Abstract
Amongst the various hypotheses that challenged to explain the coexistence of species with similar life histories, theoretical, and empirical studies suggest that spatial processes may slow down competitive exclusion and hence promote coexistence even in the absence of evident trade-offs and frequent disturbances. We investigated the effects of spatial pattern and density on the relative importance of intra- and interspecific competition in a field experiment. We hypothesized that weak competitors increased biomass and seed production within neighborhoods of conspecifics, while stronger competitors would show increased biomass and seed production within neighborhoods of heterospecifics. Seeds of four annual plant species (Capsella bursa-pastoris, Stachys annua, Stellaria media, Poa annua) were sown in two spatial patterns (aggregated vs. random) and at two densities (low vs. high) in three different species combinations (monocultures, three and four species mixtures). There was a hierarchy in biomass production among the four species and C. bursa-pastoris and S. media were among the weak competitors. Capsella and Stellaria showed increased biomass production and had more individuals in the aggregated compared to the random pattern, especially when both superior competitors (S. annua, P. annua) were present. For P. annua we observed considerable differences among species combinations and unexpected pattern effects. Our findings support the hypothesis that weak competitors increase their fitness when grown in the neighborhood of conspecifics, and suggested that for the weakest competitors the species identity is not important and all other species are best avoided through intraspecific aggregation. In addition, our data suggest that the importance of spatial pattern for the other competitors might not only depend on the position within the hierarchy but also on the identity of neighbor species, species characteristics, below ground interactions, and other nonspatial factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Competition, both within and among species, is one of the major forces determining the distribution and abundance of plant species and the biodiversity of plant communities (Tilman 2000). Although most plants compete for the same resources (light, water, and nutrients), we observe large numbers of coexisting species in many plant communities (Silvertown and Charlesworth 2001). One of the central issues in ecology remains to explain how large numbers of species are able to coexist in natural communities. Many hypotheses have attempted to explain the coexistence of species with similar life histories (see e.g., Chesson 2000; Wright 2002; Shea et al. 2004; Barot 2004). Intuitively, spatial heterogeneity of resources used by plants is probably one of the most powerful promoters of niche separation and coexistence between plants. However, niche separation alone cannot explain the more species-rich communities. Grubb (1977) emphasized the importance of the entire life cycle of an individual and its ability to become established as part of the environment, which has recently become vacant (regeneration niches). Another classical mechanism explaining coexistence is based on the existence of a trade-off between colonization and competitive ability: good competitors must be poor colonizers and vice versa (Tilman 1994; Levine and Rees 2002). In that case coexistence occurs because species with sufficiently high dispersal rates persist in sites not occupied by superior competitors. Recent studies provided empirical evidence for the importance of such trade-offs in communities of sand-dune annuals (Rees 1995; Turnbull et al. 1999, 2004). Moreover, such trade-offs are particularly important if disturbances remove strong competitors and create new gaps for colonization (Connell 1978; Huston 1979). However, explaining species coexistence in the absence of conspicuous life-history trade-offs and in relatively homogeneous environments remains challenging and controversial (see e.g., Amarasekare 2003; Barot 2004).
As a consequence of the limited seed dispersal and/or clonal growth, most plant species create aggregations of conspecifics, thereby increasing the importance of intraspecific competition relative to interspecific competition (spatial segregation hypothesis, Pacala 1997). This is particularly relevant to plant communities because most of the ecological and genetic interactions between individual plants are with their immediate neighbors. Therefore, survivorship and fecundity are affected more by local population density than by the average density of the population (Pacala and Silander 1985; Pacala 1997; Stoll and Weiner 2000; Murrell et al. 2001). There is a large body of theories that underlines the importance of spatial pattern for ecological phenomena, for example coexistence and maintenance of biodiversity (Kareiva 1990; Bergelson 1990; Rees 1995; Rees et al. 1996; Murrell et al. 2001; Coomes et al. 2002; Bolker et al. 2003; Levine and Murrell 2003). Indeed, one proposed mechanism promoting coexistence is that intraspecific aggregation caused by limited seed dispersal and local interactions might slow down competitive exclusion. Although spatial theory has made great strides in advancing the understanding of coexistence in patchy environments, progress on the empirical front has been comparatively slow and an experimental validation of spatial ecology is still largely missing (see e.g., Rejmánek 2002; Amarasekare 2003; Bolker et al. 2003). Nevertheless, an early experimental study (Schmidt 1981) with two clonal perennials showed that after 3 years, interspecific competition was reduced and coexistence of competitors facilitated, in intraspecifically aggregated populations. Bergelson (1990) in an experiment with Capsella bursa-pastoris and Senecio vulgaris showed that the performance of Capsella and Senecio was much higher when grown in a patchy matrix of Poa annua than in a matrix of randomly distributed Poa. Recently, Stoll and Prati (2001) tested the prediction, made from spatial competition models, that aggregation may promote coexistence by slowing down competitive exclusion and thus maintain biodiversity. Using an experimental plant community composed of four annual species, they showed that the spatial pattern of individuals altered the competitive interactions in plant communities and facilitated coexistence at least in the short term. In particular, they found that weaker competitors increased the above ground biomass when intraspecifically aggregated, especially at high density where competition was greater than at low density. On the other hand, competitively superior species produced lower biomass in the aggregated pattern than in the random pattern at high density. Other studies showed similar pattern effects on plant population dynamics (Harper et al. 1961; Brophy and Mundt 1991; Stauber et al. 1991; Norris et al. 2001). Nevertheless, there are still controversial views over what permits competitors to coexist in the absence of conspicuous life-history trade-offs and frequent disturbances (e.g., Neuhauser and Pacala 1999; Wright 2002; Levin and Murrell 2003; Amarasekare 2003; Barot 2004). Moreover, as empirical and experimental evidence of effects of intraspecific aggregation on species interactions is still poor, the question whether or not intraspecific aggregation of species prevents or promotes coexistence remains open (Chesson 1991; Chesson and Neuhauser 2002; Murrell et al. 2002; Bolker et al. 2003). Indeed, the simplistic view of aggregation as a mechanism of coexistence of plant species proposed by some studies (e.g., Pacala 1997; Pacala and Levin 1997; Murrell et al. 2001, 2002) has been criticized and the importance of trade-offs between life-history parameters (Bolker and Pacala 1999) in the explanation of plant species coexistence has been stressed (Chesson and Neuhauser 2002). In response to Chesson and Neuhauser (2002), Murrell et al. (2002) gave an example in which the spatial extension of a nonspatial model allowed coexistence of two species even without trade-offs. Furthermore, Murrell and Law (2003) using an explicitly spatial versions of the Lokta-Volterra model showed that weaker competitors were able to coexist with their stronger rivals when interspecific interactions occurred over shorter distances than intraspecific interactions (heteromyiopia). Thus, as the authors suggested, it is most likely that there are some conditions under which spatial structure promotes coexistence and others under which it does not.
The aim of the present experiment was to evaluate the effects of spatial pattern and density on the relative importance of intra- and interspecific competition on plant dynamics. This experiment expands the pilot experiment of Stoll and Prati (2001) and differs in three ways: (1) it relies on more natural conditions (not steam sterilized soil and less weeding), (2) plants grew on a heavy soil with high clay content, and (3) substitutes a common annual species (Cardamine hirsuta) with a rare annual species (Stachys annua). In both experiments the four plant species were annuals with different morphologies. Based on the pilot experiment we hypothesized that spatial pattern may affect the growth and the fitness of plant species in such a way that weaker competitors may benefit (i.e., would show increased biomass and seed production) in an aggregated compared to a random pattern, while stronger competitors would show increased fitness in random compared to aggregated patterns. Furthermore, as overall density of plants generally affects the intensity of competition, we expected the effect of intraspecific aggregation to be more evident at higher densities.
Materials and methods
We investigated the effects of spatial pattern and density on plant performance and community dynamics in a field experiment (at the Research Institute of Organic Agriculture (FiBL), Frick, Switzerland) using four annual plant species with different morphologies. Capsella bursa-pastoris L. (Brassicaceae) is a rosette-forming plant with a multiflowered erect stem up to 40-cm-high. Poa annua L. (Poaceae) has adventitious roots at the first nodes and tillers up to 30-cm-high. Stellaria media L. (Caryophyllaceae) is prostrate to ascending, with high adventitious rooting and a height of up to 40 cm. Stellaria and Poa are widely distributed, cosmopolitan annuals of disturbed habitats. Stachys annua L. (Lamiaceae) has a multiflowered erect stem up to 40-cm-high. Compared to the other three species, S. annua is quite rare in most parts of Europe. Moreover, members of the Brassicaceae (e.g., Capsella) and Caryophyllaceae (e.g., Stellaria) are usually considered nonmycorrhizal, while members of the Poaceae (e.g., Poa) and Lamiaceae (e.g., Stachys) are generally mycorrhizal (Harley and Harley 1987; Smith and Read 1997).
The experiment was designed as a split-plot and contained 2 blocks (0.6 m×8 m, separated by 0.5 m), established between May 20 and 24 and harvested in the fall of 2002. Each block was subdivided into an upper- and lower subblock (Fig. 1). During the first 2 months the two blocks were covered with a plastic tunnel (200 holes/m2, GVZ-Bolltec AG, Zürich, Switzerland) to protect the seedlings from adverse weather and full sunlight. Each block contained eight main plots (0.6 m×0.6 m, separated by 0.3 m). Spatial pattern and density were used as plot-level treatments and each treatment was replicated twice per block and randomly assigned to plots (Fig. 1). The plots were sown between May 30 and June 4 and watered each evening until May 6; thereafter, an automatic irrigation system (Gardena AG, Bachenbülach, Switzerland) was installed. The system was programmed to give rain cycles lasting 1 min (i.e., 1 l water) starting at 5:15, 6:15, 7:15 a.m., and 7:15, 8:15, and 9:15 p.m. The duration of the 8:15 p.m. rain cycle was changed from 1 min to 2 min on June 25.
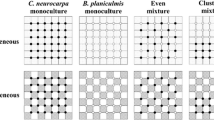
The experimental design. a Two blocks each containing four plots at either high or low density and random or aggregated pattern, twice replicated per treatment and species mixtures n=4. b Plots subdivided into nine subplots, each containing either a monoculture, one of the possible three- or four-species mixture. c An example of the intraspecifically aggregated pattern. In the four-species mixture each species occupied a single cell. In the random pattern the corresponding number of seeds of all species was distributed throughout the 20 cm×20 cm subplot
The combinations of mixtures of species (see below) and monocultures were used as within-plot treatments. The plots were subdivided into nine subplots (0.2 m×0.2 m), each of which contained either one of the four species in monoculture, one of the four possible three-species mixtures, or the four-species mixture (Fig. 1). In the random pattern, seeds of each species were sown over the subplots so that in the mixtures, the individuals experienced inter- and intraspecific encounters at the same frequency. In the aggregated pattern, the subplots were further subdivided into 16 cells (5 cm×5 cm), and each cell contained only one of the species in such a way that individuals experienced more intra- than interspecific encounters (Fig. 1). The species were randomly allocated to the cells. In the four-species mixture, each species occupied four cells, whereas in the three-species mixtures, each species occupied five cells and one-third of the sixteenth cell. At low density, we sowed 10 seeds per cell (4,000 seeds/m2) whereas at high density we sowed 100 seeds per cell (40,000 seeds/m2). After sowing, in order to increase germination, the seeds were covered by a layer (2 cm) of commercial garden soil, instead of the heavy soil (high clay content), and pressed down slightly to prevent the seeds from being washed away. The seeds were obtained from a commercial supplier (Herbiseed, Wokingham, Berkshire, UK) and counted using a mechanical seed counter (Elmor). Hundred seeds for each species were weighted to determine the mean seed weight.
A snail fence enclosed the entire experimental field and slug pellets were regularly used to curtail herbivory.
The above-ground biomass was harvested between August 20 and September 29, and the total number of individuals per species was counted. For Poa we counted ramets rather than genets. When the total number of individuals per species exceeded ten, we randomly selected ten individuals, measured their height, and separated vegetative from reproductive parts. We only separated vegetative from reproductive biomass for the remaining plants. Almost all individuals of Stellaria, Capsella, and Stachys produced flowers, while only few Poa flowered. The harvested biomass was dried at 60°C for 48 h in Frick and then stored. Before it was weighed the biomass was dried again for 17 h at 60°C.
Since the fixed automatic irrigation system might have affected the above-ground biomass production we tested (1) the correlation between the amount of water supplied by the fixed automatic irrigation system and total biomass of all fours species produced at the subplot level and (2) the effects of both factors by using an analysis of covariance. As no correlation was found and since the total biomass of all four species produced at the subplot level showed a significant covariate effect, we decided to use the total biomass as indirect measure to quantify the effects of the fixed irrigation system and other unknown factors. Since the main treatments (pattern and density) varied at the plot rather than at the subplot level, the covariate should not be confounded with the main treatments.
The data were analyzed with multifactorial analysis of covariance (ANCOVA). The main effects (pattern, density) and their interaction were tested against the plot-level residual mean square. When the effect of the species mixtures combinations was significant, we used linear contrasts to separate them into (1) the difference between monoculture and mixtures and (2) difference between the three- and four-species mixtures.
In the cases where the design became unbalanced because of missing values (i.e., subplot where plants did not grow), we used regression analysis or performed the analysis either without the corresponding subplots or restricted the analysis to the high density. In the particular case for Capsella and Stellaria when the analysis was restricted to the species combinations with Stachys and Poa, there were at the low-density two missing values: four species mixture/random pattern and four species mixture/aggregated pattern. As the results of the analysis changed significantly depending on whether we considered those missing values as ‘true zero’ or left them out, we decided to present both results. Generally we did the analysis without the factor ‘subblock’ because it was not significant. However, for Poa we integrated it in the analysis for the vegetative biomass, number of individuals, and the coefficient of variation (CV) in length because it had a significant effect. Using the ten selected individuals, the CV in length, vegetative, and reproductive biomass was evaluated to assess the mode of competition (i.e., symmetric vs. asymmetric).
The data were calculated as grams per square meter and log-transformed to obtain normal distribution of the residuals and homogeneity of variances. Back-transformed means and standard errors from the analysis are presented throughout.
All analyses were conducted using the program GENSTAT 5 (Payne et al. 1987).
Results
Stachys annua had the heaviest seeds, followed by S. media, Poa annua, and Capsella bursa-pastoris with the lightest seeds. Stachys produced the highest biomass, followed by Poa, Capsella, and Stellaria (Table 1).
The spatial pattern affected the growth and the fitness of Capsella, and to some extent, Stellaria, in such a way that there was an increase in biomass, seed production, and number of individuals in the aggregated compared to the random pattern.
The analysis for Capsella, excluding the monoculture, showed higher biomass in the aggregated (vegetative=167.11 g/m2; reproductive=19.86 g/m2) compared to the random pattern (vegetative=100.23 g/m2; reproductive=9.46 g/m2) (Table 2). In addition, the total number of individuals was significantly higher in the aggregated (851.14 ind/m2) compared to the random pattern (527.23 ind/m2) (Table 2). These spatial pattern effects were only marginally significant for both vegetative and reproductive biomass, yet they were more pronounced in the species mixtures with Stachys and Poa (Table 2, Fig. 2). In this case, vegetative biomass of Capsella increased by 186% and reproductive biomass by 126% within neighborhoods of the same species, which corresponded to an increase of about roughly 10,000 seeds/m2 (Fig. 2).
Above-ground biomass and number of individuals of Capsella bursa-pastoris and Stellaria media restricted to the species combinations with Stachys annua and Poa annua. White bars: random pattern, grey bars: aggregated pattern. The bars represented back-transformed means ±1 SE from ANCOVA of log-transformed data
Capsella in the species combinations together with Stachys and Poa at the high-density treatment showed significantly higher CV for length in the aggregated (81%) compared to the random pattern (63.9%) (F1,4=13.85, P=0.020).
For Stellaria the positive effects of aggregation occurred only in those mixtures where Stachys and Poa were present (Table 3). Stellaria increased the vegetative biomass by 288% and the reproductive biomass by 280% in the aggregated compared to the random pattern (Fig. 2). Stellaria did not show any significant differences in size variation between patterns.
The analysis for P. annua, including all combinations, showed significantly higher vegetative biomass in the aggregated compared to the random pattern (Table 4). In addition, we found highly significant differences among the species combinations (Table 4). The linear contrasts indicated that this effect was due to the differences between the four- and three-species mixtures (F 1,4=6.27; P=0.016). Moreover, they showed significant differences among three species mixtures with Stachys and without Stachys (F 1,4=10.58; P=0.002) (Fig. 3).
The total number of individuals of Poa differed significantly among species combinations (Table 4). The calculated linear contrasts showed that the differences were again due to the differences between the species mixture and the monoculture (F 1,4=9.09; P=0.004) and among three-species mixtures with Stachys and without Stachys (F 1,4=14.95; P=<0.001).
Although we restricted our analysis to the high-density treatment due to the missing values present at the low-density treatment, for S. annua we found neither treatment effects nor species combinations effects or significant interactions.
Discussion
Our experiment provided evidence that spatial pattern affected growth and reproduction of plants within an experimental community in a short run. Our results showed that compared to a pilot experiment (Stoll and Prati 2001), using a slightly ‘different’ experimental plant community and soil treatment, not only did the competitive hierarchy change, but so did the spatial pattern effects for the individual species. Our data on C. bursa-pastoris and, to some extent S. media, were consistent with the pilot experiment and support the hypothesis that weak competitors may increase their fitness (e.g., survival and seed production) within neighborhoods of conspecifics compared to neighborhoods of heterospecifcs, especially when the superior competitors were present in the community. Moreover, data on Stellaria (which was the strongest competitor in the pilot experiment, see below) suggested that for the weakest competitors the species identity is not important and all other species are best avoided through intraspecific aggregation. In addition, our findings for P. annua revealed considerable differences among species mixture and unexpected pattern effects. This suggests that the importance of spatial pattern might not only depend on competitive hierarchies, and aggregation might be beneficial, because there may be positive interactions (e.g., complimentarity, mutualisms) associated with some of the other species.
Based on the total above-ground biomass production, our results suggest two ‘main groups’: one composed of S. annua and P. annua as strong competitors and one group composed of C. bursa-pastoris and S. media as weak competitors.
Capsella was among the weaker competitors both in the pilot and the present experiment and showed increased biomass production and number of individuals in the aggregated compared to the random spatial pattern, especially in combination with the competitively superior species. By contrast, Stellaria was the strongest competitor in the pilot and a weak competitor in the present experiment. Although this species only partly confirmed our hypothesis, the data suggest a benefit of intraspecific aggregation, once again in combination with the competitively superior species. Note that in the pilot experiment Stellaria produced more above-ground biomass in the random compared to the aggregated pattern, while in the present experiment behaved like the other weak competitor Capsella. Our results are quite remarkable because they not only show the positive advantage of intraspecific aggregation for weak competitors, but also that these advantages do not seem to depend on species identity.
Our data about the two superior competitors Stachys and Poa do not agree, however, with the pilot experiment, where superior competitors were suppressed in the neighborhood of conspecifics. In fact, neither Stachys nor Poa increased their biomass in the random pattern. Furthermore, contrary to our expectations, the superior competitor Poa increased the vegetative biomass in the aggregated pattern as opposed to the random pattern. These results were unexpected and quite difficult to explain. For Stachys it is possible that the high data variability and the rather high number of missing values present in the low-density treatment may have masked a possible treatment effect. On the other hand, our findings on Poa were similar to results found in a study with two perennial grasses where the superior competitive ability of Agropyron did not emerge based on the relative performance of this species in monoculture and mixture (Huber-Sannwald et al. 1996).
Besides, Poa showed different responses depending on community composition. Poa generally increased its fitness (i.e., vegetative biomass and number of individuals) if associated with the other superior competitor Stachys. This result could be explained with some complimentarity of species’ traits and/or below-ground mutualisms (see below). Findings on Poa suggest that the position of a species within a community hierarchy is not sufficient to predict effects of spatial pattern and that the importance of spatial pattern might depend on which species composed the communities.
In contrast to Stoll and Prati (2001), we observed another plant hierarchy in the community, which might be explained by (1) different species composition; (2) different soil treatment, and (3) trade-offs. Stellaria, which was the strongest competitor in the pilot experiment, turned out to be the weakest in the present experiment. Poa changed its position from the second weakest to the second strongest competitor. Performances of Capsella did not vary between the two experiments and it remained as third weakest competitor. The newly introduced species, Stachys, was the strongest competitor. Intuitively, the substitution of C. hirsuta (a rosette-forming plant of the Brassicaceae) used in the pilot experiment with Stachys used in our experiment could have changed the competitive interactions between the experimental plant species leading to a new plant hierarchy. However, the different soil treatments, which were a steam-sterilized nutrient-rich garden soil in the pilot experiment and an unsterilized heavy soil with high clay content in the present experiment, might also explain the different hierarchies. Therefore, the presence or absence of mycorrhizal fungi in the soil could have played an important role in determining the community structure (van der Heijden et al. 1998, 2003). There is growing evidence that the below-ground biota (e.g., mycorrhizal fungi) play an important role in determining the community structure and coexistence of competitors (e.g., Hartnett and Wilson 1999; Klironomos et al. 2000; Klironomos 2002; Bever 2003). Recently, Hart et al. (2003) reviewed the importance of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) in mediating plant coexistence. For example, West (1996) showed that if a highly competitive plant species is more infected by AMF, then AMF would simply reinforce competitive dominance of that species. Based on those considerations and the mutualism and antagonism in the mycorrhizal symbiosis and the impact on plant community (Francis and Read 1995), we speculate that the two superior competitors in our experiment might have experienced a kind of below-ground mutualism between each other. However, some studies (DeMars and Boerner 1994; Ishii et al. 1998), have reported some vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhizal infection also in members of the Brassicaceae and Caryophyllaceae. Although these authors suggested that the mycorrhizas might be nonfunctional, we cannot exclude possible root interactions between our experimental plants species.
Nevertheless, also the competition/colonization trade-off (Tilman 1994; Rees 1995; Turnbull et al. 1999, 2004) could in part explain the different plant hierarchies. As expected the large-seeded Stachys was one of the superior competitors, while the small-seeded Capsella was one of the inferior competitors. By contrast, the second large-seeded (Stellaria) and the second small-seeded (Poa) were the second weakest competitor and the second strongest competitor, respectively. This suggests that the performance (i.e., competitive ability) of a plant species and therefore its position in a given hierarchy is not simply correlated with the seed size. Indeed, when appropriate biological details are included in theoretical models, the performance of individuals varies in response to other factors such environmental heterogeneity and competition with surrounding neighbors. Furthermore, there is evidence that high-competitive asymmetries in addition to competition/colonization trade-off are needed to explain coexistence (Adler and Mosquera 2000; Levine and Rees 2002). Recently, in a review about colonization, tolerance, competition, and seed-size variation, Coomes and Grubb (2003), stressed the limits on the potential of competition/colonization trade-off to allow long-term coexistence without other forms of niche differentiation. So far it remains an open question to which extent seed size, in particular the competition/colonization trade-off together with spatial pattern (i.e., intraspecific aggregation), might benefit weak competitors and hence allow long-term coexistence by slowing down competitive exclusion (see e.g., Turnbull et al. 2004).
In contrast to the pilot experiment, we could not find any interactions between density and spatial pattern. Hence, our hypothesis that the spatial pattern effect should be more evident at high density because of the higher intensity of competition must be rejected. However, we suspect that the high variability of our data might have hidden such interactions, and thus complicated the interpretation of the outcomes.
This huge variability could be partially explained by the fixed automatic irrigation system, which systematically irrigated some subplots more than others. In consideration of the fact that we did not find a direct correlation between the amount of water and the total biomass of all four species produced for each subplot, we assume that the fixed irrigation system was not the only reason for the observed variability. For instance, other factors such as the high soil water storage capacity may have favored some species and killed others.
In conclusion, we showed that spatial pattern affected an experimental plant community at least in the short run. Moreover, our findings supported the hypothesis that weaker competitors might increase their fitness (e.g., biomass and seed production) within neighborhoods of consepecifics compared to neighborhoods of heterospecifics. Furthermore, our data suggested that the advantages of intraspecific aggregation for weaker competitors might be independent of species identity and that all other species are best avoided. In addition, our findings on P. annua revealed considerable differences among species mixture and unexpected pattern effects. This suggests that the importance of spatial pattern might not only depend on competitive hierarchies, and aggregation might be beneficial because there may be positive interactions (e.g., complimentarity, mutualisms) associated with some of the other species. Although we did show that spatial pattern had an impact on the plant population dynamics, it remains unclear as how important these processes are relative to other nonspatial factors. In addition, more long-term experiments are needed in order to understand whether or not intraspecific aggregation promotes coexistence by retarding competitive exclusion. Accordingly, further studies are needed to better comprehend under which conditions the spatial pattern will affect the dynamics of a given plant community and under which conditions it may be ignored. On the other hand, a better knowledge of spatial pattern and plant population dynamics is needed in order to build predictive models and address more fundamental questions, such as the prediction of the importance, rather whether or not, a mechanism may promote coexistence in plant communities.
References
Adler FR, Mosquera J (2000) Is space necessary? Interference competition and limits to biodiversity. Ecology 81:3226–3232
Amarasekare P (2003) Competitive coexistence in spatially structured environments: a synthesis. Ecol Lett 6:1109–1122
Barot S (2004) Mechanisms promoting plant coexistence: can all the proposed processes be reconciled? Oikos 106:185–192
Bergelson J (1990) Life after death: site pre-emption by the remains of Poa annua. Ecology 71:2157–2165
Bever JD (2003) Soil community feedback and the coexistence of competitors: conceptual frameworks and empirical tests. New Phytol 157:465–473
Bolker BM, Pacala SW (1999) Spatial moment equations for plant competition: understanding spatial strategies and the advantages of short dispersal. Am Nat 153:575–602
Bolker BM, Pacala SW, Neuhauser C (2003) Spatial dynamics in model plant communities: what do we really know? Am Nat 162:135–148
Brophy LS, Mundt CC (1991) Influence of plant spatial patterns on disease dynamics, plant competition and grain-yield in genetically diverse wheat populations. Agric Ecosyst Environ 35:1–12
Chesson P (1991) A need for niches? Trends Ecol Evol 6:26–28
Chesson P (2000) Mechanisms of maintenance of species diversity. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 31:343–366
Chesson P, Neuhauser C (2002) Intraspecific aggregation and species coexistence. Trends Ecol Evol 17:210–211
Connell JH (1978) Diversity in tropical rainforests and coral reefs. Science 199:1302–1310
Coomes DA, Grubb PJ (2003) Colonization, tolerance, competition and seed-size variation within functional groups. Trends Ecol Evol 18:283–291
Coomes DA, Rees M, Turnbull LA, Ratcliffe S (2002) On the mechanisms of coexistence among annual-plant species, using neighborhood techniques and simulation models. Plant Ecol 163:23–38
DeMars BG, Boerner REJ (1994) Vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonization in Capsella bursa-pastoris (Brassicaceae). Am Midl Nat 132:377–380
Francis R, Read DJ (1995) Mutualism and antagonism in the mycorrhizal symbiosis, with special references to impacts on plant community structure. Can J Bot Suppl 1:S1301–S1309
Grubb P (1977) The maintenance of species richness in plant communities: the importance of the regeneration niche. Biol Rev 52:107–145
Harley JL, Harley EL (1987) Checklist of mycorrhizas in the British flora. New Phytol 105:1–102
Harper JL, Clatworthy JN, McNaughton IH, Sagar GR (1961) Evolution and ecology of closely related species living in the same area. Evolution 15:209–227
Hart MM, Reader RJ, Klironomos JN (2003) Plant coexistence mediated by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Trends Ecol Evol 18:418–423
Hartnett DC, Wilson GWT (1999) Mycorrhizae influence plant community structure and diversity in tallgrass prairie. Ecology 80:1187–1195
van der Heijden MGA, Klironomos JN,Ursic M, Moutoglis P, Streitwolf-Engel R, Boller T, Wiemken A, Sanders IR (1998) Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability and productivity. Nature 396:69–72
van der Heijden MGA, Wiemken A, Sanders IR (2003) Different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alter coexistence and resource distribution between co-occurring plants. New Phytol 157:569–578
Huber-Sannwald E, Pyke DA, Caldwell MM (1996) Morphological plasticity following species-specific recognition and competition in two perennial grasses. Am J Bot 83:919–931
Huston M (1979) A general hypothesis of species diversity. Am Nat 113:81–101
Ishii T, Matsumoto I, Shrestha YM, Wamocho LS, Kadoya K (1998) Observation of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal formation in the roots of some seasonal weeds proliferated in citrus orchards. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 67:556–558
Kareiva P (1990) Population dynamics in spatially complex environments: theory and data. Philos Trans R Soc B 330:175–190
Klironomos JN (2002) Feedback with soil biota contributes to plant rarity and invasiveness in communities. Nature 417:67–70
Klironomos JN, McCune J, Hart M, Neville J (2000) The influence of arbuscular mycorrhizae on the relationship between plant diversity and productivity. Ecol Lett 3:137–141
Levine JM, Murrell DJ (2003) The community-level conseuqnces of seed dispersal patterns. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 34:549–574
Levine JM, Rees M (2002) Coexistence and relative abundance in annual plant assemblages: the roles of competition and colonization. Am Nat 160:452–459
Murrell DJ, Law R (2003) Heteromyopia and the spatial coexistence of similar competitors. Ecol Lett 6:48–59
Murrell DJ, Purves DW, Law R (2001) Uniting pattern and process in plant ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 16:529–530
Murrell DJ, Purves D, Law R (2002) Intraspecific aggregation and species coexistence. Trends Ecol Evol 17:211–212
Neuhauser C, Pacala Sw (1999) An explicit spatial version of the Lotka-Volterra model with interspecific competition. Ann Appl Probab 9:1226–1259
Norris RF, Elmore CL, Rejmanek M, Akey WC (2001) Spatial arrangement, density, and competition between barnyard grass and tomato. Weed Sci 49:61–68
Pacala SW (1997) Dynamics of plant competition. In: Crawley MJ (ed) Plant ecology. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 532–555
Pacala SW, Levin SA (1997) Biologically generated spatial pattern and the coexistence of competing species. In: Tilman D, Kareiva P (eds) Spatial ecology. The role of space in population dynamics. Princeton Univ Press, Princeton, pp 204–232
Pacala SW, Silander JA (1985) Neighborhood models of plant population dynamics. 1. Single-species models of annuals. Am Nat 125:385–411
Payne RW, Lane PW, Ainsley AE, Bicknell KE, Digby PGN, Harding P, Leech K, Simpson HR, Todd AD, Verrier PJ, White RP (1987) GENSTAT 5 reference manual. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Rees M (1995) Community structure in sand dune annuals: is seed weight a key quantity? J Ecol 83:857–864
Rees M, Grubb PJ, Kelly D (1996) Quantifying the impact of competition and spatial heterogeneity on the structure and dynamic of a four-species guild of winter annuals. Am Nat 147:1–32
Rejmanek M (2002) Intraspecific aggregation and species coexistence. Trends Ecol Evol 17:209–210
Schmidt W (1981) Über das Konkurrenzverhalten von Solidago canadensis und Urtica dioica. Verh Ges Ökol 9:173–188
Shea K, Roxburgh SH, Rauschert ESJ (2004) Moving from pattern to process: coexistence mechanisms under intermediate disturbance regimes. Ecol Lett 7:491–508
Shmida A, Ellner S (1984) Coexistence of plant species with similar niches. Vegetatio 58:29–55
Silvertown J, Charlesworth D (2001) Plant population biology, 4th edn. Blackwall, Oxford
Smith SE, Read DJ (1997) Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 2nd edn. Academic, San Diego
Stauber LG, Smith RJ, Talbert RE (1991) Density and spatial interference of barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) with rice (Oryza sativa). Weed Sci 39:163–168
Stoll P, Prati D (2001) Intraspecific aggregation alters competitive interactions in experimental plant communities. Ecology 82:319–327
Stoll P, Weiner J (2000) A neighborhood view of interactions among individual plants. In: Dieckmann U, Law R, Metz JAJ (eds) The geometry of ecological interactions: simplifying spatial complexity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 11–27
Tilman D (1994) Competition and biodiversity in spatially structured habitats. Ecology 75:2–16
Tilman D (2000) Mechanisms of plant competition. In: Crawley MJ (ed) Plant ecology, 2nd edn. Blackwell, Oxford
Turnbull LA, Rees M, Crawley MJ (1999) Seed mass and the competition/colonization trade-off: a sowing experiment. J Ecol 87:899–912
Turnbull LA, Coomes D, Hector A, Rees M (2004) Seed mass and the competition/colonization trade-off: competitive interactions and spatial patterns in a guild of annual plants. J Ecol 92:97–109
Weiner J, Conte PT (1981) Dispersal and neighborhood effects in an annual plant competition model. Ecol Model 13:131–147
West HM (1996) Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal infection on competition between Holcus lanatus and Dactylis glomerata. J Ecol 84:429–438
Wright SJ (2002) Plant diversity in tropical forests: a review of mechanisms of species coexistence. Oecologia 130:1–14
Acknowledgements
We thank Jovanne Mevi-Schütz, Alexander Wacker, David Murrell, and one anonymous reviewer for helpful comments on an early draft of this paper and the FiBL staff for logistical support. This research was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation grant 3100-061572 to Peter Stoll.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Christian Koerner
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monzeglio, U., Stoll, P. Spatial patterns and species performances in experimental plant communities. Oecologia 145, 619–628 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-005-0168-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-005-0168-3