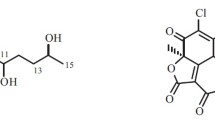
A new polyketide, 2-(7′-hydroxyoxooctyl)-3-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzeneacetic acid ethyl ester (1), together with three known compounds dothiorelone A (2), B (3), and C (4) were isolated from the mangrove endophytic fungus Phomopsis sp. ZSU-H76 obtained from the South China Sea. Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic methods, mainly 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic techniques. Primary bioassays showed that 1 exhibited cytotoxicity against HEp-2 and HepG2 cells with IC50 values of 25 and 30 μg/mL, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Marine-derived fungi have proven to be a rich source of structurally unique and biologically active secondary metabolites [1]. In our search for new metabolites from marine-derived mangrove endophytic fungi from the South China Sea, we have isolated many significant new bioactive metabolites [2–8]. This paper reports the isolation and characterization of a new polyketide, 2-(7′-hydroxyoxooctyl)-3-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzeneacetic acid ethyl ester (1), and three known compounds dothiorelone A (2), B (3), and C (4) from the mangrove endophytic fungus Phomopsis sp. ZSU-H76 isolated from the stem of the mangrove tree Excoecaria agallocha from Dong Zai, Hainan, China. Cytotoxic effects of compound 1 against HEp-2 cells and HepG2 cells were first measured.
The ethyl acetate extract of a fermentation broth of the fungus was repeatedly chromatographed on silica gel using gradient elution from petroleum to ethyl acetate to give compound 1 from the 15% ethyl acetate/petroleum fraction as a colorless oil. Compound 1 has molecular formula C19H28O6 as determined by HR-EIMS (m/z 352.1874 [M]+, calcd for C19H28O6, 352.1880) and NMR spectra (see Table 1), which is indicative of six degrees of unsaturation.

The IR spectrum (KBr) of compound 1 showed absorption bands for hydroxyl (3230 cm–1), conjugated carbonyl (1670 cm–1), ester carbonyl (1710 cm–1), and aromatic (1618, 1592, and 1445cm–1) functional groups. In the 1H NMR spectrum for 1, one D2O-exchangeable proton was observed downfield, which was shown to be a phenolic OH signal at δ 11.39 ppm. The presence of a 1,2,3,5-tetrasubstituted benzene ring was deduced from the following proton signals at δ 6.38 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz) and δ 6.36 (1H, d, J = 2.0 Hz). The remaining proton signals upfield were attributed to an aliphatic chain in 1. The 13C NMR and DEPT spectra indicated there were two methyl groups, one methoxy group, seven methylenes, three methines, and six quaternary carbons including one carbonyl carbon (δ 206.8) and an ester carbonyl carbon (δ 171.2). In the 1H–1H COSY spectrum of 1, the correlations of H-11′ and H-12′, H-2′ and H-3′, H-3′ and H-2′, H-4′, H-4′ and H-3′, H-5′, H-5′ and H-4′, H-6′, H-6′ and H-7′, H-7′ and H-6′, H-8′ showed the existence of two partial structures of C-11′–C-12′ and C-2′–C-3′–C-4′–C-5′–C-6′–C-7′–C-8′. The signals of δ 4.11 (2H, q, J = 7.2 Hz, H-11′) and δ 1.24 (3H, t, J = 7.2 Hz, H-12′) were attributed to an ethoxy group. The ethoxy group was linked to the carbonyl group at δ 171.2 (C-10′) by the HMBC correlations from H-11′ to C-10′ and C-12′.
The HMBC correlations from H-9′ to C-1, C-2, C-6, and C-10′ showed that the methylene of the sharp singlet at δ 3.60 (H-9′) was located between the carbonyl group (C-10′) and the benzene ring (C-1). Correlations in the HMBC spectrum, H-2′ to C-2, C-1′, C-3′, C-4′, suggested that C-2′ is connected to C-2 through one carbonyl group (C-1′). The methoxyl group (δ 3.80, δ 55.3) was placed at C-5 (δ 161.2) by the HMBC correlations. The HMBC correlations of the hydroxyl proton at δ 11.39 with C-2, C-3, and C-4 indicated that the hydroxyl group is located at C-3 (δ 158.7). Finally, the structure of compound 1 was determined to be 2-(7′-hydroxyoxooctyl)-3-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzeneacetic acid ethyl ester.
Furthermore, three known compounds, 2, 3, and 4, were identified as dothiorelone A, B, and C, respectively, by comparison of their spectroscopic data with the literature [9]. They were isolated for the first time from an endophytic fungus, Dothiorella sp. HTF3.
Primary bioassays showed that 1 exhibited weak cytotoxicity against HEp-2 and HepG2 cells with IC50 values of 25 and 30 μg/mL, respectively.
Experimental
NMR data were recorded on a Varian Inova-500 NB spectrometer using CDCl3 and acetone-d6 as solvent and TMS as internal standard. Mass spectra were acquired on a VG-ZAB mass spectrometer. IR spectra were obtained on a Nicolet 5DX-FTIR spectrophotometer, and UV spectra were measured on a Shimadzu UV-240 spectrophotometer. Column chromatography was carried out on silica gel (200–300 mesh; Qingdao haiyang chemicals).
Fungus Material and Culture Conditions. The fungus ZSU-H76 is an endophytic fungus, which was isolated from the stem of the mangrove tree E. agallocha. It is apospory and was identified as Phomopsis sp. by the DNA internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region. The nucleotide sequences obtained in this study have been submitting to GenBank and assigned accession numbers EU236702. Starter cultures were maintained on cornmeal seawater agar. Plugs of agar supporting mycelia growth were cut and transferred aseptically to a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 100 mL of liquid medium (glucose 10 g/L, peptone 2 g/L, yeast extract 1g/L, NaCl 30 g/L). The flask was incubated at 30°C on a rotary shaker for 5–7 days. The mycelium was aseptically transferred to 500 mL Erlenmeyer flasks containing culture liquid (200 mL).The flasks were then incubated at 30°C for 25 days.
Extraction and Separation of Metabolites. The cultures (80 L) were separated by filtration into the mycelium and the filtrate. The filtrate was concentrated to 3.5 L below 50°C and extracted five times by shaking with an equal volume of EtOAc. Collection and evaporation of EtOAc in vacuo yielded the EtOAc extract (40 g). The EtOAc extract were chromatographed on silica gel using gradient elution with petroleum ether–EtOAc (90:10 to 60:40) to give five fractions (A–E). Fraction B was purified by column chromatography on silica gel with petroleum ether–EtOAc (85:15) to give compound 1 (4 mg). Fraction C was purified by column chromatography on silica gel with petroleum ether–EtOAc (70:30) to give subfraction b. Subfraction b was separated by preparative TLC (petroleum ether–EtOAc, 50:50) to give compound 2 (3 mg), 3 (3.5 mg), and 4 (4.5 mg), respectively.
2-(7′-Hydroxyoxooctyl)-3-hydroxy-5-methoxybenzeneacetic Acid Ethyl Ester (1). Colorless oil. UV spectrum (CH3OH, λmax, nm) (logε): 240 (3.65), 276 (3.42), 298 (2.73). IR spectrum (KBr, ν, cm–1): 3230 (OH), 2930, 2856, 1710 (C=O), 1670 (C=O), 1618, 1592, 1445 (Ph), 1325, 1200, 1152, 1025. Mass spectrum (EI+, m/z, I rel, %): 352 (25) [M]+, 334 [M–H2O] (10), 237 (40), 223 (8), 210 (60), 209 (45), 181 (100), 164 (18). Mass spectrum (HR-EI+, m/z, I rel, %): 352.1874 (25.3) [M]+, (calcd 352.1880). 1H, 13C NMR see Table 1.
2-(7′-Hydroxyoxooctyl)-3,5-dihydroxybenzeneacetic Acid Ethyl Ester (2). Colorless oil. Mass spectrum (EI+, m/z, I rel, %): 338 (20) [M]+, 320 [M–H2O] (15), 277 (25), 223 (56), 195 (44), 167 (100), 150 (14). Mass spectrum (HR-EI+, m/z, I rel, %): 338.1717 (20) [M]+, (calcd 352.1723).
1H NMR (500MHz, acetone-d6, δ, ppm, J/Hz): 11.35 (OH), 9.74 (OH), 6.26 (1H, d, J = 2.2), 6.19 (1H, d, J = 2.2), 3.98 (2H, q, J = 7.2), 3.56 (1H, m), 3.53 (2H, s), 2.76 (2H, t, J = 6), 1.48 (2H, m), 1.25 (2H, m), 1.24 (2H, m), 1.20 (2H, m), 1.15 (3H, t, J = 7.2), 1.02 (3H, d, J = 5.3). 13C NMR (125 MHz, acetone-d6, δ, ppm): 206.2 (C), 171.1 (C), 159.5 (C), 157.5 (C), 135.2 (C), 120.0 (C), 110.3 (CH), 101.6 (CH), 65.8 (CH), 60.0 (CH2), 43.6 (CH2), 38.9 (CH2), 38.0 (CH2), 29.0 (CH2), 25.4 (CH2), 24.0 (CH2), 23.7 (CH3), 14.1 (CH3).
2-(6′-Hydroxyoxooctyl)-3,5-dihydroxybenzeneacetic Acid Ethyl Ester (3). Colorless oil. Mass spectrum (EI+, m/z, I rel, %): 338 (17) [M]+, 320 [M–H2O] (10), 277 (28), 223 (52), 195 (46), 167 (100), 150 (18). Mass spectrum (HR-EI+, m/z, I rel, %): 338.1719 (17) [M]+, (calcd 352.1723). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, δ, ppm, J/Hz): 11.47 (OH, br.s), 8.05 (OH, s), 6.27 (1H, s), 6.26 (1H, s), 4.19 (2H, q, J = 7.2), 3.78 (2H, s), 3.55 (1H, m), 2.86 (2H, t, J = 7.2), 1.46 (2H, m), 1.43 (2H, m), 1.26 (2H, m), 1.25 (2H, m), 1.24 (3H, t, J = 7.2), 0.94 (3H, t, J = 7.4). 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, δ, ppm): 206.6 (C), 171.2 (C), 163.7 (C), 160.5 (C), 136.6 (C), 116.9 (C), 112.7 (CH), 103.2 (CH), 73.1 (CH), 61.7 (CH2), 43.3 (CH2), 41.7 (CH2), 36.5 (CH2), 30.3 (CH2), 29.8 (CH2), 29.7 (CH3), 25.2 (CH2), 9.9 (CH3).
2-(8′-Hydroxyoxooctyl)-3,5-dihydroxybenzeneacetic Acid Ethyl Ester (4). Colorless oil. Mass spectrum (EI+, m/z, I rel, %): 338 (22) [M]+, 320 [M–H2O] (18), 277 (28), 223 (65), 195 (53), 167 (100), 150 (20). Mass spectrum (HR-EI+, m/z, I rel, %): 338.1718 (22) [M]+, (calcd 352.1723). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, δ, ppm, J/Hz): 12.06 (OH, br.s), 7.89 (OH, s), 6.32 (1H, d, J = 2.5), 6.28 (1H, d, J = 2.5), 4.17 (2H, q, J = 7.2), 3.82 (2H, s), 2.82 (2H, t, J = 7), 3.65 (2H, t, J = 6.5), 1.37 (2H, m), 1.35 (2H, m), 1.33 (2H, m), 1.28 (2H, m), 1.26 (2H, m), 1.25 (3H, t, J = 7.2). 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, δ, ppm): 206.0 (C), 171.3 (C), 164.6 (C), 160.4 (C), 136.8 (C), 112.5 (CH), 116.6 (C), 103.2 (CH), 63.1 (CH2), 61.4 (CH2), 43.3 (CH2), 41.8 (CH2), 29.8 (CH2), 29.0 (CH2), 32.7 (CH2), 25.5 (CH2), 24.9 (CH2), 14.1 (CH3).
Bioassays. The cytotoxic assays were performed using the MTT assay method [10]. Compound 1 exhibited weak cytotoxicity against HEp-2 and HepG2 cells with IC50 values of 25 and 30 μg/mL, respectively.
References
T. S. Bugni and C. M. Ireland, Nat. Prod. Rep., 21, 143 (2004).
G. Y. Chen, Y. C. Lin, L. Wen, L. L. P. Vrijmoed, and E. B. G. Jones, Tetrahedron, 59, 4907 (2003).
Y. C. Lin, H. J. Li, G. C. Jiang, S. N. Zhou, L. L. P. Vrijmoed, and E. B. G. Jones, Indian J. Chem., 41B, 1542 (2002).
Y. C. Lin, X. Y. Wu, Z. J. Deng, J. Wang, S. N. Zhou, L. L. P. Vrijmoed, and E. B. G. Jones, Phytochemistry, 59, 469 (2002).
Y. C. Lin, X. Y. Wu, S. Feng, G. C. Jiang, J. H. Luo, S. N. Zhou, L. L. P. Vrijmoed, E. B. G. Jones, K. Krohn, K. Steingroever, and F. Zsila, J. Org. Chem., 66, 6252 (2001).
Y. C. Lin, J. Wang, X. Y. Wu, S. N. Zhou, L. L. P. Vrijmoed, and E. B. G. Jones, Aust. J. Chem., 55, 225 (2002).
Y. C. Lin, X. Y. Wu, S. Feng, G. C. Jiang, J. H. Luo, S. N. Zhou, L. L. P. Vrijmoed, and E. B. G. Jones, Tetrahedron Lett., 42, 449 (2001).
Z. J. Huang, C. L. Shao, Y. G. Chen, Z. G. She, Y. C. Lin, and S. N. Zhou, Chem. Nat. Comp., 43, 655 (2007).
Q. Y. Xu, J. F. Wang, Y. J. Huang, and Z. H. Zheng, Acta Oceanol. Sin., 23, 541 (2004).
I. Camby, I. Salmon, A. Danguy, J. L. Pasteels, J. Brotchi, J. Martinez, and R. Kiss, J. Natl. Cancer. Inst., 88, 594 (1996).
Acknowledgment
The above research was made possible by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos. 20072058 and 20572136, the 863 Foundation of China Nos. 2003AA624010 and 2006AA09Z422, the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province No. 0832081, and the Science Foundation of Guangxi University for Nationalities No. 200702YJ18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 5, pp. 528–530, September–October, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Guo, Z., Yang, R. et al. Chemistry and cytotoxic activities of polyketides produced by the mangrove endophytic fungus Phomopsis SP. ZSU-H76. Chem Nat Compd 45, 625–628 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-009-9446-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-009-9446-3