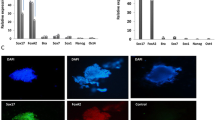
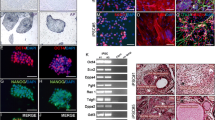
Abstract
Human pancreatic islet transplantation at present is the preferred therapeutic option for type I diabetes treatment. However, this therapy is not widely utilized because of the severe shortage of donor islets. The capacity for self-renewal and differentiation of human embryonic stem (hES) cells makes them a potential new source for generation of functional pancreatic islet cells for treating type I diabetes mellitus. Here, we report a simple and effective protocol, carried out in a serum-free system, which could induce human ES cells to differentiate into functional insulin-producing cells. Activin A was first used in the initial stage to induce definitive endoderm lineage differentiation from human ES cells. And all-trans Retinoic Acid (RA) was then utilized to promote pancreatic differentiation. After maturation in the final induction stage with bFGF and Nicotinamide, the differentiated cells expressed islet specific markers. The secretion of insulin and C-peptide by these cells corresponded to the variations in glucose levels. Our method provides a promising in vitro differentiation model for studying the mechanisms of human pancreas development and illustrates the potential of using human ES cells for the treatment of type I diabetes mellitus.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, et al. (2000) Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 343, 230–238.
Hussain MA, Theise ND. (2004) Stem-cell therapy for diabetes mellitus. Lancet 364, 203–205.
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, et al. (1998) Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 82, 1145–1147.
Cowan CA, Klimanskaya I, McMahon J, et al. (2004) Derivation of embryonic stem-cell lines from human blastocysts. N Engl J Med. 350, 1353–1356.
Assady S, Maor G, Amit M, et al. (2001) Insulin production by human embryonic stem cells. Diabetes 50, 1691–1697.
Brolén G, Heins N, Edsbagge J, et al. (2005) Signals from the embryonic mouse pancreas induce differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into insulin-producing beta-cell-like cells. Diabetes 54, 2867–2874.
Lumelsky N, Blondel O, Laeng P, et al. (2001) Differentiation of embryonic stem cells to insulin-secreting structures similar to pancreatic islets. Science 292, 1389–1394.
Segev H, Fishman B, Ziskind A, et al. (2004) Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into insulin-producing clusters. Stem Cells 22, 265–274.
Hansson M, Tonning A, Frandsen U, et al. (2004) Artifactual insulin release from differentiated embryonic stem cells. Diabetes 53, 2603–2609.
Shi Y, Hou L, Tang F, et al. (2005) Inducing embryonic stem cells to differentiate into pancreatic β cells by a novel three-step approach with activin A and all-trans retinoic acid. Stem Cells 23, 656–662.
Yasunaga M, Tada S, Torikai-Nishikawa S, et al. (2005) Induction and monitoring of definitive and visceral endoderm differentiation of mouse ES cells. Nat Biotechnol. 23(12), 1542–1550.
Jiang W, Shi Y, Zhao D, et al. (2007) In vitro derivation of functional insulin-producing cells from human embryonic stem cells. Cell Res. 17, 333–344.
D’Amour KA, Agulnick AD, Eliazer S, et al. (2005) Efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to definitive endoderm. Nat Biotechnol. 23, 1534–1541.
Maden M. (2001) Role and distribution of retinoic acid during CNS development. Int Rev Cytol. 209, 1–77.
Stafford D, Prince VE. (2002) Retinoic Acid signaling is required for a critical early step in Zebrafish pancreatic development. Curr Biol. 12, 1215–1220.
Jiang W, Bai Z, Zhang D, et al. (2008) Differentiation of mouse nuclear transfer embryonic stem cells into functional pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 51, 1671–1679.
D’Amour KA, Bang AG, Eliazer S, et al. (2006) Production of pancreatic hormone-expressing endocrine cells from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 24, 1392–1401.
Shim JH, Kim SE, Woo DH, et al. (2007) Directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells towards a pancreatic cell fate. Diabetologia 50(6), 1228–1238.
Zhang D, Jiang W, Liu M, et al. (2009) Highly efficient differentiation of human ES cells and iPS cells into mature pancreatic insulin-producing cells. Cell Res. 19(4), 429–438.
Robertson EJ. (1997) Derivation and maintenance of embryonic stem cell cultures. Methods Mol Biol. 75, 173–184.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Shi, Y. (2010). Generation of Functional Insulin-Producing Cells from Human Embryonic Stem Cells In Vitro. In: Ding, S. (eds) Cellular Programming and Reprogramming. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 636. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-691-7_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-691-7_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-60761-690-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-60761-691-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols