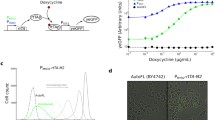
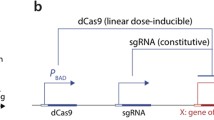
Abstract
Conditional gene expression systems are important tools for the functional analysis of essential genes. Tetracycline (tc)-binding aptamers can be exploited as artificial riboswitches for the efficient control of gene expression by inserting them into the 5′ untranslated region of an mRNA. The ligand-bound form of those mRNAs inhibits gene expression by interfering with translation initiation. In contrast to previous tc-dependent regulatory systems, where tc inhibits or activates transcription upon binding to the repressor protein TetR, the tc-binding aptamer system inhibits translation of the respective mRNA. We describe here a simple and powerful PCR-based strategy which allows easy tagging of any target gene in yeast using a tc aptamer-containing insertion cassette. The expression window can be adjusted with different promoters and protein synthesis is rapidly switched off.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnston, M. and Davis, R.W. (1984) Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 4, 1440–1448
Mountain, H.A., Bystrom, A.S., Larsen, J.T. et al., (1991) Four major transcriptional responses in the methionine/threonine biosynthetic pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 7, 781–803
Belli, G., Gari, E., Aldea, M. et al., (1998) Functional analysis of yeast essential genes using a promoter-substitution cassette and the tetracycline-regulatable dual expression system. Yeast 14, 1127–1138
Belli, G., Gari, E., Piedrafita, L., Aldea, M. et al., (1998) An activator/repressor dual system allows tight tetracycline-regulated gene expression in budding yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 26, 942–947
Gari, E., Piedrafita, L., Aldea, M.et al., (1997) A set of vectors with a tetracycline-regulatable promoter system for modulated gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 13, 837–848
Dohmen, R.J., Wu, P. Varshavsky, A. (1994) Heat-inducible degron: a method for constructing temperature-sensitive mutants. Science 263, 1273–1276
Sanchez-Diaz, A., Kanemaki, M., Marchesi, V. et al., (2004) Rapid depletion of budding yeast proteins by fusion to a heat-inducible degron. Sci. STKE 2004, PL8
Roth, A. and Breaker, R.R. (2009) The structural and functional diversity of metabolite-binding riboswitches. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 78, 305–334
Suess, B. and Weigand, J.E. (2008) Engineered riboswitches: overview, problems and trends. RNA Biol. 5, 24–29
Weigand, J.E. and Suess, B. (2009) Aptamers and riboswitches: perspectives in biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 85, 229–236
Hanson, S., Berthelot, K., Fink, B., et al., (2003) Tetracycline-aptamer-mediated translational regulation in yeast. Mol. Microbiol. 49, 1627–1637
Suess, B., Hanson, S., Berens, C., et al., (2003) Conditional gene expression by controlling translation with tetracycline-binding aptamers. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 1853–1858
Weigand, J.E. and Suess, B. (2007) Tetracycline aptamer-controlled regulation of pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 4179–4185
Kötter, P., Weigand, J.E., Meyer, B., et al., (2009) A fast and efficient translational control system for conditional expression of yeast genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, e120
Guldener, U., Heck, S., Fielder, et al., (1996) A new efficient gene disruption cassette for repeated use in budding yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 2519–2524
Entian, K.D. and Kötter, P. (2007) Yeast Genetic Strain and Plasmid Collections. In: Stansfield, I. and Stark, M.R.J. (eds) Methods in Microbiology Vol. 36, Yeast Gene Analysis. Academic Press Ltd., San Diego.
Meyer, B., Wurm, J.P., Kötter, P., et al., (2010) The Bowen-Conradi syndrome protein Nep1 (Emg1) has a dual role in eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis, as an essential assembly factor and in the methylation of Ψ 1191 in yeast 18S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq931
Itzhaki, R.F. and Gill, D.M. (1964) A Micro-Biuret Method for Estimating Proteins. Anal. Biochem. 9, 401–410
Fraenkel, D.G. (2003) The top genes: on the distance from transcript to function in yeast glycolysis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 6, 198–201
Partow, S., Siewers, V., Bjorn, S., et al., (2010) Characterization of different promoters for designing a new expression vector in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 27, 955–964
David, L., Huber, W., Granovskaia, M., et al., (2006) A high-resolution map of transcription in the yeast genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 5320–5325
Stansfield, I. and Stark, M.R.J. (2007) Yeast Genetics and Strain Construction. In: Stansfield, I. and Stark, M.R.J. (eds) Methods in Microbiology Vol. 36, Yeast Gene Analysis. Academic Press Ltd., San Diego.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Aventis Foundation and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SU402/1-2, SFB579, and the Excellence Cluster: Macromolecular Complexes).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Suess, B., Entian, KD., Kötter, P., Weigand, J.E. (2012). Aptamer-Regulated Expression of Essential Genes in Yeast. In: Lorence, A. (eds) Recombinant Gene Expression. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 824. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-433-9_20
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-433-9_20
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-61779-432-2
Online ISBN: 978-1-61779-433-9
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols