Phytochemical investigation of the seeds from Hippophae rhamnoides L. led to the isolation of a new megastigmane, named (6S,9R)-9-hydroxy-4,7-megastigmadien-3-one-9-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside (1), together with its spatial heterogeneity which is a known megastigmane (2). Compounds 3–13 are flavonoid glycosides, 9 compounds (2, 5–12) of which were isolated from the H. rhamnoides for the first time. Their structures were proposed through HR-ESI-MS, 1H, and 13C NMR data interpretation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Hippophae rhamnoides L., commonly known as sea-buckthorn, consists of approximately six species with 11 subspecies and is a plant of the genus Hippophae L. (family Elaeagnaceae) [1, 2]. H. rhamnoides grows mainly in northwestern China, such as Qinghai, Gansu, Tibet, Shaanxi, and the Inner Mongolia Provinces. H. rhamnoides has been used as an edible medicinal plant in Tibetan medicine and traditional Chinese medicine to treat hepatocarcinoma [3], cardiovascular diseases [4] with antioxidation [5] and immunoenhancement effects [6]. Previous phytochemical investigations of species of H. rhamnoides have shown the presence of flavonoids [7, 8], polysaccharides [9, 10], terpenoids [11, 12], and alkaloids [13, 14]. Among the secondary metabolites mentioned above, flavonoids, especially flavonoid glycosides and their derivatives, have been reported to have significant biological activities from H. rhamnoides. In the course of our search for natural products, phytochemistry investigations of the seeds of H. rhamnoides, led to the isolation and structural elucidation of two megastigmanes (1, 2) and 11 flavonoids (3–13). Furthermore, the isolates were evaluated for their cytotoxic effects. Reported herein are the purification, chemical elucidation, and biological evaluation of these 13 components.
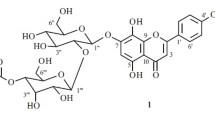
Compound 1 was obtained as a white amorphous powder and the molecular formula was suggested to be C24H38O11 owing to its HR-ESI-MS peak at m/z 503.2414 [M + H]+. The 1H NMR spectral data (Table 1) in CD3OD showed three olefinic signals at δ 5.88 (1H, br.s, H-4), 5.75 (1H, dd, J = 15.4, 6.5 Hz, H-8) and 5.63 (1H, ddd, J = 15.4, 9.4, 0.7 Hz, H-7), two characteristic anomeric protons at δ 4.98 (1H, d, J = 2.5 Hz, H-1′′) and 4.31 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-1′), a series of oxygenated methine and methylene signals, an olefinic methyl at δH 1.96 (3H, d, J = 1.1 Hz, H-13), as well as three aliphatic methyl signals (one doublet and two singlets) in the upfield region. The 13C NMR spectrum (Table 1) showed a total of 24 carbon signals, including one conjugated keto-carbonyl carbon at δ 202.1 (s, C-3), four olefinic carbons owing to two double bonds, two anomeric carbons at δ 111.0 (d, C-1′′) and 102.6 (d, C-1′), 10 oxygen-bearing sp3 carbons (one quaternary carbon, six methines, three methylenes), as well as seven aliphatic carbons in the upfield region. The above NMR features were highly similar to those of (6R,9R)-3-oxo-α-ionol β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside (2) [15], a megastigmane diglycoside, and (6R,9S).
The careful analysis of the HSQC, HMBC, and 1H–1H COSY correlations also allowed the structure of compound 1 to be established as 3-oxo-α-ionol β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside. Although measured in the same deuterium solvent, there were still some non-negligible differences of the NMR chemical shifts of the aglycone moiety, so it was reasonable to infer that compound 1 should possess a (6S,9R) form. Furthermore, the absolute configurations of the diastereomeric 3-oxo-α- ionol glucosides had been studied in depth by reliable means [16], in which some shift rules helped to determine the absolute configurations at C-6 and C-9. First, the 13C NMR chemical shifts of C-9 and C-1′ were diagnostic and could be used to determine the absolute configuration at C-9, and then the ΔδH-11, 12 allowed (6R,9R) and (6S,9R) forms of 3-oxo-α-ionol glycosides to be further distinguished. Finally, the structure of the new megastigmane diglycoside was established as (6S,9R)-3-oxo-α-ionol β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside, shown in Fig. 1.
In addition, a known megastigmane and 11 flavonoid glycosides were isolated from this plant and identified by comparison of their spectral data and related references.
EXPERIMENTAL
General. The analytical grade chemicals and solvents utilized were obtained from Tianjin Baishi Chemical Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, P. R. China). MCI Gel CHP20P for column chromatography (CC) (75–150 mm; Mitsubishi Kasei Chemical Industries, Tokyo, Japan) and an Agilent 1260 Infinity system with a 100-μL injection loop were used for HPLC analysis and preparation (Agilent Technologies Co., Ltd., Santa Clara, CA, USA). Two NP7000C series liquid phase pumps, including a 20-mL injection loop are all components of the Hanbon-NP7010 system (Jiangsu Hanbon Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Huaian, P. R. China). VIS/UV: UV-2401PC (Shimadzu, Japan). P-1020 for optical rotation (JASCO, Japan). NMR spectrometer made by Varian, located in Palo Alto, CA, USA; TMS as internal standard. HR-ESI-MS: Thermo Velos Pro with Orbitrap elite detector (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., MA, USA); in m/z. 1H NMR (600 MHz), 13C NMR (150 MHz), and 2D NMR spectra (HMBC, HSQC) were recorded on a Bruker 600 spectrometer.
Plant Material. Seeds of Hippophae rhamnoides L. were collected from Datong County, Qinghai, P. R. China, in August 2019, and were identified by Professor Qingbo Gao of the Northwest Institute of Plateau Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The voucher specimen (NWIPB-0334877) was deposited at the Northwest Institute of Plateau Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Extraction and Isolation. The crushed seeds (20.0 kg), the oil of which had been extracted utilizing supercritical fluid CO2, were refluxed three times with 200 L of 70% EtOH–H2O for 2 h each time. After filtration, the EtOH was removed under reduced pressure to yield a residue. The seed residue was subjected to a silica gel (200–300 mesh) column (20 × 100 cm2) and eluted with CH2Cl2–MeOH–H2O (7:3:0.5). Organic solvents were removed under reduced pressure, yielding a concentrated solution. The partial solution was subjected to an MCI gel column (10 × 100 cm2) and successively eluted with 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, and 100% MeOH–H2O, yielding five fractions (F1–F5, 59.12, 71.86, 22.35, 20.81, and 35.54 g, respectively). Crude F3 (22.35 g) was dissolved in a solution of 60% MeOH–H2O (110 mL) and filtered through 0.45 μm membranes to obtain a sample solution with a concentration of approximately 203 mg/mL. The preparation of the crude sample was performed on a Dubhe C18 preparation column (20 × 250 mm, 5 μm). Mobile phase A was acetonitrile, and mobile phase B was 0.1% v/v formic acid in water. The gradient step was 0–60 min, 10%–20% A. The flow rate was 19 mL/min, and the chromatogram was recorded at 254 nm. The preparation yielded six subfractions (F3a–F3f, 1.69, 1.43, 3.34, 1.44, 2.64, and 0.82 g). The preparation of F3c (3.34 g) was performed on a Kromasil 60-5-Diol preparation column (21 × 250 mm, 5 μm). Mobile phase A was acetonitrile, and mobile phase B was 0.1% v/v formic acid in water. The gradient step was 0–60 min, 100%–80% A. The flow rate was 21 mL/min, and the chromatogram was recorded at 254 nm. The preparation yielded four subsubfractions (F3c-1–F3c-4, 0.107, 0.302, 0.260, and 0.858 g). Mobile phase A was acetonitrile, and mobile phase B was 0.1% v/v formic acid in water. The preparation of F3c-1 (0.107 g) was performed on a Kromasil 100-5-C18 preparation column (21 × 250 mm, 5 μm) to obtain compounds 1 (6 mg), 2 (4 mg), and 3 (5 mg), with 15% A. The preparation of F3c-2 (0.302 g) was performed on the Kromasil 100-5-C18 preparation column (21 × 250 mm, 5 μm) to obtain compounds 4 (7 mg), 5 (213 mg), and 6 (15 mg), with 13%–16% A. The preparation of F3c-3 (0.260 g) was performed on the Kromasil 100-5-C18 preparation column (21 × 250 mm, 5 μm) to obtain compounds 7 (19 mg), with 13% A. The preparation of F3c-4 (0.858 g) was performed on the Kromasil 100-5-C18 preparation column (21 × 250 mm, 5 μm) and Xaqua C18 preparation column (20 × 250 mm, 5 μm) to obtain compounds 8 (21 mg), 9 (6 mg), 10 (60 mg), 11 (79 mg), 12 (51 mg), and 13 (241 mg), with 32% A. All the gradient step was 0–60 min. The flow rate was 21 mL/min, and the chromatogram was recorded at 254 nm.
(6R,9R)-9-Hydroxy-4,7-megastigmadien-3-one 9-O-β-D-apiofuranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside (2), white amorphous powder, C24H38O11. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 201.9 (C-1), 165.6 (C-3), 138.1 (C-8), 129.0 (C-7), 123.6 (C-2), 111.1 (C-1′′), 102.7 (C-1′), 80.5 (C-3′′), 78.3 (C-3′), 78.2 (C-5′), 77.0 (C-2′′), 76.9 (C-9), 75.3 (C-2′), 75.1 (C-4′′), 71.9 (C-4′), 68.7 (C-6′), 65.9 (C-5′′), 56.9 (C-4), 49.0 (C-6), 37.2 (C-5), 28.1 (C-11), 27.4 (C-12), 23.7 (C-13), 21.0 (C-10). ESI-MS m/z 503.2414 [M + H]+ [17].
Kaempferol 3-O-(2-O-β-D-glucoside)-β-D-glucoside-7-O-α-L-rhamnoside (3), yellow amorphous powder, C33H40O20. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 180.0 (C-4), 163.6 (C-7), 163.0 (C-5), 161.7 (C-4′), 159.5 (C-2), 158.2 (C-9), 135.2 (C-3), 132.5 (C-2′, 6′), 122.7 (C-1′), 116.4 (C-3′, 5′), 107.6 (C-10), 104.8 (C-1′′′), 100.9 (C-1′′′), 100.7 (C-6), 99.9 (C-1′′′′), 95.6 (C-8), 82.8 (C-2′′), 78.4 (C-5′′), 78.3 (C-5′′′), 78.0 (C-3′′, 3′′′), 75.7 (C-2′′′), 73.7 (C-4′′′′), 71.8 (C-2′′′′), 72.2 (C-3′′′′), 71.4 (C-4′′′), 71.3 (C-4′′, 5′′′′), 62.7 (C-6′′′), 62.6 (C-6′′), 18.1 (C-6′′′′). ESI-MS m/z 756.6690 [M + H]+ [18].
Isorhamnetin 3-O-β-D-glucoside-7-O-α-L-rhamnoside (4), yellow amorphous powder, C28H33O16. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 177.6 (C-4), 161.6 (C-7), 161.0 (C-5), 156.9 (C-2), 156.0 (C-9), 149.7 (C-3′), 147.0 (C-4′), 133.3 (C-3), 122.4 (C-6′), 121.0 (C-1′), 115.3 (C-5′), 113.5 (C-2′), 105.7 (C-10), 100.8 (C-1′′), 99.4 (C-6), 98.4 (C-1′′′), 94.7 (C-8), 77.6 (C-5′′), 76.5 (C-3′′), 74.4 (C-2′′), 71.7 (C-4′′′), 70.3 (C-3′′′), 70.1 (C-4′′), 69.9 (C-2′′′), 69.8 (C-5′′′), 60.6 (C-6′′), 55.9 (C-OMe), 18.1 (C-6′′′). ESI-MS m/z 625.1850 [M + H]+[19].
Kaempferol-3-rutinoside (5), yellow amorphous powder, C27H30O15. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 159.3 (C-2), 135.5 (C-3), 179.3 (C-4), 162.9 (C-5), 100.0 (C-6), 166.1 (C-7), 94.9 (C-8), 158.2 (C-9), 105.5 (C-10), 122.7 (C-1′), 132.3 (C-2′, 6′), 116.1 (C-3′, 5′), 161.4 (C-4′), 104.6 (C-1′′), 71.4 (C-2′′), 78.1 (C-3′′), 75.7 (C-4′′), 69.7 (C-5′′), 68.5 (C-6′′), 102.4 (C-1′′′), 72.1 (C-2′′′), 72.3 (C-3′′′), 77.2 (C-4′′′), 73.9 (C-5′′′), 17.9 (C-6′′′). ESI-MS m/z 595.1654 [M + H]+ [20].
Kaempferol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-7-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (6), yellow amorphous powder, C27H30O15. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 177.5 (C-4), 164.2 (C-7), 161.3 (C-5), 159.9 (C-4′), 156.9 (C-9), 156.6 (C-2), 133.5 (C-3), 130.9 (C-2′, 6′), 115.2 (C-3′, 5′), 101.6 (C-1′′), 100.8 (C-1′′′), 104.2 (C-10), 99.8 (C-6), 93.8 (C-8), 121.1 (C-1′), 76.7 (C-3′′), 76.0 (C-5′′), 74.4 (C-2′′), 72.1 (C-4′′′), 70.9 (C-4′′), 70.5 (C-2′′′), 70.2 (C-3′′′), 67.1 (C-6′′), 68.3 (C-5′′′), 17.7 (C-6′′′). ESI-MS m/z 595.3429 [M + H]+ [21].
Kaempferol 3-O-β-D-glucosyl-6-α-L-rampopyranoside (7), yellow amorphous powder, C27H30O16. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 177.5 (C-4), 164.0 (C-7), 161.2 (C-5), 160.5 (C-4′), 159.0 (C-2), 157.5 (C-9), 132.0 (C-3), 131.7 (C-2′, 6′), 122.5 (C-1′), 114.2 (C-3′, 5′), 105.0 (C-10), 99.0 (C-6), 93.5 (C-8), 101.5 (C-1′′), 77.15 (C-3′′), 77.15 (C-5′′), 72.5 (C-2′′), 72.23 (C-4′′), 63.0 (C-6′′), 106.90 (C-1′′′), 77.2 (C-3′′′), 77.1 (C-5′′′), 74.4 (C-2′′′), 67.0 (C-4′′′), 60.6 (C-6′′′). ESI-MS m/z 611.5260 [M + H]+ [22].
Isorhamnetin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-galactopyranoside-7-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside (8), yellow amorphous powder, C34H42O22. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 177.7 (C-4), 161.7 (C-7), 161.0 (C-5), 156.5 (C-2), 156.0 (C-9), 149.7 (C-3′), 147.2 (C-4′), 133.3 (C-3), 123.1 (C-6′), 121.0 (C-1′), 115.5 (C-5′), 113.1 (C-2′), 105.7 (C-10), 103.6 (C-1′′′), 99.4 (C-6), 98.4 (C-1′′′′), 98.3 (C-1′′), 94.7 (C-8), 82.2 (C-2′′), 77.6 (C-5′′′), 77.0 (C-3′′′), 76.7 (C-3′′), 76.6 (C-5′′), 74.4 (C-2′′′), 71.7 (C-4′′′′), 70.3 (C-3′′′′), 70.2 (C-4′′′), 69.9 (C-2′′′′), 69.8 (C-5′′′′), 69.6 (C-4′′), 60.9 (C-6′′′), 60.6 (C-6′′), 55.9 (C-OMe), 18.1 (C-6′′′′). ESI-MS m/z 771.2344 [M + H]+ [23].
Quercetin 3-O-(4′′′′-O-E-sinapoyl)-α-rhamnopyranosyl-(1′′′→2′′)[α-rhamnopyranosyl-(1′′′′→6′′)]-β- glucopyranoside (9), yellow amorphous powder, C44H51O24. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 146.9 (C-8′′′′′), 123.2 (C-6′), 117.3 (C-2′), 116.1 (C-7′′′′′), 115.9 (C-5′), 106.9 (C-2′′′′′, 6′′′′′), 102.3 (C-1′′′), 102.2 (C-1′′′′), 100.9 (C-1′′), 100.2 (C-6), 95.0 (C-8), 80.0 (C-2′′), 78.8 (C-3′′), 76.9 (C-5′′), 75.6 (C-4′′′), 73.8 (C-4′′′′), 72.4 (C-2′′′), 72.1 (C-3′′′′), 72.0 (C-2′′′′), 71.7 (C-4′′), 70.3 (C-3′′′), 69.6 (C-5′′′′), 68.4 (C-6′′), 67.7 (C-5′′′), 56.7 (C-3′′′′′OMe, C-5′′′′′OMe), 17.7 (C-6′′′′), 17.2 (C-6′′′). ESI-MS m/z 963.2738 [M + H]+ [24].
Kaempferol 3-O-β-glucopyranoside-7-O-(6-trans-feruloyl)-β-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)rhamnopyranoside (10), yellow amorphous powder, C43H48O23. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 177.5 (C-4), 166.5 (C-9′′′′′), 161.0 (C-7), 160.7 (C-5′), 160.0 (C-4′), 156.7 (C-9), 155.7 (C-2), 145.1 (C-7′′′′′), 149.2 (C-3′′′′′), 147.6 (C-2′′′′′), 133.5 (C-3), 130.9 (C-2′, 6′), 125.2 (C-COO, C-5′′′′′), 120.8 (C-1′), 115.1 (C-3′, 5′), 115.0 (C-4′′′′′, 8′′′′′), 113.9 (C-1′′′′′), 105.6 (C-10), 104.8 (C-1′′′′), 100.9 (C-1′′), 99.1 (C-6, 1′′′), 94.3 (C-8), 81.2 (C-2′′′), 78.4 (C-5′′′′), 77.4 (C-5′′, 3′′′′), 76.0 (C-3′′), 74.2 (C-2′′, 2′′′′), 73.7 (C-4′′′), 70.3 (C-4′′, 5′′′), 70.1 (C-3′′′), 69.9 (C-4′′′′), 63.4 (C-6′′′′), 60.8 (C-6′′), 55.4 (C-6′′′′′), 17.8 (C-6′′′). ESI-MS m/z 933.2691 [M + H]+ [25].
Robinin (11), yellow amorphous powder, C33H40O19. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 177.6 (C-4), 161.6 (C-7), 160.8 (C-5, 4′), 157.0 (C-2), 156.0 (C-9), 133.0 (C-3), 131.1 (C-2′, 6′), 120.6 (C-1′), 115.1 (C-3′, 5′), 105.5 (C-10), 101.8 (C-1′′), 100.0 (C-1′′′), 99.3 (C-6), 98.4 (C-1′′′′), 94.8 (C-8), 73.5 (C-5′′), 72.9 (C-3′′), 71.9 (C-4′′′), 71.6 (C-4′′′′), 71.1 (C-2′′), 70.6 (C-3′′′), 70.4 (C-2′′′), 70.2 (C-3′′′′), 70.1 (C-2′′′′), 69.8 (C-5′′′′), 68.2 (C-4′′), 67.9 (C-5′′′), 65.0 (C-6′′), 17.9 (C-6′′′, 6′′′′). ESI-MS m/z 741.2229 [M + H]+ [26].
Kaempferol 3-(2G-rhamnosylrutinoside) (12), yellow amorphous powder, C33H40O19. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 179.30 (C-4), 165.60 (C-7), 163.16 (C-5), 161.22 (C-2), 159.03 (C-4′), 158.43 (C-9), 134.34 (C-3), 132.13 (C-2′, 6′), 123.17 (C-1′), 116.14 (C-3′, 5′), 105.96 (C-10), 102.59 (C-1′′′), 102.29 (C-1′′′′), 100.46 (C-1′′), 99.77 (C-6), 94.56 (C-8), 79.90 (C-2′′), 78.94 (C-3′′), 77.10 (C-5′′), 74.06 (C-4′′′), 73.83 (C-4′′′′), 72.41 (C-2′′′), 72.33 (C-3′′′, 3′′′′), 72.12 (C-2′′′′), 71.97 (C-4′′), 69.91 (C-5′′′), 69.75 (C-5′′′′), 68.32 (C-6′′), 17.84 (C-6′′′′), 17.56 (C-6′′′). ESI-MS m/z 741.2212 [M + H]+ [27].
Kaempferol 3-O-β-D-glucoside(1→2)-β-D-glucoside-7-O-(3-O-trans-sinapoyl)-α-L-rhamnoside (13), yellow amorphous powder, C44H49O24. 13C NMR (150 MHz, CD3OD, δ, ppm): 177.9 (C-4), 166.7 (C-9′′′), 161.3 (C-5, 7, 4′), 156.4 (C-2, 9), 148.7 (C-3′′′, 5′′′), 145.4 (C-7′′′), 138.2 (C-4′′′), 133.2 (C-3), 131.1 (C-2′, 6′), 120.9 (C-1′), 120.6 (C-1′′′), 116.0 (C-3′, 5′), 113.4 (C-8′′′), 106.7 (C-2′′′, 6′′′, 10), 104.1 (C-1′′′′′), 99.3 (C-6), 98.4 (C-1′′), 98.1 (C-1′′′′), 94.0 (C-8), 82.5 (C-2′′′′), 77.5 (C-5′′′′′), 77.0 (C-3′′′′′), 76.7 (C-3′′′′, 5′′′′), 73.4 (C-3′′), 70.2 (C-4′′), 70.0 (C-4′′′′′), 69.8 (C-4′′′′), 68.6 (C-5′′), 67.6 (C-2′′), 61.0 (C-6′′′′′), 60.7 (C-6′′′′), 55.7 (3′′′′, 5′′′′-OMe), 18.0 (C-6′′). ESI-MS m/z 963.2216 [M + H]+ [28].
References
Y. Yao and P. M. Tigerstedt, J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci., 120, 691 (1995).
W. Zhou, Y. Wang, G. Zhang, G. Luan, S. Chen, J. Meng, H. Wang, N. Hu, and Y. Suo, Molecules, 23, 1048 (2018).
F. Tie, J. Ding, N. Hu, Q. Dong, Z. Chen, and H. Wang, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 22 (2021).
W. Zhou, J. Ouyang, N. Hu, G. Li, and H. Wang, Molecules, 26, 1946 (2021).
J.-S. Kim, Y.-S. Kwon, Y.-J. Sa, and M.-J. Kim, J. Agric. Food Chem., 59, 138 (2011).
J. Zhang, H.-C. Zhou, S.-B. He, X.-F. Zhang, Y.-H. Ling, X.-Y. Li, H. Zhang, and D.-D. Hou, Food Funct., 12, 7954 (2021).
W. Zhou, Z. Yuan, G. Li, J. Ouyang, Y. Suo, and H. Wang, Nat. Prod. Res., 32, 892 (2018).
J. Zhang, W. Gao, M.-S. Cao, and D.-Y. Kong, J. Asian. Nat. Prod. Res., 14, 1122 (2012).
E. Wei, R. Yang, H. Zhao, P. Wang, S. Zhao, W. Zhai, Y. Zhang, and H. Zhou, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 123, 280 (2019).
C. Shen, T. Wang, F. Guo, K. Sun, B. Wang, J. Wang, Z. Zhang, X. Zhang, Y. Zhao, and Y. Chen, Carbohyd. Polym., 274, 118648 (2021).
E. Glazunova, E. S. Mukhtarova, K. Zakharov, and N. Gachechiladze, Chem. Nat. Compd., 30, 271 (1994).
A.-A. Sorescu, A. Nuta, R.-M. Ion, and L. Iancu, Phytochem.-Source Antiox. Role Dis. Prevent., 161 (2018).
J. OuYang, W.-N. Zhou, G. Li, X.-Y. Wang, C.-X. Ding, Y.-R. Suo, and H.-L. Wang, Helv. Chim. Acta, 98, 1287 (2015).
S. Shivapriya, K. Ilango, and G. Dubey, Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 22 (5), 645 (2015).
H. Kodama, T. Fujimori, and K. Kato, Phytochemistry, 23, 583 (1984).
N. De Tommasi, R. Aquino, F. De Simone, and C. Pizza, J. Nat. Prod., 55, 1025 (1992).
A. Pabst, D. Barron, E. Semon, and P. Schreier, Phytochemistry, 31, 1649 (1992).
G. C. Kite, C. A. Stoneham, and N. C. Veitch, Phytochemistry, 68, 1407 (2007).
D. Rosch, A. Krumbein, C. Mugge, and L. Kroh, J. Agric. Food Chem., 52, 4039 (2004).
R. Xiong, J. Jiang, and Y. Chen, Nat. Prod. Res., 35, 1019 (2021).
P. Gupta, U. Sharma, P. Gupta, K. B. Siripurapu, and R. Maurya, Bioorgan. Med, Chem., 21, 1116 (2013).
B. d. S. de Sousa Nogueira, D. Antas e Silva, J. F. Tavares, E. De Oliveira Lima, F. De Oliveira Pereira, M. M. M. De Souza Fernandes, F. A. De Medeiros, R. Do Socorro Ferreira Rodrigues Sarquis, J. K. Da Silva Maciel, and M. De Fatima Vanderlei de Souza, Molecules, 18, 11086 (2013).
H. Ishida, T. Umio, K. Tsuji, and T. Kosuge, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 36, 4414 (1988).
N. C. Veitch, I. Regos, G. C. Kite, and D. Treutter, Phytochemistry, 72, 423 (2011).
H. J. Jeong, W. K. Whang, and I. H. Kim, Planta Med., 63, 329 (1997).
D. Wang, Y. Wang, S. Tan, T. Guo, A. Zhao, and J. Chang, Chem. Nat. Compd., 55, 540 (2019).
K. Kazuma, N. Noda, and M. Suzuki, Phytochemistry, 62, 229 (2003).
C. Chen, W. Gao, D.-W. Ou-Yang, J. Zhang, and D.-Y. Kong, Nat. Prod. Res., 28, 24 (2014).
Acknowledgment
Innovation Platform for the Development and Construction of Special Project of Qinghai Province (2021-ZJ-T05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, No. 1, January–February, 2024, pp. 20–23.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, J., Hu, N., Li, G. et al. Megastigmanes and Flavonoids from Seeds of Hippophae rhamnoides. Chem Nat Compd 60, 21–25 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-024-04243-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-024-04243-4