Abstract
Background
In cases of Hirschsprung disease, complete and reproducible resection of the aganglionic bowel is ideal to achieve good postoperative bowel function. Reliable identification of the upper margin of the surgical anal canal, which is the squamous-columnar junction, is necessary during transanal pull-through. Here, we describe a novel staining technique using Lugol’s iodine stain to visualize the upper margin of the surgical anal canal.
Methods
Lugol’s iodine staining was performed in five patients with Hirschsprung disease treated using a single-stage laparoscopic transanal pull-through modified Swenson procedure. In two of these patients, endocytoscopic observation with ultra-high magnification was performed using methylene blue and crystal violet to mark the border of the squamous epithelium at 1 week before surgery. The alignment between the incisional line, which was revealed using Lugol’s iodine staining and endocytoscopic marking, was evaluated. Complications, including postoperative bowel dysfunction, were evaluated.
Results
In all cases, Lugol’s iodine staining produced a well-demarcated line. The endocytoscopic marking of the upper margin of the surgical anal canal was aligned with the line revealed by Lugol’s iodine staining. There were no complications associated with the transanal pull-through procedure, including postoperative bowel dysfunction.
Conclusions
Lugol’s iodine staining could be a safe and practical method to visualize the upper margin of the surgical anal canal intraoperatively. This finding may be useful for surgeons to make a consistent removal of the aganglionic bowel during surgery for Hirschsprung disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
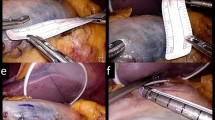
Resection of the aganglionic bowel is one of the definitive treatments for patients with Hirschsprung disease (HD), followed by reconstruction using a transanal pull-through of the ganglionic bowel. Complete removal of the aganglionic bowel without injuring the entire surgical anal canal, including the innervated anal transition zone, is crucial to ensure postoperative bowel function. [1,2,3,4] Generally, in our institution, transanal circumferential full-thickness dissection is performed from the upper margin of the surgical anal canal during a single-stage laparoscopic transanal pull-through modified Swenson procedure (Fig. 1). [5] However, without establishing a standard method for identifying the upper margin of the surgical anal canal, this boundary is detected intraoperatively through visual inspection or palpation, regardless of the surgeon’s experience. [6]
Histologically, the upper margin of the surgical anal canal defines the boundary between the stratified squamous epithelium and simple columnar epithelium, [7] corresponding to the superior margin of the levator ani muscle. [5, 8] To identify this line, we focused on Lugol’s iodine staining, which is a popular technique to stain the normal non-keratinized squamous epithelium used in the diagnosis of esophageal cancer. Oono et al. reported that Lugol’s iodine staining was useful for identifying a squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal in situ demarcated as an unstained area with Lugol chromoendoscopy. [9] However, there are no reports of the use of Lugol’s iodine staining in surgery for HD. Το the best of our knowledge, this is the first case series report, in which Lugol’s iodine staining was used to detect the upper margin of the surgical anal canal during surgery for HD.
Methods
This study aimed to describe a novel staining technique using Lugol’s iodine stain to visualize the upper margin of the surgical anal canal. Between February and October 2019, five patients with HD (including four and one cases of short- total-segment, respectively) were treated using the single-stage laparoscopic transanal pull-through modified Swenson procedure [5] at Nagoya University Hospital, Nagoya, Japan.
Briefly, after performing a full-thickness bowel biopsy to confirm the correct position of the ganglionic intestine, laparoscopic dissection was extended to the peritoneal reflection of the rectum. The rectum below the peritoneal reflection was circumferentially dissected up to the superior border of the levator ani muscle. After placement of an anal retractor (The Lone Star Retractor System™; Yufu, Tokyo, Japan), transanal circumferential full-thickness dissection was performed from the upper margin of the surgical anal canal, without leaving a muscular cuff (Fig. 1). The ganglionic bowel was pulled through and anastomosed to the anal canal.
In all five patients, Lugol’s iodine staining was performed intraoperatively, before the transanal circumferential full-thickness dissection. Lugol's solution containing iodine 1% (10 mg/mL) and potassium iodide 2% (20 mg/mL) was used. After washing out the rectal mucus with saline, 1 mL of Lugol's solution was sprayed onto the anal canal and the rectum each time for a total of approximately 5–10 mL. When the stain was inadequate, gauze soaked with Lugol's solution was placed on the mucosa for approximately 1 min. In two cases, endocytoscopy with 1% methylene blue and 0.05% crystal violet staining [10] was performed at 1 week before the radical surgery to mark the upper margin of the surgical anal canal. Endocytoscopy is a novel ultra-high magnification technique that allows microscopic observation at the cellular level using intraprocedural stains. In this technique, methylene blue clearly stains the cell nuclei, whereas the crystal violet stains the cytoplasm, allowing the rapid detection of the glandular structure. Therefore, the boundary between the squamous epithelium and columnar epithelium, corresponding to the upper margin of the surgical anal canal, was marked.
At the time of radical surgery performance, we evaluated the alignment between the endocytoscopy marking. The incisional line revealed using Lugol’s iodine staining with direct intraoperative visualization. Complications, including postoperative bowel dysfunction, were evaluated.
Results
Lugol’s iodine staining revealed a well-demarcated line, indicating the squamous-columnar junction in all patients (Fig. 2). In the two cases where we used endocytoscopy, the squamous-columnar junction marked using endocytoscopy (i.e., the upper margin of the surgical anal canal) coincided with the line demarcated with Lugol’s iodine staining. The latter indicated that Lugol's iodine staining could detect the upper margin of the surgical anal canal accurately at the cellular level (Figs. 3 and 4).
a A representative endocytoscopic image, showing the boundary (white dotted line) between the simple columnar epithelium and stratified squamous epithelium. b The simple columnar epithelium has a small regular nucleus at the marginal region of the glandular structure (a white oval). c The stratified squamous epithelium has a small nucleus with cytoplasm-rich cells, in a regular arrangement
We removed the aganglionic bowel in all five patients after full-thickness circumferential dissection completion. Pathological findings of the rectal stump showed no squamous epithelium in four patients and a slight squamous epithelium in one patient. No intra- or postoperative complications were noted, including postoperative bowel dysfunction (e.g., enterocolitis or constipation).
Discussion
The upper margin of the surgical anal canal is the circular upper border of the puborectalis (levator ani) muscle (Fig. 1). Full-thickness dissection along line indicates complete resection of the aganglionic bowel. Lugol’s iodine staining, which was previously described, was easily applied and identified the upper margin of the surgical anal canal as the distinct boundary between the squamous epithelium and columnar epithelium in the anorectal region. This was confirmed through endocytoscopy with ultra-high-power magnification at the cellular level. [10] Therefore, we recommend Lugol’s iodine staining as a reliable and easy method to detect the upper margin of the surgical anal canal.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report describing a reliable method to visualize the upper margin of the surgical anal canal during surgery. Our method enables precise detection of the starting point for mucosal (Soave procedure) or full-thickness resection (our modified Swenson procedure). Using Lugol’s iodine staining, reconstruction with transanal pull-through of the ganglionic bowel could be performed from a repeatable starting position. Such reproducibility in reconstruction would allow us to compare postoperative bowel function across different operative procedures.
The safety of Lugol’s iodine staining has been previously described in the endoscopic diagnosis for esophageal cancer. Lugol’s staining can be easily performed intraoperatively, with no special technique. Lugol’s staining can be easily introduced within the intraoperative procedures performed in any hospital. This method of visualizing the upper margin of the surgical anal canal is expected to allow surgeons start an incision on the same line during surgery for HD. This reliability in identifying the incisional line would lower the risk for postoperative fecal continence because anal sensation is preserved while the aganglionic bowel, proximal to the upper margin of the surgical anal canal, is excised. In our limited five-case report, there was no occurrence of postoperative bowel dysfunction, including enterocolitis or constipation. Long-term follow-up is required to evaluate more completely the effect of this method on postoperative bowel function.
Conclusions
Lugol’s iodine staining provides a useful method for detecting the upper margin of the surgical anal canal during surgery for HD, based on the short-term follow-up findings of postoperative bowel function in five patients with HD. Because the number of cases was limited in this study, a thorough evaluation with a larger sample size is needed in the future.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- HD:
-
Hirschsprung disease
References
Takeda M, Miyahara K, Akazawa C, Lane GJ, Yamataka A. Sensory innervation of the anal canal and anorectal line in Hirschsprung’s disease: histological evidence from mouse models. Pediatr Surg Int. 2017;33:883–6.
Yamataka A, Kaneyama K, Fujiwara N, Hayashi Y, Lane GJ, Kawashima K, et al. Rectal mucosal dissection during transanal pull-through for Hirschsprung disease: the anorectal or the dentate line? J Pediatr Surg. 2009;44:266–9.
Miyano G, Koga H, Okawada M, Doi T, Sueyoshi R, Nakamura H, et al. Rectal mucosal dissection commencing directly on the anorectal line versus commencing above the dentate line in laparoscopy-assisted transanal pull-through for Hirschsprung’s disease: prospective medium-term follow-up. J Pediatr Surg. 2015;50:2041–3.
Duthie HL, Gairns FW. Sensory nerve-endings and sensation in the anal region of man. Br J Surg. 1960;47:585–95.
Yokota K, Uchida H, Tainaka T, Tanaka Y, Shirota C, Hinoki A, et al. Single-stage laparoscopic transanal pull-through modified Swenson procedure without leaving a muscular cuff for short- and long-type Hirschsprung disease: a comparative study. Pediatr Surg Int. 2018;34:1105–10.
Yamataka A, Yazaki Y, Koga H, Lane GJ, Ochi T. How best to expose the entire surgical anal canal in the operative field during transanal pull-through for Hirschsprung’s disease: a crucial step that determines success. Pediatr Surg Int. 2019;35:199–202.
Tanaka E, Noguchi T, Nagai K, Akashi Y, Kawahara K, Shimada T. Morphology of the epithelium of the lower rectum and the anal canal in the adult human. Med Mol Morphol. 2012;45:72–9.
Swenson O, Bill AH Jr. Resection of rectum and rectosigmoid with preservation of the sphincter for benign spastic lesions producing megacolon; an experimental study. Surgery. 1948;24:212–20.
Oono Y, Fu K, Nakamura H, Iriguchi Y, Yamamura A, Kishi D, et al. Narrowband imaging colonoscopy with a transparent hood for diagnosis of a squamous cell carcinoma in situ in the anal canal. Endoscopy. 2010;42:E183–4.
Ichimasa K, Kudo SE, Mori Y, Wakamura K, Ikehara N, Kutsukawa M, et al. Double staining with crystal violet and methylene blue is appropriate for colonic endocytoscopy: an in vivo prospective pilot study. Dig Endosc. 2014;26:403–8.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KY: Design of the work, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, drafting the article, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. HA: Design of the work, data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. TK: Data collection, data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. TY: Data collection, data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. YT: Design of the work, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, drafting the article, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. TT: Design of the work, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, drafting the article, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. CS: Design of the work, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. WS: Design of the work, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. SM: Design of the work, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. AT: Design of the work, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. MN: Data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. MF: Data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. AH: Data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. HU: Conception of the work, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, critical revision of the article, and final approval of the version to be published. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This case series was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Nagoya University Hospital (2018-0425). The written informed consent was obtained from the patient to participate to this case report and any accompanying images.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
About this article
Cite this article
Yokota, K., Amano, H., Kudo, T. et al. A novel Lugol’s iodine staining technique to visualize the upper margin of the surgical anal canal intraoperatively for Hirschsprung disease: a case series. BMC Surg 20, 317 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-020-00986-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-020-00986-3