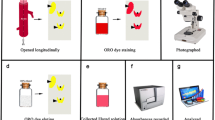
Abstract
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of lipid-rich, fibrous plaques within the arterial wall of medium and large arteries. Plaques prone to rupture are typically rich in lipids and pro-inflammatory markers. Cells within the plaque can take up lipids via different mechanisms leading to the formation and accumulation of lipid-rich foam cells, a key hallmark of the disease. Evaluation of plaque burden and lipid content is hence important to determine disease progression and severity. This chapter describes the most commonly used staining methods that enable visualization and analysis of mouse atherosclerotic plaques. These methods include en face preparation of mouse aorta, and staining sections of arteries using hematoxylin and eosin, Oil Red O, and Masson’s Trichrome.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sitia S, Tomasoni L, Atzeni F et al (2010) From endothelial dysfunction to atherosclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852(7):1498–1510
Bergheanu SC, Bodde MC, Jukema JW (2017) Pathophysiology and treatment of atherosclerosis: current view and future perspective on lipoprotein modification treatment. Neth Heart J 25(4):231–242
Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ et al (2021) Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2021 update. Circulation 143(8):e254–e743
Chan Y-H, Ramji DP (2020) A perspective on targeting inflammation and cytokine actions in atherosclerosis. Future Med Chem 12(7):613–626
Moss JWE, Ramji DP (2016) Cytokines: roles in atherosclerosis disease progression and potential therapeutic targets. Future Med Chem 8(11):1317–1330
Ko KA, Fujiwara K, Krishnan S et al (2017) En face preparation of mouse blood vessels. J Vis Exp 2017(123):55460
Fischer AH, Jacobson KA, Rose J et al (2008) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2008(2):prot4986
Chan JK (2014) The wonderful colors of the hematoxylin-eosin stain in diagnostic surgical pathology. Int J Surg Pathol 22(1):12–32
Titford M (2005) The long history of hematoxylin. Biotech Histochem 80(2):73–78
Andres-Manzano MJ, Andres V, Dorado B (2015) Oil red O and hematoxylin and eosin staining for quantification of atherosclerosis burden in mouse aorta and aortic root. Methods Mol Biol 1339:85–99
Robertson TA, Bunel F, Roberts MS (2013) Fluorescein derivatives in intravital fluorescence imaging. Cell 2(3):591–606
Mehlem A, Hagberg CE, Muhl L et al (2013) Imaging of neutral lipids by oil red O for analyzing the metabolic status in health and disease. Nat Protoc 8(6):1149–1154
Kraus NA, Ehebauer F, Zapp B et al (2016) Quantitative assessment of adipocyte differentiation in cell culture. Adipocytes 5(4):351–358
Onyije F, Ngokere A, Ligha A et al (2017) Computer-assisted image analysis in the diagnosis of gynaecological lesions: a quantitative and comparative investigation of haematoxylin-eosin with special dyes on tissue. J Cancer Res Pract 4(1):5–13
Saleh S, Hanna G, El-Nabi SH et al (2020) Dapagliflozin, a sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, protects cardiovascular function in type-2 diabetic murine model. J Genet 99:46
Acknowledgements
We thank the British Heart Foundation for financial support (grants PG/16/25/32097 and FS/17/75/33257). AA and RA received PhD studentships from the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (Jeddah University).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Chan, YH., Alahmadi, A., Alotibi, R., Ramji, D.P. (2022). Evaluation of Plaque Burden and Lipid Content in Atherosclerotic Plaques. In: Ramji, D. (eds) Atherosclerosis. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2419. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1924-7_29
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1924-7_29
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1923-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1924-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols