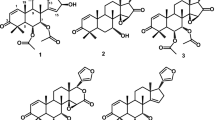
A new limonoid, named granaxylocartin A (1), was isolated from the seeds of Xylocarpus granatum, and the structure was elucidated on the basis of one- and two-dimensional NMR (including 1H, 13C NMR, DEPT, 1H–1H COSY, HSQC, HMBC, and NOESY).
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Limonoids are also known as tetranortriterpenoids and are classified by the type of four usually highly oxidized rings [1]. The genus Xylocarpus (Meliaceae) has proved to be a rich source of an array of structurally diverse limonoids, including gedunin, andirobin, mexicanolide, and phragmalin type limonoids, with a wide range of biological activities [2]. Xylocarpus granatum J. Koenig, a marine mangrove plant distributed mainly along the seashore along the Indian Ocean and in Southeast Asia, is used as a folk medicine in Southeast Asia for the treatment of diarrhea, cholera, and fever diseases such as malaria and also as an antifeedant [3]. More than 50 limonoid derivatives have been isolated from X. granatum, and they have been classified into phragmalin, mexicanolide, obacunol, and andirobin types [4,5,6,7,8,9]. Previously investigations by our group have resulted in the isolation and identication of four new mexicanolide-type limonoids from the seeds of X. granatum [10, 11]. Further investigations on the seeds of the same plant resulted in the discovery of one novel compound, granaxylocartin A (1). Herein, details of the isolation and structure elucidation of this novel compound are presented.
Granaxylocartin A (1) was obtained as a white powder. The molecular formula was deduced as C31H36O13 with 14 degrees of unsaturation by HR-TOF-MS m/z [(M·+) m/z 616.2155, calcd 616.2156]. The NMR data of 1 were almost the same as those of xyloccensin T (2) [12] isolated from the same plant, except that the 12-acetoxy group in xyloccensin T was replaced by a hydroxyl.

The 13C NMR spectrum revealed that 1 contains six olefinic carbons and three carbonyls. Therefore, the remaining eight unsaturations demonstrated that 1 consisted of eight rings. The 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra (Table 1) showed the presence of six methyls, two methylenes, 11 methines (five oxygenated and four olefinic ones), and 12 quaternary carbons (four oxygenated, three esters, and two olefinic carbons). In addition, three hydroxy groups [δH 2.62 (br.s); 3.57 (br.s); 5.00 (br.s)], three tertiary methyls [δH 1.49 (s), 1.52 (s), and 0.90 (s); δC 12.6, 16.9, and 15.1], one methoxy group (δH 3.86; δC 52.9), and a β-substituted furyl ring [δH 6.60 (br.m), 7.53 (br.s), and 7.62 (br.s); δC 109.3, 143.3, 142.0, and 121.4] were distinguished by the 1H and 13CNMR data. The aforementioned spectroscopic data implied 1 was a type of phragmalin, consisting of eight rings, designated as A1, A2, B, C, D, E, F, and G. The structure was determined by analysis of the 1H–1H COSY, HSQC, and HMBC data of 1. It was elucidated by analysis of the spectroscopic data starting from rings A1 and A2; the HMBCs between H-3/C-4, H-29/C-3, H-29/C-4, H-29/C-5, H-29/C-28, H-19/C-5, H-19/C-1, and H-19/C-10 indicated rings A1 and A2. The HMBC cross-peaks from H-17 to C-21, C-22, and C-23, from H3-18 to C-13 and C-17, and from H-15 to C-8 and C-13 indicated the location of rings C, D, and E. The relative conguration of 1 was established as that of xyloccensin T (2) by the NOE correlations: H-12/H-5, H-12/H-6, H-12/H-17, H-15/H-30, H-18/H-22, and H-19/H-6. Based on the above results, the structure of 1 was identified as 12-hydroxyxyloccensin T, named granaxylocartin A.
Experimental
General. MS: 3200QTRAPTM (Applied Biosystem Foster City, CA, USA). NMR: Bruker AV-600 spectrometer; at 600 MHz (1H) and 150 MHz (13C); δ in ppm rel. to Me4Si as internal standard, J in Hz. Chromatography: silica gel 200–300 mesh (Qingdao Marine Chemical Factory, China). Preparative HPLC: Waters Delta Prep 3000 pump, UV 2487 detector, Whatman Partisil 10 ODS-2 (9.4 × 250 mm) column.
Plant Material. Seeds of X. granatum were collected in March 2006 at Hainan Island, Southern China, dried at ambient temperature, and identified by Dr. Wen-Qing Wang, School of Life Sciences, Xiamen University, China. Several voucher specimens (No. HEBNMC-2006-1) have been deposited in the Herbarium of the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Hebei Medical University, China.
Extraction and Isolation. Dried seeds (5 kg) of X. granatum were extracted with 95% ethanol at room temperature. After evaporation of the solvent under reduced pressure, the residue was suspended in water and extracted with petroleum ether and dichloromethane, successively. The dichloromethane extract (120 g) was chromatographed on silica gel and eluted with a petroleum ether–ethyl acetate system (30:1 to 1:10) to yield nine fractions. Fraction 8 (10 g) was subjected to Si gel CC using petroleum ether–acetone (1:1) as an eluent to give six fractions (Fr. 8a–8f). Fraction 8b was subsequently separated by preparative TLC and further purified on a semipreparative HPLC column with acetonitrile–water (47:53) as a mobile phase to yield 1 (5 mg).
Granaxylocartin A (1). White powder, \( {\left[\upalpha \right]}_{\mathrm{D}}^{24}\hbox{--} {14}^{{}^{\circ}} \) (c 0.010, CHCl3). UV (CHCl3, λmax, nm): 214. IR (KBr, cm–1): 3600–3200, 1740–1715. HR-TOF-MS m/z 616.2155 (M·+), calcd 616.2156. For 1H and 13C NMR (CDCl3), see Table 1.
References
Q. G. Tan and X. D. Luo, Chem. Rev., 111, 7437 (2011).
L. R. Shen, S. M. Jin, Y. M. Yu, B. W. Yin, L. Zhao, Q. W. Shi, and C. H. Huo, Chem. Biodivers., 6, 1293 (2009).
D. A. Mulholland and D. A. H. Taylor, Phytochemistry, 31, 4163 (1992).
A. Ng and A. Fallis, Can. J. Chem., 57, 3088 (1979).
J. Wu, S. Zhang, Y. Song, Z. Xiao, Q. Xiao, and Q. Li, Z. Naturforsch., 60b, 1291 (2005).
J. Wu, H. Ding, M. Li, and S. Zhang, Z. Naturforsch., 62b, 569 (2007).
S. Yin, C. Q. Fan, X. N. Wang, L. P. Lin, J. Ding, and J. M. Yue, Org. Lett., 8, 4935 (2006).
S. Yin, X. N. Wang, C. Q. Fan, L. P. Lin, J. Ding, and J. M. Yue, J. Nat. Prod., 70, 682 (2007).
J. Cui, J. Wu, Z. Deng, P. Proksch, and W. Lin, J. Nat. Prod., 70, 772 (2007).
L. R. Shen, M. Dong, D. Guo, B. W. Yin, M. L. Zhang, Q. W. Shi, C. H. Huo, H. Kiyota, N. Suzuki, and B. Cong, Z. Naturforsch., 64c, 37 (2009).
C. H. Huo, D. Guo, L. R. Shen, B. W. Yin, F. Sauriol, L. G. Li, M. L. Zhang, Q. W. Shi, and H. Kiyota, Tetrahedron Lett., 51, 754 (2010).
J. Wu, Q. Xiao, S. Zhang, X. Li, Zh. H. Xiao, H. X. Ding, and Q. X. Li, Tetrahedron, 61, 8382 (2005).
Acknowledgment
We are grateful for financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81602978), the Hebei Medical University Development Project (2016-kyfz111), the Educational Commission of Hebei Province of China (No. QN2017098), and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (H2017206087). We also wish to extend our sincere thanks for the financial support of Syngenta Ltd. (2016-Hebei Medical University-Syngenta-05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 5, September–October, 2017, pp. 767–768.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Wang, L., Wei, X. et al. Granaxylocartin A, New Limonoid from the Seeds of Xylocarpus granatum . Chem Nat Compd 53, 901–903 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-017-2151-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-017-2151-8