Abstracts
A new guanidine derivative named plantagoguanidinic acid was isolated from the seeds of Plantago asiatica. The structure was elucidated by two-dimensional (2D) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectral and other spectral methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The seeds of Plantago asiatica are used as a crude drug for diuretic, antitussive, expectorant, and antiphlogistic purposes. Fatty acids [1, 2], polysaccharides [3, 4], aucubin [5], geniposidic acid [6], and acteoside [6] were reported as the components of the seeds. In our study of the seeds, we detected a specific spot that was not identified as the above mentioned compounds by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) experiments. Therefore, we isolated the component corresponding to the spot from the seeds. This paper deals with the structural elucidation of a new guanidine derivative named plantagoguanidinic acid (1).
Results and discussion
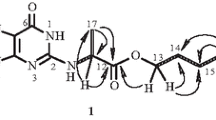
An aqueous extract of the seeds of Plantago asiatica was extracted with n-butanol (n-BuOH). The n-BuOH extract was washed with hexane to remove fat, then chromatgraphed on silica gel, Sephadex LH-20, and NH-silica gel, successively to give 1 (Fig. 1).
Compound 1 was obtained as a white amorphous powder and its molecular formula was determined to be C11H19N3O2 by high-resolution electrospray-ionization mass spectrometry (HRESI-MS). The infrared (IR) spectrum of 1 indicated the presence of a hydroxyl group (3,192 cm−1) and a carboxylic group (1,691 cm−1).
Compound 1 was positive to Dragendorff’s reagent [7], sodium nitroprusside reagent [8], and pentacyanoaquoferriate reagent [9], but negative to Ninhydrin and Sakaguchi reagent [9]. The 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra of 1 showed the presence of a prenyl group (C-4 to C-8), a guanidine carbon (C-2′) [10], a carboxylic carbon (C-1), two methine carbons (C-2 and C-4′), and two methylene carbons (C-3 and C-5′). The connections of these carbons were clarified by double quantum filter (DQF), 13C-1H, and heteronuclear multiple-bond connectivity (HMBC) spectra (Fig. 2). The DQF correlation spectroscopy (COSY) spectrum of 1 indicated 1H-1H connections from H-5 to H-5′ to establish the carbon skeleton. The HMBC correlations of H-2, H-3, and H-4′ to C-1 showed that a carboxylic group was attached to C-2. H-4′ and H-5′ showed HMBC correlations to C-2′ guanidine carbon, indicating that the guanidine group together with the C-4′ and C-5′ form an imidazoline ring. In the nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY) spectrum of 1, H-4′ showed correlations to both of H-5′ protons, so the relative configuration of H-4′ and H-5′ could not be determined, and X-ray crystallographic analysis could not performed because compound 1 gave an amorphous powder. Based on these results, the planar structure of compound 1 was identified as 2-(2-amino-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-4-yl)-6-methylhept-5-enoic acid (Fig. 1). Although similar compounds that have an imidazoline skeleton in the molecule have been isolated from some plants [11, 12], compound 1 has not been reported. Considering the plant source and the guanidinic group, we proposed the name of compound 1 as plantagoguanidinic acid (1).
Experiment
General
IR spectrum was measured using a JASCO FT/IR-4200 Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer. Specific rotation was recorded on a JASCO DIP-1000 digital polarimeter. NMR spectra were recorded on a JEOL JNM AL-400 FT NMR spectrometer. ESI mass spectrum was obtained using on a MICROMASS Q-Tof micromass spectrometer. For the NMR data, chemical shifts are expressed in δ ppm from tetramethylsilane (TMS) as an internal standard and coupling constants (J) are given in Hz. Silica gel 60 (70–230 mesh, Merck), Chromatorex NH DM1020 (NH-silica gel, 100–200 mesh, FUJI SILYSIA CHEMICAL Ltd.) and Sephadex LH-20 (Pharmacia) were used for column chromatography. Silica gel 60 F254 (0.25 mm, Merck) was used for TLC.
Extraction and isolation
Crushed seeds (1.7 kg) of Plantago asiatica (Jiangsu province, China) were extracted twice by stirring with water (5 L) at room temperature for 2 days. The aqueous solution was extracted three times with n-BuOH (3 L), and then concentrated under reduced pressure to give the n-BuOH extract (121.7 g). The n-BuOH extract was dissolved in 90% MeOH, and then partitioned with hexane (1 L) three times to give 90% MeOH extract (58.7 g). The 90% MeOH extract was chromatographed on silica gel (8.5 cm i.d. × 46 cm) eluted with CHCl3–MeOH–H2O (7:4:0.5) to give fraction A (2.6 g), which contained compound 1. Fraction A was rechromatographed on Sephadex LH-20 (7.0 cm i.d. × 70 cm) eluted with MeOH, and Chromatorex NH 20 (7.5 cm i.d. ×62 cm) eluted with EtOAc–MeOH–H2O (14:5:2), successively to give compound 1 (1.2 g).
Plantagoguanidinic acid (1)
White amorphous powder. [α]D 20+53.0° (c 1.1, MeOH), IR (KBr) cm−1: 3,192(br), 2,968, 1,691, 1,585, 1,397. HR ESI-MS m/z: 226.1553 (Calcd. for C11H20N3O2:226.1556). 1H NMR (CD3OD) δ: 1.51 (1H, m, H-3), 1.60 (1H, m, H-3), 1.61(3H, brs, H-7), 1.67(3H, brs, H-8), 2.01 (1H, m, H-4), 2.11 (1H, m, H-4), 2.33 (1H, ddd, J = 4, 8, 10, H-2), 3.53 (1H, dd, J = 6, 9, H-5′), 3.74 (1H, t, J = 9, H-5′), 4.09 (1H, ddd, J = 6, 8, 9, H-4′), 5.11 (1H, brt, J = 7, H-5). 13C NMR (CD3OD) δ: 17.9 (C-7), 25.9 (C-8), 27.1 (C-4), 30.6 (C-3), 48.4 (C-5′), 59.1 (C-4′), 59.4 (C-2), 125.3 (C-5), 132.8 (C-6), 161.2 (C-2′), 180.4 (C-1).
References
Kashimoto T (1955) Studies of Vegetable Oils and Fats. III. Nippon Kagaku Zasshi 76:664–667
Ogata A, Nishioji R (1924) Uber die Samen von Japanischen Wegerich. Yakugaku Zasshi 44:1040–1049
Tomoda M, Uno M (1971) Plant mucilages. I. Isolation and property of a mucous polysaccharide, “plantasan”, from Plantago major L. var. asiatica seeds. Chem Pharm Bull 19:1214–1217
Tomoda M, Yokoi M, Ishikawa K (1981) Plant mucilages. XXIX. Isolation and characterization of a mucous polysaccharide, “Plantago-mucilage A”, from the seeds of Plantago major var. asiatica. Chem Pharm Bull 21:2877–2884
Syukuya S (1922) Yakugaku Zasshi 42:1163
Taguchi H, Aburada M (1983) Chemistry and pharmacological actions on Chuling, Plantago seed and Gentiana. Gendai Toyo Igaku 4:47–55
Wagner H, Bladt S, Zgainski EM (1984) Plant drug analysis. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Hofmann ED, Wünsch A (1958) Verwendung von Nitro-prussidreagenz in der Papierchromatographie. Naturwiss 45:338
Smith I (1960) Chromatographic and electrophoretic techniques. Heinemann-Interscience, London
Charles JP, Jacqlynn B (1993) The Aldrich library of 13C and 1H FT NMR spectra, vol. 1, 1st edn. Aldrich Chemical Company, Milwaukee, USA, pp 1280–1281, 1329
Fellows LE, Hider RC, Bell EA (1977) 3-[2-Amino-2-imidazolin-4(5)-yl]alanine (Enduracididine) and 2-[2-amino-2-imidazolin-4(5)-yl]acetic acid in seeds of Lonchocarpus sericeus. Phytochemistry 16:1957–1959
Evans SV, Fellows LE, Bell EA (1985) Distribution and systematic significance of basic non-protein amino acids and amines in the Tephrosieae. Biochem Syst Ecol 13:271–302
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Mr. K. Kano for mass spectrum measurement. This work was supported in part by a Health and Labour Sciences Research Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goda, Y., Kawahara, N., Kiuchi, F. et al. A guanidine derivative from seeds of Plantago asiatica . J Nat Med 63, 58–60 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-008-0275-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-008-0275-7