Abstract
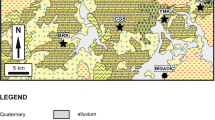
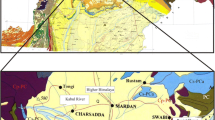
A number of different types of bentonite deposits formed by hydrothermal alteration and diagenetic processes are to be found in the Ordu area of the Eastern Black Sea region. The Ca- and Na-bentonite deposits are related to Upper Cretaceous tholeitic to calc-alkaline volcanites, predominantly dacite and andesite, and also include rhyodacite with lesser basalt and their pyroclastic equivalents. In the present study, dacite (PR1), perlite (PR2), moderately altered rocks (MPR), and Na- and Ca-bentonites were studied to describe and compare their mineralogical and geochemical properties and their conditions of formation by means of X-ray diffraction, optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and chemical analytical techniques.
Ca-bentonites, except for smectite, contain opal-CT, feldspar, biotite, and rarely pyrite, while Na-bentonites contain smectite and less feldspar, opal-CT, kaolinite, and illite.
Progressive alteration of the PR2 caused depletion in K2O and Na2O and enrichment in MgO and CaO in all of the Ca-bentonite samples. Na2O was depleted in all of the Na-bentonites and in most of the MPR. The medium and heavy rare earth elements (MREE and HREE) show mass gain or mass loss in the Na-bentonites. The HREE show nearly immobile behavior in the Ca-bentonites. The rare earth elements (REE) and transition elements (TRE) mostly gained mass in the Ca-bentonites in contrast to Na-bentonites. Large-ion lithophile elements (LILE) are strongly depleted in all of the bentonites. The LREE, MREE, and HREE were strongly depleted in most of the MPR samples. TiO2, Lu, Tm, and Tb show immobile behavior in all samples.
PR1 exhibits a slightly positive Eu anomaly. Two MPR samples show slightly positive Eu anomalies (1.03, 1.13), and one Na-bentonite sample displays a slightly positive Eu anomaly (1.04). Most of the Nabentonites have weakly negative Eu anomalies, whereas perlite and the Ca-bentonite have a strongly negative Eu anomaly. The PR1, PR2, MPR, and Na-bentonite present a positive Ce anomaly, and the Ca-bentonite shows a moderately negative Ce anomaly. The Ca-montmorillonites are mainly hydrothermal in origin and derived from alteration of volcanoclastic material in situ and/or in the subaerial environment. The Na-montmorillonites formed by alteration and diagenesis of volcanoclastic material in the sedimentary basin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arslan, M. and Abdioğlu, E. (2005) Mineralogy, geochemistry and genesis of bentonites of the Ordu area, NE Turkey. Clay Minerals, 40, 131–151.
Bau, M. (1991) Rare-earth element mobility during hydrothermal and metamorphic fluid—rock interaction and the significance of the oxidation state of europium. Chemical Geology, 93, 219–230.
Boynton, W.V. (1984) Geochemistry of rare earth elements: meteorite studies. Pp. 63–114 in: Rare Earth Element Geochemistry (P. Henderson, editor). Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Braun, J.-J., Pagel, M., Muller, J.-P., Bilong, P., Michard, A. and Guillet, B. (1990) Cerium anomalies in lateriticprof iles. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 54, 781–795.
Caballero, E., Jimanez de Cisneros, C., Huertas, F.J., Huertas, F., Poszzuoli, A. and Linares, J. (2005) Bentonites from Cabo de Gata, Almeria, Spain: a mineralogical and geochemical overview. Clay Minerals 40, 463–480.
Çağatay, M.N. (1993) Hydrothermal alteration associated with volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits. Examples from Turkey. Economic Geology, 88, 606–612.
Çelik, M., Karakaya, N. and Temel, A. (1999) Clay minerals in hydrothermally altered volcanic rocks, eastern Pontides, Turkey. Clays and Clay Minerals, 47, 708–717.
Chamley, H. (1989) Clay Sedimentology. Springer, Berlin, 623 pp.
Christidis, G. E. (1998) Comparative study of the mobility of major and trace elements during alteration of an andesite and a rhyolite to bentonite, in the islands of Milos and Kimolos, Aegean, Greece. Clays and Clay Minerals, 46, 379–399.
Christidis, G.E. and Huff, W.D. (2009) Geological aspects and genesis of bentonites. Elements, 5, 93–98.
Christidis, G. and Warren, D.H. (2009) Geologicas pects and genesis of bentonites. Elements, 5/2, 93–98.
Christidis, G.E., Scott, P.W., and Marcopoulos, T. (1995) Origin of the bentonite deposits of Eastern Milos, Aegean, Greece: geological, mineralogical and geochemical evidence. Clays and Clay Minerals 43, 63–77.
Class, C. and la Roex, A.P. (2008) Ce anomalies in Gough Island lavas — trace element characteristics of a recycled sediment component. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 265, 475–486.
Corfu, F. and Davis, D.W. (1991) Comment on “Archaean hydrothermal zircon in the Abitibi greenstone belt: constraints on the timing of gold mineralization” by J.C. Claoue-Long, R.W. King and R. Kerrich. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 104, 545–552.
Ddani, M., Meunier, A., Zahraoui, M., Beaufort, D., El Wartiti, M., Fontaine, C., Boukili, B., and El Mahi, B. (2005) Clay mineralogy and chemical composition of bentonites from the Gourougou volcanic massif (northeast Morocco). Clays and Clay Minerals, 53, 250–267.
Finlow-Bates, T. and Stumpfl, E.F. (1981) The behaviour of so-called immobile elements in hydrothermally altered rocks associated with volcanogenic submarine-exhalative ore deposits. Mineralium Deposita, 16, 319–328.
Florke, O.W., Martin, G.B., Bochum, R., and Wirth, R. (1991) Nomenclature of micro- and non-crystaline silica minerals, based on structure and microstructure. Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie-Abhandlungen, 163, 19–42.
Floyd, P.A. and Winchester, J.A. (1978) Identification and discrimination of altered and metamorphosed volcanic rocks using immobile elements. Chemical Geology, 21, 291–306.
Gill, J.B. (1981) Orogenic Andesite and Plate Tectonics. Springer, New York, 390 pp.
Gökçe, A. and Bozkaya, G. (2003) Fluid inclusion and stable isotope characteristics of the Inler Yaylası lead-zinc deposits, northern Turkey. International Geology Review, 45, 1044–1054.
Grim, R.E. (1968) Clay Mineralogy (2nd edition). McGraw- Hill, New York, 596 pp.
Grim, R. and Güven, N. (1978) Bentonite: Geology, Mineralogy, Properties and Uses. Developments in Sedimentology, 24, Elsevier, New York, 256 pp.
Güven, N. (1988) Smectites. Pp. 497–559 in: Hydrous Phyllosilicates (S.W. Bailey, editor). Reviews in Mineralogy, 19. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, D.C.
Hopf, S. (1993) Behaviour of rare earth elements in geothermal systems of New Zealand, Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 47, 333–357.
Hora, Z.D. (1998) Bentonite. Geological Fieldwork 1997. pp. 24C1–24C3. British Columbia Ministry of Employment and Investment Paper 1998-1.
Hynes, A. (1980) Carbonatization and mobility of Ti, Y and Zr in Ascot Formation metabasalts, SE Quebec. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 75, 79–87.
Inoue, A. (1995) Formation of clay minerals in hydrothermal environments. Pp. 268–303 in: Origin and Mineralogy of Clays (B. Velde, editor). Springer, Berlin.
Inoue, A., Utada, M., and Kusakabe, H. (1984) Clay mineral composition and their exchangeable interlayer cation composition from altered rocks around the Kuroko deposits in the Matsumine-Shakanai-Matsuki area of the Hokuroku district. Japan Journal of Clay Science Society Japan, 24, 69–77.
Inoue, A., Kohyama, N., Kitagawa, R., and Watanabe, T. (1987) Chemical and morphological evidence for the conversion of smectite to illite. Clays and Clay Minerals, 35, 111–120.
Jenner, G.A. (1996) Trace element geochemistry of igneous rocks: geochemical nomenclature and analytical geochemistry. Pp. 51–77 in: Trace Element Geochemistry of Volcanic Rocks: Applications for Massive Sulfide Exploration (D.A. Wyman, editor). Geological Association of Canada Short Course Notes, 12.
Jiang, S.-Y. (2000) Controls on the mobility of high field strength elements (HFSE), U, and Th in an ancient submarine hydrothermal system of the Proterozoic Sullivan Pb-Zn-Ag deposit, British Columbia, Canada. Geochemistry Journal, 34, 341–348.
Jiang, N., Sun, S., Chu, X., Mizuta, T. and Ishiyama, D. (2003) Mobilization and enrichment of high-field strength elements during late- and post-magmaticp rocesses in the Shuiquangou syenitic complex, Northern China. Chemical Geology, 200, 117–128.
Jiang, S.Y., Wang, R.C., Xu, X.S., and Zhao, K.D. (2005) Mobility of high field strength elements (HFSE) in magmatic-, metamorphic-, and submarine-hydrothermal systems. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 30, 1020–1029.
Karakaya, N. and Karakaya, M.C. (2001a) Hydrothermal alteration of the Şaplıca volcanic rocks, Şebinkarahisar, Turkey. International Geology Review, 43, 953–962.
Karakaya, N. and Karakaya, M.C. (2001b) Mineralogic and geochemical properties of hydrothermal alteration types of Şaplıca (Şebinkarahisar, Giresun) volcanites. Geological Bulletin of Turkey, 44, 75–89.
Karakaya, M.Ç., Karakaya, N., and Ekmekçi, M. (2005) Doğu Karadeniz Bölgesindeki Bazı Maden Yatakları ile Yüzey ve Yeraltısuyu Kimyası Arasındaki İlişkinin Araştırılması. TÜNBİTAK YDABÇAG-103Y016, Turkey, 159 pp.
Karakaya, N., Karakaya, M.C., Nalbantcçılar, M.T., and Yavuz, F. (2007) Relation between spring-water chemistry and hydrothermal alteration in the Şaplıca volcanic rocks, Şebinkarahisar (Giresun, Turkey). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 93, 35–46.
Keskin, İ., Yergök, F.A., Kara, H., Dönmez, M., and Arslan, M. (1998) Ünye-Fatsa-Kumru-Korgan (Ordu) dolayının jeolojisi. MTA Raport 10182 (unpublished).
Ketin, I. (1966) Tectonic units of Anatolia. Bulletin of Mineral Research and Exploration, 66, 23–34.
Lewis, A.J., Palmer, M.P.R., Sturchio, N.C., and Kemp, A.J. (1997) The rare earth element geochemistry of acid-sulphate and acid-sulphate-chloride geothermal systems from Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming, USA. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61, 695–706.
Lombardi, B., Baschini, M., and Torres Sánchez, R.M. (2003) Bentonite deposits of Northern Patagonia. Applied Clay Science 22, 309-312
MacLean, W.H. (1990) Mass change calculations in altered rock series. Mineralium Deposita, 25, 44–49.
MacLean, W.H. and Kranidiotis, P. (1987) Immobile elements as monitors of mass transfer in hydrothermal alteration. Phelps Dodge massive sulfide deposits, Matagami, Quebec. Economic Geology, 82, 951–962.
Millot, G. (1970) Geology of Clays. Springer, Berlin, New York; Masson, Paris, 425 pp.
Moore, D.M. and Reynolds, R.C. (1997) X-ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals, 2nd edition. Oxford University Press, New York, 378 pp.
Murphy, J.B. and Hynes, A. (1986) Contrasting secondary mobility of Ti, P, Zr, Nb and Y in two metabasalticsu ites in the Appalachians. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 23, 1138–1144.
Münch, P., Duplay, J., and Cochemé, J.-J. (1996) Alteration of silicic vitric tuffs interbedded in volcaniclastic deposits of the Southern Basin and Range Province, Mexico; evidences for hydrothermal reactions. Clays and Clay Minerals, 44, 49–67.
Patino, L.C., Velbel, M.P.R., Price, J.R., and Wade, J.A. (2003) Trace element mobility during spheroidal weathering of basalts and andesites in Hawaii and Guatemala. Chemical Geology, 202, 343–364.
Pearce, J.A. and Cann, J.R. (1973) Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analyses. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 19, 290–300.
Rollinson, H. (1993) Using Geochemical Data; Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation. Longman Scientific and Technical, Harlow, Essex, UK, 352 pp.
Ronov, A.B., Balashov, Y.A., and Migdisov, A.A. (1967) Geochemistry of the rare-earths in the sedimentary cycle. Geochemistry International, 4, 1–17.
Rubin, J.N., Henry, C.D., and Price, J.G. (1993) The mobility of zirconium and othe ‘immobile’ elements during hydrothermal alteration. Chemical Geology, 110, 29–47
Salvi, S. and Williams-Jones, A.E. (1996) The role of hydrothermal processes in concentrating high-field strength elements in the Strange Lake peralkaline complex, northeastern Canada. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 60, 1917–1932.
Salvi, S., Fontan, F., Monchoux, P., Williams-Jones, A.E., and Moine, B. (2000) Hydrothermal mobilization of high field strength elements in alkaline igneous systems: evidence from the Tamazeght Complex (Morocco). Economic Geology, 95, 559–576.
Saunders, A.D., Tarney, J., Marsh, N.G., and Wood, D.A. (1980) Ophiolites as ocean crust: a geochemical approach. Pp. 193–204 in: Ophiolites: Proceedings of the International Ophiolite Symposium (A. Panayiotou, editor). Ministry of Agriculture and Natural Resources, Cyprus, 1979. Geological Survey Department, Cyprus.
Schilling, J.G. (1973) Iceland Mantle Plume: geochemical study of Reykjanes ridge. Nature, 242, 565–571.
Senkai, A.L., Dixon, J.B., Hossner, L.R., Abder-Ruhman, M., and Fanning, D.S. (1984) Mineralogy and geneticrelat ionships of tonstein, bentonite, and lignite strata in the Eocene Yegua Formation of east-central Texas. Clays and Clay Minerals, 32, 259–271.
Shirozu, H. and Iwasaki, T. (1980) Clay minerals in alteration zones of Kuroko deposits, with special reference to montmorillonite. Journal of the Japanese Association of Mineralogists, Petrologists and Economic Geologists, Special Issue 2, 115–121 (in Japanese).
Sun, S.S. and McDonough, W.F. (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition processes. Pp. 313–345 in: Magmatism in the Ocean Basins (A.D. Saunders and M.J. Norry, editors). Special Publication 42, Geological Society, London.
Sverjensky, D.A. (1984) Europium redox equilibrium in aqueous solution. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 67, 70–78.
Terkado, Y. and Fujitani, T. (1998) Behavior of rare earth elements and other trace elements during interactionsbetween acidic hydrothermal solutions and silicic volcanicrocks, southwestern Japan. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62, 1903–1917.
Torres-Alvarado, I.S., Pandarinath, K., Verma, S.P., and Dulski, P. (2007) Mineralogical and geochemical effects due to hydrothermal alteration in the Los Azures geothermal field, Mexico. Revista Mexicana De Ciencias Geologicas, 24, 15–24.
Velde, B. (1985) Clay Minerals: A Physico-Chemical Explanation of their Occurrence. Developments in Sedimentology, 40, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 427 pp.
Weaver, C.E. (1989) Clays, Muds, and Shales. Developments in Sedimentology, 44, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 819 pp.
Weaver, C.E. and Pollard, L.D. (1973) The Chemistry of Clay Minerals. Developments in Sedimentology, Elsevier Science Publishing, Amsterdam, 213 pp.
Whitney, D.L. and Evans, B.W. (2010) Abbreviations for names of rock-forming minerals. American Mineralogist, 95, 185–187.
Wilson, M.J. (1987) X-ray powder diffraction methods. Pp. 26–98 in: A Handbook of Determinative Methods in Clay Mineralogy (M.J. Wilson, editor). Blackie and Sons Ltd, Glasgow, UK.
Winchester, J.A. and Floyd, P.A. (1977) Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements. Chemical Geology, 20, 245–252.
Wise, S.W. and Kelts, K.R. (1972) Inferred diagenetichi story of a weakly silicified deep sea chalk. Transactions of the Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies, 22, 177–203.
Yalçın, H. and Gümüşer, G. (2000) Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of Late Cretaceous bentonite deposits of the Kelkit Valley Region, Northern Turkey. Clay Minerals, 35, 807–825.
Yıldız, A. and Dumlupınar, İ. (2009) Mineralogy and geochemical affinities of bentonites from Kapıkaya (Eskişehir, western Turkey). Clay Minerals, 44, 339–360.
Yılmaz, Y., Tüysüz, O., Yiğitbaş, E., Gencç, Ş.C., and Şengör, A.M.C. (1997) Geology and tectonic evolution of the Pontides. Pp. 183–226 in: Regional and Petroleum Geology of the Black Sea and Surrounding Region (A. Robinson, editor). AAPG Memoir, 68, American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Tulsa, Oklahoma.
Zielinski, R.A. (1982) The mobility of uranium and other elements during alteration of rhyolite ash to montmorillonite: a case study in the Troublesome Formation, Colorado, U.S.A. Chemical Geology, 35, 185–204.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karakaya, M.Ç., Karakaya, N. & Küpeli, Ş. Mineralogical and Geochemical Properties of the Na- and Ca-Bentonites of Ordu (Ne Turkey). Clays Clay Miner. 59, 75–94 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2011.0590109
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2011.0590109