Abstract
Three-component condensation reactions between azines (isoquinoline or phenanthridine) and acetylenic esters were undertaken in the presence of phenol derivatives (2,6-di-tert-butyl-phenol, 2,4-di-tert-butyl-phenol, 2,6-dimethyl phenol and 2,4-dimethyl phenol) for generation of C-arilation in good yields. The reactions proceeded smoothly at room temperature without using any catalyst. This method is very useful to functionalize aza-aromatic compounds in a one-pot operation.
Graphical Abstract

.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The development of simple synthetic routes for widely used organic compounds from readily available reagents is one of the major tasks in organic synthesis [1]. Nitrogen-containing heterocycles are abundant in nature and exhibit divers and important biological properties [2].
Phenanthridines are important core structures found in a variety of natural products and other biologically important molecules with a wide range of biological activities and applications [3–6], including antibacterial, antiprotozoal, anticancer, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antivirial, antioxidant [7–12] and also with applications as drugs [13], DNA targeting agents [14], dyes [15], and probes [16]. Isoquinoline is also present in various natural products such as cryptaustoline and cryptowoline [17]. They are known to exhibit various biological activities [18–20] such as antileukaemic [21], tubulin polymerization inhibitory [22], and anti-tumour activities [23]. In the current work, we now describe a new three-component reaction as an efficient synthetic route of compounds 4 and 8 using isoquinoline 1 or phenanthridine 5 as the two typical categories (see Scheme 1).
Results and discussions
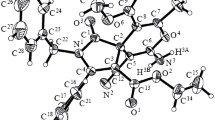
The reaction between azines (isoquinoline 1 or phenanthridine 5) and acetylenic esters 2 or 6 as a Michael acceptor [24–30] was undertaken in the presence of phenol derivatives (2,6-di-tert-butyl-phenol, 2,4-di-tert-butyl-phenol, 2,6-dimethyl phenol and 2,4-dimethyl phenol) at ambient temperature (see Scheme 2 and Table 1). Reactions were carried out by first mixing the phenanthridine or isoquinoline and phenol derivatives and then the acetylenic ester was added slowly. The reactions proceeded smoothly in CH2Cl2 and then the whole reaction mixture solidified into yellow or brown solid within a few hours. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of the crude products clearly indicated the formation of compounds 4a–g and 8 h–i. No product other than 4a–g and 8 h–i could be detected by NMR spectroscopy. The structures of compounds 4a–g and 8 h–i were confirmed by elemental analyses, mass, IR, 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra. The 1H NMR 500 MHz spectrum of 4a exhibited two singlets identified as tert-butyl (δ = 1.40, 18H, s, 2CMe3) and methoxy (δ = 3.72, 3H, s, OMe), olefinic protons (δ = 5.18 and 8.30, 2d, 3 J HH = 13.8 Hz, N–CH = CH-CO2CH3), and also two sharp line (δ = 5.16 and 5.80 ppm) for the OH and NCHC group, respectively. Aromatic protons, along with multiplets at δ = 7.02–8.20 ppm for the isoquinoline and phenol moiety. The 13C NMR spectrum of 4a showed 27 distinct resonances in agreement with the proposed structure. In addition, product 4a displayed 13C NMR resonances at δ = 90.77, 122.68 and 124.85 ppm, respectively for the NCHC, N–CH = CH–CO2CH3, and N–CH = CH–CO2CH3 units. The carbonyl group resonance in the 13C NMR spectrum of 4a appear at δ = 169.06 ppm. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of compounds 4b–g and 8 h–i are similar to those of 4a. The 1H NMR of each of the isolated product 4f–g and 8 h–i exhibited a N–C = CH proton signal at about 5.06-5.46 ppm, which is in agreement with the (Z) configuration for the vinyl moiety in 4f–g and 8 h–i [ 31, 32] (see Scheme 2 and Table 1).
Briefly, we have developed a new method to access a novel class of heterocyclic derivatives. The present procedure has the advantage that, not only is the reaction performed under neutral conditions, but also the reactants can be mixed without any prior activation or modification. It seems that, this procedure is very useful to functionalize azines in a one-pot operation.
Experimental
Melting points and IR spectra of all compounds were measured on an Electrothermal 9100 apparatus and a Shimadzu IR-460 spectrometer, respectively. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra were obtained with a BRUKER DRX-500 AVANCE instrument using CDCl3 as applied solvent and TMS as internal standard at 500.1 and 125.8 MHz, respectively. In addition, the mass spectra were recorded on a GCMS-QP5050A mass spectrometer operating at an ionization potential of 70 eV. Elemental analyses for C, H and N were performed using a Heraeus CHN-O-Rapid analyzer. All the chemicals used in this work were purchased from Fluka (Buchs, Switzerland) and were used without further purification.
General procedure for the synthesis of compounds 4 and 8
(2E)-methyl 3-(1-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)isoquinoline-2(1H)-yl) acrylate (4a).
To a magnetically stirred solution of isoquinoline (1 mmol) and 2,6-di-tert-butyl-phenol (0.21 g, 1 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (10 mL) was added, dropwise, a mixture of methyl propiolate (1 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (5 mL) at −10 °C over 10 min. After approximately a few hours stirring at ambient temperature, the whole reaction mixture solidified into a yellow solid, the solvent was then removed under reduced pressure and product washed with cold n-hexane (2 × 5 mL). Then the product was recrystallized from a mixture of n-hexane and ethyl acetate.
Yellow powder, yield 95 %, 0.40 g, mp: 191–193 °C; IR (νmax, cm−1): 1,672 cm −1 (C = O), 3,232 cm −1 (OH): 1H NMR (500.1 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 1.40 (18H, s, 2CMe 3 ), 3.72 (3H, s, OCH3), 5.16 (1H, s, OH), 5.18 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 13.8 Hz, N–CH = CH–CO2CH3), 5.80 (1H, s, NCHC), 5.87 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.4 Hz, C4-H, isoquinoline), 6.53 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.4 Hz, C3-H isoquinoline), 7.02–8.20 (7Haro, m, isoquinoline and phenol), 8.30 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 13.8 Hz, N–CH = CH-CO2Me) ppm; 13C NMR (125.8 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 30.13 (s, 2CMe 3), 50.86 (OCH3), 90.77 (NCHC), 122.68 (N–CH = CH–CO2CH3), 124.85 (N–CH = CH–CO2CH3), 126.79, 127.02, 127.63, 129.47, 131.70, 132.00, 135.85, 147.64 and 153.39 (14Caro, isoquinoline and phenol), 169.06 (C = O, ester). MS, m/z (%) = 419 (M, 5), 360 (M–CO2Me, 15), 334 (M–C4H5O2 , 10), 277 (M–C4H5O2 and CMe3, 13), 205 (C14H21O, 38), 85 (C4H5O2, 24); Anal. Calcd for C27H33NO3 (419.56): C, 77.30; H, 7.93; N, 3.34 %, Found: C, 77.15; H, 8.01; N, 3.44 %.
(2E)-ethyl 3-(1-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)isoquinoline-2(1H)-yl)acrylate(4b).
Yellow powder, yield 93 %, 0.40 g, mp: 180-182 ˚C; IR (νmax, cm−1): 1,659 cm −1 (C = O), 3,197 (OH) cm −1. 1H NMR (500.1 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 1.29 (3H, t, 3 J HH = 7.2 HZ, CO2CH2 CH 3 ), 1.39 (18H, s, 2CMe 3 ), 4.17 (2H, q, 3 J HH = 7.2 HZ, CO2 CH 2 CH3), 5.16 (1H, s, OH), 5.18 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 13.5 Hz, N–CH = CH-CO2Et), 5.81 (1H, s, NCHC), 5.87 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.8 Hz, C4-H isoquinoline), 6.52 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.8 Hz, C3-H isoquinoline), 7.08–7.29 (7Haro, m, isoquinoline and phenol), 7.57 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 13.5 Hz, N–CH = CH-CO2Et) ppm; 13C NMR (125.8 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 14.42 (CO2CH2 CH 3 ), 30.12 (2CMe 3 ), 59.39 (CO2 CH 2 CH3), 91.25 (NCHC), 122.77 (N–CH = CH-CO2Et), 124.81 (N–CH = CH–CO2Et), 126.79, 126.98, 127.61, 129.56, 131.63, 131.98, 135.81, 147.45 and 153.37 (14Caro, isoquinoline and phenol), 168.63 (C = O, ester). MS, m/z (%) = 433 (M, 22), 277 (M–C5H7O2 and CMe3, 24), 220 (M–C5H7O2 and 2CMe3, 26), 205 (C14H21O, 67); Anal. Calcd for C28H35NO3 (433.58): C, 77.57; H, 8.13; N, 3.23 %, Found: C, 77.70; H, 8.04; N, 3.35 %.
(2E)-ethyl 3-(1-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-2-hydroxyphenyl)isoquinoline-2(1H)-yl)acrylate(4c).
Yellow powder, yield 92 %, 0.40 g, mp: 176–178 °C; IR (νmax, cm−1): 1,664 cm −1 (C = O), 3,162 cm −1 (OH): 1H NMR (500.1 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 1.32 (3H, t, 3 J HH = 7.2 HZ, CO2CH2 CH 3 ), 1.43 (18H, s, 2CMe 3 ), 4.23 (2H, q, 3 J HH = 7.2 HZ, CO2 CH 2 CH3), 5.20 (1H, s, OH), 5.25 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 13.3 Hz, N–CH = CH-CO2Et), 5.89 (1H, s, NCHC), 5.97 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.6 Hz, C4–H isoquinoline), 6.52 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.6 Hz, C3-H isoquinoline), 7.12–7.37 (7Haro, m, isoquinoline and phenol), 7.64 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 13.3 Hz, N–CH = CH-CO2Et) ppm; 13C NMR (125.8 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 13.86 (CO2CH2 CH 3 ), 30.26 (2CMe 3 ), 58.79 (CO2 CH 2 CH3), 90.54 (NCHC), 121.97 (N–CH = CH–CO2Et), 123.76 (N–CH = CH–CO2Et), 125.70, 126.91, 127.54, 128.72, 131.90, 131.98, 134.80, 146.65 and 153.70 (14Caro, isoquinoline and phenol), 169.13 (C = O, ester). MS, m/z (%) = 433 (M, 9), 404 (M–Et, 48), 388 (M–OEt, 80), 360 (M–CO2Et, 56), 205 (C14H21O, 52), 129 (C9H7N, 100). Anal. Calcd for C28H35NO3 (433.58): C, 77.57; H, 8.13; N, 3.23 %, Found: C, 77.43; H, 8.19; N, 3.19 %.
(2E)-methyl 3-(1-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)isoquinoline-2(1H)-yl)acrylate(4d).
Yellow powder, yield 94 %, 0.32 g, mp: 87–89 °C; IR (νmax, cm−1): 1,670 cm −1 (C = O), 3,395 cm −1 (OH) : 1H NMR (500.1 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 2.20 (6H, s, 2Me), 3.71 (3H, s, OCH3), 5.11 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 13.5 Hz, N–CH = CH-CO2CH3), 5.76 (1H, s, OH), 5.87 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.6 Hz, C4-H, isoquinoline), 6.53 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.6 Hz, C3-H isoquinoline), 6.92 (1H, s, NCHC), 7.06–7.29 (6Haro, m, isoquinoline and phenol), 7.57 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 13.5 Hz, N–CH = CH-CO2Me) ppm; 13C NMR (125.8 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 16.16 (s, 2Me), 50.88 (OCH3), 91.01 (NCHC), 105.61 (N–CH = CH-CO2CH3), 123.45 (N–CH = CH-CO2CH3), 124.95, 125.94, 126.34, 126.74, 127.09, 127.47, 127.63, 128.49, 131.70, 133.52, 147.55 and 152.09 (14Caro, isoquinoline and phenol), 169.01 (C = O, ester). MS, m/z (%) = 335 (M, 38), 305 (M–2Me, 18), 276 (M–CO2Me, 20), 250 (M–C4H5O2 , 48), 130 (C9H8N, 100); Anal. Calcd for C21H21NO3 (335.39): C, 75.20; H, 6.31; N, 4.17 %, Found: C, 75.27; H, 6.23; N, 4.24 %.
(2E)-ethyl 3-(1-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)isoquinoline-2(1H)-yl)acrylate(4e).
Yellow powder, yield 96 %, 0.34 g, mp: 92–94 °C; IR (νmax, cm−1): 1,754 cm −1 (C = O), 3,450 cm −1 (OH): 1H NMR (500.1 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 1.28 (3H, t, 3 J HH = 7.1 HZ, CO2CH2 CH 3 ), 2.18 (6H, s, 2Me), 4.19 (2H, q, 3 J HH = 7.1 HZ, CO2 CH 2 CH3), 5.11 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 13.5 Hz, N–CH = CH–CO2Et), 5.76 (1H, s, OH), 5.82 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.4 Hz, C4–H isoquinoline), 6.54 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.4 Hz, C3-H isoquinoline), 6.99 (1H, s, NCHC), 7.05–7.20 (6Haro, m, isoquinoline and phenol), 7.58 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 13.5 Hz, N–CH = CH–CO2Et) ppm; 13C NMR (125.8 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 14.40 (CO2CH2 CH 3 ), 15.81 (2Me), 59.66 (CO2 CH 2 CH3), 91.40 (NCHC), 106.14 (N–CH = CH–CO2Et), 123.48 (N–CH = CH–CO2Et), 124.92, 125.93, 126.73, 126.99, 127.61, 128.49, 130.28, 131.52, 133.53, 147.42 and 152.11 (14Caro, isoquinoline and phenol), 168.66 (C = O, ester). MS, m/z (%) = 349 (M, 3), 334 (M–Me, 10), 228 (M–C8H9O, 26), 129 (C9H7N, 89); Anal. Calcd for C22H23NO3 (349.42): C, 75.62; H, 6.63; N, 4.01 %, Found: C, 75.49; H, 6.70; N, 4.10 %.
Dimethyl 2-(1-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)isoquinoline-2(1H)-yl)maleate(4f).
Brown powder, yield 92 %, 0.36 g, mp: 153-155 °C; IR (νmax, cm−1): 1,720 and 1,655 cm −1 (C = O), 3285 cm −1 (OH): 1H NMR (500.1 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 2.18 (6H, s, 2Me), 3.55 and 3.98 (6H, 2 s, 2OCH3), 5.20 (1H, s, N–C = CH-CO2Me), 5.75 (1H, s, OH), 5.93 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.6 Hz, C4-H, isoquinoline), 6.49 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.6 Hz, C3-H isoquinoline), 6.95 (1H, s, NCHC), 6.99–7.28 (7Haro, m, isoquinoline and phenol) ppm; 13C NMR (125.8 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 16.14 (s, 2Me), 51.86 and 53.10 (2OCH3), 91.07 (NCHC), 109.23 (N–C = CH–CO2CH3), 123.63 (N–C = CH-CO2CH3), 125.02, 125.55, 126.20, 126.43, 127.09, 127.74, 128.45, 130.65, 131.99, 132.01, 150.04 and 152.21 (14Caro, isoquinoline and phenol), 165.28 and 167.24 (2C = O, ester). MS, m/z (%) = 393 (M, 3), 334 (M–CO2Me, 36), 250 (M–C6H7O4, 46), 143 (C6H7O4, 6), 130 (C9H8N, 100); Anal. Calcd for C23H23NO5 (393.43): C, 70.22; H, 5.89; N, 3.56 %, Found: C, 70.28; H, 5.96; N, 3.68 %.
Dimethyl 2-(1-(2-hydroxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)isoquinoline-2(1H)-yl)maleate(4 g).
Brown powder, yield 91 %, 0.36 g, mp: 118-120 °C; IR (νmax, cm−1): 1,742 and 1,704 cm −1 (C = O), 3320 cm −1 (OH): 1H NMR (500.1 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 2.10 and 2,27 (6H, s, 2Me), 3.65 and 3.83 (6H, 2 s, 2OCH3), 5.43 (1H, s, N–C = CH-CO2Me), 5.71 (1H, s, OH), 5.86 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.5 Hz, C4-H, isoquinoline), 6.37 (1H, d, 3 J HH = 7.5 Hz, C3-H isoquinoline), 6.63 (1H, s, NCHC), 7.03-7.32 (6Haro, m, isoquinoline and phenol) ppm; 13C NMR (125.8 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 13.46 and 14.09 (2 s, 2Me), 51.44 and 52.63 (2OCH3), 90.17 (NCHC), 110.13 (N–C = CH-CO2CH3), 124.36 (N–C = CH-CO2CH3), 124.65, 125.22, 126.09, 126.29, 126.73, 127.19, 127.74, 128.81, 129.25, 132.80, 133.11, 149.14 and 151.82 (14Caro, isoquinoline and phenol), 166.28 and 168.17 (2C = O, ester). MS, m/z (%) = 393 (M, 7), 362 (M–OMe, 62), 334 (M–CO2Me, 11), 272 (M–C8H9O, 18), 143 (C6H7O4, 26), 129 (C9H7N, 83), 121 (C8H9O, 44); Anal. Calcd for C23H23NO5 (393.43): C, 70.22; H, 5.89; N, 3.56 %, Found: C, 70.13; H, 5.81; N, 3.69 %.
Dimethyl 2-(6-(2-hydroxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)phenanthridine-5(6H)-yl)maleate(8 h).
Brown powder, yield 90 %, 0.40 g, mp: 107-109 °C; IR (νmax, cm−1): 1,743 and 1,654 cm −1 (C = O), 3,400 cm −1 (OH): 1H NMR (500.1 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 2.13 and 2,25 (6H, s, 2Me), 3.70 and 3.81 (6H, 2 s, 2OCH3), 5.46 (1H, s, N–C = CH-CO2Me), 5.83 (1H, s, OH), 6.71 (1H, s, NCHC), 6.90–7.91 (6Haro, m, phenanthridine and phenol) ppm; 13C NMR (125.8 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 14.07 and 14.13 (2 s, 2Me), 51.64 and 52.79 (2OCH3), 91.11 (NCHC), 109.18 (N–C = CH–CO2CH3), 123.97 (N–C = CH–CO2CH3), 124.25, 125.39, 125.58, 126.09, 126.80, 127.49, 127.63, 128.80, 128.95, 130.28, 132.18, 148.74, 152.36 and 153.05 (18Caro, phenanthridine and phenol), 165.71 and 167.13 (2C = O, ester). MS, m/z (%) = 443 (M, 6), 428 (M–Me, 17), 384 (M–CO2Me, 21), 322 (M–C8H9O, 63), 300 (M–C6H7O4, 41), 143 (C6H7O4, 100), 121 (C8H9O, 8); Anal. Calcd for C27H25NO5 (443.50): C, 73.12; H, 5.68; N, 3.16 %, Found: C, 73.02; H, 5.77; N, 3.04 %.
Dimethyl 2-(6-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-2-hydroxyphenyl)phenanthridine-5(6H)-yl)maleate(8i).
Brown powder, yield 94 %, 0.50 g, mp: 142-144 °C; IR (νmax, cm−1): 1,740 and 1,665 cm −1 (C = O), 3,395 cm −1 (OH), 1H NMR (500.1 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 0.89 and 1,41 (18H, 2 s, 2CMe 3 ), 3.56 and 3.99 (6H, 2 s, 2OCH3), 5.06 (1H, s, N–C = CH–CO2Me), 5.89 (1H, s, OH), 6.04 (1H, s, NCHC), 6.95–7.89 (11Haro, m, phenanthridine and phenol) ppm; 13C NMR (125.8 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 30.11 and 30.23 (2 s, 2CMe 3), 51.70 and 53.19 (2OCH3), 92.21 (NCHC), 109.78 (N–C = CH–CO2CH3), 124.17 (N–C = CH–CO2CH3), 124.65, 124.79, 125.30, 126.39, 126.47, 127.40, 127.71, 128.12, 128.54, 131.18,, 131.91, 132.20, 148.76, 151.83 and 153.15 (18Caro,phenanthridine and phenol), 167.12 and 168.93 (2C = O, ester). MS, m/z (%) = 527 (M, 52), 496 (M–OMe, 38), 468 (M–CO2Me, 100), 322 (M–C14H21O, 30), 205 (C14H21O, 32), 180 (C13H10N, 56); Anal. Calcd for C33H37NO5 (527.65): C, 75.12; H, 7.07; N, 2.65 %, Found: C, 75.23; H, 7.16; N, 2.57 %.
References
Laszlo P (1995) Organic reactions: simplisity and logic. wiley, New York
Porter AEA (1984) In comprehencive heterocyclic chemistry. In: Katritzky AR, Ress CW (eds). Pergamon Press, Oxford
T. N. Le, S. G. Gang, W. J. Cho, J. Org. Chem. 69, 2768 (2004)
S. W. Youn, J. H. Bihn, Tetrahedron Lett. 50, 4598 (2009)
A.D.C. Parent, L. Cronin, Synthesis 1, 155 (2008)
A.D.C. Parenty, L.V. Smith, A.L. Pickering, D.L. Long, L. Cronin, J. Org. Chem. 69, 5934 (2004)
J. Suchomelova, H. Bochorakova, H. Paulova, P. Musil, E. Taborska, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 44, 283 (2007)
K. Kohno, S. Azuma, T. Choshi, J. Nobuhiro, S. Hibino, Tetrahedron Lett. 50, 590 (2009)
J. Vrba, Z. Dvorak, J. Ulrichova, M. Modriansky, Cell Biol. Toxicol. 24, 39 (2008)
C.H. Yang, M.J. Cheng, M.Y. Chiang, Y.H. Kuo, C.J. Wang, I.S. Chen, J. Nat. Prod. 71, 669 (2008)
I. Kock, D. Heber, M. Weide, U. Wolschendorf, B. Clement, J. Med. Chem. 48, 2772 (2005)
A. D. C. Parenty, K. M. Guthrie, Y. F. Song, L. V. Smith, E. Burkholder, L. Cronin, Chem. Commu. 1194 (2006). doi:10.1039/B517117B
K. Morohashi, A. Yoshino, A. Yoshimori, S. Saito, S. Tanuma, S. Sakaguchi, F. Sugawara, Biochem. Pharmacol. 70, 37 (2005)
J. Whittaker, W.D. Mcfadyen, B.C. Baguley, V. Murray, Anticancer Drug Des. 16, 81 (2001)
H. Ihmels, D. Otto, Top. Curr. Chem. 258, 161 (2005)
S.S. Pennadam, J.S. Ellis, M.D. Lavigne, D.C. Gorecki, M.C. Davies, C. Alexander, Langmuir 23, 41 (2007)
J.S. Yadav, B.V.S. Reddy, N.N. Yadav, M.K. Gupta, Tetrahedron Lett. 49, 2815 (2008)
M.K. Parai, G. Panda, K. Srivastava, S.K. Puri, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18, 776 (2008)
M. Megyesi, L. Biczok, Chem. Phys. Lett. 447, 247 (2007)
A.E. Antri, I. Messouri, M. Bouktaib, R.E. Alami, M. Bolte, B.E. Bali, M. Lachkar, Molecules 9, 650 (2004)
W.K. Anderson, A.R. Heider, N. Raju, J.A. Yucht, J. Med. Chem. 31, 2097 (1988)
M. Goldbrunner, G. Loidl, T. Polossek, A. Mannschreck, A.E. Von, J. Med. Chem. 40, 3524 (1997)
R. Ambros, A.S. Von, W. Wiegrebe, Arch. Pharm. 321, 481 (1988)
M. Nassiri, R. Heydari, N. Hazeri, S. M. Habibi-Khorassani, M. T. Maghsoodlou, F. Jalili Milani, Arkivoc. (ii), 61 (2010)
M. Nassiri, M. T. Maghsoodlou, R. Heydari, S. M. Habibi-Khorassani, Mol. Divers. 12, 111 (2008)
V. Nair, B.R. Devi, L.R. Varma, Tetrahedron Lett. 46, 5333 (2005)
V. Nair, A. R. Sreekanth, N. P. Abhilash, A. T. N. Biju, L. Varma, S. Viji, S. Mathew, Arkivoc. (xi) 178 (2005)
M.A. Terzidis, C.A. Tsoleridis, J.S. Stephanidou, Synthesis 2, 229 (2009)
I. Yavari, N. Hazeri, M.T. Maghsoodlou, S. Souri, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 264, 313 (2006)
I. Yavari, Z. Hossaini, Tetrahedron Lett. 47, 4465 (2006)
I. Yavari, A.R. Alborzi, B. Mohtat, F. Nourmohammadian, Synth. Commun. 38, 703 (2008)
E.L. Eliel, S.H. Wilen, Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds (Wiley, New York, 1994)
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Research council of graduate university of advanced tecnology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nassiri, M., Hassankhani, A. Simple and one-pot C-arilation from reaction between azines (isoquinoline or phenanthridine) and acetylenic esters in the presence of phenol derivatives. J IRAN CHEM SOC 11, 693–699 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-013-0341-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-013-0341-2