Abstract
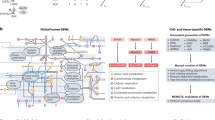
The explosion of the “omics” era has introduced a growing number of sets and tools that facilitate molecular interrogation of the metabolome. These include various bioinformatics and pharmacogenomics resources that can be utilized independently or collectively to facilitate metabolic engineering across disease, clinical oncology, and understanding of molecular changes across larger systems. This review provides starting points for accessing publicly available data and computational tools that support assessment of metabolic profiles and metabolic regulation, providing both a depth-and-breadth approach toward understanding the metabolome. We focus in particular on pathway databases and tools, which provide in-depth analysis of metabolic pathways, which is at the heart of metabolic engineering.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Copeland WB, Bartley BA, Chandran D et al (2012) Computational tools for metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 14:270–280
García-Granados R, Lerma-Escalera JA, Morones-Ramírez JR (2019) Metabolic engineering and synthetic biology: synergies, future, and challenges. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 7:36
Stephanopoulos G (2012) Synthetic biology and metabolic engineering. ACS Synth Biol 1:514–525
Ko YS, Kim JW, Lee JA et al (2020) Tools and strategies of systems metabolic engineering for the development of microbial cell factories for chemical production. Chem Soc Rev 49:4615–4636
Clish CB (2015) Metabolomics: an emerging but powerful tool for precision medicine. Mol Case Stud 1:a000588
Johnson CH, Ivanisevic J, Siuzdak G (2016) Metabolomics: beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17:451–459
Henry CS, Dejongh M, Best AA et al (2010) High-throughput generation, optimization and analysis of genome-scale metabolic models. Nat Biotechnol 28:977–982
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S et al (2004) The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D277–D280
Caspi R, Billington R, Fulcher CA et al (2018) The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D633–d639
Karp PD, Ouzounis CA, Moore-Kochlacs C et al (2005) Expansion of the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases to 160 genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 33:6083–6089
Altman T, Travers M, Kothari A et al (2013) A systematic comparison of the MetaCyc and KEGG pathway databases. BMC Bioinf 14:112
Van Leeuwen J, Ba-Alawi W, Branchard E et al (2020) Computational pharmacogenomics screen identifies synergistic statin-compound combinations as anti-breast cancer therapies. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.07.286922
Stanstrup J, Broeckling CD, Helmus R et al (2019) The metaRbolomics Toolbox in Bioconductor and beyond. Metabolites 9(10):200
Zhang JD, Wiemann S (2009) KEGGgraph: a graph approach to KEGG PATHWAY in R and bioconductor. Bioinformatics 25:1470–1471
Luo W, Brouwer C (2013) Pathview: an R/Bioconductor package for pathway-based data integration and visualization. Bioinformatics 29:1830–1831
Kramer F, Bayerlová M, Beißbarth T (2014) R-based software for the integration of pathway data into bioinformatic algorithms. Biology 3:85–100
Karp PD, Caspi R (2011) A survey of metabolic databases emphasizing the MetaCyc family. Arch Toxicol 85:1015–1033
Mubeen S, Hoyt CT, Gemünd A et al (2019) The impact of pathway database choice on statistical enrichment analysis and predictive modeling. Front Genet 10:1203
Barbie DA, Tamayo P, Boehm JS et al (2009) Systematic RNA interference reveals that oncogenic KRAS-driven cancers require TBK1. Nature 462:108–112
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK et al (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:15545–15550
Liberzon A, Subramanian A, Pinchback R et al (2011) Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 27:1739–1740
Tarca AL, Draghici S, Khatri P et al (2009) A novel signaling pathway impact analysis. Bioinformatics 25:75–82
Kubinyi H (2007) 3.40 - Chemogenomics. In: Taylor JB, Triggle DJ (eds) Comprehensive medicinal chemistry II. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 921–937
Bento AP, Gaulton A, Hersey A et al (2014) The ChEMBL bioactivity database: an update. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D1083–D1090
Glicksberg BS, Li L, Chen R et al (2019) Leveraging big data to transform drug discovery. In: Bioinformatics and drug discovery. Humana Press, New York, pp 91–118
Al Mahmud R, Najnin RA, Polash AH (2018) A survey of web-based chemogenomic data resources. In: Computational chemogenomics. Humana Press, New York, pp 3–62
Mendez D, Gaulton A, Bento AP et al (2019) ChEMBL: towards direct deposition of bioassay data. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D930–d940
Kim S, Chen J, Cheng T et al (2021) PubChem in 2021: new data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res 49:D1388–d1395
Sayers EW, Beck J, Bolton EE et al (2021) Database resources of the National Center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res 49:D10–d17
Gendoo DMA, Zon M, Sandhu V et al (2019) MetaGxData: clinically annotated breast, ovarian and pancreatic cancer datasets and their use in generating a multi-cancer gene signature. Sci Rep 9:8770
Kannan L, Ramos M, Re A et al (2016) Public data and open source tools for multi-assay genomic investigation of disease. Brief Bioinform 17:603–615
Subramanian A, Narayan R, Corsello SM et al (2017) A next generation connectivity map: L1000 platform and the first 1,000,000 profiles. Cell 171:1437–1452, e1417
Lawson CE, Martí JM, Radivojevic T et al (2021) Machine learning for metabolic engineering: a review. Metab Eng 63:34–60
Smirnov P, Safikhani Z, El-Hachem N et al (2016) PharmacoGx: an R package for analysis of large pharmacogenomic datasets. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 32:1244–1246
Gendoo DMA (2020) Bioinformatics and computational approaches for analyzing patient-derived disease models in cancer research. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 18:375–380
Stine ZE, Schug ZT, Salvino JM et al (2021) Targeting cancer metabolism in the era of precision oncology. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2021:1–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Gendoo, D.M.A. (2023). Overview of Bioinformatics Software and Databases for Metabolic Engineering. In: Selvarajoo, K. (eds) Computational Biology and Machine Learning for Metabolic Engineering and Synthetic Biology. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2553. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2617-7_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2617-7_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2616-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2617-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols