Abstract
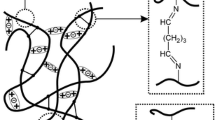
An attempt was made to prepare a thermo-sensitive membrane with switching ability. The membrane was made of porous glass and N-isopropylacrylamide gel, whose volume-phase transition is of a thermo-shrinking type. Permeation experiments have demonstrated that the composite membrane functioned as an ultrafiltration membrane, of which the cut-off molecular weight and solution permeation rate dramatically changed on the volume-phase transition. To make clear the permeation mechanism of the membrane, additional experiments were carried out, in which the diffusion rates of 3H-labeled water through the membrane were measured at various temperatures. Experimental results enabled the pore radii in the gel to be estimated. It is shown that the rejection characteristics of the membrane are predictable from the pore radii estimated.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference Citation
Chmelir, M., Kunschner, A. and Barthell, E., 1980, Water soluble acrylamide polymer. 2. Aging and viscous flow of aqueous solution of polyacrylamde and hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide, Antewalt. Makromol. Chem., 89:145
Hirokawa, Y. and Tanaka, T., 1984, Volume phase transition in a nonionic gel, J. Chem. Phys., 81:6379
Ohmine, I. and Tanaka, T., 1982, Salt effect on the phase transition of ionic gels,: J. Chem. Phys., 77:5735
Otake, K., Tsuji, T., Konno, M. and Saito, S., 1988, Permeation of a new hydrogel and porous glass composite membrane, J. Chem. Eng. Japan, 21:443
Spiegler, K. S. and Kedem, O., 1966, Thermodynamics of hyperfiltration (reverse osmosis): criteria for efficient membranes, Desalination, 1:311 (1966)
Tanaka, T., 1981, Gel, Science, 244:1241
Tanaka, T., Fillmore, D. J., Sun, S. T., Nishio, I., Swislow, G. and Shah, A., 1980, Phase transition in ionic gels, Phys. Rev. Lett., 45:1636
Tanaka, T., Nishio, I., Sun, S. T. and Nishio, S., 1982, Colaspes of gels in electric field, Science, 218:467
Tsuji, T., Otake, K., Konno, M. and Saito, S., 1989, Permeation characteristics of porous glass and hydrogel composite membrane, submitted to J. Appl. Polym. Sci.
Verniory, A., Dubois, R., Decoodt, P., Gassee, J. P. and Lambert, P. P., 1973, Measurement of the permeability of biological membranes, J. Gen. Physiol., 62:489
Wang, J. H., Robinson C. V. and Edelman, I. S., 1953, Self-diffusion and structure of liquid water. 3. Measurement of the self-diffusion of liquid water with H2, H3 and O18 as tracers, J. Am. Chem. Soc, 76: 446
Wendt, R. P., Klein, E., Bresler, E. H., Holland, F. F., Serino, R. M. and Villa, H., 1979, Sieving propaties of hemodialysis membrane, J. Memb. Sci., 5:23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1991 Plenum Press, New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Konno, M., Tsuji, T., Saito, S. (1991). Permeation Mechanism for a Thermo-Sensitive Switching-Functional Composite Membrane of Porous Glass and Hydrogel. In: DeRossi, D., Kajiwara, K., Osada, Y., Yamauchi, A. (eds) Polymer Gels. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5892-3_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-5892-3_12
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4684-5894-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4684-5892-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive