Abstract
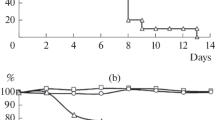
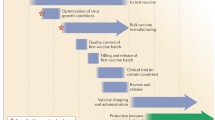
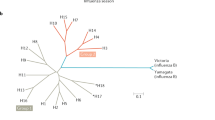
The influenza viruses are responsible for many millions of infected individuals world wide and tens of thousands of deaths annually, as well as for causing considerable economic burden. The currently available influenza vaccines consist of either attenuated or inactivated viral particles. Their effectivity is limited, mainly due to the frequent antigenic variations of the external glycoproteins of the virus (Laver and Air, 1979), each new strain presenting a new challenge to the host immune system. Among the new strategies for vaccination, contemplated to overcome such shortcomings, are synthetic vaccines, which are based on short epitopes that should elicit protective immunity.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ada, G. L. and Jones, P. D. 1986. The immune response to influenza infection. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 128: 1.
Ellouz, F., Adam, A., Ciorbaru, R. and Lederer, E. 1974. Minimal structural requirements for adjuvant activity of bacterial peptidoglycan derivatives. Biochim. Biophys. Res. Commun. 53: 1317–1325
Gao, X. M., Liew, F. Y. and Tite, J. P. 1989. Identification and characterization of T-helper epitopes in the nucleoprotein of influenza A virus J. Immunol. 143: 3007
Laver, W.G., and Air, G.M. 1979. Structure and Variation in Influenza Virus. Elsevier North Holland, Amsterdam.
Levi, R., Abaud-Pirak, E., Lowell, G.H. and Arnon, R. 1995. Intranasal administration of synthetic peptides anchored to proteosomes elicits anti influenza protective immunity. Vaccine. (In press).
Levi R. and Arnon R. 1995a. Effective protection if mice from viral challenge by an influenza synthetic recombinant vaccine with cross-strain specificity. In: Vaccines 1995: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. (In press).
Levi R. and Arnon R. 1995b. Synthetic Recombinant Influenza vaccine induces efficient long-term immunity and cross-strain protection. Vaccine. (in press).
Lowell, G. H. 1990. Proteosomes, hydrophobic anchors, ISCOMS, and liposomes for improved presentation of peptide and protein vaccines., In: New Generation Vaccines. (Ed. Woodrow G.C. and Levine M.M.) Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp. 141–160.
McEwen, J., Levi, R., Horwitz, R. J. and Arnon, R. 1992. Synthetic recombinant vaccine expressing influenza haemagglutinin epitope in Salmonella flagellin leads to partial protection in mice. Vaccine 10: 405
Müller, G.M., Shapira, M. and Arnon, R. 1982. Anti-influenza response achieved by immunization with a synthetic conjugate. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 79: 569–573.
Shapira, M., Misulovin, Z. and Arnon, R. 1985a. Specificity and cross-reactivity of synthetic peptides dervied from a major antigenic site of influenza hemagglutinin. Mol. Immunol. 22: 23–28.
Shapira, M., Jolivet, M. and Arnon. R. 1985b. Synthetic vaccine against influenza with built-in adjuvanticity. Int. J. Immunopharmac, 7: 719–723.
Taylor, P. M., Davey, J., Howland, K., Rothbard, J. and Askonas, B. A. 1987. Class I MHC molecules rather than other mouse genes dictate influenza epitope recognition by cytotoxic T-cells. Immunogen, 26: 267
Wiley, D.C., Wilson, I.A. and Skehel, J.J. 1981. Structural identiflcaiton of the antibody-binding sites of Hong Kong influenza haemagglutinin and their involvement in antegenic variation. Nature 289: 366–373.
Yap, K. L. and Ada, G. L. 1978. Cytotoxic T-cells in the lungs of mice infected with an influenza A virus Scand. J. Immunol. 7: 73
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1996 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Arnon, R., Levi, R. (1996). Synthetic Recombinant Vaccine Induces Anti-Influenza Long-Term Immunity and Cross-Strain Protection. In: Cohen, S., Shafferman, A. (eds) Novel Strategies in the Design and Production of Vaccines. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 397. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-1382-1_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-1382-1_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4899-1384-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4899-1382-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive