Abstract
Background: Oxidative stress is known to interfere with the fertilization capacity of spermatozoa damaging sperm nuclear DNA and affecting the epigenetic profile of these cells. Cinnamtannin B-1 (CINB-1) is a naturally occurring A-type proanthocyanidin found in a limited number of plants including Linderae umbellateae and L. nobilis, which exhibit antioxidant properties. It has been proven its DNA protection by the Terminal dUTP Nick-End Labeling assay (TUNEL). The objective of this study is to evaluate the CINB-1 sperm DNA protection with the Sperm Cromatine Structure Assay (SCSA®) to evaluate the fragmentation after the oxidative stress produced by incubation at 37 °C (4 h).
Access provided by Autonomous University of Puebla. Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Background: Oxidative stress is known to interfere with the fertilization capacity of spermatozoa damaging sperm nuclear DNA and affecting the epigenetic profile of these cells. Cinnamtannin B-1 (CINB-1) is a naturally occurring A-type proanthocyanidin found in a limited number of plants including Linderae umbellateae and L. nobilis, which exhibit antioxidant properties. It has been proven its DNA protection by the Terminal dUTP Nick-End Labeling assay (TUNEL). The objective of this study is to evaluate the CINB-1 sperm DNA protection with the Sperm Cromatine Structure Assay (SCSA®) to evaluate the fragmentation after the oxidative stress produced by incubation at 37 °C (4 h).
Main questions: Does CINB-1 protects or destabilize sperm DNA?
Experimental Design: Ninety samples were evaluated from 15 sperm donors. Sperm samples were collected with a period of abstinence between 48 and 72 h and were incubated at 37 °C for 4 h with 0, 10, and 100 μM of CINB-1. DNA integrity was checked by measuring the index of sperm DNA fragmentation (DFI), for which TUNEL assay and the SCSA® were used.
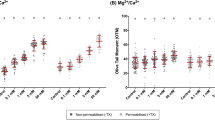
Main Results: The TUNEL assay found significant differences when comparing the samples with CINB-1 with the control at 4 h, observing a positive effect when decreasing the percentage of DFI (Control 4 h 15.12 ± 1.15; 10 μM 10.08 ± 0.93; 100 μM 9.44 ± 0.74; (p < 0.001)). The SCSA® showed significant differences (p < 0.001) between control and CINB-1 treatments (Control 0 h 21.91 ± 3.03; Control 4 h 18.69 ± 3.10; 10 μM 66.38 ± 9.38; 100 μM 92.85 ± 5.18 (p < 0.001)). We observe how the CINB-1 exerts a negative effect on the sperm, the greater the concentration of CNB-1, the greater the DFI.
Conclusions: The SCSA® and TUNEL techniques offer contradictory results regarding the protection of CINB-1 in fresh human semen samples. As other authors have already pointed out, it is probably that the TUNEL assay is a very insensitive methodology for assessing DNA damage in spermatozoa. This insensitivity has been related to the truncated base excision repair pathway in spermatozoa, lacking the abasic site endonuclease. These cells cannot create the 3′-OH termini that are required by the TUNEL assay.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
García, J.B. et al. (2021). Does Cinnamtannin B-1 Protect or Destabilize Sperm DNA? Contradictory Results of SCSA® and TUNEL. In: Björndahl, L., Flanagan, J., Holmberg, R., Kvist, U. (eds) XIIIth International Symposium on Spermatology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66292-9_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66292-9_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-66291-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-66292-9
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)