Abstract
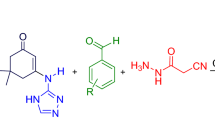
A one-pot, multi-component protocol for the synthesis of a new class of functionalized quinoline carbohydrazide derivatives via reaction of various anilines, dimedone, aromatic aldehydes, and cyanoacetohydrazide is described. The reactions are completed in the presence of catalytic amount of piperidine, respectively, in melt conditions and then in ethanol/water (1:1) as green solvent at 80 °C. Mild conditions, green medium, short reaction times, simple workup and purification process with no chromatographic technique, and good yields are the main advantages of this method.
Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Multi-component reactions (MCRs) and their improvement are of considerable interest in the current research projects [1]. They have been extensively used in the total synthesis of natural products, as well as the design and discovery of biologically active molecules and various heterocyclic compounds [2].
For more than a century, heterocycles have constituted one of the largest areas of researches in organic chemistry [3,4,5]. Among the heterocycles, N-containing heterocycles represent a highly important class of compounds which are widely used in materials science, agrochemistry, and medicinal chemistry [6]. Therefore, N-containing heterocycles are especially considered “privileged” structures for the synthesis and development of new drugs [7]. Enaminones and related compounds are versatile synthetic intermediates in organic chemistry that combine the ambient nucleophilicity of enamine and the electrophilicity of enones [8]. They are widely used for the synthesis of a variety of heterocycles especially N-heterocyclic compounds in the past several years [9,10,11,12,13,14].
Quinoline is one of the most popular N-heterocyclic compounds incorporated into the structures of many pharmaceuticals [15]. The biological activity of quinoline compounds has been found in the form of antitumor [9, 16], antimalarial, antibacterial, antiplasmodial, antiproliferative, anticancer [10, 13], antiasthmatic, antihypertensive and anti-inflammatory [17] properties. Therefore, the synthesis of quinoline and its derivatives has been of great interest in organic and medicinal chemistry [18, 19].
In continuation of our research interests regarding the development of new methods in heterocyclic synthesis [20,21,22,23], herein we report an efficient synthesis of functionalized quinoline carbohydrazide derivatives through a multi-component reaction of various anilines, dimedone, aromatic aldehydes, and cyanoacetohydrazide, respectively, in melt conditions and then in EtOH/H2O (1:1) as a green medium at 80 °C. To the best of our knowledge, there are no reports on the synthesis of these compounds in the literature.
Results and discussion
The one-pot, multi-component reactions of enaminones derived from the addition of various anilines 1 to dimedone 2 under solvent-free conditions at 80 °C, with aromatic aldehydes 3 and cyanoacetohydrazide 4 in the presence of catalytic amount of piperidine, in EtOH/H2O (1:1) as a green solvent at 80 °C, led to the corresponding quinoline carbohydrazide derivatives 5a-k, in good yields (Scheme 1).
We explored the scope of this reaction by varying the structure of the aromatic aldehyde and aniline components. The reaction proceeded very cleanly under the same reaction conditions to afford a series of functionalized quinoline carbohydrazide derivatives 5a–k in 68–83% yields. The reaction proceeds with good yields when ethanol/water (1:1) was used as the solvent at reflux. The product 5 was insoluble in ethanol/water (1:1), so easily be purified by filtration and washing with ethanol/water, and column chromatography was unnecessary. Product 5 was soluble in pure ethanol, so workup and purification was a complicated and time-consuming process. Also due to the lack of solubility of starting materials in water, the reaction was not complete in pure water. In the absence of a catalyst, the reaction did not yield any product even after long reaction times. The results are shown in Table 1.
The structures of compounds 5a–k (Table 1) were confirmed by IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and mass spectra. The IR spectrum of 5a exhibited absorption bands due to NH2 and NH groups (3449, 3385 and 3287 cm−1) and absorption bands due to C=O group (1638 cm−1), and as well as 1489 and 1265 cm−1 due to the Ar and C–N groups.
1H NMR spectrum (CDCl3) of 5a revealed two singlets for the NH2 (amine) and NH (amide) groups (δ 6.84, 8.69 ppm, respectively), two singlets for the methine and imine protons (δ 5.06, 7.73 ppm, respectively), two singlets for two CH3 groups (δ 0.68, 0.94 ppm), characteristic multiplets for two CH2 groups (δ 2.01–2.25 ppm), and multiplets for the aromatic region (δ 7.21–7.57 ppm) which completely in accord with the assigned structure. The 1H-decoupled 13C NMR spectrum (CDCl3) of 5a showed 25 distinct resonances which were consistent with the proposed structure.
The EI-MS of 5a displayed the molecular ion peak at m/z 682, which was in agreement with the proposed structure.
A plausible mechanism for the formation of product 5 is shown in Scheme 2. It is reasonable to assume that the reaction involves the initial formation of enaminone intermediate 6 between the aniline 1 and dimedone 2. Apparently, the condensation of cyanoacetohydrazide 4 with aromatic aldehyde 3 furnishes adduct 7. Intermediate 6 is activated by piperidine for the next addition reaction with aromatic aldehyde 3 to afford 9. Then, Michael addition reaction between intermediate 9 and adduct 7 affords 10 which undergoes cyclization by nucleophilic addition of the secondary amino group to cyano group, followed by successive imine-enamine tautomerization led to the formation of product 5.
Conclusion
In summary, we have developed an efficient, one-pot, multi-component approach to the synthesis of functionalized quinoline carbohydrazide derivatives based on the reaction of enaminones derived from the addition of various anilines to dimedone under solvent-free conditions at 80 °C, with aromatic aldehydes and cyanoacetohydrazide in the presence of catalytic amount of piperidine, in EtOH/H2O (1:1) at 80 °C. The significant features of this method are green methodology, easy workup, readily available starting materials, high atom economy, short reaction times, compatibility with various functional groups, and good product yields.
Experimental section
General remarks
The dimedone, various anilines, aromatic aldehydes, cyanoacetohydrazide, piperidine, and other chemicals and solvents were obtained from Merck and Aldrich and were used without further purification. NMR spectra were recorded with a Bruker DRX-300 Avance instrument (300 MHz for 1H and 75.4 MHz for 13C) with CDCl3 and DMSO as solvent. Chemical shifts are given in ppm (δ), and coupling constant (J) is reported in hertz (Hz). Melting points were measured with an electrothermal 9100 apparatus. Mass spectra were recorded with an Agilent 5975C VL MSD with Triple-Axis Detector operating at an ionization potential of 70 eV. IR spectra were measured with Bruker Tensor 27 spectrometer. Elemental analyses for C, H and N were performed using a PerkinElmer 2004 series [II] CHN elemental analyzer.
General procedure for the synthesis of product 5
A mixture of aniline 1 (1 mmol) and dimedone 2 (1 mmol, 0.140 g) was melted at 80 °C for 15 min. Then, ethanol/water (1:1, 5 mL) and one-drop piperidine were added, and the solution was stirred for 5 min at 80 °C. Next, aromatic aldehyde 3 (2 mmol) and cyanoacetohydrazide 4 (1 mmol, 0.099 g) were added and the solution was stirred at 80 °C for the time given in Table 1. Upon completion as monitored by TLC, the reaction mixture was allowed to cool to room temperature, and the precipitates were filtered and washed with ethanol/water (1:1) to give product 5 in good yields.
(31E) - N′ - (4 - bromobenzylidene) - 2 - amino - 4 - (4 - bromophenyl) - 1 - (4 - chlorophenyl) - 1,4,5,6,7,8 - hexahydro - 7,7 - dimethyl - 5 - oxoquinoline - 3 - carbohydrazide (5a, C 31 H 27 Br 2 ClN 4 O 2 )
Yellow solid: M.p.: 212–214 °C, yield: 0.518 g (76%); IR (KBr) (νmax/cm−1): 3449, 3385, 3287 (NH2, NH), 1638 (C=O), 1562 (C=O), 1489 (Ar), 1265 (C–N); MS (EI, 70 eV): m/z (%) = 682 (M+, 0.03), 623 (6), 458 (68): 431 (18), 301 (26), 198 (28), 168 (31), 127 (20), 89 (100), 63 (25); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 0.68 (3H, s, CH3), 0.94 (3H, s, CH3), 2.01–2.25 (4H, m, 2CH2), 5.06 (1H, s, CH), 6.84 (2H, s, NH2), 7.21–7.57 (12H, m, Ar), 7.73 (1H, s, CH), 8.69 (1H, s, NH); 13C NMR (75.4 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 26.3 (CH3), 29.7 (CH3), 32.2 (C(CH3)2), 33.4 (CH), 41.8 (CH2), 49.9 (CH2), 79.0, 114.5, 120.6, 123.9, 128.7, 129.0, 130.9, 131.3, 131.7, 131.9, 132.9, 134.4, 136.5, 143.5, 144.4, 149.1, 152.2, 165.8 (C=O), 195.8 (C=O); Anal. Calc. for C31H27Br2ClN4O2 (682.83): C, 54.53; H, 3.99, N, 8.21. Found: C, 54.9; H, 3.5; N, 7.9.
(31E) - N′ - (4 - chlorobenzylidene) - 2 - amino - 1,4 - bis(4 - chlorophenyl) - 1,4,5,6,7,8 - hexahydro - 7,7 - dimethyl - 5 - oxoquinoline - 3 - carbohydrazide (5b, C 31 H 27 Cl 3 N 4 O 2 )
Yellow solid: M.p.: 234–236 °C, yield: 0.439 g (74%); IR (KBr) (νmax/cm−1): 3432, 3282 (NH2, NH), 1646 (C=O), 1592 (C=O), 1487 (Ar), 1266 (C–N); MS (EI, 70 eV): m/z (%) = 593 (M+, 0.08), 535 (8), 438 (15), 412 (46), 370 (3), 301 (13), 276 (44), 249 (22), 185 (47), 165 (100), 138 (47), 111 (59), 89 (58), 63 (15); 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO): δ = 0.68 (3H, s, CH3), 0.99 (3H, s, CH3), 1.55–2.25 (4H, m, 2CH2), 5.30 (1H, s, CH), 7.28 (4H, d, 3JHH = 7.8 Hz, Ar), 7.34 (2H, s, NH2), 7.42 (4H, d, 3JHH = 8.4 Hz, Ar), 7.58 (2H, d, 3JHH = 7.8 Hz, Ar), 7.64 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.1 Hz, Ar), 8.29 (1H, s, CH), 10.70 (1H, s, NH); 13C NMR (75.4 MHz, DMSO): δ = 26.1 (CH3), 29.7 (CH3), 32.3 (C(CH3)2), 32.4 (CH), 41.4 (CH2), 49.9 (CH2), 79.7, 114.0, 116.1, 128.4, 128.5, 129.2, 129.4, 130.7, 132.5, 133.9, 134.4, 134.7, 135.5, 142.9, 146.9, 150.3, 152.7, 166.4 (C=O), 195.2 (C=O); Anal. Calc. for C31H27Cl3N4O2 (593.9): C, 62.69; H, 4.58, N, 9.43. Found: C, 63.1; H, 4.9; N, 9.0.
(30E) - N′ - (3 - methoxybenzylidene) - 2 - amino - 1 - (4 - chlorophenyl) - 1,4,5,6,7,8 - hexahydro - 4 - (3 - methoxyphenyl) - 7,7 - dimethyl - 5 - oxoquinoline - 3 - carbohydrazide (5c, C 33 H 33 ClN 4 O 4 )
Yellow solid: M.p.: 200–202 °C, yield: 0.397 g (68%); IR (KBr) (νmax/cm−1): 3414, 3345, 3241 (NH2, NH), 1624 (C=O), 1479 (Ar), 1267 (C–N); MS (EI, 70 eV): m/z (%) = 585 (M+, 0.03), 525 (8), 408 (20), 366 (6), 249 (54), 221 (12), 193 (100), 161 (38), 121 (35), 92 (19), 89 (10), 68 (43), 63 (7); 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO): δ = 0.64 (3H, s, CH3), 0.89 (3H, s, CH3), 1.58–2.26 (4H, m, 2CH2), 3.67 (3H, s, OCH3), 3.75 (3H, s, OCH3), 5.28 (1H, s, CH), 6.64–7.67 (14H, m, Ar and NH2), 8.30 (1H, s, CH), 10.65 (1H, s, NH); 13C NMR (75.4 MHz, DMSO): δ = 26.1 (CH3), 28.5 (CH3), 32.9 (C(CH3)2), 33.4 (CH), 41.5 (CH2), 50.0 (CH2), 55.2 (OCH3), 55.5 (OCH3), 80.2, 97.6, 110.8, 111.1, 114.3, 119.8, 120.1, 124.7, 129.5, 130.7, 132.4, 135.7, 137.0, 138.6 144.0, 149.6, 150.1, 152.5, 159.3, 159.9, 160.1, 166.4 (C=O), 195.8 (C=O); Anal. Calc. for C33H33ClN4O4 (585.09): C, 67.74; H, 5.68, N, 9.58. Found: C, 67.3; H, 5.9; N, 9.2.
(30E) - N′ - (4 - nitrobenzylidene) - 2 - amino - 1 - (4 - chlorophenyl) - 1,4,5,6,7,8 - hexahydro - 7,7 - dimethyl - 4 - (4 - nitrophenyl) - 5 - oxoquinoline - 3 - carbohydrazide (5d, C 31 H 27 ClN 6 O 6 )
Yellow solid: M.p.: 210–212 °C, yield: 0.498 g (81%); IR (KBr) (νmax/cm−1): 3464, 3386, 3247 (NH2, NH), 1639 (C=O), 1562 (C=O), 1513 (Ar), 1265 (C–N); MS (EI, 70 eV): m/z (%) = 615 (M+, 0.01), 298 (50), 251 (22), 176 (100), 130 (28), 76 (27); 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO): δ = 0.62 (3H, s, CH3), 0.87 (3H, s, CH3), 1.59–2.34 (4H, m, 2CH2), 5.50 (1H, s, CH), 7.48–7.82 (10H, m, Ar and NH2), 8.13 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.7 Hz, Ar), 8.22 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.7 Hz, Ar), 8.41 (1H, s, CH), 11.05 (1H, s, NH); 13C NMR (75.4 MHz, DMSO): δ = 26.1 (CH3), 29.7 (CH3), 32.3 (C(CH3)2), 33.4 (CH), 41.5 (CH2), 49.8 (CH2), 79.0, 113.3, 123.9, 124.4, 127.7, 128.8, 130.7, 132.5, 134.9, 135.3, 141.6, 142.0, 146.1, 147.6, 150.9, 153.3, 155.6, 166.3 (C=O), 195.2 (C=O); Anal. Calc. for C31H27ClN6O6 (615.04): C, 60.54; H, 4.42, N, 13.66. Found: C, 60.8; H, 4.0; N, 13.5.
(30E) - N′ - (4 - chlorobenzylidene) - 2 - amino - 1 - (4 - bromophenyl) - 4 - (4 - chlorophenyl) - 1,4,5,6,7,8 - hexahydro - 7,7 - dimethyl - 5 - oxoquinoline - 3 - carbohydrazide (5e, C 31 H 27 BrCl 2 N 4 O 2 )
Yellow solid: M.p.: 200–202 °C, yield: 0.478 g (75%); IR (KBr) (νmax/cm−1): 3452, 3380, 3219 (NH2, NH), 1636 (C=O), 1562 (C=O), 1488 (Ar), 1266 (C–N); MS (EI, 70 eV): m/z (%) = 638 (M+, 0.06), 587 (16), 458 (100), 431 (27), 368 (27), 264 (56), 226 (44), 154 (32), 124 (55), 89 (80), 57 (38); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 0.68 (3H, s, CH3), 0.95 (3H, s, CH3), 2.01–2.32 (4H, m, 2CH2), 5.06 (1H, s, CH), 6.85 (2H, s, NH2), 7.17 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.1 Hz, Ar), 7.26–7.32(4H, m, Ar), 7.42 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.1 Hz, Ar), 7.61 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.7 Hz, Ar), 7.72 (1H, s, CH), 7.73 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.4 Hz, Ar), 8.59 (1H, s, NH); 13C NMR (75.4 MHz, DMSO): δ = 26.1 (CH3), 29.8 (CH3), 32.3 (C(CH3)2), 33.5 (CH), 41.4 (CH2), 50.0 (CH2), 79.6, 114.0, 123.4, 128.4, 128.5, 129.2, 129.4, 130.6, 132.8, 133.6, 133.9, 134.5, 136.0, 142.8, 146.9, 150.2, 152.6, 166.4 (C=O), 195.2 (C=O); Anal. Calc. for C31H27BrCl2N4O2 (638.38): C, 58.32; H, 4.26, N, 8.78. Found: C, 58.8; H, 4.6; N, 8.5.
(30E) - N′ - (4 - nitrobenzylidene) - 2 - amino - 1 - (4 - bromophenyl) - 1,4,5,6,7,8 - hexahydro - 7,7 - dimethyl - 4 - (4 - nitrophenyl) - 5 - oxoquinoline - 3 - carbohydrazide (5f, C 31 H 27 BrN 6 O 6 )
Yellow solid: M.p.: 217–219 °C, yield: 0.547 g (83%); IR (KBr) (νmax/cm−1): 3462, 3385, 3251 (NH2, NH), 1637 (C=O), 1560 (C=O), 1513 (Ar), 1264 (C–N); MS (EI, 70 eV): m/z (%) = 659 (M+, 0.93), 587 (9), 368 (13), 298 (47), 264 (25), 236 (19), 178 (100), 130 (31), 103 (26), 76 (39), 43 (27); 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO): δ = 0.62 (3H, s, CH3), 0.87 (3H, s, CH3), 1.59–2.29 (4H, m, 2CH2), 5.50 (1H, s, CH), 7.43 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.4 Hz, Ar), 7.52 (2H, s, NH2), 7.68 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.7 Hz, Ar), 7.78–7.82 (4H, m, Ar), 8.14 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.7 Hz, Ar), 8.22 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.7 Hz, Ar), 8.41 (1H, s, CH), 11.06 (1H, s, NH); 13C NMR (75.4 MHz, DMSO): δ = 26.1 (CH3), 29.7 (CH3), 32.3 (C(CH3)2), 33.1 (CH), 41.5 (CH2), 49.9 (CH2), 79.0, 113.3, 123.6, 123.9, 124.5, 127.7, 128.8, 132.8, 133.7, 135.7, 141.6, 142.0, 146.1, 147.6, 150.8, 153.2, 155.5, 166.3 (C=O), 195.2 (C=O); Anal. Calc. for C31H27BrN6O6 (659.49): C, 56.46; H, 4.13, N, 12.74. Found: C, 56.9; H, 4.5; N, 12.3.
(30E) - N′ - (4 - bromobenzylidene) - 2 - amino - 1,4 - bis(4 - bromophenyl) - 1,4,5,6,7,8 - hexahydro - 7,7 - dimethyl - 5 - oxoquinoline - 3 - carbohydrazide (5 g, C 31 H 27 Br 3 N 4 O 2 )
Yellow solid: M.p.: 240–242 °C, yield: 0.567 g (78%); IR (KBr) (νmax/cm−1): 3449, 3281 (NH2, NH), 1681 (C=O), 1588 (C=O), 1540 (Ar), 1256 (C–N); MS (EI, 70 eV): m/z (%) = 727 (M+, 0.01), 669 (2), 499 (3), 434 (10), 365 (14), 337 (5), 276 (6), 249 (100), 209 (47), 182 (17), 155 (54), 127 (52), 89 (50), 63 (7); 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 0.69 (3H, s, CH3), 0.95 (3H, s, CH3), 1.96–2.26 (4H, m, 2CH2), 5.03 (1H, s, CH), 6.85 (2H, s, NH2), 7.15–7.90 (12H, m, Ar), 8.20 (1H, s, CH), 8.52 (1H, s, NH); 13C NMR (75.4 MHz, DMSO): δ = 26.1 (CH3), 29.7 (CH3), 32.3 (C(CH3)2), 32.5 (CH), 41.5 (CH2), 50.0 (CH2), 79.6, 106.4, 116.2, 124.3, 126.8, 128.8, 129.6, 129.9, 131.3, 131.4, 132.3, 132.8, 133.5, 144.1, 148.7, 150.8, 158.6, 166.3 (C=O), 195.2 (C=O); Anal. Calc. for C31H27Br3N4O2 (727.28): C, 51.19; H, 3.74, N, 7.70. Found: C, 51.7; H, 3.4; N, 7.5.
(30E) - N′ - (4 - chlorobenzylidene) - 2 - amino - 1 - (3,4 - dichlorophenyl) - 4 - (4 - chlorophenyl) - 1,4,5,6,7,8 - hexahydro - 7,7 - dimethyl - 5 - oxoquinoline - 3 - carbohydrazide (5 h, C 31 H 26 Cl 4 N 4 O 2 )
Yellow solid: M.p.: 202–204 °C, yield: 0.452 g (72%); IR (KBr) (νmax/cm−1): 3378, 3298 (NH2, NH), 1695 (C=O), 1607 (C=O), 1524 (Ar), 1245 (C–N); MS (EI, 70 eV): m/z (%) = 628 (M+, 0.13), 569 (7), 472 (9), 445 (13), 406 (8), 352 (21), 296 (9), 276 (45), 248 (15), 226 (8), 187 (6), 165 (100), 138 (21), 111 (6), 89 (25), 63 (8); 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO): δ = 0.62 (3H, s, CH3), 0.87 (3H, s, CH3), 1.61–2.30 (4H, m, 2CH2), 5.29 (1H, s, CH), 7.27 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.4 Hz, Ar), 7.40–7.46 (7H, m, Ar and NH2), 7.58 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.7 Hz, Ar), 7.82–7.85 (2H, m, Ar), 8.30 (1H, s, CH), 10.70 (1H, s, NH); 13C NMR (75.4 MHz, DMSO): δ = 26.0 (CH3), 29.8 (CH3), 32.3 (C(CH3)2), 32.5 (CH), 41.4 (CH2), 50.0 (CH2), 79.7, 114.0, 128.3, 128.5, 129.2, 129.6, 130.6, 131.1, 132.3, 132.9, 133.0, 133.2, 133.9, 134.5, 136.5, 142.9, 146.9, 150.0, 152.5, 166.4 (C=O), 195.2 (C=O); Anal. Calc. for C31H26Cl4N4O2 (628.38): C, 59.25; H, 4.17, N, 8.92. Found: C, 58.9; H, 4.6; N, 8.5.
(30E) - N′ - (4 - nitrobenzylidene) - 2 - amino - 1 - (3,4 - dichlorophenyl) - 1,4,5,6,7,8 - hexahydro - 7,7 - dimethyl - 4 - (4 - nitrophenyl) - 5 - oxoquinoline - 3 - carbohydrazide (5i, C 31 H 26 Cl 2 N 6 O 6 )
Yellow solid: M.p.: 222–224 °C, yield: 0.513 g (79%); IR (KBr) (νmax/cm−1): 3461, 3379, 3243 (NH2, NH), 1641 (C=O), 1558 (C=O), 1513 (Ar), 1264 (C–N); MS (EI, 70 eV): m/z (%) = 649 (M+, 0.05), 456 (52), 430 (10), 298 (33), 251 (14), 176 (100), 130 (23), 89 (34), 63 (21); 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO): δ = 0.62 (3H, s, CH3), 0.87 (3H, s, CH3), 1.64–2.27 (4H, m, 2CH2), 5.48 (1H, s, CH), 7.63 (2H, s, NH2), 7.48–7.93 (7H, m, Ar), 8.13 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.7 Hz, Ar), 8.23 (2H, d, 3JHH = 8.7 Hz, Ar), 8.42 (1H, s, CH), 11.06 (1H, s, NH); 13C NMR (75.4 MHz, DMSO): δ = 26.0 (CH3), 29.7 (CH3), 32.3 (C(CH3)2), 33.3 (CH), 41.4 (CH2), 49.9 (CH2), 79.1, 113.3, 123.8, 124.4, 127.7, 129.0, 131.1, 132.3, 133.0, 133.4, 136.2, 141.8, 141.9, 146.1, 147.6, 150.6, 153.1, 155.5, 166.3 (C=O), 195.2 (C=O); Anal. Calc. for C31H26Cl2N6O6 (649.48): C, 57.33; H, 4.03, N, 12.94. Found: C, 57.8; H, 4.5; N, 12.7.
(29E) - N′ - (4 - chlorobenzylidene) - 2 - amino - 4 - (4 - chlorophenyl) - 1,4,5,6,7,8 - hexahydro - 7,7 - dimethyl - 5 - oxo - 1 - phenylquinoline - 3 - carbohydrazide (5j, C 31 H 28 Cl 2 N 4 O 2 )
Yellow solid: M.p.: 204–206 °C, yield: 0.391 g (70%); IR (KBr) (νmax/cm−1): 3446, 3281 (NH2, NH), 1680 (C=O), 1587 (C=O), 1537 (Ar), 1252 (C–N); MS (EI, 70 eV): m/z (%) = 559 (M+, 0.06), 499 (9), 418 (5), 377 (100), 351 (28), 279 (38), 226 (23), 181 (15), 154 (53), 138 (26), 111 (25), 89 (45), 63 (5); 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO): δ = 0.60 (3H, s, CH3), 0.84 (3H, s, CH3), 1.53–2.24 (4H, m, 2CH2), 5.32 (1H, s, CH), 7.22 (2H, s, NH2), 7.28–7.60 (13H, m, Ar), 8.30 (1H, s, CH), 10.71 (1H, s, NH); 13C NMR (75.4 MHz, DMSO): δ = 26.2 (CH3), 29.7 (CH3), 32.3 (C(CH3)2), 32.3 (CH), 41.5 (CH2), 49.9 (CH2), 79.6, 113.9, 128.4, 128.5, 129.2, 129.4, 129.5, 130.1, 130.5, 130.6, 133.9, 134.5 136.6, 142.8, 147.0, 150.5, 152.8, 166.4 (C=O), 195.2 (C=O); Anal. Calc. for C31H28Cl2N4O2 (559.49): C, 66.55; H, 5.04, N, 10.01. Found: C, 66.9; H, 5.5; N, 10.2.
(29E) - N′ - (4 - chlorobenzylidene) - 2 - amino - 4 - (4 - chlorophenyl) - 1,4,5,6,7,8 - hexahydro - 7,7 - dimethyl - 5 - oxo - 1 - p - tolylquinoline - 3 - carbohydrazide (5 k, C 32 H 30 Cl 2 N 4 O 2 )
Yellow solid: M.p.: 226–228 °C, yield: 0.418 g (73%); IR (KBr) (νmax/cm−1): 3454, 3284 (NH2, NH), 1683 (C=O), 1594 (C=O), 1544 (Ar), 1257 (C–N); MS (EI, 70 eV): m/z (%) = 573 (M+, 0.02), 513 (11), 432 (10), 391 (100), 365 (20), 343 (8), 307 (13), 281 (21), 240 (14), 182 (32), 154 (20), 124 (18), 89 (32), 63 (8); 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO): δ = 0.60 (3H, s, CH3), 0.85 (3H, s, CH3), 1.53–2.24 (4H, m, 2CH2), 2.48 (3H, s, CH3), 5.31 (1H, s, CH), 7.23 (2H, s, NH2), 7.27–7.60 (12H, m, Ar), 8.29 (1H, s, CH), 10.66 9.42 (1H, s, NH); 13C NMR (75.4 MHz, DMSO): δ = 21.2 (CH3), 26.2 (CH3), 29.7 (CH3), 32.2 (C(CH3)2), 32.4 (CH), 41.5 (CH2), 50.0 (CH2), 79.6, 113.9, 123.5, 128.3, 128.5, 129.2, 129.4, 130.1, 130.4, 131.2, 133.9, 134.5, 139.6, 142.8, 147.0, 150.7, 152.9, 166.4 (C=O), 195.2 (C=O); Anal. Calc. for C32H30Cl2N4O2 (573.51): C, 67.02; H, 5.27, N, 9.77. Found: C, 67.4; H, 5.8; N, 9.5.
References
Alizadeh A, Moafi L (2015) An efficient synthesis of spiro-oxindole derivatives by three-component reactions in water. Helv Chim Acta 98:546–551. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.201400263
Shaabani A, Hooshmand SE, Tabatabaei AT (2016) Synthesis of fully substituted naphthyridines: a novel domino four-component reaction in a deep eutectic solvent system based on choline chloride/urea. Tetrahedron Lett 57:351–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2015.12.017
Liu T, Jia W, Xi Q, Chen Y, Wang X, Yin D (2018) Diversity-oriented synthesis of heterocycles: Al(OTf)3-promoted cascade cyclization and ionic hydrogenation. J Org Chem 83:1387–1393. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.7b02894
Chemler SR, Karyakarte SD, Khoder ZM (2017) Stereoselective and regioselective synthesis of heterocycles via copper-catalyzed additions of amine derivatives and alcohols to alkenes. J Org Chem 82:11311–11325. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.7b02072
Garcia-Valverde M, Torroba T (2005) Special issue: sulfur-nitrogen heterocycles. Molecules 10:318–320. https://doi.org/10.3390/10020318
Zhou L, Hossain ML, Xiao T (2016) Synthesis of N-containing heterocyclic compounds using visible-light photoredox catalysis. Chem Rec 16:319–334. https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.201500228
Majumder A, Gupta R, Jain A (2013) Microwave-assisted synthesis of nitrogen-containing heterocycles. Green Chem Lett Rev 6:151–182. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2012.733032
Tu SJ, Jiang B, Jia RH, Zhang JY, Zhang Y, Yao CS, Shi F (2006) An efficient one-pot, three-component synthesis of indeno[1,2-b]quinoline-9,11(6H,10H)-dione, acridine-1,8(2H,5H)-dione and quinoline-3-carbonitrile derivatives from enaminones. Org Biomol Chem 4:3664–3668. https://doi.org/10.1039/B607575D
Gao S, Tsai CH, Tseng C, Yao CF (2008) Fluoride ion catalyzed multicomponent reactions for efficient synthesis of 4H-chromene and N-arylquinoline derivatives in aqueous media. Tetrahedron 64:9143–9149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2008.06.061
Heravi MM, Alinejhad H, Bakhtiari K, Daroogheha Z, Bamoharram FF, Derikvand F, Alimadadi B (2010) Facile heteropolyacid-promoted synthesis of indeno[1,2-b]quinoline-9,11(6H,10H)-dione derivatives. Synth Commun 40:2191–2200. https://doi.org/10.1080/00397910903219591
Alafeefy AM (2015) Design, synthesis, and antitumor screening of certain novel tetrahydroquinoline sulfonamides. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 30:189–194. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756366.2014.899595
To QH, Lee YR, Kim SH (2012) Efficient one-pot synthesis of acridinediones by indium(III) triflate-catalyzed reactions of β-enaminones, aldehydes, and cyclic 1,3-dicarbonyls. Bull Korean Chem Soc 33:1170–1176. https://doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2012.33.4.1170
Singh SK, Jena S (2015) Eco-friendly and ingenious multicomponent synthesis of N-arylquinolines using DABCO/TEAB in water. Indian J Chem 54:821–824. https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.201545168
Bayat M, Nasri S, Notash B (2017) Synthesis of new 3-cyanoacetamide pyrrole and 3-acetonitrile pyrrole derivatives. Tetrahedron 73:1522–1527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2017.02.005
Wang XS, Zhang MM, Jiang H, Yao CS, Tu SJ (2007) Three-component green synthesis of N-arylquinoline derivatives in ionic liquid [Bmim+][BF4−]: reactions of arylaldehyde, 3-arylamino-5,5-dimethylcyclohex-2-enone, and active methylene compounds. Tetrahedron 63:4439–4449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2007.03.068
Paolis OD, Teixeira L, Torok B (2009) Synthesis of quinolines by a solid acid-catalyzed microwave-assisted domino cyclization–aromatization approach. Tetrahedron Lett 50:2939–2942. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.03.208
Wu J, Xia HG, Gao K (2006) Molecular iodine: a highly efficient catalyst in the synthesis of quinolines via Friedlander annulation. Org Biomol Chem 4:126–129. https://doi.org/10.1039/B514635F
Andrade A, Santos GC, Filho LCS (2015) Synthesis of quinoline derivatives by multicomponent reaction using niobium pentachloride as Lewis acid. J Heterocycl Chem 52:273–277. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhet.1980
Srivastava N, Kumar A (2013) Synthesis and study of 1-ethyl-3-carbohydrazide and 3-[1-oxo-2-hydrazino-3-{p-toluenesulfon}]quinolone derivatives against bacterial infections. Eur J Med Chem 67:464–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.06.056
Bayat M, Hosseini FS, Notash B (2017) Stereoselective synthesis of indenone-fused heterocyclic compounds via a one-pot four-component reaction. Tetrahedron 73:1196–1204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2017.01.024
Bayat M, Hosseini FS (2017) Synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-6-carbohydrazides and 1H-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidine-7-carbohydrazides. Tetrahedron Lett 58:1616–1621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2017.03.032
Bayat M, Hosseini FS, Nasri S (2017) An efficient one-pot synthesis of tetrahydrothiazolo[3,2-a]quinolin-6-one derivatives. J Sulfur Chem 39:99–111. https://doi.org/10.1080/17415993.2017.1391814
Bayat M, Nasri S (2018) Synthesis and dynamic 1H NMR study of pyrazolo substituted pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidines via a regioselective heterocyclization. J Mol Struct 1154:366–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.10.056
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masoumi, M., Hosseini, F.S. & Bayat, M. Synthesis of (E)-2-amino-N′-benzylidenehexahydroquinoline-3-carbohydrazide. Mol Divers 23, 593–601 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-018-9892-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-018-9892-6