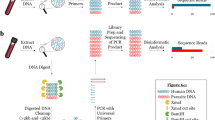
Abstract
Parasite mixed infections remain a relatively unexplored field in part due to the difficulties of unraveling complex mixtures of parasite DNA using classical methods of sequencing. Next-generation amplicon sequencing (NGS) is a powerful tool for exploring mixed infections of multiple genetic variants of the same parasite in clinical, environmental (water or soil), or food samples. Here, we provide a method for NGS-based detection of mixed parasite infections which uses the Blastocystis SSU rRNA gene as an example and includes steps for parasite concentration, DNA extraction, sequencing library preparation, and bioinformatic analysis.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grinberg A, Biggs PJ, Dukkipati VSR, George TT (2013) Extensive intra-host genetic diversity uncovered in Cryptosporidium parvum using next generation sequencing. Infect Genet Evol 15:18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2012.08.017
Maloney JG, Molokin A, Santin M (2019) Next generation amplicon sequencing improves detection of Blastocystis mixed subtype infections. Infect Genet Evol 73:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2019.04.013
Paparini A, Gofton A, Yang R, White N, Bunce M, Ryan UM (2015) Comparison of Sanger and next generation sequencing performance for genotyping Cryptosporidium isolates at the 18S rRNA and actin loci. Exp Parasitol 151–152:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2015.02.001
Vermeulen ET, Lott MJ, Eldridge MDB, Power ML (2016) Evaluation of next generation sequencing for the analysis of Eimeria communities in wildlife. J Microbiol Methods 124:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2016.02.018
Rojas-Velázquez L, Maloney JG, Molokin A, Morán P, Serrano-Vázquez A, González E, Pérez-Juárez H, Ximénez C, Santin M (2019) Use of next-generation amplicon sequencing to study Blastocystis genetic diversity in a rural human population from Mexico. Parasit Vectors 12:566. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3814-z
Maloney JG, Molokin A, da Cunha MJR, Cury MC, Santin M (2020) Blastocystis subtype distribution in domestic and captive wild bird species from Brazil using next generation amplicon sequencing. Parasite Epidemiol Control 9:e00138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parepi.2020.e00138
Calero-Bernal R, Santín M, Maloney JG, Martín-Pérez M, Habela MA, Fernández-García JL, Figueiredo A, Nájera F, Palacios MJ, Mateo M, Balseiro A, Barral M, Lima-Barberoi JF, Köster PC, Carmena D (2020) Blastocystis sp. subtype diversity in wild carnivore species from Spain. J Eukaryot Microbiol 67:273–278. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12772
Maloney JG, Molokin A, Santín M (2020) Assessment of next generation amplicon sequencing of the beta-giardin gene for the detection of Giardia duodenalis assemblages and mixed infections. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 21:e00098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fawpar.2020.e00098
Santín M, Trout JM, Fayer R (2008) A longitudinal study of cryptosporidiosis in dairy cattle from birth to 2 years of age. Vet Parasitol 155:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2008.04.018
Bushnell B, Rood J, Singer E (2017) BBMerge—Accurate paired shotgun read merging via overlap. PLoS One 12:e0185056. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185056
Rognes T, Flouri T, Nichols B, Quince C, Mahé F (2016) VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 4:e2584. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2584
Edgar RC, Bateman A (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinforma Appl NOTE 26:2460–2461. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461
Edgar RC, Flyvbjerg H (2015) Error filtering, pair assembly and error correction for next-generation sequencing reads. Bioinformatics 31:3476–3482. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv401
Edgar RC (2016) UNOISE2: improved error-correction for Illumina 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing. BioRxiv 081257. https://doi.org/10.1101/081257
Callahan BJ, Mcmurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJ, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13:581–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3869
Amir A, McDonald D, Navas-Molina JA, Kopylova E, Morton JT, Zech Xu Z, Kightley EP, Thompson LR, Hyde ER, Gonzalez A, Knight R (2017) Deblur rapidly resolves single-nucleotide community sequence patterns. mSystems 2:191–207. https://doi.org/10.1128/msystems.00191-16
Edgar RC (2016) UCHIME2: improved chimera prediction for amplicon sequencing. bioRxiv 074252. https://doi.org/10.1101/074252
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, Madden TL (2009) BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics 10:421. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-421
Santín M, Gómez-Muñoz MT, Solano-Aguilar G, Fayer R (2011) Development of a new PCR protocol to detect and subtype Blastocystis spp. from humans and animals. Parasitol Res 109:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-010-2244-9
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by USDA-ARS Project No: 8042-32000-100-00-D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Maloney, J.G., George, N.S., Molokin, A., Santin, M. (2021). An Illumina MiSeq-Based Amplicon Sequencing Method for the Detection of Mixed Parasite Infections Using the Blastocystis SSU rRNA Gene as an Example. In: de Pablos, L.M., Sotillo, J. (eds) Parasite Genomics. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2369. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1681-9_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1681-9_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1680-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1681-9
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols