lactate supply to the fetus. Bloxam and colleague demonstrate that glycolysis is impaired in the placenta when preeclampsia is complicated by fetal growth restriction, showing reduced pyruvate and lactate [43].
Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species and Preeclampsia
During oxidative phosphorylation, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are also produced at the ETC and are the primary source of ROS in most mammalian cells. Up to 2% of the electrons passing through the ETC leak primarily from complexes I and III and are partially reduced by oxygen to generate superoxide (O2•−) [44]. Superoxide produced at complex I is released into the matrix, while O2•− generated at complex III is discharged into both the matrix and intermembrane space. The superoxide anion is rapidly converted into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1, Cu, Zn-SOD) in the intermembrane space and SOD2 (Mn-SOD) in the matrix. H2O2 is then reduced to water by glutathione peroxidases (GPX1 and 4) and peroxiredoxin 3 (PRX3 and 5) (Fig. 2) [44]. At low levels, ROS, primarily H2O2 due to its stability and permeability across the membrane, function as signal molecules. For example, H2O2 could alter activities of enzymes and transcription factors by regulating the oxidative state of cysteine residue(s) [45]. Moreover, mitochondria function as cellular oxygen sensor. Hypoxia stimulates mitochondria to produce ROS and mitochondrial ROS (mtROS) in turn stabilize HIFs to regulate the metabolic adaptation in hypoxia [46]. However, mtROS at high levels produce irreversible damage to mitochondria and cells [47]. Compared to normal pregnancy, preeclampsia exhibits heightened oxidative stress in the placenta, evidenced by increased generation of ROS and reduced expression/activity of antioxidant enzymes [48]. Mitochondria appear to be the major source of ROS in the preeclamptic placenta [49•] (Fig. 1). The increase in mtROS in the preeclamptic placenta is derived from observations of increased lipid peroxidation in mitochondria [49•]. This notion is corroborated by direct detection of elevated mtROS in the preeclamptic placenta and in the placenta of rodent models of preeclampsia [31, 40•, 50]. Consistently, hypoxia or hypoxia/reoxygenation also increases mtROS in the placenta and trophoblast cell lines in vivo and in vitro [32••, 39••, 51, 52] and in animal studies [50, 53].
Mitochondria are also targets of mtROS, leading to impaired structure and function [26, 27, 29, 54••]. It should be noted that mtDNA is located and mtDNA-encoded proteins are synthesized in mitochondrial matrix. Thus, mtDNA is potentially subject to oxidative stress-induced mutation and protein processing could be disturbed by uncontrolled ROS. Increased mtDNA mutations in trophoblasts are observed in African American women with preeclampsia [55]. As mtDNA encodes a portion of ETC subunits, damage to mtDNA could cause defects in the ETC, leading to further increase in mtROS [56]. Moreover, placentas of early-onset preeclampsia also display elevated mitochondrial unfold protein response (UPR) [33]. Furthermore, excessive ROS also could activate mitochondrial permeability transition (mPTP), leading to necrotic and apoptotic cell death [57]. Indeed, preeclamptic placentas exhibit increased trophoblast apoptosis [58]. Notably, placentas from late-onset preeclampsia exhibit increased both ROS and antioxidant enzyme (e.g., GPX and PRDX3) activity, suggesting development of a compensatory mechanism against oxidative stress [26, 32••]. Oxidative stress could also impact various placental functions including spiral artery remodeling, hormone biosynthesis, and bioactive factor expression/release. In vitro studies demonstrate that ROS inhibit trophoblast invasion and induce trophoblast apoptosis [54••, 59, 60]. Increasing mtROS with the Complex I inhibitor rotenone reduce the expression of human placental lactogen (hPL) and insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) in BeWo cells, a human placental cell line [61]. sFlt-1 production in placental villous explants, primary cytotrophoblasts, and BeWo cells is increased by mtROS [31, 62].
Mitochondrial Dynamics and Preeclampsia
Mitochondria are dynamic organelles and constantly fuse and divide in response to various stresses [63]. Mitochondrial fusion involves outer membrane fusion mediated by Miotfusin 1 and 2 (MFN1 and MFN2) and inner membrane fusion controlled by Optic atrophy 1(OPA1) [64]. On the other hand, mitochondrial fission is driven by dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1) [64]. Whereas the fusion generates interconnected mitochondria, the fission results in mitochondrial fragments. Morphological changes of mitochondria dynamics play an important role in mitochondrial bioenergetics. For example, mitochondrial fusion increases oxidative phosphorylation and bioenergetic efficiency [65]. In addition, mitochondrial dynamics is important for mitochondrial quality control. The fusion provides complementation of mitochondrial proteins and DNA by mixing the contents of healthy and partially damaged mitochondria to maintain a population of functional mitochondria, while the fission facilitates the removal of damaged mitochondria by mitophagy [64]. There are studies demonstrating that early-onset preeclampsia promotes mitochondrial fission in the placenta. For example, the expression of OPA1 and DRP1 is reduced and enhanced, respectively, in the placenta of early-onset preeclampsia [33, 66]. In addition, Vangrieken and colleagues observe an increase in fission in the placenta of early-onset preeclampsia, showing an increase in protein abundance of dynamin-1-like protein (DNM1L), a key protein involved in mitochondrial fission and no change in pro-fusion proteins [25••]. However, Vishnyakova et al. [67••] demonstrate that MFN1/2 remains unchanged and OPA1 increases in the early-onset preeclamptic placenta. In the placenta of late-onset preeclampsia, the expression of MFN1/2 along with the long form OPA1 is found to be increased [19, 32••] on unchanged [67••]. In contrast, other studies find decreased expression of OPA1 and/or MFN1/2 and no change for DRP1 and fission 1 (FIS1) [19, 20]. These discrepancies may result from that only mRNAs are measured for pro-fusion and pro-fission related gene expression in some studies. Notably, there is usually poor correlation in general between mRNA and protein expression levels [68]. It is preferable that protein levels of these genes are measured since they are executors of mitochondrial dynamics. Interestingly, hypoxic treatment of BeWo cells increases the expression of Fis1 and DNM1L and decrease the expression of MFN1/2 [39••]. Similarly, hypoxia also reduces the expression of MFN2 in trophoblast cell line TEV-1 [19]. Moreover, increasing mtROS in BeWo cells by inhibiting complex I with rotenone decrease the expression MFN2 and OPA1 and increase the expression of DRP1 [61]. Furthermore, prenatal hypoxia in pregnant rats selectively suppresses the expression of the long form OPA1 in the placenta carrying the male fetus [42].
Mitophagy and Preeclampsia
To maintain a healthy mitochondrial pool, damaged or surplus mitochondria are sequestered by autophagosomes and subsequently transferred to lysosomes for degradation. This process is termed as mitophagy. The PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) and E3 ubiquitin ligase Parkin (PRKN) constitute the primary pathway of mitophagy [2]. Under physiological conditions, PINK1 is cleaved by proteases upon being transported into mitochondria and is subsequently released into the cytoplasm and degraded by the proteasome. When mitochondrial damage occurs, the import and cleavage of PINK1 are impaired. PINK1 is thus stabilized on the outer mitochondrial membrane and recruits Parkin from the cytosol to damaged mitochondria. Parkin is activated following PINK1-meidated phosphorylation and promotes ubiquitination, resulting in the engulfment of mitochondria by autophagosomes and degradation following lysosomal fusion. BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3 (BNIP3) also participates in mitophagy [69]. Moreover, and BNIP3-like (BNIP3L, also known as NIX) are implicated in PINK1-independent mitophagy [70]. Intriguingly, BNIP3 and BNIP3L are regulated by hypoxia and both of them are involved in hypoxia-induced mitophagy [70]. In addition, the recruit of light chain 3 (LC3) by FUN14 domain containing 1 (FUNDC1) on mitochondrial outer membrane also participates in hypoxia-mediated mitophagy [71]. The placental expression of BNIP3, BNIP3L, and PINK1 is increased in early-onset preeclampsia, suggesting increased mitophagy [25••, 27, 66] (Fig. 1). Consistently, the hypoxic treatment of BeWo cells results in an increase in the BNIP3 and BNIP3L expression [39••]. In contrast, late-onset preeclampsia is associated with reduced placental expression of BNIP3, implying attenuated mitophagy [20].
Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Preeclampsia
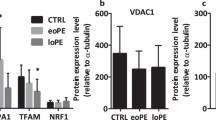
Mitochondrial biogenesis is the process to increase mitochondria numbers through the growth and division of pre-existing mitochondria. Mitochondria possess their own genome. Mammalian mtDNA exists as a circular molecular of 16.5 kb encoding 13 protein subunits of the ETC, 22 tRNAs, and 2 rRNAs. However, vast majority of mitochondrial proteins are encoded by nuclear genome, synthesized in the cytosol and imported to mitochondria. Thus, mitochondrial biogenesis requires coordinated expression of both nuclear and mitochondrial genes. Mitochondrial biogenesis involves replication of mtDNA and expression of proteins encoded by nuclear and mitochondrial DNAs, which is orchestrated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) [72]. PGC-1α is activated by AMP-dependent kinase (AMPK)-mediated phosphorylation and by Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1)-mediated deacetylation, respectively [73]. PGC-1α stimulates various transcription factors including the nuclear respiratory factors 1 and 2 (NRF1/2), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ), and estrogen-related receptor-α (ERR-α) and NRFs increase the expression of mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) [74]. TFAM determines the abundance of mtDNA by regulating packaging, stability, and replication [75]. Conflicting observations of mitochondrial biogenesis in preeclamptic placentas have been reported. Vishnyakova et al. [67••] observe elevated mitochondrial biogenesis in early-onset preeclampsia, evidenced by increased mtDNA copy number. Similarly, Holland et al. [32••] detect increased mtDNA content in late-onset preeclamptic placentas. In contrast, other groups report a reduction in mitochondrial content along with decreased PGC-1α and lower activity of citrate synthase, a biomarker of mitochondria in early-onset preeclamptic placentas [25••] and suppressed expression of PGC-1α in late-onset preeclamptic placentas [20]. Similar findings such as reduced mtDNA copy number and decreased citrate synthase activity/abundance are also obtained in vitro hypoxic treatment of villous explants and in cultured BeWo cells [39••, 76]. Circulating testosterone increases in preeclampsia [77]. In pregnant rats, elevating plasma testosterone decreases the expression of PGC-1α and NRF1 and mtDNA copy number in the placenta [78]. Nonetheless, other studies demonstrate unaltered mtDNA copy number and citrate synthase activity in early-onset/late-onset preeclamptic placentas [32••, 33, 79], which is corroborated by the observation that placental citrate synthase activity is not changed in a rat model of prenatal hypoxia [42].
Apoptosis and Preeclampsia
Mitochondria play a critical role in cell death primarily involving intrinsic apoptosis and necrosis [80]. In contrast to extrinsic apoptosis which is initiated via death receptors in the cell membrane, intrinsic apoptosis is controlled by the BCL-2 protein family in mitochondrial outer membrane. When activated by apoptotic stimuli including mtDNA damage, BCL-2-associated X protein (BAX) located in the cytosol is translocated to the outer mitochondrial membrane where it alone or together with BCL2 antagonist/killer 1 (BAK) to causes mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP) and subsequent release of cytochrome c and other apoptogenic proteins into the cytosol [81]. Cytochrome c binds to apoptotic peptidase-activating factor 1 (APAF1), forming the apoptosome which recruits and activates the initiator caspase 9. The activated caspase 9 in turn cleaves and activates executioner caspase 3 and caspase 7 leading to the cleavage of structural and regulatory proteins in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus, ultimately leading to the demise of the cell [80]. Ca2+ perturbation in mitochondria plays a critical role in cell death. Ca2+ overload could trigger the opening of mPTP in the inner mitochondrial membrane [82]. The opening of mPTP results in both ATP deprivation due to the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and mitochondrial swelling due to water flux into the mitochondrial matrix. These incidents eventually lead to cell death due to compromised bioenergetics function and structural integrity of mitochondria. Placental apoptosis is increased in preeclampsia [83] (Fig. 1). HTR-8/SVneo cells and JEG-3 cells as well as placenta explants under hypoxia or hypoxia/reoxygenation display an increase in apoptosis [52, 83]. The study by Longtine et al. [84] suggests that placental apoptosis in preeclampsia exclusively occurs in cytotrophoblasts. However, other groups demonstrate that preeclampsia promotes syncytiotrophoblast apoptosis [85, 86]. Various studies reveal increased expression of BAX and caspase 3 and reduced expression of BCL2 in both early- and late-onset preeclampsia [27, 85, 87]. Exposure of placental villous tissue explants to hypoxia-reoxygenation simulates the expression pattern of BAX and BCL2 in preeclamptic placentas [88]. Hypoxia is also found to increase the expression of BAX, caspase 9, and cleaved caspase 3 and to decrease the expression of BCL2 in cultured cytotrophoblasts and HTR-8/SVneo cells [83, 89]. In a mouse model of preeclampsia, the overexpression of HIF1α increases BAX expression and BAX/BCL2 ratio in the placenta [41]. As a result of increased apoptosis, mitochondrial swelling is frequently observed in preeclamptic placentas/trophoblasts [26, 27, 29, 33, 54••]. Interestingly, a recent study shows that late-onset preeclampsia results in reduced BAX expression and increased BCL2 expression in the placenta [32••].
Dysregulated Mitochondria and Endothelial Dysfunction in Preeclampsia
Endothelial cells play a critical role in regulating vascular tone, blood flow, and angiogenesis. Endothelial dysfunction plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia [90]. Lines of evidence suggest that bioactive factors released from the preeclamptic placentas are responsible for the maternal endothelial dysfunction, leading to clinical symptoms such as hypertension and proteinuria [91]. Here, we focus our discussion on sFlt-1 and mtDNA. The role of angiotensin II type-1 receptor autoantibody (AT1-AA) in endothelial dysfunction is also reviewed.
sFlt-1, a splice variant of the VEGF receptor lacking the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains, functions as a decoy to bind VEGF, thus reducing its bioavailability to maternal endothelial cells and causing widespread endothelial dysfunction [92••]. In preeclampsia, both sFlt-1 expression in the placenta and sFlt-1 in the circulation are increased [92••, 93] (Fig. 1). The increase occurs ~ 5 weeks prior to the onset of preeclampsia [94]. The increased circulating sFlt-1 has been detected in both early-onset and late-onset preeclampsia [95, 96]. Increased placental and circulating sFlt-1 is also demonstrated in a rat model of preeclampsia induced by reduced uteroplacental perfusion (RUPP) [97]. Heightened oxidative stress promotes sFlt-1 release from the placenta [14]. Moreover, hypoxia treatment of placental explants, primary trophoblasts and HRT-8/SVneo cells increases mtROS and sFlt-1 expression/release [31, 98, 99]. sFlt-1 contains a hypoxia response element (HRE) in its promoter region [100]. It is expected that the stabilization of HIF-1α conferred by placental hypoxia-induced mtROS promotes sFlt-1 expression and release. Elevating sFlt-1 levels in pregnant rodents through infusion of sFlt-1 or placental exosomes from preeclamptic patients or sFlt-1 overexpression induce preeclampsia-like symptoms such as hypertension, glomerular endotheliosis, and proteinuria [92••, 101, 102]. The endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia is in part conferred by sFlt-1-induced mitochondrial abnormality. The treatment of endothelial cells with sFlt-1 suppresses mitochondrial respiration, increase glycolysis, and promotes mtROS generation [103]. The impairment of endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in pregnant rats infused with sFlt-1 could be rescued by ROS scavenger Tiron [104].
During apoptosis, mtDNA could be released into the cytosol and circulation due to increased mitochondrial membrane permeability [105]. Potentially due to the bacterial origin, mtDNA with hypomethylated CpG motifs serves as a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) that is recognized by various pattern recognition receptors including Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) and activates innate immune responses [106]. For example, mtDNA released into the circulation during trauma causes systemic inflammation via TLR9 activation [107]. In addition, oxidized mtDNA during apoptosis could activate nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat and pyrin domain containing receptor 3 (NLRP3) [108]. The activation of NLRP3 triggers the cleavage of pro-interleukin (IL)-1β and pro-IL-18, which in turn trigger endothelial damage [109]. Moreover, impaired mitophagy and excessive mtROS production also lead to NLRP3 inflammasome activation [110]. Circulating mtDNA increases in both early-onset and late-onset preeclampsia [111, 112] (Fig. 1). The mtDNA in the circulation is in part released from the trophoblast decomposition [113]. The increased antiphospholipid antibodies in preeclampsia could also stimulate mtDNA release from the placenta into the circulation [114]. Intriguingly, circulating mediators (including mtDNA-triggered TLR9 activity) is increased in preeclampsia [115]. Moreover, placental exosomes containing mtDNA activates TLR9 in endothelial cells, leading to endothelial activation [114]. In pregnant rats, administration of synthetic CpG oligonucleotides leads to increased systolic blood pressure [116•]. These findings suggest that elevated circulating mtDNA in preeclampsia contributes to systemic inflammation and vascular dysfunction.
Circulating AT1-AA also increases in preeclampsia and the increase is more pronounced in early-onset than late-onset preeclampsia [117, 118]. AT1-AA binds to and activates angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptors [119]. Following injection of AT1-AA from women with pre-eclampsia, pregnant mice develops key features of preeclampsia including hypertension, glomerular endotheliosis, proteinuria, placental abnormalities, and fetal growth restriction [120•]. RUPP rats also display increased circulating AT1-AA [121]. Intriguingly, administration of AT1-AA also elevates circulating sFlt-1 in pregnant mice [122]. It appears that AT1-AA can target endothelial mitochondria to cause endothelial dysfunction. Serum from (early-onset) preeclampsia suppresses mitochondrial respiration and increases mtROS in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and the mitochondrial antioxidants MitoQ and/or MitoTempo attenuate these detrimental effects [40•, 123, 124]. Moreover, an AT1-AA inhibitor peptide reduces mtROS production in HUVECs stimulated by sera from RUPP rats and early-onset preeclampsia [124, 125]. Furthermore, MitoQ and MitoTempo lower blood pressure in RUPP rats [40•]. Together, mitochondria in endothelial cells could produce excess ROS following sFlt-1 and/or AT1-AA exposure in preeclampsia, acting as the primary mediator of oxidative stress to contribute to endothelial dysfunction.
Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Mitochondria for Preventing/Treating Preeclampsia
As discussed in previous sections, dysregulated mitochondrial function is implicated in the dysfunction of both the placenta and endothelial cells in preeclampsia. Despite being a common pregnancy complication, preeclampsia is without effective cures except delivery. Given the crucial role of mitochondrial abnormality in placental and endothelial dysfunction, targeting mitochondria to improve/restore mitochondrial function would be a promising therapeutic approach. This notion is substantiated by numerous preclinical studies discussed below.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and mitoQ
CoQ10 (ubiquinone) is best known as a component of the ETC. CoQ10 can also function as an antioxidant [126]. In a rat model of preeclampsia induced by Nω-Nitro-l-arginine-methyl ester (l-NAME), CoQ10 reduces systolic blood pressure, proteinuria, and increases birth weight along with increased mitochondrial membrane potential and mtDNA [127]. Notably, CoQ10 lowers the incidence of preeclampsia in a small-scale human clinic trial [128]. MitoQ is a synthetic compound consisting of a ubiquinone moiety linked to a triphenylphosphonium (TPP+) moiety [129••]. The TPP+ moiety allows mitoQ targeting to and accumulating within mitochondria. mitoQ normalizes hypoxia-induced elevation of ROS in cultured BeWo cells [39••] and reduces gestational hypoxia-induced oxidative stress in rat placentas [130, 131]. Consequently, the decrease in birth weight in gestational hypoxia is rescued by mitoQ [130]. The elevated ROS in endothelial cells following exposure to RUPP serum and in RUPP rat placentas are attenuated by mitoQ [40•, 54••]. Expectedly, mitoQ also reduces hypertension in RUPP rats [40•]. It should be noted that timing of the use of mitoQ is critical for the outcomes of antioxidant treatment. Using the RUPP rat model, Yang and colleagues notice that mitoQ treatment in early pregnancy exacerbates blood pressure, proteinuria and fetal growth restriction, while the treatment in late gestation alleviates the preeclamptic phenotype [54••].
Selenium
Selenium, through incorporating in the selenoproteins such as GPXs and TXRs, plays its biological roles [132]. Selenium also promotes mitochondrial biogenesis [133]. In trophoblast cell lines, selenium upregulates GPXs and TXRs, reduces mtROS, stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis by increasing PGC-1α and NRF-1 expression, and increases ATP production [134, 135]. Selenium also diminishes hypoxia-induced increase in ROS in HTR-8/SVneo cells [135]. mtROS-induced apoptosis could also be suppressed by selenium in trophoblast cell lines and placental explants [134, 136]. In human trials, selenium supplement lowers circulating sFlt-1 [137] and decreases the incidence of preeclampsia [138].
Hydrogen Sulfide Compounds
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a gasotransmitter, has been shown to be an endogenous modulator of mitochondrial function, evidenced by stimulating oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production [139]. Wang et al. [140] demonstrate that H2S producing enzyme cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE) expression is reduced in preeclamptic placentas, and inhibiting CSE activity with DL-propargylglycine reduces placental growth factor (PlGF) production in first-trimester placenta explants and inhibits the invasion of HTR-8/SVneo cells. Moreover, blocking endogenous H2S production in pregnant mice results in preeclampsia phenotype such as increased circulating sFlt1, maternal hypertension, and fetal growth restriction, which is reversed by H2S-releasing compound GYY4137 [140]. Similar findings are observed in RUPP mice when the other H2S-releasing compound MZe786 is used [141]. AP39 is a mitochondria-targeted H2S donor consisting of a H2S-donating moiety (dithiolethione) coupled to TPP+. AP39 increases mitochondrial content, reduces HIF-1α, mtROS and sFlt-1 production in hypoxia-treated human primary trophoblasts [31]. Endothelial cells exposed to AP39 display increased ETC activity and bioenergetics [142]. AP39 also abrogates the increase in mtROS and improves mitochondrial respiration in CSE-knockdown endothelial cells [143]. Therefore, it appears that AP39 is a promising therapeutic agent for preeclampsia. However, it should be aware of that AP39 at high concentrations could lead to mitochondrial dysfunction by inhibiting the ETC and disturbing redox homeostasis [144].
Melatonin
Melatonin can reduce oxidative stress by functioning as a ROS scavenger and by upregulating antioxidant enzyme expression, and plays an important role in regulating mitochondrial function [145]. Melatonin enters mitochondria probably through peptide transporters PEPT1 and PEPT2 [146], leading to its accumulation in this organelle [147]. Melatonin increases the expression of antioxidant enzymes thioredoxin, glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (the first rate-limiting enzyme of glutathione synthesis), and NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1 (NQO1) in cultured human primary trophoblasts [148]. The oxidative stress and subsequent mitochondrial apoptosis and DNA fragmentation induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation are reversed by melatonin in trophoblasts [149]. These in vitro findings are also corroborated by observations in vivo studies. Melatonin normalizes ischemia/reperfusion induced fetal growth restriction in pregnant rats by improving mitochondrial respiration and by reducing oxidative stress in the placenta [150]. Similarly, melatonin reduces sFlt-1 expression in RUPP rat placenta and lowers blood pressure [150]. Melatonin also improves endothelial function and alleviates tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-induced endothelial damage [151]. Significantly, melatonin is found to prolong pregnancy by ~ 6 days in women with early-onset preeclampsia [151].
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) such as lansoprazole, rabeprazole, and esomeprazole are found to increase endogenous antioxidant function by increasing the expression of NRF2 and its targets heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), NQO1 and thioredoxin in primary trophoblasts, placental explants from women with preterm preeclampsia, and endothelial cells [152]. Lansoprazole is shown to decrease mtROS production and to maintain mitochondrial membrane potential [153]. Accordingly, PPIs reduces sFlT-1 release from trophoblasts and placental explants from preeclamptic pregnancy, mitigates TNF-α-induced endothelial dysfunction, and decreases hypertension in a mouse model overexpression human sFlt-1 [152]. In a human trial, PPIs reduce circulating sFlt-1, hypertension, and proteinuria [154].
AMPK Activators
AMPK, serine/threonine kinase, plays a pivotal role in maintaining cellular metabolism. AMPK is activated by AMP or ADP during ATP insufficiency [155]. Its activation redirects metabolism toward increased catabolism and decreased anabolism to restore cellular energy balance in part through impacting glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation, and mitochondrial homeostasis [155]. Several AMPK activators including 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxyamide ribonucleoside (AICAR), metformin, and resveratrol have been tested for preventing/treating preeclampsia. It is worth noting that resveratrol is also a ROS scavenger. AICAR restores placental antioxidant capacity and decreases circulating sFlt-1 in RUPP rats as well as lowers RUPP-induced hypertension [156]. Gestational hypoxia-induced fetal growth restriction is also alleviated by AICAR [157]. However, activation of AMPK by AICAR suppresses metabolism and ATP production in human term placenta explants [158], which is probably due to that the metabolism and ATP production are already maximized in the term placenta. Metformin reduces sFlt-1 release from trophoblasts and preterm preeclamptic placental explants and improves endothelial dysfunction [159]. In a rat model of preeclampsia induced by lipopolysaccharide, metformin reduces oxidative stress, hypertension, proteinuria, and fetal growth restriction [160]. A phase II clinical trial of treating early-onset preeclampsia with metformin is underway in South Africa [161]. Resveratrol reduces hypoxia-induced oxidative stress and prevents hypoxia-induced apoptosis in HTR-8/SVneo cells [162]. Resveratrol also decreases sFlt-1 release from primary trophoblasts and promotes expression of HO-1, NQO1, GCLC, and TXN [163]. In a rat model of preeclampsia induced by l-NAME, resveratrol increases placental expression of SOD and decreases oxidative stress, apoptosis, and sFlt-1 expression in the placentas, leading to reduction in both hypertension and proteinuria [162, 164].
PPARγ Agonists
PPARγ is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily of ligand-activated transcription factors. It is co-activated by PGC-1α and participates in regulating oxidative metabolism in mitochondria [165]. The PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone reduces hypoxia- or hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis by decreasing caspase-9 and 3 activities and reducing cytochrome c release, and increases antioxidant capacity by upregulating the expression of catalase and SODs in first trimester placental explants and/or JEG-3 cells [165]. Remarkably, the downregulation of SOD2 in preeclamptic placentas is rescued by rosiglitazone [52]. The other PPARγ agonist pioglitazone improves hypoxia-induced fetal growth restriction [166]. In RUPP rats, rosiglitazone lowers placental and circulating sFlt-1 and alleviates endothelial dysfunction and hypertension [167].
Conclusion
Mitochondria are essential for both placental and endothelial function during pregnancy. The dysregulated mitochondria conferred by placental hypoxia or hypoxia/reoxygenation generally exhibit metabolism reprogramming, increased mtROS, fission, mitophagy, and apoptosis, and reduced biogenesis in the placenta. mtROS appear to be the centerpiece causing mitochondrial damage and are engaged in other aspects of mitochondrial dysfunction. The bioactive factors released from the preeclamptic placentas also target mitochondria in endothelial cells. Together, these changes apparently contribute to placental and endothelial dysfunction, ultimately leading to preeclampsia. Given the lack of effective cures and the important role of mitochondrial dysfunction in preeclampsia, preclinical studies provide evidence that improving/restoring mitochondrial function could be a promising therapeutic approach for treating preeclampsia.
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Roger AJ, Munoz-Gomez SA, Kamikawa R. The origin and diversification of mitochondria. Curr Biol. 2017;27(21):R1177–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.09.015.
Roca-Portoles A, Tait SWG. Mitochondrial quality control: from molecule to organelle. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(8):3853–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03775-0.
Eisner V, Picard M, Hajnoczky G. Mitochondrial dynamics in adaptive and maladaptive cellular stress responses. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(7):755–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0133-0.
Javadov S, Kozlov AV, Camara AKS. Mitochondria in health and diseases. Cells. 2020;9(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051177
Burton GJ, Fowden AL, Thornburg KL. Placental origins of chronic disease. Physiol Rev. 2016;96(4):1509–65. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00029.2015.
• Michelsen TM, Holme AM, Holm MB, Roland MC, Haugen G, Powell TL, et al. Uteroplacental Glucose Uptake and Fetal Glucose Consumption: A Quantitative Study in Human Pregnancies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2019;104(3):873-82. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2018-01154. This study described glucose consumption in the human placenta.
• Carter AM. Placental oxygen consumption. Part I: in vivo studies - a review. Placenta. 2000;21 Suppl A:S31–7. https://doi.org/10.1053/plac.1999.0513. This study described oxygen consumption in the placenta.
Vaughan OR, Fowden AL. Placental metabolism: substrate requirements and the response to stress. Reprod Domest Anim. 2016;51(Suppl 2):25–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/rda.12797.
Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia. ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 222. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;135(6):e237–60. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000003891.
Rana S, Lemoine E, Granger JP, Karumanchi SA. Preeclampsia: pathophysiology, challenges, and perspectives. Circ Res. 2019;124(7):1094–112. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313276.
Melchiorre K, Thilaganathan B, Giorgione V, Ridder A, Memmo A, Khalil A. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and future cardiovascular health. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020;7:59. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2020.00059.
•• Redman CW, Sargent IL. Latest advances in understanding preeclampsia. Science 2005;308(5728):1592–1594. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1111726. The two-stage model of preeclampsia was discussed in this review paper.
•• Torbergsen T, Oian P, Mathiesen E, Borud O. Pre-eclampsia - a mitochondrial disease? Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 1989;68(2):145–148. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016348909009902. This observational study first described a high incidence of preeclampsia in a family with mitochondrial disorder.
Marin R, Chiarello DI, Abad C, Rojas D, Toledo F, Sobrevia L. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in early-onset and late-onset preeclampsia. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(12): 165961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165961.
Taylor CT. Mitochondria and cellular oxygen sensing in the HIF pathway. Biochem J. 2008;409(1):19–26. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20071249.
Ma LN, Huang XB, Muyayalo KP, Mor G, Liao AH. Lactic Acid: A Novel Signaling Molecule in Early Pregnancy? Front Immunol. 2020;11:279. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00279.
•• Jauniaux E, Watson AL, Hempstock J, Bao YP, Skepper JN, Burton GJ. Onset of maternal arterial blood flow and placental oxidative stress. A possible factor in human early pregnancy failure. Am J Pathol. 2000;157(6):2111–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64849-3. The study examined the placental oxygen levels before and after the establishment of the uteroplacental circulation.
Schneider H. Placental oxygen consumption. Part II: in vitro studies - a review. Placenta. 2000;21 Suppl A:S38–44. https://doi.org/10.1053/plac.1999.0512
Yu J, Guo X, Chen R, Feng L. Downregulation of Mitofusin 2 in Placenta Is Related to Preeclampsia. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:6323086. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6323086.
Zhou X, Han TL, Chen H, Baker PN, Qi H, Zhang H. Impaired mitochondrial fusion, autophagy, biogenesis and dysregulated lipid metabolism is associated with preeclampsia. Exp Cell Res. 2017;359(1):195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.07.029.
Sato E, Tsunokuni Y, Kaneko M, Saigusa D, Saito R, Shimma S, et al. Metabolomics of a mouse model of preeclampsia induced by overexpressing soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;527(4):1064–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.04.079.
•• Soleymanlou N, Jurisica I, Nevo O, Ietta F, Zhang X, Zamudio S, et al. Molecular evidence of placental hypoxia in preeclampsia J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(7):4299–4308. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2005-0078. This study demonstrated that the preeclamptic placenta exhibited hypoxic phenotype.
•• Semenza GL, Roth PH, Fang HM, Wang GL. Transcriptional regulation of genes encoding glycolytic enzymes by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(3):8 23757 23763. This study demonstrated the reprogramming cell bioengeretics in hypoxia.
Sferruzzi-Perri AN, Higgins JS, Vaughan OR, Murray AJ, Fowden AL. Placental mitochondria adapt developmentally and in response to hypoxia to support fetal growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(5):1621–6. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1816056116.
•• Vangrieken P, Al-Nasiry S, Bast A, Leermakers PA, Tulen CBM, Schiffers PMH et al. Placental Mitochondrial Abnormalities in Preeclampsia. Reprod Sci. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43032-021-00464-y. This study thoroughly examined various aspects of mitochondrial dysfunction in the preeclamptic placenta.
Shi Z, Long W, Zhao C, Guo X, Shen R, Ding H. Comparative proteomics analysis suggests that placental mitochondria are involved in the development of pre-eclampsia. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(5): e64351. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0064351.
Xu Z, Jin X, Cai W, Zhou M, Shao P, Yang Z, et al. Proteomics analysis reveals abnormal electron transport and excessive oxidative stress cause mitochondrial dysfunction in placental tissues of early-onset preeclampsia. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2018;12(5): e1700165. https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.201700165.
Matsubara S, Minakami H, Sato I, Saito T. Decrease in cytochrome c oxidase activity detected cytochemically in the placental trophoblast of patients with pre-eclampsia. Placenta. 1997;18(4):255–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0143-4004(97)80059-8.
Muralimanoharan S, Maloyan A, Mele J, Guo C, Myatt LG, Myatt L. MIR-210 modulates mitochondrial respiration in placenta with preeclampsia. Placenta. 2012;33(10):816–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2012.07.002.
Beyramzadeh M, Dikmen ZG, Erturk NK, Tuncer ZS, Akbiyik F. Placental respiratory chain complex activities in high risk pregnancies. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017;30(24):2911–7. https://doi.org/10.1080/14767058.2016.1268594.
Covarrubias AE, Lecarpentier E, Lo A, Salahuddin S, Gray KJ, Karumanchi SA, et al. AP39, a modulator of mitochondrial bioenergetics, reduces antiangiogenic response and oxidative stress in hypoxia-exposed trophoblasts: relevance for preeclampsia pathogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2019;189(1):104–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.09.007.
•• Holland OJ, Cuffe JSM, Dekker Nitert M, Callaway L, Kwan Cheung KA, Radenkovic F et al. Placental mitochondrial adaptations in preeclampsia associated with progression to term delivery. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(12):1150. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1190-9 . This study examined and compared mitochondrial function/dysfunction in the placenta of normal pregnancy, early-onst and late-onset preeclampsia.
Yung HW, Colleoni F, Dommett E, Cindrova-Davies T, Kingdom J, Murray AJ, et al. Noncanonical mitochondrial unfolded protein response impairs placental oxidative phosphorylation in early-onset preeclampsia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(36):18109–18. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1907548116.
Holland OJ, Hickey AJR, Alvsaker A, Moran S, Hedges C, Chamley LW, et al. Changes in mitochondrial respiration in the human placenta over gestation. Placenta. 2017;57:102–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2017.06.011.
Bartha JL, Visiedo F, Fernandez-Deudero A, Bugatto F, Perdomo G. Decreased mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation in placentas from women with preeclampsia. Placenta. 2012;33(2):132–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2011.11.027.
Thomas MM, Haghiac M, Grozav C, Minium J, Calabuig-Navarro V, O’Tierney-Ginn P. Oxidative stress impairs fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial function in the term placenta. Reprod Sci. 2019;26(7):972–8. https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719118802054.
• Illsley NP, Caniggia I, Zamudio S. Placental metabolic reprogramming: do changes in the mix of energy-generating substrates modulate fetal growth? Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54(2-3):409-19. https://doi.org/10.1387/ijdb.082798ni. The review discussed metabolic reprogramming in the placenta under hypoxic conditions.
Colleoni F, Padmanabhan N, Yung HW, Watson ED, Cetin I, Tissot van Patot MC, et al. Suppression of mitochondrial electron transport chain function in the hypoxic human placenta: a role for miRNA-210 and protein synthesis inhibition. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55194. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055194.
•• Vangrieken P, Al-Nasiry S, Bast A, Leermakers PA, Tulen CBM, Janssen GMJ, et al. Hypoxia-induced mitochondrial abnormalities in cells of the placenta. PLoS One. 2021;16(1):e0245155. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245155. This study demonstrated that many features of mitochondrial dusfunction in the preeclamptic placenta could be simulated by hypxoic exposure.
• Vaka VR, McMaster KM, Cunningham Jr MW, Ibrahim T, Hazlewood R, Usry N, et al. Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Reactive Oxygen Species in Mediating Hypertension in the Reduced Uterine Perfusion Pressure Rat Model of Preeclampsia. Hypertension. 2018;72(3):703-711. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11290. This study demonstrated that mitochondrial dysfunction was recapitulate in an animal model of preeclampsia.
Chen G, Lin Y, Chen L, Zeng F, Zhang L, Huang Y, et al. Role of DRAM1 in mitophagy contributes to preeclampsia regulation in mice. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(3):1847–58. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11269.
Ganguly E, Kirschenman R, Spaans F, Holody CD, Phillips TEJ, Case CP, et al. Nanoparticle-encapsulated antioxidant improves placental mitochondrial function in a sexually dimorphic manner in a rat model of prenatal hypoxia. FASEB J. 2021;35(2): e21338. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202002193R.
Bloxam DL, Bullen BE, Walters BN, Lao TT. Placental glycolysis and energy metabolism in preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1987;157(1):97–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9378(87)80354-x.
Murphy MP. How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem J. 2009;417(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20081386.
Garcia-Santamarina S, Boronat S, Hidalgo E. Reversible cysteine oxidation in hydrogen peroxide sensing and signal transduction. Biochemistry. 2014;53(16):2560–80. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi401700f.
Lee P, Chandel NS, Simon MC. Cellular adaptation to hypoxia through hypoxia inducible factors and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(5):268–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-0227-y.
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M, Sollott SJ. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol Rev. 2014;94(3):909–50. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00026.2013.
Chiarello DI, Abad C, Rojas D, Toledo F, Vazquez CM, Mate A, et al. Oxidative stress: normal pregnancy versus preeclampsia. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(2): 165354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.12.005.
• Wang Y, Walsh SW. Placental mitochondria as a source of oxidative stress in pre-eclampsia. Placenta. 1998;19(8):581-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0143-4004(98)90018-2. This study provided first evidence of elevated mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in the preeclamptic placenta.
Aljunaidy MM, Morton JS, Kirschenman R, Phillips T, Case CP, Cooke CM, et al. Maternal treatment with a placental-targeted antioxidant (MitoQ) impacts offspring cardiovascular function in a rat model of prenatal hypoxia. Pharmacol Res. 2018;134:332–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2018.05.006.
Zamudio S, Kovalenko O, Vanderlelie J, Illsley NP, Heller D, Belliappa S, et al. Chronic hypoxia in vivo reduces placental oxidative stress. Placenta. 2007;28(8–9):846–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2006.11.010.
Kohan-Ghadr HR, Kilburn BA, Kadam L, Johnson E, Kolb BL, Rodriguez-Kovacs J, et al. Rosiglitazone augments antioxidant response in the human trophoblast and prevents apoptosisdagger. Biol Reprod. 2019;100(2):479–94. https://doi.org/10.1093/biolre/ioy186.
Rueda-Clausen CF, Stanley JL, Thambiraj DF, Poudel R, Davidge ST, Baker PN. Effect of prenatal hypoxia in transgenic mouse models of preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction. Reprod Sci. 2014;21(4):492–502. https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719113503401.
•• Yang Y, Xu P, Zhu F, Liao J, Wu Y, Hu M, et al. The potent antioxidant mitoq protects against preeclampsia during late gestation but increases the risk of preeclampsia when administered in early pregnancy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2021;34(2):118-36. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2019.7891. This study examined the time frame in starting anoxidant treatment in an animal model of preeclampsia and demonstrated the effectiveness of mitochondria-targeted compound mitoQ in alleviating preeclampsia-like symptoms.
Ding D, Scott NM, Thompson EE, Chaiworapongsa T, Torres R, Billstrand C, et al. Increased protein-coding mutations in the mitochondrial genome of African American women with preeclampsia. Reprod Sci. 2012;19(12):1343–51. https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719112450337.
Cline SD. Mitochondrial DNA damage and its consequences for mitochondrial gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1819(9–10):979–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.06.002.
Kowaltowski AJ, Castilho RF, Vercesi AE. Mitochondrial permeability transition and oxidative stress. FEBS Lett. 2001;495(1–2):12–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02316-x.
Tomas SZ, Prusac IK, Roje D, Tadin I. Trophoblast apoptosis in placentas from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2011;71(4):250–5. https://doi.org/10.1159/000320289.
Murata M, Fukushima K, Takao T, Seki H, Takeda S, Wake N. Oxidative stress produced by xanthine oxidase induces apoptosis in human extravillous trophoblast cells. J Reprod Dev. 2013;59(1):7–13. https://doi.org/10.1262/jrd.2012-053.
Zhou X, Zhang GY, Wang J, Lu SL, Cao J, Sun LZ. A novel bridge between oxidative stress and immunity: the interaction between hydrogen peroxide and human leukocyte antigen G in placental trophoblasts during preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2012;206(5):447 e7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2012.03.013
Walker OS, Ragos R, Wong MK, Adam M, Cheung A, Raha S. Reactive oxygen species from mitochondria impacts trophoblast fusion and the production of endocrine hormones by syncytiotrophoblasts. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(2): e0229332. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0229332.
Ushida T, Kotani T, Tsuda H, Imai K, Nakano T, Hirako S, et al. Molecular hydrogen ameliorates several characteristics of preeclampsia in the Reduced Uterine Perfusion Pressure (RUPP) rat model. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;101:524–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.10.491.
Zemirli N, Morel E, Molino D. Mitochondrial dynamics in basal and stressful conditions. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020564
Youle RJ, van der Bliek AM. Mitochondrial fission, fusion, and stress. Science. 2012;337(6098):1062–5. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1219855.
Mishra P, Chan DC. Metabolic regulation of mitochondrial dynamics. J Cell Biol. 2016;212(4):379–87. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201511036.
Ausman J, Abbade J, Ermini L, Farrell A, Tagliaferro A, Post M, et al. Ceramide-induced BOK promotes mitochondrial fission in preeclampsia. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(3):298. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0360-0.
•• Vishnyakova PA, Volodina MA, Tarasova NV, Marey MV, Tsvirkun DV, Vavina OV, et al. Mitochondrial role in adaptive response to stress conditions in preeclampsia. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32410. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32410. This study also examined various aspects of mitochondrial function/dysfunction in the placenta of normal pregnancy, early-onst and late-onset preeclampsia and demonstrated that mitochondria underwent adaptative changes in preeclampsia.
Liu Y, Beyer A, Aebersold R. On the dependency of cellular protein levels on mRNA abundance. Cell. 2016;165(3):535–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.03.014.
Kubli DA, Ycaza JE, Gustafsson AB. BNIP3 mediates mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death through Bax and Bak. Biochem J. 2007;405(3):407–15. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20070319.
Zhang J, Ney PA. Role of BNIP3 and NIX in cell death, autophagy, and mitophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2009;16(7):939–46. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.16.
Liu L, Feng D, Chen G, Chen M, Zheng Q, Song P, et al. Mitochondrial outer-membrane protein FUNDC1 mediates hypoxia-induced mitophagy in mammalian cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(2):177–85. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2422.
Wenz T. Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis and PGC-1alpha under cellular stress. Mitochondrion. 2013;13(2):134–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2013.01.006.
Canto C, Auwerx J. PGC-1alpha, SIRT1 and AMPK, an energy sensing network that controls energy expenditure. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2009;20(2):98–105. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOL.0b013e328328d0a4.
Scarpulla RC. Transcriptional paradigms in mammalian mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Physiol Rev. 2008;88(2):611–38. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00025.2007.
Filograna R, Mennuni M, Alsina D, Larsson NG. Mitochondrial DNA copy number in human disease: the more the better? FEBS Lett. 2021;595(8):976–1002. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.14021.
Knyazev EN, Zakharova GS, Astakhova LA, Tsypina IM, Tonevitsky AG, Sukhikh GT. Metabolic reprogramming of trophoblast cells in response to hypoxia. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2019;166(3):321–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-019-04342-1.
Kumar S, Gordon GH, Abbott DH, Mishra JS. Androgens in maternal vascular and placental function: implications for preeclampsia pathogenesis. Reproduction. 2018;156(5):R155–67. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-18-0278.
Mishra JS, Blesson CS, Kumar S. Testosterone decreases placental mitochondrial content and cellular bioenergetics. Biology (Basel). 2020;9(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9070176.
Mando C, De Palma C, Stampalija T, Anelli GM, Figus M, Novielli C, et al. Placental mitochondrial content and function in intrauterine growth restriction and preeclampsia. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014;306(4):E404–13. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00426.2013.
Bock FJ, Tait SWG. Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(2):85–100. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-019-0173-8.
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C. Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev. 2007;87(1):99–163. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00013.2006.
Kinnally KW, Peixoto PM, Ryu SY, Dejean LM. Is mPTP the gatekeeper for necrosis, apoptosis, or both? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813(4):616–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.09.013.
Ma L, Zhang Z, Dong K, Ma Y. TWIST1 Alleviates hypoxia-induced damage of trophoblast cells by inhibiting mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2019;385(2): 111687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111687.
Longtine MS, Chen B, Odibo AO, Zhong Y, Nelson DM. Villous trophoblast apoptosis is elevated and restricted to cytotrophoblasts in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia, IUGR, or preeclampsia with IUGR. Placenta. 2012;33(5):352–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2012.01.017.
Ishihara N, Matsuo H, Murakoshi H, Laoag-Fernandez JB, Samoto T, Maruo T. Increased apoptosis in the syncytiotrophoblast in human term placentas complicated by either preeclampsia or intrauterine growth retardation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2002;186(1):158–66. https://doi.org/10.1067/mob.2002.119176.
Heazell AE, Buttle HR, Baker PN, Crocker IP. Altered expression of regulators of caspase activity within trophoblast of normal pregnancies and pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Reprod Sci. 2008;15(10):1034–43. https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719108322438.
Park JK, Kang MY, Kim YH, Jo HC, Shin JK, Choi WJ, et al. PKC delta in preeclamptic placentas promotes Bax dissociation from 14–3-3 zeta through 14–3-3 zeta phosphorylation. Placenta. 2008;29(7):584–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2008.03.007.
Hung TH, Chen SF, Liou JD, Hsu JJ, Li MJ, Yeh YL, et al. Bax, Bak and mitochondrial oxidants are involved in hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in human placenta. Placenta. 2008;29(7):565–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2008.03.005.
Hu R, Zhou S, Li X. Altered Bcl-2 and Bax expression is associated with cultured first trimester human cytotrophoblasts apoptosis induced by hypoxia. Life Sci. 2006;79(4):351–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2006.01.011.
Gilbert JS, Ryan MJ, LaMarca BB, Sedeek M, Murphy SR, Granger JP. Pathophysiology of hypertension during preeclampsia: linking placental ischemia with endothelial dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008;294(2):H541–50. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.01113.2007.
Qu H, Khalil RA. Vascular mechanisms and molecular targets in hypertensive pregnancy and preeclampsia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020;319(3):H661–81. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00202.2020.
•• Maynard SE, Min JY, Merchan J, Lim KH, Li J, Mondal S, et al. Excess placental soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt1) may contribute to endothelial dysfunction, hypertension, and proteinuria in preeclampsia. J Clin Invest. 2003;111(5):649-58. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI17189. This study provided evidence that sFlt-1 released from the preeclamptic placenta caused endothelial dysfunction and clinical symptoms of preeclampsia.
Shibata E, Rajakumar A, Powers RW, Larkin RW, Gilmour C, Bodnar LM, et al. Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 is increased in preeclampsia but not in normotensive pregnancies with small-for-gestational-age neonates: relationship to circulating placental growth factor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(8):4895–903. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2004-1955.
Levine RJ, Maynard SE, Qian C, Lim KH, England LJ, Yu KF, et al. Circulating angiogenic factors and the risk of preeclampsia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(7):672–83. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa031884.
Holme AM, Roland MC, Henriksen T, Michelsen TM. In vivo uteroplacental release of placental growth factor and soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 in normal and preeclamptic pregnancies. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;215(6):782 e1- e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2016.07.056.
Walentowicz-Sadlecka M, Domaracki P, Sadlecki P, Siodmiak J, Grabiec M, Walentowicz P, et al. Assessment of the SFlt-1 and sFlt-1/25(OH)D ratio as a diagnostic tool in gestational hypertension (GH), preeclampsia (PE), and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). Dis Markers. 2019;2019:5870239. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5870239.
Gilbert JS, Babcock SA, Granger JP. Hypertension produced by reduced uterine perfusion in pregnant rats is associated with increased soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 expression. Hypertension. 2007;50(6):1142–7. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.096594.
Ahmad S, Ahmed A. Elevated placental soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 inhibits angiogenesis in preeclampsia. Circ Res. 2004;95(9):884–91. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000147365.86159.f5.
Nevo O, Soleymanlou N, Wu Y, Xu J, Kingdom J, Many A, et al. Increased expression of sFlt-1 in in vivo and in vitro models of human placental hypoxia is mediated by HIF-1. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006;291(4):R1085–93. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00794.2005.
Gerber HP, Condorelli F, Park J, Ferrara N. Differential transcriptional regulation of the two vascular endothelial growth factor receptor genes. Flt-1, but not Flk-1/KDR, is up-regulated by hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(38):23659–67. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.38.23659.
Bergmann A, Ahmad S, Cudmore M, Gruber AD, Wittschen P, Lindenmaier W, et al. Reduction of circulating soluble Flt-1 alleviates preeclampsia-like symptoms in a mouse model. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(6B):1857–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00820.x.
Chang X, Yao J, He Q, Liu M, Duan T, Wang K. Exosomes from women with preeclampsia induced vascular dysfunction by delivering sFlt (Soluble Fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase)-1 and sEng (Soluble Endoglin) to endothelial cells. Hypertension. 2018;72(6):1381–90. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11706.
Sanchez-Aranguren LC, Espinosa-Gonzalez CT, Gonzalez-Ortiz LM, Sanabria-Barrera SM, Riano-Medina CE, Nunez AF, et al. Soluble Fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase-1 Alters Cellular Metabolism and Mitochondrial Bioenergetics in Preeclampsia. Front Physiol. 2018;9:83. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00083.
Bridges JP, Gilbert JS, Colson D, Gilbert SA, Dukes MP, Ryan MJ, et al. Oxidative stress contributes to soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 induced vascular dysfunction in pregnant rats. Am J Hypertens. 2009;22(5):564–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajh.2009.24.
McArthur K, Whitehead LW, Heddleston JM, Li L, Padman BS, Oorschot V, et al. BAK/BAX macropores facilitate mitochondrial herniation and mtDNA efflux during apoptosis. Science. 2018;359(6378). doi:https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao6047.
Riley JS, Tait SW. Mitochondrial DNA in inflammation and immunity. EMBO Rep. 2020;21(4): e49799. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201949799.
Zhang Q, Raoof M, Chen Y, Sumi Y, Sursal T, Junger W, et al. Circulating mitochondrial DAMPs cause inflammatory responses to injury. Nature. 2010;464(7285):104–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08780.
Shimada K, Crother TR, Karlin J, Dagvadorj J, Chiba N, Chen S, et al. Oxidized mitochondrial DNA activates the NLRP3 inflammasome during apoptosis. Immunity. 2012;36(3):401–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2012.01.009.
Bai B, Yang Y, Wang Q, Li M, Tian C, Liu Y, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome in endothelial dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9):776. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02985-x.
Zhou R, Yazdi AS, Menu P, Tschopp J. A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature. 2011;469(7329):221–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09663.
Williamson RD, McCarthy FP, Khashan AS, Totorika A, Kenny LC, McCarthy C. Exploring the role of mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathophysiology of pre-eclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2018;13:248–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preghy.2018.06.012.
Marschalek J, Wohlrab P, Ott J, Wojta J, Speidl W, Klein KU, et al. Maternal serum mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) levels are elevated in preeclampsia - a matched case-control study. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2018;14:195–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.preghy.2018.10.003.
Orozco AF, Jorgez CJ, Ramos-Perez WD, Popek EJ, Yu X, Kozinetz CA, et al. Placental release of distinct DNA-associated micro-particles into maternal circulation: reflective of gestation time and preeclampsia. Placenta. 2009;30(10):891–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2009.06.012.
Tong M, Johansson C, Xiao F, Stone PR, James JL, Chen Q, et al. Antiphospholipid antibodies increase the levels of mitochondrial DNA in placental extracellular vesicles: Alarmin-g for preeclampsia. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16556. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16448-5.
Williamson RD, McCarthy FP, Kenny LC, McCarthy CM. Activation of a TLR9 mediated innate immune response in preeclampsia. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):5920. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42551-w.
• Goulopoulou S, Wenceslau CF, McCarthy CG, Matsumoto T, Webb RC. Exposure to stimulatory CpG oligonucleotides during gestation induces maternal hypertension and excess vasoconstriction in pregnant rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016;310(8):H1015-25. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00834.2015. The findings from this study implied that mtDNA released from the preeclamptic placenta could contribute to the development of preeclampsia.
Wallukat G, Homuth V, Fischer T, Lindschau C, Horstkamp B, Jupner A, et al. Patients with preeclampsia develop agonistic autoantibodies against the angiotensin AT1 receptor. J Clin Invest. 1999;103(7):945–52. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI4106.
Xia Y, Wen H, Bobst S, Day MC, Kellems RE. Maternal autoantibodies from preeclamptic patients activate angiotensin receptors on human trophoblast cells. J Soc Gynecol Investig. 2003;10(2):82–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1071-5576(02)00259-9.
Xia Y, Kellems RE. Angiotensin receptor agonistic autoantibodies and hypertension: preeclampsia and beyond. Circ Res. 2013;113(1):78–87. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.300752.
• Zhou CC, Zhang Y, Irani RA, Zhang H, Mi T, Popek EJ, et al. Angiotensin receptor agonistic autoantibodies induce pre-eclampsia in pregnant mice. Nat Med. 2008;14(8):855-62. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.1856. This study described that AT1-AA could induce preeclmapsia-like symptoms in pregnant mice.
LaMarca B, Wallukat G, Llinas M, Herse F, Dechend R, Granger JP. Autoantibodies to the angiotensin type I receptor in response to placental ischemia and tumor necrosis factor alpha in pregnant rats. Hypertension. 2008;52(6):1168–72. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.120576.
Siddiqui AH, Irani RA, Zhang W, Wang W, Blackwell SC, Kellems RE, et al. Angiotensin receptor agonistic autoantibody-mediated soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 induction contributes to impaired adrenal vasculature and decreased aldosterone production in preeclampsia. Hypertension. 2013;61(2):472–9. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.00157.
McCarthy C, Kenny LC. Therapeutically targeting mitochondrial redox signalling alleviates endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32683. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32683.
Deer E, Vaka VR, McMaster KM, Wallace K, Cornelius DC, Amaral LM, et al. Vascular endothelial mitochondrial oxidative stress in response to preeclampsia: a role for angiotension II type 1 autoantibodies. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2021;3(1): 100275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100275.
Vaka VR, Cunningham MW, Deer E, Franks M, Ibrahim T, Amaral LM, et al. Blockade of endogenous angiotensin II type I receptor agonistic autoantibody activity improves mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and hypertension in a rat model of preeclampsia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020;318(2):R256–62. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00179.2019.
Bentinger M, Brismar K, Dallner G. The antioxidant role of coenzyme Q. Mitochondrion. 2007;7(Suppl):S41-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2007.02.006.
Xu X, Pan JR, Zhang YZ. CoQ10 alleviate preeclampsia symptoms by enhancing the function of mitochondria in the placenta of pregnant rats with preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy. 2019;38(4):217–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641955.2019.1649420.
Teran E, Hernandez I, Nieto B, Tavara R, Ocampo JE, Calle A. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation during pregnancy reduces the risk of pre-eclampsia. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2009;105(1):43–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijgo.2008.11.033.
•• Murphy MP, Smith RA. Targeting antioxidants to mitochondria by conjugation to lipophilic cations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2007;47:629-56. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.47.120505.105110. The review described the design of mitochondria-targeted compounds.
Phillips TJ, Scott H, Menassa DA, Bignell AL, Sood A, Morton JS, et al. Treating the placenta to prevent adverse effects of gestational hypoxia on fetal brain development. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):9079. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06300-1.
Ganguly E, Aljunaidy MM, Kirschenman R, Spaans F, Morton JS, Phillips TEJ, et al. Sex-Specific Effects of Nanoparticle-Encapsulated MitoQ (nMitoQ) Delivery to the placenta in a rat model of fetal hypoxia. Front Physiol. 2019;10:562. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00562.
Labunskyy VM, Hatfield DL, Gladyshev VN. Selenoproteins: molecular pathways and physiological roles. Physiol Rev. 2014;94(3):739–77. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00039.2013.
Garcia-Garcia FJ, Monistrol-Mula A, Cardellach F, Garrabou G. Nutrition, Bioenergetics, and Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients. 2020;12(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092785.
Khera A, Vanderlelie JJ, Holland O, Perkins AV. Overexpression of endogenous anti-oxidants with selenium supplementation protects trophoblast cells from reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis in a Bcl-2-dependent manner. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2017;177(2):394–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0870-5.
Na JY, Seok J, Park S, Kim JS, Kim GJ. Effects of selenium on the survival and invasion of trophoblasts. Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2018;45(1):10–6. https://doi.org/10.5653/cerm.2018.45.1.10.
Habibi N, Labrinidis A, Leemaqz SY, Jankovic-Karasoulos T, McCullough D, Grieger JA, et al. Effect of Selenium and Iodine on Oxidative Stress in the First Trimester Human Placenta Explants. Nutrients. 2021;13(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13030800.
Rayman MP, Searle E, Kelly L, Johnsen S, Bodman-Smith K, Bath SC, et al. Effect of selenium on markers of risk of pre-eclampsia in UK pregnant women: a randomised, controlled pilot trial. Br J Nutr. 2014;112(1):99–111. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114514000531.
Tara F, Maamouri G, Rayman MP, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Sahebkar A, Yazarlu O, et al. Selenium supplementation and the incidence of preeclampsia in pregnant Iranian women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot trial. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;49(2):181–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1028-4559(10)60038-1.
Murphy B, Bhattacharya R, Mukherjee P. Hydrogen sulfide signaling in mitochondria and disease. FASEB J. 2019;33(12):13098–125. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201901304R.
Wang K, Ahmad S, Cai M, Rennie J, Fujisawa T, Crispi F, et al. Dysregulation of hydrogen sulfide producing enzyme cystathionine gamma-lyase contributes to maternal hypertension and placental abnormalities in preeclampsia. Circulation. 2013;127(25):2514–22. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.001631.
Saif J, Ahmad S, Rezai H, Litvinova K, Sparatore A, Alzahrani FA, et al. Hydrogen sulfide releasing molecule MZe786 inhibits soluble Flt-1 and prevents preeclampsia in a refined RUPP mouse model. Redox Biol. 2021;38: 101814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101814.
Szczesny B, Modis K, Yanagi K, Coletta C, Le Trionnaire S, Perry A, et al. AP39, a novel mitochondria-targeted hydrogen sulfide donor, stimulates cellular bioenergetics, exerts cytoprotective effects and protects against the loss of mitochondrial DNA integrity in oxidatively stressed endothelial cells in vitro. Nitric Oxide. 2014;41:120–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2014.04.008.
Sanchez-Aranguren LC, Ahmad S, Dias IHK, Alzahrani FA, Rezai H, Wang K, et al. Bioenergetic effects of hydrogen sulfide suppress soluble Flt-1 and soluble endoglin in cystathionine gamma-lyase compromised endothelial cells. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):15810. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72371-2.
Libiad M, Vitvitsky V, Bostelaar T, Bak DW, Lee HJ, Sakamoto N, et al. Hydrogen sulfide perturbs mitochondrial bioenergetics and triggers metabolic reprogramming in colon cells. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(32):12077–90. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.009442.
Reiter RJ, Ma Q, Sharma R. Melatonin in mitochondria: mitigating clear and present dangers. Physiology (Bethesda). 2020;35(2):86–95. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00034.2019.
Huo X, Wang C, Yu Z, Peng Y, Wang S, Feng S, et al. Human transporters, PEPT1/2, facilitate melatonin transportation into mitochondria of cancer cells: an implication of the therapeutic potential. J Pineal Res. 2017;62(4). https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12390.
Venegas C, Garcia JA, Escames G, Ortiz F, Lopez A, Doerrier C, et al. Extrapineal melatonin: analysis of its subcellular distribution and daily fluctuations. J Pineal Res. 2012;52(2):217–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00931.x.
Hannan NJ, Binder NK, Beard S, Nguyen TV, Kaitu’u-Lino TJ, Tong S. Melatonin enhances antioxidant molecules in the placenta, reduces secretion of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFLT) from primary trophoblast but does not rescue endothelial dysfunction: An evaluation of its potential to treat preeclampsia. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(4): e0187082. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187082.
Lanoix D, Lacasse AA, Reiter RJ, Vaillancourt C. Melatonin: the watchdog of villous trophoblast homeostasis against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013;381(1–2):35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2013.07.010.
Nagai R, Watanabe K, Wakatsuki A, Hamada F, Shinohara K, Hayashi Y, et al. Melatonin preserves fetal growth in rats by protecting against ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative/nitrosative mitochondrial damage in the placenta. J Pineal Res. 2008;45(3):271–6. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2008.00586.x.
Hobson SR, Gurusinghe S, Lim R, Alers NO, Miller SL, Kingdom JC, et al. Melatonin improves endothelial function in vitro and prolongs pregnancy in women with early-onset preeclampsia. J Pineal Res. 2018;65(3): e12508. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12508.
Onda K, Tong S, Beard S, Binder N, Muto M, Senadheera SN, et al. Proton pump inhibitors decrease soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 and soluble endoglin secretion, decrease hypertension, and rescue endothelial dysfunction. Hypertension. 2017;69(3):457–68. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08408.
Rai K, Matsui H, Kaneko T, Nagano Y, Shimokawa O, Udo J, et al. Lansoprazole inhibits mitochondrial superoxide production and cellular lipid peroxidation induced by indomethacin in RGM1 cells. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2011;49(1):25–30. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.10-133.
Saleh L, Samantar R, Garrelds IM, van den Meiracker AH, Visser W, Danser AHJ. Low soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase-1, endoglin, and endothelin-1 levels in women with confirmed or suspected preeclampsia using proton pump inhibitors. Hypertension. 2017;70(3):594–600. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.09741.
Herzig S, Shaw RJ. AMPK: guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(2):121–35. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2017.95.
Banek CT, Bauer AJ, Needham KM, Dreyer HC, Gilbert JS. AICAR administration ameliorates hypertension and angiogenic imbalance in a model of preeclampsia in the rat. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013;304(8):H1159–65. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00903.2012.
Lane SL, Houck JA, Doyle AS, Bales ES, Lorca RA, Julian CG, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase activator AICAR attenuates hypoxia-induced murine fetal growth restriction in part by improving uterine artery blood flow. J Physiol. 2020;598(18):4093–105. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP279341.
Landau D, Haghiac M, Minium J, Skomorovska-Prokvolit Y, Calabuig-Navarro V, O’Tierney-Ginn P. Activation of AMPK in human placental explants impairs mitochondrial function and cellular metabolism. Reprod Sci. 2019;26(4):487–95. https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719118776803.
Brownfoot FC, Hastie R, Hannan NJ, Cannon P, Tuohey L, Parry LJ, et al. Metformin as a prevention and treatment for preeclampsia: effects on soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 and soluble endoglin secretion and endothelial dysfunction. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2016;214(3):356 e1- e15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2015.12.019
Hu J, Zhang J, Zhu B. Protective effect of metformin on a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced preeclampsia. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2019;33(6):649–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/fcp.12501.
Cluver C, Walker SP, Mol BW, Hall D, Hiscock R, Brownfoot FC, et al. A double blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of metformin to treat preterm pre-eclampsia (PI2 Trial): study protocol. BMJ Open. 2019;9(4): e025809. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025809.
Zou Y, Zuo Q, Huang S, Yu X, Jiang Z, Zou S, et al. Resveratrol inhibits trophoblast apoptosis through oxidative stress in preeclampsia-model rats. Molecules. 2014;19(12):20570–9. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules191220570.
Hannan NJ, Brownfoot FC, Cannon P, Deo M, Beard S, Nguyen TV, et al. Resveratrol inhibits release of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase (sFlt-1) and soluble endoglin and improves vascular dysfunction-implications as a preeclampsia treatment. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1819. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01993-w.
Zou Y, Li S, Wu D, Xu Y, Wang S, Jiang Y, et al. Resveratrol promotes trophoblast invasion in pre-eclampsia by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(4):2702–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14175.
Handschin C, Spiegelman BM. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 coactivators, energy homeostasis, and metabolism. Endocr Rev. 2006;27(7):728–35. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2006-0037.
Lane SL, Dodson RB, Doyle AS, Park H, Rathi H, Matarrazo CJ, et al. Pharmacological activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-gamma) protects against hypoxia-associated fetal growth restriction. FASEB J. 2019;33(8):8999–9007. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201900214R.
McCarthy FP, Drewlo S, Kingdom J, Johns EJ, Walsh SK, Kenny LC. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma as a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of preeclampsia. Hypertension. 2011;58(2):280–6. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.172627.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Institutes of Health Grants HD083132 (LZ), HL128209 (LZ), HL137649 (LZ) and HL149608 (LZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Preeclampsia
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, XQ., Zhang, L. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia. Curr Hypertens Rep 24, 157–172 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-022-01184-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-022-01184-7