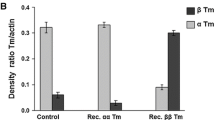
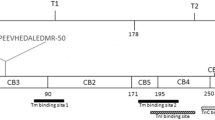
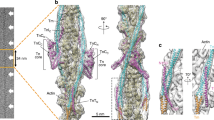
Abstract
Vertebrate skeletal muscle contraction is activated by the binding of Ca2+ to the low affinity Ca2+-pecific (regulatory) sites of troponin C (TnC), the Ca2+-binding subunit of troponin, which together with troponin I (TnI), troponin T (TnT) and tropomyosin (Tm) form the regulatory system of the contractile apparatus (Zot and Potter 1987; Moss 1992; Gergely 1998). TnC is necessary for force development in skinned muscle fibers and its selective extraction from muscle fibers results in a permanent relaxation at all Ca2+ concentrations. This process is fully reversible and reconstitution of the TnC-depleted fibers with exogenous TnC restores Ca2+-dependent contraction (Zot and Potter 1982; Szczesna et al. 1996). The structure of TnC has been solved to atomic resolution by X-ray crystallography (Herzberg and James 1985, 1988; Houdusse et al. 1997). TnC consists of two globular domains corresponding to the NH2-and COOH-termini and each domain contains two EF-hand divalent cation-binding sites. The low affinity sites of TnC, called the Ca2+-specific sites (I and II) (Potter and Gergely 1975), are located in the NH2-terminal domain of TnC and are separated from the COOH-terminal domain of TnC by a single nineturn α-helix comprising helices D and E (Herzberg and James 1985, 1988). The COOH-terminal region of TnC contains two high affinity Ca2+-binding sites designated as sites III and IV and referred to as the Ca2+-Mg2+ sites (Potter and Gergely 1975). Sites I and II bind Ca2+ specifically with KCa2+ ≅ 3 × 105M−1, whereas sites III and IV bind Ca2+ with KCa2+ ≅ 2 × 107M−1 and Mg2+ with KMg2+ ≅ 2 × 103M−1 (Potter and Gergely 1975; Grabarek et al. 1992).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe H, Komiya T, Obinata T (1986) Expression of multiple troponin T variants in neonatal chicken breast muscle. Dev Biol 118: 42 - 51
Babu A, Rao VG, Su H, Gulati J (1993) Critical minimum length of the central helix in troponin C for the Cat+ switch in muscular contraction. J Biol Chem 268: 19232 - 19238
Bing W, Fraser ID, Marston SB (1997) Troponin I and troponin T interact with troponin C to produce different Ca2tdependent effects on actin-tropomyosin filament motility. Biochem J 327: 335 - 340
Breitbart RE, Nguyen HT, Medford RM, Destree AT, Mandavi V, Nadal-Ginard B (1985) Intricate combinatorial patterns of exon splicing generate multiple regulated troponin T isoforms from a single gene. Cell 41: 67 - 82
Briggs MM, Schachat F (1989) N-terminal amino acid sequences of three functionally different troponin T isoforms from rabbit fast skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol 206: 245 - 249
Briggs MM, Maready M, Schmidt JM, Schachat F (1994) Identification of a fetal exon in the human fast troponin T gene. FEBS Lett 350: 37 - 40
Brisson JR (1986) Interaction of tropomyosin and troponin T: a proton nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biochemistry 25: 4548 - 4555
Campbell AP, Sykes BD (1991) Interaction of troponin I and troponin C. Use of the two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance transferred nuclear Overhauser effect to determine the structure of the inhibitory troponin I peptide when bound to skeletal troponin C. J Mol Biol 222: 405-421
Chandra M, da Silva EF, Sorenson MM, Ferro JA, Pearlstone JR, Nash BE, Borgford T, Kay CM, Smillie LB (1994) The effects of N helix deletion and mutant F29W on the Ca2+ binding and functional properties of chicken skeletal muscle troponin C. J Biol Chem 269: 14988 - 14994
Chandra M, McCubbin WD, Oikawa K, Kay CM, Smillie LB (1994) Ca2+, Mg', and troponin I inhibitory peptide binding to a Phe-154 to Trp mutant of chicken skeletal muscle troponin C. Biochemistry 33: 2961 - 2969
Cooper TA, Ordahl CP (1985) A single cardiac troponin T gene generates embryonic and adult isoforms via developmentally regulated alternate splicing. J Biol Chem 260: 11140 - 11148
Dalgarno D, Grand RJA, Levine BA, Moir AJG, Scott GMM, Perry SV (1982) Interaction between troponin I and troponin C. Definition of the topography by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. FEBS Lett 150: 54-58
Dobrowolski Z, Xu G-Q, Hitchcock-DeGregori SE (1991) Modified calcium-dependent regulatory function of troponin C central helix mutants. J Biol Chem 266: 5703 - 5710
Farah CS, Miyamoto CA, Ramos CHI, da Silva ACR, Quaggio RB, Fujimori K, Smillie LB, Reinach FC (1994) Structural and regulatory functions of the NH2- and COOH-terminal regions of skeletal muscle troponin I. J Biol Chem 269: 5230 - 5240
Flicker PF, Phillips GN Jr, Cohen C (1982) Troponin and its interactions with tropomyosin. An electron microscope study. J Mol Biol 162: 485-501
Francois JM, Sheng Z, Szczesna D, Potter JD (1995) The functional role of the domains of troponin-C investigated with thrombin fragments of troponin-C reconstituted into skinned muscle fibers. J Biol Chem 270: 19287 - 19293
Gagne SM, Tsuda S, Li MX, Chandra M, Smillie LB, Sykes BD (1994) Qualification of the calcium-induced secondary structural changes in the regulatory domain of troponin-C. Protein Sci 3: 1961 - 1974
Gagne SM, Tsuda S, Li MX, Smillie LB, Sykes BD (1995) Structures of troponin C regulatory domains in the apo and calcium-saturated states. Nature Struct Biol 2: 784 - 789
Gagne SM, Li MX, Sykes BD (1997) Mechanism of direct coupling between binding and induced structural change in regulatory calcium binding proteins. Biochemistry 36: 4386 - 4392
Gagne SM, Tsuda S, Spyracopoulos L, Kay LE, Sykes BD (1998) Backbone and methyl dynamics of the regulatory domain of troponin C: anisotropic rotational diffusion and contribution of conformational entropy to calcium affinity. J Mol Biol 278: 667 - 686
Geeves MA, Conibear PB (1995) The role of three-state docking of myosin Si with actin in force generation. Biophys J 68: 194s - 201s
Gergely J (1998) Molecular switches in troponin. Adv Exp Med Biol 453: 169 - 176
Grabarek Z, Leavis PC, Gergely J (1986) Calcium binding to the low affinity sites in troponin C induces conformational changes in the high affinity domain: a possible route of information transfer in activation of muscle contraction. J Biol Chem 261: 608 - 613
Grabarek Z, Tao T, Gergely J (1992) Molecular mechanism of troponin-C function. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 13: 383 - 393
Greaser ML, Gergely J (1971) Reconstitution of troponin activity from three protein components. J Biol Chem 246: 4226 - 4233
Gulati J, Babu A, Su H, Zhang Y-F (1993) Identification of the regions conferring calmodulin-like properties to troponin C. J Biol Chem 268: 11685 - 11690
Haselgrove JC (1972) X-ray evidence for a conformational change in actin-containing filaments of vertebrate striated muscle. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 37: 341 - 352
Hatakenaka M, Ohtsuki I (1992) Effect of removal and reconstitution of troponins C and I on the Ca2+-activated tension development of single glycerinated rabbit skeletal muscle fiber. Eur J Biochem 205: 985 - 993
Heeley DH, Golosinska K, Smillie LB (1987) The effects of troponin T fragments T1 and T2 on the binding of nonpolymerizable tropomyosin F-actin in the presence and absence of troponin I and troponin C. J Biol Chem 262: 9971 - 9978
Hernandez G, Blumenthal DK, Kennedy MA, Unkefer CI, Trewhella J (1999) Troponin I inhibitory peptide (96-115) has an extended conformation when bound to skeletal muscle troponin C. Biochemistry 38: 6911 - 6917
Herzberg O, James MNG (1985) Structure of the calcium regulatory muscle protein-troponin C at 2.8 t1 resolution. Nature 313: 653 - 659
Herzberg O, James MNG (1988) Refined crystal structure of troponin C from turkey skeletal muscle at 2.0-A resolution. J Mol Biol 203: 761 - 769
Herzberg O, Moult J, James MNG (1986) A model for the Ca2+-induced conformational transitions of troponin C. J Biol Chem 261: 2638 - 2644
Houdusse A, Love ML, Dominguez R, Grabarek Z, Cohen C (1997) Structures of four Ca2+-bound troponin C at 2.0-Â resolution: further insights into Ca2+-switch in the calmodulin superfamily. Structure 5: 1695 - 1711
Huxley HE (1972) Structural changes in the actin-and myosin-containing filaments during contraction. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 37: 361 - 376
Ishii Y, Lehrer SS (1991) Two-site attachment of troponin to pyrene-labeled tropomyosin. J Biol Chem 266: 6894 - 6903
Jha PK, Sarkar S (1998) A recombinant monocysteine mutant (Ser to Cys-155) of fast skeletal troponin T: identification by cross-linking of a domain involved in a physiologically relevant interaction with troponins C and I. Biochemistry 37: 12253 - 12260
Jha PK, Leavis PC, Sarkar S (1996) Interaction of deletion mutants of troponins I and T: COOHterminal truncation of troponin T abolishes troponin I binding and reduces Ca2+ sensitivity of the reconstituted regulatory system. Biochemistry 35: 16573 - 16580
Johnson JD, Collins JH, Potter JD (1978) Dansylaziridine-labeled troponin C: a fluorescent probe of Ca2+-specific regulatory sites. J Biol Chem 253: 3775 - 3777
Kerrick WGL, Secrist D, Coby R, Lucas S (1976) Development of difference between red and white muscles in sensitivity to Ca" in the rabbit from embryo to adult. Nature 260: 440 - 441
Kobayashi T Grabarek Z, Gergely J, Collins JH (1995) Extensive interactions between troponins C and I. Zero-length cross-linking of troponin I and acetylated troponin C. Biochemistry 34: 10946-10952
Kress M, Huxley HE, Faruqi AR, Hendrix J (1986) Structural changes during activation of frog muscle studies by time-resolved X-ray diffraction. J Mol Biol 188: 325 - 342
Lehrer SS, Geeves M (1998) The muscle thin filament as a classical cooperative/allosteric regulatory system. J Mol Biol 277: 1081 - 1089
Leszyk J, Collins JH, Leavis PC, Tao T (1987) Cross-linking of rabbit skeletal muscle troponin with the photoactive reagent 4-maleimidobenzophenone: identification of residues in troponin I that are close to cysteine-98 of troponin C. Biochemistry 26: 7042 - 7047
Leszyk J, Grabarek Z, Gergely J, Collins J (1990) Characterization of zero-length cross-links between rabbit skeletal muscle troponin C and troponin I: evidence for a direct interaction between the inhibitory region of troponin I and the NH2-terminal, regulatory domains of troponin C. Biochemistry 29: 299 - 304
Leszyk J, Tao T, Nuwaysir L, Gergely 1 (1998) Identification of the photo-cross-linking sites in troponin I with 4-maleidobenzophenone labelled mutant troponin-Cs having single cysteines at positions 158 and 21. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 19: 479 - 490
Liu W, Dotson DG, Lin X, Mullen III JJ, Gonzalez-Gray ML, Lu Q, Putkey JA (1994) The presence but not the sequence of the N-terminal peptide in cardiac TnC is important for function. FEBS Lett 347: 152 - 156
Luo Y, Leszyk J, Qian Y, Gergely J, Tao T (1999) Residues 48 and 82 at the N-terminal hydrophobic pocket of rabbit skeletal muscle troponin-C photo-cross-link to Met121 of troponin-I. Biochemistry 38: 6678 - 6688
Malnic B, Farah CS, Reinach FC (1998) Regulatory properties of the NH,- and COOH-terminal domains of troponin T. J Biol Chem 273: 10594 - 10601
Maytum R, Lehrer SS, Geeves MA (1999) Cooperativity and switching within the three-state model of muscle regulation. Biochemistry 38: 1102 - 1110
McKay RT, Tripet BP, Hodges RS, Sykes BD (1997) Interaction of the second binding region of troponin I with the regulatory domain of skeletal muscle troponin C as determined by NMR spectroscopy. J Biol Chem 272: 28494 - 28500
McKay RT, Pearlstone JR, Corson DC, Gagne SM, Smillie LB, Sykes BD (1998) Structure and interaction site of the regulatory domain of troponin C when complexed with 96-148 region of troponin-I. Biochemistry 37: 12419 - 12430
Medford RM, Nguyen HT, Destree AT, Summers E, Nadal-Ginard B (1984) A novel mechanism of alternative RNA splicing for the developmentally regulated generation of troponin T isoforms from a single gene. Cell 38: 409 - 421
Moncrieffe M, Eaton S, Bajzer Z, Haydock C, Potter JD, Laue TM, Prendergast FG (1999a) Rotational and translational motion of troponin C. J Biol Chem 274: 17464 - 17470
Moncrieffe M, Venyaminov SY, Miller T, Guzman G, Potter JD, Prendergast FG (1999b) Optical spectroscopic characterization of single tryptophan mutants of chicken skeletal troponin C: evidence for inter-domain interaction. Biochemistry 38: 11973 - 11983
Morris EP, Lehrer SS (1984) Troponin-tropomyosin interactions. Fluorescence studies of the binding of troponin, troponin T, and chymotryptic troponin T fragments to specifically labeled tropomyosin. Biochemistry 23: 2214-2220
Moss RL (1992) Ca2+ regulation of mechanical properties of striated muscle. Mechanistic studies using extraction and replacement of regulatory proteins. Circ Res 70: 865 - 884
Ohtsuki I (1979) Molecular arrangement of troponin-T in the thin filament. J Biochem 86: 491 - 497
Ohtsuki I (1999) Calcium ion regulation of muscle contraction: the regulatory role of troponin T. Mol Cell Biochem 190: 33 - 38
Ohtsuki I, Maruyama K, Ebashi S (1986) Regulatory and cytoskeletal proteins of vertebrate skeletal muscle. Adv Protein Chem 38: 1 - 67
Olah GA, Rokop SE, Wang C-LA, Blechner SL, Trewhella J (1994) Troponin I encompasses an extended troponin C in the Ca"-bound complex: a small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering study. Biochemistry 33: 8233 - 8239
Pan B-S, Potter JD (1992) Two genetically expressed troponin T fragments representing the a and ß isoforms exhibit functional differences. J Biol Chem 267: 23052 - 23056
Pan B-S, Gordon AM, Potter JD (1991) Deletion of the first 45 NH2-terminal residues of rabbit skeletal troponin T strengthens binding of troponin to immobilized tropomyosin. J Biol Chem 266: 12432 - 12438
Panavelil T, Guzman G, Jones M, Pan, B-S, Szczesna D, Potter JD (1997) Structural elements of the COOH-terminal region of troponin-T involved in the regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. Biophys J 72: A60
Parry DAD, Squire JM (1973) Structural role of tropomyosin in muscle regulation: analysis of the X-ray diffraction patterns from relaxed and contracting muscles. J Mol Biol 75: 33 - 55
Pearlstone JR, Smillie LB (1978) Troponin T fragments: physical properties and binding to troponin C. Can J Biochem 56: 521 - 527
Pearlstone JR, Smillie LB (1981) Identification of a second binding region on rabbit skeletal troponin-T for alpha-tropomyosin. FEBS Lett 128: 119 - 122
Pearlstone JR, Smillie LB (1985) The interaction of rabbit skeletal muscle troponin-T fragments with troponin-I. Can J Biochem Cell Biol 63: 212 - 218
Pearlstone JR, Sykes BD, Smillie LB (1997) Interactions of structural C and regulatory N domains of troponin C with repeated sequence motifs in troponin I. Biochemistry 36: 7601 - 7606
Perry SV (1998) Troponin T: genetics, properties and function. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 19: 575 - 602
Poole KJV, Lorenz M, Evans G, Rosenbaum G, Holmes KC (1994) The effect of calcium on the regulated thin filament structure. Biophys J 66: A347
Potter JD, Gergely J (1975) The calcium and magnesium binding sites on troponin and their role in the regulation of myofibrillar ATPase. J Biol Chem 250: 4628 - 4633
Potter JD, Sheng Z, Pan B-S, Zhao J (1995) A direct regulatory role for troponin T and a dual role for troponin C in the Ca" regulation of muscle contraction. J Biol Chem 270: 2557 - 2562
Potter JD, Panavelil T, Guzman G, Jones M, Zhao J, Szczesna D (1998) The role of troponin T in the regulation of contraction. Biophys J 74: A143
Ramakrishnan S, Hitchcock-DeGregori SE (1995) Investigation of the structural requirements of the troponin C central helix for function. Biochemistry 34: 16789 - 16796
Ramos CH (1999) Mapping subdomains in the C-terminal region of troponin I involved in its binding to troponin C and to thin filament. J Biol Chem 274: 18189 - 18195
Robertson SP, Johnson JD, Potter JD (1981) The time-course of Ca2+ exchange with calmodulin, troponin, parvalbumin and myosin in response to transient increases in Ca2+. Biophys J 34: 559 - 569
Schaertl S, Lehrer SS, Geeves MA (1995) Separation and characterization of the two functional regions of troponin involved in muscle thin filament regulation. Biochemistry 34: 15890 - 15894
She M, Xing J, Dong WJ, Umeda PK, Cheung HC (1998) Calcium binding to the regulatory domain of skeletal muscle troponin C induces a highly constrained open conformation. J Mol Biol 281: 445 - 452
Sheng Z, Strauss W, Francois JM, Potter JD (1990) Evidence that both Ca2+ specific sites of skeletal muscle TnC are required for full activity. J Biol Chem 265: 21554 - 21559
Sheng Z, Francois JM, Hitchcock-DeGregori SE, Potter JD (1991) Effects of mutations in the central helix of troponin Con its biological activity. J Biol Chem 266: 5711 - 5715
Sheng Z, Pan B-S, Miller T, Potter JD (1992) Isolation expression and mutation of a rabbit skeletal muscle cDNA clone for troponin I. The role of the NH2-terminus of fast skeletal muscle TnI in its biological activity. J Biol Chem 267: 25407 - 25413
Shiraishi F, Yamamoto K (1994) The effect of partial removal of troponin I and C on the Ca2+-sensitive ATPase activity of rabbit skeletal myofibrils. J Biochem 115: 171 - 173
Smillie LB, Golosinska K, Reinach FC (1988) Sequences of complete cDNAs encoding four variants of chicken skeletal muscle troponin T. J Biol Chem 263: 18816 - 18820
Smith L, Greenfield NJ, Hitchcock-DeGregori SE (1994) The effects of deletion of the aminoterminal helix on troponin C function and stability. J Biol Chem 269: 9857 - 9863
Smith L, Greenfield NJ, Hitchcock-DeGregori SE (1999) Mutations in the N- and D-helices of the N-domain of troponin C affect the C-domain and regulatory function. Biophys J 76: 400 - 408
Squire JM, Morris EP (1998) A new look at thin filament regulation in vertebrate skeletal muscle. FASEB J 12: 761 - 771
Stefancsik R, Jha PK, Sarkar S (1998) Identification and mutagenesis of a highly conserved domain in troponin T responsible for troponin I binding: potential role for coiled coil interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 957 - 962
Stone DB, Timmins PA, Schneider DK, Krylova I, Ramos CHI, Reinach FC, Mendelson RA (1998) The effect of regulatory Ca2+ on the in situ structures of troponin C and troponin I: a neutron scattering study. J Mol Biol 281: 689 - 704
Strynadka NC, Chernaia M, Sielecki AR, Li MX, Smillie LB, James MNG (1997) Structural details of a calcium-induced molecular switch: X-ray crystallographic analysis of the calcium-saturated N-terminal domain of troponin C at 1.75-A resolution. J Mol Biol 273: 238 - 255
Syska H, Wilkinson JM, Grand RJA, Perry SV (1976) The relationship between biological activity and primary structure of troponin I from white skeletal muscle of the rabbit. Biochem J 153: 375 - 387
Szczesna D, Guzman G, Miller T, Zhao J, Farokhi, K, Ellemberger H, Potter JD (1996) The role of the four Ca2+ binding sites of troponin C in the regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. J Biol Chem 271: 8381 - 8836
Szczesna D, Zhang R, Zhao J, Jones M, Potter JD (1999) The role of the N- and C-terminal domains of the inhibitory region of TnI in the regulation of contraction. J Biol Chem 274: 29536 - 29542
Talbot JA, Hodges RS (1979) Synthesis and biological activity of an icosapeptide analog of the actomyosin ATPase inhibitory region of troponin I. J Biol Chem 254: 3720 - 3723
Tripet B, Van Eyk JE, Hodges RS (1997) Mapping of a second actin-tropomyosin and second troponin C binding site within the C terminus of troponin I, and their importance in the Caz+-dependent regulation of muscle contraction. J Mol Biol 271: 728 - 750
Van Eyk JE, Kay CM, Hodges RS (1991) A comparative study of the interactions of synthetic peptides of the skeletal and cardiac troponin I inhibitory region with skeletal and cardiac troponin C. Biochemistry 30: 9974 - 9981
Van Eyk JE, Thomas LT, Tripet B, Wiesner RJ, Pearlstone JR, Farah CS, Reinach FC, Hodges RS (1997) Distinct regions of troponin I regulate Ca2+-dependent activation and Ca2+ sensitivity of the acto-S1-Tm ATPase activity of the thin filament. J Biol Chem 272: 10529 - 10537
Vassylyev DG, Takeda S, Wakatsuki S, Maeda K, Maeda Y (1998) Crystal structure of troponin C in complex with troponin I fragment at 2.3-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 4847 - 4852
Wang J, Jin J-P (1998) Conformational modulation of troponin T by configuration of the NH2-terminal variable region and functional effects. Biochemistry 37: 14519 - 14528
Wang CK, Liao R, Cheung HC (1993) Rotational dynamics of skeletal muscle troponin C. J Biol Chem 268: 14671 - 14677
White SP, Cohen C, Phillips JN Jr (1987) Structure of co-crystals of tropomyosin and troponin. Nature 325: 826 - 828
Zot HG, Potter JD (1982) A structural role for the Ca2+-Mg' sites of Troponin C (TnC) in the regulation of muscle contraction: preparation and properties of TnC-depleted myofibrils. J Biol Chem 257: 7678 - 7683
Zot AS, Potter JD (1987) Structural aspects of troponin-tropomyosin regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. Annu Rev Biophys Chem 16: 535 - 559
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2002 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Szczesna, D., Potter, J.D. (2002). The Role of Troponin in the Ca2+-Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Contraction. In: Thomas, D.D., Dos Remedios, C.G. (eds) Molecular Interactions of Actin. Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation, vol 36. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-46558-4_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-46558-4_13
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-08641-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-46558-4
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive