Abstract
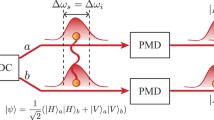
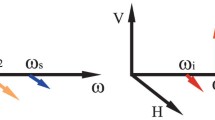
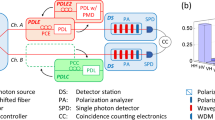
Telecom-band polarization-entangled photon-pair source has been widely used in quantum communication due to its acceptable transmission loss. It is also used in cooperation with wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) to construct entanglement distributor. However, previous schemes generally are not suitable for multinode scenario. In this paper, we construct a telecom-band polarization-entangled photon-pair source, and it shows ultrahigh fidelity and concurrence which are both greater than 90 % (raw data). Moreover, we set up a four-by-four entanglement distributor based on WDM. We check the 16 Clauser–Horne–Shimony–Holt inequalities, which show nonlocality. Lastly, as an example of practical application of this source, we estimate the quantum bit error rates and quantum secret key rates when it is used in quantum key distribution. Furthermore, the transmission of entanglement in long optical fibers is also demonstrated.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gisin N, Thew R (2007) Quantum communication. Nat Photon 1:165–171
Mattle K, Weinfurter H, Kwiat PG et al (1996) Dense coding in experimental quantum communication. Phys Rev Lett 76:4559–4656
Ekert AK (1991) Quantum cryptography based on Bell theorem. Phys Rev Lett 67:661–663
Gisin N, Ribordy G, Tittel W et al (2002) Quantum cryptography. Rev Mod Phys 74:145
Bouwmeester D, Pan JW, Mattle K et al (1997) Experimental quantum teleportation. Nature 390:575–579
Man ZX, Su F, Xia YJ (2013) Stationary entanglement of two atoms in a common reservoir. Chin Sci Bull 58:2423–2429
Sheng YB, Liu J, Zhao SY (2013) Multipartite entanglement concentration for nitrogen-vacancy center and microtoroidal resonator system. Chin Sci Bull 58:3507–3513
Lim HC, Yoshizawa A, Tsuchida H et al (2007) Broadband source of telecom-band polarization-entangled photon-pairs for wavelength-multiplexed entanglement distribution. Opt Express 16:16052–16057
Herbauts I, Blauensteiner B, Poppe A et al (2013) Demonstration of active routing of entanglement in a multi-user network. Opt Express 21:29013–29024
Lim HC, Yoshizawa A, Tsuchida H et al (2008) Distribution of polarization-entangled photon-pairs produced via spontaneous parametric down-conversion within a local-area fiber network: theoretical model and experiment. Opt Express 16:14512–14523
Ou ZY, Mandel L (1988) Violation of Bell’s inequality and classical probability in a two-photon correlation experiment. Phys Rev Lett 61:50–53
Shih YH, Alley CO (1988) New type of Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen–Bohm experiment using pairs of light quanta produced by optical parametric down conversion. Phys Rev Lett 61:2921–2924
Rarity JG, Tapster PR (1990) Experimental violation of Bell inequality based on phase and momentum. Phys Rev Lett 64:2495–2498
Franson JD (1989) Bell inequality for position and time. Phys Rev Lett 62:2205–2208
Brendel J, Gisin N, Tittel W et al (1999) Pulsed energy-time entangled twin-photon source for quantum communication. Phys Rev Lett 82:2594–2597
Mair A, Vaziri A, Weihs G et al (2001) Entanglement of the orbital angular momentum states of photons. Nature 412:313–316
Arnaut HH, Barbosa GA (2000) Orbital and intrinsic angular momentum of single photons and entangled pairs of photons generated by parametric down-conversion. Phys Rev Lett 85:286–289
Barreiro JT, Langford NK, Peters NA et al (2005) Generation of hyperentangled photon pairs. Phys Rev Lett 95:260501
Cinelli C, Di Nepi G, De Martini F et al (2004) Parametric source of two-photon states with a tunable degree of entanglement and mixing: experimental preparation of Werner states and maximally entangled mixed states. Phys Rev A 70:022321
Barbieri M, Vallone G, De Martini F et al (2007) Polarization-momentum hyper-entangled two photon states. Opt Spectrosc 103:129
Takeuchi S (2001) Beamlike twin-photon generation by use of type II parametric downconversion. Opt Lett 26:843–845
Kurtsiefer C, Oberparleiter M, Weinfurter H (2001) Generation of correlated photon pairs in type-II parametric down conversion—revisited. J Mod Opt 48:1997–2007
Kwiat PG, Waks E, White AG et al (1999) Ultrabright source of polarization-entangled photons. Phys Rev A 60:R773
Kwiat PG, Mattle K, Weinfurter H et al (1995) New high-intensity source of polarization-entangled photon pairs. Phys Rev Lett 75:4337–4341
Kim YH (2003) Quantum interference with beamlike type-II spontaneous parametric down-conversion. Phys Rev A 68:013804
James DFV, Kwiat PG, Munro WJ et al (2001) Measurement of qubits. Phys Rev A 64:052312
Hill S, Wootters WK (1997) Entanglement of a pair of quantum bits. Phys Rev Lett 78:5022–5025
Wootters WK (1998) Entanglement of formation of an arbitrary state of two qubits. Phys Rev Lett 80:2245–2248
Koashi M, Preskill J (2003) Secure quantum key distribution with an uncharacterized source. Phys Rev Lett 90:057902
Ma XF, Fung C, Lo H (2007) Quantum key distribution with entangled photon sources. Phys Rev A 76:012307
Huang YF, Liu BH, Peng L et al (2011) Experimental generation of an eight-photon Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger state. Nat Commun 2:546
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61327901, 61490711, 11274289, 11325419, 11374288 and 11104261), the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB921200), the Strategic Priority Research Program (B) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB01030300), the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (61225025), and the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (WK2470000011).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, DY., Liu, BH., Wang, Z. et al. Multiuser-to-multiuser entanglement distribution based on 1550 nm polarization-entangled photons. Sci. Bull. 60, 1128–1132 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-015-0801-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-015-0801-4