Abstract
This paper offers a thorough bibliometric review of the literature on municipal solid waste compost (MSWC), focusing on the past two decades. Using an extensive dataset of 827 documents, the research patterns are analyzed via the R-based Bibliometrix package, merging metadata from Web of Science and Scopus. The analysis reveals substantial global growth in MSWC research, with a particular surge in the last 20 years. Discipline-specific journals are the main publishers, while multidisciplinary environmental outlets gained more citations. The study identifies five major collaborative author clusters that dominate productivity and citation frequency. The thematic evolution over the past five decades shows a transition from waste disposal towards topics such as heavy metals, soil properties, and plant nutrition, with emerging themes like carbon sequestration, biochar, and microplastics signaling future research directions. Specifically, the field has experienced a 7.86% annual growth rate, with an average citation rate of 26.88 per article. The 827 publications emerged from 317 sources and 1910 authors, with an international co-authorship rate of 14.75%, reflecting the field’s interdisciplinary character. Thirteen primary sources and twenty-two key authors were identified as major contributors. On the geographical front, Spain and Italy led with the most contributions and highest citation count, respectively. In terms of keywords, “heavy metals” and “sewage sludge” were the most recurrent, indicating the prevailing topics in MSWC research. This analysis hence provides key insights into the evolution and future trajectory of MSWC studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Since the advent of industrialization, three critical components have exhibited significant growth: the human population, the development of urban metropolises to accommodate this population, and the subsequent generation of waste from their urban residences. An analysis by Rana et al. (2015) postulates a direct correlation between the volume of trash produced and the economic growth, population augmentation, urbanization, and industrialization of a nation. In 2016, the global generation of municipal solid waste (MSW) was estimated at 2010 million tons annually, with projections indicating a startling 70% increase to 3400 million tons by 2050 (Khandelwal et al. 2019). The composition of waste is as important as the quantity of waste, if not more.
Lifestyle change greatly impacts waste composition, particularly when the world is facing a boom in consumer electronics. The waste generated from societies with higher utilization of consumer electronics is complex in nature and requires sophisticated technologies to segregate and often contains toxic elements in high concentration, possessing a substantial threat to human health and ecological balance (Khan et al. 2021a, b, 2022). Open dumpsites, prevalent in developing countries due to budget constraints and insufficient skilled personnel, pose significant risks to groundwater and soil health (Azeez et al. 2011). Over time, environmental pollutants from various sources have compromised soil quality and fertility due to heavy metal accumulation. Depending on contaminant characteristics, they can either reside in soil water or leach into groundwater. Metals such as Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn can modify soil chemistry, affecting organisms and plants reliant on soil nutrients (Ali et al. 2014; Khan et al. 2021a, b).
Interestingly, the composition of MSW varies with the income levels of countries. Developed nations exhibit an organic content of about 32% in their MSW, while developing countries have over 50% organic composition (Sharma and Jain 2020). This raises important questions about the optimal waste management strategies. While recycling is a highly effective and environmentally friendly method for handling inorganic waste, composting serves as a promising solution for managing the organic fraction. This is particularly important considering the consequences of unsustainable waste management practices, which directly contribute to environmental degradation, resource depletion, and the amplification of greenhouse gas emissions, thereby intensifying the regression in sustainability.
In response to these challenges, the sustainability pyramid offers an organized framework. At the foundation level, emphasis is placed on waste reduction and optimal resource utilization. Progressing to the intermediate level, effective waste management strategies encompass recycling, composting, and employing innovative waste-to-energy technologies. At the highest level, making significant policy changes and working together to promote sustainable waste management practices is crucial. This aligns with the urgent message of the IPCC’s “code red” declaration on climate change as it is high time to take all necessary steps to slowdown climate change and its consequences (Lim 2022).
Among the array of MSW management strategies, thermal processing techniques like incineration, pyrolysis, and gasification, while widely adopted and explored for energy recovery, present a unique set of challenges to overcome. These include low technological viability due to the waste’s lower calorific value and environmental pollution concerns (Kumar 2011). Although developed countries have advanced technologies to ensure that emissions from MSW incinerators align with “cleaner energy source” guidelines, the same cannot be asserted for developing nations (Azam et al. 2020). The organic component of MSW, with its carbon to nitrogen (C:N) ratio ranging between 18 and 40, is well-suited for composting (Kumar 2011).
At present, MSW composting involves an array of physical, chemical, and microbiological processes. The application of MSW compost to agricultural lands has been extensively studied across numerous pieces of research, each dealing with different aspects of compost preparation, agricultural utilization, and its impact on crops and soil health. Given the sheer volume of research, traditional quantitative or qualitative techniques struggle to holistically grasp the research status, identify potential gaps, and discern emerging research thrusts. In response to this, bibliometric analysis serves as a comprehensive solution.
Bibliometric analysis, an effective method for discerning emerging trends, research collaborations, and the intellectual structure of current literature in a specific field (Donthu et al. 2021), can be primarily categorized into two methodologies: performance analysis and scientific literature mapping based on authors, sources, documents, or key terms (de Sousa 2021). It is a crucial tool for highlighting research trends, elucidating connections between studies, and aiding researchers in selecting the best journals for their forthcoming publications (Kokol et al. 2017). This study is an independent bibliometric analysis–based study and fulfils all the characteristics described by Lim et al. (2022), which is the article that is independent and not a part of another study and hence plays the central role of the main study; it facilitates the development of new knowledge for the field of municipal solid waste management and municipal solid waste compost; it provides the complete overview of the field; it gives an idea how the field has progressed over the time and also provides future direction. As a result, the article is not merely a reporting of existing literature based on quantitative bibliometric indices on this topic; rather, it also includes the significance of these bibliometric outcomes with real-world development of the field, their significance and implication, and future research directions which is necessary as Mukherjee et al. (2022) mentioned in their article.
Bibliometric analysis was selected as the preferred review method as it follows an established methodology, is transparent and reproducible in nature, and identifies the latest developments in the field (Kraus et al. 2022). It is also worth noting that the field (municipal solid waste compost) has a substantial amount of articles (> 40) and reached a sufficient maturation period (> 5 years) which is a rationale proposed by Paul et al. (2021) and yet does not have any review of this kind which is another strong reason to conduct the bibliometric analysis on this topic. Moreover, the scope of the review is broad as it covers all aspects of municipal solid waste compost, including composting, the composition of composts, and the consequence of MSWC application, as well as a very large number of articles; bibliometric analysis is the most suitable review mechanism in such scenario (Donthu et al. 2021).
In this novel study, we harness the power of bibliometric analysis to provide a comprehensive overview of academic research on MSW composting. Using data from the Web of Science and Scopus databases, we offer a range of bibliometric indicators, including a temporal publication trend, source, author, document analysis, and detailed network analysis. Our study is unique in its scope, tracing the academic journey of MSW composting research from its inception to 2021. This study represents one of the first exhaustive bibliometric investigations of the MSW composting research landscape. By leveraging extensive data and employing robust analysis techniques, it offers a fresh perspective on the historical trends, current status, and potential future directions of the field.
The study’s significance lies in highlighting key research trends, identifying gaps, and showcasing the most influential studies, authors, and journals in MSW composting research. As such, it provides a comprehensive roadmap to guide future research efforts, thereby having the potential to shape the future of MSW composting practices and policies. Moreover, the novelty of this study rests in its data-driven approach, as it integrates and analyzes an unparalleled volume of research output in MSW composting. Although several bibliometric and systematic analyses have been conducted on municipal solid waste, there is none on the topic of municipal solid waste compost. Identifying key research themes and tracing their evolution, the study brings forth a unique longitudinal understanding of the field. This analysis not only elucidates the academic journey of MSW composting research but also anticipates future research trajectories. Furthermore, the comprehensive network analysis presents an innovative approach to visualize the interconnections between various research elements, making this study a valuable resource for both new entrants and established researchers in the field.
Methodology
Data acquisition
The Web of Science and Scopus are the primary scientific databases often used for bibliometric analysis, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Combining the results from the two databases frequently results in the discovery of more articles because each of these databases covers distinct sources (particularly journals). The keywords that were used to search were “municipal solid waste compost” OR “urban waste compost” OR “city waste compost” OR “MSW compost,” and the search field was TOPIC for Web of Science while TITLE-ABS-KEY (title, abstract, and keywords) for Scopus. The search was conducted on 07/10/2022.
A total of 695 documents were identified in WoS, while 804 were identified from Scopus. The current year of 2022 was excluded from the database as the year was not ended at the time of data retrieval; hence, the inclusion of it could affect the yearly publication trend. The second exclusion criterion was keeping those articles written in English; hence, 25 documents were removed from the list in other languages. The bibliometric data was downloaded from WoS and Scopus in BibTex (.bib) format.
Harmonization of bibliometric data
Once the data is downloaded from databases, the two BibTex files are imported to R, converted into R data format, merged, and then exported as.xlsx format for further cleaning and harmonization using the OpenRefine software. During the harmonization process, the synonyms were merged tougher; the ambiguity of English (UK) and English (US) spelling was resolved as well a few other steps for data harmonization were performed, which have been discussed in detail by Ahmi (2022).
Bibliometric and network analysis
The R programming language-based “Bibliometrix” package that Massimo Aria and Corrado Cuccurullo developed was used for the bibliometric analysis (Aria and Cuccurullo 2017). The Bibliometrix provides one of the most extensive tools to conduct an in-depth analysis of documents and divides the whole analysis into three parts: source, author, and document analysis. Co-citation, co-occurrence, and collaboration come under network analysis. In this article, Walktrap algorithm (Pons and Latapy 2006) was used to cluster individuals; the complete flowchart of data collection, harmonization, and analysis can be seen in Fig. 1.
Results and discussion
General overview and trend of publications
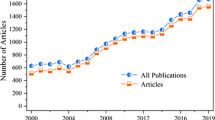
The search for the articles on MSW compost from WoS and Scopus resulted in the retrieval of 827 documents published in 317 sources from 1971 to 2021. The summary results of the dataset are represented in Table 1. The topic witnessed an annual growth rate of 7.86%. While the topic has 21457 citations, each article has received 26.88 citations on average. Authors of this topic used 1556 keywords, while the databases used 2297 indexation keywords. A total of 1910 authors were identified on this topic; 50 authors have written an article alone without any co-author. On average, each document has 3.98 co-authors, with 14. 75% of international co-authorship demonstrates that the topic is global and multidisciplinary rather than regional or subject-specific.
The number of scientific documents on this topic has significantly evolved over the years and can be seen in Fig. 2. The earliest research on municipal solid waste compost was published in 1971 in an applied microbiology journal by Stutzenberger (1971) titled “Cellulase production by Thermomonospora curvata isolated from municipal solid waste compost,” which is cited 72 times till the date of search. After 1971, no article was published on MSWC till 1988. In 1988, a study was published to assess the effect of MSWC incorporation in the soil in which they found that amendment of MSWC has a positive effect on soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, available P, exchangeable K, and micronutrients (Fe, Zn, Cu, and Mn (Giusquiani et al. 1988). Despite several ups and downs, the research on MSWC has tremendously grown over the years.
As Table 1 indicates, 317 sources have published documents on this topic. However, the contribution of all these sources is not equal, as some contributed significantly more articles than others. Bradford’s law divides all source journals into three categories, i.e., highly productive nuclear zone (Zone 1), moderately productive Zone 2, and low productive Zone 3. In this topic, 13 highly productive sources are responsible for 33.37% of document contribution, while 66 sources of Zone 2 contribute 33.73% of documents and 238 least productive Zone 3 sources contribute 32.88% of documents (Fig. 3a). The top 13 core source journals and their total document count, citation count, and starting year of publication are depicted in Fig. 3a. As the results indicate, Compost Science and Utilization is the top source with 67 publications, followed by Bioresource Technology with 29 publications, and Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis with 23 publications. Based on the number of local citations, Journal of Environmental Quality has achieved the top position with 1769 citations, followed by Bioresource Technology and Compost Science and Utilization with 1715 and 1533 citations, respectively. The trend the number of publications and the number of citations does not follow the same trend indicating that some of the sources have produced few documents yet have higher significance; most of the time, it is due to technical superiority, i.e., the novelty of the research or due to the topic which has broader appeal.
a Classification of sources based on Bradford’s law (in the lower left corner), number of publications (plotted on the top axis), total citations (plotted on the bottom axis), and starting year of publication (mentioned in front of the bar of respective source within “[]”) of core source journals, and b evolution of top five journals over the years based on the cumulative number of their publications
The evolution of the top 5 sources, concerning the number of publications, shows that all the top 5 sources have reached a plateau, especially after 2010, while Compost Science and Utilization has recorded the most significant growth, which can be understandable from the fact that it a source which primarily focuses on composts. The disparity of growth of the total number of publications and publications in top source journals indicates that the publication of documents is not concentrated on a few sources but instead getting published in many sources/journals.
Authors and countries
The result of the author’s analysis based on the number of documents, h-index, and citation, and the author’s productivity is represented in Fig. 4.
a Most productive authors who have at least 10 or more documents, b most impactful authors who have at least 10 h-index, c)top cited authors who have at least 500 citations on MSWC, d trend of top author’s productivity and citation received from the document published in that year (size of the point indicates the number of documents produced by the author, color intensity shows the number of citation received by the author from the article published in that year, the histogram on the top showing trend of the total production of documents by top ten authors in different years)
The result indicates (Fig. 4a) that there is a considerable productivity disparity among authors, as among 1910 authors; there are only 22 authors who have produced at least 10 documents on MSWC. According to the result, the most productive authors based on the number of documents (number of publications in parenthesis) are Houot, Sabine (28); Montemurro, Francesco (27); Warman, Philip R. (24); and Jedidi, Naceur (22). The remaining authors have published documents between 10 to 19 articles. As it is apparent from the data that, only 1.15% of the authors have published 10 or more articles. In comparison, 70.31% of authors have published only one document indicating numerous authors involved in the research, yet only a few high-yielding authors. The number of documents, however, is not the only measurement of the author’s contribution; it only indicates the number of documents written rather than the number of times it has been attributed by fellow researchers; hence metrics such as h-index and citations have to be accounted for. To measure the author’s impact, the h-index is widely used in the scientific community (Hirsch 2005). The h-index measures the number of documents of an author which has been cited an equal number of times. For example, the author with the highest h-index in MSWC compost research is Houot, Sabine, whose h-index is 21, which means he has 21 documents, each of which has been cited at least 21 times (Fig. 4b). However, he is the second top-cited author (Fig. 4c), and behind Montemurro, F., who has the highest citation of 1495. Montemurro, F., has 27 documents (only one less than Houot S.), yet his h-index of 14 indicates he has 14 documents, each with 14 citations. There are only 15 authors who have 10 or more h-index. The highest cited authors are depicted in Fig. 4c; the trend of not following the h-index indicates that there are authors with fewer documents yet cited many times than others. One of the advantages of the h-index as the measure of productivity is that it encourages the authors to produce high-quality articles periodically (Ahmi 2022). Among these three matrices to identify the most influential author, researchers disagree about which holds the better value: the productivity or citation or h-index (de Sousa 2021); hence, it is a better practice to include all these three matrices.
The productivity of the top productive authors is not uniform over the years; the highest activity was recorded from 2005 to 2015. The top authors have published the documents over an extended period, facilitating more time to get noticed and cited (Fig. 4d). Another interesting aspect, which can be seen in Fig. 4d, is that apart from Montemurro, F., other authors hardly received a very high number of citations from the article published in a single year; their higher number of citations is accumulated at an average pace over the times. Montemurro, F., has received 831 citations from the article published in 2010, the highest number of citations received by any author in a particular year. The primary source of the citation is a highly cited review paper published by the author that year (Diacono and Montemurro 2010).
Figure 5 illustrates the co-authorship network of the most prominent authors. In the figure, the size of the circle and names indicate the degree of collaboration/co-authorship, which is based on total link strength. The thickness of connecting links indicates the strength of collaboration between two connecting authors. The distance between the authors indicates the relatedness in terms of co-occurrence links; the closer two authors are, the more related they are to each other. Based on the collaboration, a total of 17 clustered (visualized each in a different color) have been identified with more than one author, and 64 authors are part of different co-authorship networks. Among these 17 clusters, the top five clusters are marked in Fig. 5. The network has a total of 103 links and total length strength of 538. The top 5 authors who have the highest co-authorship are also mentioned in the figure; based on the analysis, it has been found that Montemurro, F., has the highest co-authorship network link strength of 45 and followed by Castaldi, P., and Garau, G., both having link strength of 44, while Chakraborty, A., has 43 link strength and Jedidi, N., has 42 link strength. Clusters 1 and 2 are the most prominent cluster, each having 7 authors. The authors with the higher number of publications are part of these larger collaboration groups, which might play an essential role in their higher productivity.
Among 1910 authors, only 64 are part of the co-authorship network, which shows that the field has a higher opportunity to be explored and even international collaborations. The lesser degree of collaboration might be due to several facts, including inequalities of funds for research, especially in developing countries, lacking stimulation for research, and a lack of interest in establishing collaboration (de Sousa 2021).
Research documents have been published in MSWC from 61 countries; however, only 6 countries have produced more than 100 documents, and 10 countries have produced more than 50 documents (Fig. 6a). Spain produced the highest number of documents (172), followed by Italy (165) and the USA (146). Developed nations of Europe largely dominate the top-producing country. Italy holds the top position among the highest cited countries with 3696 citations so far, followed by Spain with 3308 citations and the USA with 2448 citations (Fig. 6b). On average, top-cited countries receive 50 citations each year, while interestingly, the UK receives much higher 230 citations each year despite having only 7 documents. The higher citations of UK are primarily due to a review paper that discusses the bioavailability of heavy metals in MSWC and its possible impact, and the other document discusses the ameliorating acid capacity of different composts, including MSWC (Wong et al. 1998; Smith 2009).
The top productive country’s productivity has significantly increased over the years (Fig. 6c); until 2017, USA was the most productive country; however, later, Spain and Italy surpassed the USA. At the same time, publications from the USA, Canada, and France show stagnation in publication; Spain, Italy, India, and Iran recorded significantly higher growth.
The co-authorship collaboration network among countries has been depicted in Fig. 6d. Among the 61 countries, 56 have collaborated with other countries based on co-authorship, and 9 distinct clusters have been identified with 357 total link strength. Cluster 1 has the most extensive collaboration of 15 countries, including Spain, Italy, Tunisia, Portugal, Germany, Israel, Slovakia, UK, Czech Republic, Poland, Egypt, Jordan, Ecuador, Qatar, and Vietnam. Clusters 2 and 3 each have 9 countries. Spain has the highest total link strength (41) based on collaboration, followed by Italy (37), Tunisia (27), India (25), USA (22), Canada (17); Brazil (13), Iran (12), Portugal (11), and France (10). Most of these countries are neighboring countries from Europe, while India, the USA, Canada, and Brazil also have good collaborations. The network depicts that although the topic has been globally studied, there is good potential for research collaborations, especially in Asia.
Documents
The 25 most relevant documents on MSWC are presented in Table 2. A review paper by Diacono and Montemurro (2010) titled “Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review” received 803 citations to date is the most cited document on MSWC. The review extensively discusses the possibilities of urban and industrial waste materials such as compost material, their long-term effect on soil properties, crop yield, quality, and chances of heavy metal contamination. The second and third most cited documents are also reviewed articles that primarily discuss the issues of heavy metals in MSWC and the possibility of using MSWC in crop production (Hargreaves et al. 2008; Smith 2009). The higher citation rate of these top three documents indicates that many researchers are exploring the possibility of using MSWC as an alternative to commonly used farmyard manure; however, the presence of heavy metals in bioavailable form is the most significant challenge (Smith 2009). The fourth highest cited document is an original research article titled “Long-term effects of municipal solid waste compost application on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass,” which has received a total of 400 citations and is the highest cited research article on this topic and discusses the effect of the long-term amendment of various composts on soil enzymes (García-Gil et al. 2000).
A closer look at the top cited documents indicates that the majority of the articles discuss the possibility of MSWC to improve soil physical, chemical, and biological quality, including soil enzyme, soil microbial biomass, and carbon sequestration (Giusquiani et al. 1995; Serra-Wittling et al. 1995; Albiach et al. 2000; Crecchio et al. 2001, 2004; García-Gil et al. 2004; Annabi et al. 2007; Weber et al. 2007); characterization and suitability of MSWC (He et al. 1992, 1995; Chefetz et al. 1996; Wei et al. 2007); degraded land restoration (Lakhdar et al. 2009; Yazdanpanah et al. 2016); heavy metal accumulation (Achiba et al. 2009); and effect on crop growth and yield (Mkhabela and Warman 2005; Herrera et al. 2008). The only exceptional article on the top cited document is “Purification and Characterization of Laccase from Chaetomium thermophilium and Its Role in Humification,” which discusses the isolation procedure of thermophilic bacterial strains plays a potential role in the humification of compost (Chefetz et al. 1998). In a nutshell, there is higher research interest in the application of MSWC in agriculture to improve overall soil quality; however, the presence of heavy metals is a significant concern.
A historiographic map depicts a historical network map of the most relevant direct citation resulting from a bibliographic collection and could be used to understand the origin of a particular research topic (Ahmi 2022). Each dot is an essential document in this field, while the colored connecting line depicts various citation linkage levels or strengths (Garfield 2004). The historiographic network of MSWC depicted in Fig. 7 indicates that the oldest document which has directly or indirectly influenced the most significant number of subsequent research was titled “Chemical properties of soils amended with compost of urban waste,” which was published in 1988 (Giusquiani et al. 1988). The incubated laboratory experiment reported the physiochemical characteristics of MSWC, including the concentration of Zn, Cu, Mn, Fe, and humic acid and fulvic acids, along with the positive effect of MSWC on soil organic carbon as humic acid fractions. The same author also authored two subsequent articles on the mobility of heavy metals on MSWC-amended soil and another article on the physical, chemical, and biological properties of soil amended with MSWC (Giusquiani et al. 1992, 1995). Hence, the subsequent research that had focused on the presence of heavy metals in MSWC had its roots back in these three documents, and as stated earlier, the presence of heavy metals is one of the largest sub-topics in MSWC research. In 1992, He et al. also wrote a review article on the chemical properties of MSWC and the consequence of its application; he mentioned that extensive research is needed to understand the topic fully due to the diverse origin of MSWC; this document also encouraged researchers in subsequent years (He et al. 1992).
A significantly more significant number of documents on MSWC focuses on the comparison of MSWC (both source-separated and non-separated) with sewage sludge as both are urban waste; the trace of this topic goes to a research article published in 1992 by Epstein et al., in which they had stated that even mixed sourced (source non-separated) MSWC has the lower presence of heavy metals than sewage sludge (Epstein et al. 1992).
Keywords
Keywords are carefully chosen few words representing the scientific documents’ essence. There are two types of keywords; the first is the author’s keywords, which the original authors supply to identify the document’s core theme, of the document while the second type is index keywords or keywords generated by the database for the shorting of documents. In Table 3, we have enlisted the top 25 mainly used authors and index keywords. Although the word “municipal solid waste compost” and all its acronyms and synonyms were the most used keyword in both fields, it was intentionally removed from Table 3 to identify the other keywords most frequently used in MSWC research.
Unsurprisingly heavy metals (HMs) are the most frequently used keywords as many documents (100 +) have focused on various aspects of the presence of heavy metals in compost and its subsequent impact when applied to the soil. This particular topic has various aspects, such as the effect of HMs on soil enzymes both positively and negatively (García-Gil et al. 2000; Marcote et al. 2001), disqualification as compost due to exceeding the permissible limit of HMS (Alvarenga et al. 2015), despite of increased concentration, not effecting overall soil quality possibly due to binding with organic matter (Weber et al. 2007; Achiba et al. 2009); lesser than expected translocation in the plant due to root barrier which can be further improved using chelating agents like EDTA (Carbonell et al. 2011; Zhao et al. 2011); disparity among different HMs when it comes to leaching into deeper soil layer (Kaschl et al. 2002); and requirement of proper strategies to prevent leachates of compost sites having HMs from mixing with waterbodies (Sharifi et al. 2016).
Sewage sludge (SS) is the second most used keyword and is often compared with MSWC based on the presence of HMs, its effect on soil quality, humic substances, nutrient dynamics, and finally, plant yield, as both are an organic waste of urban origin (Senesi et al. 2007; Alvarenga et al. 2015; Tella et al. 2016; Mousavi et al. 2017). In general, other highly used keywords are directly related to crop yield or soil quality. For example, the addition of MSWC has resulted in increased growth and yield unless HMs are present in higher concentration (Mamo et al. 1998; Marcote et al. 2001; Soumaré et al. 2003; Meena et al. 2016b) While estimating the HM compost, sequential extraction method was primarily used to estimate the presence of HMs in different soil fractions especially when there is a higher possibility of HMs bonding with soil and compost organic fractions (Silvetti et al. 2017b; Abou Jaoude et al. 2019; Elmaslar Ozbas and Catalbas 2021).
The composting methods and duration also play a crucial role in reducing the toxicity of HMs; with a longer duration of composting, the dissolved fraction of HMs decreases while stable-formed HMs increase owing to the formation of humus (Liu et al. 2019). Humic acid fraction is generally responsible for 15–20% of the total sorption of different HMs in MSWC, along with the additional benefit of enhanced root growth (Jindo et al. 2012; Silvetti et al. 2017a). Another alternative to traditional composting of municipal solid waste is vermicomposting of the MSW, which generally contains higher humic acid content as well as plant-friendly minerals and enzymes, the reason being a higher degree of reduction in readily degradable material as well as larger biomolecules that have been established from research involving FT-IR, thermal analysis, and SEM imaging (Soobhany et al. 2017).
Among all the keywords, the most trending author’s keywords (on average 3 keywords/year) and their trending duration are depicted in Fig. 8, where the size of the circle indicates the number of times it has been mentioned on that particular year, while the line indicates the year since when the word started getting appeared in the scientific literature till the year when it was last used. Familiar themes, such as sewage sludge, heavy metals, and organic matter, are being used for longer, while topics like biochar, vermicompost, sustainable agriculture, and phytoremediation have been trending in recent years. Biochar holds several unique benefits when managing HMs and their bio-accessibility, as research indicates that MSWC has higher cation exchange capacity, which helps in the sorption of HMs; biochar, on the other hand, has a very high specific surface area (Lima et al. 2022). A combined application of MSWC with biochar could be a valuable tool to prevent bioaccumulation of HMs while at the same time an excellent medium for raising seedlings as well as growing plants under marginal lands (Sadegh-Zadeh et al. 2018; Moradi and Jahanban 2019; Ibraheem et al. 2022; Machado et al. 2022). This holistic approach of mixing compost, especially MSWC, with biochar might be a promising approach to achieving sustainability as on one end considerable amount of bio-wastes is getting converted into compost. At the same time, on the other end, biochar will prevent heavy metals from becoming bio-accessible and act as a carbon sequestration medium. (Debiase et al. 2016; Rashtbari et al. 2020).
The dynamics of the most prominent themes can be better understood using the thematic map diagram based on co-word network and analysis and clustering (Ahmi 2022). The thematic map calculates the co-occurrence keyword network and then represents the typological theme in a 2D map (Aria and Cuccurullo 2017). The map classifies the topics into two quadrats representing centrality and density. Centrality (upward) indicates the level of interaction of a network with other networks, while density (sideways) measures the strength of the network (Ahmi 2022). Four quadrats are formed when centrality and density intersect in the center of the plot. The themes on the upper right quadrant are highly developed and significant for the formation of the research field; the upper left has those that are marginally significant or highly specific to a particular topic, as they do not interact much with other themes. The lower left quadrant is weakly developed and marginal, depicting emerging or disappearing themes. The lower right quadrant has themes that are either important or core themes or can be further explored (Ahmi 2022). We have divided the total dataset of MSWC into three-time frames, up to the year 1999, from 2000 to 2011, and from 2011 to 2011, and then analyzed each time frame for thematic maps (Fig. 9).
In earlier days (before 2000), the primary objective was finding out suitable methods for proper waste management and evaluating those methods based on ecological and economic profitability, in which MSWC came out of being one of the preferred methods as it can act as a source of organic matter in agricultural production (Golueke et al. 1989; Mennella et al. 1989; Kashmanian and Spencer 1993). Widespread evaluation of MSWC based on physical, chemical, and biological properties started during this period. The words “filtration” and “cotton” in the niche theme came from the research which identified “Thermomonospora curvata,” a thermophilic cellulose-degrading actinomycete which can withstand higher temperatures during composting (Stutzenberger 1971). It remained in the niche theme as no other research was conducted till 2000 to find such an organism that can act as a degrading microorganism under challenging scenarios. In emerging trends, the degradation of biopolymers/biodegradable plastic (which often remains mixed in municipal solid waste) was a key theme in which the number and species of biodegrading microorganisms were evaluated, later becoming an important topic of waste management research (Yue et al. 1995).
The second phase of 2000 to 2011 (Fig. 9b) witnessed a significant development in MSWC research in a different direction. The presence of HMs, the chances of their bioaccumulation in plants, and adsorption in soil which is the most prominent theme of MSWC research were explored mainly during this period as well as several review articles summarizing the outcome came out during this period (García-Gil et al. 2000; Achiba et al. 2009; Smith 2009; Diacono and Montemurro 2010). These results indicated the positive effect of good quality MSWC on soil physical, chemical, and biological properties. However, the adverse effect of MSWC was also broadly reported when compost was applied at a much higher rate (more than 60-ton ha−2), or compost had a higher concentration of HMs, or the compost was not well matured. During this period, few new themes also emerged as well as declined, such as “animal,” which was primarily due to comparing the MSWC with animal-derived farm yard manure along with a study exploring the possibility of using MSWC as a bedding material for the animal which was one of its kind and no similar kind of study was carried out since then (Zehnder et al. 2000; Riber et al. 2014). Another essential topic during this period was “bacteria” or soil microbiota. The research works on bacteria or other microorganisms were primarily divided into two phases; the first one explored the role of bacteria in composting process (Ghazifard et al. 2001; Orhan et al. 2004; Wei et al. 2007), while the second one evaluated the fate of bacterial community under MSWC amendment (Cherif et al. 2009; Crecchio et al. 2004). This topic became a research hotspot once the metagenomic approaches, especially 16S RNA sequencing techniques, were introduced and became much cheaper over time, which enabled large-scale exploration of microbial community structure under different soil conditions and soil organic matter interaction (Mokni-Tlili et al. 2010).
Since 2012, few more themes, such as “gypsum,” “saline-sodic,” and “carbon sequestration,” have emerged and currently gaining popularity. Several research works conducted during this period have pointed out the possibility of using MSWC to reclaim as well as improve physical, chemical, and biological properties of saline and sodic soils, and at the same time, enhancing crop growth and productivity both under controlled pot culture experiment as well as in more extensive field application (Ouni et al. 2014; Leogrande et al. 2016; Meena et al. 2016a, b; Sundha et al. 2018; Singh et al. 2019). This approach can simultaneously address two global issues land degradation and waste generation and disposal. As salinization and alkalinization are seriously posing an immense threat to millions of hectares of otherwise productive land, the ever-increasing amount of urban waste generation and their safe disposal do not fuel further pollution, and ultimately, climate change is also a daunting task. However, as research shows, efficient management involving the compositing of MSW and its application in degraded land might be an effective strategy. Not only that, but MSWC can also be an effective carbon sink and an excellent tool for carbon sequestration (Diacono and Montemurro 2010; Paetsch et al. 2016; Manna et al. 2021).
Synthesis of emerging trends and future research themes
While searching for available literature on MSWC on Scopus and Web of Science, we found 18 review articles on the topic, which drew several conclusions and pointed out different research gaps. The research gaps identified by the older reviews such as (He et al. 1992; Shiralipour et al. 1992, p.; Woodbury 1992; Déportes et al. 1995) had primarily focused on the presence of HMs in MSWC as well as the assessment of the maturity of MSWC and suggested long-term experiments (> 5 years) to find out the fate of HMs in soil–plant-consumer (animal/human) system which were duly addressed in considerable research conducted after 2000. During this phase, different methodologies of maturity estimation and procedures to extract and quantify the HMs in MSWC were also developed, compared, and reviewed (Chen 2003; Iwegbue et al. 2007). The economic feasibility evaluation of MSWC production was another research gap identified in the 90 s and was addressed in the 20 s (Moretti et al. 2020; Pecorini et al. 2020). While the older research gaps were periodically addressed and experimented on, the newer research gaps are also emerging in this field, largely contributing to the advent of new analytical procedures. We have extensively explored the available literature of the last 5 years and enlisted a few significant emerging trends and research gaps in Fig. 10.
As climate change has become a hot global research topic, carbon sequestration is one of the most promising strategies to curb it. While the topic of compost amendment as a source of carbon sequestration has 1200 + documents, only 8 have included MSWC. However, the use of MSWC for carbon sequestration is promising as, on one end, it will help in disposing of urban wastes (a source of pollution), and on the other, it will build up soil carbon stock. This process, however, must face the challenge of microplastic and antibiotic residues in waste and compost; hence, research on the detection, segregation, and microbial decomposition of microplastic and antibiotic residue is another research gap that has to be evaluated. Apart from the source of carbon sequestration, MSWC can also be used to reclaim saline and solid soils, which, although it has been studied, needs further long-term investigation.
The application of biochar and compost is another topic that has gained enormous momentum, especially in the last five years, which is eminent from the fact that more than 3000 documents have been published on this topic, yet only about 20 documents have MSWC as the compost source. As massive development in nanotechnology and nanomaterials has been witnessed in recent years, it has become a part of all spheres of scientific study, and MSWC is no exception. In this scenario, two topics need to be evaluated; the first one is the fate of MSWC bore nanoscale heavy metals and synthetic polymers/pollutants in soil and its possible impact on soil microbiota, plants, animals, and humans.
Exploring these new themes and research gaps needs many fields and short and longer-duration laboratory experiments. Moreover, the experiments ideally should be of sufficient depth and possibly multidisciplinary. Molecular tools might be the best workflow considering the recent trend of scientific exploration in other science domains. The recent development of different omics tools has enabled researchers to explore biological interaction and understand the larger picture of organism-level interaction in a much more vivid way. For example, the incorporation of MSWC has recorded a significant boost in soil microbial biomass; however, using metagenomics to understand the change in microbial community structure and their interaction with plants might be even better. There is also the possibility of discovering efficient synthetic polymer or microplastic degrading microbes that could effectively control microplastic pollution. Once again, the interaction between MSWC and biochar in carbon sequestration, the use of nanomaterials and biochar to prevent heavy metal build-up in MSWC application, combined application of biochar and MSWC for land reclamation, and possible change of microbiome in those areas are some of the promising research themes.
Conclusions
This article presents the global research trend on municipal solid waste compost based on all the scientific literature available on Scopus and the Web of Science database from 1971 to 2021. A total of 695 documents were retrieved from the Web of Science database, while 804 were retrieved from the Scopus database. After merging metadata and removing duplicates from two databases, 827 documents were analyzed under different bibliometric parameters.
The analysis result indicates significant progress, especially since 2000 however witnessed constant ups and down and maintained an annual growth rate of 7.86%. In the initial days, the research of the European countries was the primary driving force that later spread to other countries. Among 317 sources (journal, book chapter, conference proceedings, etc.), Bradford’s law identified 13 sources, all of which are journals that have contributed the most in this field. While most topic-specific journals (i.e., compost) have published a maximum number of documents, the sources/journals with multidisciplinary scope, especially environmental elements, have received full citations. While a huge number of authors (1910) have contributed to this topic, there are only 22 authors who have produced more than 10 documents, while 70.31% of the authors have published only one document.
The most productive and top-cited authors either have published documents for a longer period, have a good collaboration network, or both. The country-specific analysis indicates that the maximum number of documents (172) has been published in Spain, followed by Italy and USA, while Italy received the highest number of citations. These countries are also highly active when it comes to establishing international collaborations. A higher number of intercontinental collaborations is still necessary for waste management-related research as the origin and fate of the waste/compost are highly locations specific. The analysis of documents revealed that the highest cited documents are often either review articles, summarizing the different aspects such as the presence of heavy metals in compost and its consequence, characterization of compost, comparison of MSWC with sewage sludge, organic matter fractions in MSWC, and the effect of compost on soil physical, chemical, and biological properties with particular emphasis on soil enzymes. The keyword analysis provided greater insight into municipal solid waste compost research development. It indicated that the research primarily started as a method of waste disposal research, while in later stages, characterization and presence of trace elements became the most prominent themes of research.
In the last 10 years, MSWC is becoming a viable option for several global issues like land reclamation and carbon sequestration. There is much more to explore in MSWC research, such as fate, consequence, and degradation of microplastics and antibiotic residues present in compost, the interaction of compost and nanomaterials, and finally, critically examining all these interactions using new omics tools for a holistic insight.
Core takeaways from the article
-
This article is a bibliometric analysis of the scientific literature on municipal solid waste compost (MSWC) from 1971 to 2021, using data from Web of Science and Scopus databases and based on 827 documents.
-
The article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the global trends, research collaborations, intellectual structure, and thematic evolution of MSWC research over time.
-
The article uses various bibliometric indicators and network analysis techniques to analyze the data, such as publication and citation trends, source and author analysis, co-authorship and co-citation networks, keyword analysis, and historiographic mapping.
-
It has been found that MSWC research has grown significantly in the last two decades with an average growth rate of 7.86%, especially in Europe and Asia, with Spain, Italy, and the USA being the most productive and influential countries.
-
The five major clusters of authors who have worked on different aspects of MSWC research, such as composting methods, soil quality and fertility, heavy metal contamination, crop production and yield, and environmental impacts, have been identified.
-
The article reveals that MSWC research has undergone a thematic shift over time, from waste disposal and management to soil improvement and plant nutrition and from heavy metal toxicity to carbon sequestration and biochar production. The article also suggests some emerging themes for future research, such as microplastics, bioremediation, and circular economy.
Implication of the review
-
The study offers a critical understanding of the current landscape in municipal solid waste compost (MSWC) research, serving as a valuable resource for scholars, policymakers, practitioners, and interested parties in recognizing the existing hurdles, prospects, and knowledge gaps in this domain.
-
The paper underscores the immense potential of MSWC as a sustainable, cost-effective source of organic matter and nutrients. This can significantly enhance soil health and crop yield, particularly in areas dealing with soil degradation and salinity issues.
-
Importantly, the paper focuses on the environmental and health-related concerns tied to MSWC, including the risk of heavy metal build-up, greenhouse gas release, pathogenic contamination, and microplastic pollution.
-
The study also proposes a set of strategies to alleviate these concerns, encompassing methods like source segregation, rigorous quality monitoring, pre-treatment procedures, and safe application practices.
-
Emerging and promising areas for future MSWC research have been spotlighted in the paper, such as the roles of MSWC in carbon capture and biochar generation, soil bioremediation, promoting a circular economy through waste valorization, and fostering social acceptance and awareness.
-
In an endeavor to further the progress in this field, the article advocates for an increase in interdisciplinary and cross-border collaborations.
Future research directions
-
Current research is turning toward emerging issues, driven by new analytical procedures. Carbon sequestration through MSWC, for example, has become an attractive research theme as a means to manage urban waste and increase soil carbon stocks.
-
The challenge of microplastics and antibiotic residues in MSWC requires further exploration, particularly regarding detection, segregation, and microbial decomposition.
-
MSWC has shown potential for reclaiming saline and other problematic soils, though a long-term investigation is needed to fully understand its effectiveness and implications, which also includes the impact of MSWC on the soil ecosystem which can be explored using omics tools.
-
The application of biochar and compost, including MSWC, is gaining momentum, although relatively few studies have considered MSWC as a compost source.
-
The incorporation of nanotechnology into MSWC research presents new opportunities and challenges, particularly regarding the fate of nanoscale heavy metals and synthetic polymers/pollutants in soil.
-
Future MSWC research needs to be multidisciplinary, incorporating cutting-edge molecular tools like omics technologies. These could provide deeper insights into biological interactions, such as changes in microbial community structure due to MSWC.
-
MSWC’s interaction with biochar in carbon sequestration, the potential use of nanomaterials and biochar to prevent heavy metal accumulation, and the joint application of biochar and MSWC for land reclamation are also promising future research themes.
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abou Jaoude L, Garau G, Nassif N et al (2019) Metal(loid)s immobilization in soils of Lebanon using municipal solid waste compost: microbial and biochemical impact. Appl Soil Ecol 143:134–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.06.011
Achiba WB, Gabteni N, Lakhdar A et al (2009) Effects of 5-year application of municipal solid waste compost on the distribution and mobility of heavy metals in a Tunisian calcareous soil. Agr Ecosyst Environ 130:156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2009.01.001
Ahmi A (2022) Bibliometric analysis using R for non-coders: a practical handbook in conducting bibliometric analysis studies using Biblioshiny for Bibliometrix R package. https://books.google.co.in/books?id=kPhiEAAAQBAJ&newbks=0&hl=en&source=newbks_fb&redir_esc=y
Albiach R, Canet R, Pomares F, Ingelmo F (2000) Microbial biomass content and enzymatic activities after the application of organic amendments to a horticultural soil. Biores Technol 75:43–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00030-4
Ali SM, Pervaiz A, Afzal HN, Yasmin A (2014) Open dumping of municipal solid waste and its hazardous impacts on soil and vegetation diversity at waste dumping sites of Islamabad city. Journal of King Saud University-Science 26:59–65
Alvarenga P, Mourinha C, Farto M et al (2015) Sewage sludge, compost and other representative organic wastes as agricultural soil amendments: benefits versus limiting factors. Waste Manage 40:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.01.027
Annabi M, Houot S, Francou C et al (2007) Soil aggregate stability improvement with urban composts of different maturities. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:413–423. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2006.0161
Aria M, Cuccurullo C (2017) bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informet 11:959–975
Azam M, Jahromy SS, Raza W et al (2020) Status, characterization, and potential utilization of municipal solid waste as renewable energy source: Lahore case study in Pakistan. Environ Int 134:105291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105291
Azeez JO, Hassan OA, Egunjobi PO (2011) Soil contamination at dumpsites: implication of soil heavy metals distribution in municipal solid waste disposal system: a case study of Abeokuta, Southwestern Nigeria. Soil Sediment Contam 20:370–386
Carbonell G, Imperial RMD, Torrijos M et al (2011) Effects of municipal solid waste compost and mineral fertilizer amendments on soil properties and heavy metals distribution in maize plants (Zea mays L.). Chemosphere 85:1614–1623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.08.025
Chefetz B, Hatcher PG, Hadar Y, Chen Y (1996) Chemical and biological characterization of organic matter during composting of municipal solid waste. J Environ Qual 25:776–785. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1996.00472425002500040018x
Chefetz B, Chen Y, Hadar Y (1998) Purification and characterization of laccase from Chaetomium thermophilium and its role in humification. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3175–3179. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.64.9.3175-3179.1998
Chen Y (2003) Nuclear magnetic resonance, infra-red and pyrolysis: application of spectroscopic methodologies to maturity determination of composts. Compost Sci Util 11:152–168. https://doi.org/10.1080/1065657X.2003.10702121
Cherif H, Ayari F, Ouzari H et al (2009) Effects of municipal solid waste compost, farmyard manure and chemical fertilizers on wheat growth, soil composition and soil bacterial characteristics under Tunisian arid climate. Eur J Soil Biol 45:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2008.11.003
Crecchio C, Curci M, Mininni R et al (2001) Short-term effects of municipal solid waste compost amendments on soil carbon and nitrogen content, some enzyme activities and genetic diversity. Biol Fertil Soils 34:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740100413
Crecchio C, Curci M, Pizzigallo MDR et al (2004) Effects of municipal solid waste compost amendments on soil enzyme activities and bacterial genetic diversity. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1595–1605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.07.016
De Sousa FDB (2021) Management of plastic waste: a bibliometric mapping and analysis. Waste Manage Res 39:664–678
Debiase G, Montemurro F, Fiore A et al (2016) Organic amendment and minimum tillage in winter wheat grown in Mediterranean conditions: effects on yield performance, soil fertility and environmental impact. Eur J Agron 75:149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2015.12.009
Déportes I, Benoit-Guyod J-L, Zmirou D (1995) Hazard to man and the environment posed by the use of urban waste compost: a review. Sci Total Environ 172:197–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(95)04808-1
Diacono M, Montemurro F (2010) Long-term effects of organic amendments on soil fertility. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 30:401–422. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro/2009040
Donthu N, Kumar S, Mukherjee D et al (2021) How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res 133:285–296
Elmaslar Ozbas E, Catalbas A (2021) Effects of adding MSW compost, lime and commercial soil improvers on soil heavy metal concentrations. J Sci Ind Res 80:1056–1065
Epstein E, Chaney RL, Henry C, Logan TJ (1992) Trace elements in municipal solid waste compost. Biomass Bioenerg 3:227–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/0961-9534(92)90028-O
García-Gil JC, Plaza C, Soler-Rovira P, Polo A (2000) Long-term effects of municipal solid waste compost application on soil enzyme activities and microbial biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1907–1913. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00165-6
García-Gil JC, Ceppi SB, Velasco MI et al (2004) Long-term effects of amendment with municipal solid waste compost on the elemental and acidic functional group composition and pH-buffer capacity of soil humic acids. Geoderma 121:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2003.11.004
Garfield E (2004) Historiographic mapping of knowledge domains literature. J Inf Sci 30:119–145
Ghazifard A, Kasra-Kermanshahi R, Far ZE (2001) Identification of thermophilic and mesophilic bacteria and fungi in Esfahan (Iran) municipal solid waste compost. Waste Manage Res 19:257–261. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X0101900307
Giusquiani PL, Marucchini C, Businelli M (1988) Chemical properties of soils amended with compost of urban waste. Plant Soil 109:73–78
Giusquiani PL, Gigliotti G, Businelli D (1992) Mobility of heavy metals in urban waste-amended soils. J Environ Qual 21:330–335. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1992.00472425002100030004x
Giusquiani PL, Pagliai M, Gigliotti G et al (1995) Urban waste compost: effects on physical, chemical, and biochemical soil properties. J Environ Qual 24:175–182. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1995.00472425002400010024x
Golueke CG, Diaz LF, Gurkewitz S (1989) Technical analysis of multi-compost products. Biocycle 30:55–57
Hargreaves JC, Adl MS, Warman PR (2008) A review of the use of composted municipal solid waste in agriculture. Agr Ecosyst Environ 123:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2007.07.004
He X-T, Traina SJ, Logan TJ (1992) Chemical properties of municipal solid waste composts. J Environ Qual 21:318–329. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1992.00472425002100030003x
He X-T, Logan TJ, Traina SJ (1995) Physical and chemical characteristics of selected U.S. municipal solid waste composts. J Environ Qual 24:543–552. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1995.00472425002400030022x
Herrera F, Castillo JE, Chica AF, López Bellido L (2008) Use of municipal solid waste compost (MSWC) as a growing medium in the nursery production of tomato plants. Biores Technol 99:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.12.042
Hirsch JE (2005) An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:16569–16572
Ibraheem T, Hajabbasi M-A, Shariatmadari H et al (2022) Effects of applied biochar and municipal solid waste compost on saline soil properties and sorghum plant attributes. Pol J Soil Sci 55:51–65. https://doi.org/10.17951/pjss.2022.55.1.51-65
Iwegbue CMA, Emuh FN, Isirimah NO, Egun AC (2007) Fractionation, characterization and speciation of heavy metals in composts and compost-amended soils. Afr J Biotech 6:067–078
Jindo K, Martim SA, Navarro EC et al (2012) Root growth promotion by humic acids from composted and non-composted urban organic wastes. Plant Soil 353:209–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-1024-3
Kaschl A, Römheld V, Chen Y (2002) The influence of soluble organic matter from municipal solid waste compost on trace metal leaching in calcareous soils. Sci Total Environ 291:45–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(01)01091-9
Kashmanian RM, Spencer RL (1993) Cost considerations of municipal solid waste compost: production versus market price. Compost Sci Util 1:20–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/1065657X.1993.10771124
Khan S, Naushad M, Lima EC, Zhang S, Shaheen SM, Rinklebe J (2021a) Global soil pollution by toxic elements: current status and future perspectives on the risk assessment and remediation strategies—a review. J Hazard Mater 417:126039
Khan S, Naushad M, Al-Gheethi A, Iqbal J (2021b) Engineered nanoparticles for removal of pollutants from wastewater: current status and future prospects of nanotechnology for remediation strategies. J Environ Chem Eng 9:106160
Khan S, Anjum R, Raza ST, Bazai NA, Ihtisham M (2022) Technologies for municipal solid waste management: current status, challenges, and future perspectives. Chemosphere 288:132403
Khandelwal H, Dhar H, Thalla AK, Kumar S (2019) Application of life cycle assessment in municipal solid waste management: a worldwide critical review. J Clean Prod 209:630–654
Kokol P, Vošner HB, Železnik D (2017) Clinical simulation in nursing: a bibliometric analysis after its tenth anniversary. Clin Simul Nurs 13:161–167
Kraus S, Breier M, Lim WM, Dabić, Kumar S, Kanbach D, ... Ferreira J (2022) Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice. Rev Manag Sci 16: 2577–2595
Kumar S (2011) Composting of municipal solid waste. Crit Rev Biotechnol 31:112–136
Lakhdar A, Rabhi M, Ghnaya T et al (2009) Effectiveness of compost use in salt-affected soil. J Hazard Mater 171:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.132
Leogrande R, Lopedota O, Vitti C et al (2016) Saline water and municipal solid waste compost application on tomato crop: effects on plant and soil. J Plant Nutr 39:491–501. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2015.1084325
Lim WM (2022) The sustainability pyramid: a hierarchical approach to greater sustainability and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals with implications for marketing theory, practice, and public policy. Australas Mark J 30:142–150
Lim WM, Kumar S, Ali F (2022) Advancing knowledge through literature reviews: ‘what’, ‘why’, and ‘how to contribute.’ Serv Ind J 42:481–513
Lima JZ, Ferreira da Silva E, Patinha C, Rodrigues VGS (2022) Sorption and post-sorption performances of Cd, Pb and Zn onto peat, compost and biochar. J Environ Manag 321:115968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115968
Liu L, Guo X, Zhang C et al (2019) Adsorption behaviours and mechanisms of heavy metal ions’ impact on municipal waste composts with different degree of maturity. Environ Technol (United Kingdom) 40:2962–2976. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1458908
Machado RMA, Alves-Pereira I, Morais C et al (2022) Effects of coir-based growing medium with municipal solid waste compost or biochar on plant growth, mineral nutrition, and accumulation of phytochemicals in spinach. Plants 11:1893. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11141893
Mamo M, Rosen CJ, Halbach TR, Moncrief JF (1998) Corn yield and nitrogen uptake in sandy soils amended with municipal solid waste compost. J Prod Agric 11:469–475. https://doi.org/10.2134/jpa1998.0469
Manna MC, Rahman MM, Naidu R et al (2021) Organic farming: a prospect for food, environment and livelihood security in Indian agriculture. Adv Agron 170:101–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.agron.2021.06.003
Marcote I, Hernández T, García C, Polo A (2001) Influence of one or two successive annual applications of organic fertilizers on the enzyme activity of a soil under barley cultivation. Biores Technol 79:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00048-7
Meena MD, Joshi PK, Jat HS et al (2016a) Changes in biological and chemical properties of saline soil amended with municipal solid waste compost and chemical fertilizers in a mustard-pearl millet cropping system. Catena 140:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.01.009
Meena MD, Joshi PK, Narjary B et al (2016b) Effects of municipal solid waste compost, rice-straw compost and mineral fertilizers on biological and chemical properties of a saline soil and yields in a mustard-pearl millet cropping system. Soil Res 54:958–969. https://doi.org/10.1071/SR15342
Mennella VGG, Zavattiero E, Castagnoli O (1989) Low energy consumption management of agricultural residues. Waste Manage 9:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-053X(89)90407-8
Mkhabela MS, Warman PR (2005) The influence of municipal solid waste compost on yield, soil phosphorus availability and uptake by two vegetable crops grown in a Pugwash sandy loam soil in Nova Scotia. Agr Ecosyst Environ 106:57–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2004.07.014
Mokni-Tlili S, Ben Abdelmalek I, Jedidi N et al (2010) Exploitation of biological wastes for the production of value-added hydrolases by Streptomyces sp. MSWC1 isolated from municipal solid waste compost. Waste Manage Res 28:828–837. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X09357078
Moradi S, Jahanban L (2019) Municipal soil waste compost and biochar effects on soil properties and wheat grain yield. J Solid Waste Technol Manag 45:410–418. https://doi.org/10.5276/JSWTM/2019.410
Moretti B, Bertora C, Grignani C et al (2020) Conversion from mineral fertilization to MSW compost use: nitrogen fertilizer value in continuous maize and test on crop rotation. Sci Total Environ 705:135308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135308
Mousavi SM, Bahmanyar MA, Pirdashti H, Moradi S (2017) Nutritional (Fe, Mn, Ni, and Cr) and growth responses of rice plant affected by perennial application of two bio-solids. Environ Monitor Assess 189:. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6050-z
Mukherjee D, Lim WM, Kumar S, Donthu N (2022) Guidelines for advancing theory and practice through bibliometric research. J Bus Res 148:101–115
Orhan Y, Hrenović J, Büyükgüngör H (2004) Biodegradation of plastic compost bags under controlled soil conditions. Acta Chim Slov 51:579–588
Ouni Y, Mateos-Naranjo E, Lakhdar A et al (2014) Municipal solid waste compost application improves the negative impact of saline soil in two forage species. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 45:1421–1434. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2013.875209
Paetsch L, Mueller CW, Rumpel C et al (2016) Urban waste composts enhance OC and N stocks after long-term amendment but do not alter organic matter composition. Agr Ecosyst Environ 223:211–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.03.008
Paul J, Lim WM, O’Cass A, Hao AW, Bresciani S (2021) Scientific procedures and rationales for systematic literature reviews (SPAR-4-SLR). Int J Consum Stud 45:O1–O16
Pecorini I, Peruzzi E, Albini E et al (2020) Evaluation of MSW compost and digestate mixtures for a circular economy application. Sustainability (Switzerland) 12:3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12073042
Pons P, Latapy M (2006) Computing communities in large networks using random walks. J Graph Algorithms Appl 10:191–218
Rana R, Ganguly R, Gupta AK (2015) An assessment of solid waste management system in Chandigarh City, India. Electron J Geotech Eng 20:1547–1572
Rashtbari M, Hossein Ali A, Ghorchiani M (2020) Effect of vermicompost and municipal solid waste compost on growth and yield of canola under drought stress conditions. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 51:2215–2222. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2020.1820023
Riber L, Poulsen PHB, Al-Soud WA et al (2014) Exploring the immediate and long-term impact on bacterial communities in soil amended with animal and urban organic waste fertilizers using pyrosequencing and screening for horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 90:206–224. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6941.12403
Sadegh-Zadeh F, Tolekolai SF, Bahmanyar MA, Emadi M (2018) Application of biochar and compost for enhancement of rice (Oryza Sativa L.) grain yield in calcareous sandy soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 49:552–566. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2018.1431272
Senesi N, Plaza C, Brunetti G, Polo A (2007) A comparative survey of recent results on humic-like fractions in organic amendments and effects on native soil humic substances. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1244–1262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.12.002
Serra-Wittling C, Houot S, Barriuso E (1995) Soil enzymatic response to addition of municipal solid-waste compost. Biol Fertil Soils 20:226–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336082
Sharifi Z, Hossaini SMT, Renella G (2016) Risk assessment for sediment and stream water polluted by heavy metals released by a municipal solid waste composting plant. J Geochem Explor 169:202–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.08.001
Sharma KD, Jain S (2020) Municipal solid waste generation, composition, and management: the global scenario. Soc Responsib J 16:917–948
Shiralipour A, McConnell DB, Smith WH (1992) Uses and benefits of MSW compost: a review and an assessment. Biomass Bioenerg 3:267–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/0961-9534(92)90031-K
Silvetti M, Garau G, Demurtas D et al (2017b) Influence of lead in the sorption of arsenate by municipal solid waste composts: metal(loid) retention, desorption and phytotoxicity. Biores Technol 225:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.11.057
Silvetti M, Demurtas D, Garau G et al (2017) Sorption of Pb, Cu, Cd, and Zn by municipal solid waste composts: metal retention and desorption mechanisms. Clean - Soil, Air, Water 45(1). https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201600253
Singh YP, Arora S, Mishra VK et al (2019) Plant and soil responses to the combined application of organic amendments and inorganic fertilizers in degraded sodic soils of Indo-gangetic plains. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 50:2640–2654. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2019.1671446
Smith SR (2009) A critical review of the bioavailability and impacts of heavy metals in municipal solid waste composts compared to sewage sludge. Environ Int 35:142–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2008.06.009
Soobhany N, Gunasee S, Rago YP et al (2017) Spectroscopic, thermogravimetric and structural characterization analyses for comparing municipal solid waste composts and vermicomposts stability and maturity. Biores Technol 236:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.161
Soumaré M, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2003) Effects of a municipal solid waste compost and mineral fertilization on plant growth in two tropical agricultural soils of Mali. Biores Technol 86:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00133-5
Stutzenberger FJ (1971) Cellulase production by Thermomonospora curvata isolated from municipal solid waste compost. Appl Microbiol 22:147–152
Sundha P, Basak N, Rai AK et al (2018) Utilization of municipal solid waste compost in reclamation of saline-sodic soil irrigated with poor quality water. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 66:28–39. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-0228.2018.00004.X
Tella M, Bravin MN, Thuriès L et al (2016) Increased zinc and copper availability in organic waste amended soil potentially involving distinct release mechanisms. Environ Pollut 212:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.01.077
Weber J, Karczewska A, Drozd J et al (2007) Agricultural and ecological aspects of a sandy soil as affected by the application of municipal solid waste composts. Soil Biol Biochem 39:1294–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.12.005
Wei Z, Xi B, Zhao Y et al (2007) Effect of inoculating microbes in municipal solid waste composting on characteristics of humic acid. Chemosphere 68:368–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.12.067
Wong MTF, Nortcliff S, Swift RS (1998) Method for determining the acid ameliorating capacity of plant residue compost, urban waste compost, farmyard manure, and peat applied to tropical soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 29:2927–2937. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103629809370166
Woodbury PB (1992) Trace elements in municipal solid waste composts: a review of potential detrimental effects on plants, soil biota, and water quality. Biomass Bioenerg 3:239–259
Yazdanpanah N, Mahmoodabadi M, Cerdà A (2016) The impact of organic amendments on soil hydrology, structure and microbial respiration in semiarid lands. Geoderma 266:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.11.032
Yue CL, Gross RA, McCarthy SP (1995) Composting studies of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate). In: Annual Technical Conference - ANTEC, Conference Proceedings. Soc of Plastics Engineers, Brookfield, CT, United States, Boston, MA, USA, pp 2033–2036
Zehnder CM, DiCostanzo A, Thate K et al (2000) Health and environmental implications of using composted household and yard waste bedding in a cattle feedlot. J Anim Sci 78:495–503. https://doi.org/10.2527/2000.783495x
Zhao S, Lian F, Duo L (2011) EDTA-assisted phytoextraction of heavy metals by turfgrass from municipal solid waste compost using permeable barriers and associated potential leaching risk. Biores Technol 102:621–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.08.006
Acknowledgements
The first author acknowledges the Director, ICAR-National Dairy Research Institute, for providing institutional fellowship. The second author acknowledges Indian Council of Agricultural Research for providing senior research fellowship. All the authors acknowledges the contribution of researchers who did their research work on this topic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, database search, and analysis were performed by Subhradip Bhattacharjee and Amitava Panja. The first draft was written by Subhradip Bhattacharjee. Review of the selected manuscripts was performed by Rakesh Kumar, Nirmalendu Basak, Rajesh Kumar Meena, and Hardev Ram. Thematic evaluation was performed by Rakesh Kumar, Nirmalendu Basak, and Subhradip Bhattacharjee. All the authors have provided their comments on the first version of manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have provided their consent to publish the article.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharjee, S., Panja, A., Kumar, R. et al. Municipal solid waste compost: a comprehensive bibliometric data-driven review of 50 years of research and identification of future research themes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 86741–86761 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28663-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28663-x