Abstract
Aluminum-based composites have many advantages over their conventional counterparts. A major problem in such composites is the clustering of particles in the matrix. Friction stir processing (FSP) can homogenize particle distribution in aluminum-based composites. In this study, unannealed TiO2 particles were used to prepare Al-TiO2 nanocomposite using FSP. The TiO2 particles, about 1 µm, were dispersed into an aluminum matrix by 6 passes of FSP. The TiO2 particles were fractured by multiple FSP passes, leading to a nano-size particle distribution in the matrix. Nanoscale dispersion was confirmed by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The fractured TiO2 particles reacted with the aluminum matrix to form Al3Ti intermetallic and Al2O3 ceramic. The progression of the Al-TiO2 reaction from the fourth to the sixth pass of FSP was revealed by x-ray diffraction. Due to the nanoscale dispersion, the yield and ultimate tensile strength of the composite increased to 97 and 145 MPa, respectively. Ductility of the composite decreased marginally compared to the as-received aluminum. As the dispersed particles pin dislocations, the strain-hardening rate of the composite was considerably increased and the same was seen in the Kocks-Mecking plot. The TiO2 particles are mechanically activated due to their fracture during FSP, hence leading to reaction with the matrix. The particle refinement and dispersion lead to a homogeneous matrix with higher strength.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Friction stir welding (FSW), a solid-state joining process developed by the Welding Institute in Cambridge, England (Ref 1), has emerged as the method to join all aluminum alloys. In FSW, a nonconsumable rotating tool, with a specially designed pin and shoulder, is plunged into the interface between the two plates and traversed along the joint line. The workpiece is plasticized due to localized heating by the rotating tool. As the tool traverses along the joint line, the soft metal is extruded around the tool pin before being forged by the downward pressure applied by the tool shoulder (Ref 2). FSW can join dissimilar metals with widely varying melting points and hardness (Ref 3). FSW has been used to weld composites (Ref 4, 5). Based on the principle of FSW, Mishra et al. (Ref 6) developed friction stir processing (FSP) for microstructural refinement of materials (Ref 7,8,9,10). FSP is a potential tool for many applications which include (a) formation of ultrafine grains in aluminum alloys that exhibit superplasticity (Ref 6, 11,12,13), (b) homogenization of agglomerated aluminum nanocomposites (Ref 14), (c) synthesis of aluminum composites (Ref 15, 16) and (d) fabrication of a surface composite (Ref 17). Recently, FSP successfully produced an ultrafine-grained Al-Al2Cu in situ composite from an Al-Cu elemental powder mixture (Ref 18) and Al-Al3Ti nanocomposites (Ref 19).
Aluminum-based composites reinforced with hard ceramic particles have received considerable interest because of their high specific strength, stiffness and resistance to wear. Aluminum matrix composites (AMCs) have potential applications in automotive, aeronautical and aerospace industries. Therefore, simple and economical methods for fabricating AMCs are a sought-after research area. Strengthening mechanisms in the composites can be classified into direct and indirect strengthening (Ref 20). Direct strengthening occurs when loads are transferred from the weak matrix to the hard reinforcements (Ref 20, 21), while indirect strengthening results from the change in the matrix microstructure (for example, the Orowan strengthening mechanism, grain refinement, dislocation multiplication) of the composites because of the reinforcements (Ref 22,23,24). In metal matrix composites (MMC’s), damage evolution starts, preferentially, in the particle. This is because of the particle agglomeration leading to stress triaxiality, due to which, problems such as accelerated fatigue life, lower impact resistance and ductility, along with the poor predictability of properties of MMCs have been the major issues that have limited their use. To overcome these drawbacks, use of nanoparticles has been attracting attention in composite research. The ability of nanoparticles in improving mechanical and physical properties of MMCs is the reason for increasing attention in this direction. To realize the full potential of the nanoparticles, a nanoscale dispersion is essential. With the nanoscale dispersion, problems related to fatigue, fracture toughness and creep can be greatly alleviated. However, manufacturing costs and environmental concerns need to be addressed.
Nano-MMCs have been produced through the powder metallurgy route (Ref 25). Secondary processing, such as extrusion and rolling, is often needed to consolidate materials produced by this route. An alternative route is to introduce ceramic particles by stirring them into molten metal (Ref 26). However, the nanoparticles form hard agglomerates that are difficult to disperse through physical mixing (Ref 27).
FSP has successfully evolved into a method to fabricate MMCs, which are environmentally friendly and economical in terms of time and cost. During the past decade, a large number of investigations have been carried out to process MMCs by FSP. In an earlier study on the in situ FSP Al-TiO2 composite, a mixture of Al and TiO2 powders was sintered, forged and followed by FSP (Ref 28). Khodabakhshi et al. (Ref 29) directly incorporated TiO2 particles in the Al5052 alloy; however, there was no significant increase in strength, and a considerable loss in ductility was observed. In another study, Al-Mg alloy composites were prepared with a varying volume fraction of TiO2 (Ref 30). In the study, for a volume fraction of six percent, TiO2 was unevenly distributed even after 12 passes of FSP. It was also reported that for an optimum volume fraction of three percent, the ultimate tensile strength increased by 40% and the ductility was reduced by 56%. The reaction products of TiO2 and the matrix have been evaluated with elemental mapping in SEM and TEM. Visweswara et al. (Ref 31) have incorporated TiO2 by FSP to evaluate the anodizing behavior and optical appearance. To the best of the author’s knowledge, there is no report about the effect of successive FSP passes on Al-TiO2 reaction.
The objective of the present study is to fabricate a fully dense Al-TiO2 nanocomposite without any pre- or post-processing. Unannealed TiO2 particles were incorporated into the aluminum matrix by FSP. A detailed characterization of the microstructural and mechanical properties of the Al-TiO2 composite was carried out. The evidence of particle refinement by fracture, which leads to the reaction of Al-TiO2, is also presented. The reaction of TiO2 with aluminum during successive passes of FSP was characterized using x-ray diffraction.
Experimental
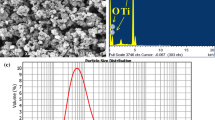
Titanium isopropoxide, commonly referred to as titanium tetra-isopropoxide (TTIP), with the chemical formula Ti{OCH (CH3)2}4 and the structure shown in Fig. 1(a), was used as a precursor to synthesize TiO2 in this study. The TTIP precursor of 5 ml was mixed with 15 ml isopropanol. This solution was slowly added to 250 ml of distilled water. The solution was maintained at a pH of 7 to 10 by adding either HNO3 or NH4OH. This mixture was heated to 60°C (± 10°C) and vigorously stirred to cause gelation. A bluish-white gel of about 50 ml was obtained after 18-20 h. The gel was washed with ethanol and dried at 100°C in a vacuum; after 3 h, a yellowish-white powder had formed (Ref 32). The particles of the powder were 1 µm in size and were measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS). To confirm that the particles were of TiO2, energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) on SEM (Sirion, Model VL 30FEG) to find elements was done (Fig. 1c). Then, the phases present were confirmed by x-ray diffraction (XRD) studies conducted on a PANalytical (JDX-8030) using a Cu-Kα radiation. The XRD of the amorphous powder revealed a broad pattern of an anatase phase with low-intensity brookite phase (Fig. 1d).
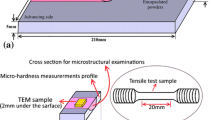
In the present work, commercially pure (CP) aluminum (99.5%) plates of 6 mm thickness, 200 mm long and 80 mm wide were used as matrix material. On these plates, grooves of 160 mm length, 3 mm width and 4 mm depth were machined. These grooves were filled with TiO2 particles and sealed with CP aluminum strips of 2 mm thickness. A high carbon steel tool with a shoulder diameter of 25 mm, and an 8 to 6 mm diameter conical pin with a thread of 1 mm pitch and a pin height of 5 mm were used. All the experiments were done on a five-axis friction stir welding machine (Make: BISS-ITW, Bangalore). The experiments were done at a tool rotation speed of 1200 rpm, traverse speed of 25 mm/min and a tool tilt of 2°. The rotating tool traversed the sealed groove of the workpiece. The tool traversed the same path up to 6 times. The workpiece was cooled to room temperature between each pass of the tool. For comparison, a CP aluminum plate was processed with six FSP passes without reinforcement under identical parameters.
The samples of as-received CP aluminum, FSPed CP aluminum and the synthesized composite were cut in a direction perpendicular to the tool traverse. The samples were carefully ground on SiC abrasive papers from 400 to 3000 grit. Then, the samples were polished with an alumina slurry and, finally, with a diamond paste of 1-2 µm particle size. To remove dust/abrasive particles, the samples were cleaned ultrasonically. All the samples were etched with freshly prepared Kroll’s reagent. For EBSD, the samples were electropolished using A2 electrolyte. Macro-images from the sample were captured on a stereo microscope. The samples were also characterized using a SEM (ESEM Qunta200, Make: FEI) and a TEM (TEC-NAI F30). The size, distribution and volume fraction of the TiO2 particles were measured using image analysis software ImageJ. Tensile samples were machined from the processed zone using a wire electric discharge machine, and the schematics of the location and dimensions were as shown in Fig. 2. Tensile tests were carried out on an Instron UTM at a strain rate of 10−3 s−1.
Results
Microstructures and Phase Analysis
The macroscopic images in Fig. 3(a), (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f) show the cross section of the processed composite from first pass to sixth pass. After first pass, the composite shows particle agglomeration near the top of the nugget below the shoulder effected region (Fig. 3a). The agglomeration is discontinuous and extends from advancing side (AS) to the retreating side (RS). The second pass also shows similar discontinuous agglomeration extending from AS to RS, but the area is reduced (Fig. 3b). After third pass, the agglomerations are concentrated in AS but are still discrete (Fig. 3c). At the end of the forth pass, discrete agglomerations are merged and located toward AS (Fig. 3d). After the fifth pass, the composite shows as marked reduction in agglomerated area and except on the AS, particles are evenly distributed in the nugget (Fig. 3e). The six pass sample shows a nugget without any macroscopic agglomeration, and the boundary between the stir zone and the base metal is clearly defined (Fig. 3f). The processed zone of the sample was about 8 mm wide and 5 mm thick.
The diffraction patterns of the four, fifth and sixth pass samples show that the intensity of the TiO2 reduced and Al2O3 increased (Fig. 4). As shown in from the reaction (1), TiO2 is reduces to form Al3Ti and Al2O3. From the XRD and reactions, it can be stated that the reaction of TiO2 with the aluminum matrix is aided by FSP. With each pass of FSP, the particles are refined. As smaller particles have higher surface energy, the activation energy tends to reduce. As the activation energy is reduced, the TiO2 reaction with aluminum proceeds at a lower temperature during FSP. The residual peaks of TiO2 in Fig. 4 indicate an incomplete reaction, which is due to larger TiO2 particles whose activation energies remain large.
The grains of as-received CP aluminum were refined from 50 µm to about 5 µm in the Al-TiO2 composite shown in Fig. 5(a) and (b). EBSD (inverse pole figure + grain boundaries) map of the processed Al-TiO2 composite is shown in Fig. 5c. The reinforcement particles are not indexed; hence, they are seen as black particles. The grain size refinement in the composite was due to combined effect of dynamic recrystallization and presence of secondary particles, which increased the nucleation sites, consequently reduced the grain size of the aluminum matrix during FSP (Ref 33, 34). The TEM image of the FSP composite also shows the sub-grain structure pinned by nanoparticles (Fig. 5d). Figure 6 shows that the particle sizes are distributed from submicron to a few microns. The larger particles are suspected to be of un-reacted TiO2.
Further, to understand the particle refinement and the reaction mechanism of Al-TiO2 composites during FSP, a TEM analysis was carried out with emphasis on particle fracture. The observed images contain particles with pores and cracks as shown in Fig. 7(a) and (b). Figure 7(a), (b), (c), (d) and (e) shows the fracture mechanism of the particle during FSP. Large particles (Fig. 7a) with pores and cracks (Fig. 7b and c) are fractured due to the stirring action of the tool pin, leading to finer particles (Fig. 7d and e). Porous particles have low fracture toughness; hence, they are easily fractured to the nanoscale by successive FSP passes. Due to this particle refinement the surface energy of the particle increases, and this, in turn, reduces the activation energy of Al-TiO2 reaction. The TEM analysis also confirmed the nanoscale dispersion of particles as shown in Fig. 8(a). The dispersed particles were identified as Al3Ti based on the selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns and the EDS analysis (Fig. 8a and b).
Tensile Behavior
Figure 9 shows the room-temperature engineering stress–strain curves of as-received, sixth pass FSPed CP aluminum and the FSP synthesized Al-TiO2 composite. The tensile test results of the as-received sixth pass FSPed CP aluminum and Al-TiO2 composite are given in Table 1. From the tensile test data in Table 1, the sixth pass FSPed aluminum showed a yield strength of 76 ± 4 MPa, an ultimate tensile strength of 111 ± 6 MPa and a 36% elongation, and the increase in strength is attributed due to the grain refinement during FSP. In this case, Al-TiO2 composite yield strength (97 ± 1 MPa) and ultimate tensile strength (145 ± 3 MPa) of the composite increased by 26 and 44% and ductility of the composite decreased to 34% from 37%, compared to as-received CP aluminum. Figure 10(a) and (b) shows fractographs of as-received aluminum and Al-TiO2 composite samples. While both samples show a ductile fracture, in the case of the Al-TiO2 composite, two different sizes of dimples were observed. Most of the dimples contain fractured particles, indicating good interfacial bonding with the matrix. The fractured particles suggest that cracks had nucleated in the particle (Fig. 10b). Two types of particles were observed in the fractographs, large fractured particles, and smaller particles without cracks. This indicates that fracture starts at the large TiO2 (un-reacted) particles.
Discussion
The combination of large stresses and heating during multi-pass FSP was responsible for the synthesis of the nanocomposite in this study. Due to frictional heating between the tool and the workpiece, the workpiece was severely deformed in a localized area (Ref 2). The agglomerated particles were stretched along the shear stress directions, which lead to particle distribution and fragmentation (Ref 35). Multi-pass stirring caused a high plastic strain (Ref 36), which resulted in the homogeneous distribution of the TiO2 particles in the matrix.
Strengthening in the stir zone is due to a combination of recrystallization and dispersion of nanoparticles in the matrix (Ref 35,36,37). Strengthening depends on dislocation interaction in the metallic materials. Any obstacle to dislocation movement leads to strengthening of the matrix. Hence, a uniform distribution of nanoparticles will affect the dislocation mobility and may lead to their multiplication. Strengthening of the Al-TiO2 composite is also due to dislocation interaction with the nanoparticles. Figure 11(a) shows dislocation movement impeded due to entanglement around the particles, and Figure 11(b) shows dislocations pinned by the nanoparticles. It is also seen that the particles have pinned the grain boundary (Fig. 11c). The particles at grain boundary retard the grain growth by pinning the grain boundaries and hence arrest the grain growth (Ref 38). The pinning of second-phase particles on grain boundaries is called Zener pinning. Assuming a uniform distribution of particles, the Zener limiting grain size (\(d_{z}\)) can be calculated using Eq 2:
where \(r\) and \(V_{\text{f}}\) are the radius and volume fraction of the particles, respectively (Ref 38). Average particle size and volume fraction of the composite (as calculated from image analysis software ImageJ) were 0.38 µm and 6.7%, respectively. Calculated Zener limiting grain size was around 4 µm, and the actual grain size was found to be 5 µm; this suggests that the grain growth in the composite is controlled by the Zener pinning pressure.
Assuming Al-TiO2 is an isotropic composite, with a volume fraction of 6.7%, from the Orowan-Ashby equation the net change in the yield strength can be calculated (Eq 3).
where \(\Delta \sigma_{\text{orowan}}\) is the change in yield strength due to the Orowan strengthening by the particles, Gm is the shear modulus of the matrix, b is Burger’s vector, \(\lambda\) is inter-particle spacing and r is the radius of the particles. The inter-particle spacing is given by
where, \(d_{\text{p}}\) is the diameter of the particle and \(V_{\text{P}}\) is the volume fraction of the particle (Ref 39). The Orowan-Ashby equation predicts a yield strength of 94 MPa, and from the tensile test a yield strength of 97 MPa was obtained. The dominant role of Orowan strengthening is confirmed by a TEM image showing the multiple pinned dislocations by a particle (Fig. 11a).
To analyze the effect of reinforcements and FSP on the work-hardening rate, a differential form of the Voces equation \(\theta = \theta_{o} \left( {1 - \frac{\sigma }{{\sigma_{\text{s}} }}} \right)\) was used to plot the Kocks-Mecking curves, where \(\theta\) is the hardening rate, \(\theta_{o}\) is the work-hardening limit, \(\sigma\) is the current flow stress and \(\sigma_{\text{s}}\) is the saturation stress [40]. It is seen that that the strain-hardening rate of as-received CP aluminum, FSPed CP aluminum and FSPed Al-TiO2 composite is 480, 1125 and 1650 MPa, respectively(Fig. 12). It is also seen from Fig. 13 that the FSPed CP aluminum and Al-TiO2 composites show stage III hardening.
Conclusions
In the current study, an Al-TiO2 composite was synthesized, and its microstructure and mechanical characterization were investigated. From the results, the following conclusions can be drawn:
-
The thermo-mechanical action during FSP leads to fracture of TiO2 particles resulting in their reaction with aluminum matrix. The progression of the reaction during successive passes was confirmed by XRD.
-
The grain size refinement of the Al-TiO2 composite was due to the combined effect of dynamic recrystallization and Zener pinning during FSP.
-
The fractographs showed a good interfacial bonding between the matrix and reinforcement, and the fracture was initiated in large un-reacted TiO2 particle.
-
The 26% increase in yield and a 44% increase in UTS were observed due to the combined effect of grain refinement and Orowan strengthening.
-
Work-hardening rate increased in Al-TiO2 composite, and it exhibited stage III hardening.
References
W. Thomas, Friction Stir butt-welding, International Patent Application No. PCT/GB92/0220 (1991)
R.S. Mishra and Z. Ma, Friction Stir Welding and Processing, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2005, 50(1), p 1–78
E.E. Patterson, Y. Hovanski, and D.P. Field, Microstructural Characterization of Friction Stir Welded Aluminum-Steel Joints, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2016, 47(6), p 2815–2829
L. Ceschini, I. Boromei, G. Minak, A. Morri, and F. Tarterini, Effect of Friction Stir Welding on Microstructure, Tensile and Fatigue Properties of the AA7005/10 vol.% Al2O3 Composite, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2007, 67(3), p 605–661
W.B. Lee, C.Y. Lee, M.K. Kim, J.I. Yoon, Y.J. Kim, Y.M. Yoen, and S.B. Jung, Microstructures and Wear Property of Friction Stir Welded AZ91 Mg/SiC Particle Reinforced Composite, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2006, 66(11), p 1513–1520
R.S. Mishra, M. Mahoney, S. McFadden, N. Mara, and A. Mukherjee, High Strain Rate Superplasticity in a Friction Stir Processed 7075 Al Alloys, Scr. Mater., 1999, 42(2), p 163–168
P.B. Berbon, W.H. Bingel, R.S. Mishra, C.C. Bampton, and M.W. Mahoney, Friction Stir Processing: A Tool to Homogenize Nanocomposite Aluminum Alloys, Scr. Mater., 2001, 44(1), p 61–66
Y. Kwon, I. Shigematsu, and N. Saito, Mechanical Properties of Fine-Grained Aluminum Alloy Produced by Friction Stir Process, Scr. Mater., 2003, 49(8), p 785–789
C. Rhodes, M. Mahoney, W. Bingel, and M. Calabrese, Fine-Grain Evolution in Friction-Stir Processed 7050 Aluminum, Scr Mater., 2003, 48(10), p 1451–1455
Z. Ma, R.S. Mishra, and M.W. Mahoney, Superplasticity in Cast A356 Induced via Friction Stir Processing, Scr Mater., 2004, 50(7), p 931–935
X.L. Shi, R.S. Mishra, and T.J. Watson, Effect of Temperature and Strain Rate on Tensile Behavior of Ultrafine-Grained Aluminum Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2008, 494(1), p 247–252
J.Q. Su, T. Nelson, and C. Sterling, Grain Refinement of Aluminum Alloys by Friction Stir Processing, Philos. Mag., 2006, 86(1), p 1–24
I. Charit and R.S. Mishra, Evaluation of Microstructure and Superplasticity in Friction Stir Processed 5083 Al Alloys, J. Mater. Res., 2004, 19(11), p 3329–3342
P.B. Berbon, W.H. Bingel, R.S. Mishra, C.C. Bampton, and M.W. Mahoney, Friction Stir Processing: A Tool to Homogenize Nanocomposite Aluminum Alloys, Scr. Mater., 2001, 44(1), p 61–66
M. Saadatmand and J.A. Mohandesi, Comparison Between Wear Resistance of Functionally Graded And Homogenous Al-SiC Nanocomposite Produced by Friction Stir Processing (FSP), J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2014, 23(3), p 736–742
R. Beygi, M.Z. Mehrizi, and G. Eisaabadi B, Friction Stir Processing of Al with Mechanically Alloyed Al-TiO2-Graphite Powder: Microstructure and Mechanical Properties, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26(3), p 1455–1462
R.S. Mishra, Z. Ma, and I. Charit, Friction Stir Processing: A Novel Technique for Fabrication of Surface Composite, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2003, 341(1), p 307–310
C. Hsu, P. Kao, and N. Ho, Ultrafine-Grained Al-Al2 Cu Composite Produced In Situ by Friction Stir Processing, Scr Mater., 2005, 53(3), p 341–345
C.J. Hsu, C.Y. Chang, P.W. Kao, N.J. Ho, and C.P. Chang, Al-Al3 Ti Nanocomposites Produced In Situ by Friction Stir Processing, Acta Mater., 2006, 54(19), p 5241–5249
N. Chawla and Y.L. Shen, Mechanical Behaviour of Particle Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2001, 3(6), p 357–370
L. Davis and J. Allison, Residual Stresses and Their Effects on Deformation, Metall. Mater. Transac. A, 1993, 24(11), p 2487–2496
M. Vogelsang, R. Arsenault, and R. Fisher, An In Situ HVEM Study of Dislocation Generation at Al/SiC Interfaces in Metal Matrix Composites, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1986, 17(3), p 379–389
R. Arsenault and S. Wu, A Comparison of PM vs. Melted SiC/Al Composites, Scr Mater., 1988, 22(6), p 767–772
P. Krajewski, J. Allison, and J. Jones, The Influence of Matrix Microstructure and Particle Reinforcement on the Creep Behavior of 2219 Aluminum, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1993, 24(1), p 2731–2741
K.S. Tun and M. Gupta, Improving Mechanical Properties of Magnesium Using Nano-yttria Reinforcement and Microwave Assisted Powder Metallurgy Method, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2007, 67(13), p 2657–2664
N. Chawla, J. Jones, C. Andres, and J. Allison, Effect of SiC Volume Fraction and Particle Size on the Fatigue Resistance of a 2080 Al/SiCp Composite, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, 29(11), p 2843–2854
F. Hou, W. Wang, and H. Guo, Effect of the Dispersibility of ZrO2 Nanoparticles in Ni–ZrO2 Electroplated Nanocomposite Coatings on the Mechanical Properties of Nanocomposite Coatings, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2006, 252(10), p 3812–3817
Q. Zhang, B. Xiao, W. Wang, and Z. Ma, Reactive Mechanism and Mechanical Properties of In Situ Composites Fabricated from an Al–TiO2 System by Friction Stir Processing, Acta Mater., 2012, 60(20), p 7090–7103
F. Khodabakhshi, A. Simchi, A. Kokabi, M. Sadeghahmadi, and A. Gerlich, Reactive Friction Stir Processing of AA 5052-TiO2 Nanocomposite: Process-Microstructure-Mechanical Characteristics, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2015, 31(4), p 426–435
F. Khodabakhshi, A. Simchi, A. Kokabi, M. Nosko, F. Simanĉik, and P. Švec, Microstructure and Texture Development During Friction Stir Processing of Al-Mg Alloy Sheets with TiO2 Nanoparticles, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2014, 605, p 108–118
V.C. Gudla, F. Jensen, A. Simar, R. Shabadi, and R. Ambat, Friction Stir Processed Al-TiO2 Surface Composites: Anodising Behaviour and Optical Appearance, Appl. Surface Sci., 2015, 324(Supplement C), p 554–562
S. Mahshid, M.S. Ghamsari, M. Askari, N. Afshar, and S. Lahuti, Synthesis of TiO2 Nanoparticles by Hydrolysis and Peptization of Titanium Isopropoxide Solution, Semicond. Phys. Quan. Electron. Optoelectron, 2006, 9(2), p 65–68
K. Jata, S. Semiatin, Continuous dynamic recrystallization during friction stir welding of high strength aluminum alloys, DTIC Document, 2000
R. Fonda, J. Bingert, and K. Colligan, Development of Grain Structure During Friction Stir Welding, Scr Mater., 2004, 51(3), p 243–248
A. Kumar, R. Raj, and S.V. Kailas, A Novel in-situ Polymer Derived Nano Ceramic MMC by Friction Stir Processing, Mater. Des., 2015, 85, p 626–634
M. Guerra, C. Schmidt, J. McClure, L. Murr, and A. Nunes, Flow Patterns During Friction Stir Welding, Mater. Charact., 2002, 49(2), p 95–101
A. Kumar, D. Yadav, C.S. Perugu, and S.V. Kailas, Influence of Particulate Reinforcement on Microstructure Evolution and Tensile Properties of in-situ Polymer Derived MMC by Friction Stir Processing, Mater. Des., 2017, 113, p 99–108
C. Chang, C. Lee, and J. Huang, Relationship Between Grain Size and Zener-Holloman Parameter During Friction Stir Processing in AZ31 Mg alloys, Scr Mater., 2004, 51(6), p 509–514
Z. Zhang and D. Chen, Consideration of Orowan Strengthening Effect in Particulate-Reinforced Metal Matrix Nanocomposites: A Model for Predicting Their Yield Strength, Scr Mater., 2006, 54(7), p 1321–1326
U. Kocks, Laws for Work Hardening and Low-Temperature Creep, J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 1976, 98(1), p 76–85
Acknowledgments
AKP and SVK would like to thank the Advanced Facility for Microscopy and Microanalysis (AFMM) at the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, for providing the facilities. HCM wishes to acknowledge support from the Department of Materials Engineering at the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, to carry out mechanical characterization. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madhu, H.C., Ajay Kumar, P., Perugu, C.S. et al. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Process Derived Al-TiO2 Nanocomposite. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 1318–1326 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3188-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3188-y