Abstract
O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) and O-GlcNAcase (OGA) catalyze the dynamic cycling of intracellular, post-translational O-GlcNAc modification on thousands of Ser/Thr residues of cytosolic, nuclear, and mitochondrial signaling proteins. The identification of O-GlcNAc modified substrates has revealed a functionally diverse set of proteins, and the extent of O-GlcNAcylation fluctuates in response to nutrients and cellular stress. As a result, OGT and OGA are implicated in widespread, nutrient-responsive regulation of numerous signaling pathways and transcriptional programs. These enzymes are required for normal embryonic development and are dysregulated in metabolic and age-related disease states. While a recent surge of interest in the field has contributed to understanding the functional impacts of protein O-GlcNAcylation, little is known about the upstream mechanisms which modulate OGT and OGA substrate targeting. This review focuses on elements of enzyme structure among splice variants, post-translational modification, localization, and regulatory protein interactions which drive the specificity of OGT and OGA toward different subsets of the cellular proteome. Ongoing efforts in this rapidly advancing field are aimed at revealing mechanisms of OGT and OGA regulation to harness the potential therapeutic benefit of manipulating these enzymes’ activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction: short and sweet overview of O-GlcNAc cycling
The reversible post-translational modification of proteins by β-O-linked N-acetyl-d-glucosamine (O-GlcNAc) is a nutrient-responsive mechanism that modulates cellular signaling. O-GlcNAc cycling on nucleocytosolic and mitochondrial proteins is controlled by only two genes, encoding O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) and O-GlcNAcase (OGA) which target proteins with diverse functions in signaling, transcription, and chromatin remodeling. Like phosphorylation, O-GlcNAc modification of Ser/Thr residues can influence protein function, protein–protein interactions, protein stability, localization, and enzyme activity (Butkinaree et al. 2010; Love and Hanover 2005; Zachara and Hart 2004). Blocking the expression of OGT splice variants or overexpressing OGT in zebrafish embryos results in morphological defects, impaired embryonic growth, and decreased cell survival (Webster et al. 2009). In murine models, OGT deficiency leads to termination of embryogenesis at day five (O’Donnell et al. 2004; Shafi et al. 2000). Likewise, knock-out of OGA impairs cellular division, embryonic growth, and is associated with early postnatal death (Yang et al. 2012). In addition to playing critical roles during embryonic development, O-GlcNAc cycling enzymes regulate glucose homeostasis and metabolism in adult animals. In the liver, the extent of protein O-GlcNAc modification fluctuates in response to nutrient status, rising with feeding and diabetes. O-GlcNAcylation of key transcription factors and co-factors regulating glucose metabolism, such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR γ), PPARγ-coactivator (PGC1α), CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 2 (CRTC2), carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP), and liver X receptor (LXR α/β), modulates lipogenic and gluconeogenic enzyme expression, thereby influencing the metabolic fate of hepatic glucose (Anthonisen et al. 2010; Dentin et al. 2008; Guinez et al. 2011; Housley et al. 2009; Ji et al. 2012; Yang et al. 2008). Also, OGT expression and protein O-GlcNAc modification are elevated in many human cancers [reviewed in (Ma and Hart 2013; Ma and Vosseller 2013; Singh et al. 2014)]. O-GlcNAc modification of glycolytic enzymes in cancer cells shifts the metabolism of glucose toward the pentose phosphate pathway, supporting the production of intermediates required for tumor cell proliferation (Yi et al. 2012). Research efforts in the field are also focused on modulating the activity of these enzymes for protection against the aggregation and formation of neurofibrillary tangles, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease [reviewed in (Yuzwa and Vocadlo 2014)], and the attenuation of ischemia/reperfusion injury [reviewed in (Vaidyanathan et al. 2014)].
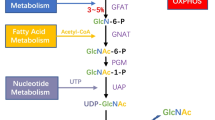
OGT and OGA are uniquely positioned to modulate nutrient-responsive intracellular signaling pathways. An estimated 2–3 % of incoming cellular glucose is metabolized by the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP) which generates uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) as its major metabolic product. This nucleotide sugar is utilized for O-GlcNAc modification of nucleocytosolic proteins, and also acts as a donor for the incorporation of GlcNAc into proteoglycans, glycolipids, and N- and O-linked glycosylation of proteins in the ER and Golgi apparatus (Boehmelt et al. 2000; Hanover et al. 2010; Marshall et al. 1991). OGT (uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine:peptide β-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase) transfers β-N-d-acetylglucosamine from UDP-GlcNAc to the hydroxyl groups of Ser/Thr residues of target protein substrates (Haltiwanger et al. 1992), while OGA (O-glycoprotein 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-β-D-glucopyranosidase) catalyzes its removal (Dong and Hart 1994; Gao et al. 2001). OGT exhibits multiple, distinct UDP-GlcNAc binding constants under different UDP-GlcNAc concentrations (Kreppel and Hart 1999; Lazarus et al. 2011), and varying UDP-GlcNAc levels also influences the incorporation of O-GlcNAc onto specific substrates (Kreppel and Hart 1999). This suggests that, in addition to changes in expression of protein substrates, fluctuations in global UDP-GlcNAc concentrations or the establishment of UDP-GlcNAc gradients within the cell alters OGT substrate specificity. Because rates of HBP flux are sensitive to alterations in glucose, amino acid, acetyl-coA and nucleotide metabolism, OGT and OGA have been characterized as cellular nutrient sensors (Butkinaree et al. 2010; Hanover et al. 2012; Hart et al. 2011; Zachara and Hart 2004).
Enduring within the field are questions regarding the mechanisms which underlie OGT and OGA interactions with over 1,000 identified protein targets. O-GlcNAc modification of target substrates is a controlled process; however, there is much which remains to be understood regarding the upstream regulation of O-GlcNAc cycling enzymes themselves. The functional impact of O-GlcNAc modification on protein targets has been reviewed elsewhere (Hart et al. 2011; Vaidyanathan et al. 2014). This review will discuss factors known and hypothesized to regulate OGT and OGA substrate bias. These mechanisms appear to be built into the cellular machinery at multiple-levels, and include inherent differences in structure and localization among OGT and OGA isoforms, post-translational modification of O-GlcNAc cycling enzymes, and interactions with regulatory protein partners which bias their actions toward specific substrate groups.
O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) and O-GlcNAcase (OGA): structure and function (Fig. 1)
OGT is expressed in all mammalian tissues but is most abundant in pancreas, brain, heart, and skeletal muscle (Lubas et al. 1997; Nolte and Muller 2002). The human Ogt gene (~43 kb) resides at the Xq13.1 genomic locus and is alternatively spliced to generate nucleocytoplasmic (nc), mitochondrial (m), and short (s) isoforms. These isoforms are distinguished by their N-terminal domains which contain a variable number of tetratricopeptide (34-amino acid) repeats (TPRs). The full-length human ncOGT isoform (~110 kDa) contains 13 TPRs, while mOGT (~103 kDa) and sOGT (~75 kDa) contain 9 and 3 TPRs, respectively (Hanover et al. 2003; Love et al. 2003). In addition, alternative usage of the fourth Ogt exon generates the N-terminal mitochondrial localization sequence and membrane-spanning α-helical region which targets mOGT to this organelle (Hanover et al. 2003; Love et al. 2003). All OGT isoforms share a common C-terminal domain which contains two catalytic regions related to the family of GT41 GT-B glycosyltransferase domains (Gao 2010). Zebrafish are the only vertebrates known to harbor two copies of the Ogt gene, resulting from a late duplication event during their speciation (Sohn and Do 2005; Webster et al. 2009). An atypical O-GlcNAc transferase, extracellular OGT (EOGT), has also been characterized in Drosophila and mice. EOGT resides within the ER lumen and is structurally unrelated to X-linked OGT. Although EOGT utilizes UDP-GlcNAc as an O-GlcNAc donor for site modification, it modifies residues residing within epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains of secreted proteins and contributes to cell–matrix interactions (Sakaidani et al. 2012; Sakaidani et al. 2011).
Structure and post-translational modification of OGT and OGA. Phosphorylated (red circles) and O-GlcNAc (blue squares) modified regions are represented on cartoons of the human a OGT and b OGA sequences. Brackets indicate peptides on which the exact site of modification is ambiguous. Also represented are interactions with select regulatory partners (gray arrows). a TPR tetratricopeptide repeats, CDI/CDII UDP-GlcNAc transferase domains, NLS nuclear localization sequence. The interaction of OGT with phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate [PI(3,4,5)P3] via a basic patch in its C-terminal domain is currently putative (Lazarus et al. 2011; Yang et al. 2008). b N-acetyl-β-d-glucosamindase and acetyltransferase-like (AT) domains are indicated (color figure online)
The OGT TPR-domain participates in substrate recognition. Deletion analysis has shown that TPRs 1–6 are necessary for glycosylation of substrates such as nucleoporin (Nup) 62 (Lubas and Hanover 2000), the RNA Pol II C-terminal domain (Comer and Hart 2001), and the OGT-interacting domain of the OGT-interacting protein (OIP) 106, also known as the motor-adaptor trafficking kinesin-binding protein-1 (TRAK1) (Iyer et al. 2003; Iyer and Hart 2003). The TPR domain is also necessary for docking of mammalian Sin3A (mSin3A), a member of the histone deacetylase (HDAC) transcriptional corepressor complex, and mediates binding of OGA to OGT (Cheung et al. 2008; Whisenhunt et al. 2006; Yang et al. 2002). The substantial surface area of the OGT N-terminal protein-interaction domain is likely a determinant of its binding plasticity. Within this region TPR motifs are packed into anti-parallel α-helices, generating an extended superhelix for substrate docking (Jinek et al. 2004). Numerous conserved asparagines, or an “asparagine ladder,” line the inner, concave-binding groove and mediate protein interactions. It has been suggested that the nature of this protein interface would enable promiscuous binding of a variety of substrate proteins (Jinek et al. 2004). In addition, a hinge-like region has been identified between TPRs 12 and 13 of ncOGT which may further regulate access of target proteins to the OGT substrate-binding cleft (Lazarus et al. 2011). While a conserved, OGT substrate consensus motif has yet to be strictly defined, several studies have demonstrated moderate enrichment of O-GlcNAc modification events within variations on the P/V-P/V-V-gS/T-S/T sequence (Alfaro et al. 2012; Vosseller et al. 2006; Wang et al. 2010b). The resolved crystal structure of ncOGT in complex with UDP and the casein kinase II (CKII)-peptide substrate revealed that the presence of prolines and branched-chain amino acids around the target Ser/Thr enforces contacts between the enzyme and the substrate peptide backbone, rather than being rigorously defined by side-chain contacts (Lazarus et al. 2011). This is consistent with reports which describe a propensity for O-GlcNAc modifications to occur on disordered protein regions, areas which are also primarily targeted for phosphorylation (Trinidad et al. 2012). Enrichment-based proteomics (Ma and Hart 2014) and protein microarray methodologies (Ortiz-Meoz et al. 2014) are enabling the identification of additional OGT substrates, and in the future may be applied to the characterization of substrate specificity among OGT isoforms.
The TPR domain may also influence OGT selectivity by mediating its oligomerization. Reported in tissues such as kidney, muscle, spleen, liver and pancreas are heterotrimeric OGT complexes comprised of two 110 kDa subunits and one 78 kDa subunit (possibly sOGT) (Akimoto et al. 1999; Haltiwanger et al. 1992; Kreppel et al. 1997; Marz et al. 2006). Multimerization of OGT into homo-oligomers has been observed as well, and this is disrupted by truncation of TPRs 1–6 (Kreppel and Hart 1999) which also reduces the auto-glycosylation of OGT (Lubas and Hanover 2000). Homo-dimerization of the OGT TPR-domain is abolished through mutation of two conserved residues (W209 and I212, hOGT numbering) within the TPR 6–7 interface, and these same mutations attenuate the O-GlcNAcylation of Nup62 (Jinek et al. 2004). This suggests that OGT:OGT association may stabilize interactions with certain native substrates. There is also limited evidence suggesting that the p78 OGT isoform can influence the interactions of ncOGT with target protein substrates. One study shows that ncOGT activity is enhanced in the presence of Ataxin 10, and this interaction is disrupted in the presence of p78, implicating the short isoform as a negative regulator of ncOGT in some contexts (Marz et al. 2006). It should also be noted that OGT can associate with thyroid hormone receptor α, glucocorticoid receptor, and p38 MAPK independently of its N-terminal TPR domain (Cheung and Hart 2008; Li et al. 2012), suggesting the C-terminal domain also plays a role in protein docking.
Further complicating the OGT regulatory model, OGT exhibits endopeptidase activity against at least one substrate, the host cell factor 1 (HCF-1) mitotic regulator. The proteolytic processing of HCF-1, which is O-GlcNAc modified at several sites (Mazars et al. 2010; Myers et al. 2011; Nagel et al. 2013; Trinidad et al. 2012; Wang et al. 2007; Wang et al. 2010a), into distinct N- and C-terminal fragments is essential for G1 entry/exit and M-phase progression. Several proteolytic repeats (20–26 amino acids) located in the central region of this protein appear to direct both the N-terminal O-GlcNAcylation and OGT-mediated proteolysis of HCF-1 (Capotosti et al. 2011). Interestingly, the mechanistic outcome of the reaction (i.e., proteolysis versus glycosylation, which take place in the same active site) may only be dependent on the presence of a single substrate-localized glutamate residue (Lazarus et al. 2013). These results define a novel role for OGT in the direct regulation of mitotic progression and cell signaling; however, additional proteolytic substrates of OGT have yet to be identified.
The gene encoding OGA was initially identified as a putative hyaluronidase [meningioma expressed antigen 5 (Mgea5)] in a screen of a human meningioma expression library. This gene was later recognized as giving rise to the OGA cycling enzyme (Comtesse et al. 2001; Heckel et al. 1998). OGA is a monomeric hexosaminidase (~130 kDa) which optimally cleaves β-linked GlcNAc moieties at near neutral pH (Braidman et al. 1974; Dong and Hart 1994; Gao et al. 2001; Wells et al. 2002). This, combined with its distribution in the nucleus and cytosol, distinguishes it from acidic hexosaminidases (A and B isoforms) which reside within the lysosomes (Comtesse et al. 2001). The human Mgea5 gene (~34 kb) is located on chromosome 10 at the 10q24.1-q24.3 locus and encodes full-length (OGA) and short (Mgea5s or sOGA) isoforms (Comtesse et al. 2001; Heckel et al. 1998). sOGA displays lower hexosaminidase activity toward protein substrates compared to the full-length variant (Keembiyehetty et al. 2011). Like OGT, OGA is ubiquitously expressed but is more abundant in certain tissues such as the brain, skeletal muscle and pancreas (Comtesse et al. 2001; Dong and Hart 1994; Gao et al. 2001). In line with its role in nutrient metabolism, an OGA allele containing a single nucleotide polymorphism is associated with age of onset of type II diabetes in a Mexican–American population (Lehman et al. 2005).
