Abstract
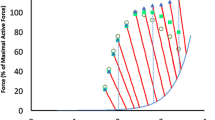
The measured stiffness of contracting smooth muscle is strongly dependent on the level of developed force. This force-dependent stiffness is a consequence of contractile activity, and it is possible that a portion of it represents the stiffness of the population of attached crossbridges. The relationship between force and stiffness is sensitive to the particular stage of the contraction-and-relaxation cycle (Meiss, 1978), to specific external mechanical constraints imposed on the muscle (Meiss, 1987), and to the length of the muscle when the stiffness is measured (Meiss, 1978; Meiss, 1990). The character of the length-dependent stiffness relationship depends on the mechanical mode of contraction, and interpretation of these effects rests on assumptions regarding how the process of stiffness measurement interacts with changing tissue dimensions. The purpose of this paper is to characterize the difference between the length-dependent stiffness measured in isotonic and isometric contractions. Possible reasons for the differences will be considered, and a tentative model to account for the isotonic length-dependence of stiffness will be proposed.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gabella, G., 1984, Structural apparatus for force transmission in smooth muscle, Physiol. Rev., 64: 455.
Gabella, G., 1976, Quantitative morphological study of smooth muscle cells of the guinea pig taenia coli. Structural changes in smooth muscles during isotonic contraction, Cell Tissue Res., 170: 161.
Meiss, R. A., 1990, The effect of tissue properties on smooth muscle mechanics, in: “Frontiers in Smooth Muscle Research”, N. Sperelakis and J. D. Wood, eds., Wiley-Liss, New York, p. 435.
Meiss, R. A., 1978, Dynamic stiffness of rabbit mesotubarium smooth muscle: Effect of isometric length, Am. J. Physiol., 3: C14.
Meiss, R. A., 1987, Stiffness of active smooth muscle during forced elongation, Am. J. Physiol., 22: C484.
Mullins, G. L. and Gutheroth, W. G., 1965, A collagen net hypothesis for force transference of smooth muscle, Nature, 206: 592.
Warshaw, D. M., McBride, W. J., and Work, S. S., 1987, Corkscrew-like shortening in single smooth muscle cells, Science, 236: 1457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Meiss, R.A. (1991). An Analysis of Length-Dependent Active Stiffness in Smooth Muscle Strips. In: Moreland, R.S. (eds) Regulation of Smooth Muscle Contraction. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 304. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-6003-2_35
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-6003-2_35
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-6005-6
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-6003-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive