Abstract
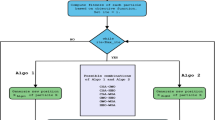
We introduce a novel bio-inspired algorithm named Horse Optimization Algorithm (HOA) which has as primary source of inspiration the hierarchical organization of the horse herds. The article presents the main principles of the proposed algorithm, the pseudo-code version of the algorithm and a modified version named Discrete Binary Horse Optimization Algorithm (DBHOA). HOA is evaluated and validated using six objective functions and is compared with Chicken Swarm Optimization (CSO) and Cat Swarm Optimization Algorithm (CSOA). Finally, the article presents the application of DBHOA in features selection for data generated in a smart grid for the classification of the stability of the system and it considers as experimental support the Electrical Grid Stability Simulated Dataset.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang, X.-S.: A new metaheuristic bat-inspired algorithm. In: Gonzalez, J.R., Pelta, D.A., Cruz, C., Terrazas, G., Krasnogor, N. (eds) Nature Inspired Cooperative Strategies for Optimization (NICSO 2010). Studies in Computational Intelligence, vol. 284, pp. 65–74. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-12538-6_6
Brabazon, A., Cui, W., O’Neill, M.: The Raven roosting optimisation algorithm. Soft Comput. 20(2), 525–545 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-014-1520-5
Shefaei, A., Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.: Wild goats algorithm: an evolutionary algorithm to solve the real-world optimization problems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 14(7), 2951–2961 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2017.2779239
Jain, M., Maurya, S., Rani, A., Singh, V.: OWL search algorithm: a novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm for global optimization. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 34(3), 1573–1582 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-169452
Arora, S., Singh, S.: Butterfly optimization algorithm: a novel approach for global optimization. Soft Comput. 23, 715–734 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3102-4
Hafez, A.I., Zawbaa, H.M., Emary, E., Mahmoud, H.A., Hassanien, A.E.: An innovative approach for feature selection based on chicken swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Soft Computing and Pattern Recognition (SoCPaR), Fukuoka, Japan, pp. 19–24 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/SOCPAR.2015.7492775
Pestov, V.: Is the k-NN classifier in high dimensions affected by the curse of dimensionality? Comput. Math. Appl. 65(10), 1427–1437 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2012.09.011
Chen, W., Li, Y., Xue, W., Shahabi, H., Li, S., Hong, H., Wang, X., Bian, H., Zhang, S., Pradhan, B., Ahmad, B.B.: Modeling flood susceptibility using data-driven approaches of naive Bayes tree, alternating decision tree, and random forest methods. Sci. Total Environ. 701, 134979 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134979
Lin, K.-C., Zhang, K.-Y., Huang, Y.-H., Hung, J.C., Yen, N.: Feature selection based on an improved cat swarm optimization algorithm for big data classification. J. Supercomput. 72, 3210–3221 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-016-1631-0
Lin, K.-C., Hsieh, Y.-H.: Classification of medical datasets using SVMs with hybrid evolutionary algorithms based on endocrine-based particle swarm optimization and artificial bee colony algorithms. J. Med. Syst. 39, 119 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-015-0306-3
Wang, Z., Wang, J.: A delay-adaptive control scheme for enhancing smart grid stability and resilience. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 110, 477–486 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2019.03.030
Aldeen, M., Saha, S., Alpcan, T.: Voltage stability margins and risk assessment in smart power grids. IFAC Proc. Vol. 47(3), 8188–8195 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3182/20140824-6-ZA-1003.02102
Shamisa, A., Majidi, B., Patra, J.C.: Sliding-window-based real-time model order reduction for stability prediction in smart grid. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 34(1), 326–337 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2018.2868850
Meng, X., Liu, Y., Gao, X., Zhang, H.: A new bio-inspired algorithm: chicken swarm optimization. In: Tan, Y., Shi, Y., Coello, C.A.C. (eds) Advances in Swarm Intelligence. ICSI 2004. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 8794, pp. 86–94. Springer, Cham (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-11857-4_10
Chu, S.-C., Tsai, P.-W., Pan, J.-S.: Cat Swarm Optimization. In: Yang, Q., Webb, G. (eds) PRICAI 2006: Trends in Artificial Intelligence. PRICAI 2006. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4099, pp. 854–858. Springer, Heidelberg (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-36668-3_94
Christ, M., Braun, N., Neuffer, J., Kempa-Liehr, A.W.: Time series feature extraction on basis of scalable hypothesis tests (tsfresh - a Python package). Neurocomputing 307, 72–77 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.03.067
Dua, D., Graff, C.: UCI Machine Learning Repository. University of California, School of Information and Computer Science, Irvine, CA (2019). https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/citation_policy.html
Arzamasov, V., Bohm, K., Jochem, P.: Towards Concise Models of Grid Stability. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Control, and Computing Technologies for Smart Grids (SmartGridComm), Aalborg, Denmark, pp. 1–6 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/SmartGridComm.2018.8587498
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Moldovan, D. (2020). Horse Optimization Algorithm: A Novel Bio-Inspired Algorithm for Solving Global Optimization Problems. In: Silhavy, R. (eds) Artificial Intelligence and Bioinspired Computational Methods. CSOC 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1225. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51971-1_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51971-1_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-51970-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-51971-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)