PURPOSE
Few studies have demonstrated the feasibility of cross innervating a skeletal muscle neosphincter with the pudendal nerve in an animal model. This study was designed to evaluate in humans the technical feasibility of anastomosing the nerve of the gracilis muscle and the pudendal nerve when the gracilis muscle is transposed around the anus.
METHODS
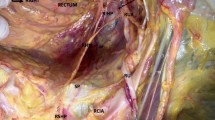
Anatomic assessment was made in 30 cases. The gracilis muscle and its principal neurovascular pedicle were dissected and the nerve to the gracilis divided at its origin. The gracilis muscle, accompanied by its nerve, was then transposed around the anus. The pudendal nerve was dissected in its extrapelvic portion and divided at its termination. Gracilis reinnervation was considered feasible when the proximal end of the nerve to the gracilis muscle and the distal end of the pudendal nerve were able to be placed into tension-free contact.
RESULTS
The mean lengths of the nerve to the gracilis and the pudendal nerve were 126.5 ± 20.6 mm and 57.5 ± 16.3 mm. Anastomosing the nerve of the gracilis muscle and the pudendal nerve was possible in 28 cases. There was a total mean surplus nerve length of 25.1 ± 20.9 mm. In 26 cases, the distal end of the pudendal nerve (mean, 3.3 ± 1.1 mm) was similar or larger than the end of the nerve to the gracilis (mean, 3 ± 0.8 mm).
CONCLUSIONS
Anal sphincter reconstruction using transposed gracilis muscle with pudendal nerve anastomosis is anatomically achievable in cadavers, and supports the potential applications of this technique for perineal reconstruction in clinical practice.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
N Ben-Hur A Gilai J Golan U Sagher M Issac (1980) ArticleTitleReconstruction of the anal sphincter by gracilis muscle transfer: the value of electromyography in the preoperative assessment and postoperative management of the patient Br J Plast Surg 33 156–60 Occurrence Handle7388204 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL3c3itFGrsw%3D%3D
Schuster MM. Symposium: anal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum 1982;25:105
CG Baeten J Konsten F Spaans et al. (1991) ArticleTitleDynamic graciloplasty for treatment of faecal incontinence Lancet 338 1163–5 Occurrence Handle1682590 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0140-6736(91)92030-6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK38%2Fkslyktw%3D%3D
RD Madoff HR Rosen CG Baeten et al. (1999) ArticleTitleSafety and efficacy of dynamic muscle plasty for anal incontinence: lessons from a prospective, multicenter trial Gastroenterology 116 549–56 Occurrence Handle10029613 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0016-5085(99)70176-9 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M7lsFaksQ%3D%3D
T Sato F Konishi (1996) ArticleTitleFunctional perineal colostomy with pudendal nerve anastomosis following ano-rectal resection: an experimental study Surgery 119 641–51 Occurrence Handle8650604 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK283kvVWktA%3D%3D
SM Congilosi DR Johnson M Medot et al. (1997) ArticleTitleExperimental model of pudendal nerve innervation of skeletal muscle neosphincter for faecal incontinence Br J Surg 84 1269–73 Occurrence Handle9313711 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2168.1997.02767.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2svlvV2gtA%3D%3D
T Sato F Konishi K Ueda H Kashiwagi K Kanazawa H Nagai (2000) ArticleTitlePhysiological anorectal reconstruction with pudendal nerve anastomosis and a colonic S-pouch after abdominoperineal resection: report of 2 successful cases Surgery 128 116–20 Occurrence Handle10876198 Occurrence Handle10.1067/msy.2000.107061 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3czjs1yrsg%3D%3D
KL Pickrell TR Broadbent FW Masters J Metzger (1952) ArticleTitleConstruction of a rectal sphincter and restoration of anal continence by transplanting the gracilis muscle: a report of four cases in children Ann Surg 135 853–62 Occurrence Handle14924540 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaG38%2FlsVKmsg%3D%3D
J Patel D Shanahan DJ Riches CS Sinnatamby NS Wil-liams (1991) ArticleTitleThe arterial anatomy and surgical relevance of the human gracilis muscle J Anat 176 270–2
SF Morris D Yang (1999) ArticleTitleGracilis muscle: arterial and neural basis for subdivision Ann Plast Surg 42 630–3 Occurrence Handle10382799 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MzhtVWksA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000637-199906000-00008
H Traxler A Windisch U Geyerhofer R Surd P Solar W Firbas (1999) ArticleTitleArterial supply of the gracilis muscle and its relevance for the dynamic graciloplasty Clin Anat 12 159–63 Occurrence Handle10340455 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3ntVarsg%3D%3D
BP Geerdes HA Kurvers J Konsten E Heineman CG Baeten (1997) ArticleTitleAssessment of ischaemia of the distal part of the gracilis muscle during transposition for anal dynamic graciloplasty Br J Surg 84 1127–9 Occurrence Handle9278660 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2168.1997.02742.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2svisVGntQ%3D%3D
T Sato F Konishi K Kanazawa (1997) ArticleTitleAnal sphincter reconstruction with a pudendal nerve anastomosis following abdominoperineal resection Dis Colon Rectum 40 1497–503 Occurrence Handle9407992 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02070719 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c%2FmvFyrsw%3D%3D
T Sato F Konishi K Kanazawa (1997) ArticleTitleFunctional perineal colostomy with pudendal nerve anastomosis following ano-rectal resection: a cadaver operation study on a new procedure Surgery 121 569–74 Occurrence Handle9142157 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0039-6060(97)90113-6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2s3oslSltw%3D%3D
OM Ramirez WM Swartz JW Futrell (1987) ArticleTitleThe gluteus maximus muscle: experimental and clinical considerations relevant to reconstruction in ambulatory patients Br J Plast Surg 40 1–10 Occurrence Handle3814892 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0007-1226(87)90002-6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2s7ivFOhsA%3D%3D
JM Devesa JM Madrid BR Gallego E Vicente J Nuno JM Enriquez (1997) ArticleTitleBilateral gluteoplasty for fecal incontinence Dis Colon Rectum 40 883–8 Occurrence Handle9269802 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02051193 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2svhtlertQ%3D%3D
CM Becker CO Gueuning GL Graff (1985) ArticleTitleSutures of fibrin glue for divided rat nerves: Schwann cell and muscle metabolism Microsurgery 6 1–10 Occurrence Handle3872987 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2M7oslClsQ%3D%3D
S Palazzi J Vila-Torres JC Lorenzo (1995) ArticleTitleFibrin glue is a sealant and not a nerve barrier J Reconstr Microsurg 11 135–9 Occurrence Handle7791138 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK2MzhtFagsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1055/s-2007-1006521
M Sames J Blahos R Rokyta V Benes (1997) ArticleTitleComparison of microsurgical suture with fibrin glue connection of the sciatic nerve in rabbits Physiol Res 46 303–6 Occurrence Handle9728497 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1czps1Kluw%3D%3D
Sunderland S, ed. Nerves and nerves injuries. 2nd ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1978:120–4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Pirro, N., Sielezneff, I., Malouf, A. et al. Anal Sphincter Reconstruction Using a Transposed Gracilis Muscle With a Pudendal Nerve Anastomosis: A Preliminary Anatomic Study. Dis Colon Rectum 48, 2085–2089 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-005-0129-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-005-0129-2