Abstract
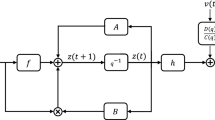
This paper considers the parameter identification of bilinear systems with unknown states, which are disturbed by an autoregressive moving average noise. The hierarchial identification principle is employed to derive new algorithms for interactively estimating the states and parameters via a bilinear state observer. However, the general bilinear state-space model involves many parameters, which causes heavy computational burden. Motivated by this fact, we propose a hierarchical generalized extended least squares (HGELS) algorithm by decomposing the original system into a series of subsystems with small dimensions for enhancing computational efficiency. The performance of the proposed algorithms is illustrated through a numerical example.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ding, F.: System Identification—New Theory and Methods. Science Press, Beijing (2013)
Ding, F.: System Identification—Performances Analysis for Identification Methods. Science Press, Beijing (2014)
Ding, F.: System Identification—Auxiliary Model Identification Idea and Methods. Science Press, Beijing (2017)
Ding, F.: System Identification—Iterative Search Principle and Identification Methods. Science Press, Beijing (2018)
Ding, F.: System Identification—Multi-innovation Identification Theory and Methods. Science Press, Beijing (2016)
Ding, F.: Modern Control Theory. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing (2018)
Nowak, R.D.: Nonlinear system identification. Circuits Syst. Sig. Process. 21(1), 109–122 (2002)
Bruni, C., Dipillo, G., Koch, G.: Bilinear systems: an appealing class of nearly linear systems in theory and applications. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 19(4), 334–348 (1974)
Svoronos, S., Stephanopoulos, G., Rutherford, A.: Bilinear approximation of general non-linear dynamic systems with linear inputs. Int. J. Control 31(1), 109–126 (1980)
Baheti, R., Mohler, R., Spang, H.: Second-order correlation method for bilinear system identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 25(6), 1141–1146 (1980)
Hara, S., Furuta, K.: Minimal order state observers for bilinear systems. Int. J. Control 24(5), 705–718 (1976)
Funahashi, Y.: Stable state estimator for bilinear systems. Int. J. Control 29(2), 181–188 (1979)
Phan, M.Q., Vicario, F., Longman, R.W.: Optimal bilinear observers for bilinear state-space models by interaction matrices. Int. J. Control 88(8), 1504–1522 (2015)
Cheng, D.: Controllability of switched bilinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 50(4), 511–515 (2005)
Li, M.H., Liu, X.M.: The least squares based iterative algorithms for parameter estimation of a bilinear system with autoregressive noise using the data filtering technique. Sig. Process. 147, 23–34 (2018)
dos Santos, P.L., Ramos, J.A., de Carvalho, J.L.M.: Identification of bilinear systems with white noise inputs: an iterative deterministic-stochastic subspace approach. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 17(5), 1145–1153 (2009)
Verdult, V., Verhaegen, M.: Kernel methods for subspace identification of multivariable LPV and bilinear systems. Automatica 41(9), 1557–1565 (2005)
Liu, Y.J., Ding, F., Shi, Y.: An efficient hierarchical identification method for general dual-rate sampled-data systems. Automatica 50(3), 962–970 (2014)
Ding, J., Ding, F., Liu, X.P., Liu, G.: Hierarchical least squares identification for linear SISO systems with dual-rate sampled-data. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 56(11), 2677–2683 (2011)
Ding, F., Chen, T.: Hierarchical identification of lifted state-space models for general dual-rate systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I: Regul. Pap. 52(6), 1179–1187 (2005)
Zhang, X., Xu, L., et al.: Combined state and parameter estimation for a bilinear state space system with moving average noise. J. Franklin Inst. 355(6), 3079–3103 (2018)
Suresh, A., Jha, M.: Automated essay grading using natural language processing and support vector machine. Int. J. Comput. Technol. 5(2), 18–21 (2018)
Murali, V., Chatrapathy, K.: BuyerPlyGround: agriculture trade market using blockchain with machine learning. Int. J. Comput. Technol. 6(5), 31–36 (2019)
Sellami, L., Zidi, S., Abderrahim, K.: Self-adaptative multi-kernel algorithm for switched linear systems identification. Int. J. Model. Ident. Control 31(1), 103–111 (2019)
Xue, J., Liu, F., Bai, J., Hou, T.: Modelling of gene signal attribute reduction based on neighbourhood granulation and rough approximation. Int. J. Model. Ident. Control 31(2), 161–168 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61873111), the Qing Lan Project, the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. 1701020A), the 333 Project of Jiangsu Province (No. BRA2018328).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, L., Zhang, X., Ding, F. (2020). Recursive Estimation Method for Bilinear Systems by Using the Hierarchical Identification Principle. In: Wang, R., Chen, Z., Zhang, W., Zhu, Q. (eds) Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control (ICMIC2019). Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, vol 582. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0474-7_92
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0474-7_92
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-15-0473-0
Online ISBN: 978-981-15-0474-7
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)