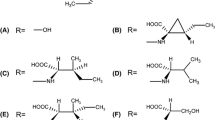
Abstract
It is customary to include under the name of phytotoxins those microbial metabolites that, with the exclusion of enzymes, damage plants at low concentrations. Many plant pathogenic bacteria and fungi produce phytotoxins in culture, but the potential role of these metabolites in pathogenesis has been seldom demonstrated. Essential conditions for attributing the function of disease determinants are: a) the demonstration that the toxin occurs in infected plants, b) the ability of the toxin to reproduce at least a portion of the syndrome when placed in a healthy plant.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aducci, P., Ballio, A., Crosetti, G. and Federico, R. (1980a) Fusicoccin receptors. Evidence for endogenous ligand. Planta 148: 208–210.
Aducci, P., Federico, R. and Ballio, A. (1980b) Interaction of a high molecular weight derivative of fusicoccin with plant membranes. Phytopathol. Mediter. 19: 187–188.
Aducci, P., Ballio, A., Fiorucci, L. and Simonetti, E. (1984) Inactivation of solubilised fusicoccin binding sites by endogenous plant hydrolases. Planta 160: 422–427.
Aducci, P., Ballio, A., Evidente, A., Federico, R., Iasiello, I., Marra, M. and Randazzo, G. (1985) On the reported occurrence of a fusicoccin conjugate in maize cobs. Phytochemistry 24: 1097–1099.
Aducci, P., Ballio, A., Blein, J.-P., Fullone, M.R., Rossignol, M. and Scalla, R. (1988) Functional reconstitution of a proton-translocating system responsive to fusicoccin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 7849–7851.
Aducci, P., Cozzella, M. L., Di Giorgio, D., Fogliano, V. and Marra, M. (1992) Cercospora beticola toxin: a reassessment of some in vitro effects. Plant Sci. 84: 53–57.
Aducci, P., Ballio, A., Fogliano, V., Fullone, M.R., Marra, M. and Proietti, N. (1993) Purification and photoaffinity labeling of fusicoccin receptors from maize. Europ. J. Biochem. 214: 339–345.
Aducci, P., Marra, M., Fogliano, V. and Fullone, M.R. (1995) Fusicoccin receptors: perception and transduction of the fusicoccin signal. J. Exp. Bot. 46: 1463–1478.
Aitken, A., Collinge, D.B., van Heusden, B.P H, Isobe, T., Roseboom P.H., Rosenfeld, G. and Sol, J. (1992) 14-3-3 proteins: a highly conserved, widespread family of eucaryotic proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 17: 498–501.
Aldridge, D.C. and Turner, V.B. (1970) 9-hydroxyl-prehelminthosphorol, a metabolite of Cochliobolus (Helminthosporium) sativus. J. Chem. Soc. (C): 686–688.
Arnone, A., Nasini, G., Merlini, L., Ragg, E. and Assante, G. (1993) Secondary mould metabolites. Part 41. Structure and biosynthesis of Cercospora beticola toxin (CBT). J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1: 145–151.
Assante, G., Locci, R., Camarda, L., Merlini, L. and Nasini, G. (1977) Screening of the genus Cercospora for secondary metabolites. Phytochemistry 16: 243–246.
Auriol, P., Strobel, G., Pio Beltran, J. and Gray, G. (1978) Rynchosporoside, a host-selective toxin produced by Rhynchosporium secalis., the causal agent of scald disease of barley. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75: 4339–4343.
Ayesu-Offei, E.N. and Clare, B.G. (1971) Symptoms of scald disease induced by toxic metabolites of Rhynchosporium secalis. Austr. J. Biol. Sci 24: 169–174.
Babakov, A.V., Bartova, L.M., Galina, U., Oganian, R.R., Voblikova, V.D., Maysurian, A.N., Dridze, I.L. and Muromtsev, G.S. (1994) Endogenous fusicoccin-like ligand revealed in higher plants by radioreceptor and radioimmunoassays. FEBS Lett. 351: 243–245.
Ballio, A., Chain, E B., De Leo, P., Erlanger, B.F., Mauri, M. and Tonolo, A. (1964) Fusicoccin: a new wilting toxin produced by Fusicoccum amygdali Del. Nature 203: 296.
Ballio, A., Brufani, M., Casinovi, C.G., Cerrini, S., Fedeli, W., Pellicciari R., Santurbano, B. and Vaciago, A. (1968a) The structure of fusicoccin. Experientia 24: 631–635.
Ballio, A., Carilli, A., Santurbano, B. and Tuttobello, L. (1968b). Produzione di fusicoccina in scala pilota. Annali dell’ Istituto Superiore di Sanita 4: 317–332.
Ballio, A., Federico, R. and Scalorbi, D. (1981) Fusicoccin structure-activity relationships: In vitro binding to microsomal preparations of maize coleoptiles Physiol. Plant. 52: 476–481.
Barash, I., Mor, H., Netzer, D. and Kashman, Y. (1981) Production of zinniol by Althernaria carthami and its phytotoxic effect on carrot. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 19: 7–16.
Barrow, K.D., Barton, D.H.R., Chain, E.B., Ohnsorge, U.V.F. and Thomas R. (1968) The constitution of fusicoccin. Chem. Comm. 1198–1200.
Barrow, K.D., Barton, D.H.R., Chain, E.B., Ohnsorge, U.V.F. and Thomas, R. (1971) The constitution of fusicoccin. J. Chem. Soc. (C) 1265–1273.
Beffagna, N., Cocucci, S. and Marre, E. (1977) Stimulating effect of fusicoccin on K–activated ATPase in plasma-lemma preparations of higher plant tissue. Plant Sci. Lett. 8: 91–98.
Betina, V. and Murin, A. (1964) Inhibition of mitotic activity in root tips of Vicia faba by the antibiotic cyanein. Cytologia (Tokyo) 29: 370–374.
Betina, V., Nemec, P., Dobias, J. and Barath, Z. (1962) Cyanein, a new antibiotic from Penicillium cyaneum. Folia Microbiol. Prague 7: 353–357.
Betina, V., Nemec, P. and Barath, Z. (1963) Growth inhibition of Allium cepa roots by the antibiotic cyanein. Naturwissenschaften 50: 696.
Blein, J.-P., Bourdil, I., Rossignol, M. and Scalla, R. (1988) Cercospora beticola toxin inhibits vanadate- sensitive H+ transport in corn root membrane vesicles. Plant Physiol. 88: 429–434.
Blum, W., Key, G. and Weiler, E.W. (1988) ATPase activity in plasmalemma-rich vesicles isolated by aqueous two-phase partitioning from Vicia faba mesophyll and epidermis: characterization and influence of abscisic acid and fusicoccin. Physiol. Plant. 72: 297–287.
Briining, A., Ishikawa, T., Kneusel, R.E., Matern, U., Lottspeich, F. and Wieland, F.T. (1992) Brefeldin A binds to glutathione S–transferase and is secreted as glutathione and cysteine conjugates by Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Biol. Chem. 267 (11): 7726–7732.
Camoni, L., Di Giorgio, D., Marra, M., Aducci, P. and Ballio A. (1995) Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae phytotoxin reversibly inhibit the the plasma membrane H+-ATPase and disrupt unilamellar liposomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 214: 118–124.
Carlson, H., Nilsson, P., Jansson, H.B. and Odham, G. (1991) Characterization and determination of prehelmin-thosphorol, a toxin from the plant pathogenic fungus Bipolaris sorokiniana, using liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Microbiol. Meth. 3: 259–269.
Chain, E.B., Mantle, P.G. and Milborrow, B.V. (1971) Further investigations on the toxicity of fusicoccins. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1: 495–514.
Che, F.S., Kasamo, K, Fukuchi, N., Isogai, A. and Suzuki, A. (1992) Bacterial phytotoxins, syringomycin, syrin- gostatin and syringotoxin exert their effect on the plasma membrane H+-ATPase partly by a detergent-like action and partly by inhibition of the enzyme. Physiol. Plant. 86: 818–824.
Cotty, P.J. and Misaghi, I.J. (1984) Zinniol production by Alternaria species. Phytopathology 74: 785–788.
Cotty, P.J., Misaghi, I.J. and Hine, R.B. (1983) Production of zinniol by Alternaria tagetica and its phytotoxic effect on Tagetes erecta. Phytopathology 73: 1326–1328.
Daly, J.M. and Knoche, H.W. (1982) The chemistry and biology of pathotoxins exibiting host–selectivity. In: D.S. Ingram and P.H. Williams (eds): Advances in Plant Pathology, Vol. 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 83–138.
Daub, M.E. and Ehrenshaft, M. (1993) The photoactivated toxin cercosporin as a tool in fungal photobiology. Physiol. Plant. 89: 227–236.
de Boer, A.H. and Korthout, H. (1996) 14-3-3 homologues play a central role in fusicoccin signal transduction pathway. J. Plant Growth Regul. 18: 99–105.
de Boer, A.H, Watson, B.A and Cleland, R.E. (1989) Purification and identification of the fusicoccin binding protein from oat root plasma membrane. Plant Physiol. 89: 250–259.
De Mayo, P., Spencer, E.Y. and White, R.W. (1961) Helminthosporal the toxin from Helminthosporium sativum I. Isolation and characterization. Can. J. Chem. 39: 1608–1612.
De Mayo, P., Williams, R.E. and Spencer, E.Y. (1965) Terpenoids VIII, the immediate precursors of helminthos-phoral and helminthosphorol. Can. J. Chem. 43: 1357–1365.
De Michelis, M.I., Rasi-Caldogno, F., Pugliarello, M.C. and Olivari, C. (1991) Fusicoccin binding to its plasma membrane receptor and activation of the plasma membrane H+–ATPase. II. Stimulation of H+-ATPase in a plasma membrane fraction purified by phase–partitioning. Bot. Acta 104: 265–271.
De Vetten, N.C., Lu, G. and Ferl, R.G. (1992) A corn protein associated with the G–box binding complex has homology to brain regulatory proteins. Plant Cell 4: 1295–1307.
Di Giorgio, D., Camoni, L. and Ballio, A. (1994) Toxins of Pseudomonas syringae pv syringae affect –transport across the plasma membrane of maize. Physiol. Plant. 91: 741 –746.
Dohrmann, U., Hertel R., Pesci, P., Cocucci, S.M., Marre, E., Randazzo, G. and Ballio A. (1977) Localization of in vitro binding of fungal toxin fusicoccin to plasma-membrane-rich fractions from corn coleoptiles. Plant Sci. Lett. 9: 291–299.
Donaldson, J.G., Lippincott–Schwartz, J., Bloom, G.S., Kreis, T.E. and Klausner R.D. (1990) Dissociation of a 110–kD peripheral membrane protein from the Golgi apparatus is an early event in brefeldin A action. J. Cell Biol. Ill: 2295–2306.
Donaldson, J.G., Finazzi, D. and Klausner, R.D. (1992) Brefeldin A inhibits Golgi membrane-catalysed exchange of guanine nucleotide onto ARF protein. Nature 360: 350–352.
Driouich, A., Zhang, G.F. and Staehelin, A.L. (1993) Effect of Brefeldin A on the structure of the Golgi apparatus and on the synthesis and secretion of proteins and polysaccharides in sycamore maple ( Acer pseudoplatanus) suspension-cultured cells. Plant Physiol. 101: 1336–1343.
Ducrot, P.-H., Milat, M.–L., Blein, J.-P. and Lallemand, J.-Y. (1994) The yellow toxins produced by Cercospora beticola. Revised structures of beticolin 1 and 3. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Comm. 2215–2216.
Feyerabend, M and Weiler, EW. (1988) Characterization and localization of fusicoccin binding sites in leaf tissues probed with a novel radioligand. Planta 174: 115–122.
Feyerabend, M. and Weiler, E.W. (1989) Photoaffinity labeling and partial purification of the putative plant recep¬tor for the fungal wilt–inducing toxin, fusicoccin. Planta 178: 282–290.
Fujiwara, T., Oda, K., Yokota, S., Takatsuki, A. and Ikehara, Y. (1988) Brefeldin A causes disassembly of the Golgi complex and accumulation of secretory proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 18545–18552.
Garbary, D.J. and Phillips, D. (1993) Cell wall deposition in the red alga Ceramium strictum-Are microtubules involved ? Am. J. Bot. 80 (suppl): 24.
Gomez, L. and Chrispeels, M.J. (1993) Tonoplast and soluble vacuolar proteins are targeted by different mechanisms. Plant Cell 5: 1113–1124.
Graniti, A. (1962) Azione fitotossica di Fusicoccum amygali Del. su mandorlo (Prunus amygdali St.). Phytopathol. Mediter. 1: 182–185.
Graniti, A. (1964) Qualche dato di fitotossicita della ‘fusicoccina A’, una tossina prodotta in vitro da Fusicoccum amygdali. Phytopathol. Mediter. 3: 125–128.
Graniti, A., Ballio, A. and Marre, E. (1994) Fusicoccum (Phomopsis) amygdali. In: U.S Sing, K. Kohmoto and R.P. Singh (eds): Pathogenesis and Host Specificity in Plant Diseases, Vol. 2., Elsevier, Oxford, pp 103 -117.
Hahn M., Jiingling S. and Knogge, W. (1993) Cultivar-specific elicitation of barley defense reactions to the phytotoxic peptide NIP1 from Rhynchosporium secalis. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 6: 745–754.
Harri, E., Loeffler, W., Sigg, H.P., Stahelin, H. and Tamm, C. (1963) Uber die Isolierung neuer Stoffwechselpro-dukte aus Penicillium brefeldianum Dodge. Helvet. Chim. Acta. 46: 1235–1243.
Henderson, J., Satiat–Jeunemaitre, B., Napier, R. and Hawes, C. (1994) Brefeldin A-induced disassembly of the Golgi apparatus is followed by disruption of the endoplasmic reticulum in plant cells. J. Exp. Bot. 45 (279): 1347–1351.
Hollander-Czytko, H. and Weiler, E.W. (1994) Isolation and biochemical characterization of fusicoccin-insensitive variant lines of Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Planta 195: 188–194.
Holwerda, B.C., Padgett, H.S. and Rogers, J.C. (1992) Proaleurain vacuolar targeting is mediated by short contiguous peptide interactions. Plant Cell 4: 307–318.
Ichimura, T., Isobe, T., Okuyama, T., Yamauchi, T. and Fujisawa, H. (1987) Brain 14-3-3 protein is an activator protein that activates tryptophan 5–monooxygenase and tyrosine 3–monooxigenase in the presence of Ca2+, calmodulin–dependent protein kinase II. FEBS Lett. 219: 79–82.
Ichimura, T., Isobe, T., Okuyama, T., Takahashi, N., Araki K, Kuwano, R. and Takahashi, Y. (1988) Molecular cloning of cDNA coding for brain-specific 14-3-3 protein, a protein kinase–dependent activator of tyrosine and tryptophan hydroxylases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 7084–7088.
Jalal, M.A.F., Hossain, M.B., Robeson, D.J. and van der Helm, D (1992) Cercospora beticola phytotoxins: cebet-ins that are photoactive, Mg2+-binding, chlorinated anthraquinone-xanthone conjugates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114: 5967–5971.
Johansson, F., Sommarin, M. and Larsson, C. (1993) Fusicoccin activates the plasma membrane H+ATPase by a mechanism involving the C–terminal inhibitory domain. Plant Cell 5: 321–327.
Jones, A.M. and Herman E.M. (1993) KDEL–containing auxin-binding protein is secreted to the plasma membrane and cell wall. Plant Physiol. 101: 595–606.
Kauss, H., Jeblick, W. and Conrath, U. (1992) Protein kinase inhibitor K–252a and fusicoccin induce similar initial changes in ion transport of parsley suspension cells. Physiol. Plant. 85: 483–488.
Klausner, R.D., Donaldson, J.D. and Lippincott-Schwartz, J. (1992) Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J. Cell Biol. 116(5): 1071–1080.
Kono, Y., Knoche, H.W. and Daly, J.M. (1981) Structure: fungal host-specific. In: R.D. Durbin (ed.): Toxins in Plant Disease, Academic Press, New York, pp 221 –257.
Korthout, H. and de Boer AH. (1994) A fusicoccin binding protein belongs to the family of 14-3-3 brain protein homologs. Plant Cell 6: 1681–1692.
Korthout, H., Van der Hoeven, P., Wagner, M.J., Van Hunnik, E. and de Boer A.H. (1994) Purification of the fusicoccin-binding protein from oat root plasma membrane by affinity chromatography with biotinylated fusicoccin. Plant Physiol. 105: 1281–1288.
Lanfermeijer, F.C. and Prins, H.B.A. (1994) Modulation of H+ATPase activity by fusicoccin in plasma membrane vesicles from oaiAvena sativa L. roots. Plant Physiol. 104: 1277–1285.
Liljeroth, E., Franzon-Almgren, I. and Gustavsson, M. (1994) Effect of prehelminthosphorol a phytotoxin produced by Bipolaris sorokiniana on barley roots. Can. J. Bot. 72: 558-563.
Lippincott–Schwartz, J., Yuan, L.C., Bonifacino, J.S. and Klausner R.D. (1989) Rapid redistribution of Golgi proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: evidence for membrane cycling from Golgi to ER. Cell 56: 807–813.
Lu, G., De Lisle, A., de Vetten, N.C. and Ferl, R. (1992) Brain protein in plants: an Arabidopsis homolog to neurotransmitter pathway activators is part of a DNA binding complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 11490– 11494.
Macri, F. and Vianello, A. (1979a) Photodynamic activity of cercosporin on plant tissues. Plant Cell Environ. 2: 267–271.
Macri, F. and Vianello, A. (1979b) Inhibition of K+ uptake, H+extrusion and Reactivated ATPase, and depolariza¬tion of transmembrane potential in plant tissue treated with Cercospora beticola toxin. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 15: 161–170.
Macri, F., Vianello, A., Cerana, R. and Rasi-Caldogno, F. (1980) Effects of Cercospora beticola toxin on ATP level of maize roots and on the phosphorylating activity of isolated pea mitochondria. Plant Sci. Lett. 18: 207– 214.
Macri, F., Dell’ Antone, P. and Vianello, A. (1983) ATP-dependent proton uptake inhibited by Cercospora beticola toxin in pea stem microsomal vesicles. Plant Cell Environ. 6: 555–558.
Marra, M., Aducci, P. and Ballio, A. (1988) Immunoaffinity chromatography of fusicoccin. J. Chromatogr. 440: 47–51.
Marra, M., Ballio, A., Fullone, M.R. and Aducci, P. (1992) Some properties of a functional reconstituted plasma– lemma H+-ATPase activated by fusicoccin. Plant Physiol. 98: 1029–1034.
Marra, M., Fullone, M.R., Fogliano, V., Masi, S., Mattei, M., Pen, J. and Aducci, P. (1994) The 30 kD protein present in purified fusicoccin receptor preparation is a 14-3-3–like protein. Plant Physiol. 106: 1497–1501.
Marra, M., Ballio, A., Battirossi, P., Fogliano, V., Fullone, M.R., Slayman, C.L. and Aducci, P. (1995) The fungal H+–ATPase from Neurospora crassa reconstituted with the fusicoccin receptors senses fusicoccin signal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 1599–1603.
Marra, M„ Fogliano, V., Zambardi, A., Fullone, M.R., Nasta, D. and Aducci, P. (1996) The H+-ATPase purified from maize root plasma membranes retains fusicoccin in vivo activation. FEBS Lett. 382: 293–296.
Marre, E. (1979) Fusicoccin: a tool in plant physiology. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 30: 273–288.
Mazars, C. and Auriol, P. (1983) Production in vitro et in vivo de rhynchosporosides par Rhynchosporium secalis. Comp. Rend. Acad. Sci. 296: 681–683.
Mazars, C., Auriol, P., Rafenomananjava, D. (1983) Rhynchosporosides binding by barley proteins. Phytopathol. Z. 107: 1–8.
Mazars, C., Hapner, K.D. and Strobel, G.A. (1984) Isolation and partial characterization of a phytotoxic glycoprotein from culture filtrates of Rhynchosporium secalis. Experientia 40: 1244–1247.
Mazars, C., Rossignol, M. and Auriol, P. (1987) Purification par HPLC de glycoproteines phytotoxiques produites par Rhynchosporium secalis ( Oud) Davis. Bio-Sci. 6: 63–68.
Mazars, C., Rossignol, M., Marquet, P.Y. and Auriol, P. (1989a) Reassessment of toxic glycoprotein isolated from Rhynchosporium secalis (Oud) Davis culture filtrates. Plant Sci. 62: 165–174.
Mazars, C., Poletti, P., Petitprez, M., Albertini, L. and Auriol, P. (1989b) Plugging of the xylem vessel of barley induced by a high molecular weight phytotoxic glycoprotein from Rhynchosporium secalis. Can. J. Bot. 67: 2077–2084.
Mazars, C., Lafitte, C., Marquet, P.Y., Rossignol, M. and Auriol, P. (1990) Elicitor-like activity of the toxic glycoprotein isolated from Rhynchosporium secalis ( Oud) Davis culture filtrates. Plant Sci. 69: 11–17.
Meyer, C., Waldkotter, R., Sprenger, A., Schlosser, U.G., Lether, M. and Weiler, E.W. (1993) Survey of the taxonomic and tissue distribution of microsomal binding sites for the non-host selective fungal phytotoxin, fusicoc¬cin. Z. Naturforsch. 48C: 595–602.
Mikes, V., Milat, M.-L., Pugin, A. and Blein J.-P. (1994a) Cercospora beticola toxins. VII. Fluorometric study of their interactions with biological membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1195: 124–130.
Mikes, V., Lavernet, S., Milat, M.-L., Collange, E., Paris, M. and Blein J.-P. (1994b) Cercospora beticola toxins. Part VI: preliminary studies of protonation and complexation equilibria. Biophys. Chem. 52: 259–265.
Milat, M.-L., Fraichard, A., Blein, J.–P. and Pugin, A. (1992a) Effects of beticolin, the yellow Cercospora beticola toxin on the plasmalemma ATPase activity and on the tonoplast ATPase and pyrophosphatase activities. In: Abstracts from the Ninth International Workshop on Plant Membrane Biology, Monterey, California, July 19– 24, 1992, p. 222.
Milat, M.-L., Prange, T., Ducrot, P.-H., Tabet, J.-C., Einhorn, J., Blein, J.-P. and Lallemand J.–Y. (1992b). Struc¬tures of the beticolins, the yellow toxins produced by Cercospora beticola. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114: 1478– 1479.
Milat, M.-L., Blein, J.-P., Einhorn, J., Tabet, J.-C., Ducrot, P.-H. and Lallemand, J.-Y. (1993) The yellow toxins produced by Cercospora beticola. Part II: isolation and structure of beticolins 3 and 4. Tetrahedron Lett. 34: 1483–1486.
Misumi, Y., Misumi, Y., Miki, K., Taratswuki, A., Tamura, G. and Ikehara, Y. (1986) Novel blockade by Brefeldin A of intracellular transport of secretory proteins in cultured rat hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 261: 11398–11403.
Moore, P.V. and Perez, V.J. (1967) Physiological and biochemical aspects of nervous integration. In: F.D. Carlson (ed.): Symposium on Physiological and Biochemical Aspects of Nervous Integration. Prentice Hall, Woods Hole, pp 343–359.
Muromtsev, G.S., Kobrina, N.S., Voblikova, V.D. and Koreneva, V.M. (1980) Fusicoccin-like substance in maize ears. Izv. Akad. Nauk. SSSR. Biol. 2: 897–902.
Muromtsev, G.S., Voblikova, V.D., Kobrina, N.S., Koreneva, V.M., Sadovskaya, V.L. and Stolpakova, V.V. (1989) Fusicoccin in higher plants. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanzen 185: 261–268.
Muromtsev, G.S., Voblikova, V.D., Kobrina, N.S., Koreneva, V.M., Krasnopolskaya, L.M. and Sadovskaya, V.L. (1994) Occurrence of fusicoccanes in plants and fungi. J. Plant Growth Regul. 13: 39–49.
Narula, N., McMorrow, I., Plopper, G., Doherty, J., Matlin, K., Burke, B. and Stow, J. (1992) Identification of a 200 kD, Brefeldin-sensitive protein on Golgi membranes. J. Cell Biol 117: 27–38.
Nilsson, P., Akesson, H., Jansson, H.B. and Odham, G. (1993) Production and release of the phytotoxin prehel-minthosphorol by Bipolaris sorokiniana during growth. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 102: 91–98.
Nukina, M. and Marumo, S. (1976) Aversion factors, antibiotics among different strains of a fungal species aversion factors of Cochliobolus setarie. Agricult. Biol Chem. 40: 2121–2123.
Nukina, M., Hattori, H. and Marumo, S. (1975) cw-Sativenediol, a plant growth promoter produced by fungi. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97: 2542–2543.
Oecking, C. and Weiler, E.W. (1991) Characterization and purification of the fusicoccin binding complex from plasma membrane of Commelina communis. Europ. J. Biochem. 199: 685–689.
Oecking, C., Eckerskorn, C. and Weiler E.W. (1994) The fusicoccin receptor of plants is a member of the 14–3–3 superfamily of eukaryotic regulatory proteins. FEBS Lett. 352: 163–166.
Olbe, M., Sommarin, M., Gustavsson, M. and Lundborg, T. (1995) Effect of the fungal pathogen Bipolaris sorokiniana toxin prehelminthosphorol on barley roots plasma membrane vesicles. Plant Pathol 44: 625–635.
Orci, L., Tagaya, M., Amherdt, M., Perrelet, A., Donaldson, J.D., Lippincott–Schwartz, J., Klausner, R.D. and Rothman, J.E. (1991) Brefeldin A, a drug that blocks secretion, prevents the assembly of non–clathrin–coated buds on Golgi cisternae. CW/64: 1183–1195.
Pena–Rodriguez, L.M. Armingeon, N.A. and Chilton, W.S. (1988) Toxins from weed pathogens. I. Phytotoxins from a Bipolaris pathogen of Johnson grass. J. Nat. Prod. 51: 821–828.
Pesci, P., Tognoli, L., Beffagna, M. and Marre, E. (1979) Solubilization and partial purification of a fusicoccin- receptor complex from maize microsomes. Plant Sci. Lett. 15: 313–322.
Pio Beltran, J. and Strobel, G. (1978) Rhynchosporoside binding proteins of barley. FEBS Lett. 96: 34–36.
Prange, T., Neuman, A., Milat, M.–L., Blein, J.–P. (1994) The yellow toxin produced by Cercospora beticola. Structure of beticolins 2 and 4. Acta Cristallogr. B51: 308–314.
Rasi-Caldogno, F. and Pugliarello, M.C. (1985) Fusicoccin stimulates the H+ATPase of plasmalemma in isolated membrane vesicles from radish. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 133: 280–285.
Rasi-Caldogno, F., De Michelis, M.I., Pugliarello, M.C. and Marre, E. (1986) H+-pumping driven by the plasma membrane ATPase in membrane vesicles from radish: stimulation by fusicoccin. Plant Physiol 82: 121–125.
Rasi-Caldogno, F., Pugliarello, M.C., Olivari, C. and De Michelis, M.I. (1993) Controlled proteolysis mimicks the effect of fusicoccin on the plasma membrane H+ATPase. Plant Physiol 103: 391–396.
Robeson, D.J. and Jalal, M.A.F. (1993) A Cercospora isolate from soybean roots produces cebetin B and cer– cosporin. Phytochemistry 33: 1546–1548.
Robinson, M.S. and Kreis, T.E. (1992) Recruitment of coat protein onto Golgi membranes in intact and permeabi– lized cells: Effects of Brefeldin A and G protein activators. Cell 69: 129–138.
Rossignol, M., Bourdil, I., Santoni, V. and Blein, J.-P. (1989) Interaction between plasma membrane H+ ATPase and phytotoxins: use of reconstituted systems. In: J. Dainty, M.I. De Michelis, E. Marre and F. Rasi-Caldogno (eds): Plant Membrane Transport: the Current Position. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 379–384.
Rubinstein, B. (1982) Regulation of H+ excretion. Role of protein released by osmotic shock. Plant Physiol 69: 945–49.
Rutten, T.L.M. and Knuiman, B. (1993) Brefeldin A effects on tobacco pollen tubes. Europ. J. Cell Biol 69: 129–138.
Satiat-Jeunemaitre, B. and Hawes, C. (1992a) Redistribution of a Golgi glycoprotein in plant cells treated with Brefeldin A. J. Cell Sci. 103: 1153–1166.
Satiat-Jeunemaitre, B. and Hawes, C. (1992b) Reversible dissociation of the plant Golgi apparatus by Brefeldin A. Biol Cellul. 74: 325–328.
Satiat–Jeunemaitre, B. and Hawes, C. (1993) The distribution of secretory products in plant cells is affected by Brefeldin A. Cell Biol Int. 17: 183–193.
Satiat-Jeunemaitre, B. and Hawes, C. (1994) G.A.T.T. ( A general agreement on traffic and transport) and Brefeldin A in plant cells. Plant Cell 6: 463–467.
Schaller, G.E. and Sussmann, M.R. (1988) Phosphorylation of the plasma membrane H+ATPase of oat roots by a calcium-stimulated protein kinase. Planta 173: 509–518.
Scheffer, R.P. and Pringle, R.B. (1964) Uptake of Helminthosporium victoriae toxin by oat tissue. Phytopathology 54: 832–835.
Schulz, S., Oelgemoller, E. and Weiler, E.W. (1990) Fusicoccin action in cell suspension culture of Corydalis sempervirens. Planta 183: 83–91.
Schlosser, E. (1971) The Cercospora beticola toxin. Phytopathol Mediter. 10: 154–158.
Sekler, I., Weiss, M. and Pick, U. (1994) Activation of the Dunaliella acidophila plasma membrane H+ATPase by trypsin cleavage of a fragment that contain a phosphorylation site. Plant Physiol 105: 1125–1132.
Simon–Plas, F., Gomes, E., Milat, M.-L. and Blein J.-P. (1995) Some aspects of the inhibition of maize roots plasmalemma H+-ATPase by beticolin-1. In: Abstracts from the 10th International Workshop on Plant Mem¬brane Biology, Regensburg, Germany, August 6–11, 1995, P 11.
Singleton, V.L., Bohonos, N. and Ullstrup, A.J. (1958) Decumbin, a new compound from a species of Penicillium. Nature 181: 1072–1073.
Starratt, A.N. (1968) Zinniol: a major metabolite of Alternaria zinniae. Can. J. Chem. 46: 767–770.
Stierle, A., Hershenhorn, J. and Strobel, G. (1993) Zinniol-related phytotoxins from Alternaria cichorii. Phytochemistry 32: 1145–1149.
Stoessl, A. (1981) Structure and biogenetic relations: fungal nonhost-specific. In: R. D. Durbin (ed.): Toxins in Plant Disease, Academic Press Inc., New York, pp 110–219.
Stoessl, C.H., Unwin, J.B. and Stothers, J.B. (1979) Metabolites of Alternaria solani. Part 5. Biosynthesis of altersolanol A and incorporation of altersolanol A-13C into altersolanol B and macrosporin. Tetrahedron Lett. 2481–2484.
Sugawara, F. and Strobel G. (1986) Zinniol, a phytotoxin, is produced by Phoma macdonaldii. Plant Sci. 43: 19–23.
Suzuki, Y.S., Wang, Y. and Takemoto, J.Y. (1992) Syringomycin-stimulated phosphorilation of the plasma membrane H+ATPase from red beet storage tissue. Plant Physiol. 99: 1314–1320.
Takatsuki, A. and Tamura, G. (1985) Brefeldin A, a specific inhibitor of intracellular translocation of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein: intracellular accumulation of high–mannose type G protein and inhibition of its cell surface expression. Agricult. Biol. Chem. 49: 899–902.
Tamura, S., Sakurai, A., Kainuma, K. and Takai, M. (1965) Isolation of helminthosphorol as a natural plant growth regulator and its chemical structure. Agricult. Biol. Chem. 29: 216–221.
Tamura, G., Ando, K., Suzuki, S., Takatsuki, A. and Arima, K. (1968) Antiviral activity of Brefeldin A and Verrucarin A. J. Antibiot. 21: 160–161.
Thuleau, P., Graziana, A., Rossignol, M., Kauss, H., Auriol, P., Ranjeva, R. (1988) Binding of the phytotoxin zinniol stimulates the entry of calcium into plant protoplast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 5932–5935.
Tietjen, K. and Matern, U. (1984) Induction and suppression of phytoalexin biosynthesis in cultured cells of safflower, Carthamus tinctorius L. by metabolites of Althernaria carthami Chowdhury. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 229: 136–144.
Tietjen, K.G., Schaller, E. and Matern, U. (1983a) Phytotoxin from Alternaria carthami Chowdhury: structural identification and physiological significance. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 23: 387–400.
Tietjen, K.G., Hunkler, D. and Matern, U. (1983b) Differential response of cultured parsley cells to elicitors from two non–pathogenic strains of fungi. I. Identification of induced products as coumarin derivatives. Europ. J. Biochem. 131: 401–407.
Tognoli, L., Beffagna, N., Pesci, P. and Marre, E. (1979) On the relationship between ATPase activity and FC binding capacity of crude and partially–purified microsomal preparations from maize coleoptiles. Plant Sci. Lett. 16: 1–14.
Toker, A., Ellis, C.A., Sellers, L.A., Amess, B. and Aitken, A. (1990) Protein kinase C inhibitor proteins. J. Biochem. 191: 421–429.
Turner, N.C. and Graniti, A. (1969) Fusicoccin, a fungal toxin that opens stomata. Nature 223: 1070.
Turner, N.C. and Graniti, A. (1976) Stomatal response of two almond cultivars to fusicoccin. Physiol. Plant Pathol 9: 175–182.
Vera-Estrella, R., Barkla, B.J., Higgins, V.J. and Blumwald, E. (1994) Plant defense response to fungal pathogen. Plant Physiol 104: 209–215.
Weiler, E.W, Meyer, C., Oecking, C., Feyerabend, M. and Mithofer, A. (1990) The fusicoccin receptor of higher plants In: C. Lamb and R. Beachy (eds): Plant Gene Transfer, Alan R.Liss, New York, pp 153–164.
Weiss, U., Merlini, L. and Nasini, G. (1987) Natural occurring perylenequinones. Prog. Chem. Org. Nat. Prod. 52: 1–71.
Wevelsiep, L., Kogel, K.-H. and Knogge, W. (1991) Purification and characterization of peptides from Rhyncho¬sporium secalis inducing necrosis in barley. Physiol Molec. Plant Pathol 39: 471 –482.
Wevelsiep, L., Rupping, E. and Knogge, W. (1993) Stimulation of barley plasmalemma H+-ATPase by phytotoxic peptides from the fungal pathogen Rhynchosporium secalis. Plant Physiol 101: 297–301.
White, G.A. and Starratt, A.N. (1967) The production of a phytotoxin substance by Alternaria zinniae. Can. J. Bot., 45: 2087–2090.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1997 Birkäuser Verlag Basel/Switzerland
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Aducci, P., Ballio, A., Marra, M. (1997). Phytotoxins as molecular signals. In: Aducci, P. (eds) Signal Transduction in Plants. MCBU Molecular and Cell Biology Updates. Birkhäuser Basel. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-9183-7_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-9183-7_5
Publisher Name: Birkhäuser Basel
Print ISBN: 978-3-0348-9938-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-0348-9183-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive