Abstract
Methotrexate is used for cure of many cancer types. It has many side effects. For this reason, obtaining a nephroprotective agent is obligatory. In the study, our aim is to determine probable effects of Vitamin B12 on MTX caused kidney damages in rats. Rats were randomly divided into 4 groups, including 8 animals in each group. Control group, VitB12 group (3 μg-kg-ip B12 throughout 15 days), MTX group (at the 8th day of experiment, a single dose of 20 mg-kg-ip MTX), Vit B12 + MTX group (3 μg-kg-ip B12 throughout 15 days and at the 8th day of experiment, a single dose of 20 mg-kg-ip MTX) Animals were anesthetized and kidney tissues were removed to evaluate biochemically, immunohistochemically and histopathologycally. There were histopathological deteriorations, rises of apoptotic cells, expressions of heat shock proteins, endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation markers in the MTX group. In the MTX group, Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), Total Antioxidant Status (TAS) and Catalase (CAT) levels decreased, but Total Oxidant Status TOS, Malondialdehyde (MDA) and interleukin-6 (IL6) levels increased. In addition, there was amelioration in kidney tissue in Vit B12 + MTX group compared to the MTX group. We suggest that Vit B12 can be used to reduce the toxic effects of MTX.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Although chemotherapeutic drugs can cause toxicity, they are important drugs used in essential diseases such as cancer. Methotrexate (MTX) is one of them. MTX, used as anticancer drug, has significant toxic effects on life-sustaining organs such as liver and kidney (Aslankoc et al. 2020) For this reason, obtaining a nephroprotective agent is obligatory.
Vitamin B12 (Vit B12- cobalamin) is a water-soluble compound that assists make blood cells and DNA (Greibe et al. 2018) Cobalamin deficiency produces clinical disorders that include mainly megaloblastic anaemia, central and peripheral neurological manifestations. In fact, there are studies showing that cobalamin intake improves damaged organs (Pannérec et al. 2018) Therefore, cobalamin is crucial for the maintenance of daily life.
Methotrexate (MTX), used in the treatment of osteosarcoma, breast cancer and acute lymphocytic leukemia, is a folate antagonist (Moodi et al. 2020) MTX, as a dihydrofolic acid analogue, inhibits the dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) enzyme which catalyses the conversion of dihydrofolate to the active tetrahydrofolate in the tetrahydrofolate synthesis. MTX, therefore, inhibits the RNA, DNA, thymidylate, protein synthesis and ultimately leads to apoptosis. Unfortunately, MTX has toxic side effects not only against cancer cells but also normal cells. Folic acid, essential for the growth of cells, is a water-soluble B-vitamin (Karabulut et al. 2020) For this reason, enough folate intake may be substantial in prohibiting MTX caused kidney damages (Calvert 2002)
Molecular chaperones provide the accurate folding of proteins synthesized in the cell, frustrate their aggregation and ensure protein homeostasis (Dahiya and Buchner 2019) Protein folding and production may be influenced in the existence of nonphysiological several chemicals and high temperatures (Karabulut et al. 2021) Additively, disrupted protein synthesis leads endoplasmic reticulum stress in the cell. Glucose regulated protein 78 chaperon arranges endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) (Elfiky et al. 2020) Sustained ERS causes apoptosis (Iurlaro and Muñoz-Pinedo 2016)
MTX is known to cause inflammation, mitochondrial damage, increase cell death, ERS, heat shock proteins and lipid peroxidation in rat kidney (Aladaileh et al. 2019; Mahmoud et al. 2019) In our study, we aimed to investigate in the possible cell death, inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) in the kidney and the oxidant/antioxidant leves in the cell after MTX-induced nephrotoxicity. We also form an estimate of the possible effects of Vit B12 on nephrotoxicity.
Materials and methods
Experimental design
The study protocol was accepted by the Erciyes University’s Experimental Animal and Local Ethics Committee with date 2018, decision no: 18/116. In the present study, all the animals accepted human care according to standart guidelines. In this study, 32 male wistar albino rats (10 weeks old, weighing 220–240) were gotten from Experimental and Clinic Research Center, Erciyes University, Kayseri, Turkey. Rats were allowed ad libitum Access to food and water and kept at a 12-h light: dark cycle at room temperature (20–24 °C) Firstly rats were randomly divided into four groups as follows: The control goup (n = 8) was administered intraperitoneally (ip) saline throughout the experiment to this group, The Vit B12 group (n = 8) given 3 µg-kg-ip B12 (15 days) per day throughout the experiment, MTX group (n = 8) injected with a single dose of 20 mg-kg-ip MTX on 8 th day of experiment. The MTX + Vit B12 administered 3 µg-kg-ip Vit B12 per day and 20 mg-kg-ip MTX 8 th day of experiment. At the end of the experiment, animals were anesthetized with 75 mg-kg-ip ketamine and 10 mg-kg-ip and they were euthanized after blood samples were collected for serum isolation. Collected serum samples were centrifuged during 10 min at 3000 r-min. After euthanizing, kidney tissues were extracted from the animals for the histopathological and immunohistochemical examinations. Serum samples were kept at −80 °C for later biochemical assays.
Histopathological evaluation
The kidney tissues were fixed in % 4 formaldehyde fixative for histopathological evaluation. Following dehydration (50%, 70%, 80%, 96% and three times absolute alcohol) and clearing (xylene) embedded in paraffin. 5-µm-thick sections were stained with periodic acid schiff (PAS) Photographs were taken with a light microscope (Olympus BX51, Center Valley, PA, USA)
Immunohistochemistry
To determine the differences in expression of Caspase-3 (Cas3) (ab4051, anti-caspase-3 antibody, abcam), Cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2) (E- AB- 30999, Elabsciens, China), Interleukin 17 (IL-17), Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), HSP70 Heat Shock Protein 70 (HSP70) (sc-33575, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA), Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90) (PB9635; Boster Biological Technology, Pleasanton, CA), C/EBP Homologous Protein (CHOP, GADD153) (sc-56107, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, USA) and Glucose Regulated Protein (GRP78) (bs-1219R; Bioss) in kidney tissue, streptavidin-biotin-peroxidase method was used for marking. Under the light microscope (Olympus BX51, Center Valley, PA, USA) and images were obtained. Cas3, Cox-2, IL-17, TNFα, HSP70, HSP90, GADD153 and GRP78 immunoreactivity were measured with image J programme.
Apoptosis (TUNEL)
The terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase 20 -deoxyuridine, 50 -triphosphate nick-end labeling (TUNEL) method was used to demonstrate apoptosis of kidney tissue, as previously described. An in situ Cell Death Detection Kit Fluorescein Kit (11684795910; Roche, Mannheim, Germany) was utilized. After casing the tissues with a solution containing glycerol, they were all examined with the Olympus BX51 fluorescence microscope at 450–500 nm wavelength. Cells were considered to be apoptotic when the cell nuclei demonstrated positive TUNEL staining. For quantification of TUNEL positive cells, 10 fields per section were analyzed and counted at 400 fold magnification.
ELİSA assay
We centrifuged blood samples taken from rats at 10,000 g at 4 °C for 15 min. Total antioxidant status (TAS) (DZE201112672, Sunred Biological Technology Co., Ltd., 96 wells ELISA kit, Shanghai, China), Total oxidant status (TOS) (DZE201111669, Sunred Biological Technology Co., Ltd., 96 wells ELISA kit, Shanghai, China), Interleukin 6 (IL6) (Cat. No: 201-11-0136, Sun Red), Superoxide dismutase (SOD) (Cat. No: 201-11-0169, Sun Red), Catalase (CAT) (Cat. No: 201-11-5106, Sun Red), Malondialdehyde (MDA) (Cat. No: Cat. No: 201-11-0157, Sun Red) were measured in kidney tissue. The ELISA procedure was done according to the protocol recommended by the manufacturers. Creatinine and Uric acid values of blood serum sample taken at the end of the experiment were analyzed by taking service in Erciyes University Central Biochemistry Laboratory.
Statistical analyses
All statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS statistical software (SPSS for Windows, version 24.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA) and graphs were drawn using GraphPad Prism 8.0 software. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was used to identify normal distribution of the data. In case of normal distribution, quantitative variables were compared using one-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s post hoc test. The data were presented as the mean of normalized data + standard deviation of mean. The value of P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Each experiment was repeated at least three times.
Results
Histopathological findings
Kidney tissues had normal histomorphology in the control and Vit B12 groups. Light microscopic examinations exhibited normal renal corpuscles and tubules in the both groups. Dilatation and epithelial desquamation in to the lumen of the tubules, dilatation of Bowman’s space, narrowing of the glomerular were observed in MTX group. MTX + Vit B12 group exhibited normal renal histology (Fig. 1)
PAS staining of kidney tissue. A–B In control and Vit B12 groups, normal kidney appearance were shown. C In MTX group, epithelial desquamation into the lumen of the tubules (black arrow), degeneration in epithelial cells (black arrow), dilatation in tubules, decrease in glomeruli, increase in bowman gap were showm (star) D In MTX + Vit B12 group, normal kidney architecture was exhibited
Immunohistochemical findings
Immunohistochemical staining was performed using the avidin–biotin method to determine the kidney tissue expressions of ERS, inflammation, heat shock protein and apoptosis markers. Expressions of Cas3, GRP78, GADD153, HSP90, HSP70, Cox-2, IL-17 and TNFα were observed in the distal tubules and collecting ducts in MTX group (Figs. 2, 3) Expressions of the markers in the kidney of Vit B12 group were similar to those in the control group. In MTX + Vit B12 group, levels of the markers of were significantly less compared to those in the MTX group (Table 1; Figs. 4 and 5)
HSP90, HSP70, IL17 and TNF-α immunoreactivity results. Values are presented as means ± SD. (*) indicates statistical difference between groups. Abbreviations: MTX Methotrexate, Vit B12 Vitamin B12, HSP90 Heat shock protein 90, HSP70 Heat shock protein 70, IL17 Interleukin 17, TNF-α Tumor necrosis factor alpha
Biochemical findings
Evaluation of the SOD, CAT, MDA and IL6 levels
SOD level decreased slightly in MTX group. This decrease was not statistically significant compared to other groups (P > 0.05) The SOD level in MTX + Vit B12 group was similar to both the control and Vit B12 groups (Table 2)
CAT level was lower in the MTX group compared to the control group. This decrease was statistically important (P < 0.05) The CAT level in the MTX + Vit B12 group decreased slightly, but the rate was not statistically substantial compared to control group (Table 2).
MDA and IL6 levels were increased substantially in MTX group when compared to the control and Vit B12 groups (P < 0.05), (Table 2)
Evaluation of the oxidant/antioxidant system
TAS levels were lower in the MTX group compared to the other groups. However, TOS levels were importantly higher in the MTX group than in the other groups. There were no statistically importance in TAS and TOS levels among the other groups excluding MTX group (P > 0.05), (Table 2) There was also a decrease in TAS level in MTX + B12 group compared to control and B12 groups. Also, there was a significant increase compared to the MTX group. When the TOS level was examined, it was seen that there was a statistically significant decrease in the MTX + B12 group compared to the MTX group (P < 0,05)
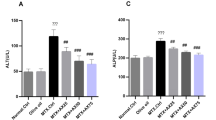
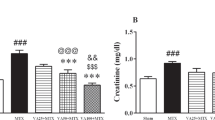
Evaluation of serum Creatinine and Uric acid results
Serum creatinine and uric acid levels increased slightly in MTX group, but this increase was not statistically significant compared to control group (P > 0.05) Similar results to the control were observed in the MTX + Vit B12 group. Creatinine and uric acid are given in Table 2. The changes observed in creatinine and uric acid were not statistically significant, pointing at minimal or no adversity. There may be multiple reasons for this, including limited toxicity of the compound, too low doses, number of animals included in the study, from a device in the laboratory (Table 3)
Apoptotic findings
TUNEL staining was performed to determine apoptotic cells in kidney tissues (Table 4, Fig. 6) The apoptotic cells in the kidney of control group and Vit B12 group were found 0.35 ± 0.60 and 0.22 ± 0.53, respectively. There was no statistically significance among this group. The increase in the apoptotic cell number in MTX group was found 2.21 ± 1.59 and was statistically significant when compared to the control group (P < 0.05) In MTX + Vit B12 group, there was a decrease in TUNEL-positive cells and the apoptotic cell number (0.25 ± 0.45) The decrease in the apoptotic cell number was statistically different in MTX + Vit B12 when compared to the MTX group (P < 0.05)
Discussion
Methotrexate, a folic acid antagonist, is commonly used for the treatment of many ailments including psoriasis and cancer (Rajitha et al. 2017) However, MTX is known to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) in both cancer and normal cells resulting in oxidative damage (Conklin 2004) The anticancer, anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive actions of MTX has been shown to occur via ROS generation and induction of apoptosis. MTX has been reported to induce renal and hepatic toxicity via oxidative stress and its efficacy has been limited by severe organ toxicity (Saigal et al. 2012) Previous studies have been reported many side effects of short and long term administration of MTX (Campbell et al. 2016; Wang et al. 2018) For example, MTX causes toxic effects in the kidney, gastrointestinal tract, liver, reproductive and nervous system in animals and humans (Shao et al. 2019; Morsy et al. 2020) In our bodies, Vit B12 is essential in cell division as it stimulates DNA synthesis It has been shown that vitamin B12 has a positive effect on muscle pain caused by formalin, and that vitamin B12 supplementation has a positive effect on organ damage (Harb et al. 2020; Tamaddonfard et al. 2018)
MTX has possible side effects on vital organs, specially on the kidney and liver (Abd El-Twab et al. 2019; Ewees et al. 2019) Several studies submit that MTX causes cystic dilatation of the renal tubules, epithelial desquamation in to the lumen of the tubules, dilatation and congestion of the peritubuler vessels of the kidney tissue (Arab et al. 2018; Ulusoy et al. 2016) Our results were similar to previous studies.
Vit B12 is a B vitamin that has an substantial role in cellular metabolism, especially in DNA synthesis, methylation and mitochondrial metabolism (Green et al. 2017) Many studies have reported that vitamin B12 has a protective effect on organ damage occurring in experimental studies (Elsaed et al. 2018; Hajihashemi et al. 2017) We investigated the effect of Vit B12 in an amount close to the dose in previous literature studies on the kidney damage caused by methotrexate (Elsaed et al. 2018; Beltrame et al. 2019) The mechanism of the nephrotoxic effect of MTX is not yet fully understood. In the present study, we aimed to evaluate MTX nephrotoxicity, particularly to show the presence of inflammation, ERS and apoptosis by immunohistochemistry. We used Vit B12 nephroproective against MTX loss. Therefore, we evaluated the connection of apoptosis with inflammation, ERS and oxidant/antioxidant systems in the tissue.
Molecular chaperones, which prevent inefficient interactions for the folding of target proteins, allow the proteins to fold efficiently into their natural structure. HSP70 and HSP90 chaperones are among them. HSP90, which functions together with HSP70, has been demonstrated to be include in cell-cycle regulation, signal transduction, and apoptotic pathways (Genest et al. 2019; Otaka et al. 2006) Remerkable increase in HSP70 and HSP90 expressions against ischemia–reperfusion injury was shown in the rat kidney (Zhang et al. 2008) In another study, it was reported that there was a significant increase in HSP70 expression in kidney damage caused by methotrexate compared to the control group (Ulusoy et al. 2016) In this study, there was a significant increase in the expressions of HSP70 and 90 in the kidney tissues of rats treated with methotrexate compared to the other groups.
There was an important increase in levels of TNFα, IL17 and Cox-2 in MTX group. These proteins are pro-inflammatory cytokine produced in response to MTX (Araujo et al. 2012; Mahmoud et al. 2014) Previous studies reported that inflammatory cytokine levels as Cox-2, IL17 and TNFα increased in MTx induced rats (El-Sheikh et al. 2015) In this study, we demonstreated that MTX increased expressions of Cox-2, IL17 as well as TNFα. These results were similar to previous studies (Oguz et al. 2015)
Endoplasmic reticulum has an significant role for the modification, folding and synthesis of proteins. If proteins are misfolded or cannot fold, stress will occur in the Endoplasmic reticulum (Ibrahim et al. 2019) Until now, there are only a few studies involving endoplasmic reticulum stress and methotrexate (Lv et al. 2020; Song et al. 2021) In these studies, it was observed that there was an increase in ERS protein expressions in organ damage in rats treated with methotrexate. Also, In this study, we evaluated the expression of GRP78 and GADD153 (CHOP) proteins, which are ERS markers. We found an increase in GRP78 and GADD153 markers in the MTX group. We found a decrease in the MTX group given with Vit B12. Our study found similar results to other studies.
Caspase 3 is accepted to be the most substantial of the executioner caspases and is activated by any of the initiator caspases (caspase 8, 9, 10) In addition to, caspase 3 leads to cytoskeletal reorganization and disintegration of the cell into apoptotic bodies (Cohen 1997; García-Argüello et al. 2020) In the present study, we evaluated caspase 3 with Immunohistochemical method. MTX group showed a significant increase in caspase 3 expression compared to the control and other groups (Hafez et al. 2015)
Since MTX is known to be a proapoptotic agent, the apoptotic cells in the kidney tissues are showed by apoptosis (TUNEL) staining. Many studies have reported increase in the rate of apoptosis in kidney tissues in the MTX group (Ulusoy et al. 2016; Yuksel et al. 2017) In the present study, we demonstrated that the number of apoptotic cells substantially increased in the MTX group compared to the other group.
Many studies report that MTX leads to oxidative stress and induces renal toxicity. MTX produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) and therefore leads to lipid peroxidation and causes impairment in mitochondrial function (Arab et al. 2018) In our study, we found that MDA and IL6 levels importantly increased in MTX group, but SOD and CAT levels are statistically lower in MTX group compared to control group. Until now, there are very few studies about TAS and TOS values in studies on methotrexate (Erdogan and Yalcin 2018) The results we found were consistent with these studies. We found that TOS levels substantially increased in MTX group, however TAS levels are significantly lower in MTX group compared to the other groups.
Many studies have reported that vitamin B12 has a protective effect on organ damage occurring in experimental studies (Elsaed et al. 2018; Hajihashemi et al. 2017) However, there is scarcely any experimental study involving methotrexate and vitamin B12. Therefore, in this study we evaluated the effect of Vitamin B12 against methotrexate induced kidney damage. Vitamin B12 gave statistically substatial results at histopathologic, immunohistochemical and biochemical assays after MTX nephrotoxicity.
References
Abd El-Twab SM, Hussein OE, Hozayen WG, Bin-Jumah M, Mahmoud AM (2019) Chicoric acid prevents methotrexate-induced kidney injury by suppressing NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome activation and up-regulating Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 signaling. Inflamm Res 68(6):511–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-019-01241-z.
Aladaileh SH, Hussein OE, Abukhalil MH, Saghir SAM, Bin-Jumah M, Alfwuaires MA, et al (2019) Formononetin Upregulates Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling and Prevents Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Kidney Injury in Methotrexate-Induced Rats. Antioxidants (Basel) 8(10):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8100430.
Arab HH, Salama SA, Maghrabi IA (2018) Camel milk attenuates methotrexate-induced kidney injury via activation of PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling and intervention with oxidative aberrations. Food Funct 9(5):2661–2672. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8fo00131f.
Araujo LP, Truzzi RR, Mendes GE, Luz MA, Burdmann EA, Oliani SM (2012) Annexin A1 protein attenuates cyclosporine-induced renal hemodynamics changes and macrophage infiltration in rats. Inflamm Res 61(3):189–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-011-0400-z.
Aslankoc R, Ozmen O, Ellidag HY (2020) Ameliorating effects of agomelatine on testicular and epididymal damage induced by methotrexate in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 34(3):e22445. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22445.
Beltrame FL, de Santi F, Vendramini V, Cabral REL, Miraglia SM, Cerri PS, et al (2019) Vitamin B(12) Prevents Cimetidine-Induced Androgenic Failure and Damage to Sperm Quality in Rats. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10:309. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00309.
Calvert H (2002) Folate status and the safety profile of antifolates. Semin Oncol 29(2 Suppl 5):3–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0093-7754(02)70209-1.
Campbell JM, Bateman E, Stephenson MD, Bowen JM, Keefe DM, Peters MD (2016) Methotrexate-induced toxicity pharmacogenetics: an umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 78(1):27–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3043-5.
Cohen GM (1997) Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis. Biochem J 326:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3260001.
Conklin KA (2004) Chemotherapy-associated oxidative stress: impact on chemotherapeutic effectiveness. Integr Cancer Ther 3(4):294–300. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534735404270335.
Dahiya V, Buchner J (2019) Functional principles and regulation of molecular chaperones. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 114:1–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apcsb.2018.10.001.
El-Sheikh AA, Morsy MA, Abdalla AM, Hamouda AH, Alhaider IA (2015) Mechanisms of Thymoquinone Hepatorenal Protection in Methotrexate-Induced Toxicity in Rats. Mediators Inflamm 2015:859383. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/859383.
Elfiky AA, Baghdady AM, Ali SA, Ahmed MI (2020) GRP78 targeting: hitting two birds with a stone. Life Sci 260:118317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118317.
Elsaed WM, Bedeer RF, Eladl MA (2018) Ameliorative effect of vitamin B12 on seminiferous epithelium of cimetidine-treated rats: a histopathological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Anat Cell Biol 51(1):52–61
Erdogan MA, Yalcin A (2018) Protective effects of benfotiamine on irisin activity in methotrexate-induced liver injury in rats. Arch Med Sci 16(1):205–11. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2018.80002.
Ewees MG, Abdelghany TM, Abdel-Aziz AH, Abdelbakky MS (2019) Enoxaparin prevents fibrin accumulation in liver tissues and attenuates methotrexate-induced liver injury in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 392(5):623–631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01618-1.
García-Argüello SF, Lopez-Lorenzo B, Cornelissen B, Smith G (2020) Development of [(18)F]ICMT-11 for Imaging Caspase-3/7 Activity during Therapy-Induced Apoptosis. Cancers (Basel) 12(8):2191. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082191.
Genest O, Wickner S, Doyle SM (2019) Hsp90 and Hsp70 chaperones: collaborators in protein remodeling. J Biol Chem 294(6):2109–2120. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.REV118.002806.
Green R, Allen LH, Bjørke-Monsen AL, Brito A, Guéant JL, Miller JW, et al (2017) Vitamin B(12) deficiency. Nat Rev Dis Primers.3:17040. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.40.
Greibe E, Nymark O, Fedosov SN, Heegaard CW, Nexo E (2018) Dietary Intake of Vitamin B12 is Better for Restoring a Low B12 Status Than a Daily High-Dose Vitamin Pill: an Experimental Study in Rats. Nutrients 10(8):1096. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10081096. PMID: 30111759
Hafez HM, Ibrahim MA, Ibrahim SA, Amin EF, Goma W, Abdelrahman AM (2015) Potential protective effect of etanercept and aminoguanidine in methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 768:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.08.047.
Hajihashemi S, Hamidizad Z, Rahbari A, Ghanbari F, Motealeghi ZA (2017) Effects of Cobalamin (Vitamin B12) on Gentamicin Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rat. Drug Res (Stuttg) 67(12):710–718. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-117418.
Harb Z, Deckert V, Bressenot AM, Christov C, Guéant-Rodriguez RM, Raso J, et al (2020) The deficit in folate and vitamin B12 triggers liver macrovesicular steatosis and inflammation in rats with dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. J Nutr Biochem. 84, 108415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108415.
Ibrahim IM, Abdelmalek DH, Elfiky AA (2019) GRP78: a cell’s response to stress. Life Sci 226:156–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.022.
Iurlaro R, Muñoz-Pinedo C (2016) Cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Febs J 283(14):2640–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13598.
Karabulut D, Ozturk E, Kaymak E, Akin AT, Yakan B (2021) Thymoquinone attenuates doxorubicin-cardiotoxicity in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 35(1):e22618. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22618.
Karabulut D, Ozturk E, Kuloglu N, Akin AT, Kaymak E, Yakan B (2020) Effects of vitamin B12 on methotrexate hepatotoxicity: evaluation of receptor-interacting protein (RIP) kinase. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 393(12):2473–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01992-1.
Lv S, Wu N, Wang Q, Yang LH (2020) Endogenous hydrogen sulfide alleviates methotrexate-induced cognitive impairment by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis via CHOP and caspase-12. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 34(5):559–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/fcp.12543.
Mahmoud AM, Ahmed OM, Galaly SR (2014) Thymoquinone and curcumin attenuate gentamicin-induced renal oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rats. Excli J 13:98–110
Mahmoud AM, Hussein OE, Abd El-Twab SM, Hozayen WG (2019) Ferulic acid protects against methotrexate nephrotoxicity via activation of Nrf2/ARE/HO-1 signaling and PPARγ, and suppression of NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Food Funct 10(8):4593–607. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9fo00114j.
Moodi H, Hosseini M, Abedini MR, Hassanzadeh-Taheri M, Hassanzadeh-Taheri M (2020) Ethanolic extract of Iris songarica rhizome attenuates methotrexate-induced liver and kidney damages in rats. Avicenna J Phytomed 10(4):372–383
Morsy MA, Abdel-Aziz AM, Abdel-Hafez SMN, Venugopala KN, Nair AB, Abdel-Gaber SA (2020) The Possible Contribution of P-Glycoprotein in the Protective Effect of Paeonol against Methotrexate-Induced Testicular Injury in Rats. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 13(9):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13090223.
Oguz E, Kocarslan S, Tabur S, Sezen H, Yilmaz Z, Aksoy N (2015) Effects of Lycopene Alone or Combined with Melatonin on Methotrexate-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Rats. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16(14):6061–6. https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.14.6061.
Otaka M, Odashima M, Watanabe S (2006) Role of heat shock proteins (molecular chaperones) in intestinal mucosal protection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.028.
Pannérec A, Migliavacca E, De Castro A, Michaud J, Karaz S, Goulet L, et al (2018) Vitamin B12 deficiency and impaired expression of amnionless during aging. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 9:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12260. PMID: 29159972
Rajitha P, Biswas R, Sabitha M, Jayakumar R (2017) Methotrexate in the treatment of psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis: mechanistic ınsights, current ıssues and novel delivery approaches. Curr Pharm Des 23(24):3550–66. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612823666170601105439.
Saigal S, Singh RK, Poddar B (2012) Acute methotrexate toxicity presenting as multiorgan failure and acute pneumonitis: a rare case report. Indian J Crit Care Med 16(4):225–7. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-5229.106509.
Shao Y, Tan B, Shi J, Zhou Q (2019) Methotrexate induces astrocyte apoptosis by disrupting folate metabolism in the mouse juvenile central nervous system. Toxicol Lett 301:146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.11.016.
Song Y, Liu L, Liu B, Liu R, Chen Y, Li C, et al (2021) Interaction of nobiletin with methotrexate ameliorates 7-OH methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity through endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent PERK/CHOP signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res 165:105371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105371.
Tamaddonfard E, Tamaddonfard S, Cheraghiyan S (2018) Effects of intracerebroventricular injection of vitamin B(12) on formalin-induced muscle pain in rats: role of cyclooxygenase pathway and opioid receptors. Vet Res Forum 9(4):329–335. https://doi.org/10.30466/vrf.2018.33104.
Ulusoy HB, Öztürk İ, Sönmez MF (2016) Protective effect of propolis on methotrexate-induced kidney injury in the rat. Ren Fail 38(5):744–570. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2016.1158070.
Wang W, Zhou H, Liu L (2018) Side effects of methotrexate therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Eur J Med Chem 158:502–516 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.09.027.
Yuksel Y, Yuksel R, Yagmurca M, Haltas H, Erdamar H, Toktas M, et al (2017) Effects of quercetin on methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 36(1):51–61. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327116637414.
Zhang PL, Lun M, Schworer CM, Blasick TM, Masker KK, Jones JB et al (2008) Heat shock protein expression is highly sensitive to ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat kidneys. Ann Clin Lab Sci 38(1):57–64
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Erciyes University Scientific Research Projects Unit (TSA-2019-8673)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EÖ, DK and BY designed the study, EÖ, DK, EK, ATA, NK and MS performed the experiment. EK, ATA contributed in analyzing the data. EÖ and BY wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozturk, E., Karabulut, D., Akin, A.T. et al. Evaluation by different mechanisms of the protective effects of vitamin B12 on methotrexate nephrotoxicity. J Mol Histol 53, 133–143 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10027-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10027-9