Abstract
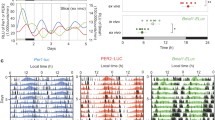
High densities of the mRNA of three rhythm-related genes, rPeriod1 (rPer1), rPer2, and rClock, which share high homology in Drosophila and mammals, are found in the rat hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN). The SCN, however, is not the only brain region that expresses these genes. To understand the possible physiological roles of these rhythm-related genes, we examined expression of these genes in different brain regions at various time points in male Sprague--Dawley rats. Using semi quantitativein situ hybridization with 35S-riboprobes to evaluate mRNA levels, the diurnal rhythmicity of rPer1, and rPer2 mRNA levels was found in the SCN, arcuate nucleus, and median eminence/pars tuberalis. Expression patterns of mRNA for rPer1 and rPer2, however, were not similar in these brain regions. The rhythmicity in these brain regions was specific, because it was not observed in the cerebellum or hippocampus. Moreover, diurnal changes in rClock mRNA expression were not detected in any of the brain regions examined. These findings suggest that the different expression patterns observed for rPer1, rPer2, and rClock mRNAs may be attributed to their different physiological roles in these brain regions, and support previous work indicating that circadian rhythms in the brain are widespread.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Hastings E.S. Maywood (2000) ArticleTitleCircadian clocks in the mammalian brain Bioassays 22 23–31
J.C. Dunlap (1999) ArticleTitleMolecular bases for circadian clocks Cell 96 271–290 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80566-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXotlyqsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9988221
S.M. Reppert D.R. Weaver (2002) ArticleTitleCoordination of circadian timing in mammals Nature 418 935–941 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature00965 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XmsFWksb0%3D Occurrence Handle12198538
K. Wager-Smith S.A. Kay (2000) ArticleTitleCircadian rhythm genetics: from flies to mice to humans Nat. Genet. 26 23–27
M.W. Young S.A. Kay (2001) ArticleTitleTime zones: a comparative genetics of circadian clocks Nat. Rev. Genet. 2 702–715
Z.S. Sun U. Albrecht O. Zhuchenko J. Bailey G. Eichele C.C. Lee (1997) ArticleTitleRIGUI, a putative mammalian ortholog of the Drosophila period gene Cell 90 1003–1011 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80366-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmtlOgtb8%3D Occurrence Handle9323128
H. Tei H. Okamura Y. Shigeyoshi C. Fukuhara R. Ozawa M. Hirose Y. Sakaki (1997) ArticleTitleCircadian oscillation of a mammalian homologue of the Drosophila period gene Nature 389 512–516
Y. Shigeyoshi K. Taguchi S. Yamamoto S. Takekida L. Yan H. Tei T. Moriya S. Shibata J.J. Loros J.C. Dunlap H. Okamura (1997) ArticleTitleLight-induced resetting of a mammalian circadian clock is associated with rapid induction of the mPer1 transcript Cell 91 1043–1053
P.E. Hardin J.C. Hall M. Rosbash (1990) ArticleTitleFeedback of the drosophila period gene product on circadian cycling of its messenger RNA levels Nature 343 536–540 Occurrence Handle10.1038/343536a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXhslGqt74%3D Occurrence Handle2105471
N. Gekakis D. Staknis H.B. Nguyen F.C. Davis L.D. Wilsbacher D.P. King J.S. Tahahashi C.J. Weitz (1998) ArticleTitleRole of the CLOCK protein in the mammalian circadian mechanism Science 288 1564–1569
X. Jin L.P. Shearman D.R. Weaver M.J. Zylka Vries G.J. de S.M. Reppert (1999) ArticleTitleA molecular mechanism regulating rhythmic output from the suprachiasmatic nucleus Cell 96 57–68 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80959-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXmslagtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9989497
K. Kume M.J. Zylka S. Sriram L.P. Shearman D.H. Weaver X. Jin E. Maywood M.H. Hastings S.M. Reppert (1999) ArticleTitlemCRY1 and mCRY2 are essential components of the negative limb of the circadian clock feedback loop Cell 98 193–205
A.M. Sangoram L. Saez M.P. Antoch N. Gekakis D. Staknis A. Whiteley E.M. Fruechte M.H. Vitaterna K. Shimomura D.P. King M.W. Young C.J. Weitz J.S. Takahashi (1998) ArticleTitleMammalian circadian autoregulatory loop: a timeless ortholog and mPer1 interact and negatively regulate CLOCK-BMAL1-induced transcription Neuron 21 1101–1113
S. Yamaguchi S. Mitsui L. Yan K. Yagita S. Miyake H. Okamura (2000) ArticleTitleRole of DBP in the circadian oscillatory mechanism Mol. Cell Biol. 20 4773–4781
K.R. Shieh (2003) ArticleTitleDistribution of the rhythm-related genes,rPeriod 1, rPeriod2, and rClock, in the rat brain Neuroscience 118 831–843
L. Yan H. Okamura (2002) ArticleTitleGradients in the circadian expression of Per1 and Per2 genes in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus Eur. J. Neurosci 15 1153–1162
L. Yan S. Takekida Y. Shigeyoshi H. Okamura (1999) ArticleTitlePer1 and Per2 gene expression in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus: circadian profile and the compartment-specific response to light Neuroscience 94 141–150
M.Y. Cheng C.M. Bullock C. Li A.G. Lee J.C. Bermak J. Belluzzi D.R. Weaver F.M. Leslie Q.Y. Zhou (2002) ArticleTitleProkineticin 2 transmits the behavioural circadian rhythm of the suprachiasmatic nucleus Nature 417 405–410
A. Kramer F.C. Yang P. Snodgrass X. Li T.E. Scammell F.C. Davis C.J. Weitz (2001) ArticleTitleRegulation of daily locomotor activity and sleep by hypothalamic EGF receptor signaling Science 294 2511–2515 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1067716 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xnt1Gl Occurrence Handle11752569
R. Silver J. LeSauter P.A. Tresco M.N. Lehman (1996) ArticleTitleA diffusible coupling signal from the transplanted suprachiasmatic nucleus controlling circadian locomotor rhythms Nature 382 810–813 Occurrence Handle10.1038/382810a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XltlWqsrc%3D Occurrence Handle8752274
H. Abe S. Honma M. Namihira S. Masubuchi K.I. Honma (2001) ArticleTitleBehavioural rhythm splitting in the CS mouse is related to clock gene expression outside the suprachiasmatic nucleus Eur. J. Neurosci. 14 1121–1128
M.K. Bunger L.D. Wilsbacher S.M. Moran C. Clendenin L.A. Radcliffe J.B. Hogenesch M.C. Simon J.S. Takahashi C.A. Bradfield (2000) ArticleTitleMop3 is an essential component of the master circadian pacemaker in mammals Cell 103 1009–1017
T. Hamada J. LeSauter J.M. Venuti R. Silver (2001) ArticleTitleExpression of Period genes: rhythmic and nonrhythmic compartments of the suprachiasmatic nucleus pacemaker J. Neurosci. 21 7742–7750
S.J. Kuhlman J.E. Quintero D.G. McMahon (2000) ArticleTitleGFP fluorescence reports Period 1 circadian gene regulation in the mammalian biological clock Neuroreport 11 1479–1482
S. Masubuchi S. Honma H. Abe K. Ishizaki M. Namihira M. Ikeda K. Honma (2000) ArticleTitleClock genes outside the suprachiasmatic nucleus involved in manifestation of locomotor activity rhythm in rats Eur. J. Neurosci. 12 4206–4214
E.S. Maywood N. Mrosovsky M.D. Field M.H. Hastings (1999) ArticleTitleRapid down-regulation of mammalian period genes during behavioral resetting of the circadian clock Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96 15211–15216
N. Preitner F. Damiola L.M. Luis J. Zakany D. Duboule U. Albrecht U. Schibler (2002) ArticleTitleThe orphan nuclear receptor REV-ERB alpha controls circadian transcription within the positive limb of the mammalian circadian oscillator Cell 110 251–260 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00825-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XlvV2htrk%3D Occurrence Handle12150932
L.P. Shearman M.J. Zylka D.R. Weaver L.F. Kolakowski S.M. Reppert (1997) ArticleTitleTwo period homologs: circadian expression and photic regulation in the suprachiasmatic nuclei Neuron 19 1261–1269
T. Takumi C. Matsubara Y. Shigeyoshi K. Taguchi K. Yagita Y. Maebayashi Y. Sakakida K. Okumura N. Takashima H. Okamura (1998) ArticleTitleA new mammalian period gene predominantly expressed in the suprachiasmatic nucleus Gene. Cells 3 167–176
C. Gall Particlevon M.L. Garabette C.A. Kell S. Frenzel F. Dehghani P.M. Schumm-Draeger D.R. Weaver H.W. Korf M.H. Hastings J.H. Stehle (2002) ArticleTitleRhythmic gene expression in pituitary depends on heterologous sensitization by the neurohormone melatonin Nat. Neurosci. 5 234–238
L.D. Wilsbacher S. Yamazaki E.D. Herzog E.J. Song L.A. Radcliffe M. Abe G. Block E. Spitznagel M. Menaker J.S. Takahashi (2002) ArticleTitlePhotic and circadian expression of luciferase in mPeriod1-luc transgenic micein vivo Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 489–494
S. Yamazaki R. Numano M. Abe A. Hida R. Takahashi M. Ueda G.D. Block Y. Sakaki M. Menaker H. Tei (2000) ArticleTitleResetting central and peripheral circadian oscillators in transgenic rats Science 288 682–685 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.288.5466.682 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXivFGgs7s%3D Occurrence Handle10784453
M.J. Zylka L.P. Shearman D.R. Weaver S.M. Reppert (1998) ArticleTitleThree period homologs in mammals: differential light responses in the suprachiasmatic circadian clock and oscillating transcripts outside of brain Neuron 20 1103–1110
G.A. Lincoln H. Andersson D. Hazlerigg (2003) ArticleTitleClock genes and the long-term regulation of prolactin secretion: evidence for a photoperiod/circannual timer in the pars tuberalis J. Neuroendocrinol. 15 390–397
G.A. Lincoln S. Messager H. Andersson D. Hazlerigg (2002) ArticleTitleTemporal expression of seven clock genes in the suprachiasmatic nucleus and the pars tuberalis of the sheep: evidence for an internal coincidence timer Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 13890–13895
S. Messager M.L. Garabette M.H. Hastings D.G. Hazlerigg (2001) ArticleTitleTissue-specific abolition of Per1 expression in the pars tuberalis by pinealectomy in the Syrian hamster Neuroreport 12 579–582 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00001756-200103050-00029 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXitV2jtbc%3D Occurrence Handle11234767
S. Messager D.G. Hazlerigg J.G. Mercer P.J. Morgan (2000) ArticleTitlePhotoperiod differentially regulates the expression of Per1 and ICER in the pars tuberalis and the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the Siberian hamster Eur. J. Neurosci. 12 2865–2870
A. Sumova M. Jac M. Sladek I. Sauman H. Illnerova (2003) ArticleTitleClock gene daily profiles and their phase relationship in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus are affected by photoperiod J. Biol. Rhythms 18 134–144
S. Messager A.W. Ross P. Barrett P.J. Morgan (1999) ArticleTitleDecoding photoperiodic time through Per1 and ICER gene amplitude Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96 9938–9943
H. Dardente J.S. Menet V.J. Poirel D. Streicher F. Gauer B. Vivien-Roels P. Klosen P. Pevet M. Masson-Pevet (2003) ArticleTitleMelatonin induces Cry1 expression in the pars tuberalis of the rat Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 114 101–106
M. Abe E.D. Herzog S. Yamazaki M. Straume H. Tei Y. Sakaki M. Menaker G.D. Block (2002) ArticleTitleCircadian rhythms in isolated brain regions J. Neurosci. 22 350–356
L.J. Kriegsfeld R. Korets R. Silver (2003) ArticleTitleExpression of the circadian clock gene Period 1 in neuroendocrine cells: an investigation using mice with a Per1:: GFP transgene Eur. J. Neurosci. 17 212–220
K.R. Shieh J.T. Pan (1995) ArticleTitleAn endogenous cholinergic rhythm may be involved in the circadian changes of tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic neuron activity in ovariectomized rats treated with or without estrogen Endocrinology 136 2383–2388
K.R. Shieh J.T. Pan (1996) ArticleTitleSexual differences in the diurnal changes of tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic neuron activity in the rat: role of cholinergic control Biol. Reprod. 54 987–992
K.R. Shieh Y.S. Chu J.T. Pan (1997) ArticleTitleCircadian change of dopaminergic neuron activity: effects of constant light and melatonin Neuroreport 8 2283–2287
D. Morse P. Sassone-Corsi (2002) ArticleTitleTime after time: inputs to and outputs from the mammalian circadian oscillators Trends Neurosci. 25 632–637
X.Y. Lu K.R. Shieh M. Kabbaj G.S. Barsh H. Akil S.J. Watson (2002) ArticleTitleDiurnal rhythm of agouti-related protein and its relation to corticosterone and food intake Endocrinology 143 3905–3915
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shieh, KR., Yang, SC., Lu, XY. et al. Diurnal rhythmic expression of the rhythm-related genes, rPeriod1, rPeriod2, and rClock, in the rat brain. J Biomed Sci 12, 209–217 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-004-8176-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-004-8176-6