Abstract
Blockchain has been used to solve problems from different sectors. In agriculture, Blockchain is being applied for improving food safety, and transaction times. The increasing interest of Blockchain technology in agriculture calls for a clear, systematic overview. In this sense, we present a systematic literature review (SLR) whose objective is to collect all relevant research on Blockchain technology in agriculture to detect current research topics, main contributions, and benefits of applying Blockchain in agriculture. We have extracted 10 primary studies from scientific databases and web sources published between 2016 and 2018, which means that Blockchain is a recent research area in the agricultural sector. The results show that 60% of papers are focused on food supply chain. Also, 50% of the studies on Blockchain in Agriculture are dominated by Asian community researchers, especially from China. Similarly, the half of the studies addressed challenges related to privacy and security of the Internet of Things with Blockchain technology.
Access provided by CONRICYT-eBooks. Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
Agriculture is one of the most important sectors in the world. The agricultural productivity is important for a country’s economy as well as the security, nutrition, and health of its population. In recent years, farmers have adopted different technologies such as IoT and Blockchain aiming to obtain greater yields in the agricultural process.
Blockchain technology has been used for responding to a wide range of challenges from different domains such as financial [1, 2], health [3, 4], and energy [5, 6], to mention but a few. In the agriculture sector, Blockchain is being applied in supply chain management systems to provide transparency, security, neutrality, and reliability of all the operations in a supply chain. Blockchain will also help in solving most of the Internet of things challenges related to security and reliability.
It is important to identify what topics related to the agriculture sector have been already studied and addressed in Blockchain and what are currently the biggest challenges and limitations that need further studies. To address these questions, we presented a Systematic Literature Review (SLR) to identify relevant papers related to Blockchain in agriculture. The systematic literature review presented was performed by following the methodology proposed by Brereton et al. [7]. This information could help other researchers in identifying possible research areas for future research as well as farmers to know technologies and approaches that are being used.
Although there are currently several works that present a systematic literature review of the Blockchain [8,9,10,11,12], there is still no proposal that presents a systematic literature review of Blockchain in agriculture.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Sect. 2 presents the research methodology which is divided into three parts: systematic review planning, systematic review execution, and results, while Sect. 3 presents a discussion of the obtained results. Finally, our conclusions are presented in Sect. 4.
2 Research Methodology
The main goal of a systematic literature review is to detect relevant literature in the subject area. This systematic literature review presented was performed by following the methodology proposed by Brereton et al. [7]. The process consists of three major phases: planning, execution, and result analysis. The first phase refers to planning the review, identifying its needs and defining its protocol which involves (a) research questions, (b) search strategy and (c) studies selection. The second phase consists of the execution of the established plan extracting relevant information. Finally, the third phase consists of providing results and conclusions.
2.1 Systematic Review Planning
This phase defines the way the systematic review will be performed and the research objectives. Hence, we define research questions to be addressed, and planned how the information sources and studies will be selected. This phase is composed of three steps: question formulation, search strategy, and studies selection.
Research Questions
This section presents the three research questions that guided us throughout the research and helped us meet the goals of the Systematic literature review. Table 1 presents the questions and the main motivations.
Search Strategy
The search strategy is at the core of a systematic review. The first stage of our search strategy was to identify the digital libraries and web sources wherein the search for primary studies would be carried out. We selected four digital libraries:
-
1.
IEEE Xplore Digital Library,
-
2.
ACM Digital Library,
-
3.
ScienceDirect (Elsevier),
-
4.
Springer
Furthermore, we selected two Web sources to broaden or results:
-
5.
Google Scholar,
-
6.
Web of science.
The second stage consists of a keyword-based search. To this end, two tasks were performed: (1) we identified a set of keywords related to our research topic; and (2) we identified synonyms for the keywords and related concepts (see Table 2).
The search strings were built by combining the keywords presented in Table 2 with the connectors “AND” and “OR”. Thus, the search chain that we use is the following:
(Agriculture OR e-agriculture OR Agribusiness OR Farming OR Agricultural) AND Blockchain.
Studies Selection
Regarding the studies selection, it began with the selection of only the studies that included at least one keyword referring to the Agricultural sector (e.g. Agriculture, farming, agricultural, e-agriculture), and the other one concerning to the Blockchain technology (Blockchain).
Secondly, we discarded those papers that were not directly related to the Blockchain technology and the agricultural sector.
Thirdly, the set of results obtained was reduced by applying the following exclusion criteria:
-
1.
Papers written in other languages than English.
-
2.
Master and doctoral dissertations.
-
3.
Duplicated articles obtained from Google Scholar and Web of Science.
The objective of this step was to determine which piece of literature found by the search string provides important contributions to the agricultural sector. In cases where we were uncertain about the relevance of the paper, the full-paper was downloaded and sections such as introduction and conclusions were reading.
2.2 Systematic Review Execution
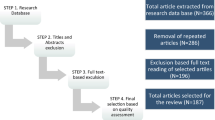
This phase consisted in executing the search in the digital libraries and web sources selected to evaluate the obtained studies considering the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The result of this process was a set of about 44 studies which were filtered by using the inclusion criteria established to give a set of about 18 relevant studies. This set of works was again filtered according to the exclusion criteria.
We obtained 10 primary studies in total (see Table 3). The inclusion and exclusion criteria help us to ensure that the studies were relevant for the research questions established at the planning phase.
Information Extraction
Therefore, aiming to answer the research questions, we extracted from studies (1) basic information (publication title and authors), (2) information related to the study (main contribution, objective), and (3) results (topics that have been addressed, their benefits on agricultural sector, and cases applicable to the IoT).
Table 4 provides a general perspective of all studies selected.
Basic Information of the Studies
Figure 1 shows the publication year distribution of the selected primary studies. Most studies were published after the year 2016. This shows that Blockchain is a very recent research area in the agricultural sector. As can be seen, one paper (1%) was published in 2016, five papers (50%) were published in 2017 and four (40%) papers were published in 2018. This shows an increasing number of publications in recent years, which shows also a growing interest in Blockchain technology in the agricultural sector.
Figure 2 shows the geographical distribution of the selected papers. Most of them (30%) were published by universities or companies in China. Another common publication country was Singapore with 2 papers (20%). The rest of countries (USA, Australia, Malaysia, and Taiwan) had one paper published. The geographical distribution of the selected primary papers shows that Blockchain technology of agriculture sector has gathered research interest around the world.
Figure 3 shows the publication type of the selected papers. Publication type means the channel where the paper was published. The publication types included in this study were conference, journal, and symposium. Most of the papers were published in conferences (6) (60%). The rest of the papers were published in journals (3) (30%), as a symposium (1) (10%). In addition, Table 2 shows the publication channel of each selected paper. As can be seen, each paper was published in different publication channels (Table 5).
2.3 Results
Table 6 shows the studies selected in this systematic literature review, as well as a comparison of them regarding the relevant information established in the previous section. The order of the studies does not determine its importance regarding the goals of this study.
3 Result Analysis: Discussion
Taking into account the results obtained from the systematic literature review presented in this work, nowadays, several researchers are focusing their efforts in the supply chain for the agricultural sector. For instance, Tian [13] studied Agri-food supply chains including production (planting/feeding), picking/slaughter, processing, warehousing, distribution and sales. In [15], authors proposed a system to improve the efficiency of food supply chain. Lin et al. [18] presented an agricultural supply chain system based on double chain architecture that considers the security of the data and the privacy of enterprise data. Lucena et al. [19] presented a case of study to measure the quality throughout the transportation of grains along its supply chain. In [20], authors proposed a supply chain platform which is used in the fresh food area where agriculture sustainability is an important issue to address. Finally, Vinod Kumar [21] proposed a supply chain system which allows monitor security and quality of warehouse and transportation of rice from farmers to companies. Meanwhile, secured data storage, remote monitoring, and automation are the least studied.
The Internet of Things technology has been widely applied in agriculture, however, there are some challenges related to privacy and security that need to be addressed. To overcome these challenges, several authors use Blockchain which allows the creation of a distributed digital ledger of transactions that is shared among the nodes on IoT network.
With regards to the effects of Blockchain in agriculture, Blockchain technology has been applied with positive results. To name a few, some of its benefits are: (1) all the information in the supply chain is transparent and open, (2) it addresses challenges on the Internet of Things such as decentralization, anonymity, and security, (3) it improve reliability, faster and efficient operations and scalability.
4 Conclusions
The goal of this study was to identify research topics, main contributions, and benefits of the Blockchain technology in agriculture. We obtained and analyzed 10 primary studies from scientific databases and web sources.
The review papers on Blockchain in agriculture is very dominated by Asian research community, especially from China. Only 3 of the 10 reviewed papers are from non-Asian countries. We attribute this to the fact that agriculture is an important sector in China. In other continents, the concept of Blockchain was up to recently adopted. The most frequently addresses research topic is food supply chains. The dominance of studies dealing with food supply chains can be attributed to the importance management for food safety and food quality. Furthermore, 5 of 10 studies present the combination the IoT and Blockchain in order to addressed challenges related to privacy and security of the IoT.
As future work, we plan to extend this work by including a wider set of digital libraries such as the Wiley Online Library. Furthermore, we expect this systematic literature review to include more issues and proposed solutions to overcome challenges and limitations of Blockchain technology. Finally, we plan to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed solutions in an objective way.
References
Treleaven, P., Gendal Brown, R., Yang, D.: Blockchain technology in finance. Computer (Long Beach, Calif.) 50, 14–17 (2017)
Guo, Y., Liang, C.: Blockchain application and outlook in the banking industry. Financ. Innov. 2, 24 (2016)
Angraal, S., Krumholz, H.M., Schulz, W.L.: Blockchain technology: applications in health care. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 10, e003800 (2017)
Mettler, M.: Blockchain technology in healthcare: the revolution starts here. In: 2016 IEEE 18th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), pp. 1–3. IEEE (2016)
Mengelkamp, E., Notheisen, B., Beer, C., Dauer, D., Weinhardt, C.: A Blockchain-based smart grid: towards sustainable local energy markets. Comput. Sci. Res. Dev. 33, 207–214 (2018)
Mannaro, K., Pinna, A., Marchesi, M.: Crypto-trading: Blockchain-oriented energy market. In: 2017 AEIT International Annual Conference, pp. 1–5. IEEE (2017)
Brereton, P., Kitchenham, B.A., Budgen, D., Turner, M., Khalil, M.: Lessons from applying the systematic literature review process within the software engineering domain. J. Syst. Softw. 80, 571–583 (2007)
Conoscenti, M., Vetro, A., De Martin, J.C.: Blockchain for the internet of things: a systematic literature review. In: 2016 IEEE/ACS 13th International Conference of Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2016)
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., Park, S., Smolander, K.: Where is current research on Blockchain technology?—A systematic review. PLoS ONE 11, e0163477 (2016)
Hawlitschek, F., Notheisen, B., Teubner, T.: The limits of trust-free systems: a literature review on Blockchain technology and trust in the sharing economy. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 29, 50–63 (2018)
Seebacher, S., Schüritz, R.: Blockchain technology as an enabler of service systems: a structured literature review. In: Za, S., Drăgoicea, M., Cavallari, M. (eds.) IESS 2017. LNBIP, vol. 279, pp. 12–23. Springer, Cham (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-56925-3_2
Chitchyan, R., Murkin, J.: Review of Blockchain technology and its expectations: case of the energy sector (2018)
Tian, F.: An agri-food supply chain traceability system for China based on RFID & Blockchain technology. In: 2016 13th International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management (ICSSSM), pp. 1–6. IEEE (2016)
Xie, C., Sun, Y., Luo, H.: Secured data storage scheme based on block chain for agricultural products tracking. In: 2017 3rd International Conference on Big Data Computing and Communications (BIGCOM), pp. 45–50. IEEE (2017)
Tse, D., Zhang, B., Yang, Y., Cheng, C., Mu, H.: Blockchain application in food supply information security. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM), pp. 1357–1361. IEEE (2017)
Patil, A.S., Tama, B.A., Park, Y., Rhee, K.-H.: A framework for Blockchain based secure smart green house farming. In: Park, J.J., Loia, V., Yi, G., Sung, Y. (eds.) CUTE/CSA -2017. LNEE, vol. 474, pp. 1162–1167. Springer, Singapore (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7605-3_185
Leng, K., Bi, Y., Jing, L., Fu, H.-C., Van Nieuwenhuyse, I.: Research on agricultural supply chain system with double chain architecture based on Blockchain technology. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. (2018)
Lin, Y.-P., et al.: Blockchain: the evolutionary next step for ICT E-agriculture. Environments 4, 50 (2017)
Lucena, P., Binotto, A.P.D., Momo, F.S., Kim, H.: A case study for grain quality assurance tracking based on a Blockchain business network. In: Symposium on Foundations and Applications of Blockchain (FAB 2018), pp. 1–6 (2018)
Carbone, A., Davcev, D., Mitreski, K., Kocarev, L., Stankovski, V.: Blockchain based distributed cloud fog platform for IoT supply chain management. In: Eighth International Conference on Advances in Computing, Electronics and Electrical Technology - CEET 2018, pp. 51–58. Institute of Research Engineers and Doctors (2018)
Vinod Kumar, M., Iyengar, N.C.S.N.: A framework for Blockchain technology in rice supply chain management. Adv. Sci. Technol. Lett. 146, 125–130 (2017)
Papa, S.F.: Use of Blockchain technology in agribusiness: transparency and monitoring in agricultural trade. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Management Science and Management Innovation (MSMI 2017). Atlantis Press, Paris (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Bermeo-Almeida, O., Cardenas-Rodriguez, M., Samaniego-Cobo, T., Ferruzola-Gómez, E., Cabezas-Cabezas, R., Bazán-Vera, W. (2018). Blockchain in Agriculture: A Systematic Literature Review. In: Valencia-García, R., Alcaraz-Mármol, G., Del Cioppo-Morstadt, J., Vera-Lucio, N., Bucaram-Leverone, M. (eds) Technologies and Innovation. CITI 2018. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 883. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00940-3_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00940-3_4
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-00939-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-00940-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)