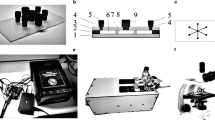
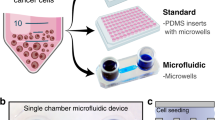
Abstract
Microfluidic technologies allow the generation of large datasets using smaller quantities of cells and reagents than with traditional well plate assays. Such miniaturized methods can also facilitate the generation of complex 3D preclinical models of solid tumors with controlled size and cell composition. This is particularly useful in the context of recreating the tumor microenvironment for preclinical screening of immunotherapies and combination therapies at a scale, to reduce the experimental costs during therapy development while using physiologically relevant 3D tumor models, and to assess the therapy’s efficacy. Here, we describe the fabrication of microfluidic devices and the associated protocols to culture tumor-stromal spheroids for assessing the efficacy of anticancer immunotherapies as monotherapies and as part of combination therapy regimes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mulholland T, McAllister M, Patek S, Flint D, Underwood M, Sim A, Edwards J, Zagnoni M (2018) Drug screening of biopsy-derived spheroids using a self-generated microfluidic concentration gradient. Sci Rep 8(1):1–17
Velve-Casquillas G, Le Berre M, Piel M, Tran PT (2010) Microfluidic tools for cell biological research. Nano Today 5(1):28–47
Nielsen JB, Hanson RL, Almughamsi HM, Pang C, Fish TR, Woolley AT (2020) Microfluidics: innovations in materials and their fabrication and functionalization. Anal Chem 92(1):150–168
Tsai HF, Trubelja A, Shen AQ, Bao G (2017) Tumour-on-a-chip: microfluidic models of tumour morphology, growth and microenvironment. J R Soc Interface 14(131):20170137
Polini A, del Mercato LL, Barra A, Zhang YS, Calabi F, Gigli G (2019) Towards the development of human immune-system-on-a-chip platforms. Elsevier Ltd, pp 517–525
Kapara A, Findlay Paterson KA, Brunton VG, Graham D, Zagnoni M, Faulds K (2021) Detection of estrogen receptor alpha and assessment of Fulvestrant activity in MCF-7 tumor spheroids using microfluidics and SERS. Anal Chem 93(14):5862–5871
Gupta N, Liu JR, Patel B, Solomon DE, Vaidya B, Gupta V (2016) Microfluidics-based 3D cell culture models: utility in novel drug discovery and delivery research. Bioeng Transl Med 1(1):63–81
Convery N, Gadegaard N (2019) 30 years of microfluidics. Micro Nano Eng 2:76–91
Fetah KL, DiPardo BJ, Kongadzem E-M, Tomlinson JS, Elzagheid A, Elmusrati M, Khademhosseini A, Ashammakhi N (2019) Cancer modeling-on-a-chip with future artificial intelligence integration. Small 15(50):1901985
Dhandapani M, Goldman A (2017) Preclinical cancer models and biomarkers for drug development: new technologies and emerging tools. J Mol Biomark Diagn 8(5):356
Edmondson R, Broglie JJ, Adcock AF, Yang L (2014) Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay Drug Dev Technol 12(4):207–218
Bassez A, Vos H, Van Dyck L, Floris G, Arijs I, Desmedt C, Boeckx B, Vanden Bempt M, Nevelsteen I, Lambein K, Punie K, Neven P, Garg AD, Wildiers H, Qian J, Smeets A, Lambrechts D (2021) A single-cell map of intratumoral changes during anti-PD1 treatment of patients with breast cancer. Nat Med 27(5):820–832
Gao M, Wang T, Ji L, Bai S, Tian L, Song H (2020) Therapy with carboplatin and anti-PD-1 antibodies before surgery demonstrates sustainable anti-tumor effects for secondary cancers in mice with triple-negative breast cancer. Front Immunol 11:366
Srivastava S, Furlan SN, Jaeger-Ruckstuhl CA, Sarvothama M, Berger C, Smythe KS, Garrison SM, Specht JM, Lee SM, Amezquita RA, Voillet V, Muhunthan V, Yechan-Gunja S, Pillai SPS, Rader C, Houghton AM, Pierce RH, Gottardo R, Maloney DG, Riddell SR (2020) Immunogenic chemotherapy enhances recruitment of CAR-T cells to lung tumors and improves antitumor efficacy when combined with checkpoint blockade. Cancer Cell 39(2):193–208
Emens LA, Middleton G (2015) The interplay of immunotherapy and chemotherapy: harnessing potential synergies. Cancer Immunol Res 3(5):436–443
Bailly C, Thuru X, Quesnel B (2020) Combined cytotoxic chemotherapy and immunotherapy of cancer: modern times. NAR Cancer 2(1):zcaa002
Hartl CA, Bertschi A, Puerto RB, Andresen C, Cheney EM, Mittendorf EA, Guerriero JL, Goldberg MS (2019) Combination therapy targeting both innate and adaptive immunity improves survival in a pre-clinical model of ovarian cancer. J Immunother Cancer 7(1):199
Paterson K, Paterson S, Mulholland T, Coffelt SB, Zagnoni M (2022) Assessment of CAR-T mediated and targeted cytotoxicity in 3D microfluidic TBNC co-culture models for combination therapy. IEEE OJEMB, 3: 86–95
Ibidi (2015) Live/dead staining with FDA and PI, Application Note 33; Version 2.0: Available from: https://ibidi.com/img/cms/support/AN/AN33_Live_Dead_staining_with_FDA_and_PI.pdf
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by AMS Biotechnology Europe Ltd. (industrial PhD studentship to K.P and M.Z) and internal funds by Strathclyde University to M.Z. and K.P.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Paterson, K., Zagnoni, M. (2023). Microfluidic Protocols for the Assessment of Anticancer Therapies in 3D Tumor-Stromal Cocultures. In: Garcia-Cordero, J.L., Revzin, A. (eds) Microfluidic Systems for Cancer Diagnosis . Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2679. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3271-0_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-3271-0_8
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-3270-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-3271-0
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols