Abstract
Cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9) is involved in metabolism of many important drugs and its genotype variations is thought to affect drug efficacy and the treatment process. The aim of this study was to assess the distribution of CYP2C9 allele and genotypic variants in Sistani ethnic group, living in Gorgan, South East of Caspian Sea and North East of Iran. This study included 140 Sistani, referred to the health center of Gorgan. CYP2C9 genotyping was carried out by polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism technique. The allele frequency of CYP2C9*1, CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 was 76.1, 16.1 and 7.8%, respectively. The frequency of CYP2C9*1/*1, CYP2C9*1/*2, CYP2C9*1/*3, CYP2C9*2/*2, CYP2C9*2/*3 and CYP2C9*3/*3 genotypes was 53.9, 22.1, 11.4, 2.9, 4.3% and nil, respectively. In this study the genotypic variations of the CYP2C9 allele among the Sistani ethnic group was investigated and great differences were observed in comparison to other populations. Our findings suggest that different genotypes of CYP2C9 may influence the pharmacokinetics of some drugs. More studies on the pharmacokinetic effects of CYP2C9 genotypes may help physicians choose optimal dosage of some drugs for treatment and prevention of their side effects. Since different ethnic groups from all over the world use medications, it suggests to investigate the pharmacokinetic effects of CYP2C9 genotypes in different populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Cytochrome P450 2C (CYP 2C) subfamily of enzymes metabolizes approximately 20–30% of most pharmaceutical drugs and CYP2C9 is known as its main isoform [1, 2]. This enzyme is encoded by a gene located on chromosome 10q24 which shows genetic polymorphism [3]. Variations during genetic polymorphism of this enzyme may change catalytic activity of the enzyme in drug response [3, 4]. The CYP2C9 allele frequencies vary among different populations and many studies on CYP2C9 polymorphism in different populations have shown a significant difference in the frequency of alleles and genotypes [5]. This may be the cause of possible ethnic differences in drug response. Variations in genotype of enzyme have shown that the effect of some genotype is the most acute with S-warfarin metabolism when compared to the wild type genotype. Clinical studies have also indicated that subjects with the mutated genotypes need 10–20 and/or 20–50% lower doses of S-warfarin, when compared to wild type subjects [5]. CYP2C9 is involved in the metabolism of important drugs such as (S)-warfarin, losartan, rosuvastatine, tolbutamide, glipizide, glibenclamide, the diuretic torsemide, phenytoin, flurbiprofen, ibuprofen and diclofenac [6, 7]. The mutated alleles of CYP2C9 are CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3, CYP2C9*6, CYP2C9*15, and CYP2C9*25, but CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 are the most prevalent variants [8, 9]. These alleles are also the most common variants in white populations (CYP2C9*2 = 0.08–0.14% and CYP2C9*3 = 0.04–0.16%) while, some studies indicated a significantly lower frequency of these alleles among Asian and African populations [10, 11]. Some studies have shown that the CYP2C9*2 allele is considered in European, Middle Eastern and Central and South Asian populations. This allele was absent or considered at very low frequencies in Africa, East Asia, Oceania and the Americas. The CYP2C9*3 allele is the highest allele frequencies in European and Central/South Asian populations [12]. Some other studies have revealed that the frequency of the CYP2C9*3 allele among Japanese and Taiwanese populations are 2.1 and 1.7%, respectively. Meanwhile, the CYP2C9*2 allele was not detected among the Han Chinese, Japanese and Taiwanese populations [13]. As mentioned earlier, these alleles may change the catalytic activity of CYP2C9 [6] and on the other hand, many studies have shown the variations among different ethnic groups. We have previously studied the genetic polymorphism of CYP2C9 gene among different ethnic groups in Golestan province [14, 15]. This study aimed to assess the distribution of CYP2C9 allele and its genotypic variants in Sistani ethnic group in the city of Gorgan, South East of Caspian Sea, and North East of Iran.
Results
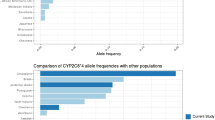
The distributions of the CYP2C9 alleles and genotype frequencies in Sistani ethnic groups are shown in Table 1. The allele frequency of CYP2C9*1, CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 were 76.10% (95% CI 71–81.20), 16.10% (95% CI 11.70–20.50) and 7.80% (95% CI 4.60–11), respectively (Table 1). Tables 2 and 3 demonstrate the differences in allele and genotype frequencies between the Sistani ethnic group and other populations using the Fisher exact test. Table 2 shows a significant difference in CYP2C9*1 allele of the Sistani ethnic group with Iranian Turkmen (88%) [18], Southern Iranians (64.88%) [19], Mongolian in China (97%) [21], Japenese (97.30%) [22], Russians (82.70%) [25], Macedonians (83.10 [27] %) and Mestizo in Mexicans (91%) [29] (Table 2). There were no significant differences in all allele’s frequencies between the Sistani and Saudi Arabian, Greek and Italian [20, 23, 24]. The results also showed that The genotype frequency of CYP2C9*1/*1, CYP2C9*1/*2 CYP2C9*1/*3, CYP2C9*2/*2, CYP2C9*2/*3 and CYP2C9*3/*3 were 59.30% (95% CI 51–67.60), 22.10% (95% CI 115.10–29.10), 11.40% (95% CI 6.0–16.80), 2.90% (95% CI 0.10–5.70), 4.30% (95% CI 0.9–7.70) and 0% (95% CI 0), respectively (Table 1).
Table 3 is shown that the prevalence of CYP2C9*1/*1 among Sistanee (59.30%) ethnic group was higher when compared with Southern Iran (41.21%) [19], but it lower in comparison with IranianTurkman (76.36%) [18], Mongolian in China (93%) [21], Japanese (94.70%) [22], Macedonians (79.80%) [27], and Mestizo Mexicicans (83%) [29]. The most frequently observed mutant allele was CYP2C9*1/*2 allele (22.10%). Our results showed that CYP2C9*1/*3 genotype (11.4%) was higher in the Sistani ethnic group compared to the Japanese (5.3%) [22], Macedonians (0%) [27] and Mestizo Mexicans (6.8%) [29] (Table 3).
The prevalence of CYP2C9*2/*2 genotype (2.90%) was higher than Mongolians in China (0%) [21], Japanese (0%) [22], Southern Europe (0.60%) and Mestizo Mexicans (0.40%) [29].The prevalence of CYP2C9*2/*3 genotype (4.30%) was higher than Mongolians in China (0%) [21], Japanese (0%) [22], Hungarians (1.50%) [26] and Mestizo Mexicans (0.70%) [29] (Table 3).
Methods
This study involved 140 healthy Sistani (people who speak Sistani as native language) who were referred to a health center in Gorgan (South East of Caspian Sea, North East of Iran). The sample size was determined under supervision of statistical expert. This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Research Deputy of Golestan University of Medical Sciences. Written consent was obtained from all the study subjects. The distribution of CYP2C9 allele and its genotypic variants in Sistani ethnic group were determined and compared with other populations. First, 5 ml of blood was obtained from all the subjects into EDTA tubes. Peripheral white blood cells were used for DNA extraction by salting-out method [16].
Two times distillated water was used to dissolve the extracted DNA. Collected samples were stored at −20 °C. CYP2C9*1, CYP2C9*2, and CYP2C9*3 alleles genotyping were performed by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) technique using Genetix CG palm-thermocycler (India) [17]. The PCR was done in a 25 μl reaction mixture including: PCR buffer (10 mM Tris–HCl, pH 9, 2 mM MgCl2 (Fermentas), 50 mM KCl (Fermentas), 0.2 mM deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate (dNTP) mix, 1 U/μl Taq polymerase (Fermentas), 0.4 μM of each primer (Bioneer), 100 ng DNA (Genomic) and two times distillated water. Digestion of PCR products (10 μl) was performed using restriction enzymes (Fermentas), Ava II for CYP2C9*2 and Kpn I for CYP2C9*3 at 37 °C for 16 h. Primer amplification was done using the method explained previously by Aithal et al. [18].
The PCR amplification conditions for CYP2C9*2 included: Initial denaturation (95 °C, 10 min), number of cycle (45 cycles at 95 °C for 5 s), denaturation (67 °C, 10 s), annealing (72 °C, 15 s), extension and final extension (72 °C, 5 min). The parameters for CYP2C9*3 were 94 °C, 5 min.; 33; 94 °C, 45 s.; 66 °C, 45 s.; 72 °C, 60 s and 72 °C, 5 min, respectively.
Figure 1a, b show the PCR products before and after digestion with the restriction enzyme for CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 genotypes. Agarose gel (3%) was used to perform electrophoresis of (Apelex, France) CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 DNA fragments. The gel was stained with ethidium bromide, and a Polaroid Gel Camera with black and white film was used to detect the bands. Detection of CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 mutations were done using sense and antisense primers as described below:
For CYP2C9*2 detection:
-
Sense primer: 3′-CAC TGG CTG AAA GAGS CTA ACA GAG-5′
-
Antisense primer: 3′-GTG ATA TGG AGT AGG GTC ACC CAC-5′
For CYP2C9*3 detection:
-
Sense primer: 5′-AATTACAACCAGAGCTTGGC-3′
-
Antisense primer: 5′-TATCACTTTCCATAAAAGCAAG-3′
Chi squared test was carried out to determine and compare the allele and genotype frequencies of CYP2C9. The frequency of alleles variant was determined using 95% confidence intervals (95% CI). Fisher exact test was used to compare the variations of allele and genotype frequencies between Sistani ethnic group and other populations. The analysis of data was done using SPSS version 16.0 and p value of less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Discussion
Genotype identification is the most important challenges in the future. There are different ethnic groups in various areas of Iran. Many drugs are metabolized by the cytochrome P450 2C9 enzyme [7, 19]. Decreased metabolism of some drugs may be associated with the presence of CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 alleles [20,21,22,23,24]. Alteration in CYP 2C9 genetic polymorphism may affect drug response and enzyme activity. The results of this study showed CYP2C9*1 as the most prevalent allele in the Sistani ethnic group (76.1%).
Table 3 shows significant differences in the frequencies of CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 allelic variants between different populations. The prevalence of CYP2C9*2 in Southern Iranian [25] was higher compared with the Sistanis, but the prevalence of CYP2C9*2 in the Sistani ethnic group was higher than other ethnic groups [21, 22, 25, 27,28,29]. The prevalence of CYP2C9*3 polymorphism in Sistanis (7.8%) was higher than other populations [21, 22, 29]. Studies have shown that the CYP2C9*3 and CYP2C9*2 alleles are responsible for reduction in metabolic activity when compared with CYP2C9*1 [1]. Metabolism of some drugs such as glibenclamide and glimepiride may affect by different genetic polymorphisms of CYP2C9 [37]. Studies have also shown that metabolism of glibenclamide in heterozygous and homozygotes subjects with the CYP2C9*3 allele, was decreased 2.8 and 0.5 folding in comparison to the wild-type genotypes, respectively [1, 30]. Comparison of different genotypes in various populations may affect drug metabolism [31]. Some other studies on glipizide have revealed that homozygotes subjects with the CYP2C9*3 allele may be involved in complications of hypoglycemia [38]. The prevalence of CYP2C9*1/*1 in the Sistani ethnic group was higher than Southern Iranian (41.21%) [19] and lower than Iranian Turkmen (76.36%), Mongolian in China (93%), Japanese (94.70%), Macedonian (79.80%) and Mestizo Mexican (83%) [21, 22, 29].The prevalence of CYP2C9*1/*2 genotype was lower [19] and higher [21, 22, 29] in comparison with other ethnic groups. Our results show that CYP2C9*1/*3 genotype was higher [22, 27, 29] than other populations. The prevalence of CYP2C9*2/*2 [21, 22, 28, 29] and CYP2C9*2/*3 [21, 22, 26, 27, 29] genotypes were higher than different other populations.
In our study, the prevalence of CYP2C9*3/*3 genotype (0%) showed no significant differences with other populations. Numerous studies have demonstrated that frequency of CYP2C9*3/*3 genotype is either very low or undetectable [19, 23, 25, 32,33,34,35,36,37]. Variation of CYP2C9*3/*3 genotype may affect drug effectiveness in some ethnic group. Genetic polymorphisms, especially the homozygous with CYP2C9*3 allele, can lead to a significant impairment in metabolic activity of CYP2C9 in different ethnic groups.
Conclusion
In this study the genotypic variations of the CYP2C9 allele among the Sistani ethnic group was investigated and great differences were observed in comparison to other populations. Our findings suggest that different genotypes of CYP2C9 may influence the pharmacokinetics of some drugs. More studies on the pharmacokinetic effects of CYP2C9 genotypes may help physicians choose optimal dosage of some drugs for treatment and prevention of their side effects. Since different ethnic groups from all over the world use medications, it suggests to investigate the pharmacokinetic effects of CYP2C9 genotypes in different populations.
References
Lee CR, Goldstein JA, Pieper JA. Cytochrome P450 2C9 polymorphisms: a comprehensive review of the in vitro and human data. Pharmacogenetics. 2002;12:251–63.
Goldstein JA, de Morais SM. Biochemistry and molecular biology of the human CYP2C subfamily. Pharmacogenetics. 1994;4:285–99.
Goldstein JA. Clinical relevance of genetic polymorphisms in the human CYP2C subfamily. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2001;52:349–55.
Garcıá-Martıń E, Martıńez C, Ladero JM, Aguńdez JA. Interethnic and intraethnic variability of CYP2C8 and CYP2C9 polymorphisms in healthy individuals. Mol Diagn Ther. 2006;10(1):29–40.
Sanderson S, Emery J, Higgins J. CYP2C9 gene variants, drug dose, and bleeding risk in warfarin-treated patients: a HuGEnet systematic review and meta-analysis. Genet Med. 2005;7:97–104.
Miners J, Birkett D. Cytochrome P4502C9: an enzyme of major importance in human drug metabolism. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998;45:525–38.
Zanger U, Turpeinen M, Klein K, Schwab M. Functional pharmacogenetics/genomics of human cytochromes P450 involved in drug biotransformation. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008;392:1093–108.
Burian M, Grösch S, Tegeder I, Geisslinger G. Validation of a new fluorogenic real-time PCR assay for detection of CYP2C9 allelic variants and CYP2C9 allelic distribution in a German population. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002;54:518–21.
Veenstra DL, Blough DK, Higashi MK, Farin FM, Srinouanprachan S, Rieder MJ, et al. CYP2C9 haplotype structure in European American warfarin patients and association with clinical outcomes. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;77:353–64.
Van Booven D, Marsh S, McLeod H, Carrillo MW, Sangkuhl K, Klein TE, et al. Cytochrome P450 2C9-CYP2C9. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2010;20:277–81.
Kurose K, Sugiyama E, Saito Y. Population differences in major functional polymorphisms of pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics-related genes in Eastern Asians and Europeans: implications in the clinical trials for novel drug development. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2012;27:9–54.
Ross KA, Bigham AW, Edwards M, Gozdzik A, Suarez-Kurtz G, Parra EJ. World allele frequency distribution of four polymorphisms associated with warfarin dose requirements. J Hum Genet. 2010;55:582–9.
Obayashi K, Nakamura K, Kawana J, Ogata H, Hanada K, Kurabayashi M, et al. VKORC1 gene variations are the major contributors of variation in warfarin dose in Japanese patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2006;80:169–78.
Ghiyas Tabari M, Naseri F, Agh Ataby M, Marjani A. Genetic polymorphism of cytochrome p450 (2C9) enzyme in Iranian Baluch Ethnic Group. Open Biochem J. 2015;9:37–41.
Agh Ataby O, Ghiyas Tabari R, Mansourian AR, Mansour Samai N, Marjani A. Genetic polymorphism of cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9) in two ethnic groups in Iran. Am J Biomed Sci. 2013;5(3):177–87.
Chang M, Dahl M-L, Tybring G, Gotharson E, Bertilsson L. Use of omeprazole as a probe drug for CYP2C19 phenotype in Swedish Caucasians: comparison with S-mephenytoin hydroxylation phenotype and CYP2C19 genotype. Pharmacogenetics. 1995;5:358–63.
Brosen K, de Morais SMF, Meyer UA, Goldstein JA. A multifamily study on the relationship between CYP2C19 genotype and S-mephenytoin oxidation phenotype. Pharmacogenetics. 1995;5:312–7.
Aithal GP, Day CP, Kesteven PJ, Daly AK. Association of polymorphisms in the cytochrome P450 CYP2C9 with warfarin dose requirement and risk of bleeding complications. Lancet. 1999;353:717–9.
Azarpira N, Namazi S, Hendijani F, Banan M, Darai M. Investigation of allele and genotype frequencies of CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and VKORC1 in Iran. Pharmacol Rep. 2010;62(4):740–6.
Mirghani RA, Chowdhary G, Elghazali G. Distribution of the major cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C9 genetic variants in a Saudi population. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2011;109(2):111–4.
Yang Z, Cui H, Hasi T, Jia S, Gong M, Su X. Genetic polymorphisms of cytochrome P450 enzymes 2C9 and 2C19 in a healthy Mongolian population in China. Genet Mol Res. 2010;9(3):1844–51.
Ota T, Kamada Y, Hayashida M, Iwao-Koizumi K, Murata S, Kinoshita K. Combination analysis in genetic polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing enzymes CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A5 in the Japanese population. Int J Med Sci. 2015;12(1):78.
Arvanitidis K, Ragia G, Iordanidou M, Kyriaki S, Tavridou A, Manolopoulos VG. Genetic polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing enzymes CYP2D6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP3A5 in the Greek population. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2007;21(4):419–26.
Scordo MG, Caputi AP, D’Arrigo C, Fava G, Spina E. Allele and genotype frequencies of CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 in an Italian population. Pharmacol Res. 2004;50(2):195–200.
Gaikovitch EA, Cascorbi I, Mrozikiewicz PM, Brockmöller J, Frötschl R, Köpke K, et al. Polymorphisms of drug-metabolizing enzymes CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP1A1, NAT2 and of P-glycoprotein in a Russian population. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2003;59(4):303–12.
Sipeky C, Lakner L, Szabo M, Takacs I, Tamasi V, Polgar N, et al. Interethnic differences of CYP2C9 alleles in healthy Hungarian and Roma population samples: relationship to worldwide allelic frequencies. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2009;43(3):239–42.
Jakjovski K, Labachevski N, Petlichkovski A, Senev A, Trojacanec J, Atanasovska E, et al. Distribution of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 gene polymorphisms in healthy Macedonian male population. Maced J Med Sci. 2013;6(4):339–43.
Buzoianu AD, Trifa AP, Mureşanu DF, Crişan S. Analysis of CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3 and VKORC1-1639 G>A polymorphisms in a population from South-Eastern Europe. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16(12):2919–24.
Castelán-Martínez OD, Hoyo-Vadillo C, Sandoval-García E, Sandoval-Ramírez L, González-Ibarra M, Solano-Solano G, et al. Allele frequency distribution of CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 polymorphisms in six Mexican populations. Gene. 2013;523(2):167–72.
Niemi M, Cascorbi I, Timm R, Kroemer HK, Neuvonen PJ, Kivisto KT. Glyburide and glimepiride pharmacokinetics in subjects with different CYP2C9 genotypes. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002;72:326–32.
Kirchheiner J, Brockmoller J, Meineke I, Bauer S, Rohde W, Meisel C, et al. Impact of CYP2C9 amino acid polymorphisms on glyburide kinetics and on the insulin and glucose response in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2002;71:286–96.
Yasar U, Eliasson E, Dahl ML, Johansson I, Ingelman- Sundberg M, Sjöqvist F. Validation of methods for CYP2C9 genotyping: frequencies of mutant alleles in a Swedish population. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;254:628–31.
Herman D, Dolzan V, Breskvar K. Genetic polymorphism of cytochromes P450 2C9 and 2C19 in Slovenian population. ZDRAV VESTN. 2003;72:347–51.
Sconce EA, Khan TI, Wynne HA, Avery P, Monkhouse L, King BP, et al. The impact of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genetic polymorphism and patient characteristics upon warfarin dose requirements: proposal for a new dosing regimen. Blood. 2005;106:2329–33.
Hamdy SI, Hiratsuka M, Narahara K, El-Enany M, Moursi N, Ahmed MS, et al. Allele and genotype frequencies of polymorphic cytochromes P450 (CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2E1) and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPYD) in the Egyptian population. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002;53:596–603.
Isaza C, Henao J, Martínez JH, Arias JC, Beltrán L. Phenotype-genotype analysis of CYP2C19 in Colombian mestizo individuals. BMC Clin Pharmacol. 2007;7:6.
Zand N, Tajik N, Moghaddam AS, Milanian I. Genetic polymorphisms of cytochrome P450 enzymes 2C9 and 2C19 in a healthy Iranian population. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007;34:102–5.
Kidd RS, Straughn AB, Meyer MC, Blaisdell J, Goldstein JA, Dalton JT. Pharmacokinetics of chlorpheniramine, phenytoin, glipizide and nifedipine in an individual homozygous for the CYP2C9*3 allele. Pharmacogenetics. 1999;9(1):71–80.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Research Deputy of Golestan University of Medical Sciences for financial support. This research project was derived from research proposal in Clinical Biochemistry. The corresponding author wishes to thank Mr. Aman Mohammad Gharanjik for his sincere help.
Funding
This work has been supported by the Research Deputy of Golestan University of Medical Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marjani, A., Gharanjik, A.M. Genetic Polymorphism of CYP2C9 Among Sistani Ethnic Group in Gorgan. Ind J Clin Biochem 33, 208–213 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-017-0660-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-017-0660-7