Summary
Congenital defects of glycosylation (CDG) are genetic diseases due to deficient glycosylation of glycoconjugates (glycoproteins, glycolipids) and to deficient synthesis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors. Since the first clinical description, in 1980, of patients with a CDG, this disease family has shown an exponential expansion. At least 145 CDG have been reported. They can be divided into five groups: (1) defects in protein N-glycosylation, (2) defects in protein O-glycosylation, (3) defects in lipid glycosylation, (4) defects in multiple glycosylation pathways, and (5) defects in glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor biosynthesis. In 2009, a novel, transparent CDG nomenclature was introduced that covers all (known and still to be discovered) CDG. It consists of the official gene symbol (unitalicized) followed by “-CDG.” The majority of CDG patients show neurological disease associated with variable involvement of nearly all other organs. Only a few CDG are mono-organ diseases (e.g., ALG2-CDG, ALG14-CDG, GFPT1-CDG (retina), EXT1/EXT2-CDG (cartilage), GNE-CDG (skeletal muscles), POFUT1-CDG (skin), POGLUT1-CDG (skin or skeletal muscles), SEC23B-CDG (erythrocytes), ST3GAL3-CDG (brain), TMEM199-CDG (liver), TUSC3-CDG (brain)). The known CDG present autosomal recessive inheritance except for ALG13-CDG, ATP6AP1-CDG, MAGT1-CDG, PIGA-CDG, SLC35A2-CDG, and SSR4-CDG (X-linked) and EXT1/EXT2-CDG, GANAB-CDG, POFUT1-CDG, POGLUT1-CDG, and PRKCSH-CDG (autosomal dominant). Some CDG can be diagnosed clinically such as EXT1/EXT2-CDG and the typical PMM2-CDG presentation. Two screening techniques are available: serum transferrin isoelectrofocusing (or similar techniques such as capillary zone electrophoresis) for the diagnosis of protein N-glycosylation disorders associated with sialic acid deficiency and serum apolipoprotein C-III isoelectrofocusing for the diagnosis of core 1 mucin-type O-glycans. Treatment possibilities are still frustratingly limited. An efficient therapy is available for only two CDG, namely, oral mannose for MPI-CDG and oral uridine for CAD-CDG. Since about 1–2% of the human genome is involved in glycosylation, it appears that a substantial number of CDG have still to be discovered. Elucidation of the basic defects of these CDG will increasingly require next-generation sequencing techniques such as whole exome and whole genome sequencing. Metabolomics and glycomics technology will reveal novel insights into the molecular basis of CDG.
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG) are genetic diseases caused by defective glycosylation of glycoproteins and glycolipids and defective synthesis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors (reviews in Abu Bakar et al. (2018), Ferreira et al. (2018), Jaeken and Péanne (2017), Ng and Freeze (2018); reviews on specific aspects of CDG in Coman et al. (2008) (skeleton), Francisco et al. (2018b), Morava et al. (2009) (eyes), Marques-da-Silva et al. (2017b) (heart), Marques-da-Silva et al. (2017a) (liver), Monticelli et al. (2016) (immune system)). A novel CDG nomenclature was recently introduced that covers all (known and still to be discovered) CDG. It consists of the official gene symbol (unitalicized) followed by “-CDG” (Jaeken et al. 2009). Among the 145 known CDG, 118 are disorders of glycoprotein glycosylation. This CDG group comprises disorders of N-glycosylation, disorders of O-glycosylation, and disorders with a combined N- and O-glycosylation defect. C-Glycosylation defects have not yet been reported. The N-glycosylation pathway encompasses three cellular compartments: the cytosol, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and the Golgi. It starts in the cytosol with the formation of the mannose donor GDP-mannose from fructose 6-phosphate, an intermediate of the glycolytic pathway. In the ER, the dolichol-linked oligosaccharide GlcNAc2Man9Glc3 is assembled and subsequently transferred from dolichol to selected asparagines of nascent proteins. Still in the ER, this glycan starts to be processed by trimming off the three glucoses. This processing is continued in the Golgi by trimming off six mannoses and replacing them by two residues each of N-acetylglucosamine, galactose and finally sialic acid. O-Glycosylation is usually limited to the Golgi and has no processing pathway. The O-glycans are linked to the hydroxyl group of selected threonine and serine residues.
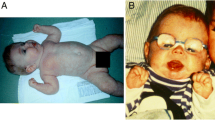
The first report on CDG was on patients who were subsequently shown to have an N-glycosylation disorder, phosphomannomutase 2 deficiency (PMM2-CDG) (Jaeken et al. 1980; Van Schaftingen and Jaeken 1995; Matthijs et al. 1997). It is a cytosolic assembly defect and turned out to be, by far, the most frequent N-glycosylation disorder with around 900 patients known worldwide. They show mild to severe neurological disease and variable involvement of many other organs. Dysmorphism ranges from mild and aspecific to a characteristic abnormal subcutaneous adipose tissue distribution with fat pads and nipple retraction. Mortality is about 20% in the first years of life (review in Grünewald 2009). The second most frequent N-glycosylation disorder is an ER assembly defect, glucosyltransferase 1 deficiency (ALG6-CDG). It is mainly a neurological disorder but usually milder than that of PMM2-CDG, with limb anomalies in some 10% of these patients (92 patients reported) (review in Morava et al. 2016). The third most reported N-glycosylation disorder is ALG1-CDG with 58 patients, also a predominant neurological disease (review in Ng et al. 2016). The fourth place is occupied by two CDG, on the one hand MAN1B1-CDG and on the other mannose phosphate isomerase deficiency (MPI-CDG), each with around 40 reported patients. MPI-CDG (review in Jaeken et al. 2014) is a remarkable disorder not only because of its pure hepatic-intestinal presentation but particularly because it is one of only two, more or less efficiently, treatable CDG (with oral mannose). The other is CAD-CDG, a defect in pyrimidine biosynthesis causing a deficiency in uridine diphosphate (UDP) (Koch et al. 2017). UDP monosaccharides are necessary for the transport of monosaccharides into the Golgi.
The protein N-glycosylation disorders can be divided into three groups: (1) defects in nucleotide-sugar biosynthesis (e.g., PMM2-CDG, MPI-CDG), (2) defects in lipid-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis (e.g., DPAGT1-CDG, ALG1-CDG), and (3) defects in protein-linked oligosaccharide biosynthesis (e.g., MAN1B1-CDG, MGAT2-CDG).
A number of protein N-glycosylation disorders are associated with a protein O-glycosylation defect. These comprise defects in dolichol phosphate biosynthesis (e.g., DK1-CDG, SRD5A3-CDG), in dolichol phosphomannose synthesis (e.g., DPM1-CDG, DPM3-CDG), in dolichol phosphomannose utilization (MPDU1-CDG), in galactosylation (B4GALT1-CDG), in sialylation (SLC35A1-CDG), in fucosylation (SLC35C1-CDG), in ER-Golgi intermediate compartment proteins (SEC23B-CDG), and in other vesicular transport proteins (e.g., COG-CDG, ATP6V0A2-CDG). The latter two groups comprise defects in proteins that are not only involved in glycosylation but also in other functions (such as Golgi pH regulation). It has been proposed to name them “CDG-plus.”
The protein O-glycosylation disorders can be divided on the basis of the monosaccharide which links the glycan to the protein. Seven groups have been described: (1) defects in O-xylosylglycan synthesis (e.g., XYLT1-CDG, B4GALT7-CDG, EXT1/EXT2-CDG, CHSY1-CDG); (2) defect in O-N-acetylglucosaminylglycan synthesis (EOGT-CDG); (3) defect in O-N-acetylgalactosaminylglycan synthesis (GALNT3-CDG); (4) defect in O-xylosyl/N-acetylgalactosaminylglycan synthesis (SLC35D1-CDG); (5) defects in O-mannosylglycan synthesis (e.g., POMT1/POMT2-CDG, POMGNT1-CDG, B3GALNT2-CDG, LARGE-CDG); (6) defects in O-fucosylglycan synthesis (POFUT1-CDG, B3GALTL-CDG, LFNG-CDG); and (7) defect in O-glucosylglycan synthesis (POGLUT1-CDG). Several of these diseases have also a descriptive name, based on their typical clinical presentation: multiple cartilaginous exostoses (EXT1/EXT2-CDG), familial tumoral calcinosis (GALNT3-CDG), Schneckenbecken dysplasia (SLC35D1-CDG), muscle-eye-brain disease (POMGNT1-CDG, POMT1/POMT2-CDG), and spondylocostal dysostosis type 3 (LFNG-CDG).
Most CDG present an autosomal recessive inheritance. ALG13-CDG, ATP6AP1-CDG, MAGT1-CDG, PIGA-CDG, SLC35A2-CDG, and SSR4-CDG are X-linked, and EXT1/EXT2-CDG, GANAB-CDG, POFUT1-CDG, POGLUT1-CDG, and PRKCSH-CDG display an autosomal dominant inheritance.
Essentially two techniques are available for CDG screening: serum transferrin isoelectrofocusing (IEF) detects protein N-glycosylation disorders associated with sialic acid deficiency (Jaeken et al. 1984), and serum apolipoprotein C-III IEF detects core 1 mucin-type O-glycosylation defects (Wopereis et al. 2003). Serum transferrin IEF can be replaced by other techniques such as capillary zone electrophoresis (Carchon et al. 2004). Serum transferrin IEF detects only about 50% of the known CDG. It does not pick up the O-glycosylation disorders that are not associated with an N-glycosylation defect, the lipid glycosylation defects, and the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor synthesis defects, as well as defects in the N-glycosylation pathway that do not show a deficiency of sialic acid (PMM2-CDG due to a promotor defect, GMPPA-CDG, GMPPB-CDG, TUSC3-CDG, MOGS-CDG, GANAB-CDG, PRKCSH-CDG, FUT8-CDG, GNE-CDG, NANS-CDG, DHDDS-CDG, SLC35A1-CDG, SLC35A3-CDG, SLC35C1-CDG, SEC23B-CDG, PGM3-CDG). In case of an abnormal transferrin IEF profile, first an artifact, a protein polymorphism, and a secondary CDG (fructosemia, galactosemia, alcohol abuse, bacterial sialidase) should be excluded. Two types of abnormal transferrin IEF profiles can be distinguished: a type 1 pattern, characterized by an increase of di- and/or asialoprotein (CDG-I), and a type 2 pattern, characterized by an increase of tri-, di-, mono-, and/or asialoprotein (CDG-II). A type 1 pattern points to an assembly or transfer defect of the dolichol-linked glycan (in the cytosol or the ER). When there is a typical PMM2-CDG or MPI-CDG phenotype, measurement of the phosphomannomutase or mannose phosphate isomerase activity in fibroblasts or leukocytes is the next step, or direct mutation analysis of the involved genes. If there is no typical phenotype, next-generation sequencing (CDG gene panel analysis, WES, or WGS) is indicated. A type 2 pattern indicates a glycan processing defect (in the ER or the Golgi). If this is associated with a typical MAN1B1-CDG, MGAT2-CDG, or PGM1-CDG phenotype, mutation analysis is indicated, preceded or not by structural analysis of serum transferrin glycans. In the absence of a typical phenotype, CDG gene panel analysis, WES, or WGS should be performed. In order to know whether there is an associated O-glycosylation defect, apolipoprotein C-III IEF can be performed. When there is a normal serum transferrin IEF pattern but a strong clinical and/or biochemical suspicion (e.g., fat pads, cerebellar hypoplasia, and decreased coagulation factor XI (PMM2-CDG); intellectual disability with increased serum alkaline phosphatases (GPI anchor synthesis defect)), mutation analysis of the suspected gene or next-generation sequencing (using gene panels, WES, and/or WGS) should be performed (Francisco et al. 2018a).
The nomenclature and signs and symptoms tables are limited in this article to 124 CDG, namely, 30 disorders of N-linked glycosylation, 16 disorders of O-mannosylglycan synthesis, 1 disorder of O-N-acetylgalactosaminylglycan synthesis, 2 disorders of O-N-acetylglucosaminylglycan synthesis, 1 disorder of O-glucosylglycan synthesis, 2 disorders of O-fucosylglycan synthesis, 1 disorder of a galactosyltransferase-specific chaperone, 8 disorders of dolichol metabolism, 4 disorders of monosaccharide synthesis and interconversion, 1 disorders of nucleotide-sugar synthesis, 6 disorders of Golgi transport, 1 disorder of plasma membrane transport, 8 disorders of Golgi homeostasis, 24 disorders of glycosaminoglycan synthesis, and 19 GPI anchor synthesis disorders. N-Glycanase 1 deficiency (68.125) is not a CDG but a congenital disorder of deglycosylation (CDDG).
Nomenclature
No. | Disorder | Alternative names | Gene symbol | Chromosomal localization | Mode of inheritance | Affected protein | OMIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
PMM2-CDG | Phosphomannomutase 2 deficiency | PMM2 | 16p13.2 | AR | Phosphomannomutase 2 | 601785 | |
MPI-CDG | Phosphomannose isomerase deficiency | MPI | 15q24.1 | AR | Phosphomannose isomerase | 602579 | |
DPAGT1-CDG | UDP-GlcNAc:Dol-P-GlcNac-P transferase deficiency | DPAGT1 | 11q23.3 | AR | UDP-GlcNAc:dolichol-phosphate-N-Acetylglucosamine-1-phosphotransferase | 608093 | |
ALG13-CDG | X-linked recessive UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase catalytic subunit deficiency | ALG13 | Xq23 | XLR | UDP-GlcNAc:dolichol pyrophosphate N-acetylglucosamine transferase (cytosolic) | 300884 | |
ALG13-CDG | X-linked dominant UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase catalytic subunit deficiency | ALG13 | Xq23 | XLD | UDP-GlcNAc:dolichol pyrophosphate N-acetylglucosamine transferase (cytosolic) | 300884 | |
ALG14-CDG | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transferase anchoring subunit deficiency | ALG14 | 1p21.3 | AR | UDP-GlcNAc:dolichol pyrophosphate N-acetylglucosamine transferase (membrane-bound) | 616227, 612866 | |
ALG1-CDG | Mannosyltransferase 1 deficiency | ALG1 | 16p13.3 | AR | GDP-Man:GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol mannosyltransferase | 608540 | |
ALG2-CDG | Mannosyltransferase 2 deficiency | ALG2 | 9q22.33 | AR | GDP-mannose:Man1GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol mannosyltransferase | 607906 | |
ALG11-CDG | Mannosyltransferase 4–5 deficiency | ALG11 | 13q14.3 | AR | GDP-Man:Man3-4GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol mannosyltransferase | 613661 | |
RFT1-CDG | Flippase of Man5GlcNAc2-PP-Dol deficiency | RFT1 | 3p21.1 | AR | Flippase of Man5GlcNAc2-PP-Dol | 612015 | |
ALG3-CDG | Mannosyltransferase 6 deficiency | ALG3 | 3q27.1 | AR | Dolichol-P-mannose: Man5GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol mannosyltransferase | 601110 | |
ALG9-CDG | Mannosyltransferase 7–9 deficiency | ALG9 | 11q23.1 | AR | Dolichol-P-mannose:α1,2 mannosyltransferase | 608776 | |
ALG12-CDG | Mannosyltransferase 8 deficiency | ALG12 | 22q13.33 | AR | Dolichol-P-mannose: Man7GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol mannosyltransferase | 607143 | |
ALG6-CDG | Glucosyltransferase 1 deficiency | ALG6 | 1p22.3 | AR | Dolichol-P-glucose:Man9GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol glucosyltransferase | 603147 | |
ALG8-CDG | Glucosyltransferase 2 deficiency | ALG8 | 11q14.1 | AR | Dolichol-P-glucose: Glc1Man9GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol- α1,3-glucosyltransferase | 608104 | |
TUSC3-CDG | Oligosaccharyltransferase subunit TUSC3 deficiency | TUSC3 | TUSC3 | AR | Subunit N33-TUSC3 of the OST complex | 611093 | |
DDOST-CDG | Oligosaccharyltransferase subunit DDOST deficiency | DDOST | 1p36.12 | AR | Subunit DDOST of the OST complex | 614507, 602202 | |
STT3A-CDG | Oligosaccharyltransferase subunit STT3A deficiency | STT3A | 11q24.2 | AR | Subunit STT3A of the OST complex | 615596, 601134 | |
STT3B-CDG | Oligosaccharyltransferase subunit STT3B deficiency | STT3B | 3p23 | AR | Subunit STT3B of the OST complex | 615597 | |
MAGT1-CDG | Magnesium transporter 1 deficiency | MAGT1 | Xq21.1 | XL | Magnesium transporter 1 | 300716, 300853 | |
SSR4-CDG | Translocon-associated protein δ subunit deficiency | SSR4 | Xq28 | XL | Signal sequence receptor 4 protein of the TRAP complex | 300934 | |
MOGS-CDG | Glucosidase 1 deficiency | MOGS | 2p13.1 | AR | Endoplasmic reticulum glucosidase I | 606056 | |
GANAB-CDG | Polycyctic kidney disease 3 | GANAB | 11q12.3 | AD | Alpha subunit of glucosidase II | 600666 | |
PRKCSH-CDG | α-1,3-glucosidase II subunit β deficiency | PRKCSH | 19p13.2 | AD | Protein kinase C substrate, 80-KD, heavy chain | 174050 | |
MAN1B1-CDG | Mental retardation, autosomal recessive 15 | MAN1B1 | 9q34.3 | AR | Endoplasmic reticulum 1,2-α-mannosidase | 614202, 604346 | |
MGAT2-CDG | N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 deficiency | MGAT2 | 14q21.3 | AR | Golgi N-acetyl-glucosaminyltransferase II | 212066 | |
B4GALT1-CDG | Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1 deficiency | B4GALT1 | 9p21.1 | AR | Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1 | 607091 | |
FUT8-CDG | α-1,6-fucosyltransferase deficiency | FUT8 | 14q23.3 | AR | Fucosyltransferase 8 | 602589 | |
POMT1-CDG | Protein O-mannosyltransferase 1 deficiency | POMT1 | 9q34.13 | AR | O-mannosyltransferase 1 | 236670, 613555, 609308 | |
POMT2-CDG | Protein O-mannosyltransferase 2 deficiency | POMT2 | 14q24.3 | AR | O-mannosyltransferase 2 | 613150, 613156, 613158 | |
POMGNT1-CDG | O-mannose beta-1,2-N-acetyglucosaminyltransferase deficiency | POMGNT1 | 1p34.1 | AR | O-Mannose beta-1,2-N-acetyglucosaminyltransferase | 253280, 613151, 613157 | |
POMGNT2-CDG | O-mannose β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase deficiency | POMGNT2 | 3p22.1 | AR | Protein O-mannose beta-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 2 | 614830 | |
B3GALNT2-CDG | β-1,3-galactosaminyltransferase 2 deficiency | B3GALNT2 | 1q42.3 | AR | Beta-1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2 | 615181 | |
POMK-CDG | O-mannose kinase deficiency | POMK | 8p11.21 | AR | Protein-O-mannose kinase | 616094; 615249 | |
CRPPA-CDG | Methylerythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase deficiency | CRPPA | 7p21.2 | AR | 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate cytidylyltransferase | ||
FKTN-CDG A | Fukutin type A deficiency | FKTN | 9q31.2 | AR | Fukutin | 253800 | |
FKTN-CDG B | Fukutin type B deficiency | FKTN | 9q31.3 | AR | Fukutin | 613152 | |
FKTN-CDG C | Fukutin limb-girdle type C deficiency | FKTN | 9q31.4 | AR | Fukutin | 611588 | |
FKRP-CDG A | FKRP type A deficiency | FKRP | 19q13.32 | AR | Fukutin-related protein | 613153 | |
FKRP-CDG B | FKRP type B deficiency | FKRP | 19q13.33 | AR | Fukutin-related protein | 606612 | |
FKRP-CDG C | FKRP limb-girdle type C deficiency | FKRP | 19q13.34 | AR | Fukutin-related protein | 606596 | |
RXYLT1-CDG | Ribitol β1,4-xylosyltransferase deficiency | RXYLT1 | 12q14.2 | AR | Ribitol β1,4-xylosyltransferase | 615041 | |
B4GAT1-CDG | β-1,4-glucuronyltransferase 1 deficiency | B4GAT1 | 11q13.2 | AR | Beta-1,4-glucuronyltransferase 1 | 615287 | |
LARGE1-CDG | β-1,3-glucuronyltransferase/α-1,3-xylosytransferase deficiency | LARGE1 | 22q12.3 | AR | Acetylglucosaminyltransferase-like protein | 613154; 608840 | |
XYLT1-CDG | Xylosyltransferase 1 deficiency | XYLT1 | 16p12.3 | AR | Xylosyltransferase 1 | 615777 | |
XYLT2-CDG | Xylosyltransferase 2 deficiency | XYLT2 | 17q21.33 | AR | Xylosyltransferase 2 | 605822 | |
B4GALT7-CDG | β-1,4-galactosyltransferase 7 deficiency | B4GALT7 | 5q35.3 | AR | Golgi UDP-galactose:N-acetylglucosamine β-1,4-galactosyltransferase | 130070 | |
B3GALT6-CDG | β-1,3-galactosyltransferase 6 deficiency | B3GALT6 | 1p36.33 | AR | Beta-1,3-galactosyltransferase 6 | 271640; 615349 | |
B3GAT3-CDG | β-1,3-glucuronyltransferase 3 deficiency | B3GAT3 | 11q12.3 | AR | Beta-1,3-glucuronyltransferase 3 | 245600 | |
EXT1-CDG | Exostosin 1 deficiency | EXT1 | 8q24.11 | AD | Exostosin glycosyltransferase 1 | 133700 | |
EXT2-CDG | Exostosin 2 deficiency | EXT2 | 11p11.2 | AD | Exostosin glycosyltransferase 2 | 133701 | |
EXT2-CDG | Autosomal recessive exostosin 2 deficiency | EXT2 | 11p11.2 | AR | Exostosin glycosyltransferase 2 | 616682 | |
EXTL3-CDG | Exostosin-like glycosyltransferase 3 deficiency | EXTL3 | 8p21.1 | AR | Exostosin-like glycosyltransferase 3 | 617425 | |
CHSY1-CDG | Chondroitin sulfate synthase 1 deficiency | CHSY1 | 15q26.3 | AR | Chondroitin sulfate synthase 1 | 605282 | |
CHST11-CDG | Chondroitin 4-sulfotransferase 1 deficiency | CHST11 | 12q23.3 | AR | Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 11 | 610128 | |
CHST3-CDG | Chondroitin 6-sulfotransferase deficiency | CHST3 | 10q22.1 | AR | Chondroitin 6-sulfotransferase 3 | 143095 | |
CHST14-CDG | Dermatan 4-sulfotransferase 1 deficiency | CHST14 | 15q15.1 | AR | Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 14 | 601776 | |
DSE-CDG | Dermatan sulfate epimerase deficiency | DSE | 6q22.1 | AR | Dermatan sulfate epimerase | 615539 | |
CSGALNACT1-CDG | Chondroitin sulfate N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1 deficiency | CSGALNACT1 | 8p21.3 | AR | Chondroitin sulfate N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1 | 616615 | |
CHST6-CDG | Corneal N-acetylglucosamine 6-O-sulfotransferase deficiency | CHST6 | 16q23.1 | AR | N-Acetylglucosamine 6-O-sulfotransferase | 217800 | |
NDST1-CDG | Heparan sulfate N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 1 deficiency | NDST1 | 5q33.1 | AR | N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase 1 | 616116 | |
HS6ST1-CDG | Heparan sulfate 6-O-sulfate transferase 1 deficiency | HS6ST1 | 2q14.3 | AD | Heparan sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase 1 | 614880 | |
CANT1-CDG | Calcium-activated nucleotidase 1 deficiency | CANT1 | 17q25.3 | AR | Calcium-activated nucleotidase 1 | 251450; 617719 | |
SLC26A2-CDG | Sulfate transporter deficiency | SLC26A2 | 5q32 | AR | Solute carrier family 26 (sulfate transporter), member 2 | 226900; 222600; 256050; 600972 | |
PAPSS2-CDG | Phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate synthetase 2 deficiency | PAPSS2 | 10q23.2-q23.3 | AR | 3-Prime-phosphoadenosine 5-prime-phosphosulfate synthase 2 | 612847 | |
IMPAD1-CDG | Inositol monophosphate domain-containing protein 1 deficiency | IMPAD1 | 8q12.1 | AR | Inositol monophosphatase domain-containing protein 1 | 614078 | |
TGDS-CDG | TDP-D-glucose 4,6-dehydrogenase deficiency | TGDS | 13q32.1 | AR | TDP-D-glucose 4,6-dehydrogenase | 616145 | |
GALTNT3-CDG | Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 3 deficiency | GALNT3 | 2q24.3 | AR | Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 3 | 211900 | |
C1GATLT1C1-CDG | Core 1 β-1,3-galactosyltransferase chaperone deficiency | C1GALT1C1 | Xq24 | XL | C1GALT1-specific chaperone 1 | 300622 | |
OGT-CDG | O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase deficiency | OGT | Xq13.1 | XL | O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase | 300997 | |
EOGT-CDG | Adams-Oliver syndrome type 4 | EOGT | 3p14.1 | AR | EGF domain-specific O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase | 615297 | |
POGLUT1-CDG | Muscular dystrophy, limb-girdle, type 2Z | POGLUT1 | 3q13.33 | AR | Endoplasmic reticulum O-glucosyltransferase | 617232 | |
POGLUT2-CDG | Dowling-Degos disease 4 | POGLUT2 | 3q13.34 | AR | Endoplasmic reticulum O-glucosyltransferase | 615696 | |
POFUT1-CDG | Protein O-fucosyltransferase deficiency | POFUT1 | 20q11.21 | AD | Protein o-fucosyltransferase 1 | 615327 | |
LFNG-CDG | O-fucose-specific beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase deficiency | LFNG | 7p22.3 | AR | O-Fucose-specific beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase | 609813 | |
B3GLCT-CDG | O-fucose-specific beta-1,3-N-glucosyltransferase deficiency | B3GLCT | 13q12.3 | AR | O-Fucose-specific beta-1,3-N-glucosyltransferase | 261540 | |
PIGA-CDG | PIGA deficiency | PIGA | Xp22.2 | XL | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class A protein | 300868; 300818 | |
PIGC-CDG | PIGC deficiency | PIGC | 1q24.3 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class C protein | 617816 | |
PIGQ-CDG | PIGQ deficiency | PIGQ | 16p13.3 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class Q protein | 618548 | |
PIGP-CDG | PIGP deficiency | PIGP | 21q22.13 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class P protein | 617599 | |
PIGY-CDG | PIGY deficiency | PIGY | 1p36.11 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class Y protein | 239300 | |
PIGH-CDG | PIGH deficiency | PIGH | 14q24.1 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class H protein | 618010 | |
PIGL-CDG | PIGL deficiency | PIGL | 17p11.2 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class L protein | 280000 | |
PIGW-CDG | PIGW deficiency | PIGW | 17q12 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class W protein | 616025 | |
PIGM-CDG | PIGM deficiency | PIGM | 1q23.2 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class M protein | 610293 | |
PIGV-CDG | PIGV deficiency | PIGV | 1p36.11 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class V protein | 239300 | |
PIGN-CDG | PIGN deficiency | PIGN | 18q21.33 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class N protein | 614080 | |
PIGO-CDG | PIGO deficiency | PIGO | 9p13.3 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class O protein | 614749 | |
PIGG-CDG | PIGG deficiency | PIGG | 4p16.3 | AR | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis G protein | 616917 | |
PIGT-CDG | PIGT deficiency | PIGT | 20q13.12 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class T protein | 615398 | |
GPAA1-CDG | GPAA1 deficiency | GPAA1 | 8q24.3 | AR | Glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor attachment protein 1 | 617810 | |
PGAP1-CDG | PGAP1 deficiency | PGAP1 | 2q33.1 | AR | GPI deacylase | 615802 | |
PGAP3-CDG | PGAP3 deficiency | PGAP3 | 17q12 | AR | PER1-like domain-containing protein 1 | 615716 | |
PGAP2-CDG | PGAP2 deficiency | PGAP2 | 11p15.4 | AR | Post-gpi attachment to proteins 2 | 614207 | |
PIGS-CDG | PIGS deficiency | PIGS | 17q11.2 | AR | Phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class S protein | 618143 | |
DHDDS-CDG | Dehydrodolichyl diphosphate synthase deficiency | DHDDS | 1p36.11 | AR | Dehydrodolichyl diphosphate synthase | 613861, 608172 | |
NgBR-CDG | Nogo-B receptor deficiency | NUS1 | 6q22.1 | AR | Subunit of cis-prenyltransferase (cis-PTase) | 617082 | |
SRD5A3-CDG | Steroid 5 alpha-reductase 3 deficiency | SRD5A3 | 4q12 | AR | Steroid 5 alpha-reductase 3 | 612379 | |
DK1-CDG | Dolichol kinase deficiency | DOLK | 9q34.11 | AR | Dolichol kinase | 610768 | |
DPM1-CDG | GDP-Man:Dol-P mannosyltransferase subunit 1 deficiency | DPM1 | 20q13.13 | AR | GDP-Man:Dol-P mannosyltransferase subunit 1 | 608799 | |
DPM2-CDG | Dolichol-P-mannose synthase-2 deficiency | DPM2 | 9q34.11 | AR | Dolichol-P-mannose synthase-2 | 615042 | |
DPM3-CDG | GDP-Man:Dol-P mannosyltransferase 3 deficiency | DPM3 | 1q22 | AR | Dolichol-P-mannose synthase 3 | 612937 | |
MPDU1-CDG | Dol-P-Man utilization 1 deficiency | MPDU1 | 17p13.1 | AR | Dol-P-Man utilization 1 | 609180 | |
GFPT1-CDG | Glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate transaminase deficiency | GFPT1 | 2p13.3 | AR | Glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 1 | 610542 | |
PGM1-CDG | Phosphoglucomutase 1 deficiency | PGM1 | 1p31.3 | AR | Phosphoglucomutase 1 | 614921 | |
PGM3-CDG | Phosphoglucomutase 3 deficiency | PGM3 | 6q14.1 | AR | Phosphoglucomutase 3 | 615816, 172100 | |
G6PC3-CDG | Glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit 3 deficiency | G6PC3 | 17q21.31 | AR | Glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit 3 | 612541 | |
GMPPA-CDG | GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase α subunit deficiency | GMPPA | 2q35 | AR | GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase subunit A | 615510 | |
GMPPB-CDG | GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase β subunit deficiency | GMPPB | 3p21.31 | AR | GDP-mannose pyrophosphorylase subunit B | 615350, 615351, 615352 | |
CAD-CDG | Epileptic encephalopathy, early infantile, 50 | CAD | 2p23.3 | AR | Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase, aspartate transcarbamoylase, and dihydroorotase trifuntional protein (CPSase/ATCase/DHOase) | 616457 | |
SLC35A1-CDG | CMP-sialic acid transporter deficiency | SLC35A1 | 6q15 | AR | CMP-sialic acid transporter | 603585 | |
SLC35A2-CDG | UDP-galactose transporter deficiency | SLC35A2 | Xp11.23 | XL | Golgi UDP-galactose transporter | 314375 | |
SLC35A3-CDG | UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transporter deficiency | SLC35A3 | 1p21.2 | AR | Solute carrier family 35 (udp-n-acetylglucosamine transporter), member 3 | 615553 | |
SLC35C1-CDG | GDP-fucose transporter deficiency | SLC35C1 | 11p11.2 | AR | GDP-fucose transporter | 266265 | |
SLC35D1-CDG | UDP-glucuronic acid/UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine dual transporter deficiency | SLC35D1 | 1p31.3 | AR | UDP-glucuronic acid-UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine dual transporter | 269250 | |
SLC39A8-CDG | Solute carrier family 39 (Zn transporter) deficiency | SLC39A8 | 4q24 | AR | SLC39A8 transporter of divalent cations, including manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), and iron (Fe) | 616721 | |
ATP6V0A2-CDG | V0 subunit a2 of vesicular H(+)-ATPase deficiency | ATP6V0A2 | 12q24.31 | AR | The multisubunit vacuolar-type proton pump (H(+)-ATPase or V-ATPase) | 219200, 278250 | |
ATP6V1A-CDG | Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive, type IID | ATP6V1A | 3q13.31 | AR | V-ATPase A subunit 1 | 617403 | |
ATP6V1E1-CDG | Cutis laxa, autosomal recessive, type IIC | ATP6V1E1 | 22q11.21 | AR | ATPase subunit E, ATP6E | 617402 | |
ATP6AP1-CDG | Immunodeficiency 47 | ATP6AP1 | Xq28 | XL | Accessory subunit 1 of the vacuolar-ATPase protein | 300972 | |
ATP6AP2-CDG | X-linked mental retardation, Hedera type | ATP6AP2 | Xp11.4 | XL | ATPase, h + transporting, lysosomal, accessory protein 2 | 300423 | |
TMEM199-CDG | TMEM199 deficiency | TMEM199 | 17q11.2 | AR | Transmembrane protein 199 | 616829 | |
CCDC115-CDG | CCDC115 deficiency | CCDC115 | 2q21.1 | AR | Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 115 | 616828 | |
TMEM165-CDG | TMEM165 deficiency | TMEM165 | 4q12 | AR | TMEM165 (TPARL) protein | 614727, 614726 | |
NGLY1-CDDG | N-glycanase 1 deficiency | NGLY1 | 3p24.2 | AR | N-glycanase 1 | 615273 |
Metabolic Pathway
Abbreviated scheme of the synthesis of a biantennary N-glycan linked to dolichol pyrophosphate (Dol-PP) and subsequently, in the Golgi apparatus, to proteins (Prot). 68.1, PMM2-CDG; 68.2, MPI-CDG; 68.3, DPAGT1-CDG; 68.4, ALG13-CDG; 68.5, ALG13-CDG; 68.6, ALG14-CDG; 68.7, ALG1-CDG; 68.8, ALG2-CDG; 68.9, ALG11-CDG; 68.10, RFT1-CDG; 68.11, ALG3-CDG; 68.12, ALG9-CDG; 68.13, ALG12-CDG; 68.14, ALG6-CDG; 68.15, ALG8-CDG; 68.16, TUSC3-CDG; 68.17, DDOST-CDG; 68.18, STT3A-CDG; 68.19, STT3B-CDG; 68.20, MAGT1-CDG; 68.22, MOGS-CDG; 68.23, GANAB-CDG; 68.24, PRKCSH-CDG; 68.25, MAN1B1-CDG; 68.26, MGAT2-CDG; 68.27, B4GALT1-CDG; 68.28, FUT8-CDG; 68.96, DHDDS-CDG; 68.97, NgBR-CDG; 68.98, SRD5A3-CDG; 68.99, DK1-CDG; 68.100, DPM1-CDG; 68.101, DPM2-CDG; 68.102, DPM3-CDG; 68.108, GMPPA-CDG; 68.109, GMPPB-CDG; 68.111, SLC35A1-CDG; 68.112, SLC35A2-CDG; 68.113, SLC35A3-CDG; 68.114, SLC35C1-CDG; 68.115, SLC35D1-CDG; 68.116, SLC39A8-CDG; 68.117, ATP6V0A2-CDG; 68.118, ATP6V1A-CDG; 68.119, ATP6V1E1-CDG; 68.120, ATP6AP1-CDG; 68.121, ATP6AP2-CDG; 68.122, TMEM199-CDG; 68.123, CCDC115-CDG; 68.124, TMEM165-CDG. GDP guanosine diphosphate, Man mannose, GlcNAc N-acetylglucosamine, Dol dolichol, P phosphate, Glc glucose, Gal galactose, Sia sialic acid. Dotted arrow indicates multiple steps
Signs and Symptoms
Reference Values
*Serum sialotransferrins (isoelectrofocusing) (P3–P97 centiles, n = 96, all ages) | |
|---|---|
Monosialotransferrins | 0.0–3.7 |
Disialotransferrins | 2.0–6.1 |
Trisialotransferrins | 5.5–15.1 |
Tetrasialotransferrins | 48.5–65.3 |
Pentasialotransferrins | 14.9–28.7 |
Hexasialotransferrins | 2.3–8.1 |
*Enzyme analyses | |
|---|---|
Phosphomannose mutase (mU/mg protein) | |
Leukocytes | 1.8–3.2 (range); 2.2 (median) |
Fibroblasts | 3.8 ± 0.9 (mean ± 1 SD) |
Phosphomannose isomerase (mU/mg protein) | |
Leukocytes | 860–1800 (nmol/h/mg protein, range) |
Fibroblasts | 6.8 ± 1.0 (mean ± 1 SD) |
Pathological Values
Disease | Sialotransferrin IEF pattern (S) |
|---|---|
68.1–68.15 | Type 1 patterna |
68.17–68.21 | |
68.96–68.104 | |
68.25–68.27 | Type 2 pattern° |
68.105, 68.111, 68.112 | |
68.116–68.124 | |
All other CDG | Normal pattern |
Disease | Apolipoprotein C-III IEF pattern (S) |
|---|---|
68.117–68.124 | Cathodal shift |
All other CDG | Normal pattern |
Specimen Collection
Test | Precondition | Material | Handling | Pitfalls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Sialotransferrins | S | Frozen (−20 °C) | No EDTA plasma | |
Apolipoprotein C-III | S | Frozen (−20 °C) | ||
Phosphomannomutase | WBC, FB | Frozen (−20 °C) | ||
Phosphomannose isomerase | WBC, FB | Frozen (−20 °C) |
Prenatal Diagnosis
Disorder | Material | Timing, trimester |
|---|---|---|
All (68.1–68.125) | CV sampling or cultured AFC | I, II |
Prenatal diagnosis is performed by DNA diagnostics on genomic DNA when the genetic defect has been established in a particular family. Maternal contamination has to be excluded by haplotype (CA repeat) testing of the AFC and maternal blood.
DNA Testing
Disorder | Material | Methodology |
|---|---|---|
All (68.1–68.125) | F, WBC | Direct sequencing of genomic DNA |
Treatment
Besides the well-established symptomatic and supportive therapies for all CDG, there are very few specific/curative treatments: mannose for MPI-CDG, fucose for some patients with SLC35C1-CDG, benzoate for the neurological symptoms of PIGM-CDG, and uridine for CAD-CDG. Galactose is on trial for several CDG mainly PGM1-CDG, SLC35A2-CDG, and TMEM165-CDG. Also on trial is manganese for SLC39A8-CDG. A minority of patients with PMM2-CDG present recurrent stroke-like episodes, thromboses (probably at least in part due to hyperaggregability of blood platelets), and/or bleeding episodes. Guidelines for the preventive and curative treatment of these features are being established by the Paris MetabERN center. The same center also prepares guidelines for the hormonal treatment of pubertal problems in PMM2-CDG.
Standard Treatment
-
68.2 Phosphomannose isomerase deficiency
Mannose circumvents the defective step because it can be directly converted to mannose-6-phosphate by hexokinases. Oral mannose, 0.2 g/kg of body weight per 4 h, is recommended. The clinical symptoms usually disappear rapidly, but it takes several months for the serum transferrin isoform pattern to improve or normalize.
-
68.114 GDP-fucose transporter deficiency
Oral fucose, 150 mg/kg of body weight, five times a day, abolishes or prevents infections and normalizes neutrophil counts in some patients (depending on genotype).
-
68.85 PIGM deficiency
Oral sodium phenylbutyrate (a histone deacetylase inhibitor), 20–30 mg/kg body weight, three times a day, has been given to three patients with a clearly beneficial effect on seizures and psychomotor development.
Dangers/Pitfalls
-
68.2 Higher mannose doses can induce osmotic diarrhea. Some patients develop hemolytic jaundice under mannose therapy. The alternative is then liver transplantation.
-
68.114 Higher fucose doses can induce autoimmune neutropenia.
Experimental Treatment
-
68.105 Phosphoglucomutase 1 deficiency
In pilot studies, oral galactose administration (1 g/kg per day) caused an improvement of liver transaminases, antithrombin and factor XI, endocrine parameters (to a variable degree), and glycosylation and a decreased frequency of rhabdomyolysis (review in Witters et al. 2017).
-
68.110 CAD trifunctional protein deficiency
Oral uridine administration (100 mg/kg per day) abolished the epilepsy and the anemia, improved psychomotor development, and normalized UDP sugars in fibroblasts (Koch et al. 2017).
-
68.112 UDP-galactose transporter deficiency
On oral galactose, seizures tend to improve. In one patient, glycosylation was nearly completely restored, but serum transaminases remained elevated (review in Witters et al. 2017).
-
68.116 SLC39A8 deficiency
In two patients, oral MnSO4 administration (15 and 20 mg/kg per day) considerably improved motor abilities, hearing, and other neurological functions and completely normalized enzyme dysfunctions (Park et al. 2018).
-
68.124 Transmembrane protein 165 deficiency
In two patients, oral galactose administration caused a substantial improvement of N-glycosylation, endocrine function, and some coagulation parameters (Morelle et al. 2017).
References
Abu Bakar N, Lefeber DJ, van Scherpenzeel M. Clinical glycomics for the diagnosis of congenital disorders of glycosylation. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018;41:499–513.
Carchon H, Chevigné R, Falmagne JB, Jaeken J. Diagnosis of congenital disorders of glycosylation by capillary zone electrophoresis of serum transferrin. Clin Chem. 2004;50:101–11.
Coman D, Irving M, Kannu P, Jaeken J, Savarirayan R. The skeletal manifestations of the congenital disorders of glycosylation. Clin Genet. 2008;73:507–15.
Ferreira CR, Altassan R, Marques-Da-Silva D, Francisco R, Jaeken J, Morava E. Recognizable phenotypes in CDG. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018;41:541–53.
Francisco R, Marques-da-Silva D, Brasil S, et al. The challenge of CDG diagnosis. Mol Genet Metab. 2018a; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2018.11.003.
Francisco R, Pascoal C, Marques-da-Silva D, et al. Keeping an eye on congenital disorders of O-glycosylation: a systematic literature review. J Inherit Metab Dis doi. 2018b; https://doi.org/10.1007/s10545-017-0119-2.
Grünewald S. The clinical spectrum of phosphomannomutase 2 deficiency (CDG-Ia). Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792:827–34.
Jaeken J, Hennet T, Matthijs G, Freeze HH. CDG nomenclature: time for a change! Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792:825–6.
Jaeken J, Lefeber D, Matthijs G. Clinical utility gene card for : phosphomannose isomerase deficiency. Eur J Hum Genet. 2014; https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2014.29.
Jaeken J, Péanne R. What is new in CDG? J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017;40:569–86.
Jaeken J, van Eijk HG, van der Heul C, et al. Sialic acid-deficient serum and cerebrospinal fluid transferrin in a newly recognized syndrome. Clin Chim Acta. 1984;144:245–7.
Jaeken J, Vanderschueren-Lodeweyckx M, Casaer P, et al. Familial psychomotor retardation with markedly fluctuating serum proteins, FSH and GH levels, partial TBG-deficiency, increased serum arylsulphatase a and increased CSF protein: a new syndrome? Pediatr Res. 1980;14:179.
Koch J, Mayr JA, Alhaddad B, et al. CAD mutations and uridine-responsive epileptic encephalopathy. Brain. 2017;140:279–86.
Marques-da-Silva D, Dos Reis Ferreira V, Monticelli M, et al. Liver involvement in congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG): a systematic review. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017a;40:195–207.
Marques-da-Silva D, Francisco R, Webster D, Dos Reis Ferreira V, Jaeken J, Pulinilkunnil T. Cardiac complications of congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG): a systematic literature review. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017b;40:657–72.
Matthijs G, Schollen E, Pardon E, et al. Mutations in PMM2, a phosphomannomutase gene on chromosome 16p13, in carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein type I syndrome (Jaeken syndrome). Nat Genet. 1997;16:88–92. (erratum in Nat Genet 1997 Jul; 16(3): 316)
Monticelli M, Ferro T, Jaeken J, Dos Reis Ferreira V, Videira PA. Immunological aspects of congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG): a review. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2016;39:765–80.
Morava E, Thiemes V, Thiel C, et al. ALG6-CDG: a recognizable phenotype with epilepsy, proximal muscle weakness, ataxia and behavioral and limb anomalies. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2016;39:713–23.
Morava E, Wosik HN, Sykut-Cegielska J, et al. Ophthalmological abnormalities in children with congenital disorders of glycosylation type I. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009;93:350–4.
Morelle W, Potelle S, Witters P, et al. Galactose supplementation in patients with TMEM165-CDG rescues the glycosylation defects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102:1375–86.
Ng BG, Freeze HH. Perspectives on glycosylation and its congenital disorders. Trends Genet. 2018;34:466–76.
Ng BG, Shiryaev SA, Rymen D, et al. ALG1-CDG: clinical and molecular characterization of 39 unreported patients. Hum Mutat. 2016;37:653–60.
Park JH, Hogrebe M, Fobker M, et al. SLC39A8 deficiency: biochemical correction and major clinical improvement by manganese therapy. Genet Med. 2018;20:259–68.
Van Schaftingen E, Jaeken J. Phosphomannomutase deficiency is a cause of carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome type I. FEBS Lett. 1995;370:318–20.
Witters P, Cassiman D, Morava E. Nutritional therapies in congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG). Nutrients. 2017; https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9111222.
Wopereis S, Grünewald S, Morava E, et al. Apolipoprotein C-III isofocusing in the diagnosis of genetic defects in O-glycan biosynthesis. Clin Chem. 2003;49:1839–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Jaeken, J., van den Heuvel, L. (2022). Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation. In: Blau, N., Dionisi Vici, C., Ferreira, C.R., Vianey-Saban, C., van Karnebeek, C.D.M. (eds) Physician's Guide to the Diagnosis, Treatment, and Follow-Up of Inherited Metabolic Diseases. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67727-5_68
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-67727-5_68
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-67726-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-67727-5
eBook Packages: MedicineMedicine (R0)