Abstract
The diversity of lncRNAs has expanded within mammals in tandem with the evolution of increased brain complexity, suggesting that lncRNAs play an integral role in this process. In this chapter, we will highlight the identification and characterization of lncRNAs in nervous system development. We discuss the potential role of lncRNAs in nervous system and brain evolution, along with efforts to create comprehensive catalogues that analyze spatial and temporal changes in lncRNA expression during nervous system development. Additionally, we focus on recent endeavors that attempt to assign function to lncRNAs during nervous system development. We highlight discrepancies that have been observed between in vitro and in vivo studies of lncRNA function and the challenges facing researchers in conducting mechanistic analyses of lncRNAs in the developing nervous system. Altogether, this chapter highlights the emerging role of lncRNAs in the developing brain and sheds light on novel, RNA-mediated mechanisms by which nervous system development is controlled.
Access provided by CONRICYT-eBooks. Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
9.1 Evolution of the Brain and Emergence of lncRNAs
The emergence of a true nervous system can be traced back to the evolution of the Bilateria, organisms that displayed two sides that are virtual mirror images, a hollow gut tube and a clustering of nerve cells into a nerve cord. The brain evolved from the clustering of the nerve cells at the anterior pole of the organism, connecting to other clusters of nerve cells, or ganglia, distributed along the central nerve cord. With the evolution of the vertebrates, this ventrally located nerve cord evolved into the dorsally located spinal cord. Likewise, throughout evolution, nervous system development is controlled by a largely conserved set of transcription factors and signaling molecules [1, 2]. Many of the same gene sets are even present and function orthologously in the more evolutionary primitive “nerve nets” of Cnidaria [3, 4]. These findings raise the question: How do the same gene sets function to control the great diversity of structures and cell types that are found in the nervous system across evolution? While some of this diversity is undoubtedly generated by gene duplications and repurposing of orthologous gene functions [5, 6], other mechanisms are certainly at work. These questions are most pertinent for the development of highly complex mammalian brains, particularly those of higher primates. In this section, we explore the potential central role of lncRNAs in the evolution of the mammalian nervous system.
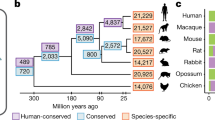
During vertebrate and more specifically hominid evolution, the brain has undergone an evolutionarily rapid expansion in size. In mammals with larger, more convoluted cortices, the expansion in size correlates with an expanded diversity of progenitor cells [7] that possess an increased proliferative capacity [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. In primates, the greatly increased size of the cerebral cortex appears to result from a dramatic expansion of progenitors in the outer subventricular zone [15, 16]. Interestingly, when brain size is normalized to body size using the encephalization quotient (EQ), the expansion in size of the brain across mammalian evolution shows a strong, nonlinear correlation with the expansion in the numbers of individual lncRNAs (Fig. 9.1).
Graph depicting the number of lncRNAs identified in given species relative to the encephalization quotient (EQ). EQ is indicative of the deviation from the expected brain size based on body mass, with larger numbers indicative of larger than expected brain size (normalized to the cat brain/body ratio equivalent) [17, 18]. Number of lncRNAs for a given species is taken from Gencode (Homo sapiens, Version 25 (March 2016, GRCh38)—Ensembl 85) [19, 20] or from published reports [21]. Trendline represents nonlinear fit with R 2 = 0.8343
Consistent with the notion that lncRNAs have co-evolved with the expanded repertoire of brain functions, a majority of lncRNAs examined to date display specific expression within neuroanatomical regions or neuronal cell types in mouse [22, 23]. Many of these brain-enriched lncRNAs are co-expressed with, and display genomic localizations in close proximity to, known neurodevelopmental regulators [24] and likely regulate similar processes during neurodevelopment. Together, this has led to the general hypothesis that the expanded diversity in lncRNAs is pivotal to the expansion in higher-order cognitive ability of humans and primates and the diversity of neuronal cell types and function. Accordingly, roughly one-third of ~13,800 lncRNAs examined are specific to the primate lineage, with ~40% of the lncRNAs displaying nervous system-specific expression [19, 25,26,27]. The emergence of brain-specific lncRNAs during primate/human evolution likely occurred through gene duplication, since brain-specific lncRNAs are more likely to originate from genomic regions that have undergone recent duplication than are more ubiquitously expressed or non-brain-enriched lncRNAs [25, 28, 29]. With the continued annotation of genomes and transcriptomes of various species across evolution, we are better able to assess the evolutionary conservation of lncRNAs and their role in the emergence of human-specific traits [30].
Interestingly, although lncRNAs display poor overall primary sequence conservation when compared to protein-coding genes [29, 31], brain-specific lncRNAs display two interesting evolutionary attributes: (1) brain-specific lncRNAs display higher sequence conservation than lncRNAs expressed in other tissues [24, 32] and (2) the spatiotemporal expression patterns of orthologous brain-enriched lncRNAs are maintained across multiple species [32]. This suggests that the expansion in the number of lncRNAs has played a critical role in the development of brain structures throughout the mammalian lineage. To further support the hypothesis that lncRNAs are vital to the evolutionary expansion of relative brain size and cognitive ability, researchers have identified genomic loci that display high conservation throughout vertebrate evolution but have undergone rapid evolution in humans [33,34,35,36]. These sequences are postulated to, therefore, play a role in human-specific brain functions. ~2700 “human accelerated regions (HARs),” which had selectively undergone rapid evolution following the divergence of the ancestors of humans and chimpanzees, were identified in these studies. Most HARs mapped to noncoding regions throughout the human genome. Of these, an estimated 30% of HARs mapped to identified brain-specific enhancers. A total of 15 HARs mapped to sequences annotated as long intergenic noncoding RNAs [37]; however, the extent to which the majority of HARs overlap unannotated, intronic, or antisense lncRNAs remains to be analyzed.
Most notably, researchers identified one specific HAR, HAR1, which overlaps the HAR1F brain-expressed lncRNA [35]. HAR1 showed the most accelerated substitution rate of any genomic region examined (18 bp of substitution in 118 bp since the last common ancestor of humans and chimpanzees). The HAR1F lncRNA was further examined and is expressed developmentally in the Cajal-Retzius neurons of the cortex, the upper cortical plate, the hippocampal primordium, dentate gyrus, cerebellar cortex, and a handful of hindbrain nuclei. HAR1F expression in both cortical and extra-cortical regions overlapped with expression of reelin, a known regulator of neurodevelopment. Of particular interest are the Cajal-Retzius neurons. The Cajal-Retzius cells populate the subpial granular layer, a region of the brain that is enlarged in humans [38,39,40,41]. To date, the function of HAR1F, and many other HARs, remains unknown. It will be of great interest to determine the role of HAR1F in Cajal-Retzius cell development.
Aside from HARs that overlap annotated lncRNA sequences, the degree of lncRNA contribution to the evolution of the brain is difficult to assess, given the poor degree of primary sequence conservation that is seen for most lncRNAs [42]. To further address the evolutionary emergence and contributions of lncRNAs in organisms with more complex brains, researchers examined “micro-synteny” of human genomic regions that contained lncRNAs across both large- and small-brained species [43]. These efforts first identified 187 human lncRNAs that are differentially expressed in progenitors or mature neurons of the developing embryonic human brain. When comparing the degree of conservation in genomic architecture surrounding the lncRNA across 30 species (29 mammals plus the chicken), species with large brains (high gyrencephalic indices (GI) >1.5; corresponding on average to approximately one billion cortical neurons [11]) displayed higher than expected conservation of the syntenic genomic landscape surrounding the lncRNA [43]. Conversely, smaller-brained species, with fewer sulci and gyri, displayed lower than expected lncRNA gene-neighborhood conservation. There were, however, two key exceptions: (1) the marmoset, a low-GI primate thought to have recently evolved from a high-GI ancestor [44], and (2) the manatee, a large but lissencephalic species [45]. Both of these species had higher than anticipated degrees of micro-synteny conservation. Importantly, when examining lncRNAs that are expressed in non-neuronal cells across all species, there was no similar correlation between the degree of micro-synteny and brain size [43]. This data suggests an evolutionary pressure to maintain the genomic architecture of regions that include lncRNAs, which in turn is likely to be important for regulation of neurogenesis and brain size. Further supporting this hypothesis, the researchers observed that the degree of micro-synteny conservation of lncRNAs was highest when the lncRNAs were positioned in close proximity to transcription factors that control neuronal development [43].
Additional research both identifying and characterizing nervous system-expressed lncRNAs will continue to aid in our understanding of the evolutionary changes that have enabled the development of the human brain. Our current understanding of the identity (Sect. 9.2) and function (Sect. 9.3) of lncRNAs involved in nervous system development comprises the remainder of the chapter.
9.2 Building a Catalogue of lncRNAs Expressed in the Developing Nervous System
While functional studies on lncRNAs in nervous system development are still lagging considerably (see Sect. 9.3), transcriptomic analyses have identified thousands of lncRNAs. In fact, with much greater coverage of the developing and mature brain by RNA-Seq analysis, recent studies have identified numbers of lncRNAs within given species that approach, or even exceed, the number of protein-coding genes [46]. For example, the NONCODEv4 collection estimates ~56,000 or ~46,000 independent lncRNAs for human and mouse, respectively [47].
While these numbers likely overestimate the true number of lncRNA transcripts, we expect the number of validated lncRNAs to increase beyond the annotated numbers from GENCODE (~15,000 for human, ~9000 for mouse [19]) for two main reasons. First, recent analysis has revealed that lncRNAs show a higher degree of tissue- and cell-type specificity than protein-coding genes [22, 23, 48,49,50,51,52]. It is thus almost certain that large numbers of lncRNAs may have escaped detection in previous RNA-Seq experiments—in particular, many have likely been lost in libraries prepared from bulk tissue, due to highly specific expression in rare cell types and/or low levels of overall expression. This is especially relevant in the nervous system, where the numerous brain structures and nuclei are comprised of highly diverse neuronal subtypes. Advances in single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-Seq) along with systematic characterization of individual cell types through efforts such as the BRAIN Initiative [53] will overcome these technical limitations. The power of scRNA-Seq analysis was underlined in a recent study that identified >5500 novel lncRNAs from single cells of the mouse cleavage stage embryo [54]. In addition, experimental design may also be limiting our detection of lncRNAs. Many RNA-Seq experiments are designed to capture only polyadenylated transcripts, in order to deplete the fraction of regulatory RNAs from the sequencing runs. While many lncRNAs are polyadenylated, significant fractions of lncRNAs persist as non-polyadenylated transcripts [19]. Moreover, detection and identification of antisense lncRNAs remains difficult unless strand-specific RNA-Seq libraries are generated, a technique currently not employed for many publically available datasets.
The second reason is our rapidly advancing understanding of the immense complexity of the mammalian transcriptome. Our current knowledge of the transcriptome is substantially limited by the sequencing technologies we employ. Sequencing reads that do not map in a linear fashion to the reference genome are frequently discarded as aberrant or false sequences. The presence of circular RNAs is an example of novel lncRNA species that have only recently been detected in large numbers through more rigorous analyses of RNA-Seq datasets [55,56,57,58]. Additional complexity of the transcriptome is being uncovered through the use of targeted RNA-Seq or Capture-Seq [59]. This has identified intragenic splicing events and enabled reliable identification of novel lncRNAs, including lowly expressed or rare lncRNA variants [60,61,62].
Many studies have begun to examine the expression of lncRNAs in embryonic stem (ES) that have undergone controlled differentiation both in vitro and within progenitor and neural precursor cells within the native developing nervous system in vivo. Here, we summarize these results.
9.2.1 Identification of lncRNAs from In Vitro Studies
Many exploratory studies characterizing lncRNA expression during neuronal development, particularly those assessing human development, focus on analysis of neural progenitors generated through in vitro controlled differentiation from pluripotent stem cells. These studies allow researchers to both easily obtain large quantities of relatively pure cells for in-depth analysis of transcript profiles and to control the precise developmental environment to analyze temporal changes in gene expression. The high degree of cell purity that can often be obtained using these approaches also aids in the detection of transcripts expressed at low levels, a category that includes many lncRNAs. A series of recent studies have shed considerable light on the identity of lncRNAs expressed in pluripotent stem cells and the highly dynamic patterns of lncRNA expression seen during directed differentiations toward specific neuronal cell type fates.
Initial studies of pluripotent stem cells reported that twice as many lncRNAs were selectively expressed in undifferentiated ES cells relative to more differentiated stages [63]. This is consistent with previous observations that analyzed the number of protein-coding genes expressed during pluripotent stages [64,65,66] and is also consistent with the high overall fraction of the genome that is present as euchromatin in ES cells [67,68,69]. All told, studies have identified over 250 lncRNAs that are selectively expressed in pluripotent stem cells [63, 70, 71].
Other studies have aimed to identify lncRNAs that are candidates for controlling neuronal identity based on differential expression of lncRNAs during progressive differentiation of stem cells toward neuronal lineages. In one study, researchers examined the expression profiles of lncRNAs during the differentiation of mouse embryonic forebrain-derived neural stem cells using microarrays [72]. These studies examined the bipotent sonic hedgehog-responsive, Nkx2.1-positive stem cells that generate both cortical GABAergic interneurons and oligodendrocytes. Comparing the bipotent progenitor cells, GABAergic interneurons, oligodendrocytes, and oligodendrocyte progenitor cells to neural stem cells, the researchers identified 169 lncRNAs (out of 3659 probes on the arrays) with differential expression during neural progenitor cell differentiation. Of particular interest, four lncRNAs were selectively activated upon GABAergic neuronal commitment. One of these, Ak044422, appears to function as a pre-miR for miR-124a, which accounts for nearly half of all brain-expressed miRNAs [73]. miR-124a is known to promote neuronal differentiation at least in part through repression of Ptbp1 [74]. Consistent with this, Ak044422 shows complementary expression to Ptbp1 during neuronal differentiation [72]. However, the researchers suggest that expression of Ak044422 transcript in the mature nervous system, and posttranscriptional modifications that include alternative splicing and polyadenylation, imply that the Ak044422 transcript may have additional functions in nervous system development independent of miR-124a. This same study identified 100 additional lncRNAs that displayed differential expression upon oligodendrocyte progenitor specification [72].
Similar experiments profiling lncRNA expression were performed on the directed differentiations of human ES cells to dopamine neurons [75]. Microarray profiling of lncRNA expression in ES cells, neurogenic progenitors, and mature dopamine neurons were used to identify lncRNAs that were candidates for regulating maintenance of pluripotency or neurogenic commitment. Over 900 lncRNAs were identified as differentially expressed during neurogenic commitment, with three lncRNAs identified as exclusively expressed in undifferentiated ES cells and 35 lncRNAs highly enriched in neural progenitor cells.
Together, these studies have provided a foundation for examining the considerable diversity of lncRNA expression during neurogenic differentiation and neuronal cell fate commitment. However, in most cases, the extent to which the in vitro expression of individual lncRNAs correlate with their in vivo expression patterns remains undetermined.
9.2.2 LncRNAs Identified Through In Vivo Studies of Neuronal Differentiation
While in vitro studies of cultured cells have provided a wealth of data identifying lncRNA expression with respect to neuronal differentiation from pluripotent stem cells, the extent of lncRNA expression in the nervous system has been further advanced through the profiling of primary tissue samples. Techniques such as customized microarrays for lncRNAs, serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE), and RNA-Seq analysis of primary nervous system tissue have identified thousands of lncRNAs expressed in the nervous system of multiple species [19, 20, 22, 23, 30, 46,47,48,49,50, 61, 76,77,78]. Additionally, highly cell and tissue-specific lncRNAs can be identified by expression profiling of micro-dissected or sorted tissue and/or cell populations.
Early studies examined the global transcript expression across a time series of retinal development using SAGE [49], identifying multiple noncoding transcripts that showed both temporally dynamic and spatially restricted expression patterns. These analyses identified and examined the retinal expression patterns of lncRNAs including Six3os (Rncr1), Neat1 or Gomafu (Rncr2), and RncrR3 (the previously mentioned Ak044422). Importantly, these studies indicated that some lncRNAs display exceptionally high levels of expression during retinal development, including Rncr2 which comprised ~0.2% of all polyadenylated RNA transcripts in the neonatal retina [49, 79].
More recent studies have begun to examine the complexity of the transcriptome within defined progenitors and neuronal cell types. In one such study, researchers examined the diversity of transcript expression within three defined subtypes of cortical pyramidal neurons including the sub-cerebral projection neurons, callosal projection neurons, and corticothalamic projection neurons [80]. RNA-Seq analysis of FACS-sorted cells across neurodevelopment identified 806 lncRNAs with significant differential expression between cell types and developmental stages. Four hundred forty-nine of these lncRNAs were selectively expressed in one of these pyramidal cell subtypes, supporting the high degree of cell-type specificity of lncRNAs [23].
LncRNA expression in adult neural stem cells of the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricles and the subgranular zone (SGZ) has been profiled extensively. The first study to address this question was a large-scale in situ hybridization analysis conducted by the Allen Brain Atlas. This effort identified 849 brain-expressed lncRNAs, a number of which were selectively expressed in adult neural stem cells [22]. Later studies have examined the expression of lncRNAs within neurogenic progenitor niches of the adult mouse subventricular zone [77]. Transcript profiles were compared to neurons of the mature olfactory bulb, to which the differentiating cells of the SVZ migrate, neural stem cells of the SGZ, ES cells, and ES cell-derived neurogenic progenitors. This study identified 6876, 5044, or 3680 novel lncRNA transcripts beyond those annotated in the RefSeq, UCSC, or Ensembl reference genome builds, respectively [77]. Consistent with previous reports, lncRNAs displayed more highly spatially and temporally restricted expression than protein-coding genes. To further profile these cell types, RNA Capture-Seq was used and identified an additional 3500 lncRNA transcripts within the SVZ, olfactory bulb, and dentate gyrus [77].
As previously mentioned, additional lncRNAs continue to be identified as sequencing technology advances, particularly with the recent optimization of single-cell RNA-Seq [54]. Recently, researchers profiled the transcript profiles of both bulk tissue samples and individual cells from micro-dissected human neocortices [78]. In bulk-sequencing experiments of tissue across human neocortical development, over 8000 novel lncRNAs were identified. When examining lncRNA expression across 276 individual cells, over 1400 lncRNAs were detected. Interestingly, when the expression levels of individual lncRNAs were analyzed in individual cells, it was found that lncRNAs displayed similar expression levels to protein-coding genes. However, when analyzing expression of the same lncRNAs in bulk tissue samples or within the pooled reads of the 276 individual cells, lncRNA expression levels were detected at much lower levels. This further supports the hypothesis that while lncRNAs are expressed at similar levels to protein-coding genes within individual cells, they display a much higher level of cell type-specific expression.
Numerous studies have now indicated the extensive expression of lncRNAs during all stages of brain development. Global sequencing/profiling experiments have identified thousands of brain-specific lncRNAs. Large-scale efforts, including the Allen Brain Atlas, have begun to examine both the spatial and temporal expression of individual lncRNAs [22, 81]. Additional studies have complemented these large-scale efforts, focusing on more discrete cell populations, including the primary auditory cortex and medial geniculate body [76] or restricted numbers of lncRNAs including, but not limited to, linc-RBE [82], linc-00320 [83], Dio3os [84], Evf1 [85, 86], and Evf2 [87]. Other studies have observed changes in brain lncRNA expression that are associated with genetic mutants in neurological and psychiatric diseases [88,89,90,91,92,93,94] and pharmacological treatments [95, 96] in the brain. Yet despite the large number of lncRNAs that show highly dynamic expression patterns during brain development, many researchers still remain skeptical of their functional importance. A key challenge moving forward is the need to carefully design studies to both address the function of lncRNAs in nervous system development and to identify the mechanisms by which they act.
9.3 LncRNA Function in Nervous System Development
We have previously conducted an extensive review of the role of lncRNAs in regulation of neural development [97]. Here we will briefly discuss the major findings previously reviewed and highlight more recent studies that further demonstrate the importance of lncRNAs in nervous system development.
9.3.1 Lessons Learned from In Vitro Studies
Most large-scale studies of lncRNA function have focused on identifying the regulation of pluripotency states and neural induction. As previously mentioned, numerous lncRNAs display dynamic expression during neural differentiation of ES cells. To identify regulatory role of these lncRNAs, researchers have performed loss of function studies using short hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated knockdown and analyzed effects on ES cell differentiation. In particular, inhibition of five lncRNAs resulted in a propensity of the stem cells to adopt a neuroectoderm lineage [98], suggesting a role of these lncRNAs in repressing neural commitment. Additionally, 30% of lncRNAs with selective expression in ES cells interacted with chromatin-modifying proteins, leading the authors to suggest that these lncRNAs function to promote pluripotency through regulation of chromatin architecture [98]. Similarly, further analysis of lincRNA1230 (linc1230) identified that this lncRNA is both necessary and sufficient to repress neural commitment of mouse ES cells [99]. Linc1230 modulates H3K4me3 accumulation on the promoters of the transcription factors Pax6 and Sox1 by interacting with the Trithorax complex component WDR5 [99]. Overexpression of linc1230 results in reduced WDR5 occupancy and H3K4me3 histone marks at promoters of genes that promote neuronal differentiation, suggesting that linc1230 inhibits neural induction by sequestering WDR5.
The lncRNA Tuna (also known as megamind [29]) and 19 additional lncRNAs were identified as regulators of pluripotency through a large-scale RNA-interference screen in mouse ES cells [100]. Interestingly, Tuna shows a high degree of sequence homology across vertebrates and is selectively expressed in the nervous system in zebrafish, mouse, and humans. In ES cells, knockdown of Tuna results in reduced proliferation, while overexpression of Tuna in ES cells resulted in the opposite phenotype, leading to increased proliferation. In differentiating neuronal cultures, loss of Tuna expression resulted in reduced expression of neural progenitor markers and genes involved in neural lineage commitment. Consistent with this, knockdown of megamind in zebrafish resulted in embryos with small brains and eyes, a phenotype that was rescued by expression of the orthologous zebrafish, human, or mouse isoforms [29]. Further analysis showed that Tuna interacts with three RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) [100]. Knockdown of each of these RBPs mimicked the loss of Tuna expression within ES cells. Further analyses indicated that Tuna expression is required to recruit the RBPs to the promoters of pluripotency factors including Nanog, Sox2, and Fgf4. Chromatin isolation by RNA purification (ChIRP) was used to identify Tuna/DNA interactions [101]. ChiRP experiments revealed that Tuna was associated with the promoters of pluripotency factors in ES cells [100]. Similarly, the lncRNA LOC646329 was found to be expressed in radial glia, which functions as neural stem cells during brain development, and in both primary glioblastoma multiforme tumors and glioblastoma-derived cell lines [78]. Inhibition of LOC646329 expression reduced the propagation of the tumor cell line, identifying an additional lncRNA that regulates the proliferative capacity of stem cells [78].
Other studies have focused on the function of lncRNAs selectively expressed upon neuronal induction or in regulation of cell fate specification in subventricular zone neural stem cells (SVZ NSCs) [77]. Six3os expression is enriched in the stem cells of the SVZ relative to SVZ-derived neural precursors, and its knockdown resulted in fewer neurons and oligodendrocytes and an increase in astrocytes [77]. In contrast, Dlx1as also displays robust expression in the SVZ, and inhibition of Dlx1as expression inhibited neurogenesis and decreased astrocyte formation, but had no effect on oligodendrocyte production [77]. This phenotype, seen following Dlx1as knockdown, may result from altered expression of nearby protein coding genes, as this study observed a decrease in transcript levels of both Dlx1 and Dlx2. Short interfering RNA (siRNA) loss of function was used to analyze the function of four lncRNAs (Rmst, Ak124684, Ak091713, and Ak055040) that displayed enriched expression upon neuronal induction of human ES cells. In each case, knockdown of the lncRNA resulted a roughly fivefold decrease in the number of neurons generated, instead promoting oligodendrocyte production [75]. Further analysis of these lncRNAs suggests that they control neuronal fate specification through a variety of different mechanisms. These include regulation of chromatin structure through interactions with SUZ12 (Ak055040), regulating expression of the neurogenic miRNAs miR-125b and let-7 (Ak091713), interaction with the REST/coREST complex (Ak124684), and by functioning as a transcriptional co-regulator, recruiting SOX2 to its transcriptional targets (RMST) [75, 102]. Further characterization of the lncRNA Rmst has discovered that the miRNA miR-135a2 is encoded in the last intron of Rmst [103]. Recent studies have identified a feedback loop where Lmx1b, in response to Wnt/beta-catenin pathway activation, increases expression of Rmst/miR-135a2 and miR-135a2, which in turn decreases Wnt1 expression levels. This regulatory circuit thus controls the size of dopaminergic progenitor pool of the midbrain [103,104,105]. In light of this, it will be interesting to determine the extent of which Rmst regulates neural induction independent of miR-135a2 expression.
LncRNAs have also been identified as regulators of oligodendrocyte specification. While many lncRNAs have been identified as selectively expressed in intermediate neural progenitors prior to oligodendrocyte specification [72], relatively few have been directly identified in oligodendrocyte precursors. In one study, the regulatory function of the antisense transcript Nkx2.2as was identified to be a positive regulator of oligodendrocyte specification. Nkx2.2as overexpression resulted in an increased number of Nestin + stem cells and a bias toward oligodendrocyte lineage during differentiation of neural stem cells [106]. As Nkx2.2 is required for oligodendrocyte specification [107], the result of overexpression of Nkx2.2as on Nkx2.2 transcript abundance was examined. It was determined that the sense-antisense pairing of Nkx2.2as and Nkx2.2 stabilized Nkx2.2 mRNA [106]. However, the effect on Nkx2.2 protein levels remains undetermined. In other studies, the expression of lncRNAs during the controlled differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPC) from neural stem cells was examined. These studies identified that lnc-OPC (long noncoding RNA-oligodendrocyte precursor cell) shows highly specific expression in OPCs [108]. Olig2, a transcription factor that is necessary and in some contexts sufficient, for OPC specification from neural progenitors [109,110,111], was found to bind the proximal promoter of lnc-OPC and induce its expression upon OPC specification [108]. These data implicate lncRNAs in the regulation of both neuronal and glial differentiation.
As many lncRNAs are primate or even human specific [52], studies of such lncRNAs remain limited to cultured cells. Recently, researchers identified the lncRNA LncND in a screen for lncRNA transcripts that may function as miRNA sponges during human brain development [112]. LncRNAs, along with transcribed pseudogenes and circular RNAs [58, 113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120], can fine-tune miRNA concentration by sequestering and stabilizing miRNAs within Argonaute protein complexes [121], thereby controlling translation during development [113, 116, 119, 122]. Interestingly, LncND is expressed from a genomic locus that is deleted in individuals with certain neurodevelopmental disorders [123,124,125,126]. Expression of LncND increases during neurogenesis and rapidly drops upon neuronal differentiation [112]. Similarly, LncND is expressed at high levels within the ventricular zone of the developing cerebral cortex [112]. In silico analysis predicted 16 putative miR-143-3p seed sites within LncND, which were confirmed using luciferase assays [112]. Interaction of LncND with AGO2, a component of the RISC complex, further supported the hypothesis that LncND functions as a miRNA sponge [112]. Analysis of mRNA transcripts for miR-143-3p binding sites identified putative binding sites of miR-143-3p in the 3′ UTRs of both Notch1 and Notch2 [112]. Consistent with a role in regulating the Notch signaling pathway, knockdown of LncND resulted in decreased Notch pathway activation and a corresponding increase in neurogenesis [112]. Overexpression of LncND in cerebral organoids resulted in expansion of the radial glial cell population [112], which phenocopies the effects of increased Notch pathway activation [127,128,129]. These results suggest that LncND functions to sequester and stabilize miR-143-3p within neural progenitors, in order to maintain Notch signaling and prevent premature neuronal differentiation [112].
Many lncRNAs, such as Meg3 and Dio3os, are expressed in the brain and other tissues from imprinted loci [84, 130]. The lncRNA Meg3 acts as a tumor suppressor, likely by regulating apoptosis and angiogenesis [130]. Dio3os is also expressed in the brain from an imprinted locus. In contrast to the usual pattern seen with imprinted lncRNAs and associated protein-coding genes, Dio3os and Dio3 are both expressed from the same chromosome [84, 131]. It will be interesting to determine if Dio3os facilitates imprinting of its locus through silencing of the opposite chromosome.
9.3.2 Lessons Learned from In Vivo Analysis of lncRNAs
9.3.2.1 lncRNAs in Retinal Development
One neuronal tissue that has provided a wealth of information regarding lncRNA regulation of nervous system development is the developing retina. The retina serves as a simplified neural tissue that arises from a multipotent pool of progenitor cells capable of generating each of the seven major classes of retinal cell types (six neural—retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), amacrine cells (ACs), bipolar cells (BCs), rod photoreceptors, and cone photoreceptors; one glial cell—Müller glial cells (MG)). SAGE analysis, qRT-PCR, and in situ hybridization experiments on retinal tissue across mouse retinal development indicated the presence and abundance of lncRNAs and identified cell-type specific expression of many lncRNAs within discrete retinal cell types [49, 132]. Characterization of the function of these lncRNAs in retinal development has subsequently been performed through in vivo gain and loss of function studies [49, 133,134,135,136].
The lncRNA Tug1 was identified in a screen examining genes upregulated after exposure of RPCs to taurine, which induces rod photoreceptor differentiation [133]. Knockdown of Tug1 resulted in abnormal inner and outer segments of photoreceptors, increased cell death, and an increase in the cone photoreceptor marker PNA, consistent with a role of Tug1 in promoting rod genesis and inhibiting production of cones [133]. Additional studies of Tug1 first indicated that Tug1 regulates cell fate decisions through its interaction with the polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) and through regulation chromatin structure [137]. Interestingly, Tug1 expression is induced by p53, and loss of Tug1 expression resulted in an increase of cell-cycle regulator transcript expression, implying that Tug1 inhibits cell proliferation during cellular damage/stress [133].
The lncRNA Gomafu, also known as RNCR2 or Miat, is the most abundantly expressed lncRNA in the developing retina, comprising 0.2% of all polyadenylated transcripts in neonatal mouse retina [49, 135, 138, 139]. Functional studies indicate that Gomafu negatively regulates both AC and MG cell differentiation, with loss of function resulting in increased production of ACs and MG [135]. More recently, it was shown that Gomafu functions by regulating alternative splicing through interaction with the splicing regulators QKI and SF1 [140]. It will be interesting to determine if Gomafu’s role in controlling retinal cell fate specification is mediated by regulation of alternative splicing.
Six3os is a lncRNA that is both divergently transcribed and co-expressed with the homeodomain transcription factor Six3. Six3os is shown to promote BC specification and inhibit MG development [136]. Six3os regulates SIX3 transcriptional activity by acting as a transcriptional scaffold, stabilizing a complex including SIX3, EYA1, and EZH2 and directly regulating expression of SIX3 target genes [136, 141]. In other studies, researchers characterized the expression and function of the natural antisense transcript Vax2os1. Overexpression of Vax2os1 indicates that it functions to maintain the proliferative potential of retinal progenitor cells and prevents premature differentiation of rods [142].
Finally, recent work in the retina has examined functional role of RNCR4. RNCR4 is divergently transcribed from a locus that contains the pre-miRNA cluster miR-183/96/182. The mature miR-183/96/182 and RNCR4 both display robust expression in photoreceptor cells, beginning at P5 and increasing into adulthood [134]. It was shown that RNCR4 expression results in increased processing of the pre-mIR-183/96/182 to the mature miRNAs by acting as a repressor to the pri-miR-183/96/182 processing inhibitor Ddx3x [134]. Increases in the mature miR-183/96/182 expression levels result in aberrant cellular organization of multiple retinal cell types and the appearance of whorls and rosettes in the outer retina as a consequence of premature miR-183/96/182 expression, which in turn disrupts outer limiting membrane formation by altering Crb1 expression [134]. This suggests that RNCR4 expression controls the timing of pri-miR-183/96/182 processing to guide retinal histogenesis and outer limiting membrane formation.
9.3.2.2 lncRNAs in Brain Development
As our understanding of genome complexity expands, and tools to manipulate the genome to assess gene function improve, researchers are beginning to assess the requirement of lncRNAs in vivo during brain and nervous system development. In particular, genetic knockout or knockdown experiments are being used to assess the necessity of individual lncRNAs in control of nervous system development. Surprisingly, in many cases in vivo gain and loss of function analysis of individual lncRNAs gives discordant results when compared to in vitro manipulations. Additionally, phenotypes observed following targeted deletions of large regions of DNA that include lncRNA transcript sequence have often been viewed skeptically, due to the potential loss of important cis-regulatory elements of neighboring genes. In this section, we will review our current understanding of the regulation of neural development by lncRNAs in vivo (Sect. 9.3.2.2.1) and highlight the functions attributed to lncRNAs resulting from genetic manipulations of lncRNA expression on nervous system development (Sect. 9.3.2.2.2).
9.3.2.2.1 Regulation of Nervous System Development, by lncRNAs In Vivo
Recent studies have identified the neural-specific lncRNA Pinky (Pnky) as a regulator of neurogenesis in the embryonic and postnatal brain [143]. Pnky is expressed at high levels in the ventricular-subventricular zone of the adult brain, a neurogenic niche that is maintained into adulthood [143, 144]. However, Pnky expression is downregulated upon activation of the differentiation program of the neural stem cells [143]. Interestingly, when Pnky expression is decreased using shRNAs either in vitro or in vivo, the researchers observed an increase in neurogenesis, with a concomitant decrease in the fraction of cells expressing markers of neural stem cells. This likely resulted from an increase in proliferation of transient amplifying cells and decrease in cell death [143]. To further investigate the mechanisms by which Pnky functions, the researchers analyzed its protein partners using RNA pulldown followed by mass spectrometry, demonstrating that Pnky interacted with PTBP1 [143]. PTBP1 has previously been shown to function as a repressor of neuronal differentiation by both regulating pre-mRNA splicing and by inhibiting expression of the neurogenesis-promoting gene Ptbp2 [145,146,147,148,149,150]. Like Pnky knockdown, Ptbp1 knockdown also resulted in expanded production of neurons, regulating a highly overlapping gene set as Pnky [143]. The physical interaction between Pnky and PTBP1 interaction, the identical phenotype seen following loss of expression, the highly overlapping set of regulated genes, and additional epistasis experiments allowed the researchers to conclude that Pnky regulates neurogenesis of ventricular-subventricular zone stem cells through regulation of PTBP1 function [143].
9.3.2.2.2 Genetic Loss of Function Studies of lncRNAs in Brain Development
While much of our knowledge about the mechanisms by which lncRNAs regulate neural development stems from in vitro studies, recent efforts have begun to increase the number of genetic models of lncRNA loss of function. Here we will highlight the importance of carefully designed loss of function studies (Fig. 9.2) and compare the results from in vivo genetic manipulations to those seen in cell line-based in vitro studies.
Examples of the effects of lncRNA deletion or insertion of a strong transcriptional stop (pA) on genomic architecture and neighboring gene expression. Careful design of genetic strategies targeting lncRNA loss of function must be implored to ensure that resulting outcomes are the result of lncRNA function and not a consequence of changes to the genome architecture that result in unintended outcomes
One of the more thoroughly analyzed lncRNAs that regulates brain development is Evf2 (Dlx6as1) [87, 151,152,153]. Evf2 is expressed in the Shh-responsive cells of the ventral telencephalon during embryonic development and is transcribed from a region that partially overlaps ei, one of the two ultra-conserved enhancers (ei + eii) for the neighboring genes Dlx5 and Dlx6 [87]. Transcriptional initiation of Evf2 occurs just 3′ to the eii enhancer [87]. Initial in vitro experiments suggested that Evf2 supplied in trans was required for DLX2 recruitment and activation of the Dlx5/Dlx6 enhancer sequence, which in turn activated Dlx5 and Dlx6 transcription [87]. However, when Evf2 expression was inhibited by targeted insertion of a premature polyadenylation signal, Dlx6 expression was actually increased, suggesting that Evf2 transcription can also function to inhibit Dlx6 expression [151]. Interestingly, the regulation of Dlx6 expression by Evf2 seems to occur in cis, as low levels of ectopic Evf2 expression fail to rescue Dlx6 expression in Evf2-mutant mice [151]. However, when high levels of Evf2 are ectopically expressed in Evf2 mutants, both Dlx5 and Dlx6 transcript levels increase, suggesting a trans-acting effect of Evf2 similar to those that are observed in vitro [87, 151]. Genetic disruption of Evf2 expression initially resulted in a decrease in the number of hippocampal interneurons, which resolved as the mice matured [151]. However, although the number of interneurons in the adult mice remained similar to wild-type controls, the researchers observed reduced inhibition of the CA1 pyramidal neuron activity [151], the postsynaptic targets of the hippocampal interneurons, implying the presence of a persistent functional defect in these cells.
Other experiments investigating Evf2 function suggested that loss of Evf2 expression resulted in a failure to recruit both DLX proteins and the transcriptional repressor MECP2 to the Dlx5/Dlx6 enhancers [151]. Evf2 was found to prevent DNA methylation of enhancer ei, suggesting that regulation of ei methylation modulates the binding affinities of DLX1/DLX2 and MECP2 to the enhancer, which in turn regulates Dlx5/Dlx6 expression [152]. Since Evf2 is required for recruitment of DLX1/DLX2 to the Dlx5/Dlx6 enhancer, but does not bind DLX1/DLX2 directly [87, 151], the researchers employed immuno-affinity purification followed by mass spectrometry to identify additional proteins that are part of the Evf2-DLX1/DLX2 complex, and which potentially contribute to the Evf2-mutant phenotype [153]. These experiments indicated that DLX1 interacts directly with the chromatin remodeling proteins BRG1 and BAF170 in the developing mouse forebrain [153]. DLX1-BRG1 complexes were found to associate with the Dlx5/Dlx6 enhancers and were enriched in the presence of Evf2, suggesting a functional role of the DLX1-BRG1 complex formation in regulation of Dlx5/Dlx6 expression [153]. Furthermore, BRG1 was found to bind Evf2 through its RNA-binding domain [153]. Absence of Evf2 expression decreases DLX1-BRG1 complex formation at the enhancers that control Dlx5/Dlx6 transcription and also leads to a corresponding decrease in both H3AcK9 and H3AcK18 histone modifications locally [153]. Interestingly, Evf2 inhibits the ATPase domain of BRG1, suggesting that Evf2 directs the BRG1-DLX1/DLX2 complex to the Dlx5/Dlx6 enhancer but that high levels of Evf2 transcripts within the complex also inhibit the chromatin remodeling activity of BRG1, thus inhibiting Dlx5/Dlx6 enhancer activity [153].
Much like the approach used to generate Evf2 knockout animals, Dlx1as expression was genetically disrupted through targeted insertion of a premature polyadenylation sequence [154]. Contrary to in vitro reports, where loss of Dlx1as resulted in compensatory decrease in Dlx1 and Dlx2 expression [77], loss of Dlx1as in vivo results in a modest increase Dlx1 and Mash1 transcript expression [154]. Since Dlx1-mutant mice display profound defects in hippocampal GABAergic interneuron specification [155,156,157], the researchers next examined expression of Gad67, a marker of GABAergic cells. However, the increase in Dlx1 expression induced as a consequence of Dlx1as loss had no effect on GABAergic interneuron number [154], consistent with previous reports where Dlx1 overexpression did not induce GABAergic interneuron specification, in sharp contrast to its paralogues Dlx2 and Dlx5 [158, 159]. While expression of genes that control GABAergic neuronal specification such as Dlx1, Mash1, and Lhx6 is altered within Dlx1as brains, no other neurological phenotypes were observed [154]. Instead, slight defects in the alicochlear commissure were observed in Dlx1as mutants [154]. Further investigations will be required to determine if any behavioral phenotypes are observed as a consequence of Dlx1as loss of function, akin to those observed for Evf2-mutant mice, despite the absence of altered GABAergic interneuron cell number [151].
Recently, a consortium of researchers generated a cohort of targeted deletions of individual mouse lncRNAs to explore their developmental function in vivo [160]. As many lncRNAs overlap protein-coding sequences, the researchers focused on intergenic lncRNAs, so as to investigate phenotypes not attributable to loss of protein-coding gene sequence. Using a combination of cell-based functional assays, RNA-sequencing and computational analyses, the group selected 18 lncRNAs, many with shared homology to human transcript sequences, for targeted deletion in mouse [160]. Of relevance to this review, 12 of the 18 lncRNAs display expression within adult mouse brain or ES cell-derived neural stem cells. Seven of the 12 brain-expressed lncRNAs have human orthologues that display differential expression during human neuronal stem cell differentiation [160].
In order to generate the lncRNA knockouts, the entire lncRNA transcript sequence was replaced with a lacZ reporter cassette, allowing a highly sensitive assessment of lncRNA expression patterns using lacZ/beta-Gal staining [160]. Targeted inactivation of the lncRNA Peril, which is expressed at high levels in mouse ES cells, and shows both temporally and spatially restricted expression within the brain and spinal cord of developing mouse embryos, resulted in reduced viability relative to wild-type or heterozygous littermates [160]. RNA-seq and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of Peril −/− brains revealed that genes involved in multiple essential processes including cell cycle regulation and energy metabolism were downregulated [160]. However, the mechanism by which Peril loss contributes to lethality remains unknown. The knockout of an additional lncRNA, Fendrr, which is expressed at low levels in the developing brain, likewise results in increased lethality. In two separate knockout models, either by gene replacement [160] or insertion of premature polyadenylation signals [161, 162], lethality was observed, as a result of either cardiac [162] or respiratory defects [160]. The role of this lncRNA in brain development, however, remains unexplored.
Interestingly, the locus that encodes the transcription factor Brn1 (Pou3f3), a well-studied regulator of cortical development [163,164,165], also contains two lncRNAs (Pantr1, also known as linc-Brn1a, and Pantr2, also known as linc-Brn1b) that were both deleted as part of this knockout project [160]. Pantr1 and Pantr2 both have conserved human orthologues and were identified as differentially expressed during neural stem cell differentiations [160]. Pantr1 is transcribed from a region immediately upstream of the transcriptional start site of Brn1, and on the opposite strand. Deletion of Pantr1, therefore, may also delete portions of the proximal promoter of Brn1 and is likely to lead to a decrease in Brn1 transcription. Pantr2, however, is transcribed from a region ~10 kb downstream of the Brn1 locus, again on the opposite DNA strand. Using the lacZ knock-in, it was shown that Pantr2 is expressed within neural progenitors of the mouse dorsal and ventral telencephalon at E13.5. Expression is maintained within both the subventricular and ventricular zones at E15.5, but more restricted expression is observed in the superior cortical layers by E18.5. Upon deletion of Pantr2, Brn1 transcript and BRN1 protein levels were both decreased by ~50%. Pantr1 expression, however, was increased [160]. Deletion of Pantr2 resulted in a reduction in the thickness of all cortical layers, likely the result of reduced proliferation of the intermediate progenitors of the subventricular zone that subsequently give rise to cortical neurons. Examination of the cortex of Pantr2 −/− mice revealed that a subset of upper-layer cortical neurons were converted to deep layer neurons [160]. This cortical thinning phenotype is similar to what is observed for Brn1/Brn2 (Pou3f3/Pou3f2) double, but not single, mutants [163,164,165], suggesting that Pantr2 functions in the specification of upper cortical neuron identity independent of its role in regulating Brn1 expression [160].
To expand on the preliminary studies of each of the knockout lines, RNA-Seq was conducted at E14.5 and adult stages on brains from knockout and wild-type littermates for the 13 lncRNAs that displayed any brain expression [166]. Interestingly, loss of Pantr1 or Pantr2 did not affect Brn1 expression in whole brains at either time point. Conversely, Brn1 (Pou3f3), Brn2 (Pou3f2), and Brn4 (Pou3f4) all displayed increased expression in Pantr1 knockout brains at E14.5 [166]. Additionally, of the 13 lncRNA knockout lines studied in these experiments, only five showed significant differences in the expression levels of neighboring gene expression at either the time point [166]. Together, these data further suggest that brain-expressed lncRNAs may function to regulate gene expression both locally in cis but also in trans [166]. Further characterization of each knockout line will be required to determine the specific function of each individual lncRNA.
Some lncRNAs expressed during nervous system development, however, show no or very mild phenotypes following targeted inactivation. Two examples of brain-expressed lncRNAs in which knockout models that fail to produce obvious phenotypes are Malat1 and Visc2 [167,168,169,170]. Other lncRNA knockouts display only minor phenotypes. The lncRNA Neat1, which displays enriched expression in neurons compared to their neural precursors [72], is expressed in a nuclear subdomain known as paraspeckles [171,172,173]. Paraspeckles are nuclear bodies composed of more than 40 RNA-binding proteins [174]. Neat1 is required for paraspeckle formation in both in vitro and in vivo studies [171,172,173, 175, 176]. However, the physiological function of paraspeckle formation is unclear, as mice lacking Neat1 expression and paraspeckle formation fail to display any clear developmental phenotype [176], with one notable exception. It was recently determined that Neat1 knockout mice display a stochastic infertility resulting from corpus luteum dysfunction [177, 178]. However, the contribution of Neat1 and paraspeckle formation to brain development or nervous system diseases such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), where elevated Neat1 expression is observed during early stages of the disease [179], remains to be determined.
The lncRNA Gomafu (also known as RNCR2 or Miat) was previously identified to function in retinal cell fate specification [135], and decrease in Gomafu expression is associated with mRNA splicing defects in schizophrenia [140]. Knockout mice, however, display no gross developmental defects. Instead, behavioral tests performed on Gomafu knockouts suggest that these mice display a mild hyperactivity phenotype and enhanced hyperactivity to repeated psychostimulant exposure [180]. Analysis of extracellular dopamine within the nucleus accumbens revealed increased dopamine levels compared to wild-type controls, consistent with the observed hyperactivity [180]. Likewise, schizophrenia patients also exhibit hyperactivity, and Gomafu expression is downregulated in postmortem brain samples of schizophrenia patients [140]. However, RNA-Seq analysis of hippocampal cultures from wild-type and Gomafu knockout mice revealed only 18 transcripts that displayed differential expression [180]. As Gomafu is previously predicted to regulate mRNA splicing through its interactions with the splicing regulators QKI, SF1, and CELF3 [140, 181, 182], alternative splicing of a handful of transcripts was assessed in hippocampal cells of Gomafu knockout mice [180]. However, unlike the changes observed in postmortem brain samples from schizophrenia patients, where Gomafu showed decreased expression [140], Gomafu −/− mice displayed little change in alternative splicing [180].
Despite these studies, our knowledge of the in vivo contributions of lncRNAs to nervous system development remains clouded by emerging discrepancies between in vitro and in vivo results. To further complicate matters, the design of knockout targeting strategies for in vivo loss of function studies can significantly affect interpretations of any phenotypes obtained (Fig. 9.2). For example, three different targeting strategies were used to generate Malat1 knockout mice. Importantly, while no gross phenotypes were observed in any of the studies [167,168,169], the effect of Malat1 loss of function on Neat1 expression depended on the mechanism by which Malat1 expression was inhibited. Deletion of either the promoter and proximal 5′ transcript sequence or the entire gene body of Malat1 resulted in an increase in Neat1 expression [167, 169]. However, insertion of lacZ and two premature polyadenylation sequences into the Malat1 locus resulted in decreased Neat1 expression [168]. Together, these data indicate the context-dependent sequence requirement for genome architecture. It remains to be determined, however, if Malat1-dependent regulation of Neat1 expression occurs solely by controlling the activity of cis-regulatory elements or whether Malat1 also regulates Neat1 transcription in trans.
9.4 Conclusions
With the emergence of vastly improved sequencing technologies, we are beginning to understand the full complexity of the transcriptome. These analyses have revealed that the numbers of lncRNAs have expanded in parallel with the evolutionary increase in brain complexity. Emerging experiments profiling the transcriptomes of nervous system tissue continue to identify many novel lncRNAs. As we continue to identify and characterize the diverse cell types of the brain across development through single-cell RNA-Seq, and continue to explore the complexity of alternative splicing through Capture-seq profiling, we expect that the number of validated lncRNAs will expand dramatically. While considerable effort is now going into investigating the function of these lncRNAs during nervous system development, it is important to keep in mind exactly how these studies are performed. In vitro studies expand the repertoire of mechanistic analyses that we can perform, but results from such studies require in vivo validation, as the lncRNAs are likely functioning in a cell type- and context-specific manner that is often only imperfectly recapitulated in cultured cells. Furthermore, in vivo studies of lncRNA function need to be carefully designed to directly examine the function of the lncRNA transcripts themselves. This is especially important for genetic loss of function studies, where changing the genomic locus that encodes the lncRNA in question may disrupt the activity of important cis-regulatory elements. Additional challenges remain in the design of efforts to address the function of natural-antisense or opposite strand transcripts, due to their genomic proximity to protein-coding genes.
Given the abundance of functions being attributed to lncRNAs, it is especially important to understand their mechanisms of action. Since lncRNAs in many cases function as molecular scaffolds—that bind DNA, RNA, protein, or combinations of these biomolecules—understanding the precise composition of these complexes will be pivotal. However, given the low cellular expression levels and/or scarcity of cell types in which the lncRNAs are expressed, traditional pulldown/mass spectrometry experiments will prove challenging. In any case, recent years have clearly shown that lncRNAs are central to regulation of neuronal differentiation, and our appreciation of their importance will likely grow substantially in the years ahead.
References
Arendt D, Denes AS, Jekely G, Tessmar-Raible K (2008) The evolution of nervous system centralization. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 363(1496):1523–1528
Hirth F (2010) On the origin and evolution of the tripartite brain. Brain Behav Evol 76(1):3–10
Galliot B, Quiquand M, Ghila L, de Rosa R, Miljkovic-Licina M, Chera S (2009) Origins of neurogenesis, a cnidarian view. Dev Biol 332(1):2–24
Nakanishi N, Renfer E, Technau U, Rentzsch F (2012) Nervous systems of the sea anemone Nematostella vectensis are generated by ectoderm and endoderm and shaped by distinct mechanisms. Development 139(2):347–357
Ohno S (1970) Evolution by gene duplication. Springer, Berlin
Zhang J (2003) Evolution by gene duplication: an update. TRENDS Ecol Evol 18(6):292–298
Betizeau M, Cortay V, Patti D, Pfister S, Gautier E, Bellemin-Menard A, Afanassieff M, Huissoud C, Douglas RJ, Kennedy H, Dehay C (2013) Precursor diversity and complexity of lineage relationships in the outer subventricular zone of the primate. Neuron 80(2):442–457
Borrell V, Calegari F (2014) Mechanisms of brain evolution: regulation of neural progenitor cell diversity and cell cycle length. Neurosci Res 86:14–24
Florio M, Huttner WB (2014) Neural progenitors, neurogenesis and the evolution of the neocortex. Development 141(11):2182–2194
Lewitus E, Kelava I, Huttner WB (2013) Conical expansion of the outer subventricular zone and the role of neocortical folding in evolution and development. Front Hum Neurosci 7:424
Lewitus E, Kelava I, Kalinka AT, Tomancak P, Huttner WB (2014) An adaptive threshold in mammalian neocortical evolution. PLoS Biol 12(11):e1002000
Lui JH, Hansen DV, Kriegstein AR (2011) Development and evolution of the human neocortex. Cell 146(1):18–36
Stahl R, Walcher T, De Juan Romero C, Pilz GA, Cappello S, Irmler M, Sanz-Aquela JM, Beckers J, Blum R, Borrell V, Gotz M (2013) Trnp1 regulates expansion and folding of the mammalian cerebral cortex by control of radial glial fate. Cell 153(3):535–549
Sun T, Hevner RF (2014) Growth and folding of the mammalian cerebral cortex: from molecules to malformations. Nat Rev Neurosci 15(4):217–232
Kaskan PM, Finlay BL (2001) Bigger is better: primate brain size in relationship to cognition. In: Falk D, Gibson KR (eds) Evolutionary anatomy of the primate cerebral cortex. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 79–97
Finlay BL, Darlington RB (1995) Linked regularities in the development and evolution of mammalian brains. Science (New York, NY) 268(5217):1578–1584
Roth G, Dicke U (2005) Evolution of the brain and intelligence. Trends Cogn Sci 9(5):250–257
Jerison HJ (1973) Evolution of the brain and intelligence, XIV edn. Academic, New York
Derrien T, Johnson R, Bussotti G, Tanzer A, Djebali S, Tilgner H, Guernec G, Martin D, Merkel A, Knowles DG, Lagarde J, Veeravalli L, Ruan X, Ruan Y, Lassmann T, Carninci P, Brown JB, Lipovich L, Gonzalez JM, Thomas M, Davis CA, Shiekhattar R, Gingeras TR, Hubbard TJ, Notredame C, Harrow J, Guigo R (2012) The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res 22(9):1775–1789
Harrow J, Frankish A, Gonzalez JM, Tapanari E, Diekhans M, Kokocinski F, Aken BL, Barrell D, Zadissa A, Searle S, Barnes I, Bignell A, Boychenko V, Hunt T, Kay M, Mukherjee G, Rajan J, Despacio-Reyes G, Saunders G, Steward C, Harte R, Lin M, Howald C, Tanzer A, Derrien T, Chrast J, Walters N, Balasubramanian S, Pei B, Tress M, Rodriguez JM, Ezkurdia I, van Baren J, Brent M, Haussler D, Kellis M, Valencia A, Reymond A, Gerstein M, Guigo R, Hubbard TJ (2012) GENCODE: the reference human genome annotation for the ENCODE project. Genome Res 22(9):1760–1774
Necsulea A, Soumillon M, Warnefors M, Liechti A, Daish T, Zeller U, Baker JC, Grutzner F, Kaessmann H (2014) The evolution of lncRNA repertoires and expression patterns in tetrapods. Nature 505(7485):635–640
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Sunkin SM, Mehler MF, Mattick JS (2008) Specific expression of long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(2):716–721
Luo H, Sun S, Li P, Bu D, Cao H, Zhao Y (2013) Comprehensive characterization of 10,571 mouse large intergenic noncoding RNAs from whole transcriptome sequencing. PLoS One 8(8):e70835
Ponjavic J, Oliver PL, Lunter G, Ponting CP (2009) Genomic and transcriptional co-localization of protein-coding and long non-coding RNA pairs in the developing brain. PLoS Genet 5(8):e1000617
Francescatto M, Vitezic M, Heutink P, Saxena A (2014) Brain-specific noncoding RNAs are likely to originate in repeats and may play a role in up-regulating genes in cis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 54:331–337
Kaushik K, Leonard VE, Kv S, Lalwani MK, Jalali S, Patowary A, Joshi A, Scaria V, Sivasubbu S (2013) Dynamic expression of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in adult zebrafish. PLoS One 8(12):e83616
Washietl S, Kellis M, Garber M (2014) Evolutionary dynamics and tissue specificity of human long noncoding RNAs in six mammals. Genome Res 24(4):616–628
Kelley D, Rinn J (2012) Transposable elements reveal a stem cell-specific class of long noncoding RNAs. Genome Biol 13(11):R107. doi:10.1186/gb-2012-13-11-r107
Ulitsky I, Shkumatava A, Jan CH, Sive H, Bartel DP (2011) Conserved function of lincRNAs in vertebrate embryonic development despite rapid sequence evolution. Cell 147(7):1537–1550
Lipovich L, Hou ZC, Jia H, Sinkler C, McGowen M, Sterner KN, Weckle A, Sugalski AB, Pipes L, Gatti DL, Mason CE, Sherwood CC, Hof PR, Kuzawa CW, Grossman LI, Goodman M, Wildman DE (2016) High-throughput RNA sequencing reveals structural differences of orthologous brain-expressed genes between western lowland gorillas and humans. J Comp Neurol 524(2):288–308
Basu S, Muller F, Sanges R (2013) Examples of sequence conservation analyses capture a subset of mouse long non-coding RNAs sharing homology with fish conserved genomic elements. BMC Bioinformatics 14(Suppl 7):S14. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-14-S7-S14. Epub 2013 Apr 22.
He Z, Bammann H, Han D, Xie G, Khaitovich P (2014) Conserved expression of lincRNA during human and macaque prefrontal cortex development and maturation. RNA (New York, NY) 20(7):1103–1111
Bird CP, Stranger BE, Liu M, Thomas DJ, Ingle CE, Beazley C, Miller W, Hurles ME, Dermitzakis ET (2007) Fast-evolving noncoding sequences in the human genome. Genome Biol 8(6):R118
Bush EC, Lahn BT (2008) A genome-wide screen for noncoding elements important in primate evolution. BMC Evol Biol 8:17. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-8-17
Pollard KS, Salama SR, Lambert N, Lambot MA, Coppens S, Pedersen JS, Katzman S, King B, Onodera C, Siepel A, Kern AD, Dehay C, Igel H, Ares M Jr, Vanderhaeghen P, Haussler D (2006) An RNA gene expressed during cortical development evolved rapidly in humans. Nature 443(7108):167–172
Prabhakar S, Visel A, Akiyama JA, Shoukry M, Lewis KD, Holt A, Plajzer-Frick I, Morrison H, Fitzpatrick DR, Afzal V, Pennacchio LA, Rubin EM, Noonan JP (2008) Human-specific gain of function in a developmental enhancer. Science (New York, NY) 321(5894):1346–1350
Capra JA, Erwin GD, McKinsey G, Rubenstein JL, Pollard KS (2013) Many human accelerated regions are developmental enhancers. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 368(1632):20130025
Meyer G, Soria JM, Martinez-Galan JR, Martin-Clemente B, Fairen A (1998) Different origins and developmental histories of transient neurons in the marginal zone of the fetal and neonatal rat cortex. J Comp Neurol 397(4):493–518
Rakic S, Zecevic N (2003) Emerging complexity of layer I in human cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex (New York, NY: 1991) 13(10):1072–1083
Meyer G, Wahle P (1999) The paleocortical ventricle is the origin of reelin-expressing neurons in the marginal zone of the foetal human neocortex. Eur J Neurosci 11(11):3937–3944
Zecevic N, Rakic P (2001) Development of layer I neurons in the primate cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 21(15):5607–5619
Pang KC, Frith MC, Mattick JS (2006) Rapid evolution of noncoding RNAs: lack of conservation does not mean lack of function. Trends Genet 22(1):1–5
Lewitus E, Huttner WB (2015) Neurodevelopmental LincRNA Microsyteny conservation and mammalian brain size evolution. PLoS One 10(7):e0131818
Kelava I, Reillo I, Murayama AY, Kalinka AT, Stenzel D, Tomancak P, Matsuzaki F, Lebrand C, Sasaki E, Schwamborn JC, Okano H, Huttner WB, Borrell V (2012) Abundant occurrence of basal radial glia in the subventricular zone of embryonic neocortex of a lissencephalic primate, the common marmoset Callithrix jacchus. Cereb Cortex (New York, NY: 1991) 22(2):469–481
Kelava I, Lewitus E, Huttner WB (2013) The secondary loss of gyrencephaly as an example of evolutionary phenotypical reversal. Front Neuroanat 7:16
Carninci P, Kasukawa T, Katayama S, Gough J, Frith MC, Maeda N, Oyama R, Ravasi T, Lenhard B, Wells C, Kodzius R, Shimokawa K, Bajic VB, Brenner SE, Batalov S, Forrest AR, Zavolan M, Davis MJ, Wilming LG, Aidinis V, Allen JE, Ambesi-Impiombato A, Apweiler R, Aturaliya RN, Bailey TL, Bansal M, Baxter L, Beisel KW, Bersano T, Bono H, Chalk AM, Chiu KP, Choudhary V, Christoffels A, Clutterbuck DR, Crowe ML, Dalla E, Dalrymple BP, de Bono B, Della Gatta G, di Bernardo D, Down T, Engstrom P, Fagiolini M, Faulkner G, Fletcher CF, Fukushima T, Furuno M, Futaki S, Gariboldi M, Georgii-Hemming P, Gingeras TR, Gojobori T, Green RE, Gustincich S, Harbers M, Hayashi Y, Hensch TK, Hirokawa N, Hill D, Huminiecki L, Iacono M, Ikeo K, Iwama A, Ishikawa T, Jakt M, Kanapin A, Katoh M, Kawasawa Y, Kelso J, Kitamura H, Kitano H, Kollias G, Krishnan SP, Kruger A, Kummerfeld SK, Kurochkin IV, Lareau LF, Lazarevic D, Lipovich L, Liu J, Liuni S, McWilliam S, Madan Babu M, Madera M, Marchionni L, Matsuda H, Matsuzawa S, Miki H, Mignone F, Miyake S, Morris K, Mottagui-Tabar S, Mulder N, Nakano N, Nakauchi H, Ng P, Nilsson R, Nishiguchi S, Nishikawa S, Nori F, Ohara O, Okazaki Y, Orlando V, Pang KC, Pavan WJ, Pavesi G, Pesole G, Petrovsky N, Piazza S, Reed J, Reid JF, Ring BZ, Ringwald M, Rost B, Ruan Y, Salzberg SL, Sandelin A, Schneider C, Schonbach C, Sekiguchi K, Semple CA, Seno S, Sessa L, Sheng Y, Shibata Y, Shimada H, Shimada K, Silva D, Sinclair B, Sperling S, Stupka E, Sugiura K, Sultana R, Takenaka Y, Taki K, Tammoja K, Tan SL, Tang S, Taylor MS, Tegner J, Teichmann SA, Ueda HR, van Nimwegen E, Verardo R, Wei CL, Yagi K, Yamanishi H, Zabarovsky E, Zhu S, Zimmer A, Hide W, Bult C, Grimmond SM, Teasdale RD, Liu ET, Brusic V, Quackenbush J, Wahlestedt C, Mattick JS, Hume DA, Kai C, Sasaki D, Tomaru Y, Fukuda S, Kanamori-Katayama M, Suzuki M, Aoki J, Arakawa T, Iida J, Imamura K, Itoh M, Kato T, Kawaji H, Kawagashira N, Kawashima T, Kojima M, Kondo S, Konno H, Nakano K, Ninomiya N, Nishio T, Okada M, Plessy C, Shibata K, Shiraki T, Suzuki S, Tagami M, Waki K, Watahiki A, Okamura-Oho Y, Suzuki H, Kawai J, Hayashizaki Y, FANTOM Consortium & RIKEN Genome Exploration Research Group and Genome Science Group (Genome Network Project Core Group) (2005) The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science (New York, NY) 309(5740):1559–1563
Xie C, Yuan J, Li H, Li M, Zhao G, Bu D, Zhu W, Wu W, Chen R, Zhao Y (2014) NONCODEv4: exploring the world of long non-coding RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D98–103
Lv J, Liu H, Huang Z, Su J, He H, Xiu Y, Zhang Y, Wu Q (2013) Long non-coding RNA identification over mouse brain development by integrative modeling of chromatin and genomic features. Nucleic Acids Res 41(22):10044–10061
Blackshaw S, Harpavat S, Trimarchi J, Cai L, Huang H, Kuo WP, Weber G, Lee K, Fraioli RE, Cho SH, Yung R, Asch E, Ohno-Machado L, Wong WH, Cepko CL (2004) Genomic analysis of mouse retinal development. PLoS Biol 2(9):E247
Aprea J, Prenninger S, Dori M, Ghosh T, Monasor LS, Wessendorf E, Zocher S, Massalini S, Alexopoulou D, Lesche M, Dahl A, Groszer M, Hiller M, Calegari F (2013) Transcriptome sequencing during mouse brain development identifies long non-coding RNAs functionally involved in neurogenic commitment. EMBO J 32(24):3145–3160
Mehler MF, Mattick JS (2007) Noncoding RNAs and RNA editing in brain development, functional diversification, and neurological disease. Physiol Rev 87(3):799–823
Cabili MN, Trapnell C, Goff L, Koziol M, Tazon-Vega B, Regev A, Rinn JL (2011) Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes Dev 25(18):1915–1927
Jorgenson LA, Newsome WT, Anderson DJ, Bargmann CI, Brown EN, Deisseroth K, Donoghue JP, Hudson KL, Ling GS, MacLeish PR, Marder E, Normann RA, Sanes JR, Schnitzer MJ, Sejnowski TJ, Tank DW, Tsien RY, Ugurbil K, Wingfield JC (2015) The BRAIN initiative: developing technology to catalyse neuroscience discovery. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 370(1668). doi:10.1098/rstb.2014.0164
Zhang K, Huang K, Luo Y, Li S (2014) Identification and functional analysis of long non-coding RNAs in mouse cleavage stage embryonic development based on single cell transcriptome data. BMC Genomics 15:845. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-15-845
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, Slevin MK, Burd CE, Liu J, Marzluff WF, Sharpless NE (2013) Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA (New York, NY) 19(2):141–157
Salzman J, Gawad C, Wang PL, Lacayo N, Brown PO (2012) Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS One 7(2):e30733
Barrett SP, Salzman J (2016) Circular RNAs: analysis, expression and potential functions. Development 143(11):1838–1847
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer M, Loewer A, Ziebold U, Landthaler M, Kocks C, le Noble F, Rajewsky N (2013) Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 495(7441):333–338
Bussotti G, Leonardi T, Clark MB, Mercer TR, Crawford J, Malquori L, Notredame C, Dinger ME, Mattick JS, Enright AJ (2016) Improved definition of the mouse transcriptome via targeted RNA sequencing. Genome Res 26(5):705–716
Mercer TR, Gerhardt DJ, Dinger ME, Crawford J, Trapnell C, Jeddeloh JA, Mattick JS, Rinn JL (2011) Targeted RNA sequencing reveals the deep complexity of the human transcriptome. Nat Biotechnol 30(1):99–104
Clark MB, Mercer TR, Bussotti G, Leonardi T, Haynes KR, Crawford J, Brunck ME, Cao KA, Thomas GP, Chen WY, Taft RJ, Nielsen LK, Enright AJ, Mattick JS, Dinger ME (2015) Quantitative gene profiling of long noncoding RNAs with targeted RNA sequencing. Nat Methods 12(4):339–342
Mercer TR, Clark MB, Crawford J, Brunck ME, Gerhardt DJ, Taft RJ, Nielsen LK, Dinger ME, Mattick JS (2014) Targeted sequencing for gene discovery and quantification using RNA Capture-Seq. Nat Protoc 9(5):989–1009
Dinger ME, Amaral PP, Mercer TR, Pang KC, Bruce SJ, Gardiner BB, Askarian-Amiri ME, Ru K, Solda G, Simons C, Sunkin SM, Crowe ML, Grimmond SM, Perkins AC, Mattick JS (2008) Long noncoding RNAs in mouse embryonic stem cell pluripotency and differentiation. Genome Res 18(9):1433–1445
Bruce SJ, Gardiner BB, Burke LJ, Gongora MM, Grimmond SM, Perkins AC (2007) Dynamic transcription programs during ES cell differentiation towards mesoderm in serum versus serum-freeBMP4 culture. BMC Genomics 8:365
Ivanova NB, Dimos JT, Schaniel C, Hackney JA, Moore KA, Lemischka IR (2002) A stem cell molecular signature. Science (New York, NY) 298(5593):601–604
Ramalho-Santos M, Yoon S, Matsuzaki Y, Mulligan RC, Melton DA (2002) "Stemness": transcriptional profiling of embryonic and adult stem cells. Science (New York, NY) 298(5593):597–600
Meshorer E, Yellajoshula D, George E, Scambler PJ, Brown DT, Misteli T (2006) Hyperdynamic plasticity of chromatin proteins in pluripotent embryonic stem cells. Dev Cell 10(1):105–116
Meshorer E, Misteli T (2006) Chromatin in pluripotent embryonic stem cells and differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7(7):540–546
Gaspar-Maia A, Alajem A, Polesso F, Sridharan R, Mason MJ, Heidersbach A, Ramalho-Santos J, McManus MT, Plath K, Meshorer E, Ramalho-Santos M (2009) Chd1 regulates open chromatin and pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. Nature 460(7257):863–868
Guttman M, Amit I, Garber M, French C, Lin MF, Feldser D, Huarte M, Zuk O, Carey BW, Cassady JP, Cabili MN, Jaenisch R, Mikkelsen TS, Jacks T, Hacohen N, Bernstein BE, Kellis M, Regev A, Rinn JL, Lander ES (2009) Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 458(7235):223–227
Guttman M, Garber M, Levin JZ, Donaghey J, Robinson J, Adiconis X, Fan L, Koziol MJ, Gnirke A, Nusbaum C, Rinn JL, Lander ES, Regev A (2010) Ab initio reconstruction of cell type-specific transcriptomes in mouse reveals the conserved multi-exonic structure of lincRNAs. Nat Biotechnol 28(5):503–510
Mercer TR, Qureshi IA, Gokhan S, Dinger ME, Li G, Mattick JS, Mehler MF (2010) Long noncoding RNAs in neuronal-glial fate specification and oligodendrocyte lineage maturation. BMC Neurosci 11:14. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-11-14
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A, Meyer J, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2002) Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr Biol 12(9):735–739
Makeyev EV, Zhang J, Carrasco MA, Maniatis T (2007) The MicroRNA miR-124 promotes neuronal differentiation by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 27(3):435–448
Ng SY, Johnson R, Stanton LW (2012) Human long non-coding RNAs promote pluripotency and neuronal differentiation by association with chromatin modifiers and transcription factors. EMBO J 31(3):522–533
Guo Y, Zhang P, Sheng Q, Zhao S, Hackett TA (2016) lncRNA expression in the auditory forebrain during postnatal development. Gene 593(1):201–216
Ramos AD, Diaz A, Nellore A, Delgado RN, Park KY, Gonzales-Roybal G, Oldham MC, Song JS, Lim DA (2013) Integration of genome-wide approaches identifies lncRNAs of adult neural stem cells and their progeny in vivo. Cell Stem Cell 12(5):616–628
Liu SJ, Nowakowski TJ, Pollen AA, Lui JH, Horlbeck MA, Attenello FJ, He D, Weissman JS, Kriegstein AR, Diaz AA, Lim DA (2016) Single-cell analysis of long non-coding RNAs in the developing human neocortex. Genome Biol 17:67. doi:10.1186/s13059-016-0932-1
Rapicavoli NA, Blackshaw S (2009) New meaning in the message: noncoding RNAs and their role in retinal development. Dev Dyn 238(9):2103–2114
Molyneaux BJ, Goff LA, Brettler AC, Chen HH, Brown JR, Hrvatin S, Rinn JL, Arlotta P (2015) DeCoN: genome-wide analysis of in vivo transcriptional dynamics during pyramidal neuron fate selection in neocortex. Neuron 85(2):275–288
Lein ES, Hawrylycz MJ, Ao N, Ayres M, Bensinger A, Bernard A, Boe AF, Boguski MS, Brockway KS, Byrnes EJ, Chen L, Chen L, Chen TM, Chin MC, Chong J, Crook BE, Czaplinska A, Dang CN, Datta S, Dee NR, Desaki AL, Desta T, Diep E, Dolbeare TA, Donelan MJ, Dong HW, Dougherty JG, Duncan BJ, Ebbert AJ, Eichele G, Estin LK, Faber C, Facer BA, Fields R, Fischer SR, Fliss TP, Frensley C, Gates SN, Glattfelder KJ, Halverson KR, Hart MR, Hohmann JG, Howell MP, Jeung DP, Johnson RA, Karr PT, Kawal R, Kidney JM, Knapik RH, Kuan CL, Lake JH, Laramee AR, Larsen KD, Lau C, Lemon TA, Liang AJ, Liu Y, Luong LT, Michaels J, Morgan JJ, Morgan RJ, Mortrud MT, Mosqueda NF, Ng LL, Ng R, Orta GJ, Overly CC, Pak TH, Parry SE, Pathak SD, Pearson OC, Puchalski RB, Riley ZL, Rockett HR, Rowland SA, Royall JJ, Ruiz MJ, Sarno NR, Schaffnit K, Shapovalova NV, Sivisay T, Slaughterbeck CR, Smith SC, Smith KA, Smith BI, Sodt AJ, Stewart NN, Stumpf KR, Sunkin SM, Sutram M, Tam A, Teemer CD, Thaller C, Thompson CL, Varnam LR, Visel A, Whitlock RM, Wohnoutka PE, Wolkey CK, Wong VY, Wood M, Yaylaoglu MB, Young RC, Youngstrom BL, Yuan XF, Zhang B, Zwingman TA, Jones AR (2007) Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature 445(7124):168–176
Kour S, Rath PC (2015) Age-dependent differential expression profile of a novel intergenic long noncoding RNA in rat brain. Int J Dev Neurosci 47(Pt B):286–297
Mills JD, Chen J, Kim WS, Waters PD, Prabowo AS, Aronica E, Halliday GM, Janitz M (2015) Long intervening non-coding RNA 00320 is human brain-specific and highly expressed in the cortical white matter. Neurogenetics 16(3):201–213
Dietz WH, Masterson K, Sittig LJ, Redei EE, Herzing LB (2012) Imprinting and expression of Dio3os mirrors Dio3 in rat. Front Genet 3:279
Kohtz JD, Baker DP, Corte G, Fishell G (1998) Regionalization within the mammalian telencephalon is mediated by changes in responsiveness to sonic hedgehog. Development 125(24):5079–5089
Kohtz JD, Fishell G (2004) Developmental regulation of EVF-1, a novel non-coding RNA transcribed upstream of the mouse Dlx6 gene. Gene Expr Patterns 4(4):407–412
Feng J, Bi C, Clark BS, Mady R, Shah P, Kohtz JD (2006) The Evf-2 noncoding RNA is transcribed from the Dlx-5/6 ultraconserved region and functions as a Dlx-2 transcriptional coactivator. Genes Dev 20(11):1470–1484
Davis CJ, Taishi P, Honn KA, Koberstein JN, Krueger JM (2016) P2X7 receptors in body temperature, locomotor activity, and brain mRNA and lncRNA responses to sleep deprivation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 311(6):R1004–R1012. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00167.2016
Zhong J, Jiang L, Cheng C, Huang Z, Zhang H, Liu H, He J, Cao F, Peng J, Jiang Y, Sun X (2016) Altered expression of long non-coding RNA and mRNA in mouse cortex after traumatic brain injury. Brain Res 1646:589–600
Jiang H, Good DJ (2016) A molecular conundrum involving hypothalamic responses to and roles of long non-coding RNAs following food deprivation. Mol Cell Endocrinol 438:52–60
D’haene E, Jacobs EZ, Volders PJ, De Meyer T, Menten B, Vergult S (2016) Identification of long non-coding RNAs involved in neuronal development and intellectual disability. Sci Rep 6:28396
Chen R, Liu L, Xiao M, Wang F, Lin X (2016) Microarray expression profile analysis of long noncoding RNAs in premature brain injury: a novel point of view. Neuroscience 319:123–133
Kraus TF, Haider M, Spanner J, Steinmaurer M, Dietinger V, Kretzschmar HA (2016) Altered long noncoding RNA expression precedes the course of Parkinson’s disease-a preliminary report. Mol Neurobiol 54(4):2869–2877
Faedo A, Quinn JC, Stoney P, Long JE, Dye C, Zollo M, Rubenstein JL, Price DJ, Bulfone A (2004) Identification and characterization of a novel transcript down-regulated in Dlx1/Dlx2 and up-regulated in Pax6 mutant telencephalon. Dev Dyn 231(3):614–620
Kour S, Rath PC (2016) All-trans retinoic acid induces expression of a novel Intergenic long noncoding RNA in adult rat primary hippocampal neurons. J Mol Neurosci 58(2):266–276
Chen X, Zhou X, Lu D, Yang X, Zhou Z, Chen X, Chen Y, He W, Feng X (2016) Aberrantly expressed long noncoding RNAs are involved in sevoflurane-induced developing hippocampal neuronal apoptosis: a microarray related study. Metab Brain Dis 31(5):1031–1040
Clark BS, Blackshaw S (2014) Long non-coding RNA-dependent transcriptional regulation in neuronal development and disease. Front Genet 5:164
Guttman M, Donaghey J, Carey BW, Garber M, Grenier JK, Munson G, Young G, Lucas AB, Ach R, Bruhn L, Yang X, Amit I, Meissner A, Regev A, Rinn JL, Root DE, Lander ES (2011) lincRNAs act in the circuitry controlling pluripotency and differentiation. Nature 477(7364):295–300
Wang C, Li G, Wu Y, Xi J, Kang J (2016) LincRNA1230 inhibits the differentiation of mouse ES cells towards neural progenitors. Sci China Life Sci 59(5):443–454
Lin N, Chang KY, Li Z, Gates K, Rana ZA, Dang J, Zhang D, Han T, Yang CS, Cunningham TJ, Head SR, Duester G, Dong PD, Rana TM (2014) An evolutionarily conserved long noncoding RNA TUNA controls pluripotency and neural lineage commitment. Mol Cell 53(6):1005–1019
Chu C, Qu K, Zhong FL, Artandi SE, Chang HY (2011) Genomic maps of long noncoding RNA occupancy reveal principles of RNA-chromatin interactions. Mol Cell 44(4):667–678
Ng SY, Bogu GK, Soh BS, Stanton LW (2013) The long noncoding RNA RMST interacts with SOX2 to regulate neurogenesis. Mol Cell 51(3):349–359
Anderegg A, Lin HP, Chen JA, Caronia-Brown G, Cherepanova N, Yun B, Joksimovic M, Rock J, Harfe BD, Johnson R, Awatramani R (2013) An Lmx1b-miR135a2 regulatory circuit modulates Wnt1/Wnt signaling and determines the size of the midbrain dopaminergic progenitor pool. PLoS Genet 9(12):e1003973
Anderegg A, Awatramani R (2015) k the size of the midbrain and the dopaminergic progenitor pool. Neurogenesis (Austin, TX) 2(1):e998101
Caronia-Brown G, Anderegg A, Awatramani R (2016) Expression and functional analysis of the Wnt/beta-catenin induced mir-135a-2 locus in embryonic forebrain development. Neural Dev 11:9. doi:10.1186/s13064-016-0065-y
Tochitani S, Hayashizaki Y (2008) Nkx2.2 antisense RNA overexpression enhanced oligodendrocytic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 372(4):691–696
Qi Y, Cai J, Wu Y, Wu R, Lee J, Fu H, Rao M, Sussel L, Rubenstein J, Qiu M (2001) Control of oligodendrocyte differentiation by the Nkx2.2 homeodomain transcription factor. Development 128(14):2723–2733
Dong X, Chen K, Cuevas-Diaz Duran R, You Y, Sloan SA, Zhang Y, Zong S, Cao Q, Barres BA, Wu JQ (2015) Comprehensive identification of long non-coding RNAs in purified cell types from the brain reveals functional LncRNA in OPC fate determination. PLoS Genet 11(12):e1005669
Yang N, Zuchero JB, Ahlenius H, Marro S, Ng YH, Vierbuchen T, Hawkins JS, Geissler R, Barres BA, Wernig M (2013) Generation of oligodendroglial cells by direct lineage conversion. Nat Biotechnol 31(5):434–439
Lu QR, Sun T, Zhu Z, Ma N, Garcia M, Stiles CD, Rowitch DH (2002) Common developmental requirement for Olig function indicates a motor neuron/oligodendrocyte connection. Cell 109(1):75–86
Zhou Q, Choi G, Anderson DJ (2001) The bHLH transcription factor Olig2 promotes oligodendrocyte differentiation in collaboration with Nkx2.2. Neuron 31(5):791–807
Rani N, Nowakowski TJ, Zhou H, Godshalk SE, Lisi V, Kriegstein AR, Kosik KS (2016) A primate lncRNA mediates notch signaling during neuronal development by sequestering miRNA. Neuron 90(6):1174–1188
Cesana M, Cacchiarelli D, Legnini I, Santini T, Sthandier O, Chinappi M, Tramontano A, Bozzoni I (2011) A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 147(2):358–369
Ebert MS, Sharp PA (2010) Emerging roles for natural microRNA sponges. Curr Biol 20(19):R858–R861
Hansen TB, Kjems J, Damgaard CK (2013) Circular RNA and miR-7 in cancer. Cancer Res 73(18):5609–5612
Kallen AN, Zhou XB, Xu J, Qiao C, Ma J, Yan L, Lu L, Liu C, Yi JS, Zhang H, Min W, Bennett AM, Gregory RI, Ding Y, Huang Y (2013) The imprinted H19 lncRNA antagonizes let-7 microRNAs. Mol Cell 52(1):101–112
Tay Y, Kats L, Salmena L, Weiss D, Tan SM, Ala U, Karreth F, Poliseno L, Provero P, Di Cunto F, Lieberman J, Rigoutsos I, Pandolfi PP (2011) Coding-independent regulation of the tumor suppressor PTEN by competing endogenous mRNAs. Cell 147(2):344–357
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP (2014) The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 505(7483):344–352
Wang Y, Xu Z, Jiang J, Xu C, Kang J, Xiao L, Wu M, Xiong J, Guo X, Liu H (2013) Endogenous miRNA sponge lincRNA-RoR regulates Oct4, Nanog, and Sox2 in human embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Dev Cell 25(1):69–80
Zhang Z, Zhu Z, Watabe K, Zhang X, Bai C, Xu M, Wu F, Mo YY (2013) Negative regulation of lncRNA GAS5 by miR-21. Cell Death Differ 20(11):1558–1568
Bail S, Swerdel M, Liu H, Jiao X, Goff LA, Hart RP, Kiledjian M (2010) Differential regulation of microRNA stability. RNA (New York, NY) 16(5):1032–1039
Legnini I, Morlando M, Mangiavacchi A, Fatica A, Bozzoni I (2014) A feedforward regulatory loop between HuR and the long noncoding RNA linc-MD1 controls early phases of myogenesis. Mol Cell 53(3):506–514
Stevens SJ, van Ravenswaaij-Arts CM, Janssen JW, Klein Wassink-Ruiter JS, van Essen AJ, Dijkhuizen T, van Rheenen J, Heuts-Vijgen R, Stegmann AP, Smeets EE, Engelen JJ (2011) MYT1L is a candidate gene for intellectual disability in patients with 2p25.3 (2pter) deletions. Am J Med Genet A 155A(11):2739–2745
Rio M, Royer G, Gobin S, de Blois MC, Ozilou C, Bernheim A, Nizon M, Munnich A, Bonnefont JP, Romana S, Vekemans M, Turleau C, Malan V (2013) Monozygotic twins discordant for submicroscopic chromosomal anomalies in 2p25.3 region detected by array CGH. Clin Genet 84(1):31–36
Doco-Fenzy M, Leroy C, Schneider A, Petit F, Delrue MA, Andrieux J, Perrin-Sabourin L, Landais E, Aboura A, Puechberty J, Girard M, Tournaire M, Sanchez E, Rooryck C, Ameil A, Goossens M, Jonveaux P, Lefort G, Taine L, Cailley D, Gaillard D, Leheup B, Sarda P, Genevieve D (2014) Early-onset obesity and paternal 2pter deletion encompassing the ACP1, TMEM18, and MYT1L genes. Eur J Hum Genet 22(4):471–479
Bonaglia MC, Giorda R, Zanini S (2014) A new patient with a terminal de novo 2p25.3 deletion of 1.9 Mb associated with early-onset of obesity, intellectual disabilities and hyperkinetic disorder. Mol Cytogenet 7:53. doi:10.1186/1755-8166-7-53
Gaiano N, Nye JS, Fishell G (2000) Radial glial identity is promoted by Notch1 signaling in the murine forebrain. Neuron 26(2):395–404
Shimojo H, Ohtsuka T, Kageyama R (2008) Oscillations in notch signaling regulate maintenance of neural progenitors. Neuron 58(1):52–64
Yoon KJ, Koo BK, Im SK, Jeong HW, Ghim J, Kwon MC, Moon JS, Miyata T, Kong YY (2008) Mind bomb 1-expressing intermediate progenitors generate notch signaling to maintain radial glial cells. Neuron 58(4):519–531
Gordon FE, Nutt CL, Cheunsuchon P, Nakayama Y, Provencher KA, Rice KA, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Klibanski A (2010) Increased expression of angiogenic genes in the brains of mouse meg3-null embryos. Endocrinology 151(6):2443–2452
Sun S, Payer B, Namekawa S, An JY, Press W, Catalan-Dibene J, Sunwoo H, Lee JT (2015) Xist imprinting is promoted by the hemizygous (unpaired) state in the male germ line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(47):14415–14422
Alfano G, Vitiello C, Caccioppoli C, Caramico T, Carola A, Szego MJ, McInnes RR, Auricchio A, Banfi S (2005) Natural antisense transcripts associated with genes involved in eye development. Hum Mol Genet 14(7):913–923
Young TL, Matsuda T, Cepko CL (2005) The noncoding RNA taurine upregulated gene 1 is required for differentiation of the murine retina. Curr Biol 15(6):501–512
Krol J, Krol I, Alvarez CP, Fiscella M, Hierlemann A, Roska B, Filipowicz W (2015) A network comprising short and long noncoding RNAs and RNA helicase controls mouse retina architecture. Nat Commun 6:7305
Rapicavoli NA, Poth EM, Blackshaw S (2010) The long noncoding RNA RNCR2 directs mouse retinal cell specification. BMC Dev Biol 10:49. doi:10.1186/1471-213X-10-49
Rapicavoli NA, Poth EM, Zhu H, Blackshaw S (2011) The long noncoding RNA Six3OS acts in trans to regulate retinal development by modulating Six3 activity. Neural Dev 6:32. doi:10.1186/1749-8104-6-32
Khalil AM, Guttman M, Huarte M, Garber M, Raj A, Rivea Morales D, Thomas K, Presser A, Bernstein BE, van Oudenaarden A, Regev A, Lander ES, Rinn JL (2009) Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(28):11667–11672
Ishii N, Ozaki K, Sato H, Mizuno H, Saito S, Takahashi A, Miyamoto Y, Ikegawa S, Kamatani N, Hori M, Saito S, Nakamura Y, Tanaka T (2006) Identification of a novel non-coding RNA, MIAT, that confers risk of myocardial infarction. J Hum Genet 51(12):1087–1099
Sone M, Hayashi T, Tarui H, Agata K, Takeichi M, Nakagawa S (2007) The mRNA-like noncoding RNA Gomafu constitutes a novel nuclear domain in a subset of neurons. J Cell Sci 120(Pt 15):2498–2506
Barry G, Briggs JA, Vanichkina DP, Poth EM, Beveridge NJ, Ratnu VS, Nayler SP, Nones K, Hu J, Bredy TW, Nakagawa S, Rigo F, Taft RJ, Cairns MJ, Blackshaw S, Wolvetang EJ, Mattick JS (2014) The long non-coding RNA Gomafu is acutely regulated in response to neuronal activation and involved in schizophrenia-associated alternative splicing. Mol Psychiatry 19(4):486–494
Zhao J, Ohsumi TK, Kung JT, Ogawa Y, Grau DJ, Sarma K, Song JJ, Kingston RE, Borowsky M, Lee JT (2010) Genome-wide identification of polycomb-associated RNAs by RIP-seq. Mol Cell 40(6):939–953
Meola N, Pizzo M, Alfano G, Surace EM, Banfi S (2012) The long noncoding RNA Vax2os1 controls the cell cycle progression of photoreceptor progenitors in the mouse retina. RNA (New York, NY) 18(1):111–123
Ramos AD, Andersen RE, Liu SJ, Nowakowski TJ, Hong SJ, Gertz CC, Salinas RD, Zarabi H, Kriegstein AR, Lim DA (2015) The long noncoding RNA Pnky regulates neuronal differentiation of embryonic and postnatal neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 16(4):439–447
Kriegstein A, Alvarez-Buylla A (2009) The glial nature of embryonic and adult neural stem cells. Annu Rev Neurosci 32:149–184
Zheng S, Gray EE, Chawla G, Porse BT, O’Dell TJ, Black DL (2012) PSD-95 is post-transcriptionally repressed during early neural development by PTBP1 and PTBP2. Nat Neurosci 15(3):381–388, S1.
Yap K, Lim ZQ, Khandelia P, Friedman B, Makeyev EV (2012) Coordinated regulation of neuronal mRNA steady-state levels through developmentally controlled intron retention. Genes Dev 26(11):1209–1223
Keppetipola N, Sharma S, Li Q, Black DL (2012) Neuronal regulation of pre-mRNA splicing by polypyrimidine tract binding proteins, PTBP1 and PTBP2. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 47(4):360–378
Shibasaki T, Tokunaga A, Sakamoto R, Sagara H, Noguchi S, Sasaoka T, Yoshida N (2013) PTB deficiency causes the loss of adherens junctions in the dorsal telencephalon and leads to lethal hydrocephalus. Cereb Cortex (New York, NY: 1991) 23(8):1824–1835
Boutz PL, Stoilov P, Li Q, Lin CH, Chawla G, Ostrow K, Shiue L, Ares M Jr, Black DL (2007) A post-transcriptional regulatory switch in polypyrimidine tract-binding proteins reprograms alternative splicing in developing neurons. Genes Dev 21(13):1636–1652
Licatalosi DD, Yano M, Fak JJ, Mele A, Grabinski SE, Zhang C, Darnell RB (2012) Ptbp2 represses adult-specific splicing to regulate the generation of neuronal precursors in the embryonic brain. Genes Dev 26(14):1626–1642
Bond AM, Vangompel MJ, Sametsky EA, Clark MF, Savage JC, Disterhoft JF, Kohtz JD (2009) Balanced gene regulation by an embryonic brain ncRNA is critical for adult hippocampal GABA circuitry. Nat Neurosci 12(8):1020–1027
Berghoff EG, Clark MF, Chen S, Cajigas I, Leib DE, Kohtz JD (2013) Evf2 (Dlx6as) lncRNA regulates ultraconserved enhancer methylation and the differential transcriptional control of adjacent genes. Development 140(21):4407–4416
Cajigas I, Leib DE, Cochrane J, Luo H, Swyter KR, Chen S, Clark BS, Thompson J, Yates JR 3rd, Kingston RE, Kohtz JD (2015) Evf2 lncRNA/BRG1/DLX1 interactions reveal RNA-dependent inhibition of chromatin remodeling. Development 142(15):2641–2652
Kraus P, Sivakamasundari V, Lim SL, Xing X, Lipovich L, Lufkin T (2013) Making sense of Dlx1 antisense RNA. Dev Biol 376(2):224–235
Cobos I, Calcagnotto ME, Vilaythong AJ, Thwin MT, Noebels JL, Baraban SC, Rubenstein JL (2005) Mice lacking Dlx1 show subtype-specific loss of interneurons, reduced inhibition and epilepsy. Nat Neurosci 8(8):1059–1068
Jones DL, Howard MA, Stanco A, Rubenstein JL, Baraban SC (2011) Deletion of Dlx1 results in reduced glutamatergic input to hippocampal interneurons. J Neurophysiol 105(5):1984–1991
Petryniak MA, Potter GB, Rowitch DH, Rubenstein JL (2007) Dlx1 and Dlx2 control neuronal versus oligodendroglial cell fate acquisition in the developing forebrain. Neuron 55(3):417–433
Niwa H, Yamamura K, Miyazaki J (1991) Efficient selection for high-expression transfectants with a novel eukaryotic vector. Gene 108(2):193–199
Stuhmer T, Anderson SA, Ekker M, Rubenstein JL (2002) Ectopic expression of the Dlx genes induces glutamic acid decarboxylase and Dlx expression. Development 129(1):245–252
Sauvageau M, Goff LA, Lodato S, Bonev B, Groff AF, Gerhardinger C, Sanchez-Gomez DB, Hacisuleyman E, Li E, Spence M, Liapis SC, Mallard W, Morse M, Swerdel MR, D’Ecclessis MF, Moore JC, Lai V, Gong G, Yancopoulos GD, Frendewey D, Kellis M, Hart RP, Valenzuela DM, Arlotta P, Rinn JL (2013) Multiple knockout mouse models reveal lincRNAs are required for life and brain development. elife 2:e01749
Grote P, Herrmann BG (2013) The long non-coding RNA Fendrr links epigenetic control mechanisms to gene regulatory networks in mammalian embryogenesis. RNA Biol 10(10):1579–1585
Grote P, Wittler L, Hendrix D, Koch F, Wahrisch S, Beisaw A, Macura K, Blass G, Kellis M, Werber M, Herrmann BG (2013) The tissue-specific lncRNA Fendrr is an essential regulator of heart and body wall development in the mouse. Dev Cell 24(2):206–214
McEvilly RJ, de Diaz MO, Schonemann MD, Hooshmand F, Rosenfeld MG (2002) Transcriptional regulation of cortical neuron migration by POU domain factors. Science (New York, NY) 295(5559):1528–1532
Sugitani Y, Nakai S, Minowa O, Nishi M, Jishage K, Kawano H, Mori K, Ogawa M, Noda T (2002) Brn-1 and Brn-2 share crucial roles in the production and positioning of mouse neocortical neurons. Genes Dev 16(14):1760–1765
Dominguez MH, Ayoub AE, Rakic P (2013) POU-III transcription factors (Brn1, Brn2, and Oct6) influence neurogenesis, molecular identity, and migratory destination of upper-layer cells of the cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex (New York, NY: 1991) 23(11):2632–2643
Goff LA, Groff AF, Sauvageau M, Trayes-Gibson Z, Sanchez-Gomez DB, Morse M, Martin RD, Elcavage LE, Liapis SC, Gonzalez-Celeiro M, Plana O, Li E, Gerhardinger C, Tomassy GS, Arlotta P, Rinn JL (2015) Spatiotemporal expression and transcriptional perturbations by long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(22):6855–6862
Eissmann M, Gutschner T, Hammerle M, Gunther S, Caudron-Herger M, Gross M, Schirmacher P, Rippe K, Braun T, Zornig M, Diederichs S (2012) Loss of the abundant nuclear non-coding RNA MALAT1 is compatible with life and development. RNA Biol 9(8):1076–1087
Nakagawa S, Ip JY, Shioi G, Tripathi V, Zong X, Hirose T, Prasanth KV (2012) Malat1 is not an essential component of nuclear speckles in mice. RNA (New York, NY) 18(8):1487–1499
Zhang B, Arun G, Mao YS, Lazar Z, Hung G, Bhattacharjee G, Xiao X, Booth CJ, Wu J, Zhang C, Spector DL (2012) The lncRNA Malat1 is dispensable for mouse development but its transcription plays a cis-regulatory role in the adult. Cell Rep 2(1):111–123
Oliver PL, Chodroff RA, Gosal A, Edwards B, Cheung AF, Gomez-Rodriguez J, Elliot G, Garrett LJ, Lickiss T, Szele F, Green ED, Molnar Z, Ponting CP (2015) Disruption of Visc-2, a brain-expressed conserved long noncoding RNA, does not elicit an overt anatomical or behavioral phenotype. Cereb cortex (New York, NY: 1991) 25(10):3572–3585
Sunwoo H, Dinger ME, Wilusz JE, Amaral PP, Mattick JS, Spector DL (2009) MEN epsilon/beta nuclear-retained non-coding RNAs are up-regulated upon muscle differentiation and are essential components of paraspeckles. Genome Res 19(3):347–359
Sasaki YT, Ideue T, Sano M, Mituyama T, Hirose T (2009) MENepsilon/beta noncoding RNAs are essential for structural integrity of nuclear paraspeckles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(8):2525–2530
Clemson CM, Hutchinson JN, Sara SA, Ensminger AW, Fox AH, Chess A, Lawrence JB (2009) An architectural role for a nuclear noncoding RNA: NEAT1 RNA is essential for the structure of paraspeckles. Mol Cell 33(6):717–726
Fox AH, Bond CS, Lamond AI (2005) P54nrb forms a heterodimer with PSP1 that localizes to paraspeckles in an RNA-dependent manner. Mol Biol Cell 16(11):5304–5315
Chen LL, Carmichael GG (2009) Altered nuclear retention of mRNAs containing inverted repeats in human embryonic stem cells: functional role of a nuclear noncoding RNA. Mol Cell 35(4):467–478
Nakagawa S, Naganuma T, Shioi G, Hirose T (2011) Paraspeckles are subpopulation-specific nuclear bodies that are not essential in mice. J Cell Biol 193(1):31–39
Nakagawa S, Shimada M, Yanaka K, Mito M, Arai T, Takahashi E, Fujita Y, Fujimori T, Standaert L, Marine JC, Hirose T (2014) The lncRNA Neat1 is required for corpus luteum formation and the establishment of pregnancy in a subpopulation of mice. Development 141(23):4618–4627
West JA, Mito M, Kurosaka S, Takumi T, Tanegashima C, Chujo T, Yanaka K, Kingston RE, Hirose T, Bond C, Fox A, Nakagawa S (2016) Structural, super-resolution microscopy analysis of paraspeckle nuclear body organization. J Cell Biol 214(7):817–830
Nishimoto Y, Nakagawa S, Hirose T, Okano HJ, Takao M, Shibata S, Suyama S, Kuwako K, Imai T, Murayama S, Suzuki N, Okano H (2013) The long non-coding RNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1_2 induces paraspeckle formation in the motor neuron during the early phase of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol Brain 6:31. doi:10.1186/1756-6606-6-31
Ip JY, Sone M, Nashiki C, Pan Q, Kitaichi K, Yanaka K, Abe T, Takao K, Miyakawa T, Blencowe BJ, Nakagawa S (2016) Gomafu lncRNA knockout mice exhibit mild hyperactivity with enhanced responsiveness to the psychostimulant methamphetamine. Sci Rep 6:27204
Tsuiji H, Yoshimoto R, Hasegawa Y, Furuno M, Yoshida M, Nakagawa S (2011) Competition between a noncoding exon and introns: Gomafu contains tandem UACUAAC repeats and associates with splicing factor-1. Genes Cells 16(5):479–490
Ishizuka A, Hasegawa Y, Ishida K, Yanaka K, Nakagawa S (2014) Formation of nuclear bodies by the lncRNA Gomafu-associating proteins Celf3 and SF1. Genes Cells 19(9):704–721
Acknowledgments
B.S.C. was supported by F32EY024201 from the NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Clark, B.S., Blackshaw, S. (2017). Understanding the Role of lncRNAs in Nervous System Development. In: Rao, M. (eds) Long Non Coding RNA Biology. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 1008. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5203-3_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5203-3_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN: 978-981-10-5202-6
Online ISBN: 978-981-10-5203-3
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)