Abstract
In this paper, the organic pigments indigo and isatin were detected by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) in The Mural of Four Buddhas which is in Cave 3 from the ancient Chinese Tiantishan grottoes (Ming Dynasty, East Slope). By analysing the preservation conditions of the mural and the environmental conditions of the place where the Tiantishan grottoes are located, we speculated that the isatin detected in this mural was mainly produced by the oxidative decomposition of indigo by ozone (O3), rather than by photodegradation of indigo. We have used theoretical calculation software Gaussian09 (G09) and Amsterdam Density Functional (ADF) module in the Amsterdam Modeling Suite (AMS) software to simulate the reaction mechanism of O3 oxidation of indigo, and the end products of the oxidation of the natural plant dye indigo by O3 were identified as isatin, C16H10N2O3 and C8H6NO3 using HPLC, fluorescence spectroscopy and high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry(HPLC–MS). This finding confirmed the accuracy of the mechanism of indigo fading by O3 oxidation. These findings provided a theoretical basis for subsequent research into the derivation of natural organic dyes in the face of increasing O3 pollution and for better protection of valuable historical and cultural heritage such as ancient Chinese grottoes murals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The Mural of Four Buddhas was created in the Ming Dynasty, and the second Buddha from right to left in this mural is elegantly coloured, with a naturalistic and realistic look, and even and strong lines that rise and fall and stutter, making it a masterpiece of the Ming dynasty and with high artistic value. Figures 1a and d showed the mural near the top of Cave 3 of the Tiantishan grottoes (Wuwei, China) before it was saved in another place, and with a huge earthen wall to shield it from the sun, and the mural of Four Buddha was in darkness most of the time. Figure 1b showed the second Buddha statue from right to left in Fig. 1a. In 1954 the Dunhuang Research Academy removed the mural for better conservation and sealed it in a wooden box for constant storage in the dark (as shown in Fig. 1c). Through our research, we found that the local inhabitants had a custom of burning incense and worshipping in the grottoes (as shown in Fig. 1a). In this process, a large amount of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) are produced [1, 2], and VOCs and NOx produce ozone when exposed to sunlight [3, 4]. Jia Weiping’s research also showed that the complex topography of Wuwei, China, where the Tiantishan grottoes are located, contains NOx and VOCs emitted from various sources and is prone to photochemical reactions leading to high levels of ozone pollution, and his research showed that ozone pollution in Wuwei, China, has been increasing year on year since 2015 [5].
a The Mural of Four Buddhas, the flotsam shown in the top left of this picture is the black flotsam produced by local people when they burn incense and worship; b The second Buddha from right to left in The Mural of Four Buddhas; c Conditions of off-site conservation of The Mural of Four Buddhas (darkness); d Exterior view of the location of Cave 3 in the Tiantishan Grottoes
In ancient times, the limitations of productivity and the pursuit of beauty led to the extraction of numerous natural pigments and dyes from plants and animals [6,7,8,9,10]. Indigo is a natural organic pigment extracted from plants. According to the current literature, indigo is the oldest identified dye and it has been used worldwide for over 3000 years [11, 12]. The deep, mysterious colour of indigo, which imparts a sense of sacred beauty and a sense of the work’s long history, is often used in the production of paintings and murals. Indigo is usually extracted from the blue grasses of Isatis indigotica Fortune, Strobilanthes cusia (Nees) Kuntze, Polygonum tinctorium Ait, and Indigofera tinctoria Linn [13, 14], all of which are grown in China. In India, the Philippines, the USA, and Europe, the tropical plant Indigofera tinctoria Linn is commonly used to extract indigo, while in Japan, indigo is mainly extracted through Polygonum tinctorium Ait.
Some studies have detected the presence of indigo in Western wall paintings, but there are few studies on the use of indigo in ancient Chinese grottoes murals [15,16,17]. The degradation mechanism and products of indigo under natural light and ultraviolet light have been studied extensively, and it is generally accepted that isatin is one of the products of photodegradation of indigo [18,19,20,21], the photodegradation products of indigo were studied by Wikos et al. using HPLC–MS and they also identified seven other degradation products other than isatin in the photodegradation products of indigo [22]. N. Tello-Burgos et al. used different detection methods to study the possible degradation pathways and degradation products of indigo [23]. In addition to indigo, some research has been carried out on keto and leuco forms of indigo [24, 25]. Daniel GrosJea et al. used mass spectrometry to make a preliminary guess at the mechanism of the reaction between O3 and indigo molecules and identified isatin as one of the reaction products, but the study could not explain why O3 tends to add to C=C in the indigo molecule and failed to identify further pathways for the reaction of O3 with indigo [26]. Some research into the molecular structure and properties of organic pigments has been carried out [27,28,29]. This paper applied HPLC to successfully detect the organic pigment indigo in The Mural of Four Buddha (Ming Dynasty), further demonstrated the use of indigo in ancient Chinese grottoes murals. And we analyzed the molecular structure, the average local ionization energy (ALIE), the frontline molecular orbitals, the Fukui and condensed Fukui functions, the dual descriptor(DD) and the condensed dual descriptor(CDD) of the indigo molecule using G09 at a higher level (M062X/6–311 + g(d,p)) [30,31,32,33,34], Multiwfn_3.8_bin_Win64 [35], VMD193 [36]. It clearly explained the reason of O3 reacting with the C=C in the indigo molecule in an electrophilic addition reaction. On this basis, we further simulated the reaction process of indigo and O3 at the GGA: PBE/DZP level using ADF and obtained a possible reaction pathway [37,38,39,40,41], then the reaction pathway was verified by experiments, which finally established the reaction mechanism of indigo with O3.
Materials and instruments
Materials
Blue mural sample of The Mural of Four Buddhas in Tiantishan grottoes (from Dunhuang Research Academy, Dunhuang, China), Indigo (HPLC ≥ 98.70%, Chengdu Manster Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Chengdu, China), Isatin (AR, Shanghai Maclean Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), Methanol (HPLC grade), Acetonitrile (HPLC grade), Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (HPLC grade), Ultrapure Water.
Instruments
Waters 2487 HPLC (Chromatographic Conditions A: CAPCELL PAK C18 MGIIS-5 column, acetonitrile and water as mobile phases, flow rate 0.55 ml/min, gradient elution (0–10 min, 18.2% CH3CN; 10–20 min, CH3CN increased linearly from 18.2% to 72.7%; 20–60 min, 72.7% CH3CN; 60–70 min, CH3CN decreased linearly from 72.7% to 18.2%), detection wavelength 254 nm, column temperature 35 °C; Chromatographic Condition B: CAPCELL PAK C18 MGIIS-5 column, methanol and water as mobile phases (methanol: water = 60%:40%), flow rate 0.5 ml/min, detection wavelength 287 nm, column temperature 35 °C). Fluorescence-phosphorescence spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer LS-55) (excitation wavelength 330 nm, excitation wide slit size 15 um, emission slit width 10 um). Ultimate 3000 UHPLC—Q Exactive Liquid Mass Spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, US) (ion source: HESI, sheath gas rate: 40 arb, auxiliary gas rate: 10 arb, spray voltage: positive ion 3.8 kV, capillary temperature: 320 °C, auxiliary gas temperature: 300 °C, S-lens. 50%, scan mode: fullms/dd-ms2 top10, collision voltages: NCE15, 30, 45).
OG-50A Ozone Generator (Guangzhou Quanju Ozone Technology Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China). Model TH-150A Intelligent Medium Flow Rate Air Sampler (Wuhan Tianhong Instruments Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China). Gaussian 09. Multiwfn_3.8_bin_Win64. VMD193. ADF2022.
Methods
Collection of mural sample
One blue mural sample (0.0137 g) of The Mural of Four Buddhas in Tiantishan grottoes was collected from the blue area of the second Buddha from right to left, covering an area of approximately 0.33 cm2. A picture of the sample studied is in Additional file 1: Figure S1.
Pre-treatment of mural sample
1. Place the mural sample in a test tube and add 2 ml of DMSO (HPLC grade) to the tube; 2. Grind and mash the mural sample with a glass rod; 3. Shake the tube for 30 min to dissolve the organic pigments in the DMSO solution; 4. Leave to settle; 5. Transfer the supernatant to a 2 ml volumetric flask and subsequently fix the volume to 2 ml with DMSO; 6. Filter the solution using nylon 66 (0.45um) prior to injection.
Experimental methods
The chromatograms of The Mural of Four Buddhas sample were measured using a Waters 2487 HPLC and Chromatographic Conditions A. The indigo and isatin standards were then tested under the same chromatographic conditions, and the organic pigments used in The Mural of Four Buddhas were identified by comparing the chromatograms of the sample with those of the indigo and isatin standards. Two glass-fiber sampling membranes A and B, each uniformly covered with 40 mg of indigo standard, were exposed to air and O3 at a flow rate of 100 L/min for 2.5 h under the action of the sampler. The experiments were carried out in the darkness and the O3 was prepared by an O3 generator at a rate of 10 m3/h and released uniformly into the room environment. When the reaction was finished, we took 1/4 of the sampling film A and B respectively, dissolved the indigo with DMSO, and fixed the volume to 100 ml. The difference in colour between the DMSO solution of indigo made from indigo after a 2.5 h reaction with air, the DMSO solution prepared from indigo after a 2.5 h reaction with O3, and the standard solution of 0.1 mg/ml indigo was observed to determine initially whether a reaction had occurred. The DMSO solution of indigo after reaction with air and O3 was then detected by HPLC, Fluorescence Spectrometry, and HPLC–MS.
Calculation method
The geometric configuration of indigo was optimized at the M062X/6–311 + g(d,p) level using the DFT method. On this basis, the ALIE, front-line orbitals, Fukui functions, DD, condensed Fukui functions, and CDD of indigo were analyzed using Multiwfn and VMD, and the front-line molecular orbitals of O3 were also analyzed. These works were used to predict the type of reaction and reaction sites for the reaction of indigo with O3. After this, the geometrical configuration of the structurally optimised indigo molecule was imported into the ADF, and a flexible scan of its reaction with O3 at the GGA: PBE/DZP level was carried out, a frequency analysis of the possible transition states was carried out and an IRC analysis based on the transition states was performed. We also calculated the Gibbs free energies of the reactants, products, and different intermediates in different reaction pathways, and finally determined the reaction mechanism of the reaction of indigo with O3. All the above operations refer to the ground state molecule under dark conditions.
Results and discussion
Analysis of organic pigment composition in The Mural of Four Buddhas from Chinese Tiantishan grottoes
HPLC analysis was carried out on the sample of The Mural of Four Buddhas from the Tiantishan grottoes using a Waters 2487 HPLC instrument and Chromatographic Conditions A. The presence of the organic pigment indigo and the organic pigment isatin in this sample was determined by comparison with pigment standards (Fig. 2d). In ancient China, isatin was not used to paint murals, and in order to make the pigment firmly adhere to the ground layer, people would mix the pigment with colloid and apply it to the ground layer. So the reduction method, as one of the methods of dyeing textiles, was not suitable for the mural sample we studied. Therefore, we believed that the organic pigment isatin can be detected in blue mural sample was the result of the decomposition of indigo molecules, and no or only a very small amount of the indigo radical and the leuco form were involved in this process.
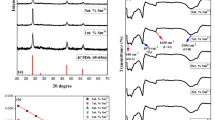
a 0.1 mg/ml DMSO solution of the indigo standard; b 10 mg of indigo dissolved in 100 ml of DMSO after 2.5 h contact with air at a flow rate of 100 L/min; c Indigo DMSO solution of 10 mg of indigo dissolved in 100 ml of DMSO after 2.5 h contact with O3, the O3 flow rate was 100 L/min; d HPLC of The Mural of Four Buddhas, indigo standard and isatin standard, measured under the parameters of Chromatographic Condition A
The analytical methods used in this section were repeated, with each sample and standard being repeated three times (or more) at the time of detection, and the relative standard deviations for retention time and peak area were less than 2%.
Analysis of the molecular structure of indigo
Additional file 1: Figure S2a shows the structural formula of the indigo molecule and Additional file 1: Figure S2b illustrates the molecular structure and optimal geometrical configuration of the indigo molecule calculated using the G09 at the level of the M062X/6–311 + g(d,p), the main structural parameters of which are presented in Additional file 1: Table S1. Structurally, the indigo molecule is a centrosymmetric, non-polar molecule belonging to the C2h point group, and the out-of-nuclear electrons of each atom form a relatively stable large π-bond on the surface of the indigo molecule. The "H-chromophore" structure in the indigo molecule (Additional file 1: Figure S2c) is widely believed to be responsible for the deep blue colour of indigo [42, 43]. The N atoms in the H-chromophore give electrons because it is weakly bound to the electrons outside the nucleus of their own atom, while the O atoms in the carbonyl group get electrons because it is more attractive to electrons and is called electron acceptor.
Mechanism of the electrophilic addition reaction of O3 with C=C in the indigo molecule
ALIE analysis of indigo molecules
ALIE was first proposed by Per Sjoberg [44], ALIE is calculated as follows:
Where ρ_i(r) is the electron density of the i-th molecular orbital at r, |ε_i| is the absolute value of the energy of the i-th molecular orbital, which can be considered as the ionisation energy of the electrons in the i orbital, and ρ(r) is the total electron density at position r. A smaller ALIE value at a point on the surface of a molecule means that the average energy of the electrons at that point is higher and more active and that the atoms adjacent to it are more likely to become reaction sites for electrophilic and radical reactions. Since O3 are more oxidising and more prone to nucleophilic reactions, the smaller the ALIE value on the surface of the indigo molecule the easier it is for O3 to attack it when it reacts with O3. Figure 3 demonstrates the average local ionisation energy distribution on the surface of the indigo molecule. The cyan spheres represent the minimal values points of ALIE on the surface of the indigo molecule, and the smaller ALIE values represented by the blue areas can be seen in the figure distributed near the benzene ring, C=C and N atoms, indicating that these positions have a greater potential to be attacked by O3. Additional file 1: Table S2 shows the statistics of the ALIE sites on the surface of the indigo molecule. From the data in the table, it can be seen that the ALIE values around sites 2, 8, 12, 17, and 23 are relatively lower and close to each other, and the reaction sites for the electrophilic reaction of the indigo molecule are most likely to be located at C5&C5’, C2&C2’, N1&N1’ atoms which are close to them.
Frontline molecular orbital analysis of indigo molecules
Frontline molecular orbital theory states that the electrons in the outermost orbital, the highest occupied orbital (HOMO), and the lowest vacant orbital (LUMO), play a major role in the chemical reaction of a molecule. When two molecules react, electrons are transferred from the HOMO of one molecule to the LUMO of the other molecule, the direction of the electron transfer being determined by the smallest energy level difference. Additional file 1: Figure S3 shows the positions of the electrons in the HOMO and the LUMO of the indigo and O3. Where the electrons in the HOMO of the indigo molecule are mainly present in the C=C, N atoms, and the C atoms on the benzene ring, and the electrons in the LUMO are mainly present in the C atoms of C=C and the C atoms adjacent to its O atoms. The electrons in the LUMO are more evenly distributed among the three O atoms.
Analysis of the Fukui function and the condensed Fukui function of the indigo molecule
The Fukui function was proposed by Parr and Yang in 1984 and it has been widely used to study the reaction sites at which chemical reactions occur [45, 46]. The specific expressions are:
where N represents the current number of electrons in the system, μ is the electrostatic potential of the system and ν(r) is the attraction potential of the nucleus for electrons. This is usually simplified when using the Fukui function as:
The magnitude of f −(r) represents the change in electron density at each position as the molecule is attacked by an electrophilic reagent, with larger values indicating that the position is more vulnerable to attack by the electrophilic reagent. To visualise the distribution of the Fukui function on the surface of the indigo molecule we have made an isosurface diagram of the Fukui function on the surface of the indigo molecule (Additional file 1: Figure S4) (we only look at the area covered by the green part of the diagram), the more an atom is covered by the equivalence surface of the Fukui function f −(r), the more likely it is to be attacked by electrophilic reagents, and C5&C5’ on the benzene ring and C=C and N atoms are more susceptible to O3 attack. To further verify the accuracy, the abbreviated Fukui function was calculated by contracting the Fukui function specifically to the atoms and the values are tallied in Additional file 1: Table S3. From Additional file 1: Table S3, the f − values for C=C, N atoms, and C5&C5’ on the benzene ring are the highest (although the value of the condensed Fukui function for O atom is higher than that for C atoms on C=C and C5&C5’ and N atoms on the benzene ring, the O atoms are more strongly bound to the electrons outside the nucleus and are less likely to lose electrons, so these positions are less susceptible to oxidation and are unlikely to be a reaction site for the reaction between indigo and O3, further verifying the accuracy of Fukui function analysis was further verified.
DD analysis and CDD analysis of indigo molecules
DD proposed by Morell, Grand, and Toro-Labbé in 2005 is also a method that is commonly used to predict reaction sites [47] and is relatively more effective than any other method. It is calculated as follows:
The regions with negative DD values are vulnerable to electrophilic attack and those with positive values are vulnerable to nucleophilic attack. To better observe the distribution of the DD on the surface of the indigo molecule we have made an isosurface diagram of the DD on the surface of the indigo molecule (Additional file 1: Figure S5), the green part represents positive DD values and the blue part represents negative DD values, where the greater the extent of the isosurface covered by negative DD values, the more vulnerable to electrophilic attack. The N1&N1’, C atoms on the benzene ring and C=C position are more susceptible to attack by O3. To further verify the accuracy, the reduced Fukui function was calculated by contracting the Fukui function specifically to the atoms, and the values are tabulated in Additional file 1: Table S4. From Additional file 1: Table S4, the N atoms, the C atoms on the benzene ring and the C atoms on C=C have the most negative CDD values, further validating the accuracy of the DD analysis.
Analysis of the reaction pathway of indigo molecules with O3
The above predictions for the sites of electrophilic reactions in indigo suggest that the C=C and N atoms in the indigo molecule are the most likely sites for reactions with the O3 molecule, and for this reason, we have carried out simulations to verify this conclusion, and analysed the reaction process for both reaction pathways, as shown in Fig. 4.
The attack of O3 on the C=C of the indigo molecule and the formation of isatin and Criegee radicals is the main pathway for the oxidative decomposition of indigo by O3, as the reaction does not need to cross the reaction energy barrier and the energy of the system continues to decrease throughout the reaction, which proceeds completely spontaneously. The O atoms of the O3 molecule attack the C atoms on the C=C of the indigo molecule in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the indigo molecule at distances ranging from 2.10 Å to 1.2 Å. During the attack of the O atoms on the C atom, the O atoms at the ends of the O3 molecule first combine with the C=C of the indigo molecule to form a five-membered ring, and O1 of the original O3 molecule breaks with O2, followed by a C–C break to form an isatin molecule and criegee radical, as shown in Additional file 1: Figure S6a. The more the Gibbs free energy of the reaction system is reduced, the easier the reaction proceeds, given the same temperature, entropy, pressure, and volume. The Gibbs free energy of the reaction process was calculated for the reactants, products, and major intermediates at 298 K, 1 atm, using ADF at the GGA: PBE/DZP level and the change in Gibbs free energy of the reaction process is shown in Fig. 5. At the end of the reaction, the O atom with a single electron in the Criegee radical approaches the H atom attached to the N atom to form an intramolecular interaction, resulting in a more stable structure of the Criegee radical, which then otherwise traps an H atom to produce the final product with the molecular formula C8H6NO3, the structure of which is shown in Additional file 1: Figure S6b. The electrostatic potential of the reaction product C8H6NO3 is calculated and plotted at the M062X/6–311 + g(d,p) level using software such as G09,Multiwfn_3.8_bin_Win64 and VMD193 (Additional file 1: Figure S7). As shown in Additional file 1: Figure S7, C8H6NO3 is not a simple structure of R-O–O•, and the electrostatic potential near the oxygen atom containing a single electron is very small, while the electrostatic potential near the H atom connected with the N atom is very high, so the oxygen atom with a single electron and the H atom connected with the N atom will approach each other to form intramolecular hydrogen bonds under electrostatic action, which makes the structure relatively stable.
During the reaction of the O3 molecule attacking the N atoms in the indigo molecule, we searched for a possible transition state structure during the reaction (shown in Additional file 1: Figure S6c) and performed a frequency analysis of the transition state at the GGA: PBE/DZP level, and found that the transition state has only one imaginary frequency and its vibrational direction is stretching along the N–O. The vibrational mode is consistent with our expectations, indicating that the transition state is structurally sound. During this reaction, one O atom at each end of the O3 molecule is preferentially bonded to the N atom, which requires crossing the reaction energy barrier of 3.67 kcal/mol. The other O atom at each end of the O3 molecule then snatches the H atom originally attached to the N atom to form O–H. Subsequently, both O1 and O2 of the original O3 molecule split to form a HO2. and C16H9N2O3 radical (shown in Additional file 1: Figure S6d), this C16H9N2O3 radical then otherwise captures an H atom to form the final product with the molecular formula C16H10N2O3, whose structure is shown in Additional file 1: Figure S6e. The Gibbs free energy of the reaction process was calculated using ADF at the GGA: PBE/DZP level for the reactants, products, and transition state structures under the same environmental conditions, and the change in Gibbs free energy of the reaction process is shown in Fig. 5.
The above reactions take place in the dark and are the reaction of the ground state indigo molecule with O3.
Verification of the reaction mechanism by experiment
As shown in Fig. 2b, when the air was exposed to indigo at a constant flow rate for 2.5 h the colour of indigo barely changed and was subsequently dissolved in DMSO and detected by HPLC and fluorescence-phosphorescence spectrophotometry, no new chromatographic or fluorescence peaks were found, thus indicating that the effect of air on indigo was almost negligible. After O3 was exposed to indigo at a constant flow rate for 2.5 h and dissolved in DMSO, the colour of the indigo solution changed more significantly (as shown in Fig. 2c). The standard solution of indigo at 0.1 mg/ml and the DMSO solution of indigo reacted with O3 for 2.5 h were analysed by HPLC using a Waters 2487 HPLC instrument and Chromatographic Conditions B (as shown in Fig. 6a), and only one peak was found at RT 14.90 min for the standard solution of indigo not reacted with O3 (impurity peak at RT 5.7 min); while the DMSO solution of indigo reacted with O3 was found to have three peaks at RT 9.43 min, RT 14.90 min, and RT 16.31 min. The isatin standard was measured under the same chromatographic conditions and the peak with RT 9.43 min was verified to be the isatin peak. The presence of isatin in the product of the reaction of indigo with O3 was confirmed.
The fluorescence spectrum of the solution prepared from the standard solution of indigo and the solution prepared from the reaction of indigo with O3 was analysed at the same conditions (as shown in Fig. 6b). It was shown that there was no obvious fluorescence peak at around 410 nm for the standard solution of indigo, while there was an obvious fluorescence peak at around 410 nm for the solution of indigo reacted with O3. We measured the fluorescence spectrum of the solution of isatin under the same conditions, and it can be seen from Fig. 6b that there is no fluorescence of isatin under these conditions, so it is presumed that the reaction of indigo with O3 may result in the presence of other reaction products in addition to isatin.
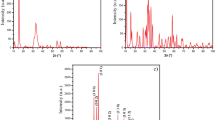
The mass spectrometry of the standard solution of indigo showed only one molecular ion peak at [M + H]+263 and identified the substance represented by this peak as an indigo molecule (as shown in Fig. 7a). Four molecular ion peaks were found at [M + H]+148, [M + H]+263, [M + H]+165 and [M + H]+279 after the reaction of indigo with O3. The molecular ion peak at [M + H]+148 was the molecular ion peak of isatin, and one of the products of the above reaction could be identified as isatin (as shown in Fig. 7c); [M + H]+263 is the indigo molecule not involved in the reaction (as shown in Fig. 7b); [M + H]+165 was the reaction product C8H6NO3 (as shown in Fig. 7d); [M + H]+279 was another reaction product C16H10N2O3 (shown in Fig. 7e). The above mass spectrometric results indicated that one of the products of the reaction of indigo with O3 was isatin, and the other two products were organic molecules C16H10N2O3 and C8H6NO3. The reaction mechanism for the oxidative decomposition of indigo was successfully justified by the oxidation pathway of the organic pigment indigo in the O3 environment.
a Mass spectra of indigo molecules detected in indigo standard solution; b Mass spectra of residual indigo molecules detected in indigo solution after reaction with O3; c Mass spectra of product isatin molecules detected in indigo solution after reaction with O3; d Mass spectra of product C8H6NO3 detected in indigo solution after reaction with O3; e Mass spectra of product molecules C16H10N2O3 detected in indigo solution after reaction with O3
The analytical methods used in this section were repeated, with each sample and standard being repeated three times (or more) at the time of detection, and the relative standard deviations for retention time and wavelength of the fluorescence peak and peak area were less than 2%.
Conclusion
In this paper, the organic pigments indigo and isatin were successfully detected from The Mural of Four Buddhas in Chinese Tiantishan grottoes by using HPLC. The reaction mechanism between indigo and O3 was also theoretically analysed and experimentally verified. The M062X/6–311 + G(d,p) method was used to study the geometrical configuration of the indigo molecule, the ALIE, the frontline molecular orbital, the Fukui and condensed Fukui functions, the DD and the CDD. On this basis, it was justified that it is reasonable O3 reacts with C=C in the indigo molecule in an electrophilic addition reaction, it was further shown that the other active site for the reaction of the indigo molecule with O3 is on the N atom. Flexible scanning and transition state search of the O3 oxidation of indigo molecules by the GGA: PBE/DZP method in ADF, and it was found that there are two main reaction pathways for the oxidation of the organic pigment indigo by O3: Pathway 1: O3 attacks the C=C in the indigo molecule and generates the products isatin and C8H6NO3; Pathway 2: O3 attacks the N atoms in the indigo molecule to generate C16H10N2O3 and HO2. and reaction pathway 1 is the main pathway. The reaction mechanism was verified by exposing indigo to O3. The final products of O3 oxidation of indigo was measured to be isatin and C16H10N2O3 and C8H6NO3 by HPLC, fluorescence-phosphorescence spectrophotometry and HPLC–MS. These findings provided a theoretical basis for subsequent research into the derivation of natural organic dyes in the face of increasing ozone pollution and for the better protection of valuable historical and cultural heritage such as ancient Chinese grottoes murals.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- G09:
-
Gaussian09
- HPLC–MS:
-
High performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
- VOCs:
-
Volatile organic compounds
- NOx:
-
Nitrogen oxides
- ALIE:
-
The average local ionization energy
- DD:
-
The dual descriptor
- CDD:
-
The condensed dual descriptor
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
References
Li YJ, Yeung JWT, Leung TPI, et al. Characterization of organic particles from incense burning using an aerodyne high-resolution time-of-flight aerosol mass spectrometer. Aerosol Sci Technol. 2012;46(6):654–65.
Manoukian A, Buiron D, Temime-Roussel B, et al. Measurements of VOC/SVOC emission factors from burning incenses in an environmental test chamber: influence of temperature, relative humidity, and air exchange rate. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2016;23(7):6300–11.
Zhao YS, Li YT, Kumar A, et al. Separately resolving NOx and VOC contributions to ozone formation. Atmos Environ. 2022;285: 119224.
Du XH, Tang W, Zhang ZZ, et al. Responses of ozone concentrations to the synergistic control of NOx and VOCs emissions in the Chengdu metropolitan area. Front Environ Sci. 2022;10:1024795.
Ren S, Ji X, Zhang X, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of ozone pollution in Wuwei. Gansu Sci Tech. 2019;35(01):8–11.
Sigurdson GT, Tang PP, Giusti MM. Natural colorants: food colorants from natural sources. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2017;8:261–80.
Franco-Maass S, Arredondo-Ayala GM, Cruz-Balderas Y, et al. The use of dye plants in a Mazahua community in central Mexico. Econ Bot. 2019;73(1):13–27.
Celis F, Segura C, Gomez-Jeria JS, et al. Analysis of biomolecules in cochineal dyed archaeological textiles by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):6560.
de Luca E, Redaelli M, Zaffino C, et al. A SERS and HPLC study of traditional dyes from native Chinese plants. Vib Spectrosc. 2018;95:62–7.
Junsongduang A, Sirithip K, Inta A, et al. Diversity and traditional knowledge of textile dyeing plants in northeastern Thailand. Econ Bot. 2017;71(3):241–55.
Zhang Y-M, Huang Y-Z, Wan H-H, et al. Advances in biosynthesis of indigo in plants. China J Chinese Materia Medica. 2020;45(3):491–6.
Splitstoser JC, Dillehay TD, Wouters J, et al. Early pre-Hispanic use of indigo blue in Peru. Sci Adv. 2016;2(9): e1501623.
Garcia-Macias P, John P. Formation of natural indigo derived from woad (Isatis tinctoria L.) in relation to product purity. J Agric Food Chem. 2004;52(26):7891–6.
Gilbert KG, Cooke DT. Dyes from plants: Past usage, present understanding and potential. Plant Growth Regul. 2001;34(1):57–69.
Straulino-Mainou L, Pi-Puig T, Lailson-Tinoco B, et al. Maya blue used in wall paintings in Mexican colonial convents of the XVI century. Coatings. 2021;11(1):88.
Vandenabeele P, Bode S, Alonso A, et al. Raman spectroscopic analysis of the Maya wall paintings in Ek’Balam, Mexico. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2005;61(10):2349–56.
Domenech A, Domenech-Carbo MT, De Agredos Pascual MLV. Chemometric study of Maya Blue from the voltammetry of microparticles approach. Anal Chem. 2007;79(7):2812–21.
Vasileiadou A, Karapanagiotis I, Zotou A. UV-induced degradation of wool and silk dyed with shellfish purple. Dyes Pigm. 2019;168:317–26.
Vasileiadou A, Karapanagiotis I, Zotou A. A chromatographic investigation on ageing of natural dyes in silk under UV light. Archaeol Anthropol Sci. 2022;14(1):21.
Mantzouris D, Karapanagiotis I, Panayiotou C. Comparison of extraction methods for the analysis of Indigofera tinctoria and Carthamus tinctorius in textiles by high performance liquid chromatography. Microchem J. 2014;115:78–86.
Sousa MM, Miguel C, Rodrigues I, et al. A photochemical study on the blue dye indigo: from solution to ancient Andean textiles. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2008;7(11):1353–9.
Witkos K, Lech K, Jarosz M. Identification of degradation products of indigoids by tandem mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom. 2015;50(11):1245–51.
Tello-Burgos N, Lopez-Montes AM, Ballesta-Claver J, et al. Identification of Indigo dye (Indigofera tinctoria) and its degradation products by separation and spectroscopic techniques on historic documents and textile fibers. Stud Conserv. 2021;66(1):7–22.
Seixas de Melo J, Moura AP, Melo MJ. Photophysical and spectroscopic studies of Indigo derivatives in their Keto and Leuco forms. J Phys Chem A. 2004;108:6975–81.
Srividya N, Paramasivan G, Seetharaman K, et al. Two-step reduction of Indigo Carmine by Dithionite: a stopped-flow study. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans. 1994;90(17):2525–30.
Grosjean D, Whitmore PM, Cass GR, et al. Ozone fading of natural organic colorants: mechanisms and products of the reaction of ozone with indigos. Environ Sci Technol. 1988;22(3):292–8.
Jacquemin D, Preat J, Wathelet V, et al. Substitution and chemical environment effects on the absorption spectrum of indigo. J Chem Phys. 2006;124(7):74104.
Lechner MH, Neese F, Izsak R. An excited state coupled-cluster study on indigo dyes. Mol Phys. 2021;119:21–2.
Volkov VV, Chelli R, Righini R, et al. Indigo chromophores and pigments: structure and dynamics. Dyes Pigm. 2020;172: 107761.
Singh JS. IR and Raman spectra with Gaussian-09 molecular analysis of some other parameters and vibrational spectra of 5-fluoro-uracil. Res Chem Intermed. 2020;46(5):2457–79.
Kadir MA, Abdul Razak FI, Haris NSH. Experimental and DFT data of p-chlorocalix 4 arene as drugs receptor. Data Brief. 2020;32:106263.
Dunning TH. Gaussian basis sets for use in correlated molecular calculations. The atoms boron through neon and hydrogen. J Chem Phys. 1989;90(2):1007–23.
Zhao Y, Truhlar DG. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theoret Chem Acc. 2008;120(1–3):215–41.
Zhao Y, Truhlar DG. A new local density functional for main-group thermochemistry, transition metal bonding, thermochemical kinetics, and noncovalent interactions. J Chem Phys. 2006;125(19): 194101.
Lu T, Chen FW. Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J Comput Chem. 2012;33(5):580–92.
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph. 1996;14(1):33–8.
Baerends EJTZ, Autschbach J, Bashford D, et al. ADF2022, SCM, Theoretical chemistrY, Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. http://www.scm.com.
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett. 1996;77(18):3865–8.
Swart M, Ehlers AW, Lammertsma K. Performance of the OPBE exchange-correlation functional. Mol Phys. 2004;102(23–24):2467–74.
Fonseca Guerra C, Snijders JG, Te Velde GT, Baerends EJ. Towards an order- N DFT method. Theor Chem Acc. 1998;99(6):391–403.
Te Velde GT, Bickelhaupt FM, Baerends EJ, Fonseca Guerra C, van Gisbergen SJ, Snijders JG, Ziegler T. Chemistry with ADF. J Comput Chem. 2001;22(9):931–67.
Klessinger M, Lüttke W. Theoretische und spektroskopische untersuchungen an indigo-farbstoffen — II: Das chromophore system der Indigo-Farbstoffe. Tetrahedron. 1963;19:315–35.
Lüttke W, Hermann H, Klessinger M. Theoretically and experimentally determined properties of the fundamental Indigo chromophore. Angewandte Chemie Int Ed Engl. 1966;5(6):598–9.
Sjoberg P, Murray JS, Brinck T, Polizer P. Average local ionization energies on the molecular surfaces of aromatic systems as guides to chemical reactivity. Can J Chem. 1990;68(8):1440–3.
Mohamed IPK, Subramani K. Structure-property analysis of l-ornithine and its substituted analogues. Acta Phys Chim Sin. 2009;25(11):2357–65.
Parr RG, Yang W. Density functional approach to the frontier-electron theory of chemical reactivity. J Am Chem Soc. 1984;106(14):4049–50.
Morell C, Grand A, Toro-Labbe A. New dual descriptor for chemical reactivity. J Phys Chem A. 2005;109(1):205–12.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by Key Research & Development Program of Gansu Province (No. 21YF5FA083), the central government guides local science and technology development funds (2021), Youth Ph.D. Fund of Gansu Provincial Department of Education (2021), the West Light Foundation of The Chinese Academy of Sciences (2019), Gansu Leading Talents Program (2020) and Feitian Scholar Program (2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JXL: conceptualization, methodology, resources, writing—original draft, visualization. YT, XL: methodology, data curation. GYW, GFS: writing—original draft, writing—review & editing, supervision, funding acquisition. ZRY, BWS: funding sample, editing. Others: review & editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1:
Figure S1. A sample of the mural(0.0137 g, 0.33 cm2) used for this study, which comes from the blue area of the mural shown in Figure 1b. Due to the long history of The Mural of Four Buddhas, some areas of the mural had fallen off naturally. Carefully take off the blue mural residue (the mural sample we studied) with tweezer and put it in a sample tube for the next stage of the experiment. Figure S2. (a) Structural formula of the indigo molecule; (b) Geometric optimization of the indigo molecule at the M062X/6-311+g(d,p) level using G09 to obtain the optimal geometric configuration; (c) "H-chromophore", which is commonly believed to be responsible for the colour development of the indigo molecule. Figure S3. HOMO, LUMO of indigo and O3 calculated at the M062X/6-311+g(d,p) level. Figure S4. Isosurface plot of the Fukui function on the surface of the indigo molecule, Isosurface = 0.004. Figure S5. Isosurface plot of the DD on the surface of the indigo molecule, Isosurface = 0.003. Figure S6. (a) Structure of the Criegee radical produced by C=C in an O3 attack on an indigo molecule; (b) structure of C8H6NO3, the more stable product resulting from the acquisition of an H atom by compound (a); (c) transition state produced by an N atom in an O3 attack on an indigo molecule; (d) structure of the radical produced by an N atom in an O3 attack on an indigo molecule; (e) structure of C16H10N2O3, the stable product resulting from the acquisition of an H atom by compound (d). Figure S7. Figure of the electrostatic potential of the reaction product C8H6NO3 from the oxidative decomposition of indigo by O3 (the bluer the region where each atom is located, the more negative the electrostatic potential is, and the redder the region where each atom is located, the more positive the electrostatic potential is). Table S1. Main structural parameters of the indigo molecule. Table S2. Statistics of ALIE minima data on the surface of indigo molecules. Table S3. Statistical table of indigo molecular condensed Fukui functions. Table S4. Indigo molecular CDD statistics.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Yu, Z., Shui, B. et al. A study of the oxidation mechanism of the organic pigment indigo in grottoes murals by ozone under dark conditions. Herit Sci 11, 50 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-023-00887-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40494-023-00887-7