OGA contains an N-terminal N-acetyl-β-d-glucosamindase domain and, within its C-terminal domain, a region which shares sequence homology with acetyltransferase (AT) enzymes (Comtesse et al. 2001). The AT-like domain is lacking in the sOGA isoform due to a missed splicing event within intron 10. The functional role of the AT-like domain remains to be clarified. While one study reported comparable levels of histone AT (HAT) activity between OGA and CREB-binding protein/p300 histone acetyltransferase against synthetic and free core histones (Toleman et al. 2004), these results have not been confirmed (Butkinaree et al. 2008). A more recent study reported a lack of detectable binding between acetyl-CoA and the recombinant AT-like domain of human OGA (Rao et al. 2013). It is possible that the C-terminal domain of OGA mediates protein interactions or the proper folding of OGA. For instance, the OGA C-terminal domain is cleaved from the N-terminal domain by the apoptotic protein caspase 3 during activation of programmed cell death. Although neither fragment alone is able to recapitulate the activity of the full-length isoform, equivalent levels of OGA activity were detected in cells expressing both N-terminal and C-terminal fragments. It was determined that these truncated fragments interact with one another in vivo, suggesting their association following cleavage (Butkinaree et al. 2008). Therefore, the presence of the C-terminal domain appears to be necessary for the function of the full-length isoform; however, the mechanisms regulating substrate targeting of OGA are not known.
The crystal structure of human OGA has not been resolved; however, three-dimensional structures of related GH84 glycoside hydrolases from Gram-positive Clostridium perfringens and Gram-negative Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron bacteria have provided structural insights (Dennis et al. 2006; Rao et al. 2006). Both bacterial hydrolases contain catalytic machinery which is housed within a triosephosphate-isomerise (TIM)-barrel [(β/α)8] domain, and a high degree of sequence similarity between OGA and bacterial homolog catalytic domains suggests a conserved enzymatic mechanism (Dennis et al. 2006). This is further supported by the finding that the B. thetaiotaomicron GH84 enzyme can de-glycosylate O-GlcNAc modified eukaryotic proteins in vitro; however, it does not possess hyaluronidase activity.
OGT/OGA are regulated through their post-translational modification (Fig. 1)
Differential post-translational modification of the OGT and OGA enzyme pool may further regulate the function and substrate specificity of O-GlcNAc cycling enzymes. OGT O-GlcNAc modification appears to depend on TPR-mediated contacts (Kreppel et al. 1997; Kreppel and Hart 1999; Lubas and Hanover 2000), and O-GlcNAc modified peptides from both the TPR- and C-terminal domains have been observed (Lubas and Hanover 2000; Tai et al. 2004; Trinidad et al. 2012). OGT is phosphorylated at multiple Ser, Thr, and Tyr residues as well (Kreppel et al. 1997; Kreppel and Hart 1999; Olsen et al. 2010). Acute insulin stimulation enhances insulin receptor-mediated OGT tyrosine phosphorylation and activity (Whelan et al. 2008). In addition, OGT is phosphorylated by the nutrient-sensitive AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) within its 12th TPR domain, and constitutive phosphorylation of this site (T444), as approximated by a phosphomimetic, alters OGT substrate binding under both basal and AMPK-stimulated conditions (Bullen et al. 2014). Interplay also exists between OGT and the insulin-regulated mitotic protein glycogen synthase kinase (GSK3). GSK3β-mediated phosphorylation of OGT at Ser3 or 4 enhances OGT activity (Kaasik et al. 2013), consistent with previous reports of altered global protein O-GlcNAcylation profiles in mammalian cells treated with a GSK3 inhibitor (Wang et al. 2007). Interestingly, Ser3 and 4 are also sites of O-GlcNAcylation (Kaasik et al. 2013). Numerous reviews have focused on the potential for cross-talk between O-GlcNAc modification and phosphorylation in cell signaling due to their shared ability to occupy Ser/Thr residues (Butkinaree et al. 2010; Hart et al. 2011; Zeidan and Hart 2010), and it is possible that such interplay may regulate the function of OGT itself. In addition, both AMPK and GSK3β are substrates of OGT and their activities are altered in response to perturbations in global O-GlcNAc cycling (Bullen et al. 2014; Kazemi et al. 2010; Lubas and Hanover 2000), exemplifying the dynamic regulation between OGT/OGA and kinase/phosphatase enzymes which is necessary for the coordination of protein signaling networks (Fig. 2).
Partitioning of the OGT and OGA enzyme pool. This cartoon depicts mechanisms which may partition the nucleocytosolic OGT and OGA pool (gray backdrop) toward interaction/activity against substrate subsets (colored quadrants) within different signaling contexts. Interaction between OGT/OGA and protein kinases is indicative of cross-talk between phosphorylation and O-GlcNAc modification which are cycled on both classes of modifying enzymes. Although represented here as distinct events, pathways contributing to OGT and OGA substrate bias are not necessarily mutually exclusive (e.g., OGT likely associates with RNA Pol IIA as part of a larger epigenetic complex), and in some circumstances may dynamically regulate one another (color figure online)
An exact site of O-GlcNAc modification has been described on OGA at Ser405 within the region which mediates its interaction with OGT (Khidekel et al. 2007; Whisenhunt et al. 2006). Interestingly, an O-linked N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) modification event was also identified at this site (Steentoft et al. 2013). While both of these studies employed tandem mass spectrometry for site identification, which is unable to distinguish between GalNAc and GlcNAc, OGA has been independently verified as a substrate of ncOGT (Lazarus et al. 2006). The differential modification of OGA by both sugars at different stages of protein maturation has not been ruled out.
OGT and OGA activity may be further modulated through modification of redox-sensitive cysteine residues. The synthesis of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), an enzyme which catalyzes the production of NO, is associated with the immune response (Lechner et al. 2005). Interestingly, LPS stimulation of macrophages led to the de-nitrosylation and enhanced activity of cytosolic- but not nuclear-localized OGT. This suggests, somewhat counterintuitively, the presence of a mechanism which may promote OGT de-nitrosylation against an enhanced NO gradient, although the details of such a mechanism have yet to be defined (Ryu and Do 2011). It also remains to be demonstrated whether a cysteine residue within the OGA active site may indicate a similar mode of redox-dependent regulation of this enzyme (Rao et al. 2006), analogous to control of protein tyrosine phosphatase activation (Tonks 2006).
Intracellular partitioning of the OGT and OGA enzyme pool (Fig. 2)
The divergent subcellular localization of OGT and OGA isoforms further influences their interactions with subsets of the cellular proteome. ncOGT contains a putative nuclear localization sequence (NLS) preceding its catalytic region (Kreppel et al. 1997; Lubas et al. 1997) and is active within both the nucleus and the cytosol (Akimoto et al. 1999; Love et al. 2003; Lubas et al. 1997). In line with its nutrient-sensing role, OGT is rapidly redistributed from the nuclear compartment to the cytosol and plasma membrane upon insulin stimulation in adipocytes and fibroblasts, respectively (Whelan et al. 2008; Yang et al. 2008). In myotubes, glucose- and nutrient/growth factor-deprivation induces distinct effects on OGT localization, promoting the primarily nuclear or cytosolic localization of OGT, respectively (Bullen et al. 2014). The mechanisms which modulate intracellular trafficking of OGT are not well understood. One potential mechanism is the interaction of OGT with TRAK1, a microtubule-associated protein, which appears to target the enzyme to RNA polymerase II (Iyer et al. 2003). The reciprocal modification of the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain by O-GlcNAc or phosphorylation may, respectively, modulate its association with pre-initiation or elongation complexes (Comer and Hart 2001; Kelly et al. 1993). Therefore, TRAK1 could target OGT to sites of transcriptional initiation for modification of RNA polymerase II or additional proteins associated with the transcriptional machinery.
OGA is also nucleocytosolic although some have described its preferential localization within the cytosol. While the sOGA isoform was initially reported as a nuclear-localized variant (Comtesse et al. 2001), more recent findings suggest that sOGA also localizes to the surface of nascent lipid droplets where it modulates proteasome-mediated droplet remodeling (Keembiyehetty et al. 2011).
Mitochondria display low levels of O-GlcNAc modification relative to other cellular fractions (Holt and Hart 1986; Love and Hanover 2005; Love et al. 2003), yet evidence supports a role for O-GlcNAc cycling in the regulation of mitochondrial function. O-GlcNAc modification events have been identified on functionally relevant mitochondrial proteins including the mtDNA-encoded complex IV subunit COX1, as well as the genomically encoded mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase NDUFA9 subunit of complex 1, core 1 and 2 subunits of complex III, and the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) (Gawlowski et al. 2012; Hu et al. 2009; Jones et al. 2008; Ngoh et al. 2008). Although OGA has yet to be localized within the mitochondria, overexpression of OGA diminishes O-GlcNAc modification of the mitochondrial fraction, and low levels of OGA activity have been detected within purified mouse heart mitochondria (Hu et al. 2009; Tan et al. 2014). The role of O-GlcNAc cycling in mitochondrial dynamics appears complex. Some studies have demonstrated detrimental effects of increased O-GlcNAc cycling on mitochondrial dynamics. For example, overexpression of mOGT triggers cellular cytotoxicity and apoptosis (Lubas et al. 1997; Shin et al. 2011). Also, exposure of cardiac myocytes to high glucose conditions stimulates an increase in global mitochondrial and COX1 specific O-GlcNAc modification and impairs respiratory complex function, while OGA overexpression prevents these effects (Hu et al. 2009). Increased O-GlcNAcylation of the mitochondrial fission and fusion proteins GTPase dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1) and optical atrophy 1 (OPA1), respectively, is associated with their impaired function and mitochondrial instability (Gawlowski et al. 2012; Makino et al. 2011). On the other hand, overexpression of either OGT or OGA in a neuroblastoma cell line altered mitochondrial protein expression, disrupted mitochondrial morphology, and impaired respiration (Tan et al. 2014), suggesting that adequate dosing of the modification may be necessary for optimal mitochondrial function in this cell type. In addition, expression of OGT was shown to be protective against hypoxia-induced loss of mitochondrial membrane potential in neonatal cardiac myocytes (Ngoh et al. 2008). Altogether these data indicate that the tissue and/or stimulus-specific context of increased O-GlcNAcylation may produce distinct functional outcomes on mitochondrial processes.
The cellular role of nucleocytosolic sOGT is probably the least understood of the three OGT isoforms (Love and Hanover 2005). Reports are conflicting regarding the ability of sOGT to glycosylate peptide/protein targets (Feng et al. 2013; Lazarus et al. 2006; Liu et al. 2014; Ortiz-Meoz et al. 2014); however, as previously mentioned, this isoform may regulate ncOGT substrate specificity (Marz et al. 2006). sOGT has also been identified as a protective factor against growth factor withdrawal-mediated apoptosis in myeloid progenitor cells (Fletcher et al. 2002), and for this reason it has been postulated that sOGT may counteract the pro-apoptotic activity of mOGT to coordinate cellular survival pathways (Hanover et al. 2012; Shin et al. 2011).
Yeast two-hybrid screens of brain tissue cDNA libraries have revealed numerous, functionally distinct OGT-interacting proteins which may predispose this enzyme toward glycosylation of specific substrates (Butkinaree et al. 2010; Cheung et al. 2008; Iyer et al. 2003; Iyer and Hart 2003). The myosin phosphatase targeting protein 1 (MYPT1), a regulatory subunit of protein phosphatases (PP1) β and δ, enhances OGT interaction with select binding partners, although, interestingly, this association does not appear to be a determinant for OGT’s interaction with myosin or PP1β/δ (Cheung et al. 2008). OGT and OGA also co-localize with the microtubule-associated protein Aurora B kinase and PP1C at midbody structures in mitotic cells. This association indicates the centralization of these enzymes’ actions within modifying complexes for the reciprocal regulation of cytokinetic substrates such as vimentin (Slawson et al. 2005, 2008). Interaction of OGT with p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38MAPK) under conditions of glucose deprivation in a neuroblastoma cell line does not result in its phosphorylation, but contributes to the p38MAPK-mediated O-GlcNAc modification of the neurofilament-H structural protein, suggesting that this is a targeting association (Cheung and Hart 2008).
OGT and OGA are also targeted to chromatin-remodeling complexes where they coordinate active and repressed transcriptional states through O-GlcNAc modification of histones, chromatin-remodeling enzymes, and transcription factors (Fujiki et al. 2009; Hanover et al. 2012; Love et al. 2010a; Sakabe et al. 2010; Tai et al. 2004; Trinidad et al. 2012; Whisenhunt et al. 2006; Yang et al. 2002). OGA can co-localize with OGT and mSin3A at repressed promoters, potentially important for the timely reversal of repressed genes which are associated with high levels of O-GlcNAcylation (Whisenhunt et al. 2006; Yang et al. 2002). On the other hand, ManNAc induction of murine orexin (Hcrt) neurons, which integrate sleep/wake states and feeding behaviors, is associated with decreased occupancy of OGT, mSin3A, and SIRT1, and increased recruitment of OGA, CREBBP, and p300, at active Hcrt promoters (Hayakawa et al. 2013). This suggests that the simultaneous co-localization of OGT and OGA does not represent a universal mechanism for O-GlcNAc-mediated regulation of transcriptional programs. Also, recently elucidated interactions between OGT and the ten-eleven translocation (TET) proteins are thought to recruit the O-GlcNAc cycling enzyme to sites of transcriptional initiation (Chen et al. 2013; Deplus et al. 2013; Vella et al. 2013). The TET family of α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase enzymes modulates removal of DNA methylation marks through conversion of 5-methylcytosine to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmc), triggering pathways which result in the conversion of 5-hmc to an unmodified cytosine (Solary et al. 2014). Interestingly, the interaction of OGT with TET2/3 does not alter cytosine hydroxylation, but is necessary for formation of the SET1/COMPASS complex (containing OGT, O-GlcNAc modified HCF-1 and the SETD1A H3K4 methyltransferase) and activation of TET2/3-OGT-H3K4me3 gene targets (Deplus et al. 2013). Similarly, the OGT/TET2 interaction modulates the O-GlcNAc modification of histone H2B at Ser112 and is associated with transcriptional activation (Chen et al. 2013).
Regulation of OGT and OGA expression: many questions remain
OGT and OGA transcript and protein levels fluctuate with cell cycle progression (Dehennaut et al. 2007; Dehennaut et al. 2008; Drougat et al. 2012; Lefebvre et al. 2004; Slawson et al. 2005; Yang et al. 2012), during tissue specification (Andres-Bergos et al. 2012; Ogawa et al. 2012), and among tissue types. OGT transcription, protein expression, and activity are also impacted by various stressors (e.g., oxidative, UV-induced, osmotic, thermal, and nutrient stress) (Cheung and Hart 2008; Zachara and Hart 2004; Zachara et al. 2004), consistent with its role as a stress modulator and nutrient sensor. A recent study demonstrated significantly lower expression of OGT transcripts in male versus female human and mouse placental tissues, and showed that induction of prenatal maternal stress in murine models decreased OGT transcript expression to the greatest extent in male placental tissue. This not only exemplifies stress-induced impacts on OGT expression in a physiological setting, but also suggests that the maternal stress response is linked to sex-specific impacts on OGT-mediated embryonic development, possibly leading to changes in the early neonatal neurodevelopmental program (Howerton et al. 2013). The expression of OGA is likely also developmentally modulated, as it is required for neonatal survival (Yang et al. 2012). OGA protein levels are reduced upon induction of OGT knock-out, implicating the involvement of OGT in the regulation of OGA expression or stability. This effect was attenuated in the short term by pharmacological elevation of O-GlcNAc levels, suggesting that OGA protein levels are sensitive to changes in the relative abundance of this modification (Kazemi et al. 2010). Indeed, it has been suggested that the location of the OGA gene within the highly conserved NK homeobox gene cluster may have implications for its regulation by OGT, since this region is targeted by the PcG repressor complex of which OGT is a component (Gambetta et al. 2009; Love et al. 2010b; Sinclair et al. 2009). Such compensatory mechanisms may allow the cell to more effectively control its response to sudden changes in nutrient concentrations or levels of either OGT or OGA.
Some evidence also suggests that tissue-specific regulation of OGA and OGT is impacted during normal physiological aging. Congruent with the imbalanced O-GlcNAc cycling observed in various age-related diseases, O-GlcNAcylation profiles are elevated in tissues such as brain, thymus, heart, lung, testes, and skin of senescent rats and mice. This phenomenon, however, does not always correlate with anticipated changes in enzyme levels or markers of enhanced HBP flux (Fulop et al. 2008; Yang et al. 2012). It is possible that one or more senescence-associated characteristics, such as alterations in growth factor signaling, oxidative and inflammatory responses, and glucose metabolism (Basu et al. 2006; Boss and Seegmiller 1981; Licastro et al. 2005; Lopez-Otin et al. 2013), converge to uncouple OGT and OGA activity and/or disrupt one or more mechanisms contributing to substrate bias. Continuing to define the impact of such parameters on the regulation of these enzymes under normal, aged, and disease-state metabolic conditions will be important for a comprehensive understanding of the roles of OGT and OGA in the maintenance of homeostatic cell functions.
Summary (Fig. 3)
The O-GlcNAc post-translational modification is a critical mechanism for the regulation of cell development and survival; however, the upstream regulation of OGT and OGA, which target a wide variety of substrates, requires further definition. As we have explored within this review, there is evidence to support the regulation of OGA and OGT activity at every level of their processing. Structural variation among OGT and OGA enzyme isoforms is built into the genomic code, and these inherent differences in amino acid composition among splice variants influence the subcellular distribution and substrate targeting of both enzymes. Additional modulation of enzyme activity is imparted by availability of their protein and/or sugar-donor substrates which are altered by glucose-, growth- and stress-activated signaling in a tissue-specific manner. The cell may further regulate OGT and OGA substrate specificity through their post-translational modification, stable associations with regulatory protein partners, or through the temporal control of enzyme expression/stability. An integrated model describing factors which bias the action of OGT and OGA toward specific substrates under different metabolic states may provide new insights for the manipulation of O-GlcNAc cycling during development, and in the treatment of common pathophysiological conditions arising in adults.
A full understanding of the O-GlcNAc signaling paradigm includes a definition of the upstream mechanisms (e.g., post-translational modification, localization, partner associations, expression/stability, or any combination thereof) influencing OGT/OGA substrate bias under different metabolic states and with disease progression. A future model (outlined here in a highly simplified form) may be developed in which the effects of one or multiple stimuli on such mechanisms are more completely characterized under both normal and pathological conditions (color figure online)
References
Akimoto Y, Kreppel LK, Hirano H, Hart GW (1999) Localization of the O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase in rat pancreas. Diabetes 48:2407–2413
Olsen JV et al (2010) Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveals widespread full phosphorylation site occupancy during mitosis. Sci Signal 3:ra3. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2000475
Alfaro JF et al (2012) Tandem mass spectrometry identifies many mouse brain O-GlcNAcylated proteins including EGF domain-specific O-GlcNAc transferase targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:7280–7285. doi:10.1073/pnas.1200425109
Andres-Bergos J, Tardio L, Larranaga-Vera A, Gomez R, Herrero-Beaumont G, Largo R (2012) The increase in o-linked N-acetylglucosamine protein modification stimulates chondrogenic differentiation both in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 287:33615–33628. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.354241
Anthonisen EH, Berven L, Holm S, Nygard M, Nebb HI, Gronning-Wang LM (2010) Nuclear receptor liver X receptor is O-GlcNAc-modified in response to glucose. J Biol Chem 285:1607–1615. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.082685
Basu R et al (2006) Effects of age and sex on postprandial glucose metabolism: differences in glucose turnover, insulin secretion, insulin action, and hepatic insulin extraction. Diabetes 55:2001–2014. doi:10.2337/db05-1692
Boehmelt G et al (2000) Decreased UDP-GlcNAc levels abrogate proliferation control in EMeg32-deficient cells. The EMBO journal 19:5092–5104. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.19.5092
Boss GR, Seegmiller JE (1981) Age-related physiological changes and their clinical significance. West J med 135:434–440
Braidman I et al (1974) Characterisation of human N-acetyl-beta-hexosaminidase C. FEBS Lett 41:181–184
Bullen JW, Balsbaugh JL, Chanda D, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Neumann D, Hart GW (2014) Cross-talk between two essential nutrient-sensitive enzymes: O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) and AMP-ACTIVATED protein kinase (AMPK). J Biol Chem 289:10592–10606. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.523068
Butkinaree C, Cheung WD, Park S, Park K, Barber M, Hart GW (2008) Characterization of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase cleavage by caspase-3 during apoptosis. J Biol Chem 283:23557–23566. doi:10.1074/jbc.M804116200
Butkinaree C, Park K, Hart GW (2010) O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc): extensive crosstalk with phosphorylation to regulate signaling and transcription in response to nutrients and stress. Biochim Biophys Acta 1800:96–106. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.07.018
Capotosti F et al (2011) O-GlcNAc transferase catalyzes site-specific proteolysis of HCF-1. Cell 144:376–388. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.030
Chen Q, Chen Y, Bian C, Fujiki R, Yu X (2013) TET2 promotes histone O-GlcNAcylation during gene transcription. Nature 493:561–564. doi:10.1038/nature11742
Cheung WD, Hart GW (2008) AMP-activated protein kinase and p38 MAPK activate O-GlcNAcylation of neuronal proteins during glucose deprivation. J Biol Chem 283:13009–13020. doi:10.1074/jbc.M801222200
Cheung WD, Sakabe K, Housley MP, Dias WB, Hart GW (2008) O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase substrate specificity is regulated by myosin phosphatase targeting and other interacting proteins. J Biol Chem 283:33935–33941. doi:10.1074/jbc.M806199200
Comer FI, Hart GW (2001) Reciprocity between O-GlcNAc and O-phosphate on the carboxyl terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Biochemistry 40:7845–7852
Comtesse N, Maldener E, Meese E (2001) Identification of a nuclear variant of MGEA5, a cytoplasmic hyaluronidase and a beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 283:634–640. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.4815
Dehennaut V et al (2007) O-linked N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase inhibition prevents G2/M transition in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem 282:12527–12536. doi:10.1074/jbc.M700444200
Dehennaut V et al (2008) Identification of structural and functional O-linked N-acetylglucosamine-bearing proteins in Xenopus laevis oocyte. MCP 7:2229–2245. doi:10.1074/mcp.M700494-MCP200
Dennis RJ et al (2006) Structure and mechanism of a bacterial beta-glucosaminidase having O-GlcNAcase activity. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13:365–371. doi:10.1038/nsmb1079
Dentin R, Hedrick S, Xie J, Yates J, 3rd, Montminy M (2008) Hepatic glucose sensing via the CREB coactivator CRTC2. Science (New York, NY) 319:1402–1405. doi:10.1126/science.1151363
Deplus R et al (2013) TET2 and TET3 regulate GlcNAcylation and H3K4 methylation through OGT and SET1/COMPASS. EMBO J 32:645–655. doi:10.1038/emboj.2012.357
Dong DL, Hart GW (1994) Purification and characterization of an O-GlcNAc selective N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase from rat spleen cytosol. J Biol Chem 269:19321–19330
Drougat L et al (2012) Characterization of O-GlcNAc cycling and proteomic identification of differentially O-GlcNAcylated proteins during G1/S transition. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820:1839–1848. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.08.024
Feng Z, Hui Y, Ling L, Xiaoyan L, Yuqiu W, Peng W, Lianwen Z (2013) FBXW10 is negatively regulated in transcription and expression level by protein O-GlcNAcylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 438:427–432. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.07.091
Fletcher BS, Dragstedt C, Notterpek L, Nolan GP (2002) Functional cloning of SPIN-2, a nuclear anti-apoptotic protein with roles in cell cycle progression. Leukemia 16:1507–1518. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2402557
Fujiki R et al (2009) GlcNAcylation of a histone methyltransferase in retinoic-acid-induced granulopoiesis. Nature 459:455–459. doi:10.1038/nature07954
Fulop N et al (2008) Aging leads to increased levels of protein O-linked N-acetylglucosamine in heart, aorta, brain and skeletal muscle in Brown-Norway rats. Biogerontology 9:139–151. doi:10.1007/s10522-007-9123-5
Gambetta MC, Oktaba K, Muller J (2009) Essential role of the glycosyltransferase sxc/Ogt in polycomb repression. Science (New York, NY) 325:93–96. doi:10.1126/science.1169727
Gao Y (2010) Mechanism, structure, and inhibition of O-GlcNAc processing enzymes. Curr Signal Transduct Ther 5:74–91
Gao Y, Wells L, Comer FI, Parker GJ, Hart GW (2001) Dynamic O-glycosylation of nuclear and cytosolic proteins: cloning and characterization of a neutral, cytosolic beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from human brain. J Biol Chem 276:9838–9845. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010420200
Gawlowski T et al (2012) Modulation of dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1) function by increased O-linked-beta-N-acetylglucosamine modification (O-GlcNAc) in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 287:30024–30034. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.390682
Guinez C et al (2011) O-GlcNAcylation increases ChREBP protein content and transcriptional activity in the liver. Diabetes 60:1399–1413. doi:10.2337/db10-0452
Haltiwanger RS, Blomberg MA, Hart GW (1992) Glycosylation of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins. Purification and characterization of a uridine diphospho-N-acetylglucosamine:polypeptide beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. J Biol Chem 267:9005–9013
Hanover JA, Yu S, Lubas WB, Shin SH, Ragano-Caracciola M, Kochran J, Love DC (2003) Mitochondrial and nucleocytoplasmic isoforms of O-linked GlcNAc transferase encoded by a single mammalian gene. Arch Biochem Biophys 409:287–297
Hanover JA, Krause MW, Love DC (2010) The Hexosamine Signaling Pathway: O-GlcNAc cycling in feast or famine. Biochim Biophys Acta 1800:80. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.07.017
Hanover JA, Krause MW, Love DC (2012) Bittersweet memories: linking metabolism to epigenetics through O-GlcNAcylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:312–321. doi:10.1038/nrm3334
Hart GW, Slawson C, Ramirez-Correa G, Lagerlof O (2011) Cross talk between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation: roles in signaling, transcription, and chronic disease. Annu Rev Biochem 80:825–858. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-060608-102511
Hayakawa K et al (2013) Epigenetic switching by the metabolism-sensing factors in the generation of orexin neurons from mouse embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem 288:17099–17110. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.455899
Heckel D, Comtesse N, Brass N, Blin N, Zang KD, Meese E (1998) Novel immunogenic antigen homologous to hyaluronidase in meningioma. Hum Mol Genet 7:1859–1872
Holt GD, Hart GW (1986) The subcellular distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine moieties. Localization of a novel protein-saccharide linkage, O-linked GlcNAc. J Biol Chem 261:8049–8057
Housley MP, Udeshi ND, Rodgers JT, Shabanowitz J, Puigserver P, Hunt DF, Hart GW (2009) A PGC-1alpha-O-GlcNAc transferase complex regulates FoxO transcription factor activity in response to glucose. J Biol Chem 284:5148–5157. doi:10.1074/jbc.M808890200
Howerton CL, Morgan CP, Fischer DB, Bale TL (2013) O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) as a placental biomarker of maternal stress and reprogramming of CNS gene transcription in development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:5169–5174. doi:10.1073/pnas.1300065110
Hu Y et al (2009) Increased enzymatic O-GlcNAcylation of mitochondrial proteins impairs mitochondrial function in cardiac myocytes exposed to high glucose. J Biol Chem 284:547–555. doi:10.1074/jbc.M808518200
Iyer SP, Hart GW (2003) Roles of the tetratricopeptide repeat domain in O-GlcNAc transferase targeting and protein substrate specificity. J Biol Chem 278:24608–24616. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300036200
Iyer SP, Akimoto Y, Hart GW (2003) Identification and cloning of a novel family of coiled-coil domain proteins that interact with O-GlcNAc transferase. J Biol Chem 278:5399–5409. doi:10.1074/jbc.M209384200
Ji S, Park SY, Roth J, Kim HS, Cho JW (2012) O-GlcNAc modification of PPARgamma reduces its transcriptional activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 417:1158–1163. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.12.086
Jinek M, Rehwinkel J, Lazarus BD, Izaurralde E, Hanover JA, Conti E (2004) The superhelical TPR-repeat domain of O-linked GlcNAc transferase exhibits structural similarities to importin alpha. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:1001–1007. doi:10.1038/nsmb833
Jones SP et al (2008) Cardioprotection by N-acetylglucosamine linkage to cellular proteins. Circulation 117:1172–1182. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.107.730515
Kaasik K et al (2013) Glucose sensor O-GlcNAcylation coordinates with phosphorylation to regulate circadian clock. Cell Metab 17:291–302. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.12.017
Kazemi Z, Chang H, Haserodt S, McKen C, Zachara NE (2010) O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) regulates stress-induced heat shock protein expression in a GSK-3beta-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 285:39096–39107. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.131102
Keembiyehetty CN, Krzeslak A, Love DC, Hanover JA (2011) A lipid-droplet-targeted O-GlcNAcase isoform is a key regulator of the proteasome. J Cell Sci 124:2851–2860. doi:10.1242/jcs.083287
Kelly WG, Dahmus ME, Hart GW (1993) RNA polymerase II is a glycoprotein. Modification of the COOH-terminal domain by O-GlcNAc. J Biol Chem 268:10416–10424
Khidekel N et al (2007) Probing the dynamics of O-GlcNAc glycosylation in the brain using quantitative proteomics. Nat Chem Biol 3:339–348. doi:10.1038/nchembio881
Kreppel LK, Hart GW (1999) Regulation of a cytosolic and nuclear O-GlcNAc transferase. Role of the tetratricopeptide repeats. J Biol Chem 274:32015–32022
Kreppel LK, Blomberg MA, Hart GW (1997) Dynamic glycosylation of nuclear and cytosolic proteins. Cloning and characterization of a unique O-GlcNAc transferase with multiple tetratricopeptide repeats. J Biol Chem 272:9308–9315
Lazarus BD, Love DC, Hanover JA (2006) Recombinant O-GlcNAc transferase isoforms: identification of O-GlcNAcase, yes tyrosine kinase, and tau as isoform-specific substrates. Glycobiology 16:415–421. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwj078
Lazarus MB, Nam Y, Jiang J, Sliz P, Walker S (2011) Structure of human O-GlcNAc transferase and its complex with a peptide substrate. Nature 469:564–567. doi:10.1038/nature09638
Lazarus MB et al (2013) HCF-1 is cleaved in the active site of O-GlcNAc transferase. Science (New York, NY) 342:1235–1239. doi:10.1126/science.1243990
Lechner M, Lirk P, Rieder J (2005) Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in tumor biology: the two sides of the same coin. Semin Cancer Biol 15:277–289. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2005.04.004
Lefebvre T, Baert F, Bodart JF, Flament S, Michalski JC, Vilain JP (2004) Modulation of O-GlcNAc glycosylation during Xenopus oocyte maturation. J Cell Biochem 93:999–1010. doi:10.1002/jcb.20242
Lehman DM et al (2005) A single nucleotide polymorphism in MGEA5 encoding O-GlcNAc-selective N-acetyl-beta-D glucosaminidase is associated with type 2 diabetes in Mexican Americans. Diabetes 54:1214–1221
Li MD et al (2012) O-GlcNAc transferase is involved in glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transrepression. J Biol Chem 287:12904–12912. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.303792
Licastro F, Candore G, Lio D, Porcellini E, Colonna-Romano G, Franceschi C, Caruso C (2005) Innate immunity and inflammation in ageing: a key for understanding age-related diseases. Immunity and ageing: I and A 2:8. doi:10.1186/1742-4933-2-8
Liu X, Li L, Wang Y, Yan H, Ma X, Wang PG, Zhang L (2014) A peptide panel investigation reveals the acceptor specificity of O-GlcNAc transferase. FASEB J. doi:10.1096/fj.13-246850
Lopez-Otin C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G (2013) The hallmarks of aging. Cell 153:1194–1217. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039
Love DC, Hanover JA (2005) The hexosamine signaling pathway: deciphering the “O-GlcNAc code”. Science’s STKE : signal transduction knowledge environment 2005:re13. doi:10.1126/stke.3122005re13
Love DC, Kochan J, Cathey RL, Shin SH, Hanover JA (2003) Mitochondrial and nucleocytoplasmic targeting of O-linked GlcNAc transferase. J Cell Sci 116:647–654
Love DC et al (2010a) Dynamic O-GlcNAc cycling at promoters of Caenorhabditis elegans genes regulating longevity, stress, and immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:7413–7418. doi:10.1073/pnas.0911857107
Love DC, Krause MW, Hanover JA (2010b) O-GlcNAc cycling: emerging roles in development and epigenetics. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21:646–654. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.05.001
Lubas WA, Hanover JA (2000) Functional expression of O-linked GlcNAc transferase. Domain structure and substrate specificity. J Biol Chem 275:10983–10988
Lubas WA, Frank DW, Krause M, Hanover JA (1997) O-Linked GlcNAc transferase is a conserved nucleocytoplasmic protein containing tetratricopeptide repeats. J Biol Chem 272:9316–9324
Ma J, Hart GW (2013) Protein O-GlcNAcylation in diabetes and diabetic complications. Expert Rev proteomics 10:365–380. doi:10.1586/14789450.2013.820536
Ma J, Hart GW (2014) O-GlcNAc profiling: from proteins to proteomes. Clin Proteomics 11:8. doi:10.1186/1559-0275-11-8
Ma Z, Vosseller K (2013) O-GlcNAc in cancer biology. Amino acids 45:719–733. doi:10.1007/s00726-013-1543-8
Makino A, Suarez J, Gawlowski T, Han W, Wang H, Scott BT, Dillmann WH (2011) Regulation of mitochondrial morphology and function by O-GlcNAcylation in neonatal cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300:R1296–R1302. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00437.2010
Marshall S, Bacote V, Traxinger RR (1991) Discovery of a metabolic pathway mediating glucose-induced desensitization of the glucose transport system. Role of hexosamine biosynthesis in the induction of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem 266:4706–4712
Marz P et al (2006) Ataxin-10 interacts with O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine transferase in the brain. J Biol Chem 281:20263–20270. doi:10.1074/jbc.M601563200
Mazars R et al (2010) The THAP-zinc finger protein THAP1 associates with coactivator HCF-1 and O-GlcNAc transferase: a link between DYT6 and DYT3 dystonias. J Biol Chem 285:13364–13371. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.072579
Myers SA, Panning B, Burlingame AL (2011) Polycomb repressive complex 2 is necessary for the normal site-specific O-GlcNAc distribution in mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:9490–9495. doi:10.1073/pnas.1019289108
Nagel AK, Schilling M, Comte-Walters S, Berkaw MN, Ball LE (2013) Identification of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc)-modified osteoblast proteins by electron transfer dissociation tandem mass spectrometry reveals proteins critical for bone formation. MCP 12:945–955. doi:10.1074/mcp.M112.026633
Ngoh GA, Watson LJ, Facundo HT, Dillmann W, Jones SP (2008) Non-canonical glycosyltransferase modulates post-hypoxic cardiac myocyte death and mitochondrial permeability transition. J Mol Cell Cardiol 45:313–325. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.04.009
Nolte D, Muller U (2002) Human O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT): genomic structure, analysis of splice variants, fine mapping in Xq13.1. Mamm Gen: Off J Intern Mamm Gen Soc 13:62–64
O’Donnell N, Zachara NE, Hart GW, Marth JD (2004) Ogt-dependent X-chromosome-linked protein glycosylation is a requisite modification in somatic cell function and embryo viability. Mol Cell Biol 24:1680–1690
Ogawa M, Mizofuchi H, Kobayashi Y, Tsuzuki G, Yamamoto M, Wada S, Kamemura K (2012) Terminal differentiation program of skeletal myogenesis is negatively regulated by O-GlcNAc glycosylation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820:24–32. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.10.011
Ortiz-Meoz RF, Merbl Y, Kirschner MW, Walker S (2014) Microarray discovery of new OGT substrates: the medulloblastoma oncogene OTX2 is O-GlcNAcylated. J Am Chem Soc 136:4845–4848. doi:10.1021/ja500451w
Rao FV, Dorfmueller HC, Villa F, Allwood M, Eggleston IM, van Aalten DM (2006) Structural insights into the mechanism and inhibition of eukaryotic O-GlcNAc hydrolysis. EMBO J 25:1569–1578. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601026
Rao FV, Schuttelkopf AW, Dorfmueller HC, Ferenbach AT, Navratilova I, van Aalten DM (2013) Structure of a bacterial putative acetyltransferase defines the fold of the human O-GlcNAcase C-terminal domain. Open biology 3:130021. doi:10.1098/rsob.130021
Ryu IH, Do SI (2011) Denitrosylation of S-nitrosylated OGT is triggered in LPS-stimulated innate immune response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 408:52–57. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.03.115
Sakabe K, Wang Z, Hart GW (2010) Beta-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) is part of the histone code. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:19915–19920. doi:10.1073/pnas.1009023107
Sakaidani Y et al (2011) O-linked-N-acetylglucosamine on extracellular protein domains mediates epithelial cell-matrix interactions. Nature Commun 2:583. doi:10.1038/ncomms1591
Sakaidani Y et al (2012) O-linked-N-acetylglucosamine modification of mammalian Notch receptors by an atypical O-GlcNAc transferase Eogt1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 419:14–19. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.01.098
Shafi R et al (2000) The O-GlcNAc transferase gene resides on the X chromosome and is essential for embryonic stem cell viability and mouse ontogeny. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5735–5739. doi:10.1073/pnas.100471497
Shin SH, Love DC, Hanover JA (2011) Elevated O-GlcNAc-dependent signaling through inducible mOGT expression selectively triggers apoptosis. Amino Acids 40:885–893. doi:10.1007/s00726-010-0719-8
Sinclair DA et al (2009) Drosophila O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) is encoded by the Polycomb group (PcG) gene, super sex combs (sxc). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:13427–13432. doi:10.1073/pnas.0904638106
Singh JP, Zhang K, Wu J, Yang X (2014) O-GlcNAc signaling in cancer metabolism and epigenetics. Cancer Lett. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.04.014
Slawson C, Zachara NE, Vosseller K, Cheung WD, Lane MD, Hart GW (2005) Perturbations in O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine protein modification cause severe defects in mitotic progression and cytokinesis. J Biol Chem 280:32944–32956. doi:10.1074/jbc.M503396200
Slawson C, Lakshmanan T, Knapp S, Hart GW (2008) A mitotic GlcNAcylation/phosphorylation signaling complex alters the posttranslational state of the cytoskeletal protein vimentin. Mol Biol Cell 19:4130–4140. doi:10.1091/mbc.E07-11-1146
Sohn KC, Do SI (2005) Transcriptional regulation and O-GlcNAcylation activity of zebrafish OGT during embryogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 337:256–263. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.09.049
Solary E, Bernard OA, Tefferi A, Fuks F, Vainchenker W (2014) The Ten-Eleven Translocation-2 (TET2) gene in hematopoiesis and hematopoietic diseases. Leukemia 28:485–496. doi:10.1038/leu.2013.337
Steentoft C et al (2013) Precision mapping of the human O-GalNAc glycoproteome through SimpleCell technology. EMBO J 32:1478–1488. doi:10.1038/emboj.2013.79
Tai HC, Khidekel N, Ficarro SB, Peters EC, Hsieh-Wilson LC (2004) Parallel identification of O-GlcNAc-modified proteins from cell lysates. J Am Chem Soc 126:10500–10501. doi:10.1021/ja047872b
Tan EP et al (2014) Altering O-linked beta-N-Acetylglucosamine cycling disrupts mitochondrial function. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.525790
Toleman C, Paterson AJ, Whisenhunt TR, Kudlow JE (2004) Characterization of the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) domain of a bifunctional protein with activable O-GlcNAcase and HAT activities. J Biol Chem 279:53665–53673. doi:10.1074/jbc.M410406200
Tonks NK (2006) Protein tyrosine phosphatases: from genes, to function, to disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:833–846. doi:10.1038/nrm2039
Trinidad JC, Barkan DT, Gulledge BF, Thalhammer A, Sali A, Schoepfer R, Burlingame AL (2012) Global identification and characterization of both O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation at the murine synapse. MCP 11:215–229. doi:10.1074/mcp.O112.018366
Vaidyanathan K, Durning S, Wells L (2014) Functional O-GlcNAc modifications: implications in molecular regulation and pathophysiology. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 49:140–163. doi:10.3109/10409238.2014.884535
Vella P et al (2013) Tet proteins connect the O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase Ogt to chromatin in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell 49:645–656. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2012.12.019
Vosseller K et al (2006) O-linked N-acetylglucosamine proteomics of postsynaptic density preparations using lectin weak affinity chromatography and mass spectrometry. MCP 5:923–934. doi:10.1074/mcp.T500040-MCP200
Wang Z, Pandey A, Hart GW (2007) Dynamic interplay between O-linked N-acetylglucosaminylation and glycogen synthase kinase-3-dependent phosphorylation. MCP 6:1365–1379. doi:10.1074/mcp.M600453-MCP200
Wang Z, Udeshi ND, O’Malley M, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Hart GW (2010a) Enrichment and site mapping of O-linked N-acetylglucosamine by a combination of chemical/enzymatic tagging, photochemical cleavage, and electron transfer dissociation mass spectrometry. MCP 9:153–160. doi:10.1074/mcp.M900268-MCP200
Wang Z et al (2010b) Extensive crosstalk between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation regulates cytokinesis. Sci Signal 3: ra2. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2000526
Webster DM et al (2009) O-GlcNAc modifications regulate cell survival and epiboly during zebrafish development. BMC Dev Biol 9:28. doi:10.1186/1471-213x-9-28
Wells L, Gao Y, Mahoney JA, Vosseller K, Chen C, Rosen A, Hart GW (2002) Dynamic O-glycosylation of nuclear and cytosolic proteins: further characterization of the nucleocytoplasmic beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase, O-GlcNAcase. J Biol Chem 277:1755–1761
Whelan SA, Lane MD, Hart GW (2008) Regulation of the O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine transferase by insulin signaling. J Biol Chem 283:21411–21417. doi:10.1074/jbc.M800677200
Whisenhunt TR, Yang X, Bowe DB, Paterson AJ, Van Tine BA, Kudlow JE (2006) Disrupting the enzyme complex regulating O-GlcNAcylation blocks signaling and development. Glycobiology 16:551–563. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwj096
Yang X, Zhang F, Kudlow JE (2002) Recruitment of O-GlcNAc transferase to promoters by corepressor mSin3A: coupling protein O-GlcNAcylation to transcriptional repression. Cell 110:69–80
Yang X et al (2008) Phosphoinositide signalling links O-GlcNAc transferase to insulin resistance. Nature 451:964–969. doi:10.1038/nature06668
Yang YR et al (2012) O-GlcNAcase is essential for embryonic development and maintenance of genomic stability. Aging Cell 11:439–448. doi:10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00801.x
Yi W et al (2012) Phosphofructokinase 1 glycosylation regulates cell growth and metabolism. Science (New York, NY) 337:975–980. doi:10.1126/science.1222278
Yuzwa SA, Vocadlo DJ (2014) O-GlcNAc and neurodegeneration: biochemical mechanisms and potential roles in Alzheimer’s disease and beyond. Chem Soc Rev. doi:10.1039/c4cs00038b
Zachara NE, Hart GW (2004) O-GlcNAc a sensor of cellular state: the role of nucleocytoplasmic glycosylation in modulating cellular function in response to nutrition and stress. Biochim Biophys Acta 1673:13–28. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2004.03.016
Zachara NE, O’Donnell N, Cheung WD, Mercer JJ, Marth JD, Hart GW (2004) Dynamic O-GlcNAc modification of nucleocytoplasmic proteins in response to stress. A survival response of mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 279:30133–30142. doi:10.1074/jbc.M403773200
Zeidan Q, Hart GW (2010) The intersections between O-GlcNAcylation and phosphorylation: implications for multiple signaling pathways. J Cell Sci 123:13–22. doi:10.1242/jcs.053678
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagel, A.K., Ball, L.E. O-GlcNAc transferase and O-GlcNAcase: achieving target substrate specificity. Amino Acids 46, 2305–2316 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1827-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-014-1827-7