Abstract
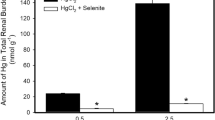
Co-administration of selenium compounds with mercuric mercury resulted in remarkable depression of acute toxicity of mercury through 1) reduction of mercury accumulation in the kidneys, a major target of acute toxicity of inorganic mercury, by forming high molecular weight complexes consisting of Hg, Se and proteins in the blood, which were hardly filtered through glomerulus; 2) elongation of retention of mercury and selenium as inert high molecular weight complexes in the blood, especially in the erythrocytes; 3) formation of stable and non-diffusible complexes of Hg and Se in various organs such as the liver and kidneys.
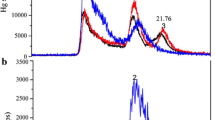
Methylmercury was found to form a complex with selenium, bis(methylmercuric) selenide (BMS), in various tissues on concurrent administration with selenite. However, the reduction of methylmercury toxicity by selenium as reported in numerous papers seems to be hardly explainable by the formation of BMS which showed a relatively low stability in the blood and other tissues.
Using the assay methods developed in the studies described above to detect interactions between selenium and other metals, we indicated that more than 18 metal ions might be subjected to interactions with selenium in animal body, showing important roles of this essential metalloid as a modifying factor of metal toxicity. Although, according to the experimental data so far obtained, selenium appears not to be clinically applicable as an antidote for mercury intoxication, we could develop a possible application of selenium for reducing dose-limiting toxicity of cis-platinum, a platinum complex most widely used in cancer chemotherapy, without compromising its anti-tumor activity.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ganther, H. E., Gondie, C., Sunde, M. L., Kopecky, M. J., Wanger, P. A., Oh, S. H., and Hoekstra, W. G., 1972, Selenium: Relation to decreased toxicity of methylmercury added to diets contain tuna, Science, 175:1122.
Imura N. and Naganuma, A., 1978, Interaction of inorganic mercury and selenite in rabbit blood after intravenous administration, J. Pharmacobio-Dyn., 1:67.
Imura, N. and Naganuma, A., 1985, Mode of modifying action of selenite on toxicity and behavior of mercury and other metals, Nurt. Res. Suppl. I: 499.
Iwata, H., Okamoto, H., and Ohsawa, Y., 1973, Effect of selenium on methylmercury poisoning. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol., 5:673.
Naganuma, A. and Imura. N., 1980a, Bis(methylmercuric) selenide as a reaction product from methylmercury and selenite in rabbit blood. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol., 27:163.
Naganuma, A. and Imura, N., 1980b, Changes in distribution of mercury and selenium in soluble fractions of rabbit tissues after simultaneous administration. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 13:537.
Naganuma, A. and Imura, N. 1981, Properties of mercury and selenium in a high-molecular weight substance in rabbit tissues formed by simultaneous administration, Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 15:449.
Naganuma, A. and Imura, N. 1983, Mode of interaction of mercuric mercury with selenite to form high-molecular weight substance in rabbit blood in vitro, Chem.-Biol. Interact., 43:271.
Naganuma, A., Ishii, Y., and Imura, N., 1984a, Effect of administration sequence of mercuric chloride and sodium selenite on their fates and toxicities in mice, Exotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 8:572.
Naganuma, A., Kojima, Y., and Imura, N., 1980, Interaction of methylmercury and selenium in mouse: Formation and decomposition of bis(methylmercuric) selenide, Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol., 30:301.
Naganuma, A., Kosugi, K., and Imura, N., 1981, Behavior of inorganic mercury and selenium in insoluble fractions of rabbit tissues after simultaneous administration, Toxicol Lett., 8:43.
Naganuma, A., Pan, S. K., and Imura, N., 1978, In vitro studies on interaction of mercuric mercury and selenite in rabbit blood, Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol., 20:139.
Naganuma, A., Satoh, M., and Imura, N. 1984b, Effect of selenite on renal toxicity and antitumor activity of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum in mice inoculated with Ehrlich ascites tumor cell, J. Pharmacobio-Dyn., 7:217.
Naganuma, A., Satoh, M., Yokoyama, M., and Imura, N., 1983a, Selenium efficiently depressed toxic side effects of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol., 42:127.
Naganuma, A., Tanaka, T. A., Maeda, K., Matsuda, R., Tabata-Hanyu, J., and Imura, N., 1983b, The interaction of selenium with various metals in vitro and in vivo, Toxicology, 29:77.
Parizek, J. and Ostadalova, I., 1967, The protective effect of small amounts of selenium in sublimate intoxication, Experientia, 23:142.
Satoh, M., Naganuma, A., and Imura, N., 1989, Optimum schedule of selenium administration to reduce lethal and renal toxicities of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum in mice, J. Pharmacobio-Dyn., 12:246.
Sumino, K., Yamamoto, R., and Kitamura, S., 1977, A role of selenium against methylmercury toxicity, Nature, 268:73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Imura, N., Naganuma, A. (1991). Possible Mechanism of Detoxifying Effect of Selenium on the Toxicity of Mercury Compounds. In: Suzuki, T., Imura, N., Clarkson, T.W. (eds) Advances in Mercury Toxicology. Rochester Series on Environmental Toxicity. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-9071-9_17
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-9071-9_17
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4757-9073-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-4757-9071-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive