Abstract
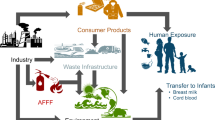
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of at least 4730 chemicals with clearly important surfactant properties. They are used in coatings, paints, stain repellents, and firefighting foams as well as other industrial processes. Their high use and recalcitrance to degradation coupled with their lipophilicity and bioaccumulation makes them persistent organic pollutants or forever chemicals. In turn, they are measured in the serum of most humans, especially long-chain PFAS. The toxicity of most PFASs have not been studied, and the USEPA is starting a National PFAS-testing strategy to prioritize PFAS testing because testing all PFASs is not feasible. Some PFASs such as PFOA and PFOS are currently banned in many countries because of their persistence and bioaccumulation. Many PFASs have been observed in the environment and bioconcentrate in aquatic food webs. These chemicals are associated with immunotoxicity, cardiovascular disease, liver disease, reproductive and developmental disorders, and other human health issues.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 6:2 FTS:
-
1H, 1H, 2H, 2H-perfluorooctane sulfonic acid
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AhR:
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor
- AR:
-
Androgen receptor
- BCF:
-
Bioconcentration factor
- CPT1:
-
Carnitine Palmitoyl transferase 1
- CYP11A1:
-
Cytochrome P450 11A1
- CYP17A1:
-
Cytochrome P450 17A1
- ER:
-
Estrogen Receptor
- FABP:
-
Fatty acid-binding protein
- FASN:
-
Fatty acid synthase
- FOSA:
-
Perfluorooctane sulfonamide
- FXR:
-
Farnesoid X receptor
- GAC:
-
Granular activated carbon
- GR:
-
Glucocorticoid receptor
- HFPO-DA :
-
Hexafluoropropylene oxide-dimer acid
- HSD11B1:
-
Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 11B1
- HSD17B:
-
Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 17B
- HSD3B1:
-
Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 3B1
- IARC:
-
International Agency for Research on Cancer
- Koc:
-
Organic carbon-partitioning coefficient
- Kow:
-
Octanol-water-partitioning coefficient
- LDL:
-
Low-density lipoprotein
- logP:
-
Partitioning coefficient
- LPL:
-
Lipoprotein lipase
- LXR:
-
Liver X receptor
- MC4:
-
Melanocortin 4
- MetFOSA:
-
N-methyl perfluoro-1-octanesulfonamide
- NK:
-
Natural killer
- NRF2:
-
Nuclear receptor erthyroid-2-related factor 2
- OAT:
-
Organic anion transporter
- OATP:
-
Organic anion transport protein
- PFAS:
-
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances
- PFBA:
-
Perfluorobutanoate
- PFCA:
-
Perfluorinated carboxylic acids
- PFDA:
-
Perfluorodecanoate
- PFDoD :
-
Perfluorododecanoic acid
- PFHpA:
-
Perfluoroheptanoic acid
- PFHxA :
-
Per-fluorohexanoic acid
- PFHxS:
-
Per-fluorohexanesulfonate
- PFMOBA:
-
Perfluoro-4-methoxybutanioc acid
- PFNA:
-
Perfluorononanoic acid
- PFOA:
-
Perfluorooctanoic acid
- PFOS:
-
Perfluorooctanesulfonate
- PFPeA :
-
Perfluoropentanoic acid
- PFSA:
-
Perfluorinated sulfonic acids
- PFTeDA :
-
Per- fluorotetradecanoic acid
- PFTrDA :
-
Perfluorotridecanoic acid
- PFUnDA:
-
Perfluoroundecanoic acid
- PGRMC1:
-
Progesterone receptor membrane-associated component 1
- POP:
-
Persistent organic pollutant
- PPAR:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- PXR:
-
Pregnane X receptor
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RXR:
-
Retinoid X receptor
- SCD1:
-
Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase 1
- Srebf-1c:
-
Sterol-regulatory element-binding factor 1c
- STARD1:
-
Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein
- TAG:
-
Triacylglycerol
- THR:
-
Thyroid hormone receptors
- TNFα:
-
Tumor necrose factor α
- URAT1:
-
Urate transporter 1
References
Baldwin WS, Bain LJ, Di Giulio R, Kullman S, Rice CD, Ringwood AH, den Hurk PV. 20th pollutant responses in marine organisms (PRIMO 20): global issues and fundamental mechanisms caused by pollutant stress in marine and freshwater organisms. Aquat Toxicol. 2020;227:105620.
Baldwin WS. Phase 0 of the xenobiotic response: nuclear receptors and other transcription factors as a first step in protection from xenobiotics. Nucl Recep Res. 2019;6:101447.
Biegel LB, Hurtt ME, Frame SR, O’Connor JC, Cook JC. Mechanisms of extrahepatic tumor induction by peroxisome proliferators in male CD rats. Toxicol Sci. 2001;60:44–55.
Blake BE, Fenton SE. Early life exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and latent health outcomes: a review including the placenta as a target tissue and possible driver of peri- and postnatal effects. Toxicology. 2020;443:152565.
Brendel S, Fetter É, Staude C, Vierke L, Biegel-Engler A. Short-chain perfluoroalkyl acids: environmental concerns and a regulatory strategy under REACH. Environ Sci Eur. 2018;30:9–9.
Brusseau ML. Estimating the relative magnitudes of adsorption to solid-water and air/oil-water interfaces for per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances. Environ Pollut. 2019;254:113102.
Canova C, Di Nisio A, Barbieri G, Russo F, Fletcher T, Batzella E, Dalla Zuanna T, Pitter G. PFAS concentrations and cardiometabolic traits in highly exposed children and adolescents. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:12881.
Coperchini F, Croce L, Ricci G, Magri F, Rotondi M, Imbriani M, Chiovato L. Thyroid disrupting effects of old and new generation PFAS. Front Endocrinol. 2021;11
Corton CJ, Cunningham ML, Hummer TB, Lau C, Meek B, Peters JM, Popp JA, Rhomberg L, Seed J, Klaunig JE. Mode of action framework analysis for receptor-mediated toxicity: the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) as a case study. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014;44:1–49.
Costello E, Rock S, Stratakis N, Eckel SP, Walker DI, Valvi D, Cserbik D, Jenkins T, Xanthakos SA, Kohli R, Sisley S, Vasiliou V, La Merrill MA, Rosen H, Conti DV, McConnell R, Chatzi L. Exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and markers of liver injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Health Perspect. 2022;130:46001.
Das KP, Wood CR, Lin MT, Starkov AA, Lau C, Wallace KB, Corton JC, Abbott BD. Perfluoroalkyl acids-induced liver steatosis: effects on genes controlling lipid homeostasis. Toxicology. 2017;378:37–52.
Development, Organization for Economic and Community. Results of the 2006 survey on the production and use of PFOS, PFAS, PFOA, PFCA, their related substances and products/mixtures containing these substances OECD Environment, Health and Safety Publications Series on Risk Management. 2006:22.
Erinc A, Davis MB, Padmanabhan V, Langen E, Goodrich JM. Considering environmental exposures to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) as risk factors for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Environ Res. 2021;197:111113.
Fair PA, Romano T, Schaefer AM, Reif JS, Bossart GD, Houde M, Muir D, Adams J, Rice C, Hulsey TC, Peden-Adams M. Associations between perfluoroalkyl compounds and immune and clinical chemistry parameters in highly exposed bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). Environ Toxicol Chem. 2013;32:736–46.
Fei C, McLaughlin JK, Lipworth L, Olsen J. Maternal levels of perfluorinated chemicals and subfecundity. Hum Reprod. 2009;24:1200–5.
Foguth R, Sepúlveda MS, Cannon J. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) neurotoxicity in sentinel and non-traditional laboratory model systems: potential utility in predicting adverse outcomes in human health. Toxics. 2020;8:42.
Frisbee SJ, Brooks AP Jr, Maher A, Flensborg P, Arnold S, Fletcher T, Steenland K, Shankar A, Knox SS, Pollard C, Halverson JA, Vieira VM, Jin C, Leyden KM, Ducatman AM. The C8 health project: design, methods, and participants. Environ Health Perspect. 2009;117:1873–82.
Furuhata R, Kabe Y, Kanai A, Sugiura Y, Tsugawa H, Sugiyama E, Hirai M, Yamamoto T, Koike I, Yoshikawa N, Tanaka H, Koseki M, Nakae J, Matsumoto M, Nakamura M, Suematsu M. Progesterone receptor membrane associated component 1 enhances obesity progression in mice by facilitating lipid accumulation in adipocytes. Commun Biol. 2020;3:479.
Gleason JA, Post GB, Fagliano JA. Associations of perfluorinated chemical serum concentrations and biomarkers of liver function and uric acid in the US population (NHANES), 2007-2010. Environ Res. 2015;136:8–14.
Goeritz I, Falk S, Stahl T, Schäfers C, Schlechtriem C. Biomagnification and tissue distribution of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in market-size rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Toxicol Chem. 2013;32:2078–88.
Grandjean P, Andersen EW, Budtz-Jørgensen E, Nielsen F, Mølbak K, Weihe P, Heilmann C. Serum vaccine antibody concentrations in children exposed to perfluorinated compounds. JAMA. 2012;307:391–7.
Gribble MO, Bartell SM, Kannan K, Wu Q, Fair PA, Kamen DL. Longitudinal measures of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in serum of Gullah African Americans in South Carolina: 2003-2013. Environ Res. 2015;143:82–8.
Hamilton MC, Heintz MM, Pfohl M, Marques E, Ford L, Slitt AL, Baldwin WS. Increased toxicity and retention of perflourooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in humanized CYP2B6-transgenic mice compared to Cyp2b-null mice is relieved by a high-fat diet (HFD). Food Chem Toxicol. 2021;152:112175.
Han X, Nabb DL, Russell MH, Kennedy GL, Rickard RW. Renal elimination of perfluorocarboxylates (PFCAs). Chem Res Toxicol. 2012;25:35–46.
He A, Lu Y, Chen F, Li F, Lv K, Cao H, Sun Y, Liang Y, Li J, Zhao L, Zhang X, Li L, Wang Y, Jiang G. Exploring the origin of efficient adsorption of poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances in household point-of-use water purifiers: deep insights from a joint experimental and computational study. Sci Total Environ. 2022;831:154988.
Heindel JJ, Blumberg B. Environmental obesogens: mechanisms and controversies. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019;59:89–106.
Hernandez JP, Mota LC, Baldwin WS. Activation of CAR and PXR by dietary, environmental and occupational chemicals alters drug metabolism, intermediary metabolism, and cell proliferation. Curr Pharmacogenomics Pers Med. 2009;7:81–105.
Houck KA, Patlewicz G, Richard AM, Williams AJ, Shobair MA, Smeltz M, Clifton MS, Wetmore B, Medvedev A, Makarov S. Bioactivity profiling of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) identifies potential toxicity pathways related to molecular structure. Toxicology. 2021;457:152789.
Howell JJ, Stoffel M. Nuclear export-independent inhibition of Foxa2 by insulin. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:24816–24.
Jin R, McConnell R, Catherine C, Xu S, Walker DI, Stratakis N, Jones DP, Miller GW, Peng C, Conti DV, Vos MB, Chatzi L. Perfluoroalkyl substances and severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver in children: an untargeted metabolomics approach. Environ Int. 2020;134:105220.
Kato K, Wong LY, Jia LT, Kuklenyik Z, Calafat AM. Trends in exposure to polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in the U.S. population: 1999-2008. Environ Sci Technol. 2011;45:8037–45.
Khazaee M, Christie E, Cheng W, Michalsen M, Field J, Ng C. Perfluoroalkyl acid binding with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α, γ, and δ, and fatty acid binding proteins by equilibrium dialysis with a comparison of methods. Toxics. 2021;9:45.
Kim J, Park J, Kim N, Park H, Lim K. Inhibition of androgen receptor can decrease fat metabolism by decreasing carnitine palmitoyltransferase I levels in skeletal muscles of trained mice. Nutrit Metabol. 2019;16:82.
Kim S, Chen J, Cheng T, Gindulyte A, He J, He S, Li Q, Shoemaker BA, Thiessen PA, Yu B, Zaslavsky L, Zhang J, Bolton EE. PubChem in 2021: new data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:D1388–d95.
Lee JE, Choi K. Perfluoroalkyl substances exposure and thyroid hormones in humans: epidemiological observations and implications. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metabol. 2017;22:6–14.
Levin BE. Metabolic imprinting: critical impact of the perinatal environment on the regulation of energy homeostasis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2006;361:1107–21.
Li J, Quan X, Lei S, Huang Z, Wang Q, Xu P. PFOS inhibited normal functional development of placenta cells via PPARγ signaling. Biomedicine. 2021;9:677.
Li L, Li D, Heyward S, Wang H. Transcriptional regulation of CYP2B6 expression by hepatocyte nuclear factor 3β in human liver cells. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0150587.
Li Y, Andersson A, Xu Y, Pineda D, Nilsson CA, Lindh CH, Jakobsson K, Fletcher T. Determinants of serum half-lives for linear and branched perfluoroalkyl substances after long-term high exposure—a study in Ronneby, Sweden. Environ Int. 2022;163:107198.
Liu S, Yang R, Yin N, Faiola F. The short-chain perfluorinated compounds PFBS, PFHxS, PFBA and PFHxA, disrupt human mesenchymal stem cell self-renewal and adipogenic differentiation. J Environ Sci. 2020;88:187–99.
Lopez-Espinosa MJ, Carrizosa C, Luster MI, Margolick JB, Costa O, Leonardi GS, Fletcher T. Perfluoroalkyl substances and immune cell counts in adults from the mid-Ohio Valley (USA). Environ Int. 2021;156:106599.
Marques E, Pfohl M, Wei W, Tarantola G, Ford L, Amaeze O, Alesio J, Ryu S, Jia X, Zhu H, Bothun GD, Slitt A. Replacement per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are potent modulators of lipogenic and drug metabolizing gene expression signatures in primary human hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022;442:115991.
Martin JW, Mabury SA, Solomon KR, Muir DC. Dietary accumulation of perfluorinated acids in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Toxicol Chem. 2003a;22:189–95.
Martin JW, Mabury SA, Solomon KR, Muir DCG. Bioconcentration and tissue distribution of perfluorinated acids in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Toxicol Chem. 2003b;22:196–204.
Mattsson K, Rignell-Hydbom A, Holmberg S, Thelin A, Jönsson BAG, Lindh CH, Sehlstedt A, Rylander L. Levels of perfluoroalkyl substances and risk of coronary heart disease: findings from a population-based longitudinal study. Environ Res. 2015;142:148–54.
McDonough CA, Choyke S, Barton KE, Mass S, Starling AP, Adgate JL, Higgins CP. Unsaturated PFOS and other PFASs in human serum and drinking water from an AFFF-impacted community. Environ Sci Technol. 2021;55:8139–48.
Meneguzzi A, Fava C, Castelli M, Minuz P. Exposure to perfluoroalkyl chemicals and cardiovascular disease: experimental and epidemiological evidence. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12.
Miranda DA, Benskin JP, Awad R, Lepoint G, Leonel J, Hatje V. Bioaccumulation of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in a tropical estuarine food web. Sci Total Environ. 2021;754:142146.
Nguyen TMH, Bräunig J, Thompson K, Thompson J, Kabiri S, Navarro DA, Kookana RS, Grimison C, Barnes CM, Higgins CP, McLaughlin MJ, Mueller JF. Influences of chemical properties, soil properties, and solution pH on soil-water partitioning coefficients of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Environ Sci Technol. 2020;54:15883–92.
Ochoa-Herrera V, Sierra-Alvarez R. Removal of perfluorinated surfactants by sorption onto granular activated carbon, zeolite and sludge. Chemosphere. 2008;72:1588–93.
Olsen GW, Zobel LR. Assessment of lipid, hepatic, and thyroid parameters with serum perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) concentrations in fluorochemical production workers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2007;81:231–46.
Pérez F, Nadal M, Navarro-Ortega A, Fàbrega F, Domingo JL, Barceló D, Farré M. Accumulation of perfluoroalkyl substances in human tissues. Environ Int. 2013;59:354–62.
Qian Y, Ducatman A, Ward R, Leonard S, Bukowski V, Lan Guo N, Shi X, Vallyathan V, Castranova V. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) induces reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in human microvascular endothelial cells: role in endothelial permeability. J Toxic Environ Health A. 2010;73:819–36.
Rosen MB, Schmid JR, Corton JC, Zehr RD, Das KP, Abbott BD, Lau C. Gene expression profiling in wild-type and PPARα-null mice exposed to perfluorooctane sulfonate reveals PPARα-independent effects. PPAR Res. 2010;2010:794739.
Salimi A, Nikoosiar Jahromi M, Pourahmad J. Maternal exposure causes mitochondrial dysfunction in brain, liver, and heart of mouse fetus: an explanation for perfluorooctanoic acid induced abortion and developmental toxicity. Environ Toxicol. 2019;34:878–85.
Salter DM, Wei W, Nahar PP, Marques E, Slitt AL. Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) thwarts the beneficial effects of calorie restriction and metformin. Toxicol Sci. 2021;182:82–95.
Sen P, Qadri S, Luukkonen PK, Ragnarsdottir O, McGlinchey A, Jäntti S, Juuti A, Arola J, Schlezinger JJ, Webster TF, Orešič M, Yki-Järvinen H, Hyötyläinen T. Exposure to environmental contaminants is associated with altered hepatic lipid metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2022;76:283–93.
Shearer JJ, Callahan CL, Calafat AM, Huang W, Jones RR, Sabbisetti VS, Freedman ND, Sampson JN, Silverman DT, Purdue MP, Hofmann JN. Serum concentrations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and risk of renal cell carcinoma. JNCI. 2020;113:580–7.
Steenland K, Winquist A. PFAS and cancer, a scoping review of the epidemiologic evidence. Environ Res. 2021;194:110690.
Tang CY, Fu QS, Criddle CS, Leckie JO. Effect of flux (transmembrane pressure) and membrane properties on fouling and rejection of reverse osmosis and Nanofiltration membranes treating Perfluorooctane sulfonate containing wastewater. Environ Sci Technol. 2007;41:2008–14.
Tarapore P, Ouyang B. Perfluoroalkyl chemicals and male reproductive health: do PFOA and PFOS increase risk for male infertility? Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18:3794.
Timmermann CAG, Jensen KJ, Nielsen F, Budtz-Jørgensen E, van der Klis F, Benn CS, Grandjean P, Fisker AB. Serum perfluoroalkyl substances, vaccine responses, and morbidity in a cohort of Guinea-Bissau children. Environ Health Perspect. 2020;128:87002.
Toni D, Luca CM, Radu IS, Di Nisio A, Dall’Acqua S, Guidolin D, Spampinato S, Campello E, Simioni P, Foresta C. Increased cardiovascular risk associated with chemical sensitivity to perfluoro–octanoic acid: role of impaired platelet aggregation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:399.
Tukker AM, Bouwman LMS, van Kleef RGDM, Hendriks HS, Legler J, Westerink RHS. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) acutely affect human α1β2γ2L GABAA receptor and spontaneous neuronal network function in vitro. Sci Rep. 2020;10:5311.
Varsi K, Huber S, Averina M, Brox J, Bjørke-Monsen AL. Quantitation of linear and branched perfluoroalkane sulfonic acids (PFSAs) in women and infants during pregnancy and lactation. Environ Int. 2022;160:107065.
Wang M, Li Q, Hou M, Chan LLY, Liu M, Ter SK, Dong T, Xia Y, Chotirmall SH, Fang M. Inactivation of common airborne antigens by perfluoroalkyl chemicals modulates early life allergic asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2021;118:e2011957118.
Wen L, Lin C, Chou H, Chang C, Lo H, Juan S. Perfluorooctanesulfonate mediates renal tubular cell apoptosis through PPARgamma inactivation. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0155190–e90.
Yoshikawa T, Ide T, Shimano H, Yahagi N, Amemiya-Kudo M, Matsuzaka T, Yatoh S, Kitamine T, Okazaki H, Tamura Y, Sekiya M, Takahashi A, Hasty AH, Sato R, Sone H, Osuga J, Ishibashi S, Yamada N. Cross-talk between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha and liver X receptor (LXR) in nutritional regulation of fatty acid metabolism. I. PPARs suppress sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c promoter through inhibition of LXR signaling. Mol Endocrinol. 2003;17:1240–54.
Yu J, Cheng W, Jia M, Chen L, Gu C, Ren H, Wu B. Toxicity of perfluorooctanoic acid on zebrafish early embryonic development determined by single-cell RNA sequencing. J Hazard Mater. 2022;427:127888.
Zhang Z, Wang F, Zhang Y, Yao J, Bi J, He J, Zhang S, Wei Y, Guo H, Zhang X, He M. Associations of serum PFOA and PFOS levels with incident hypertension risk and change of blood pressure levels. Environ Res. 2022;212:113293.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Baldwin, W.S., Davis, T.T., Eccles, J.A. (2023). Per- and Polyfluoroalkylsubstances (PFAS) and Their Toxicology as Evidenced Through Disease and Biomarkers. In: Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R., Rajendram, R. (eds) Biomarkers in Toxicology. Biomarkers in Disease: Methods, Discoveries and Applications. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87225-0_67-2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87225-0_67-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-87225-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87225-0
eBook Packages: Springer Reference Biomedicine and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences
Publish with us
Chapter history
-
Latest
Per- and Polyfluoroalkylsubstances (PFAS) and Their Toxicology as Evidenced Through Disease and Biomarkers- Published:
- 08 March 2023
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87225-0_67-2
-
Original
Per- and Polyfluoroalkylsubstances (PFAS) and Their Toxicology as Evidenced Through Disease and Biomarkers- Published:
- 03 August 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87225-0_67-1